The Characteristics of Microbiome and Cytokines in Healthy Implants and Peri-Implantitis of the Same Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Recruitment and Data Collection
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Cytokine Assessment in the PICF
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
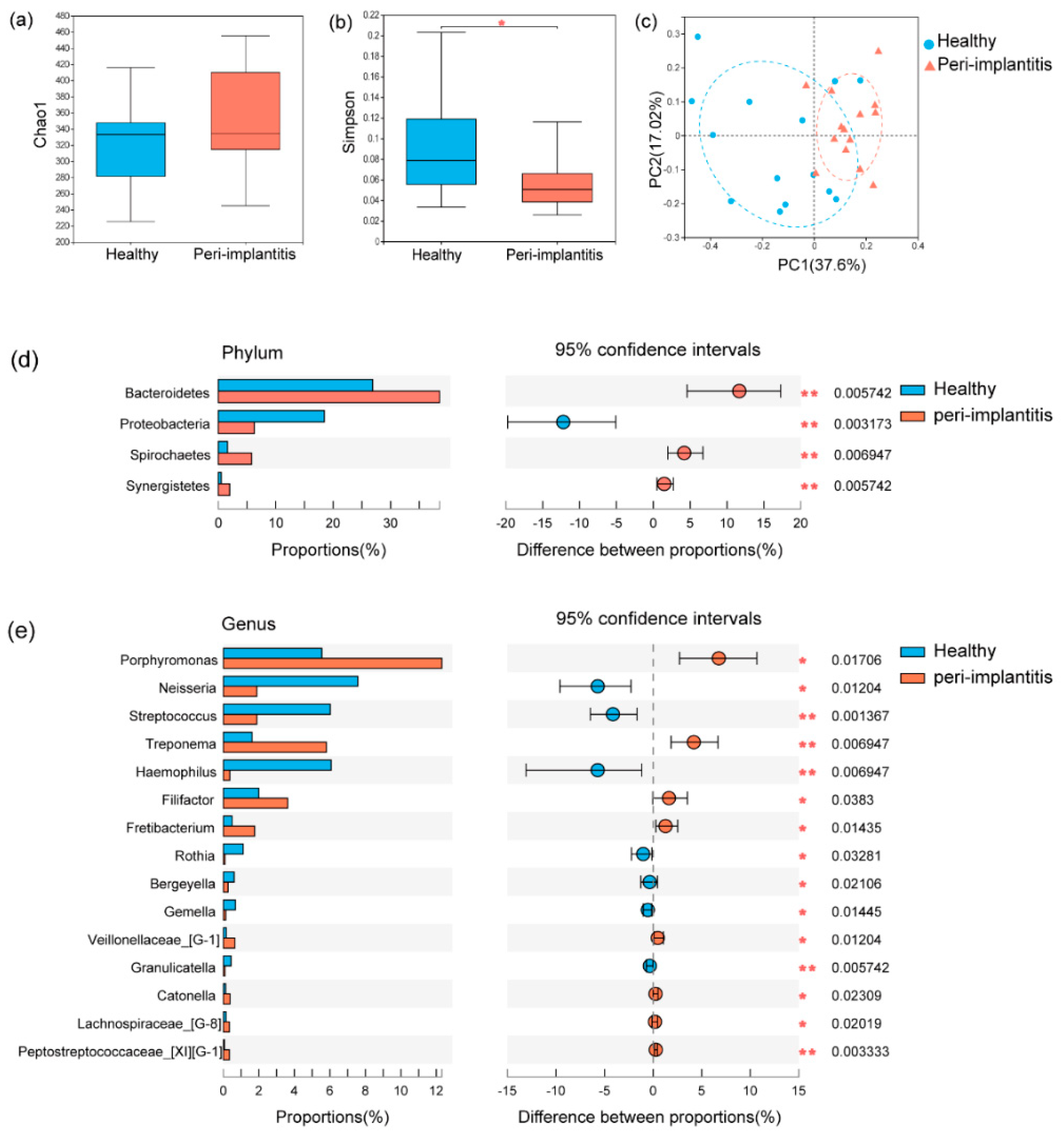
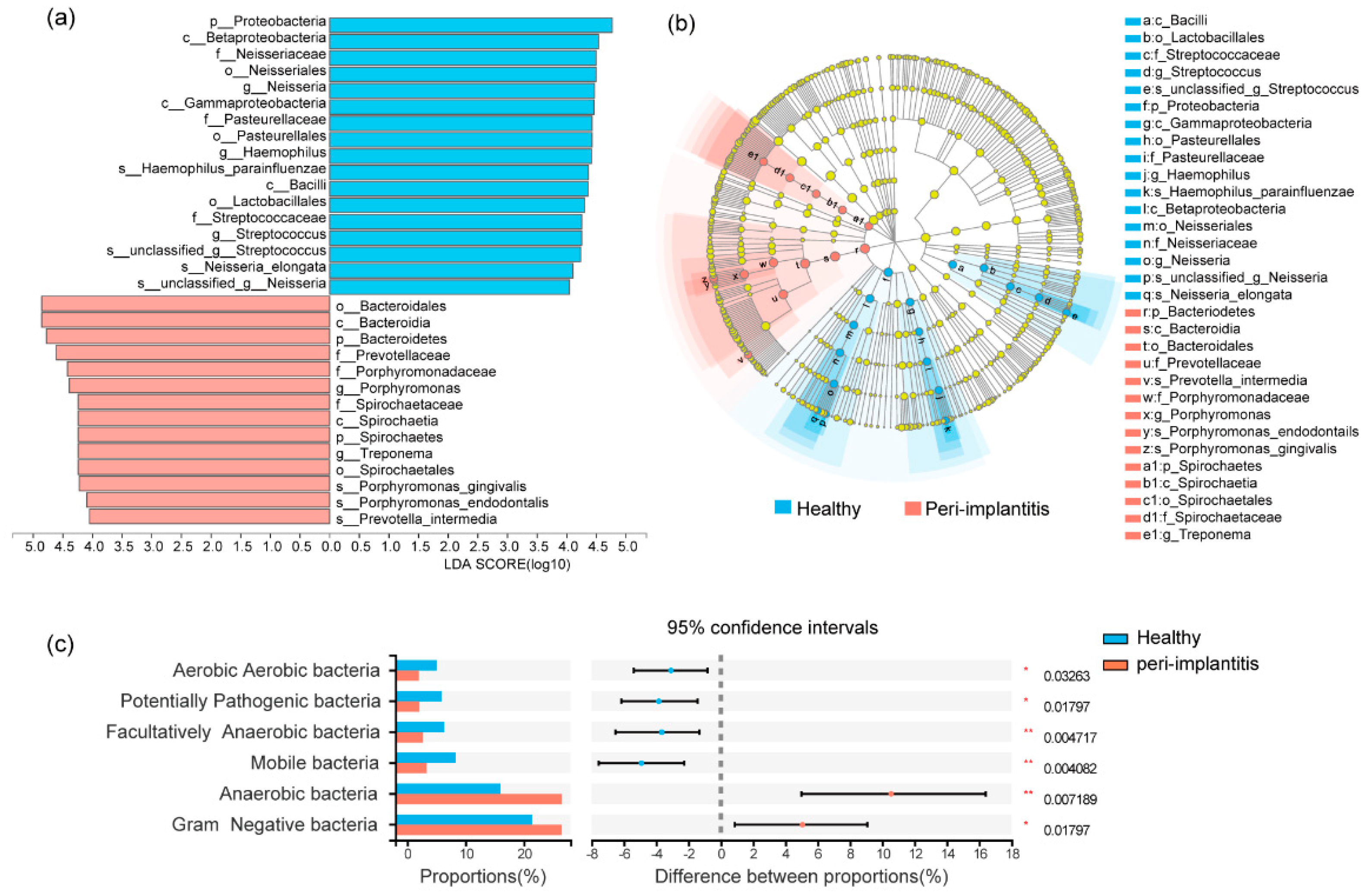
3.2. Microbial Profile of Healthy Implant Sites and Peri-Implantitis Sites
3.3. Cytokine Levels in PICF of Healthy and Peri-Implantitis Sites
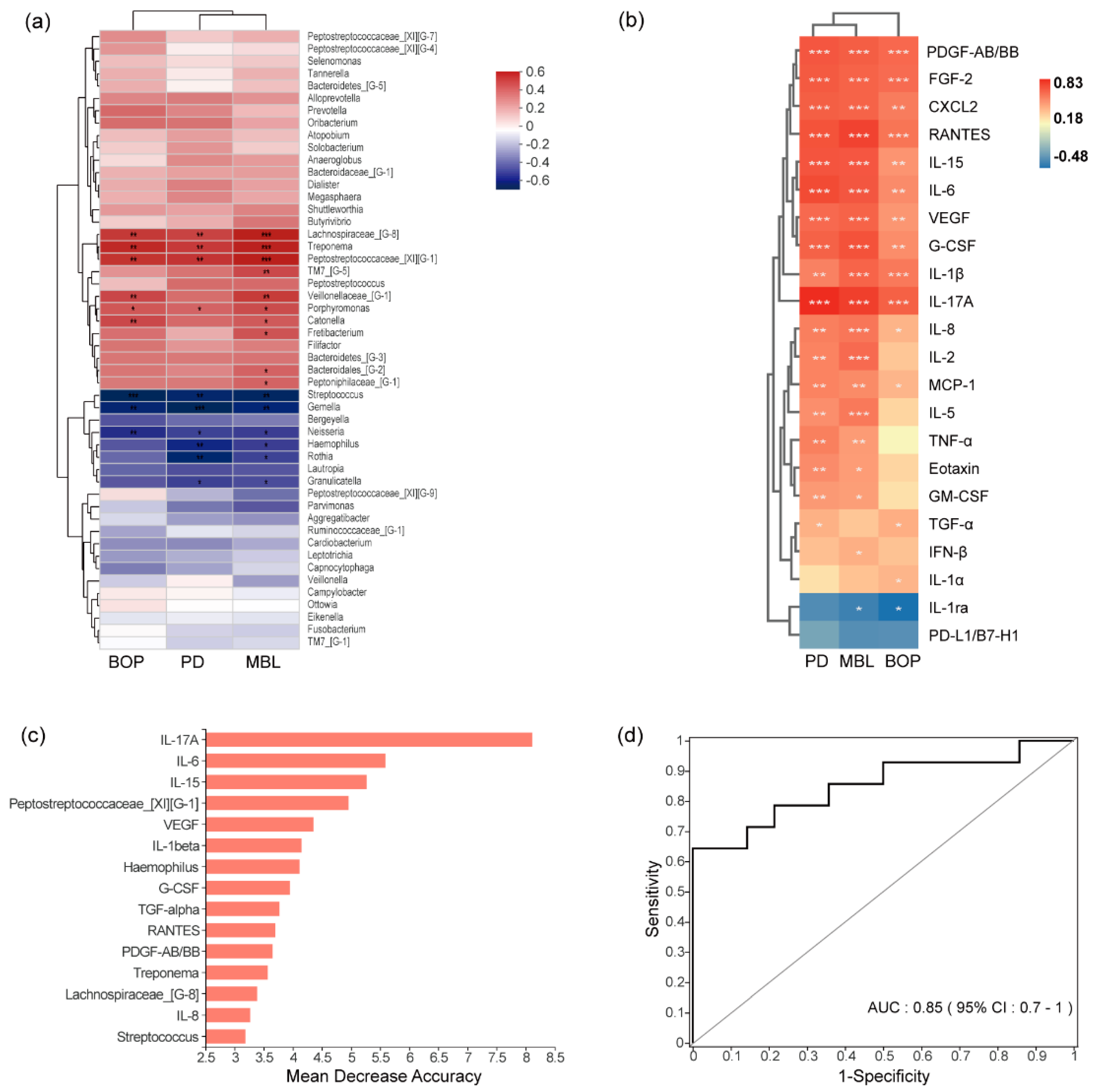
3.4. Correlations between Clinical Indexes and Microorganisms or Cytokines
3.5. Combined Diagnostic Ability of Microbiota and Cytokines
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, J.H.; Wang, H.L. Breaking the wave of peri-implantitis. Periodontology 2000 2020, 84, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S158–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovski, S.L.R. Comparison of peri-implant and periodontal marginal soft tissues in health and disease. Periodontology 2000 2018, 76, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsakis, G. Peri-implantitis is not periodontitis: Scientific discoveries shed light on microbiome-biomaterial interactions that may determine disease phenotype. Periodontology 2000 2021, 86, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Aaboe, M.; Araujo, M.; Carrión, J.B.; Cavalcanti, R.; Cionca, N.; Cochran, D.; Darby, I.; Funakoshi, E.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C.; et al. Group 4 ITI Consensus Report: Risks and biologic complications associated with implant dentistry. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 16), 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Manoil, D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampakis, G.; Belibasakis, G.N. Microbiome of peri-implant infections: Lessons from conventional, molecular and metagenomic analyses. Virulence 2015, 6, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, F.; Milanesi, F.C.; Angst, P.D.M.; Oppermann, R.V. A systematic review of the microbiota composition in various peri-implant conditions: Data from 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 117, 104776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Mason, M.R.; Brooker, M.R.; O’Brien, K. Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Muzafferiy, F.; Anderson, A.C.; Wölber, J.P.; Ratka-Krüger, P.; Fretwurst, T.; Nelson, K.; Vach, K.; Hellwig, E. Shift of microbial composition of peri-implantitis-associated oral biofilm as revealed by 16S rRNA gene cloning. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apatzidou, D.; Lappin, D.F.; Hamilton, G.; Papadopoulos, C.A.; Konstantinidis, A.; Riggio, M.P. Microbiome of peri-implantitis affected and healthy dental sites in patients with a history of chronic periodontitis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2017, 83, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Gilli, F.; Wiedemeier, D.B.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Karygianni, L. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensara, A.; Hefni, E.; Williams, M.A.; Saito, H.; Mongodin, E.; Masri, R. Microbiological Profile and Human Immune Response Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 210–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, P.M.; Serrao, C.R.; Miranda, T.S.; Zanatta, L.C.S.; Bastos, M.F.; Faveri, M.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Feres, M. Could cytokine levels in the peri-implant crevicular fluid be used to distinguish between healthy implants and implants with peri-implantitis? A systematic review. J. Periodontal Res. 2016, 51, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassib, I.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.L. Use of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 biomarkers to distinguish peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat Res. 2019, 21, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsi, A.S.; Moreno, F.; Petridis, H. Biomarkers associated with periodontitis and peri-implantitis: A systematic review. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2021, 51, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Zitzmann, N. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I. Treatment of pathologic peri-implant pockets. Periodontology 2000 2018, 76, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F. The Sampling Strategy of Oral Microbiome. iMeta 2022, 1, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Inflammatory cytokine profiles in the crevicular fluid around clinically healthy dental implants compared to the healthy contralateral side during the early stages of implant function. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 108, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincón, M.V.; Gómez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.L.; Chan, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Lai, H.C.; Lang, N.P.; Keung Leung, W.; Watt, R.M. Intra-oral single-site comparisons of periodontal and peri-implant microbiota in health and disease. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 760–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alassy, H.; Parachuru, P.; Wolff, L. Peri-Implantitis Diagnosis and Prognosis Using Biomarkers in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, S.R.; Moss, K.; Shibli, J.A.; Teixeira, E.R.; de Oliveira Mairink, R.; Onuma, T.; Feres, M.; Teles, R.P. Peri-implant crevicular fluid biomarkers as discriminants of peri-implant health and disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinkovic, I.; Djinic Krasavcevic, A.; Nikolic, N.; Aleksic, Z.; Carkic, J.; Jezdic, M.; Jankovic, S.; Milasin, J. Notch down-regulation and inflammatory cytokines and RANKL overexpression involvement in peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentenaar, D.F.M.; De Waal, Y.C.M.; Vissink, A.; Van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Meijer, H.J.; Liefers, S.C.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Raghoebar, G.M. Biomarker levels in peri-implant crevicular fluid of healthy implants, untreated and non-surgically treated implants with peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, F.J.; Moraes Junior, M.; Lourenco, E.J.; Teles Dde, M.; Figueredo, C.M. Cytokines expression in saliva and peri-implant crevicular fluid of patients with peri-implant disease. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, e68–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, V.O.; Napimoga, M.H.; de Lima Pereira, S.A. Expression of IL-6, IL-10, IL-17 and IL-8 in the peri-implant crevicular fluid of patients with peri-implantitis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2011, 56, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.K.S.; Lira-Junior, R.; Telles, D.M.; Lourenço, E.J.V.; Figueredo, C.M. Th17-related cytokines in mucositis: Is there any difference between peri-implantitis and periodontitis patients? Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charo, I.F.; Ransohoff, R.M. The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Huang, J.; Zhu, H.; Ju, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Overexpression of GRO-beta is associated with an unfavorable outcome in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Asami, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Harada, A.; Hanazawa, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Mori, G.; Yajima, Y. Rat peri-implant soft tissue specifically expressed CXCL2 on titanium implant during wound healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2022, 110, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. 3), 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, G.; Zizzi, A.; Rubini, C.; Ciolino, F.; Aspriello, S.D. VEGF, Microvessel Density, and CD44 as Inflammation Markers in Peri-implant Healthy Mucosa, Peri-implant Mucositis, and Peri-implantitis: Impact of Age, Smoking, PPD, and Obesity. Inflammation 2019, 42, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W. G-CSF: A key regulator of neutrophil production, but that’s not all! Growth Factors 2005, 23, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, T.; Lu, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) mediates bone resorption in periodontitis. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, G.; Santagati, M.; Guni, A.; Torrisi, P.; Spitale, A.; Stefani, S.; Ferlito, S.; Nibali, L. Microbiome differences in periodontal, peri-implant, and healthy sites: A cross-sectional pilot study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, X.; Zhu, B.; Meng, H. Peri-implant mucositis sites with suppuration have higher microbial risk than sites without suppuration. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, L.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Pourlak, T.; Eslami, H.; Taghizadeh, S.; Ganbarov, K.; Yousefi, M.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, B.; Kafil, H.S. Oral spirochetes: Pathogenic mechanisms in periodontal disease. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 144, 104193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Si, M.; He, F. Microbial profiles of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: Submucosal microbial dysbiosis correlates with disease severity. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, A.; Hülsmann, C.; Fickl, S.; Spinell, T.; Hüttig, F.; Kaufmann, F.; Heimbach, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Enkling, N.; Renvert, S.; et al. The severity of human peri-implantitis lesions correlates with the level of submucosal microbial dysbiosis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaura, H.; Marahleh, A.; Ohori, F.; Noguchi, T.; Shen, W.R.; Qi, J.; Nara, Y.; Pramusita, A.; Kinjo, R.; Mizoguchi, I. Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Collins, A.; Ong, H.; Chudri, R.; Giannobile, W.V. Protein biomarkers and microbial profiles in peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomforest. R News. 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, F.; Alcoforado, G.; Guerrero, A.; Jönsson, D.; Klinge, B.; Lang, N.; Heitz-Mayfield, L. Peri-implantitis: Summary and consensus statements of group 3. The 6th EAO Consensus Conference 2021. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32 (Suppl. 21), 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, L.; Stiesch, M.; Grischke, J. The effect of keratinized mucosa on the severity of peri-implant mucositis differs between periodontally healthy subjects and the general population: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windael, S.; Vervaeke, S.; De Buyser, S.; De Bruyn, H.; Collaert, B. The Long-Term Effect of Smoking on 10 Years’ Survival and Success of Dental Implants: A Prospective Analysis of 453 Implants in a Non-University Setting. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Peri-Implantitis | Healthy | p-Values * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mPD (mm, mean ± SD) | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 0.001 |
| mBOP (%, mean ± SD) | 65.5 ± 28.1 | 0 | 0.001 |
| mMBL (mm, mean ± SD) | 3.4 ± 1.4 | 0 | 0.001 |
| PICF volume (μL, mean ± SD) | 0.3 ± 0.04 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | 0.001 |
| KGW (<2 mm/≥2 mm) | 4/10 | 4/10 | 1.0 |
| Implant position (Maxillary/Mandibular) (Anterior/Posterior) | 9/5 5/9 | 8/6 1/13 | 0.7 0.2 |
| Diameter (mm, mean ± SD) | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Length (mm, mean ± SD) | 11.7 ± 1.2 | 11.3 ± 1.1 | 0.3 |
| Bone augmentation (GBR/sinus lift/none) | 1/5/8 | 3/3/8 | 0.5 |
| Prosthetic types (single crown/bridge) | 6/8 | 9/5 | 0.3 |
| Concentration [pg/mL, Median (Q1, Q3)] | Quantity [pg, Median (Q1, Q3)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokines | Healthy | Peri-Implantitis | Healthy | Peri-Implantitis | p-Value | q-Value | log2 (fc) |
