Clinical Performance of Oral Anticoagulants in Elderly with Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight: Insight into Italian Cohort of PREFER-AF and PREFER-AF Prolongation Registries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Outcomes
Statistical Analysis
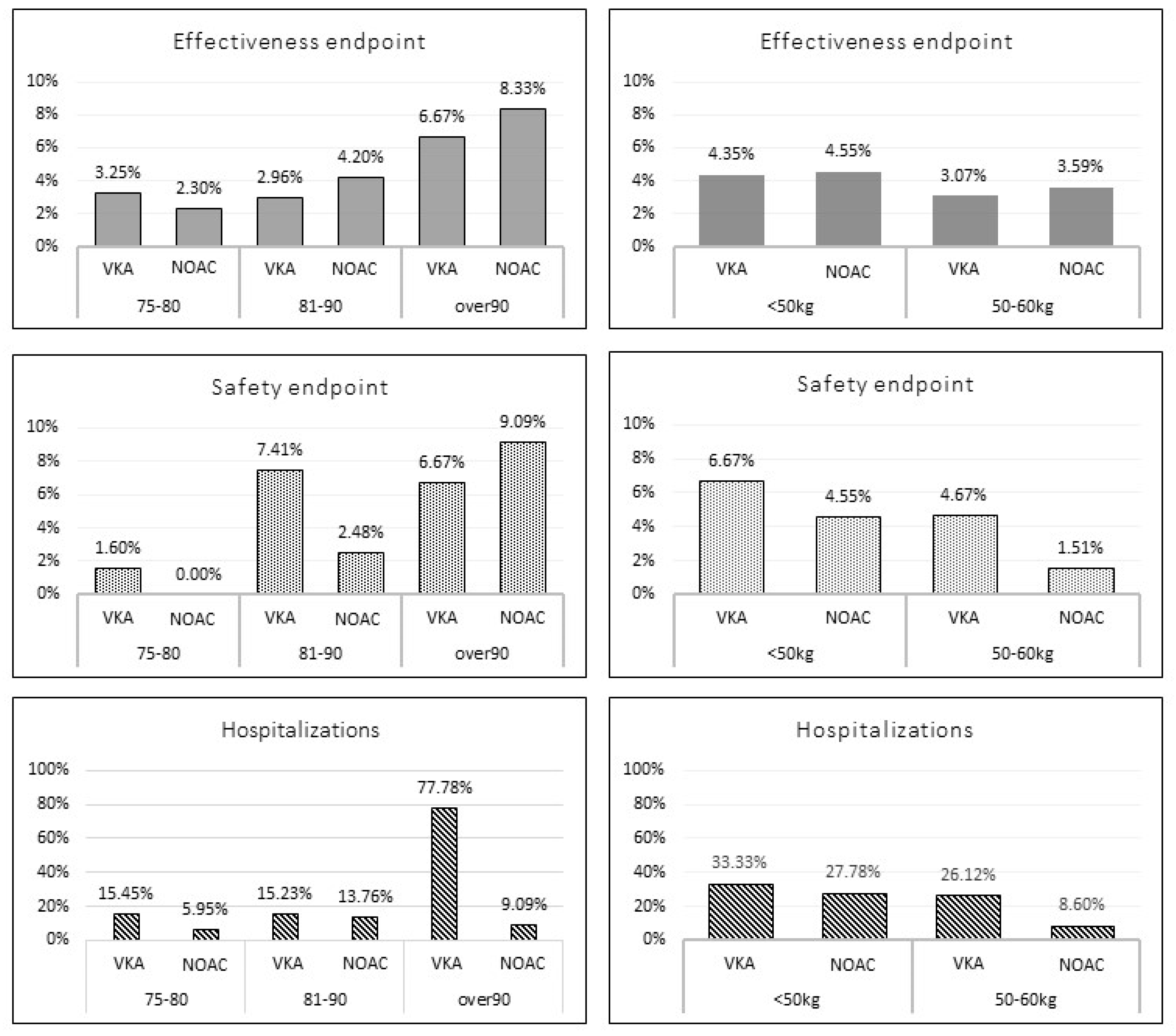
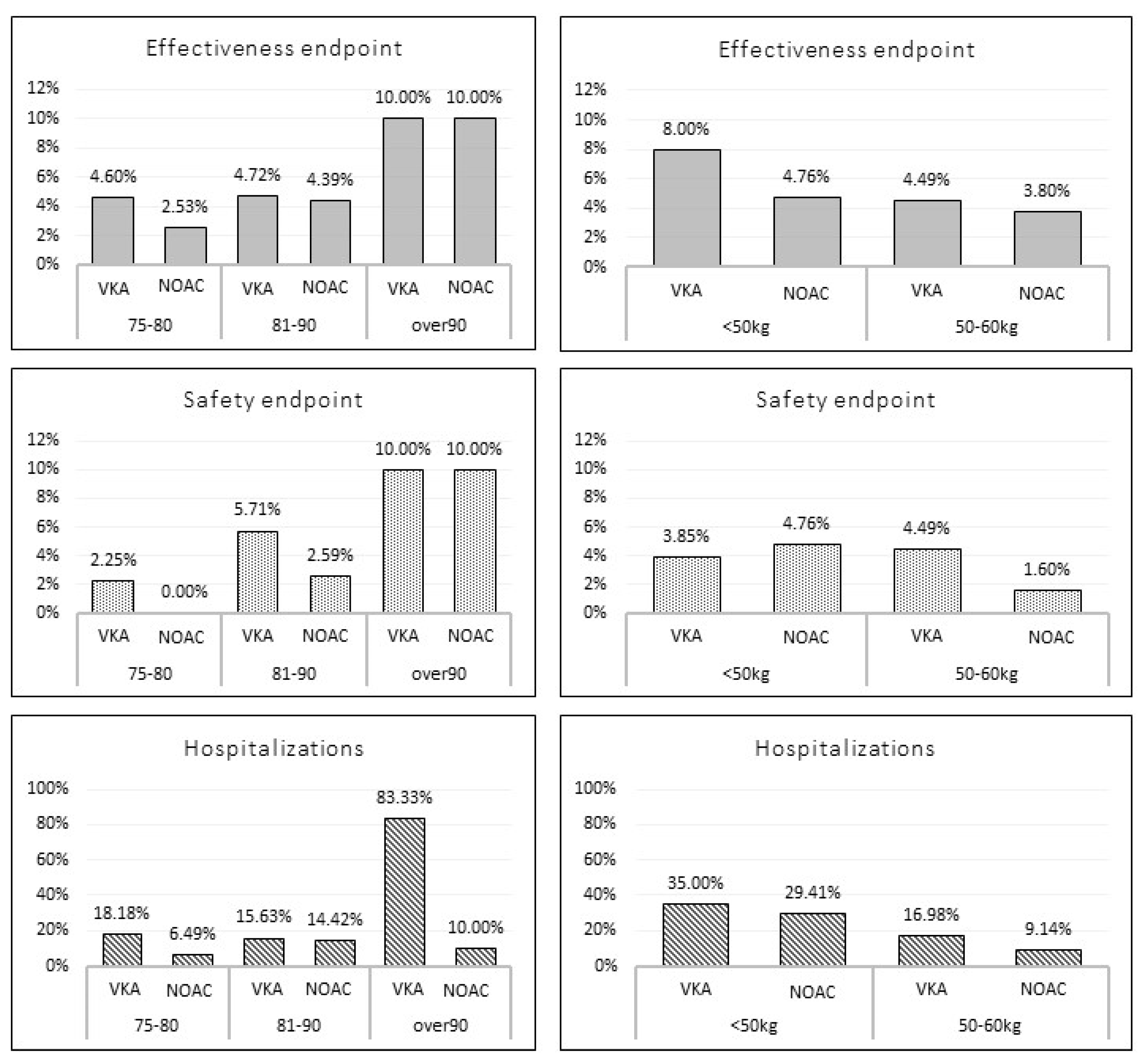
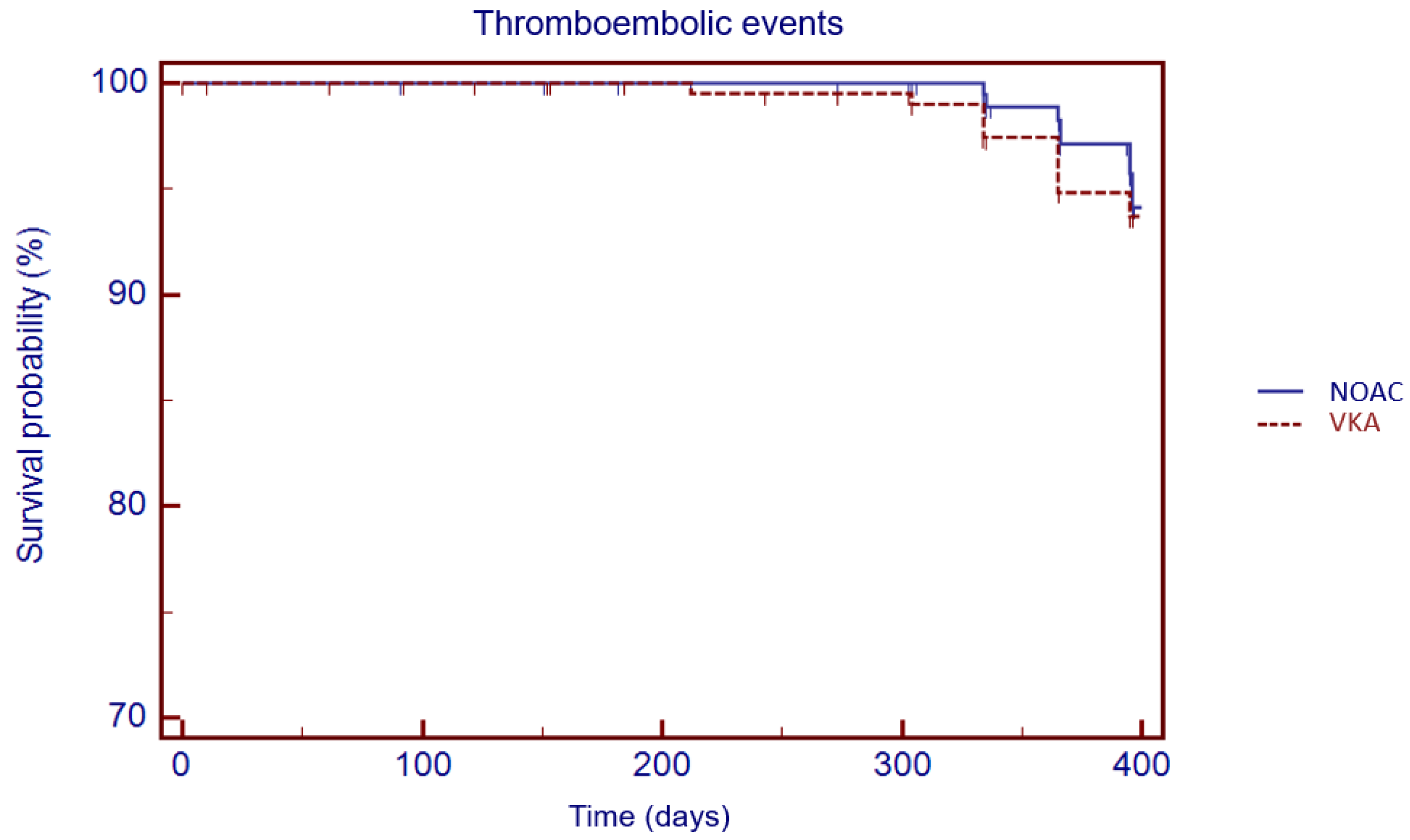
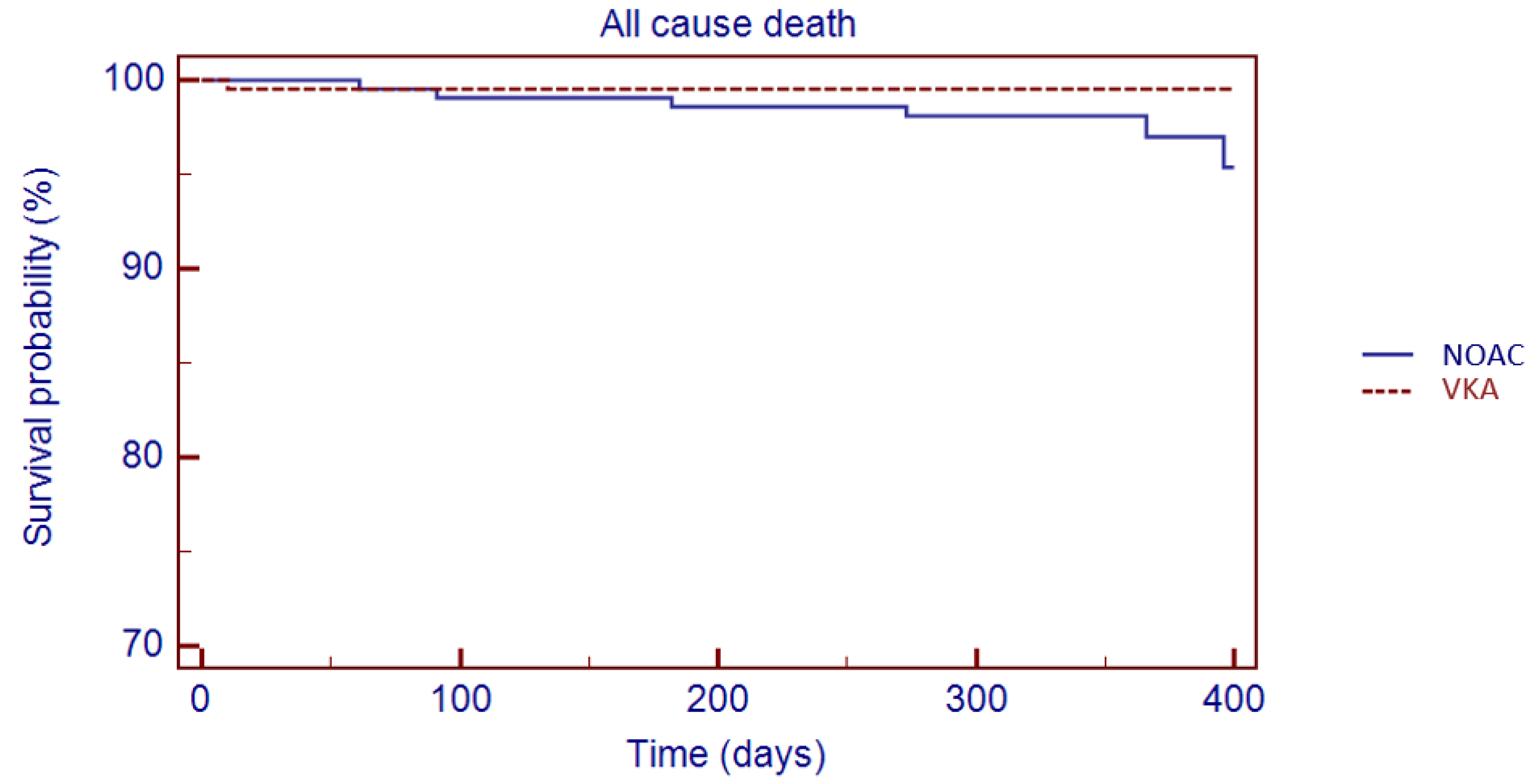
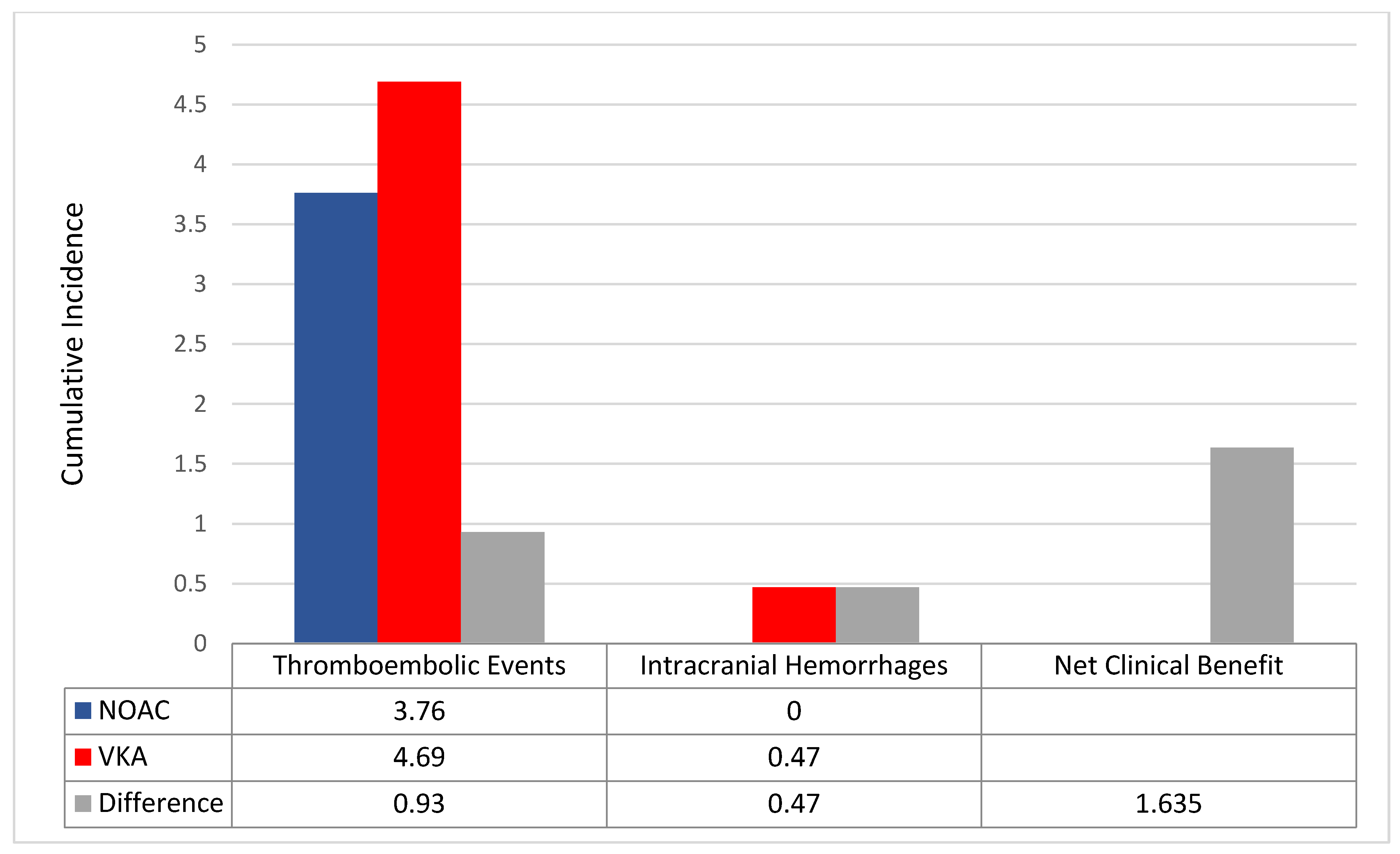
3. Results
Matched Population
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, C.S.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, S.R.; Cha, M.J.; Oh, S. Increased risk of major bleeding in underweight patients with atrial fibrillation who were prescribed non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants. Heart Rhythm 2017, 14, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Inden, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Kato, H.; Miyoshi-Fujii, A.; Mizutani, Y.; Ito, T.; Kamikubo, Y.; Kanzaki, Y.; Hirai, M.; et al. Body mass index is associated with prognosis in Japanese elderly patients with atrial fibrillation: An observational study from the outpatient clinic. Heart Vessel. 2016, 31, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonyawat, K.; Caron, F.; Li, A.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Lim, W.; Iorio, A.; Lopes, R.D.; Garcia, D.; Crowther, M.A. Association of body weight with efficacy and safety outcomes in phase III randomized controlled trials of direct oral anticoagulants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Caterina, R.; Lip, G.Y.H. The