White Matter Correlates of Early-Onset Bipolar Illness and Predictors of One-Year Recurrence of Depression in Adults with Bipolar Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical Assessments
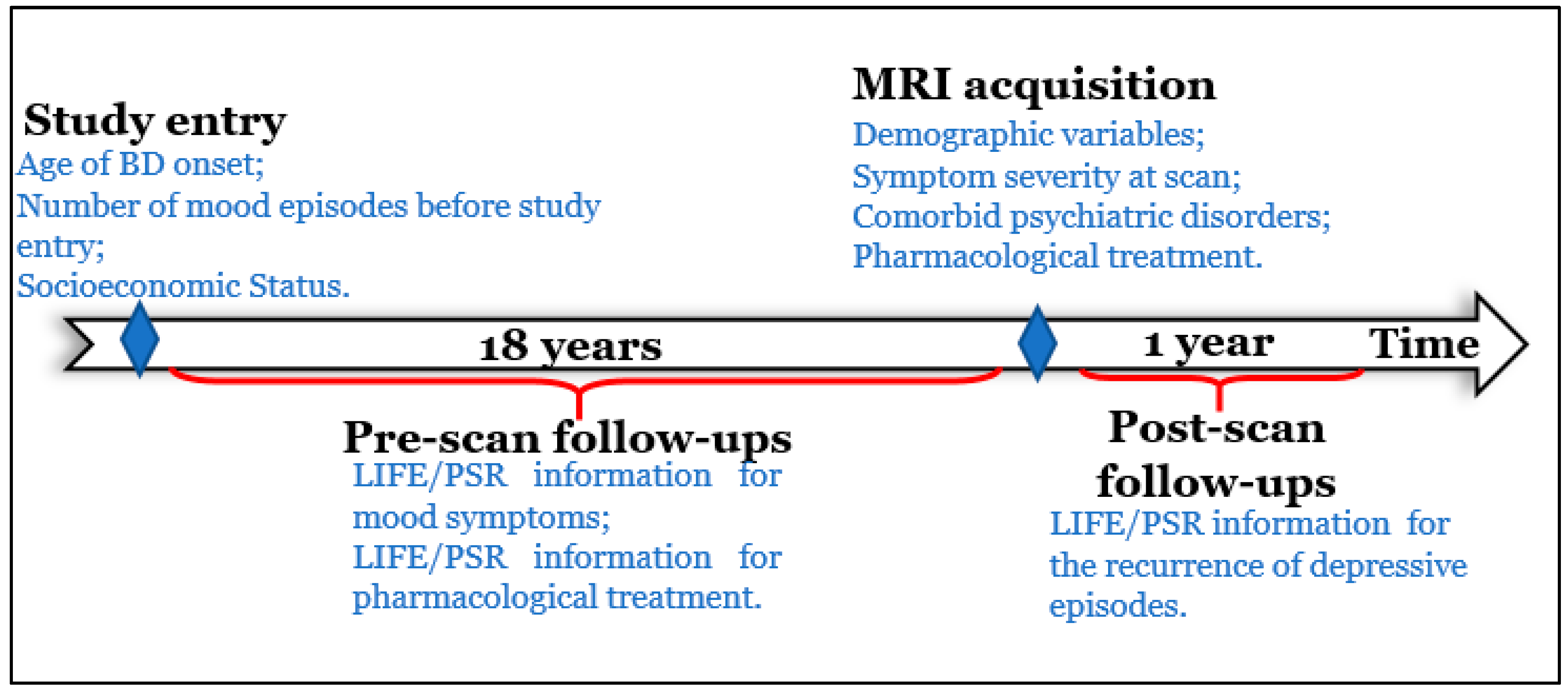
2.2.1. Pre-Scan Longitudinal Variables
2.2.2. Post-Scan Longitudinal Variables
2.2.3. Additional Clinical and Demographic Measures
2.3. Neuroimaging Data
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Level 1: Primary Hypothesis Testing
2.4.2. Level 2: Secondary Hypothesis Testing
2.4.3. Exploratory Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Level 1: Primary Hypothesis Testing
3.2. Level 2: Secondary Hypothesis Testing
3.3. Exploratory Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World Report on Disability 2011; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grande, I.; Berk, M.; Birmaher, B.; Vieta, E. Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2016, 387, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Dell’Osso, B.; Ketter, T.A. The prevalence and burden of bipolar depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 169, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Calabrese, J.R. Bipolar depression: The clinical characteristics and unmet needs of a complex disorder. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rote, J.; Dingelstadt, A.M.L.; Aigner, A.; Bauer, M.; Fiebig, J.; König, B.; Kunze, J.; Pfeiffer, S.; Pfennig, A.; Quinlivan, E.; et al. Impulsivity predicts illness severity in long-term course of bipolar disorder: A prospective approach. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2018, 52, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J.; Geddes, J.R.; Tunbridge, E.M. The emerging neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2018, 41, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, M.L.; Swartz, H.A. A critical appraisal of neuroimaging studies of bipolar disorder: Toward a new conceptualization of underlying neural circuitry and a road map for future research. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L.; Vieta, E. Identifying functional neuroimaging biomarkers of bipolar disorder: Toward DSM-V. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.K.; Leemans, A. Diffusion tensor imaging. In Magnetic Resonance Neuroimaging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, A.M.; Maniega, S.M.; Lymer, G.K.S.; McKirdy, J.; Hall, J.; Sussmann, J.E.; Bastin, M.E.; Clayden, J.D.; Johnstone, E.C.; Lawrie, S.M. White matter tractography in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Weng, S.; Xie, B.; Wu, G.; Lei, H. Abnormal frontal cortex white matter connections in bipolar disorder: A DTI tractography study. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 131, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.H.; Her, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; Ha, K. Similarities and differences of white matter connectivity and water diffusivity in bipolar I and II disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 505, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, A.; Andreazza, A.C.; Young, L.; Fournier, J.C.; Almeida, J.R.; Stiffler, R.S.; Lockovich, J.C.; Aslam, H.A.; Pollock, M.H.; Park, H. Elevated serum measures of lipid peroxidation and abnormal prefrontal white matter in euthymic bipolar adults: Toward peripheral biomarkers of bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caseras, X.; Murphy, K.; Lawrence, N.S.; Fuentes-Claramonte, P.; Watts, J.; Jones, D.K.; Phillips, M.L. Emotion regulation deficits in euthymic bipolar I versus bipolar II disorder: A functional and diffusion-tensor imaging study. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foley, S.F.; Bracher-Smith, M.; Tansey, K.E.; Harrison, J.R.; Parker, G.D.; Caseras, X. Fractional anisotropy of the uncinate fasciculus and cingulum in bipolar disorder type I, type II, unaffected siblings and healthy controls. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 213, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linke, J.; King, A.V.; Poupon, C.; Hennerici, M.G.; Gass, A.; Wessa, M. Impaired anatomical connectivity and related executive functions: Differentiating vulnerability and disease marker in bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, F.; Absinta, M.; Rocca, M.A.; Radaelli, D.; Poletti, S.; Bernasconi, A.; Dallaspezia, S.; Pagani, E.; Falini, A.; Copetti, M. Tract-specific white matter structural disruption in patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2011, 13, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsell, L.; Leemans, A.; Langan, C.; Van Hecke, W.; Barker, G.J.; McCarthy, P.; Jeurissen, B.; Sijbers, J.; Sunaert, S.; Cannon, D.M. Limbic and callosal white matter changes in euthymic bipolar I disorder: An advanced diffusion magnetic resonance imaging tractography study. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, S.; Poupon, C.; Linke, J.; Wessa, M.; Phillips, M.; Delavest, M.; Versace, A.; Almeida, J.; Guevara, P.; Duclap, D. A multicenter tractography study of deep white matter tracts in bipolar I disorder: Psychotic features and interhemispheric disconnectivity. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnea-Goraly, N.; Chang, K.D.; Karchemskiy, A.; Howe, M.E.; Reiss, A.L. Limbic and corpus callosum aberrations in adolescents with bipolar disorder: A tract-based spatial statistics analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, J.D.; Dougherty, R.F.; Myall, N.J.; Wandell, B.A.; Feldman, H.M. Tract profiles of white matter properties: Automating fiber-tract quantification. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49790. [Google Scholar]