| G-CSF | 73.9 (32.8, 99.4) | 350.7 (148.2, 477.9) | 4.4 (2.0, 6.0) | 21.0 (8.9, 28.7) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 2.01 |
| IL-15 | 1.3 (1.1, 1.5) | 2 (1.6, 2.2) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.65 |
| PDGF-AB/BB | 1.8 (1.6, 2.1) | 3.4 (2.2, 3.6) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.2) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 1.12 |
| IL-8 | 2113 (864.3, 2749.0) | 3533 (2363.5, 3697.8) | 126.8 (51.9, 164.9) | 212.0 (141.8, 221.9) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.76 |
| CXCL2 | 331.7 (214.1, 672.8) | 1220.5 (726.3, 1880.0) | 19.9 (12.8, 40.4) | 73.2 (43.6, 112.8) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 1.77 |
| VEGF | 324.7 (177.9, 409.2) | 945.7 (456.8, 1343.0) | 19.5 (10.7, 24.6) | 56.7 (27.4, 80.6) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 1.61 |
| IL-2 | 14.9 (9.4, 17.9) | 19.8 (17.3, 21.0) | 0.9 (0.6, 1.1) | 1.2 (1.0, 1.3) | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.47 |
| FGF-2 | 15.5 (7.3, 19.1) | 37.3 (23.4, 61.7) | 0.9 (0.4, 1.1) | 2.2 (1.4, 3.7) | <0.001 | 0.003 | 2.50 |
| IL-1β | 1403.0 (735.8, 2083.8) | 4311 (2388.5, 5502.5) | 84.2 (44.2, 125.0) | 258.7 (143.3, 330.2) | <0.001 | 0.004 | 1.41 |
| IL-17A | 3.7 (3.0, 4.4) | 10.5 (6.6, 25) | 0.2 (0.2, 0.3) | 0.6 (0.4, 1.5) | 0.002 | 0.006 | 2.41 |
| RANTES | 108.7 (99.6, 119.4) | 162.4 (122.2, 191.7) | 6.5 (6.0, 7.1) | 9.7 (7.3, 11.5) | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.65 |
| IL-6 | 5.4 (4.5, 8.2) | 38.3 (16.2, 221.7) | 0.3 (0.3, 0.5) | 2.3 (1.0, 13.3) | 0.002 | 0.006 | 6.82 |
| IL-5 | 1.9 (1.8, 2.1) | 2.4 (2.1, 2.5) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.2) | 0.004 | 0.014 | 0.46 |
| TGF-α | 52.7 (37.3, 75.4) | 72.8 (65.7, 88.1) | 3.2 (2.2, 4.5) | 4.3 (4.0, 5.3) | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.64 |
| Eotaxin | 16.3 (13.7, 18.1) | 19.5 (16.5, 22.8) | 1.0 (0.8, 1.1) | 1.2 (1.0, 1.4) | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.43 |
| TNF-α | 8.6 (4.7, 9.1) | 11.3 (6.5, 40.4) | 0.5 (0.3, 0.5) | 0.7 (0.4, 2.4) | 0.007 | 0.018 | 1.75 |
| IL-1α | 2593.5 (1814.7, 4590.0) | 6263.0 (4030.0, 8863.0) | 155.6 (108.9, 275.4) | 375.8 (241.8, 531.8) | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.80 |