non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants(NOACs) and extremes of body weight—A systematicliterature review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2017, 106, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Attena, E.; Di Maio, M.; Carbone, A.; Parisi, V.; Rago, A.; Grieco, F.V.; Buonauro, A.; Golino, P.; Nigro, G. Non-vitamin K vs vitamin K oral anticoagulants in patients aged > 80 year with atrial fibrillation and low body weight. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Choi, E.K.; Park, C.S.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y. Direct oral anticoagulants in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and low body weight. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Ammentorp, B.; Darius, H.; De Caterina, R.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Schilling, R.J.; Schmitt, J.; Zamorano, J.L. Management of atrial fibrillation in seven European countries after the publication of the 2010 ESC Guidelines on atrial fibrillation: Primary results of the Prevention of Thromboemolic events–European Registry in Atrial Fibrillation (PREFER in AF). Europace 2014, 16, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renda, G.; Pecen, L.; Patti, G.; Ricci, F.; Kotecha, D.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Schnabel, R.B.; Wachter, R.; Sellal, J.M.; Rohla, M.; et al. Antithrombotic management and outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation treated with NOACs early at the time of market introduction: Main results from the PREFER in AF Prolongation Registry. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, S.; Kearon, C. Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in non-surgical patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, D.E.; Chang, Y.; Fang, M.C.; Borowsky, L.H.; Pomernacki, N.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Go, A.S. The net clinical benefit of warfarin anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Attena, E.; Rago, A.; Melillo, E.; Di Micco, P.; Papa, A.A.; Napolitano, G.; D’Onofrio, A.; Golino, P.; Nigro, G. Clinical Outcome of Edoxaban vs. Vitamin K Antagonists in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Multicenter, Propensity-Matched, Real-World Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, S.S.; Havmoeller, R.; Narayanan, K.; Singh, D.; Rienstra, M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Kim, Y.-H.; McAnulty, J.H., Jr.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation 2014, 129, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patti, G.; Lucerna, M.; Pecen, L.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Cavallari, I.; Kirchhof, P.; De Caterina, R. Thromboembolic risk, bleeding outcomes and effect of different antithrombotic strategies in very elderly patients with atrial fibrillation: A sub-analysis from the PREFER in AF (PREvention oF Thromboembolic Events- European Registry in Atrial Fibrillation). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruff, C.T.; Giugliano, R.P.; Braunwald, E.; Hoffman, E.B.; Deenadayalu, N.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Camm, A.J.; Weitz, J.I.; Lewis, B.S.