Proposal of a Standardized Questionnaire to Structure Clinical Peer Reviews of Mortality and Failure of Rescue in Pancreatic Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
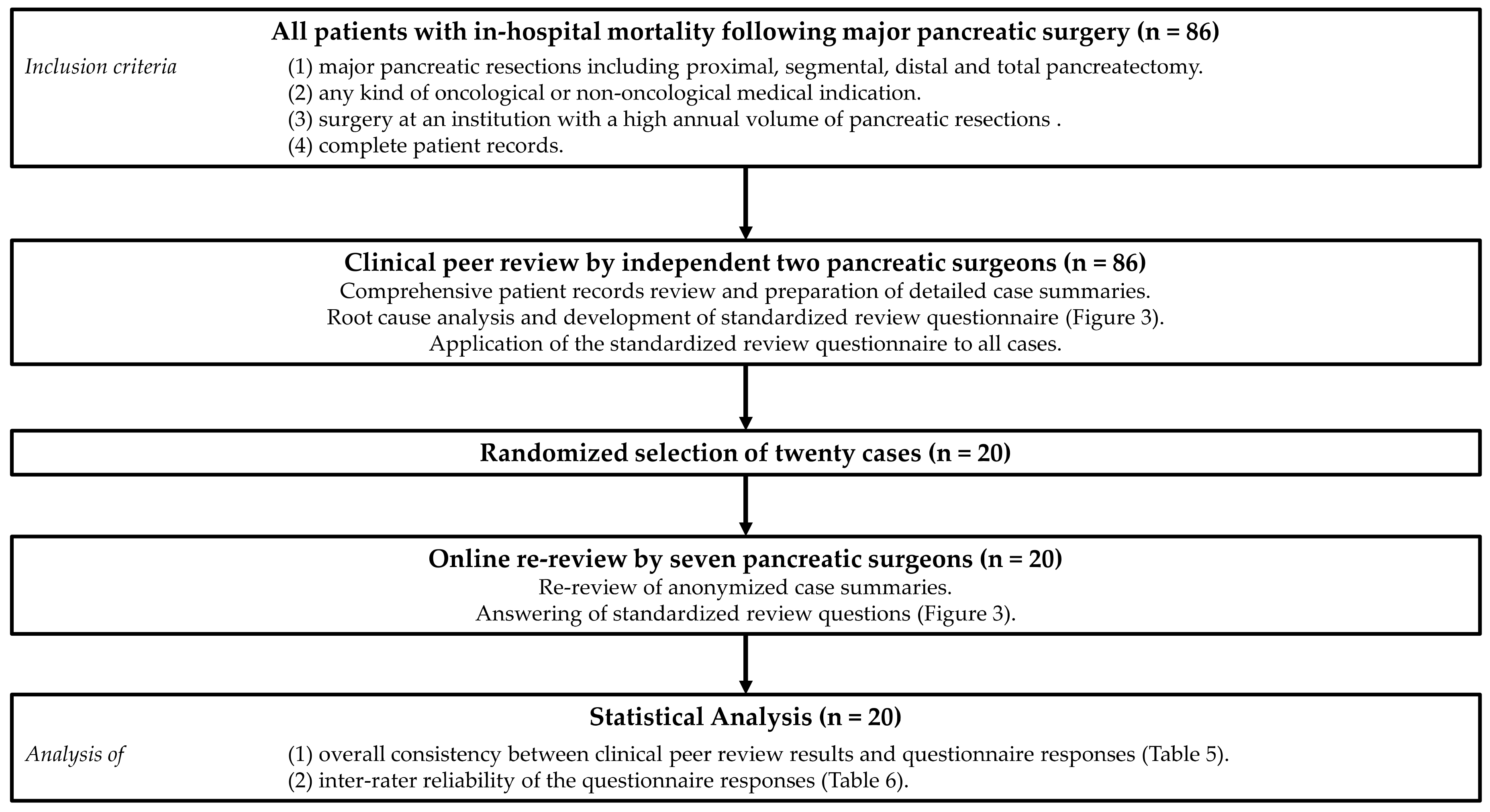
2. Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
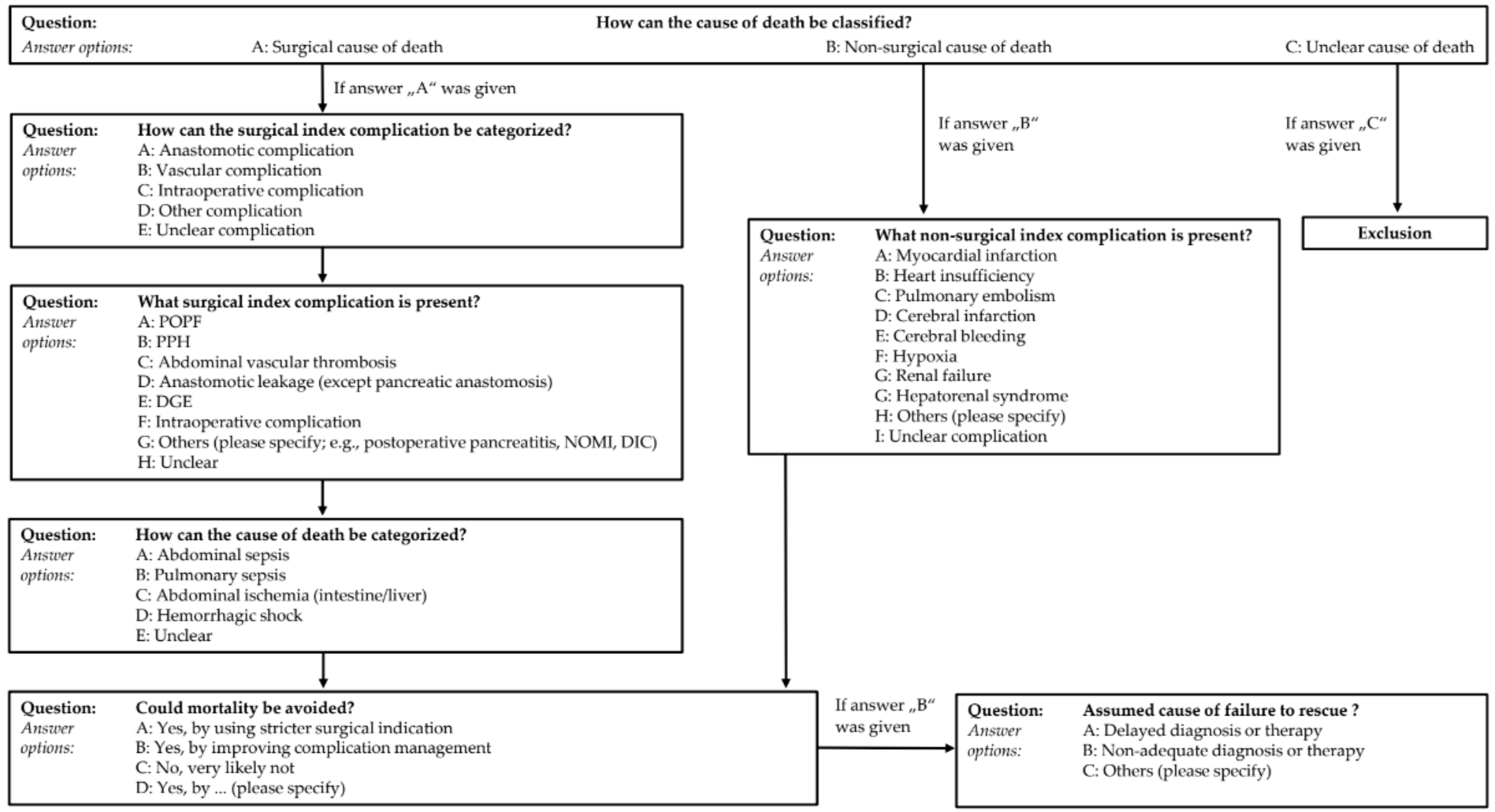
2.2. Clinical Peer Review
2.3. Online Re-Review
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Characteristics of the Patients
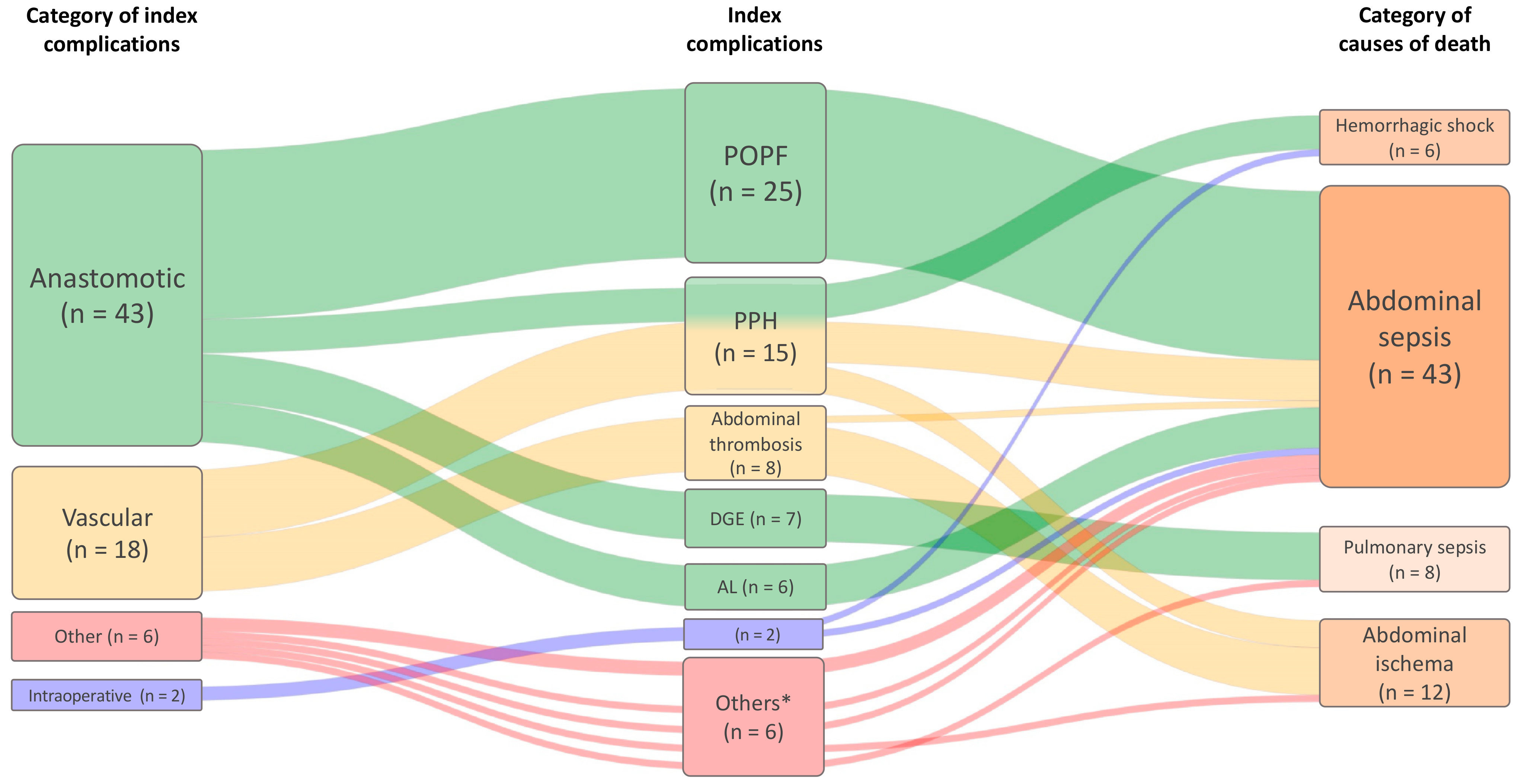
3.2. Clinical Peer Review
3.3. Distribution of Questionnaire Responses According to Patient Characteristics and Surgical Parameters
3.4. Online Re-Review
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| POPF | Post-operative pancreatic fistula |
| PPH | Post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage |
| PPPD | Pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy |
References
- Nimptsch, U.; Krautz, C.; Weber, G.F.; Mansky, T.; Grützmann, R. Nationwide In-hospital Mortality Following Pancreatic Surgery in Germany is Higher than Anticipated. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Serrano, J.F.; Velez-Serrano, D.; Hernandez-Barrera, V.; Jimenez-Garcia, R.; Lopez de Andres, A.; Garrido, P.C.; Alvaro-Meca, A. Prediction of in-hospital mortality after pancreatic resection in pancreatic cancer patients: A boosting approach via a population-based study using health administrative data. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwall, C.A.; Maxwell, J.G.; Brinker, C.C.; Koch, G.G.; Covington, D.L. National estimates of mortality rates for radical pancreaticoduodenectomy in 25,000 patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 9, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautz, C.; Nimptsch, U.; Weber, G.F.; Mansky, T.; Grützmann, R. Effect of Hospital Volume on In-hospital Morbidity and Mortality Following Pancreatic Surgery in Germany. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautz, C.; Denz, A.; Weber, G.F.; Grützmann, R. Influence of Hospital Volume Effects and Minimum Caseload Requirements on Quality of Care in Pancreatic Surgery in Germany. Visc. Med. 2017, 33, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, J.S.; Zhou, Z.; Simons, J.P.; Ng, S.C.; McDade, T.P.; Whalen, G.F.; Tseng, J.F. A simple risk score to predict in-hospital mortality after pancreatic resection for cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, C.B.; Cramer, L.D.; Hoskins, W.J.; Brennan, M.F. Impact of Hospital Volume on Operative Mortality for Major Cancer Surgery. JAMA 1998, 280, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Heek, N.T.; Kuhlmann, K.F.; Scholten, R.J.; de Castro, S.M.; Busch, O.R.; van Gulik, T.M.; Obertop, H.; Gouma, D.J. Hospital volume and mortality after pancreatic resection: A systematic review and an evaluation of intervention in the Netherlands. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautz, C.; Haase, E.; Elshafei, M.; Saeger, H.-D.; Distler, M.; Grützmann, R.; Weber, G.F. The impact of surgical experience and frequency of practice on perioperative outcomes in pancreatic surgery. BMC Surg. 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vyas, D.; E Hozain, A. Clinical peer review in the United States: History, legal development and subsequent abuse. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6357–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chop, I.; Eberlein-Gonska, M. The peer review procedure and its place in medicine. Z. Evid. Fortbild. Qual. Gesundhwes. 2012, 106, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.P.; Bause, H. Peer review in ICU. Z. Evid. Fortbild. Qual. Gesundhwes. 