Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Operational Definitions
2.2. Data Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in the BP
3.2. Achievement of BP Goals According to International Guidelines
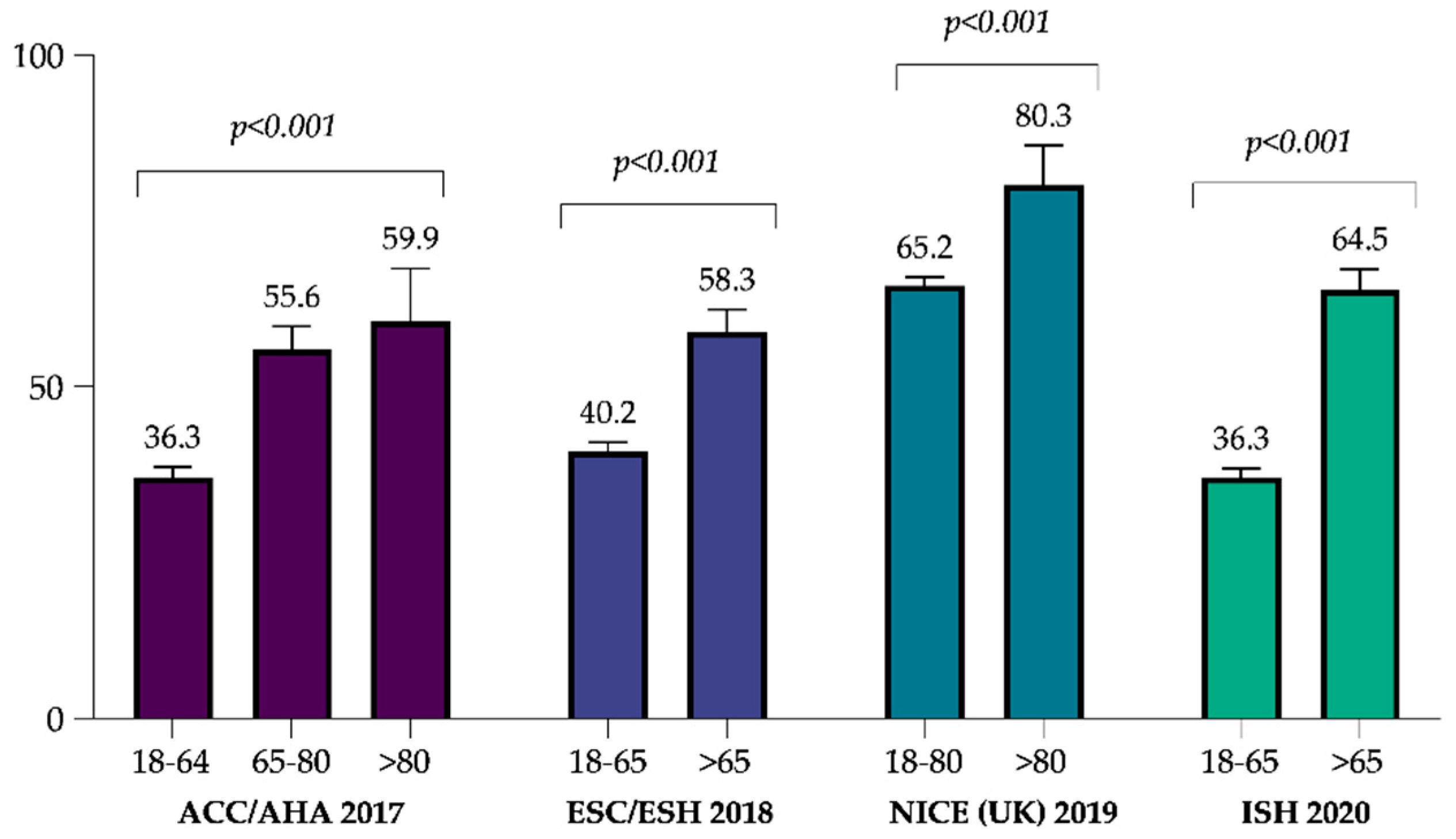
3.3. Factors Associated with the Achievement of Guideline-Recommended BP Goals
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egan, B.M.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Grassi, G.; Esler, M.; Mancia, G. The global burden of hypertension exceeds 1.4 billion people: Should a systolic blood pressure target below 130 become the universal standard? J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Liu, P.; Roth, G.A.; Ng, M.; Biryukov, S.; Marczak, L.; Alexander, L.; Estep, K.; Hassen Abate, K.; Akinyemiju, T.F.; et al. Global Burden of Hypertension and Systolic Blood Pressure of at Least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA 2017, 317, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Atkins, E.; Lv, J.; Bennett, A.; Neal, B.; Ninomiya, T.; Woodward, M.; MacMahon, S.; Turnbull, F.; Hillis, G.S.; et al. Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on cardiovascular and renal outcomes: Updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Toklu, B.; Gianos, E.; Schwartzbard, A.; Weintraub, H.; Ogedegbe, G.; Messerli, F.H. Optimal Systolic Blood Pressure Target After SPRINT: Insights from a Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 707–719.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, H.; Fujiwara, A.; Kai, H.; Kumagai, E.; Okamoto, R.; Shibata, R.; Ohtsubo, T.; Tamura, K.; Maemura, K.; Arima, H. Effects of blood pressure lowering in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakima, A.; Satonaka, H.; Nishida, N.; Yatsu, K.; Arima, H. Optimal blood pressure targets for patients with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajngarten, M.; Silva, G.S. Hypertension and Stroke: Update on Treatment. Eur. Cardiol. 