| IFN-β | 1.3 (1.1, 1.9) | 2.4 (1.6, 3.4) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.2) | 0.014 | 0.033 | 0.87 |
| IL-1ra | 18,813.0 (16,475.0, 20,163.0) | 15,480.0 (14,761.0, 17,251.0) | 1128.8 (988.5, 1209.8) | 928.8 (885.7, 1035.1) | 0.013 | 0.033 | −0.10 |
| MCP-1 | 50.0 (29.7, 115.4) | 176.0 (72.5, 415.1) | 3.0 (1.8, 7.0) | 10.6 (4.3, 24.9) | 0.017 | 0.037 | 1.47 |
| GM-CSF | 10.2 (8.0, 18.9) | 25.7 (10.3, 83.4) | 0.6 (0.5, 1.1) | 1.5 (0.6, 5.0) | 0.020 | 0.041 | 2.09 |
| PD-L1/B7-H1 | 219.0 (133.0, 248.8) | 141.1 (96.5, 215.3) | 13.1 (8.0, 15.0) | 8.5 (5.8, 12.9) | 0.020 | 0.041 | −0.44 |
| IL-12p70 | 6.8 (6.4, 7.1) | 7.23 (6.6, 8.3) | 0.4 (0.4, 0.4) | 0.4 (0.4, 0.5) | 0.041 | 0.077 | 0.35 |
| IL-3 | 13.8 (6.2, 27.4) | 5.7 (4.7, 9.6) | 0.8 (0.4, 1.6) | 0.3 (0.3, 0.6) | 0.042 | 0.077 | −1.01 |
| IL-17E | 9.8 (9.5, 10.6) | 11.8 (10.8, 13.7) | 0.6 (0.6, 0.6) | 0.7 (0.6, 0.8) | 0.048 | 0.081 | 0.28 |
| TRAIL | 51.7 (34.7, 71.4) | 71.1 (45.7, 120.6) | 3.1 (2.1, 4.3) | 4.3 (2.7, 7.2) | 0.049 | 0.081 | 0.62 |
| IL-7 | 1.1 (1.0, 1.2) | 1.3 (1.2, 1.0) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.1) | 0.046 | 0.081 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; He, F. The Characteristics of Microbiome and Cytokines in Healthy Implants and Peri-Implantitis of the Same Individuals. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195817
Song L, Jiang J, Li J, Zhou C, Chen Y, Lu H, He F. The Characteristics of Microbiome and Cytokines in Healthy Implants and Peri-Implantitis of the Same Individuals. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(19):5817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195817
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Lu, Jimin Jiang, Jia Li, Chuan Zhou, Yanqi Chen, Hongye Lu, and Fuming He. 2022. "The Characteristics of Microbiome and Cytokines in Healthy Implants and Peri-Implantitis of the Same Individuals" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 19: 5817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195817
APA StyleSong, L., Jiang, J., Li, J., Zhou, C., Chen, Y., Lu, H., & He, F. (2022). The Characteristics of Microbiome and Cytokines in Healthy Implants and Peri-Implantitis of the Same Individuals. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(19), 5817. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11195817






