Effectiveness of Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization on Type II Endoleak-Related Complications after Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Inclusion Criteria
- Population: Patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm who underwent EVAR.
- Intervention: Embolization of only inferior mesenteric artery without any additional embolization of aneurysm sac or other aortic side branches.
- Comparators/controls: Patients who underwent EVAR procedure without IMA embolization.
- Outcomes: The rate of type II endoleaks and secondary reinterventions.
- Study design: Observational case-control studies and randomized controlled trials were included.
2.2. Data Extraction and Assessment of Strengths and Weaknesses of Included Studies
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
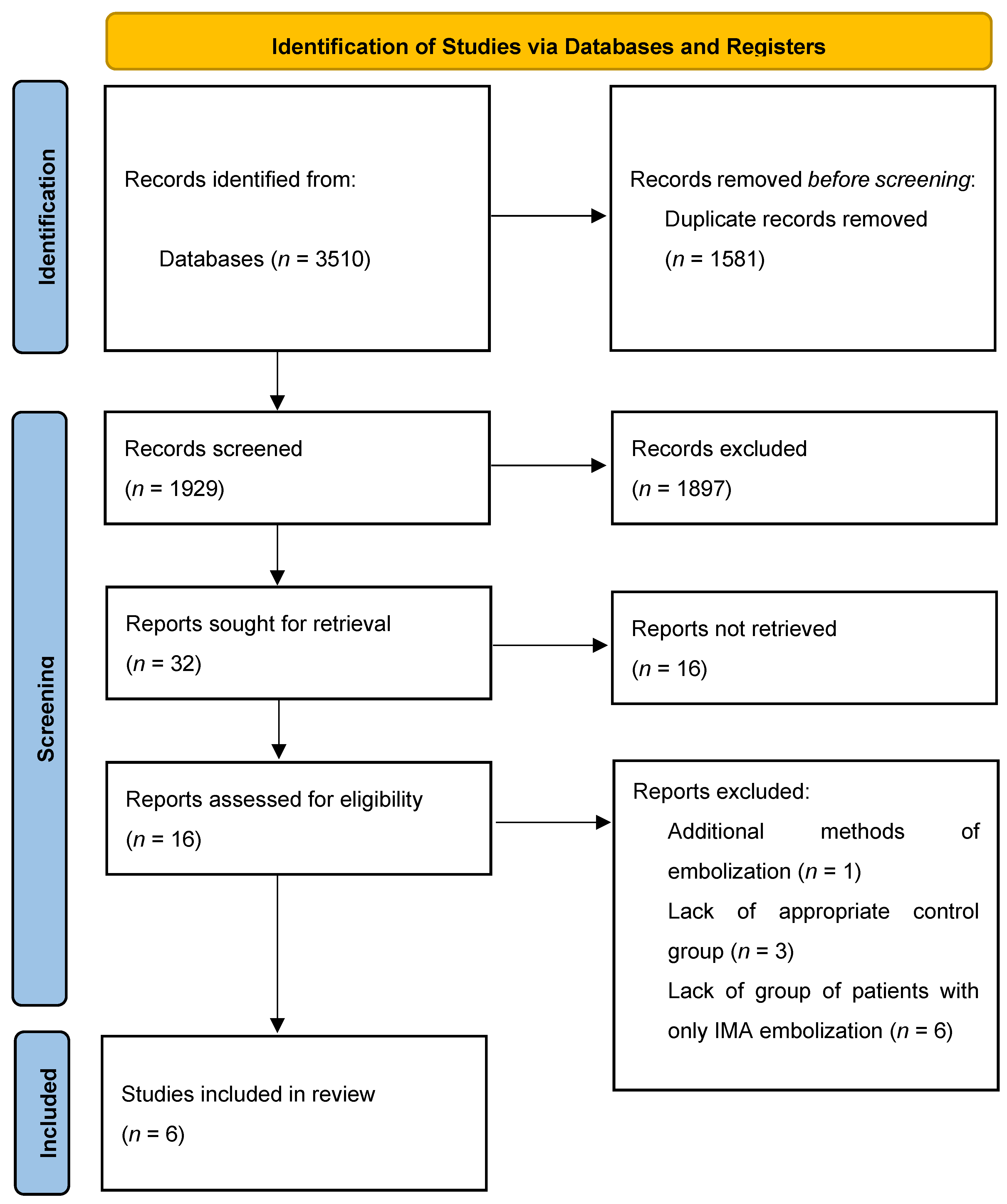
3.1. Study Identification
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Patients’ Characteristics
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
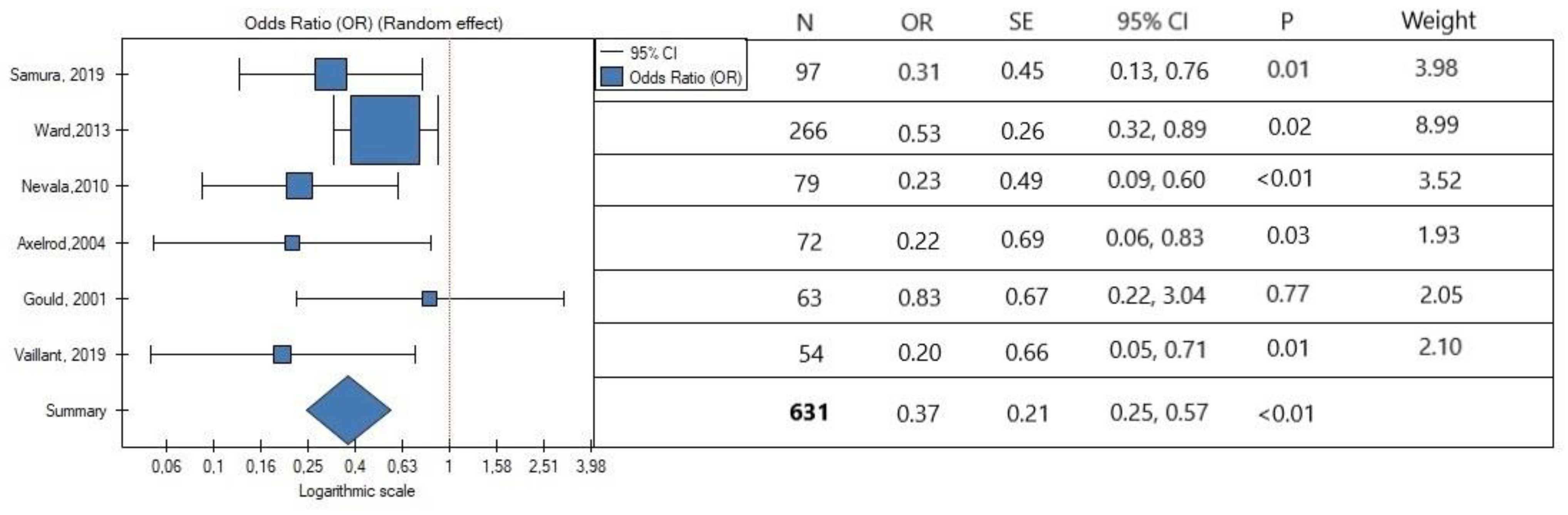
3.5. Data synthesis
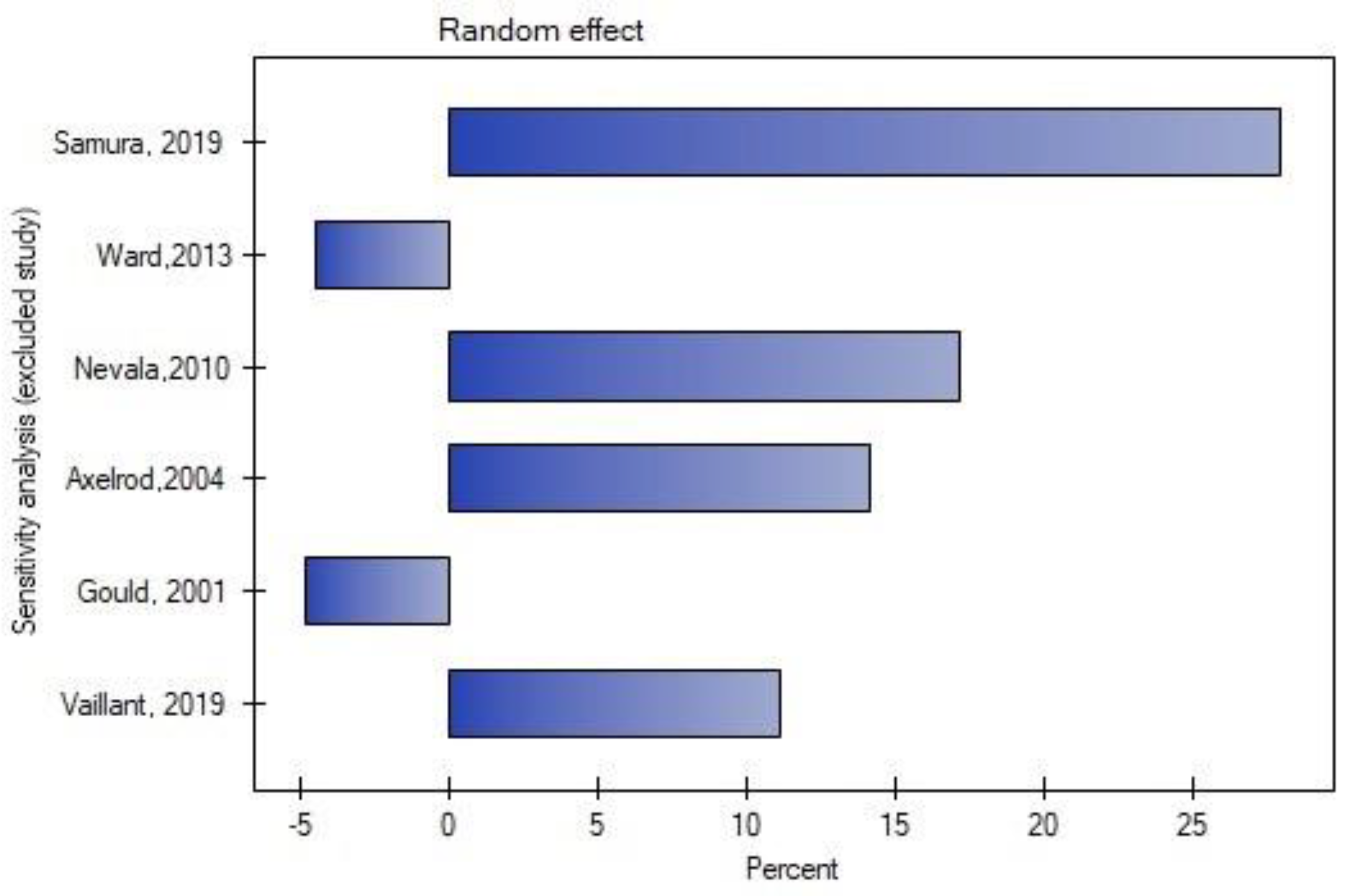
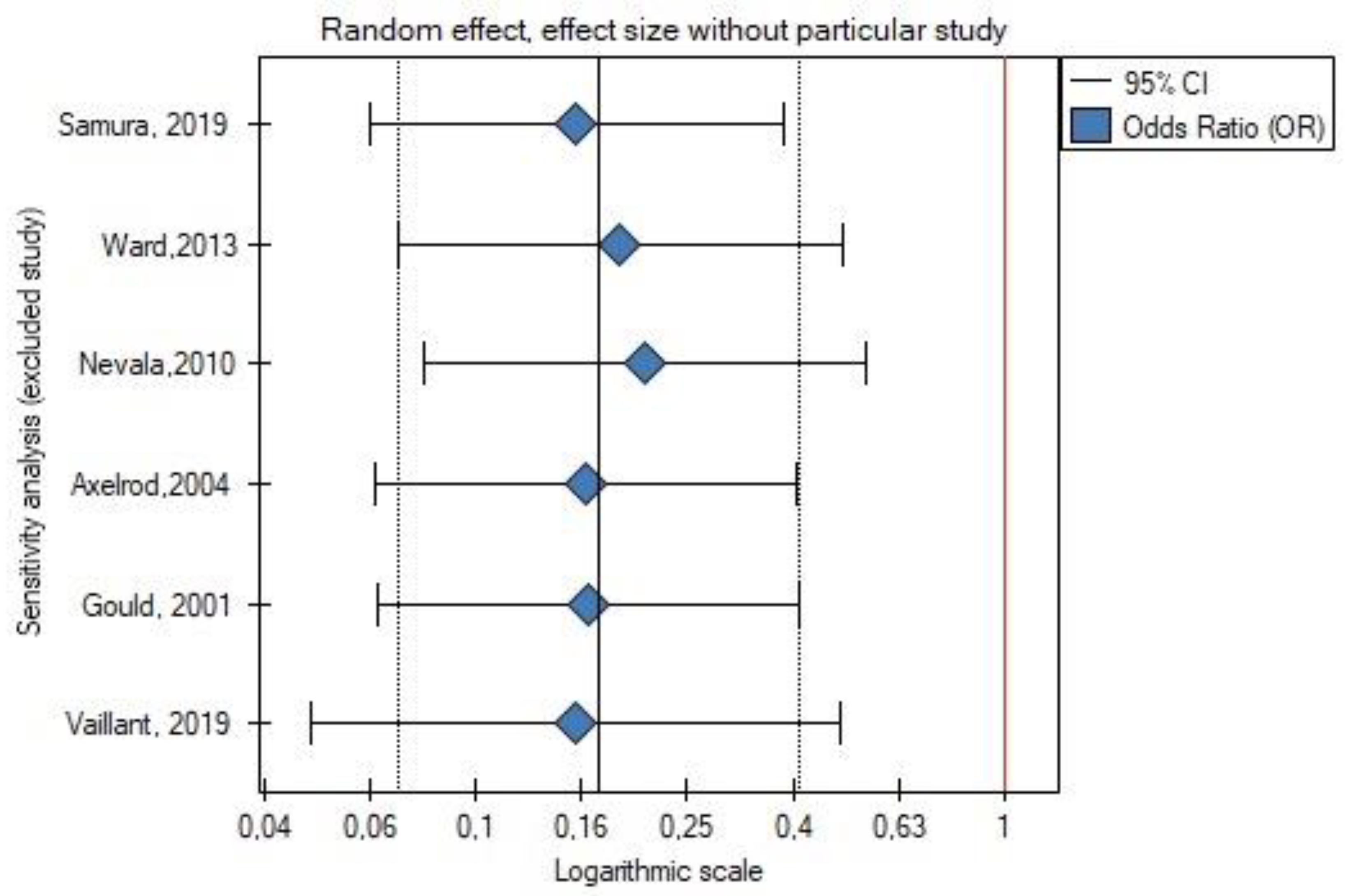
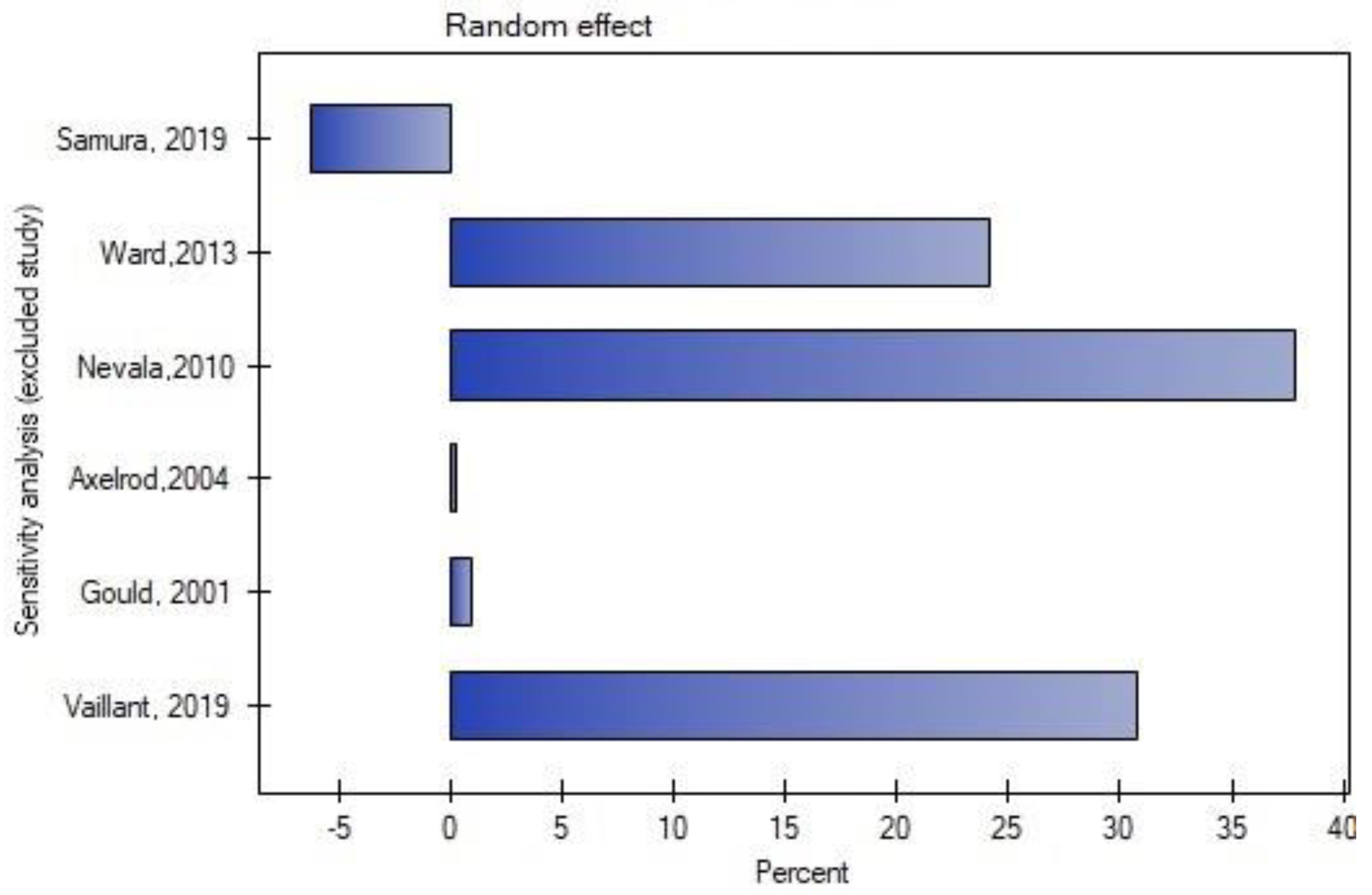
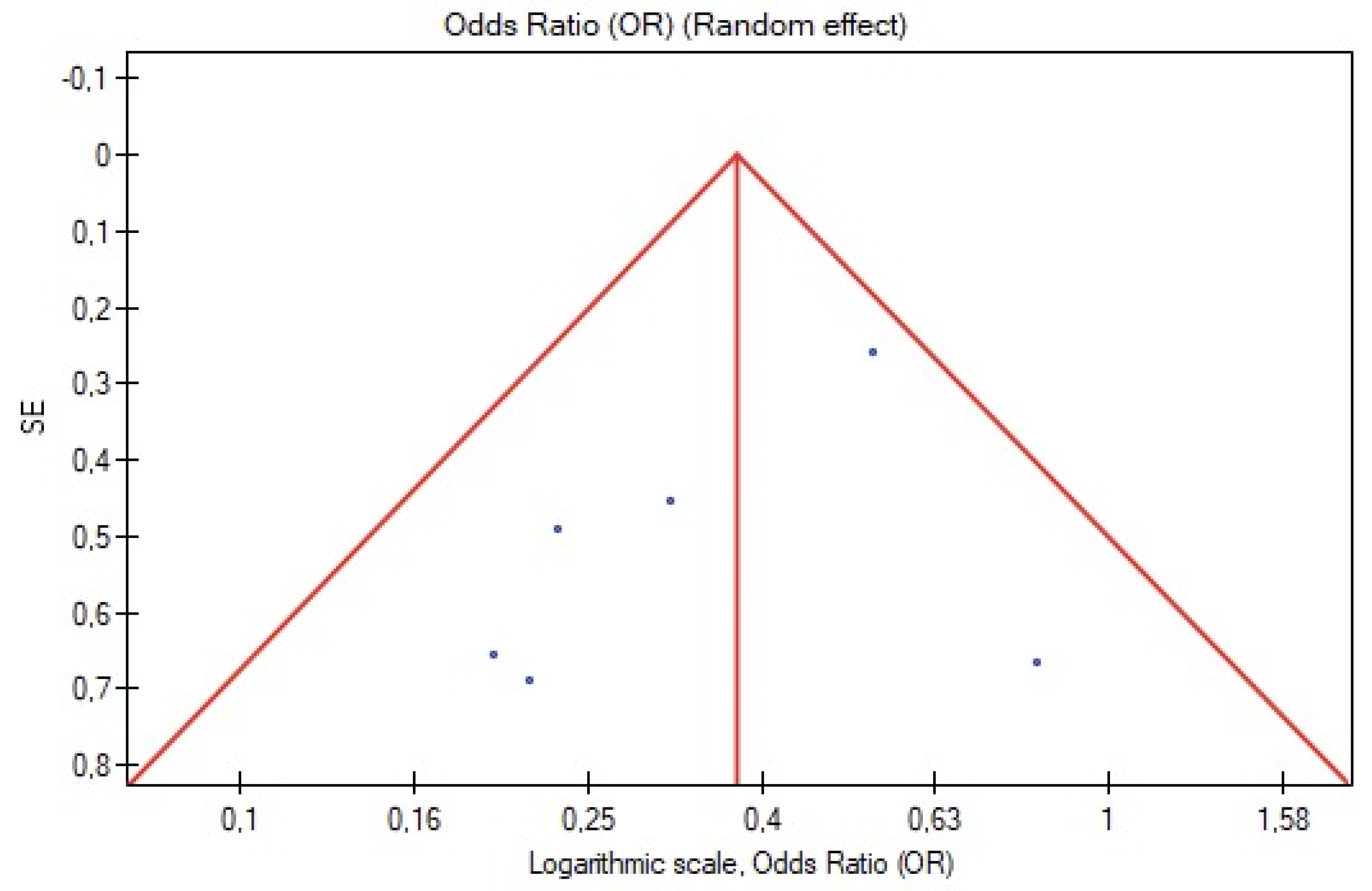
3.6. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, D.C.; Parina, R.P.; Wilson, S.E. Survival after endovascular vs open aortic aneurysm repairs. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daye, D.; Walker, T.G. Complications of endovascular aneurysm repair of the thoracic and abdominal aorta: Evaluation and management. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunga, J.M.; Cragg, A.; Garberich, R.; Urbach, J.A.; Skeik, N.; Alexander, J.; Titus, J.; Stephenson, E.; Alden, P.; Sullivan, T.M. Preoperative Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization: A Valid Method to Reduce the Rate of Type II Endoleak after EVAR? Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2017, 39, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancari, F.; Mäkelä, J.; Juvonen, T.; Venermo, M. Is Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization Indicated Prior to Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm? Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2015, 50, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.; Hertault, A.; Mesnard, T.; Bianchini, A.; Lopez, B.; Patterson, B.O.; Haulon, S.; Sobocinski, J. Outcomes of Preventive Embolization of the Inferior Mesenteric Artery during Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 1360–1370.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samura, M.; Morikage, N.; Mizoguchi, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nagase, T.; Harada, T.; Suehiro, K.; Hamano, K. Effectiveness of Embolization of Inferior Mesenteric Artery to Prevent Type II Endoleak Following Endovascular Aneurysm Repair: A Review of the Literature. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2018, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yin, J.; Hongpeng, Z.; Wei, G. Systematic review and network meta-analysis of pre-emptive embolization of the aneurysm sac side branches and aneurysm sac coil embolization to improve the outcomes of endovascular aneurysm repair. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 947809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hou, P. Sac Embolization and Side Branch Embolization for Preventing Type II Endoleaks After Endovascular Aneurysm Repair: A Meta-analysis. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2020, 27, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu HY, H.; Lindström, D.; Wanhainen, A.; Tegler, G.; Hassan, B.; Mani, K. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prophylactic aortic side branch embolization to prevent type II endoleaks. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 1783–1792.