2019, 14, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackland, D.T.; Carey, R.M.; Conforto, A.B.; Rosendorff, C.; Whelton, P.K.; Gorelick, P.B. Implications of Recent Clinical Trials and Hypertension Guidelines on Stroke and Future Cerebrovascular Research. Stroke 2018, 49, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Tsoi, M.F.; Cheung, B. Determining the Optimal Systolic Blood Pressure for Hypertensive Patients: A Network Meta-analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.D.; Li, C.; Stuchlik, P.; Bu, X.; Kelly, T.N.; Mills, K.T.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J. Systolic Blood Pressure Reduction and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufali, A.; Bazargani, N.; Agrawal, A.; Muhammed, K.; Obaid, H.; Gabroun, A.; Albadwawi, M.; Albawab, A.; Musa, A.; Alraeesi, F.; et al. May Measurement Month 2017: An analysis of blood pressure screening results from the United Arab Emirates-Northern Africa and Middle East. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2019, 21, D118–D120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPRINT Research Group. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettehad, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Kiran, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Callender, T.; Emberson, J.; Chalmers, J.; Rodgers, A.; Rahimi, K. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, R.G.; Lynch, K.; Li, N.; Blyler, C.; Muhammad, E.; Handler, J.; Brettler, J.; Rashid, M.; Hsu, B.; Foxx-Drew, D.; et al. A Cluster-Randomized Trial of Blood-Pressure Reduction in Black Barbershops. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R. Implications of blood pressure measurement technique for implementation of Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Anna Dominiczak, A.; et al. ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Hypertension in Adults: Diagnosis and Management. 2019. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng136 (accessed on 21 August 2020).
