Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke—Effect Modification by Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Population and Outcome Data
2.3. Exposure and Meteorological Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with AIS
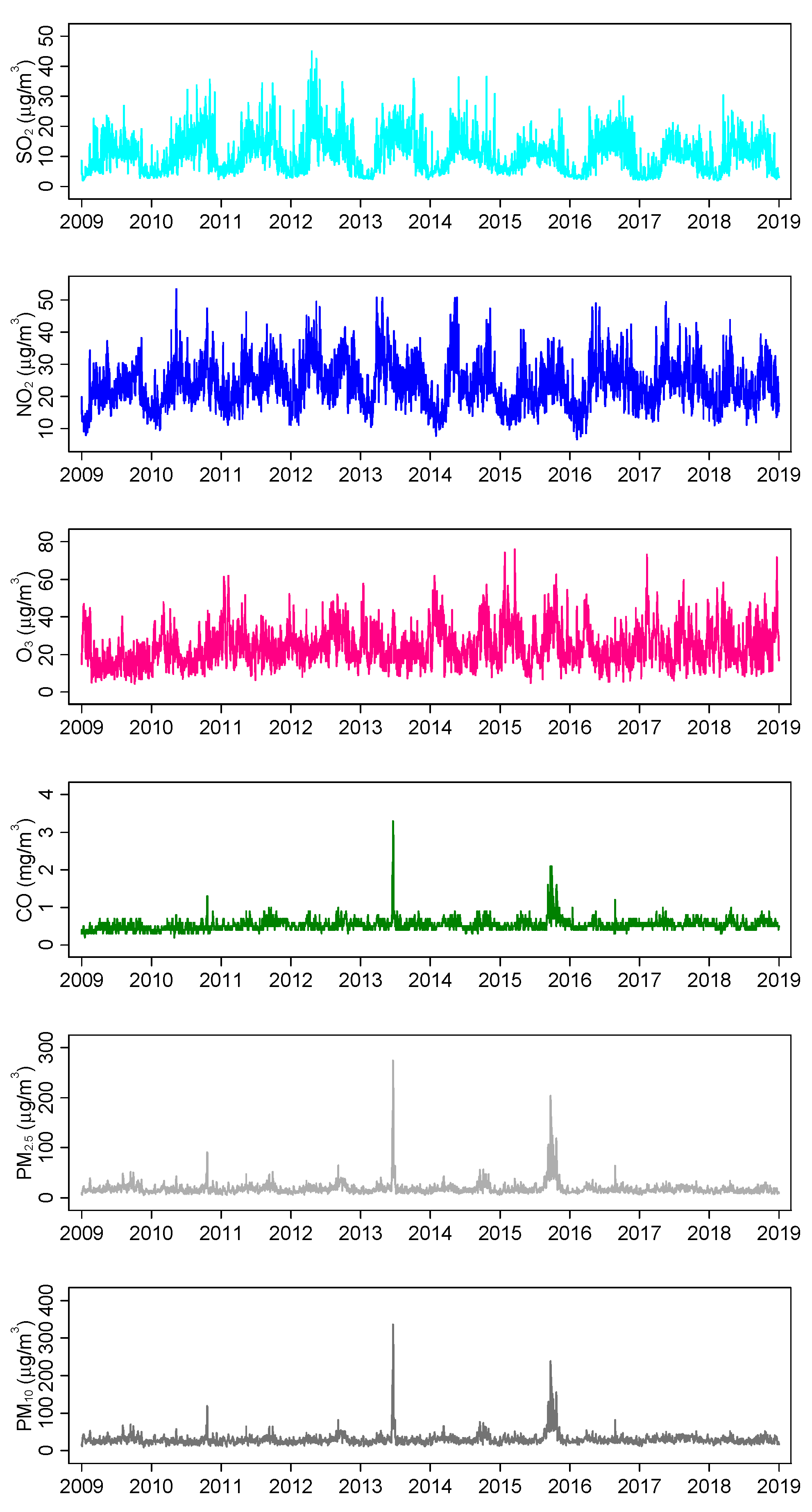
3.2. Air Pollutant Concentrations and Meteorological Levels
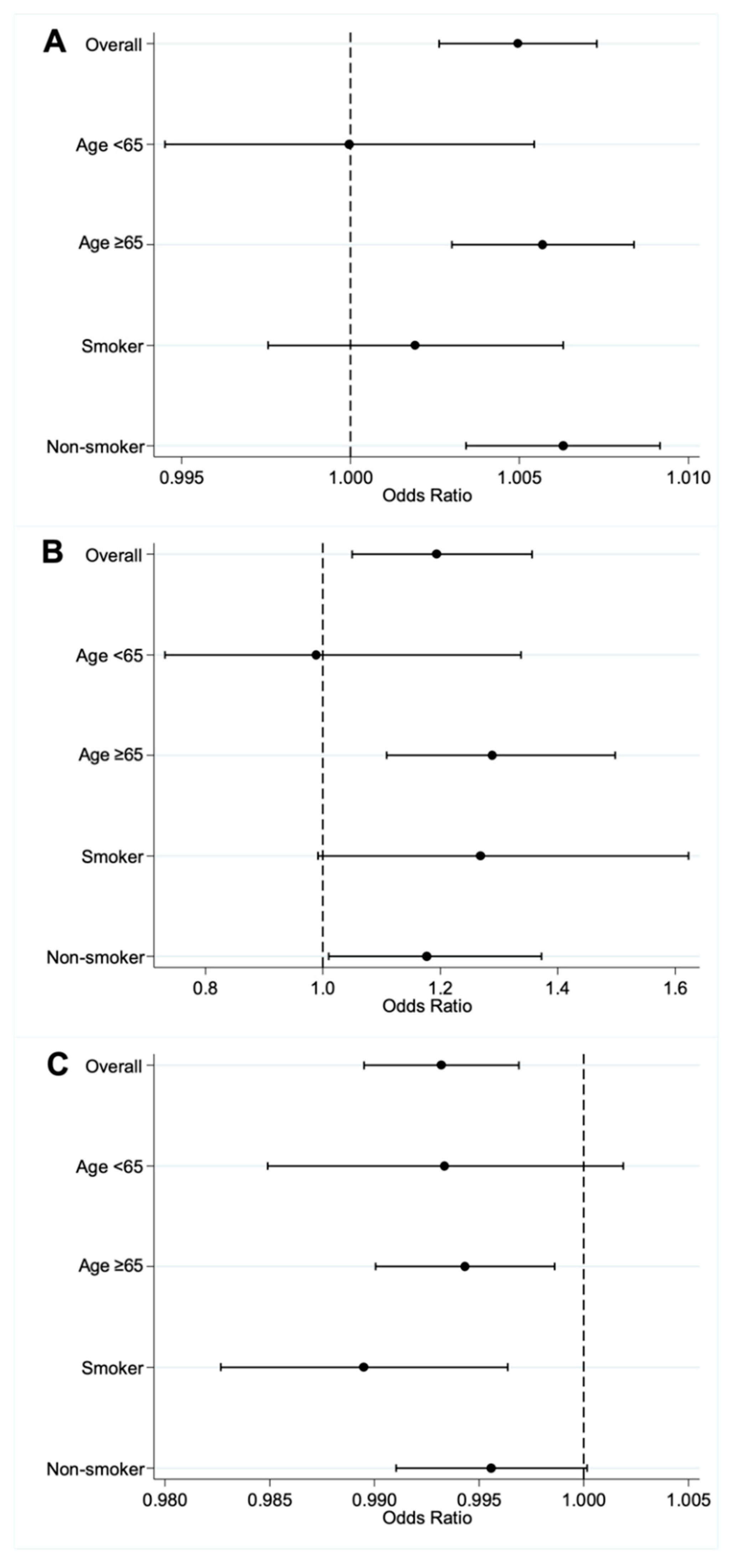
3.3. Effect Modification of AF on Air Pollutant and AIS
3.4. Effect Modification of AF on Air Pollutants and AIS in Subgroups of AF Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M.; et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Lee, K.K.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.; Nair, H.; Whiteley, W.; Langrish, J.P.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudin, A.; Forsberg, B.; Jakobsson, K. Air Pollution and Stroke. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Fang, J.; Mittleman, M.A.; Kapral, M.K.; Wellenius, G.A.; Investigators of the Registry of the Canadian Stroke Network. Fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5) and the risk of acute ischemic stroke. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.-H.; McAnulty, J.H., Jr.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.; Okin, P.M.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Iadecola, C. Atrial Fibrillation and Mechanisms of Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudin, A.; Strömberg, U.; Jakobsson, K.; Stroh, E.; Lindgren, A.G.; Norrving, B.; Pessah-Rasmussen, H.; Engström, G.; Björk, J. Hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: Does long-term exposure to air pollution interact with major risk factors? Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2011, 31, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, E.; Roth, M. Review of Singapore’s air quality and greenhouse gas emissions: Current situation and opportunities. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungman, P.L.; Mittleman, M.A. Ambient Air Pollution and Stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 3734–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, B.G. Fixed factors that modify the effects of time-varying factors: Applying the case-only approach. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich David, Q.; Mittleman Murray, A.; Link Mark, S.; Schwartz, J.; Luttmann-Gibson, H.; Catalano Paul, J.; Speizer Frank, E.; Gold Diane, R.; Dockery Douglas, W. Increased Risk of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Episodes Associated with Acute Increases in Ambient Air Pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrotin, J.B.; Zeller, M.; Lorgis, L.; Cottin, Y.; Giroud, M.; Béjot, Y. Evidence of the role of short-term exposure to ozone on ischaemic cerebral and cardiac events: The Dijon Vascular Project (DIVA). Heart 2010, 96, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Ha, S.; Talbott, E.O.; Lissaker, C.T.K. Association between Ozone Exposure and Onset of Stroke in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, USA, 1994–2000. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Liu, T.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, G. Association between air pollution and development of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Heart Lung J. Cardiopulm. Acute Care 2016, 45, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhinehart, Z.J.; Kinnee, E.; Essien, U.R.; Saul, M.; Guhl, E.; Clougherty, J.E.; Magnani, J.W. Association of Fine Particulate Matter and Risk of Stroke in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2011760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-W.; Bang, O.Y.; Ahn, K.; Park, S.-S.; Park, T.H.; Kim, J.G.; Ko, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, J.; et al. Air Pollution Is Associated With Ischemic Stroke via Cardiogenic Embolism. Stroke 2017, 48, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-C.; Lee, J.-T.; Kim, H.; Ha, E.-H.; Schwartz, J.; Christiani David, C. Effects of air pollutants on acute stroke mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Lin, H.M.; Stewart, W.F.; Kong, L.; Xu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, S.; Chen, W.; Shah, N.; et al. Seasonal pattern of the acute mortality effects of air pollution. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, A.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Meng, X.; Knibbs, L.D.; Bell, M.L.; Abramson, M.J.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Survival After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodani, E.; Akao, M. Atrial fibrillation and stroke prevention: State of the art—Epidemiology and pathophysiology: New risk factors, concepts and controversies. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2020, 22, O1–O13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurhanewicz, N.; McIntosh-Kastrinsky, R.; Tong, H.; Walsh, L.; Farraj, A.K.; Hazari, M.S. Ozone co-exposure modifies cardiac responses to fine and ultrafine ambient particulate matter in mice: Concordance of electrocardiogram and mechanical responses. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboul, C.; Thireau, J.; Meyer, G.; André, L.; Obert, P.; Cazorla, O.; Richard, S. Carbon monoxide exposure in the urban environment: An insidious foe for the heart? Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2012, 184, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A. Oral anticoagulation to reduce risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation: Current and future therapies. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cowan, C.; Healicon, R.; Robson, I.; Long, W.R.; Barrett, J.; Fay, M.; Tyndall, K.; Gale, C.P. The use of anticoagulants in the management of atrial fibrillation among general practices in England. Heart 2013, 99, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, X.; Lei, L.; Zhou, H.; Deng, S.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bao, J.; Peng, J.; Huang, C. Short-term associations between ambient air pollution and stroke hospitalisations: Time-series study in Shenzhen, China. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e032974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: The euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, T.; Lisi, M.; Dragoni, S.; Leone, M.C.; Forconi, S.; Munzel, T.; Parker, J.D. Smoking-induced preconditioning: Acute, but not chronic, smoking paradoxically protects the endothelium from ischemia and reperfusion. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34 (Suppl. S1), 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, C.-H.; Ko, J.; Zheng, H.; Ho, A.F.-W.; Foo, D.; Foo, L.-L.; Lim, P.Z.-Y.; Liew, B.W.; Chai, P.; Yeo, T.-C.; et al. Association between smoking status and outcomes in myocardial infarction patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No AF n = 40,951 | With AF n = 10,722 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 65 (57–75) | 77 (69–84) | <0.001 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 25,478 (62.2) | 4888 (45.6) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Chinese | 30,312 (74.0) | 8627 (80.5) | |
| Malay | 6664 (16.3) | 1533 (14.3) | |
| Indian | 3256 (7.9) | 386 (3.6) | |
| Others | 719 (1.8) | 176 (1.6) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 18,690 (45.6) | 4424 (41.3) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 33,116 (80.9) | 9595 (89.5) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidaemia, n (%) | 37,363 (91.2) | 9587 (89.4) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Current smoker | 11,471 (28.0) | 1216 (11.3) | |