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Carbone, A.; Rago, A.; Golino, P.; Nigro, G. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Octogenarians with Atrial Fibrillation: It Is Never Too Late. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 73, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, V.; Attena, E.; Di Maio, M.; Mazzone, C.; Carbone, A.; Parisi, V.; Rago, A.; D’Onofrio, A.; Golino, P.; Nigro, G. Clinical profile of direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K anticoagulants in octogenarians with atrial fibrillation: A multicentre propensity score matched real-world cohort study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellenbart, E.L.; Faulkenberg, K.D.; Finks, S.W. Evaluation of bleeding in patients receiving direct oral anticoagulants. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savioli, G.; Ceresa, I.F.; Luzzi, S.; Gragnaniello, C.; Giotta Lucifero, A.; Del Maestro, M.; Marasco, S.; Manzoni, F.; Ciceri, L.; Gelfi, E.; et al. Rates of Intracranial Hemorrhage in Mild Head Trauma Patients Presenting to Emergency Department and Their Management: A Comparison of Direct Oral Anticoagulant Drugs with Vitamin K Antagonists. Medicina 2020, 56, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggenjürgen, B.; Schliephacke, T.; Darius, H.; De Caterina, R.; Le Heuzey, J.Y.; Pittrow, D.; Reimitz, P.E.; Schilling, R.J.; Zamorano, J.L.; Kirchhof, P. Discontinuation and Hospitalisation Rates in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Follow-Up Results of the Prefer in Af Registry. Value Health 2014, 