2012, 106, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Roessel, S.; Mackay, T.M.; van Dieren, S.; van der Schelling, G.P.; Nieuwenhuijs, V.B.; Bosscha, K.; van der Harst, E.; van Dam, R.M.; Liem, M.S.L.; Festen, S.; et al. Dutch Pancreatic Cancer Group. Textbook Outcome: Nationwide Analysis of a Novel Quality Measure in Pancreatic Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheetz, K.H.; Dimick, J.B.; Nathan, H. Centralization of High-Risk Cancer Surgery Within Existing Hospital Systems. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geest, L.G.; Besselink, M.G.; Busch, O.R.; de Hingh, I.H.; van Eijck, C.H.; Dejong, C.H.; Lemmens, V.E. Elderly Patients Strongly Benefit from Centralization of Pancreatic Cancer Surgery: A Population-Based Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finks, J.F.; Osborne, N.H.; Birkmeyer, J.D. Trends in Hospital Volume and Operative Mortality for High-Risk Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2128–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gawande, A.A.; Thomas, E.J.; Zinner, M.J.; Brennan, T.A. The incidence and nature of surgical adverse events in Colorado and Utah in 1992. Surgery 1999, 126, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kable, A.K.; Gibberd, R.W.; Spigelman, A.D. Adverse events in surgical patients in Australia. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2002, 14, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.L.; Reid, J.L.; Babidge, W.J.; Maddern, G.J. Peer review of mortality after pancreaticoduodenectomy in Australia. HPB 2019, 21, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, J.S.; Scholz, M.; Ellmann, S.; Uder, M.; Grützmann, R.; Weber, G.F.; Krautz, C. Cinematic Rendering in Anatomy: A Crossover Study Comparing a Novel 3D Reconstruction Technique to Conventional Computed Tomography. Anat. Sci. Educ. 2021, 14, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafei, M.; Binder, J.; Baecker, J.; Brunner, M.; Uder, M.; Weber, G.F.; Grützmann, R.; Krautz, C. Comparison