- Unger, T.; Borghi, C.; Charchar, F.; Khan, N.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Prabhakaran, D.; Ramirez, A.; Schlaich, M.; Stergiou, G.S.; Tomaszewski, M.; et al. International Society of Hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines. Hypertension 2020, 75, 1334–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufali, A.; Bazargani, N.; Bin Belaila, B.A.; Suhail, A.M.; Shuri, H.H.; Agrawal, A.; Muhammed, K.; Gabroun, A.; Albawab, A.; Vazir, Z.; et al. Measurement Month 2018: An analysis of blood pressure screening results from United Arab Emirates. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2020, 22, H128–H131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, C.; Harrison, O.; Al Siksek, Z. Weqaya: A population-wide cardiovascular screening program in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusufali, A.M.; Khatib, R.; Islam, S.; Alhabib, K.F.; Bahonar, A.; Swidan, H.M.; Khammash, U.; Alshamiri, M.Q.; Rangarajan, S.; Salim, Y. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in four Middle East countries. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet 2021, 398, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula, A.S.; Shah, S.M.; Aburawi, E.H. Medication Adherence and Treatment-Resistant Hypertension in Newly Treated Hypertensive Patients in the United Arab Emirates. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Dobson, J.E.; Dahlöf, B.; Sever, P.S.; Poulter, N.R. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010, 375, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Whittle, J.; Lynch, A.I.; Colantonio, L.D.; Simpson, L.M.; Einhorn, P.T.; Levitan, E.B.; Whelton, P.K.; Cushman, W.; Louis, G.T.; et al. Visit-to-visit variability of blood pressure and coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and mortality: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drawz, P.E.; Agarwal, A.; Dwyer, J.P.; Horwitz, E.; Lash, J.; Lenoir, K.; McWilliams, A.; Oparil, S.; Rahbari-Oskoui, F.; Rahman, M.; et al. Concordance Between Blood Pressure in the Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial and in Routine Clinical Practice. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Kumar, S.; Volodarskiy, A.; Messerli, F.H. Blood pressure targets in patients with coronary artery disease: Observations from traditional and Bayesian random effects meta-analysis of randomised trials. Heart 2013, 99, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, I.A.; Hamoui, O.; Hammoudeh, A.; Mallat, S. Blood pressure control in treated hypertensive Middle Eastern patients: A post hoc analysis based on JNC8 definitions. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jia, L.; Lu, B.; Gu, G.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, L.; Cui, W. Updated hypertension prevalence, awareness, and control rates based on the 2017ACC/AHA high blood pressure guideline. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 21, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manard, W.; Scherrer, J.F.; Salas, J.; Schneider, F.D. Patient portal use and blood pressure control in newly diagnosed hypertension. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2016, 29, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shnaimer, J.A.; Gosadi, I.M. Primary health care physicians’ knowledge and adherence regarding hypertension management guidelines in southwest of Saudi Arabia. Medicine 2020, 99, e19873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, O.; Braimoh, R.W. Awareness of hypertension guidelines and the diagnosis and evaluation of hypertension by primary care physicians in Nigeria. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2017, 28, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teoh, S.H.; Razlina, A.R.; Norwati, D.; Siti Suhaila, M.Y. Patients’ blood pressure control and doctors’ adherence to hypertension clinical practice guideline in managing patients at health clinics in Kuala Muda district, Kedah. Med. J. Malays. 2017, 72, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Muntner, P.; Carey, R.M.; Gidding, S.; Jones, D.W.; Taler, S.J.; Wright, J.T.; Whelton, P.K. Potential US Population Impact of the 2017 ACC/AHA High Blood Pressure Guideline. Circulation 2018, 137, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garies, S.; Hao, S.; McBrien, K.; Williamson, T.; Peng, M.; Khan, N.A.; Padwal, R.S.; Quan, H.; Leung, A.A. Prevalence of hypertension, treatment, and blood pressure targets in Canada associated with the 2017 American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Blood Pressure Guidelines. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e190406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijón-Conde, T.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Graciani, A.; Cruz, J.J.; López-García, E.; Ortolá, R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Banegas, J.R. Impact of the European and American guidelines on hypertension prevalence, treatment, and cardiometabolic goals. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocci, G.; Presta, V.; Citoni, B.; Figliuzzi, I.; Bianchi, F.; Ferrucci, A.; Volpe, M. Blood Pressure Target Achievement under Monotheraphy: A Real-Life Appraisal. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2020, 27, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, S.; Conolly, A.; Mindell, J.S. Income-based inequalities in hypertension and in undiagnosed hypertension: Analysis of health survey for England data. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, T.; Krenn, C.; Jeitler, K.; Berghold, A.; Horvath, K.; Siebenhofer, A. Long-term effects of weight-reducing diets in people with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2, CD008274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neter, J.E.; Stam, B.E.; Kok, F.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Geleijnse, J.M. Influence of weight reduction on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hypertension 2003, 42, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billups, S.J.; Saseen, J.J.; Vande Griend, J.P.; Schilling, L.M. Blood pressure control rates measured in specialty vs. primary care practices within a large integrated health system. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahat, Y.I.; Bakir, S.Z.; Farjou, N.; Hashim, T.; Bohaliga, A.; Al-Hossani, H.; Jaffar, A.R. Hypertension in UAE Citizens—Preliminary Results of a Prospective Study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 1999, 10, 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Burnier, M.; Wuerzner, G.; Struijker-Boudier, H.; Urquhart, J. Measuring, analyzing, and managing drug adherence in resistant hypertension. Hypertension 2013, 62, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Chen, G.; Kaplan, G.G.; Lix, L.M.; Drummond, N.; Lucyk, K.; Garies, S.; Lowerison, M.; Weibe, S.; Quan, H. Methods of defining hypertension in electronic medical records: Validation against national survey data. J. Public Health 2016, 38, e392–e399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.; Peters, T.; Rahme, E.; Dasgupta, K. Validity of Health Administrative Database Definitions for Hypertension: A Systematic Review. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
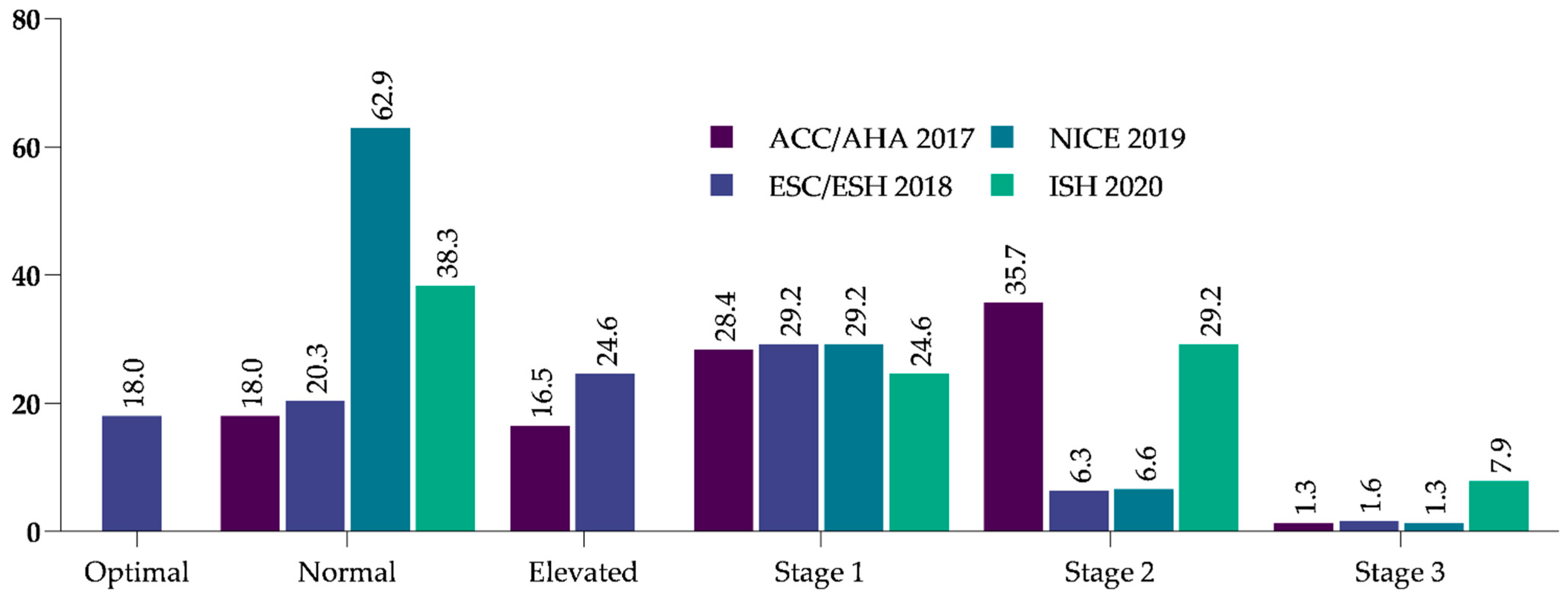

| ACC/AHA 2017 | ESC/ESH 2018 | NICE 2019 | ISH 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal BP | systolic <120 mm Hg and diastolic <80 mm Hg | systolic 120–129 mm Hg and/or diastolic 80–84 mm Hg | <140 and/or <90 mm Hg | <130 mm Hg and/or diastolic <85 mm Hg |
| elevated BP | systolic 120–129 mm Hg and <80 mm Hg | systolic 130–139 and/or diastolic 85–89 | high normal (systolic 130–139 mm Hg and/or diastolic 85–89 mm Hg) | |
| stage 1 hypertension | systolic 130–139 mm Hg or diastolic 80–89 mm Hg | systolic 140–159 mm Hg and/or diastolic 90–99 mm Hg | systolic 140–159 mm Hg and/or diastolic 90–99 mm Hg | systolic 140/159 mm Hg and/or diastolic 90–99 mm Hg |
| stage 2 hypertension | systolic ≥ 140 mm Hg or diastolic ≥90 mm Hg | systolic 160–179 mm Hg and/or diastolic 100–109 mm Hg | systolic 160–179 mm Hg and/or diastolic 100–120 mm Hg | systolic ≥ 160 mm Hg and/or diastolic ≥ 100 mm Hg |
| hypertension crises | systolic >180 and/or diastolic >120 | systolic ≥180 mm Hg and/or diastolic ≥110 mm Hg | systolic ≥180 mm Hg and/or diastolic ≥120 mm Hg | - |
| BP targets (age) | ||||
| 18 to <65 | <130/80 mmHg | 130/80 mmHg (18–65 years) | <140/90 mmHg (18–80 years) | <130/80 mmHg |
| 65–80 | <140/80 mmHg | <140/80 mmHg (>65 years) | <140/90 mmHg | |
| >80 | <140/80 mmHg | - | <150/90 mmHg | - |
| Characteristics | Total | <120 and <80 | 120–129 and <80 | 130–139 or 80–89 | ≥140 or ≥90 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number (%) | 5308 (100.0) | 958 (18.0) | 874 (16.5) | 2099 (39.5) | 1377 (25.9) | |
| age, mean (±SD) | 54.8 (±11.5) | 55.2 (±11.8) | 55.3 (±11.9) | 54.5 (±10.9) | 54.8 (±12.1) | 0.164 |
| gender, n (%) | 0.223 | |||||
| men | 2459 (46.3) | 422 (44.1) | 391 (44.7) | 996 (47.5) | 650 (47.2) | |
| women | 2849 (53.7) | 536 (55.9) | 483 (55.3) | 1103 (52.5) | 727 (52.8) | |
| health center location, n (%) | 0.662 | |||||
| rural | 2595 (48.9) | 479 (50.0) | 412 (47.1) | 1027 (48.9) | 677 (49.2) | |
| urban | 2713 (51.1) | 479 (50.0) | 462 (52.9) | 1072 (51.1) | 700 (50.8) | |
| healthcare setting, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||
| primary | 3189 (60.1) | 468 (48.9) | 488 (55.8) | 1388 (66.1) | 845 (61.4) | |
| secondary | 795 (15.0) | 220 (23.0) | 135 (15.4) | 243 (11.6) | 197 (14.3) | |
| tertiary | 1324 (24.9) | 270 (28.2) | 251 (28.7) | 468 (22.3) | 335 (24.3) | |