17, A473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Santelli, F.; Bottino, R.; Attena, E.; Mazzone, C.; Parisi, V.; D’Andrea, A.; Golino, P.; Nigro, G.; Russo, V. Prevalence and clinical predictors of inappropriate direct oral anticoagulant dosage in octagenarians with atrial fibrillation. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | NOAC Group n: 225 | VKA Group n: 317 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 82.46 ± 4.85 | 82.21 ± 4.87 | 0.62 |
| Sex (males) | 21 (9.3%) | 49 (15.4%) | 0.03 |
| Weight, kg | 55.73 ± 4.46 | 54.76 ± 5.07 | 0.02 |
| Height, cm | 157.99 ± 6.34 | 158.42 ± 6.46 | 0.53 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.40 ± 2.35 | 21.90 ± 2.27 | 0.02 |
| CHADS2 | 2.7 ± 1.24 | 2.56 ± 1.21 | 0.56 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 4.7 ± 1.34 | 4.68 ± 1.38 | 0.19 |
| HAS-BLED | 2.26 ± 0.9 | 2.32 ± 1.03 | 0.12 |
| Arterial Hypertension, n (%) | 174 (77%) | 227 (72%) | 0.13 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 34 (15%) | 40 (13%) | 0.40 |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 75 (33%) | 90 (28%) | 0.14 |
| COPD, n (%) | 19 (8.4%) | 40 (13%) | 0.12 |
| Heart Failure, n (%) | 55 (24%) | 113 (35%) | 0.05 |
| CHD, n (%) | 43 (19%) | 66 (21%) | 0.6 |
| PAD, n (%) | 14 (6.2%) | 14 (4.4%) | 1 |
| Previous Stroke, n (%) | 40 (17.7%) | 38 (12%) | 0.06 |
| Previous TIA, n (%) | 43 (19%) | 31 (9.7%) | 0.002 |
| Previous Major Bleeding, n (%) | 3 (1.3%) | 7 (2.2%) | 0.45 |
| CKD, n (%) | 56 (25%) | 61 (19%) | 0.11 |
| Chronic Hepatic Disease | 1 (0.4%) | 8 (2.5%) | 0.06 |