| Ex-smoker | 5866 (14.3) | 1687 (15.7) | |
| Non-smoker | 22,617 (55.2) | 7422 (69.2) | |
| Unknown smoking status | 997 (2.4) | 397 (3.7) |
| Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meteorological factors | ||||
| Average temperature, °C | 27.8 (1.1) | 27.9 (27.1–28.7) | 22.8 | 30.8 |
| Relative humidity, % | 79.5 (5.4) | 79.4 (75.6–83.2) | 59.2 | 96.9 |
| Total rainfall, mm | 5.5 (12.6) | 0.0 (0.0–4.2) | 0.0 | 216.2 |
| Air pollutants | ||||
| PM2.5, µg/m3 | 18.4 (12.9) | 15.9 (12.7–20.5) | 5.1 | 274.4 |
| PM10, µg/m3 | 30.0 (15.8) | 27.3 (22.7–33.4) | 9.7 | 335.9 |
| O3, µg/m3 | 24.3 (10.1) | 22.5 (17.3–29.8) | 4.4 | 76.0 |
| NO2, µg/m3 | 23.9 (7.0) | 23.3 (18.8–28.4) | 6.8 | 53.4 |
| SO2, µg/m3 | 10.8 (6.1) | 10.2 (5.6–14.4) | 2.0 | 45.0 |
| CO, mg/m3 | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.5 (0.5–0.6) | 0.2 | 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, B.Y.-Q.; Ho, J.S.Y.; Ho, A.F.-W.; Pek, P.P.; Leow, A.S.-T.; Raju, Y.; Sia, C.-H.; Yeo, L.L.-L.; Sharma, V.K.; Ong, M.E.-H.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke—Effect Modification by Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185429
Tan BY-Q, Ho JSY, Ho AF-W, Pek PP, Leow AS-T, Raju Y, Sia C-H, Yeo LL-L, Sharma VK, Ong ME-H, et al. Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke—Effect Modification by Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(18):5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185429
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Benjamin Yong-Qiang, Jamie Sin Ying Ho, Andrew Fu-Wah Ho, Pin Pin Pek, Aloysius Sheng-Ting Leow, Yogeswari Raju, Ching-Hui Sia, Leonard Leong-Litt Yeo, Vijay Kumar Sharma, Marcus Eng-Hock Ong, and et al. 2022. "Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke—Effect Modification by Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 18: 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185429
APA StyleTan, B. Y.-Q., Ho, J. S. Y., Ho, A. F.-W., Pek, P. P., Leow, A. S.-T., Raju, Y., Sia, C.-H., Yeo, L. L.-L., Sharma, V. K., Ong, M. E.-H., Aik, J., & Zheng, H. (2022). Ambient Air Pollution and Acute Ischemic Stroke—Effect Modification by Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(18), 5429. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11185429