| smoking, n (%) | 0.955 | |||||
| smoker | 1883 (35.5) | 346 (36.1) | 313 (35.8) | 740 (35.3) | 484 (35.1) | |
| non-smoker | 3425 (64.5) | 612 (63.9) | 561 (64.2) | 1359 (64.7) | 893 (64.9) | |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (±SD) | 31.2 (±7.5) | 30.6 (±6.8) | 30.6 (±6.3) | 31.6 (±8.4) | 31.4 (±6.9) | 0.001 |
| missing | 720 (13.6) | 159 (16.6) | 116 (13.3) | 236 (11.2) | 209 (15.2) | |
| diabetes, n (%) | 0.590 | |||||
| no | 4437 (83.6) | 796 (83.1) | 730 (83.5) | 1744 (83.1) | 1167 (84.7) | |
| yes | 871 (16.4) | 162 (16.9) | 144 (16.5) | 355 (16.9) | 210 (15.3) |
| Characteristics | Change in SBP | p-Value * | p-Value ** | Change in DBP | p-Value * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sex | 0.035 | <0.001 | ||||
| men | −1.68 (−2.46 to −0.91) | <0.001 | −1.15 (−1.69 to −0.60) | <0.001 | ||
| women | −0.84 (−1.57 to −0.12) | 0.046 | 0.22 (−0.29 to 0.73) | 0.795 | ||
| age (years) | 0.951 | 0.012 | ||||
| 18–40 | −0.81 (−2.48 to 0.85) | 0.262 | −0.72 (−1.96 to 0.52) | 0.289 | ||
| 41–50 | −1.39 (−2.46 to −0.32) | 0.013 | −1.25 (−2.03 to −0.47) | 0.002 | ||
| 51–60 | −1.03 (−1.83 to −0.22) | 0.006 | −0.09 (−0.64 to 0.45) | 0.244 | ||
| 61–75 | −1.82 (−3.15 to −0.49) | 0.016 | −0.81 (−1.74 to 0.11) | 0.104 | ||
| >75 | −1.07 (−3.30 to 1.15) | 0.246 | 2.17 (0.63 to 3.70) | 0.027 | ||
| health center location | 0.713 | 0.912 | ||||
| rural | −1.11 (−1.87 to −0.35) | 0.004 | −0.46 (−0.99 to 0.06) | 0.039 | ||
| urban | −1.35 (−2.09 to −0.61) | <0.001 | −0.37 (−0.90 to 0.16) | 0.068 | ||
| healthcare setting | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| primary | −2.31 (−2.99 to −1.63) | <0.001 | −2.15 (−2.60 to −1.70) | <0.001 | ||
| secondary | 1.01 (−0.36 to 2.37) | 0.144 | 3.38 (2.34 to 4.42) | <0.001 | ||
| tertiary | 0.02 (−1.05 to 1.09) | 0.877 | 1.48 (0.69 to 2.28) | <0.001 | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.277 | 0.077 | ||||
| <18.5 | −0.20 (−7.22 to 6.83) | 0.909 | 0.78 (−3.46 to 5.02) | 0.630 | ||
| 18.5–25 | −0.16 (−1.69 to 1.38) | 0.646 | 0.22 (−0.89 to 1.32) | 0.401 | ||
| 25–30 | −1.56 (−2.54 to −0.57) | <0.001 | −0.74 (−1.42 to −0.05) | 0.007 | ||
| >30 | −0.89 (−1.65 to −0.13) | 0.044 | 0.07 (−0.48 to 0.62) | 0.939 | ||
| smoking | 0.838 | 0.259 | ||||
| smoker | −1.32 (−2.21 to −0.42) | 0.004 | −0.75 (−1.37 to −0.14) | 0.011 | ||
| non-smoker | −1.19 (−1.85 to −0.53) | <0.001 | −0.23 (−0.70 to 0.24) | 0.128 |
| Characteristics | Total (%) | ACC/AHA 2017 | ESC/ESH 2018 | NICE 2019 | ISH 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age (years) | ≤40 | 536 (10.1) | 31.7 (27.9–35.8) | 37.1 (33.1–41.3) | 61.6 (57.4–65.6) | 31.7 (27.9–35.8) |
| >40 | 4772 (89.9) | 40.4 (39.0–41.8) | 43.4 (42.0–44.8) | 66.1 (64.8–67.4) | 41.7 (40.3–43.1) | |
| smoking | smoker | 1883 (35.5) | 45.4 (43.2–47.7) | 47.4 (45.2–49.7) | 66.7 (64.5–68.8) | 48.6 (46.3–50.9) |
| non-smoker | 3245 (64.5) | 36.3 (34.7–37.9) | 40.2 (38.5–41.8) | 65.1 (63.5–66.7) | 36.3 (34.7–37.9) | |
| BMI | <25 kg/m2 | 672 (12.6) | 44.2 (40.5–48.0) | 47.5 (43.7–51.2) | 68.2 (64.5–71.6) | 44.9 (41.2–48.7) |
| ≥25 kg/m2 | 3910 (73.6) | 37.5 (36.0–39.1) | 40.8 (39.3–42.4) | 65.2 (63.7–66.7) | 38.8 (37.3–40.3) | |