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muka, T.; Glisic, M.; Milic, J.; Verhoog, S.; Bohlius, J.; Bramer, W.; Chowdhury, R.; Franco, O.H. A 24-step guide on how to design, conduct, and successfully publish a systematic review and meta-analysis in medical research. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 351, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmet, L.; Cook, L.; Lee, R. Standard Quality Assessment Criteria for Evaluating Primary Research Papers from a Variety of Fields; Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research: Alberta, GA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Muthu, C.; Maani, J.; Plank, L.D.; Phil, D.; Holden, A.; Hill, A. Strategies to Reduce the Rate of Type II Endoleaks: Routine Intraoperative Embolization of the Inferior Mesenteric Artery and Thrombin Injection Into the Aneurysm Sac. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2007, 14, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alerci, M.; Giamboni, A.; Wyttenbach, R.; Porretta, A.P.; Antonucci, F.; Bogen, M.; Toderi, M.; Guerra, A.; Sartori, F.; Tutta, P.; et al. Endovascular Abdominal Aneurysm Repair and Impact of Systematic Preoperative Embolization of Collateral Arteries: Endoleak Analysis and Long-term Follow-up. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2013, 20, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Chikazawa, G.; Ishida, A. Preoperative Coil Embolization of Side Branches and Postoperative Antifibrinolytic Therapy in Endovascular Aneurysm Repair: A Propensity Score Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.J.; Kessel, D.O.; Robertson, I.; Denton, L.; Dcr, R.; Patel, J.V.; Berridge, D.C.; Kester, R.C.; Scott, D.J.A.; Kingdom, U. Type II endoleaks: Predictable, preventable, and sometimes treatable? J. Vasc. Surg. 2002, 36, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Matsuda, H.; Tanaka, H.; Sanda, Y.; Morita, Y.; Seike, Y. Selective Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization during Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair to Prevent Type II Endoleak. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2017, 63, E130. [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh, R.S.; Chang, H.; Butler, J.R.; Rockman, C.B. Prophylactic sac out fl ow vessel embolization is associated with improved sac regression in patients undergoing endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 76, 113–121.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, A.; Maruta, K.; Omoto, T.; Masuda, T. Midterm Outcomes of Endovascular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair with Prevention of type 2 Endoleak by Intraoperative Aortic Side Branch Coil. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 78, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzan, D.; Geisler, A.; Steiner, S.; Doss, M. Type II endoleak and aortic aneurysm sac shrinkage after preemptive embolization of aneurysm sac side branches. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 73, 1973–1979.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Toma, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sato, Y. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Shrinkage up to 2 Years Following Endovascular Repair with PEmbolization for Preventing Type 2 Endoleak: A Retrospective Single Center Study. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samura, M.; Morikage, N.; Otsuka, R.; Mizoguchi, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Nagase, T.; Harada, T.; Yamashita, O.; Suehiro, K.; Hamano, K. Endovascular aneurysm repair with inferior mesenteric artery embolization for preventing type II Endoleak: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, T.J.; Cohen, S.; Fischman, A.M.; Kim, E.; Nowakowski, F.S.; Ellozy, S.H.; Faries, P.L.; Marin, M.L.; Lookstein, R.A. Preoperative inferior mesenteric artery embolization before endovascular aneurysm repair: Decreased incidence of type II endoleak and aneurysm sac enlargement with 24-month follow-up. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevala, T.; Biancari, F.; Manninen, H.; Matsi, P.; Mäkinen, K.; Ylönen, K.; Perälä, J. Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization before Endovascular Repair of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Effect on Type II Endoleak and Aneurysm Shrinkage. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, D.J.; Lookstein, R.A.; Guller, J.; Nowakowski, F.S.; Ellozy, S.; Carroccio, A.; Teodorescu, V.; Marin, M.L.; Mitty, H.A. Inferior mesenteric artery embolization before endovascular aneurysm repair: Technique and initial results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, M.; Barral, P.A.; Mancini, J.; De Masi, M.; Bal, L.; Piquet, P.; Gaudry, M. Preoperative Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization is a Cost-effective Technique that May Reduce the Rate of Aneurysm Sac Diameter Enlargement and Reintervention After EVAR. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 60, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, D.A.; McWilliams, R.; Edwards, R.D.; Martin, J.; White, D.; Joekes, E.; Rowlands, P.C.; Brennan, J.; Gilling-Smith, G.; Harris, P.L. Aortic side branch embolization before endovascular aneurysm repair: Incidence of type II endoleak. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Sweeting, M.J.; Powell, J.T.; Greenhalgh, R.M. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in 15-years’ follow-up of the UK endovascular aneurysm repair trial 1 (EVAR trial 1): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Powell, J.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Epstein, D.M.; Sculpher, M.J.; Greenhalgh, R.M. The UK EndoVascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) trials: Randomised trials of EVAR versus standard therapy. Health Technol. Assess. 