| Ejection fraction (%) | 58.93 ± 10.12 | 57.25 ± 12.08 | 0.11 |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | 36.02 ± 9.36 | 29.23 ± 9.99 | 0.0003 |
| Variables | NOAC Group n: 213 | VKA Group n: 213 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 82.57 ± 4.82 | 82.15 ± 4.93 | 0.37 |
| Sex (males) | 19 (8.9%) | 32 (15%) | 0.06 |
| Weight, kg | 55.79 ± 4.46 | 55.11 ± 4.82 | 0.13 |
| Height, cm | 158.06 ± 6.39 | 158.47 ± 6.58 | 0.50 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.41 ± 2.38 | 22.01 ± 2.26 | 0.07 |
| CHADS2 | 2.66 ± 1.21 | 2.61 ± 1.24 | 0.67 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 4.66 ± 1.29 | 4.54 ± 1.52 | 0.38 |
| HAS-BLED | 2.29 ± 0.6 | 2.38 ± 1.16 | 0.31 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 164 (77%) | 149 (70%) | 0.10 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 31 (14.5%) | 22 (10%) | 0.16 |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 73 (34%) | 55 (26%) | 0.07 |
| COPD, n (%) | 18 (8.4%) | 26 (12%) | 0.22 |
| Heart Failure, n (%) | 53 (25%) | 67 (31%) | 0.13 |
| CHD, n (%) | 41 (19%) | 47 (22%) | 0.44 |
| PAD, n (%) | 14 (6.5%) | 10 (4.7%) | 0.42 |
| Previous Stroke, n (%) | 39 (18%) | 25 (12%) | 0.08 |
| Previous TIA, n (%) | 43 (20%) | 22 (10%) | 0.004 |
| Previous Major Bleeding, n (%) | 3 (1.4%) | 3 (1.4%) | 1 |
| CKD, n (%) | 53 (25%) | 42 (20%) | 0.22 |
| Chronic Hepatic Disease | 1 (0.5%) | 6 (2.8%) | 0.06 |
| Ejection fraction (%) | 59.16 ± 10.15 | 57.31 ± 12.13 | 0.11 |