of Cinematic Rendering and Computed Tomography for Speed and Comprehension of Surgical Anatomy. JAMA Surg. 2019, 154, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Demographics | n (%) or Mean [Range] | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number | 86 | |
| Age (years) | 67 [39–87] | |
| Gender | Male | 53 (62) |
| Female | 33 (38) | |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) (kg/m2) | 25.8 [16.7–37.0] | |
| ASA | II | 31 (36) |
| III | 44 (51) | |
| IV | 5 (6) | |
| unknown | 6 (7) | |
| Alcohol abusus | No | 44 (51) |
| Yes | 27 (31) | |
| unknown | 15 (17) | |
| Smoking | No | 55 (64) |
| Yes | 22 (26) | |
| Unknown | 9 (11) | |
| Pre-existing diseases | <2 | 38 (44) |
| ≥2 | 48 (56) | |
| Metastatic disease | No | 79 (92) |
| Yes | 7 (8) | |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | No | 74 (86) |
| Yes | 12 (14) | |
| Indication of surgery | Oncological | 70 (81) |
| Non-oncological | 16 (19) | |
| Type of surgery | Whipple/PPPD | 68 (79) |
| Left pancreatectomy | 14 (16) | |
| Total Pancreatectomy | 4 (5) | |
| Extented surgery | No | 44 (51) |
| Vascular resection | 14 (16) | |
| Multivisceral resection | 20 (23) | |
| Vascular and multivisceral resection | 8 (9) |
| Non-Surgical Index Complication | n (%) or Mean [Range] |
|---|---|
| Myocardial infarction | 5 (29) |
| Pulmonary embolism | 3 (18) |
| Cerebral infarction | 2 (12) |
| Cerebral bleeding | 2 (12) |
| Heart insufficiency | 2 (12) |
| Hepatorenal syndrom | 2 (12) |
| Hypoxia | 1 (6) |
| First Deviation from Textbook Outcome * (POD) | First Clinical Sign Specific to Index Complication (POD) | p-Value | Potential of Improvement | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of Indication | Complication Management | None | ||||||
| Delay in Diagnosis or Therapy | Non-Adequate Diagnosis or Therapy | |||||||