2012, 16, 1–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, R.M.; Brown, L.C.; Kwong, G.P.; Powell, J.T.; Thompson, S.G.; EVAR Trial Participants. Comparison of endovascular aneurysm repair with open repair in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 1), 30-day operative mortality results: Randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.; Atkins, M.D.; Brewster, D.C.; Chung, T.K.; Kwolek, C.J.; LaMuraglia, G.M.; Hodgman, T.M.; Cambria, R.P. Persistent type 2 endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with adverse late outcomes. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Hori, T.; Kohno, H.; Ishida, K.; Nakaya, M.; Matsumiya, G. Analysis of anatomical risk factors for persistent type II endoleaks following endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair using CT angiography. Surg. Today 2016, 46, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timaran, C.H.; Ohki, T.; Rhee, S.J.; Veith, F.J.; Gargiulo, N.J.; Toriumi, H.; Malas, M.B.; Suggs, W.D.; Wain, R.A.; Lipsitz, E.C. Predicting aneurysm enlargement in patients with persistent type II endoleaks. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, Y.; Schiro, B.; Cooper, K.; Ganguli, S.; Khayat, M.; Lam, C.K.; Oklu, R.; Vatakencherry, G.; Gandhi, R.T. Type II endoleaks: Diagnosis and treatment algorithm. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 8, S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoun, J.; Nicolas, D.; Brown, J.R.; Jaber, B.L. Maximum Allowable Contrast Dose and Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury Following Cardiovascular Procedures. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Category | Criteria | Response | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Partial | No | ||
| Clearly defined objective? | Clear hypothesis stated and tested. Objective easily identified in introductory section (or first paragraph of methods section).