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) | 36.27 ± 9.54 | 30.47 ± 10.99 | 0.008 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, V.; Attena, E.; Baroni, M.; Trotta, R.; Manu, M.C.; Kirchhof, P.; De Caterina, R. Clinical Performance of Oral Anticoagulants in Elderly with Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight: Insight into Italian Cohort of PREFER-AF and PREFER-AF Prolongation Registries. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133751
Russo V, Attena E, Baroni M, Trotta R, Manu MC, Kirchhof P, De Caterina R. Clinical Performance of Oral Anticoagulants in Elderly with Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight: Insight into Italian Cohort of PREFER-AF and PREFER-AF Prolongation Registries. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(13):3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133751
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Vincenzo, Emilio Attena, Matteo Baroni, Roberta Trotta, Marius Constantin Manu, Paulus Kirchhof, and Raffaele De Caterina. 2022. "Clinical Performance of Oral Anticoagulants in Elderly with Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight: Insight into Italian Cohort of PREFER-AF and PREFER-AF Prolongation Registries" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 13: 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133751
APA StyleRusso, V., Attena, E., Baroni, M., Trotta, R., Manu, M. C., Kirchhof, P., & De Caterina, R. (2022). Clinical Performance of Oral Anticoagulants in Elderly with Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight: Insight into Italian Cohort of PREFER-AF and PREFER-AF Prolongation Registries. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(13), 3751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133751