| BMI | <30 kg/m2 | 2156 (47.1) | 41.5 (39.4–43.6) | 44.9 (42.9–47.1) | 67.9 (65.9–69.8) | 42.8 (40.7–44.9) |
| ≥30 kg/m2 | 2426 (52.9) | 35.9 (34.0–37.8) | 39.0 (37.1–41.0) | 63.6 (61.7–65.5) | 36.9 (35.0–38.9) | |
| diabetes | no | 4437 (83.6) | 39.9 (38.5–41.4) | 43.2 (41.8–44.7) | 66.2 (64.8–67.6) | 41.3 (39.8–42.7) |
| yes | 871 (16.4) | 37.5 (34.4–40.8) | 40.2 (37.0–43.5) | 62.9 (59.7–66.1) | 37.5 (34.4–40.8) | |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC/AHA 2017 | ESC/ESH 2018 | NICE 2019 | ISH 2020 | |||||
| Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | |
| age | ||||||||
| <65 | 0.44 (0.38–0.51) | 0.47 (0.39–0.58) | 0.54 (0.46–0.62) | 0.59 (0.48–0.73) | 0.92 (0.79–1.07) | 1.04 (0.84–1.28) | 0.33 (0.28–0.39) | 0.34 (0.28–0.42) |
| ≥65 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| sex | ||||||||
| men | 1.06 (0.95–1.18) | 0.99 (0.88–1.12) | 1.04 (0.93–1.16) | 0.97 (0.86–1.10) | 1.00 (0.89–1.12) | 0.95 (0.84–1.07) | 1.06 (0.95–1.18) | 1.00 (0.88–1.12) |
| women | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| health center location | ||||||||
| rural | 1.02 (0.91–1.13) | 0.93 (0.80–1.08) | 1.04 (0.93–1.16) | 0.96 (0.82–1.11) | 1.07 (0.95–1.19) | 0.97 (0.83–1.13) | 1.01 (0.90–1.12) | 0.92 (0.79–1.07) |
| urban | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| healthcare setting | ||||||||
| primary | 0.96 (0.84–1.10) | 1.09 (0.92–1.30) | 0.99 (0.87–1.13) | 1.12 (0.95–1.32) | 1.05 (0.92–1.20) | 1.15 (0.97–1.37) | 0.96 (0.84–1.09) | 1.11 (0.94–1.32) |
| secondary | 1.19 (0.99–1.42) | 1.31 (1.03–1.66) * | 1.23 (1.03–1.47) * | 1.32 (1.05–1.67) * | 1.26 (1.04–1.52) * | 1.41 (1.11–1.81) ** | 1.18 (0.99–1.42) | 1.34 (1.05–1.70) * |
| tertiary | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| smoking status | ||||||||
| non-smoker | 0.69 (0.61–0.77) | 0.97 (0.83–1.13) | 0.74 (0.66–0.83) | 0.95 (0.82–1.11) | 0.93 (0.83–1.05) | 0.93 (0.80–1.09) | 0.60 (0.54–0.68) | 0.97 (0.83–1.13) |
| smoker | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||||
| <25 | 1.32 (1.12–1.55) ** | 1.26 (1.07–1.49) ** | 1.31 (1.11–1.54) ** | 1.27 (1.08–1.50) ** | 1.14 (0.96–1.36) | 1.14 (0.96–1.37) | 1.29 (1.09–1.52) ** | 1.22 (1.03–1.44) * |
| ≥25 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| diabetes | ||||||||
| yes | 0.90 (0.78–1.05) | 1.07 (0.90–1.26) | 0.88 (0.76–1.02) | 1.00 (0.85–1.17) | 0.87 (0.75–1.01) | 0.90 (0.76–1.07) | 0.85 (0.74–0.99) | 1.07 (0.90–1.26) |
| no | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhagavathula, A.S.; Shah, S.M.; Suliman, A.; Oulhaj, A.; Aburawi, E.H. Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010047
Bhagavathula AS, Shah SM, Suliman A, Oulhaj A, Aburawi EH. Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhagavathula, Akshaya Srikanth, Syed Mahboob Shah, Abubaker Suliman, Abderrahim Oulhaj, and Elhadi Husein Aburawi. 2022. "Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010047
APA StyleBhagavathula, A. S., Shah, S. M., Suliman, A., Oulhaj, A., & Aburawi, E. H. (2022). Hypertension Control and Guideline-Recommended Target Blood Pressure Goal Achievement at an Early Stage of Hypertension in the UAE. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010047