| x | ||
| Vaguely/incompletely reported (e.g., “describe the effect of” or “examine the role of”) OR substantial information must be collected from parts of the paper other than introduction/background/objective section. | x | |||
| Question or objective is not reported, or is incomprehensible. | x | |||
| Prospective study design? | Hypothesis designed prior to selection of participants. | x | ||
| x | |||
| Selection criteria well described? | Selection strategy designed to obtain un unbiased sample of the relevant target population.
| x | ||
Selection methods (and inclusion/exclusion criteria) are not completely described OR selection methods described elsewhere.
| x | |||
| No information provided OR obviously inappropriate selection procedures. | x | |||
| Was an objective definition of patent IMA used? | Appropriate definition of patent IMA used, including both of the following criteria:
| x | ||
Limited definition of patent IMA described:
| x | |||
| No definition of patent IMA described. | x | |||
| Assessment of outcome—Was an appropriate technical method used for IMA embolization? | Method of IMA embolization well described:
| x | ||
Method of IMA embolization well described:
| x | |||
| Method of IMA embolization not described OR limited description provided AND no assessment of reproducibility made. | x | |||
| Sample size calculation/estimation reported in methodology? | Details of sample size calculation/estimation reported in methodology. | x | ||
| Required sample size reported, but no details on how this was calculated/estimated. | x | |||
| No sample size calculation/estimation conducted. | x | |||
| What was the sample size? | <50 OR 50–100 OR >100 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Not reported. | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Did all participants undergo a CT scan prior to IMA embolization and during the follow-up? | For all patients, CT data were present both before the IMA embolization and during the follow-up. | x | ||
| Were participant characteristics adequately described? | Sufficient relevant baseline information clearly characterizing the participants is provided (or reference to previously published baseline data is provided). Includes at least five of the following:
| x | ||
Poorly defined criteria or incomplete relevant baseline/demographic information (e.g., information on likely confounders not reported).
| x | |||
| No baseline/demographic information provided. | x | |||
| Study | Reason for Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Muthu et al. (2007) [13] | Addition of thrombin to the aneurysmal sac. |
| Alerci et al. (2013) [14] | Lack of control group. |
| Hiraoka et al. (2017) [15] | Lack of group of patients with only IMA embolization. |
| Parry et al. (2002) [16] | Lack of control group. |
| Fukuda et al. (2017) [17] | Groups of patients incompatible with our inclusion criteria; lack of separate group of patients with IMA embolization |
| Rokosh et al. (2021) [18] | Lack of group of patients with only IMA embolization. |
| Atsushi et al. (2021) [19] | Lack of group of patients with only IMA embolization. |
| Branzan et al. (2020) [20] | Lack of group of patients with only IMA embolization. |
| Nakayama et al. (2022) [21] | Lack of group of patients with only IMA embolization. |
| Petit et al. (2021) [5] | Lack of appropriate control group; study also involved patients who underwent fenestrated EVAR (F-EVAR). |
| Study | Country | Study Design | Sample Size | Embolization Group | Non-Embolization Group | Inclusion Criteria for Embolization Group | Inclusion Criteria for Non-Embolization Group | Groups Matched? | Devices Used for IMA Embolization | Study Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samura, et al., 2019 [22] | Japan | Randomized controlled trial | 97 | 46 | 51 | Patients with diagnosis of AAAs and anatomical suitability for EVAR, risk factors of T2EL (IMA patency with IMA ≥3 mm, LAs ≥2 mm, or an aortoiliac-type aneurysm) | The same criteria as for the embolization group; randomly assigned | No | Amplatzer Vascular Plug, metallic coils | Primary: occurrence of T2EL Secondary: maximal aneurysmal diameter change (mm), occurrence of aneurysmal sac growth, validity of defined risk factors, complications after IMA embolization, and secondary reintervention rate due to T2EL |
| Ward et al., 2013 [23] | United States | Retrospective cohort study | 266 | 108 | 158 | Patients with AAAs and a patent IMA visualized on preprocedural computed tomography (CT) angiography and subsequent conventional angiography | Patients with AAAs and a patent IMA visualized on preprocedural CT angiography but not on conventional angiography | No | coils | Incidence of T2EL, aneurysm sac volume enlargement at 24 months, and secondary interventions |
