Radiation Exposure among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Medical-Center Retrospective Analysis in Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
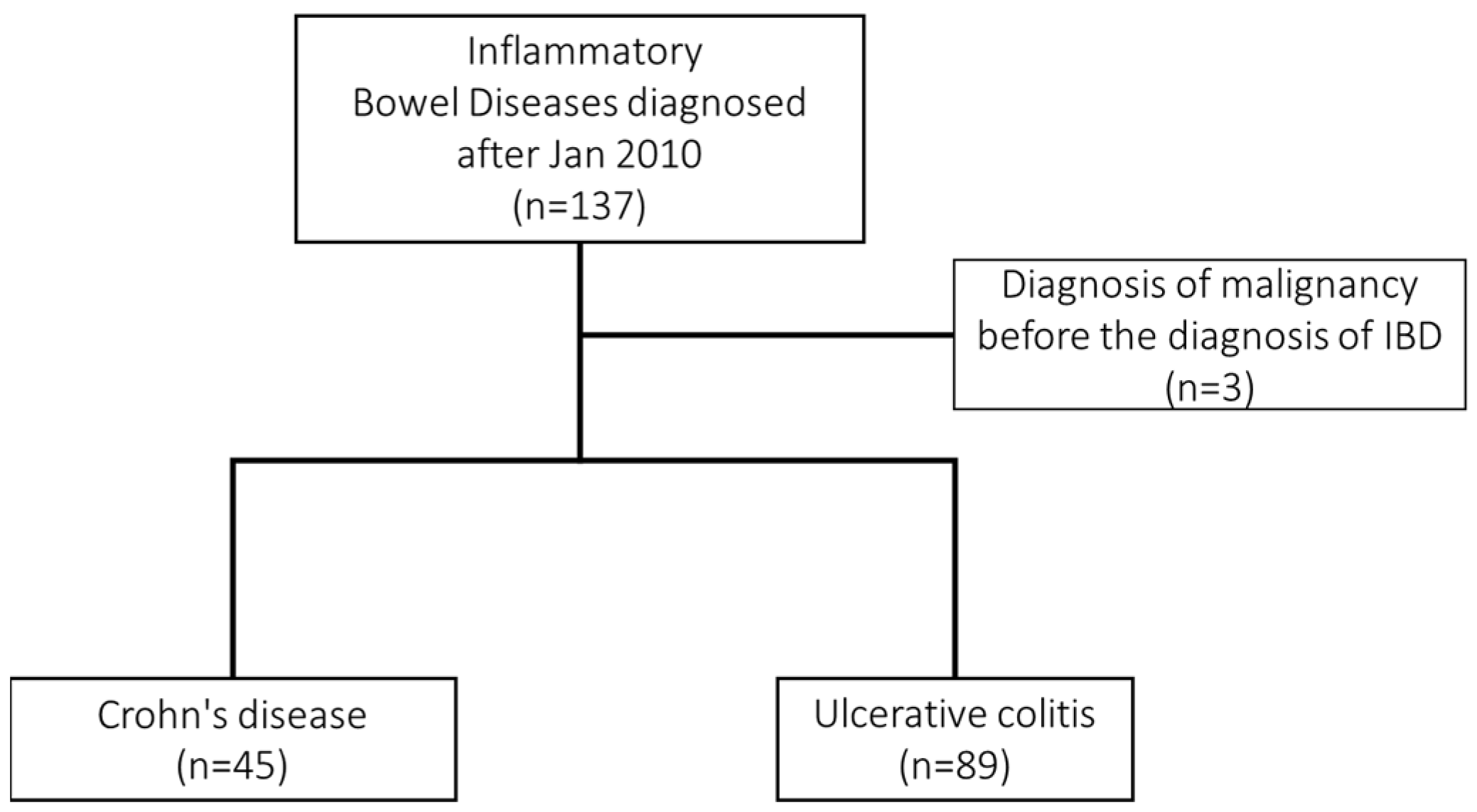
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Medical Radiation Exposure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Euers, L.; Abughazaleh, S.; Glassner, K.; Gajula, P.; Jones-Pauley, M.; Ezeana, C.; Puppala, M.; Wang, L.; Wong, S.; Oglat, A.; et al. Risk Factors for and Frequency of CT Scans, Steroid Use, and Repeat Visits in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Seen at a Single-Center Emergency Department: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, M.T.; Stevenson, R.; Abdul-Aema, B.; Zou, G.; Jairath, V.; Radford, S.; Marciani, L.; Moran, G.W. Diagnostic Accuracy of Non-Invasive Imaging for Detection of Colonic Inflammation in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukawska, A.; Slosarz, D.; Zimoch, A.; Serafin, K.; Poniewierka, E.; Kempinski, R. Cumulative Effective Dose from Medical Imaging in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed tomography—An increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Ricciuto, A.; Lewis, A.; D’Amico, F.; Dhaliwal, J.; Griffiths, A.M.; Bettenworth, D.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sands, B.E.; Reinisch, W.; et al. STRIDE-II: An Update on the Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE) Initiative of the International Organization for the Study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining Therapeutic Goals for Treat-to-Target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatu, S.; Subramanian, V.; Pollok, R.C. Meta-analysis: Diagnostic medical radiation exposure in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.C.; Low, D.; Chong, R.Y.; Diong, C.; Chawla, T. Utilization of Diagnostic Imaging and Ionization Radiation Exposure Among an Inflammatory Bowel Disease Inception Cohort. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatu, S.; Poullis, A.; Holmes, R.; Greenhalgh, R.; Pollok, R.C. Temporal trends in imaging and associated radiation exposure in inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2013, 67, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, C.; Normandeau, L.; Bouin, M. Diagnostic Radiation Exposure in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 2030735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, N.; Pollok, R.C. Diagnostic imaging and radiation exposure in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, T.J.; Tabari, A.; Gee, M.S.; McCarthy, C.J. Factors influencing cumulative radiation dose from percutaneous intra-abdominal abscess drainage in the setting of inflammatory bowel disease. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.H.; Su, P.Y.; Huang, S.P.; Wu, L.; Hsu, T.C.; Zeng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.Y. Evaluation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with inflammatory bowel disease using controlled attenuation parameter technology: A Taiwanese retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.H.; Hsu, T.C.; Chen, M.W.; Su, P.Y.; Chen, Y.Y. Clinical features and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in a low-incidence area: A hospital-based retrospective cohort study in Taiwan. Medicine 2021, 100, e25090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.H.; Weng, M.T.; Tung, C.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Chang, Y.T.; Chang, C.H.; Shieh, M.J.; Wong, J.M.; Wei, S.C. Epidemiological trend in inflammatory bowel disease in Taiwan from 2001 to 2015: A nationwide populationbased study. Intest. Res. 2019, 17, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.H.; Chen, M.W.; Chang, Y.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Hsu, T.C.; Chen, Y.Y. Predictive values of stool-based tests for mucosal healing among Taiwanese patients with ulcerative colitis: A retrospective cohort analysis. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.-H.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Hsu, T.-C.; Chen, Y.-Y. Real-world experience of adalimumab therapy for patients with ulcerative colitis: A single tertiary medical center experience in Central Taiwan. Adv. Dig. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Chou, J.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, P.J.; Cheng, K.S.; Chen, T.W. ABO blood type and clinical characteristics of patients with ulcerative colitis: A hospital-based study in central Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0260018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.H.; Chiu, C.T.; Yeh, P.J.; Pan, Y.B.; Chiu, C.H. Clostridium innocuum infection in hospitalised patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Infect. 2022, 84, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Kwan, M.L.; Marlow, E.C.; Theis, M.K.; Bolch, W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Bowles, E.J.A.; Duncan, J.R.; Greenlee, R.T.; Kushi, L.H.; et al. Trends in Use of Medical Imaging in US Health Care Systems and in Ontario, Canada, 2000–2016. Jama 2019, 322, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, U.; Khan, N. Treat to Target in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Updated Review of Literature. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2017, 15, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K. Clinical management for small bowel of Crohn’s disease in the treat-to-target era: Now is the time to optimize treatment based on the dominant lesion. Intest. Res. 2020, 18, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, R.O.; Nixon, E.; Sapundzieski, M.; Filobbos, R.; Limdi, J.K. Radiation exposure in patients with inflammatory bowel disease--primum non nocere? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmond, A.N.; O’Regan, K.; Curran, C.; McWilliams, S.; Fitzgerald, T.; Maher, M.M.; Shanahan, F. Crohn’s disease: Factors associated with exposure to high levels of diagnostic radiation. Gut 2008, 57, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.S.; Park, D.I.; Kim, E.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Chan Huh, K.; Jung, S.A.; Yoon, S.M.; et al. Quantifying exposure to diagnostic radiation and factors associated with exposure to high levels of radiation in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estay, C.; Simian, D.; Lubascher, J.; Figueroa, C.; O’Brien, A.; Quera, R. Ionizing radiation exposure in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Are we overexposing our patients? J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, Z.; Fraser, A.; Krongrad, R.; Hazazi, R.; Benjaminov, O.; Meyerovitch, J.; Tal, O.B.; Choen, A.; Niv, Y.; Fraser, G. Factors associated with radiation exposure in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambadakone, A.R.; Chaudhary, N.A.; Desai, G.S.; Nguyen, D.D.; Kulkarni, N.M.; Sahani, D.V. Low-dose MDCT and CT enterography of patients with Crohn disease: Feasibility of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, W743–W752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, O.; O’Neill, S.; O’Neill, F.; McLaughlin, P.; McGarrigle, A.; McWilliams, S.; O’Connor, O.; Desmond, A.; Walsh, E.K.; Ryan, M.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography using lower doses of radiation for patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, D.; Lombardi, S.; Trattenero, C.; Franzesi, C.T.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Sironi, S. CT enterography: Diagnostic value of 4th generation iterative reconstruction algorithm in low dose studies in comparison with standard dose protocol for follow-up of patients with Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, A.Y.; Yang, S.K.; Yun, S.C.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, G.S.; Ha, H.K. A prospective comparison of standard-dose CT enterography and 50% reduced-dose CT enterography with and without noise reduction for evaluating Crohn disease. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.B.; Mc Laughlin, P.D.; Crush, L.; O’Connor, O.J.; Mc Williams, S.R.; Craig, O.; Mc Garrigle, A.M.; O’Neill, F.; Bye, J.; Ryan, M.F.; et al. A prospective feasibility study of sub-millisievert abdominopelvic CT using iterative reconstruction in Crohn’s disease. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Yanagawa, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Miyata, T.; Tsubamoto, M.; Honda, O.; Tomiyama, N. Combination of Deep Learning-Based Denoising and Iterative Reconstruction for Ultra-Low-Dose CT of the Chest: Image Quality and Lung-RADS Evaluation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Park, E.A.; Lee, W.; Ahn, C.; Kim, J.H. Incremental Image Noise Reduction in Coronary CT Angiography Using a Deep Learning-Based Technique with Iterative Reconstruction. Korean J. Radiol. 2020, 21, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govani, S.M.; Guentner, A.S.; Waljee, A.K.; Higgins, P.D. Risk stratification of emergency department patients with Crohn’s disease could reduce computed tomography use by nearly half. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1702–1707.e1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, D.; Goertz, R.S.; Bernatik, T. Diagnostics in inflammatory bowel disease: Ultrasound. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 3192–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, G.; Behara, R.; Braun, R.; Keshavarzian, A. Diagnostic medical radiation in inflammatory bowel disease: How to limit risk and maximize benefit. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 2501–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amitai, M.M.; Ben-Horin, S.; Eliakim, R.; Kopylov, U. Magnetic resonance enterography in Crohn’s disease: A guide to common imaging manifestations for the IBD physician. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.C. Radiation risk from medical imaging. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Type of Radiological Imaging | Effective Dose (mSv) |
|---|---|
| Abdominal and pelvic CT | 10 |
| Barium enema | 8 |
| Upper GI series | 6 |
| Small bowel series | 5 |
| Abdominal radiography | 0.7 |
| Chest radiography | 0.02 |
| IBD (n = 134) | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 89) | |||
| Male gender, n (%) | 82 (61.2%) | 28 (62.2%) | 54 (60.7%) | 0.862 |
| Age at diagnosis, yr, median (IQR) | 40 (30–51) | 34 (28–48) | 43 (33–52) | 0.039 |
| Disease duration, yr, median (IQR) | 4 (2–5) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (2–6) | 0.891 |
| 5-ASA, n (%) | 126 (94.0%) | 40 (88.9%) | 86 (96.6%) | 0.118 |
| Steroids, n (%) | 66 (49.3%) | 25 (55.6%) | 41 (46.1%) | 0.299 |