- Birmaher, B.; Axelson, D.; Strober, M.; Gill, M.K.; Valeri, S.; Chiappetta, L.; Ryan, N.; Leonard, H.; Hunt, J.; Iyengar, S. Clinical course of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmaher, B.; Gill, M.K.; Axelson, D.A.; Goldstein, B.I.; Goldstein, T.R.; Yu, H.; Liao, F.; Iyengar, S.; Diler, R.S.; Strober, M. Longitudinal trajectories and associated baseline predictors in youths with bipolar spectrum disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birmaher, B.; Axelson, D.; Goldstein, B.; Strober, M.; Gill, M.K.; Hunt, J.; Houck, P.; Ha, W.; Iyengar, S.; Kim, E. Four-year longitudinal course of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders: The Course and Outcome of Bipolar Youth (COBY) study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaddock, C.A.; Barker, G.J.; Marshall, N.; Schulze, K.; Hall, M.H.; Fern, A.; Walshe, M.; Bramon, E.; Chitnis, X.A.; Murray, R. White matter microstructural impairments and genetic liability to familial bipolar I disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 194, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedetti, F.; Yeh, P.-H.; Bellani, M.; Radaelli, D.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Poletti, S.; Falini, A.; Dallaspezia, S.; Colombo, C.; Scotti, G. Disruption of white matter integrity in bipolar depression as a possible structural marker of illness. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.; Williams, J.; Karg, R.; Spitzer, R. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders–Research Version (SCID-5-RV); American Psychiatric Assocation: Arlington, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rive, M.M.; van Rooijen, G.; Veltman, D.J.; Phillips, M.L.; Schene, A.H.; Ruhe, H.G. Neural correlates of dysfunctional emotion regulation in major depressive disorder. A systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2529–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.B.; Lavori, P.W.; Friedman, B.; Nielsen, E.; Endicott, J.; McDonald-Scott, P.; Andreasen, N.C. The longitudinal interval follow-up evaluation: A comprehensive method for assessing outcome in prospective longitudinal studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1987, 44, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.A.; Levenson, J.C.; Merranko, J.; Gill, M.K.; Hower, H.; Yen, S.; Strober, M.; Goldstein, T.R.; Goldstein, B.I.; Ryan, N.D. The effect of traumatic events on the longitudinal course and outcomes of youth with bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelson, D.A.; Birmaher, B.; Strober, M.A.; Goldstein, B.I.; Ha, W.; Gill, M.K.; Goldstein, T.R.; Yen, S.; Hower, H.; Hunt, J.I. Course of subthreshold bipolar disorder in youth: Diagnostic progression from bipolar disorder not otherwise specified. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 50, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafeman, D.M.; Rooks, B.; Merranko, J.; Liao, F.; Gill, M.K.; Goldstein, T.R.; Diler, R.; Ryan, N.; Goldstein, B.I.; Axelson, D.A. Lithium versus other mood-stabilizing medications in a longitudinal study of youth diagnosed with bipolar disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 59, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warshaw, M.G.; Dyck, I.; Allsworth, J.; Stout, R.L.; Keller, M.B. Maintaining reliability in a long-term psychiatric study: An ongoing inter-rater reliability monitoring program using the longitudinal interval follow-up evaluation. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2001, 35, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAMILTON, M. A rating scale for depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1960, 23, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, R.C.; Biggs, J.T.; Ziegler, V.E.; Meyer, D.A. A rating scale for mania: Reliability, validity and sensitivity. Br. J. Psychiatry 1978, 133, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.D.; Greenberg, B.R.; Serper, M.R. The affective lability scales: Development, reliability, and validity. J. Clin. Psychol. 1989, 45, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J.H.; Stanford, M.S.; Barratt, E.S. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 51, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, M.; Eysenck, S.B.; Eysenck, H.J. Sensation seeking in England and America: Cross-cultural, age, and sex comparisons. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1978, 46, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.; Gorsuch, R.; Lushene, R.; Vagg, P.; Jacobs, G. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory; Consulting Psychologists Press Inc.: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.; Weber, K.; Assenheimer, J.S.; Clark, L.A.; Strauss, M.E.; McCormick, R.A. Testing a tripartite model: I. Evaluating the convergent and discriminant validity of anxiety and depression symptom scales. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1995, 104, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yendiki, A.; Panneck, P.; Srinivasan, P.; Stevens, A.; Zöllei, L.; Augustinack, J.; Wang, R.; Salat, D.; Ehrlich, S.; Behrens, T. Automated probabilistic reconstruction of white-matter pathways in health and disease using an atlas of the underlying anatomy. Front. Neuroinform. 2011, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastie, T.; Qian, J. Glmnet Vignette. Available online: http://www.web.stanford.edu/~hastie/Papers/Glmnet_Vignette (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Grömping, U. Relative importance for linear regression in R: The package relaimpo. J. Stat. Softw. 2006, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochunov, P.; Williamson, D.E.; Lancaster, J.; Fox, P.; Cornell, J.; Blangero, J.; Glahn, D.C. Fractional anisotropy of water diffusion in cerebral white matter across the lifespan. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebel, C.; Gee, M.; Camicioli, R.; Wieler, M.; Martin, W.; Beaulieu, C. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter tract evolution over the lifespan. Neuroimage 2012, 60, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlye, L.T.; Walhovd, K.B.; Dale, A.M.; Bjornerud, A.; Due-Tonnessen, P.; Engvig, A.; Grydeland, H.; Tamnes, C.K.; Ostby, Y.; Fjell, A.M. Life-span changes of the human brain white matter: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and volumetry. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simmonds, D.J.; Hallquist, M.N.; Asato, M.; Luna, B. Developmental stages and sex differences of white matter and behavioral development through adolescence: A longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) study. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abe, O.; Aoki, S.; Hayashi, N.; Yamada, H.; Kunimatsu, A.; Mori, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Okubo, T.; Ohtomo, K. Normal aging in the central nervous system: Quantitative MR diffusion-tensor analysis. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, M. Diffusion tensor imaging and aging—A review. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabri, M.; Pierpaoli, C.; Barbaresi, P.; Polonara, G. Functional topography of the corpus callosum investigated by DTI and fMRI. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, E.J.; Metzler-Baddeley, C.; Aggleton, J.P. The cingulum bundle: Anatomy, function, and dysfunction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 92, 104–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.P.L.; Versace, A.; Stiffler, R.S.; Aslam, H.A.; Lockovich, J.C.; Bonar, L.; Bertocci, M.; Iyengar, S.; Bebko, G.; Skeba, A. White matter predictors of worsening of subthreshold hypomania severity in non-bipolar young adults parallel abnormalities in individuals with bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 306, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.P.L.; Brent, D.; Bertocci, M.; Mailliard, S.; Bebko, G.; Goldstein, T.; Kim, T.; Iyengar, S.; Hafeman, D.; Fenster-Ehrlich, V.C. White matter correlates of suicidality in adults with bipolar disorder who have been prospectively characterized since childhood. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Pardini, M.; Monacelli, F.; Orso, B.; Girtler, N.; Brugnolo, A.; Amore, M.; Nobili, F. Neuroprogression as an Illness Trajectory in Bipolar Disorder: A Selective Review of the Current Literature. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, C.E.; Hoffman, K.M.; Cannon, T.D. The neuropsychology and neuroanatomy of bipolar affective disorder: A critical review. Bipolar Disord. 2001, 3, 106–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, T.; Giridharan, V.V.; Bhatti, G.; Sayana, P.; Doifode, T.; Macedo, D.; Quevedo, J. Inflammation as a Mechanism of Bipolar Disorder Neuroprogression. In Bipolar Disorder: From Neuroscience to Treatment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 215–237. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, G.R.; Pfaffenseller, B.; Stertz, L.; Paz, A.V.C.; Dargél, A.A.; Kunz, M.; Kapczinski, F. Staging and neuroprogression in bipolar disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, T.W.J.; McKirdy, J.; Sussmann, J.E.; Hall, J.; Lawrie, S.M.; Johnstone, E.C.; McIntosh, A.M. Progressive gray matter loss in patients with bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 62, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.N.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Caetano, S.C.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Hatch, J.P.; Brambilla, P.; Mallinger, A.G.; Soares, J.C. Illness duration and total brain gray matter in bipolar disorder: Evidence for neurodegeneration? Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 18, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, C.; Lind, J.; Ryden, E.; Ingvar, M.; Landen, M. Manic episodes are associated with grey matter volume reduction—A voxel-based morphometry brain analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2010, 122, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Versace, A.; Ladouceur, C.; Graur, S.; Acuff, H.; Bonar, L.; Monk, K.; McCaffrey, A.; Yendiki, A.; Leemans, A.; Travis, M. Diffusion imaging markers of bipolar versus general psychopathology risk in youth at-risk. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ou, S. Segmentation of the cingulum bundle in the human brain: A new perspective based on DSI tractography and fiber dissection study. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heilbronner, S.R.; Haber, S.N. Frontal cortical and subcortical projections provide a basis for segmenting the cingulum bundle: Implications for neuroimaging and psychiatric disorders. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10041–10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dondé, C.; Neufeld, N.H.; Geoffroy, P.A. The impact of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on bipolar depression, mania, and euthymia: A systematic review of preliminary data. Psychiatr. Q. 2018, 89, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascha, C.; Bockting, C.L.; Koeter, M.W.; Schene, A.H. Prediction of recurrence in recurrent depression: A 5.5-year prospective study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 984–991. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Have, M.; De Graaf, R.; Van Dorsselaer, S.; Tuithof, M.; Kleinjan, M.; Penninx, B. Recurrence and chronicity of major depressive disorder and their risk indicators in a population cohort. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2018, 137, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, M.; Ising, M.; Künzel, H.; Binder, E.; Holsboer, F.; Modell, S.; Zihl, J. Impaired divided attention predicts delayed response and risk to relapse in subjects with depressive disorders. Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlis, R.H.; Ostacher, M.J.; Patel, J.K.; Marangell, L.B.; Zhang, H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Ketter, T.A.; Miklowitz, D.J.; Otto, M.W.; Gyulai, L. Predictors of recurrence in bipolar disorder: Primary outcomes from the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program for Bipolar Disorder (STEP-BD). Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.L.; Skare, S.; Ashburner, J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: Application to diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 870–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.E.; Berg, H.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Rushworth, M.F.; Woolrich, M.W. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? Neuroimage 2007, 34, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I.; Flitney, D.E. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 2004, 23, S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yendiki, A.; Koldewyn, K.; Kakunoori, S.; Kanwisher, N.; Fischl, B. Spurious group differences due to head motion in a diffusion MRI study. Neuroimage 2014, 88, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total (N = 109) | HC (N = 39) | BD (N = 70) | t(107) or χ2 | p Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 26.2 (4.0) | 25.4 (4.5) | 26.3 (3.9) | −1.2 | 0.254 |
| Sex, No. (%) | |||||
| Men | 52 (47.7%) | 17 (42.6%) | 35 (50.0%) | 0.4 | 0.521 |
| Women | 57 (52.3%) | 22 (56.4%) | 35 (50.0%) | ||
| Educational Level, b No. (%) | |||||
| Higher | 40 (36.7%) | 26 (66.7%) | 14 (20.0%) | 23.5 | <0.001 |
| Lower | 69 (63.3%) | 13 (33.3%) | 56 (80%) | ||
| Handedness, No. (%) | |||||
| Left | 17 (15.6%) | 6 (15.4%) | 11 (15.7%) | <0.1 | 0.964 |
| Right | 92 (84.4%) | 33 (84.6%) | 59 (84.3%) | ||
| Race, No. (%) | |||||
| Caucasian | 72 (66.1%) | 20 (51.3%) | 52 (74.3%) | 5.9 | 0.015 |
| Non-Caucasian | 37 (33.9%) | 19 (48.7%) | 18 (25.7%) | ||
| Employment Status, No. (%) | |||||
| Employed | 64 (58.7%) | 14 (35.9%) | 50 (71.4%) | 36.4 | <0.001 |
| Unemployed | 15 (13.8%) | 1 (2.6%) | 14 (20.0%) | ||
| Full-time student | 30 (27.5%) | 24 (61.5%) | 6 (8.6%) | ||
| Clinical characteristics at-scan, mean (SD) | |||||
| HDRS | 6.8 (6.6) | 1.4 (1.6) | 9.8 (6.5) | −10.3 | <0.001 |
| YMRS | 2.6 (3.0) | 0.4 (0.9) | 3.9 (3.1) | −8.8 | <0.001 |
| BIS | 60.2 (13.1) | 51.8 (10.2) | 64.9 (12.2) | −5.7 | <0.001 |
| ALS | 40.3 (36.1) | 17.8 (18.7) | 52.9 (37.5) | −6.5 | <0.001 |
| SSS | 17.7 (4.5) | 18.7 (5.9) | 17.2 (6.2) | 1.3 | 0.206 |
| STAIY State total | 34.6 (10.8) | 28.4 (8.9) | 38.1 (10.3) | −4.9 | <0.001 |
| STAIY Trait total | 37.1 (11.1) | 30.0 (7.7) | 41.1 (10.8) | −6.2 | <0.001 |
| MASQ90 Anhedonic depression | 57.1 (14.4) | 50.8 (12.0) | 60.5 (14.5) | −2.5 | 0.001 |
| MASQ90 Anxious arousal | 20.8 (7.1) | 17.9 (1.4) | 22.5 (8.4) | −4.4 | <0.001 |
| MASQ90 Loss of interest | 12.7 (5.6) | 9.7 (1.7) | 14.4 (6.3) | −5.8 | <0.001 |
| MASQ90 General distress—Depressive | 18.5 (8.6) | 14.2 (2.6) | 20.9 (9.8) | −5.4 | <0.001 |