| Nevala et al., 2010 [24] | Finland | Retrospective cohort study | 79 | 40 | 39 | Patent IMA detected on computed tomographic (CT) angiography; patients at Kuopio University Hospital | Patients who underwent EVAR at Oulu University Hospital | No | Interlocking detachable coils | The presence of type II endoleak, aneurysm sac size change, and secondary procedures |
| Axelrod et al., 2004 [25] | United States | Retrospective cohort study | 72 | 18 | 54 | Patients with AAAs and a patent IMA on preoperative CT angiography + visualization of IMA on routine flush calibrated aortography | Lack of visualization of IMA on flush aortography or technically unsuccessful prior embolization | No | Platinum microcoils | The presence of T2EL, incidence of secondary procedures, and change in the diameter of the infrarenal aorta |
| Gould et al., 2001 [27] | United Kingdom | Retrospective cohort study | 63 | 20 | 43 | Patients with AAAs with assessed IMA on helical CT and calibrated angiography; the decision of final IMA embolization was made by operators | Patients with failed embolization (4), small technically unsuitable vessels (16), and with no available angiographic room time immediately before endovascular aortic repair (23) | No | Coils | The presence of T2EL, the mean sac diameter change, and secondary interventions |
| Vaillant et al., 2019 [26] | France | Retrospective cohort study | 82 | 37 | 45 | Patients eligible for EVAR (with favorable anatomical characteristics), IMA > 3 mm with no ostial occlusion or stenosis, treated after 2014 | Patients treated for EVAR before 2014 with a patent IMA > 3 mm visualized on preprocedural CT scan | No | Coils, plugs | Primary: the rate of aneurysm sac enlargement Secondary: the rate of T2EL, rate of reinterventions, and overall cost of management in each group |
| Embolization Group | Non-Embolization Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Samura et al., 2019 [22] | ||
| Age (y) | 75.5 | 77.5 |
| Male sex (%) | 90.6% | 73.6% |
| Aneurysm diameter (mm) | 53.2 | 50.5 |
| Ward et al., 2013 [23] | ||
| Age (y) | 73.5 | 75.0 |
| Male sex (%) | 88 | 84 |
| Aneurysm diameter (mm) | 54 | 56 |
| Patent lumbar arteries | 7.0 | 6.3 |
| Nevala et al., 2010 [24] | ||
| Age (y) | 71.2 | 73.4 |
| Male sex (%) | 85 | 90 |
| Vaillant et al., 2019 [26] | ||
| Age (y) | 73.78 | 76.73 |
| Male sex (%) | 97.3 | 100 |
| Aneurysm diameter (mm) | 53.19 | 53.07 |
| Patent lumbar arteries | 3.86 | 4.44 |
| Study | Clearly Defined Objective? | Prospective Study Design? | Selection Criteria Well Described? | Objective Definition of Patent IMA? | Well-Described Technical Aspect of Embolization? | Sample Size | Inclusion of CT Scan before IMA Embolization and during the Follow-up? | Participants’ Characteristics Described? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samura et al., 2019 [22] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 50–100 | Yes | Yes |
| Ward et al., 2013 [23] | Yes | No | Yes | Partial | Yes | >100 | Yes | Partial |
| Nevala et al., 2010 [24] | Yes | No | Yes | Partial | Yes | 50–100 | Yes | Yes |
| Axelrod et al., 2004 [25] | Yes | No | Yes | Partial | Yes | 50–100 | Yes | Partial |
| Gould et al., 2001 [27] | Yes | No | Partial | Partial | Yes | 50–100 | Yes | No |
| Vaillant et al., 2019 [26] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | 50–100 | Yes | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niklas, N.; Malec, M.; Gutowski, P.; Kazimierczak, A.; Rynio, P. Effectiveness of Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization on Type II Endoleak-Related Complications after Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185491
Niklas N, Malec M, Gutowski P, Kazimierczak A, Rynio P. Effectiveness of Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization on Type II Endoleak-Related Complications after Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185491
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiklas, Natalia, Michalina Malec, Piotr Gutowski, Arkadiusz Kazimierczak, and Paweł Rynio. 2022. "Effectiveness of Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization on Type II Endoleak-Related Complications after Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185491
APA StyleNiklas, N., Malec, M., Gutowski, P., Kazimierczak, A., & Rynio, P. (2022). Effectiveness of Inferior Mesenteric Artery Embolization on Type II Endoleak-Related Complications after Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185491