| AZA, n (%) | 50 (37.3%) | 34 (75.6%) | 16 (18.0%) | <0.001 |
| Biologics, n (%) | 46 (34.3%) | 30 (66.7%) | 16 (18.0%) | <0.001 |
| CED ≥ 50 mSv, n (%) | 4 (3%) | 3 (6.7%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.110 |
| Median CED during follow-up, mSv, median (IQR) | 4.9 (0.7–18.4) | 21.2 (12.1–32.8) | 2.1 (0–5.6) | <0.001 |
| Total CT times ≥ 3, n (%) | 14 (10.4%) | 12 (26.7%) | 2 (2.2%) | <0.001 |
| Total MRI times ≥ 3, n (%) | 5 (3.7%) | 4 (8.9%) | 1 (1.1%) | 0.043 |
| Total X-ray, times, median (IQR) | 3 (1–7) | 8 (4–14) | 2 (0–4) | <0.001 |
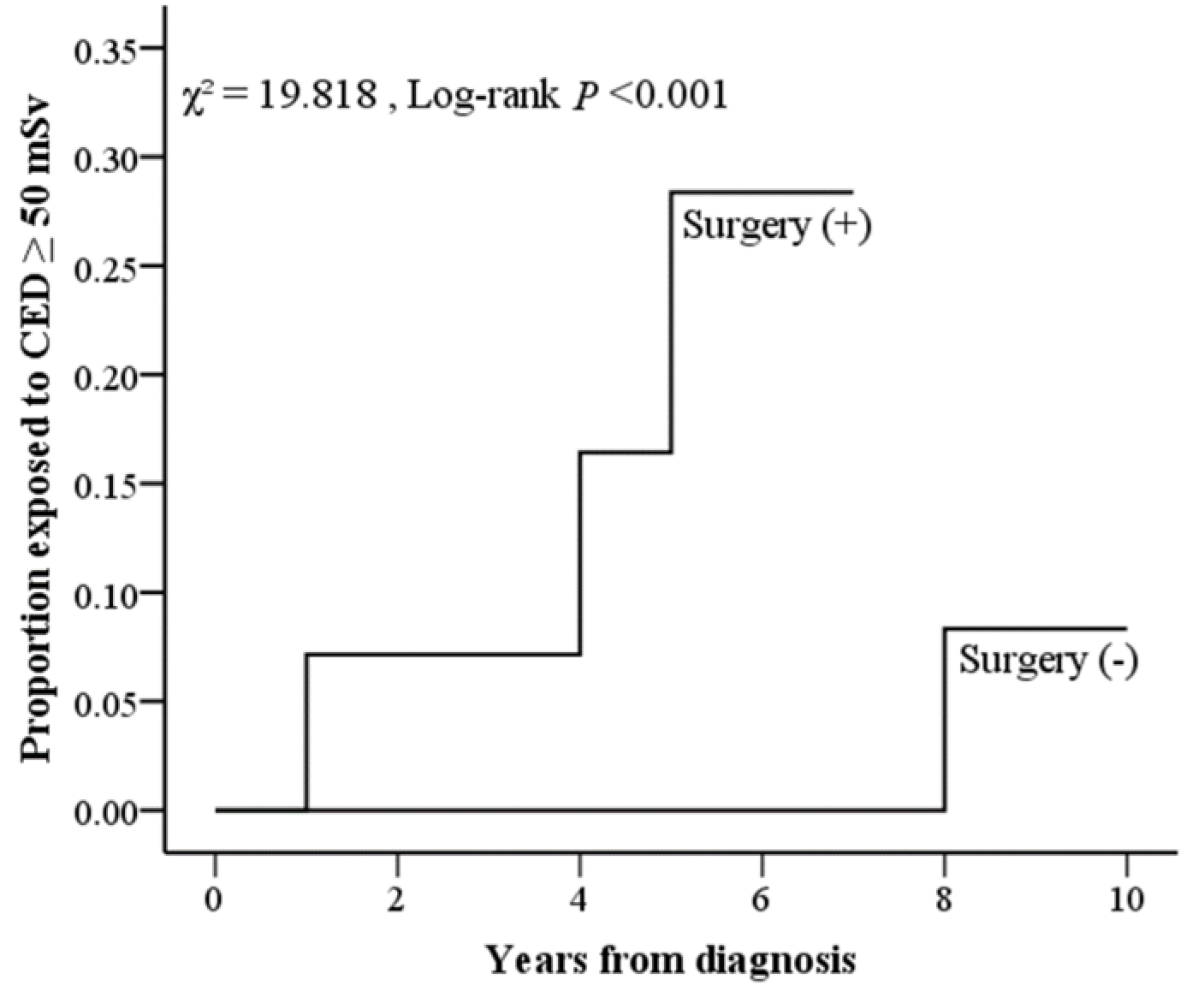
| Surgery, n (%) | 15 (11.2%) | 14 (31.1%) | 1 (1.1%) | <0.0001 |
| IBD-related admission, n (%) | 46 (34.3%) | 28 (62.2%) | 18 (20.2%) | <0.0001 |
| Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | |
|---|---|---|
| (n = 45) | (n = 89) | |
| UC Location/disease extent, n (%) | ||
| E1: Proctitis | -- | 16 (18.0%) |
| E2: Left-side colitis | -- | 40 (44.9%) |
| E3: Extensive colitis | -- | 33 (37.1%) |
| CD Location/disease extent, n (%) | ||
| L1: Ileum | 15 (33.3%) | |
| L2: Colon | 5 (11.1%) | |
| L3: Ileo-colon | 23 (51.1%) | |
| L4: UGI tract | 2 (4.4%) | |
| CD Behaviour/disease behavior, n (%) | ||
| B1: Non-stricturing | 16 (35.6%) | |
| B2: Stricturing | 14 (31.1%) | |
| B3: Penetrating | 15 (33.3%) | |
| p: Perianal involvement, n (%) | 4 (8.9%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.-T.; Yen, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Su, P.-Y.; Huang, S.-P. Radiation Exposure among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Medical-Center Retrospective Analysis in Taiwan. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175050
Yang C-T, Yen H-H, Chen Y-Y, Su P-Y, Huang S-P. Radiation Exposure among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Medical-Center Retrospective Analysis in Taiwan. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(17):5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175050
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chen-Ta, Hsu-Heng Yen, Yang-Yuan Chen, Pei-Yuan Su, and Siou-Ping Huang. 2022. "Radiation Exposure among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Medical-Center Retrospective Analysis in Taiwan" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 17: 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175050
APA StyleYang, C.-T., Yen, H.-H., Chen, Y.-Y., Su, P.-Y., & Huang, S.-P. (2022). Radiation Exposure among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Single-Medical-Center Retrospective Analysis in Taiwan. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(17), 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11175050