| MASQ90 General distress—Anxious | 16.4 (6.1) | 13.4 (2.9) | 18.0 (6.8) | −5.0 | <0.001 |
| MASQ90 General distress—Mixed | 27.8 (11.0) | 20.2 (3.7) | 32.0 (11.4) | −7.9 | <0.001 |
| Level 1 Analysis—Pre-Scan Predictors of White Matter Fiber Collinearity at Scan | |
| Variables | Coefficient |
| Age at scan | −0.02 |
| Caucasian | −0.09 |
| Number of depressive episodes during childhood/adolescence | −0.05 |
| Percentage of time experiencing syndromic depression | −0.09 |
| Level 2 Analysis—Predictors of Recurrence of Depressive Episodes One Year after Scan | |
| Variables | Coefficient |
| BIS total score | 0.17 |
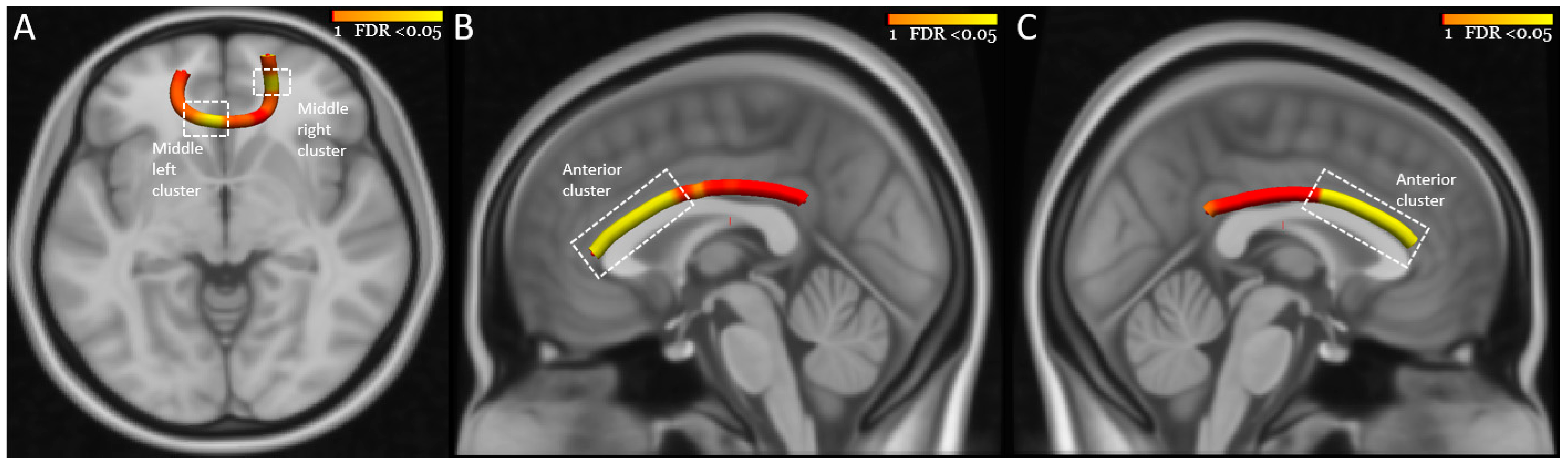
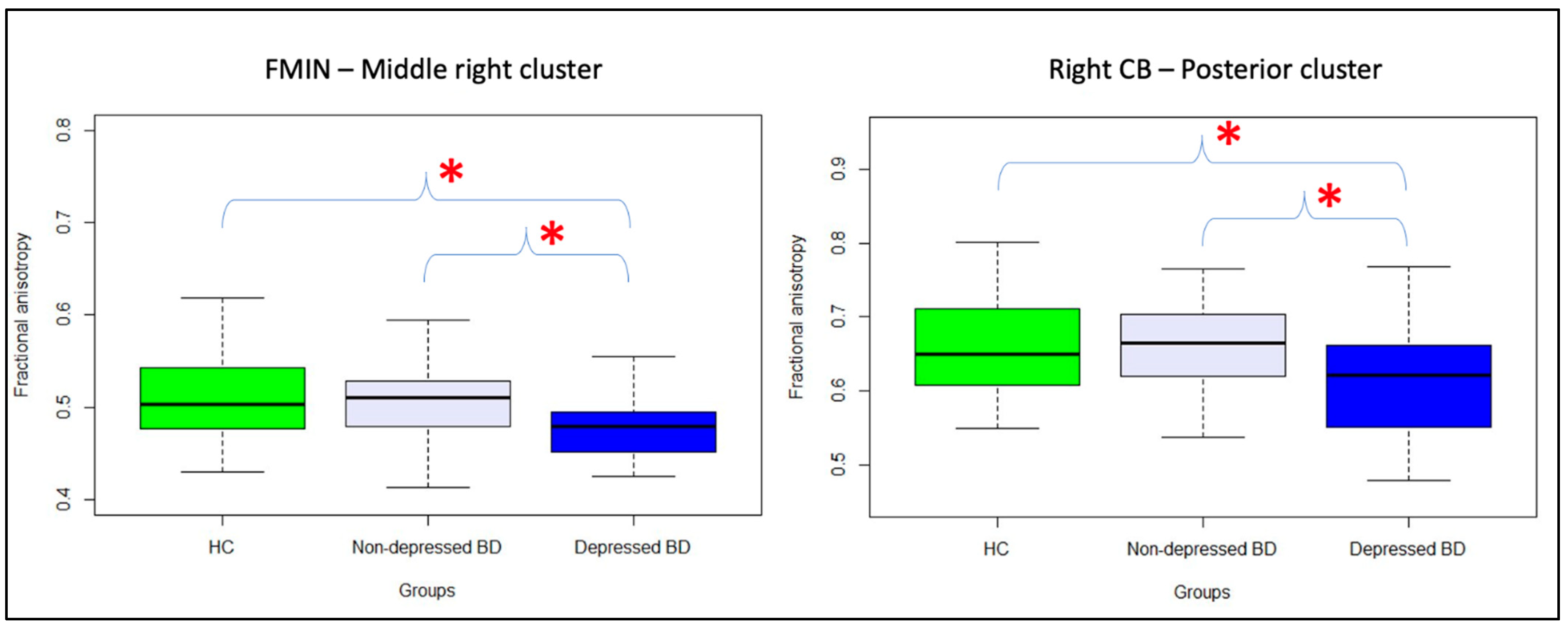
| FMIN middle right cluster | −0.04 |
| Percentage of time experiencing syndromic depression | 0.34 |
| Right CB posterior cluster | −0.02 |
| Variables | B | Wald | p Value a | AOR | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS total score | 0.88 | 6.65 | 0.010 | 2.42 | 1.24 | 4.72 |
| Percentage of time experiencing syndromic depression | 1.20 | 7.30 | 0.007 | 3.33 | 1.39 | 7.99 |
| FMIN middle right cluster | −0.84 | 5.66 | 0.017 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.86 |
| Right CB posterior cluster | −0.70 | 4.58 | 0.032 | 0.50 | 0.26 | 0.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima Santos, J.P.; Bertocci, M.; Bebko, G.; Goldstein, T.; Kim, T.; Iyengar, S.; Bonar, L.; Gill, M.; Merranko, J.; Yendiki, A.; et al. White Matter Correlates of Early-Onset Bipolar Illness and Predictors of One-Year Recurrence of Depression in Adults with Bipolar Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123432
Lima Santos JP, Bertocci M, Bebko G, Goldstein T, Kim T, Iyengar S, Bonar L, Gill M, Merranko J, Yendiki A, et al. White Matter Correlates of Early-Onset Bipolar Illness and Predictors of One-Year Recurrence of Depression in Adults with Bipolar Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(12):3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123432
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima Santos, João Paulo, Michele Bertocci, Genna Bebko, Tina Goldstein, Tae Kim, Satish Iyengar, Lisa Bonar, MaryKay Gill, John Merranko, Anastasia Yendiki, and et al. 2022. "White Matter Correlates of Early-Onset Bipolar Illness and Predictors of One-Year Recurrence of Depression in Adults with Bipolar Disorder" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 12: 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123432
APA StyleLima Santos, J. P., Bertocci, M., Bebko, G., Goldstein, T., Kim, T., Iyengar, S., Bonar, L., Gill, M., Merranko, J., Yendiki, A., Birmaher, B., Phillips, M. L., & Versace, A. (2022). White Matter Correlates of Early-Onset Bipolar Illness and Predictors of One-Year Recurrence of Depression in Adults with Bipolar Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(12), 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11123432