| All patients (n = 86) | 6 [0–34] | 12 [0–122] | 0.002 | 9 (11) | 36 (42) | 7 (8) | 34 (40) | - |
| Classification of cause of death | ||||||||
| Surgical (n = 69) | 5 [0–21] | 10 [0–83] | 0.004 | 5 (7) | 35 (51) | 7 (10) | 22 (32) | 0.001 |
| Non-surgical (n = 17) | 8 [0–34] | 17 [0–122] | 0.165 | 4 (24) | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | 12 (71) | |
| Surgical index complication | ||||||||
| POPF (n = 25) | 5 [1–14] | 8 [1–29] | 0.036 | 1 (4) | 16 (64) | 2 (8) | 6 (24) | 0.362 |
| PPH (n = 15) | 6 [1–20] | 16 [1–83] | 0.117 | 1 (7) | 8 (53) | 3 (20) | 3 (20) | |
| Abdominal thrombosis (n = 8) | 4 [1–10] | 4 [1–10] | 0.351 | 1 (13) | 3 (38) | 1 (13) | 3 (38) | |
| DGE (n = 7) | 8 [0–21] | 20 [3–63] | 0.186 | 1 (14) | 2 (29) | 0 (0) | 4 (57) | |
| Anastomotic leakage ** (n = 6) | 5 [1–9] | 7 [4–9] | 0.189 | 0 (0) | 4 (67) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | |
| Intraoperative complication (n =2) | 0 | 0 | - | 1 (50) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (50) | |
| Others (n = 6) | 7 [1–20] | 9 [1–25] | 0.325 | 0 (0) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 4 (67) | |
| Oncological n = 70 | Non-Oncological n = 16 | p-Value | Pre-Existing Diseases <2 n = 38 | Pre-Existing Diseases ≥2 n = 48 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to death (days) | 35 [1–146] | 31 [3–62] | 0.854 | 40 [3–146] | 30 [1–126] | 0.050 |
| Classification of cause of death | ||||||
| Surgical | 56 (80) | 13 (81) | 1.000 | 32 (84) | 37 (77) | 0.432 |
| Non-surgical | 14 (20) | 3 (19) | 6 (16) | 11 (23) | ||
| Category of surgical index complication | ||||||
| Anastomotic | 37 (66) | 6 (46) | 0.358 | 19 (59) | 24 (65) | 0.427 |
| Vascular | 13 (23) | 5 (39) | 9 (28) | 9 (24) | ||
| Other | 5 (9) | 1 (8) | 2 (6) | 4 (11) | ||
| Intraoperative | 1 (2) | 1 (8) | 2 (6) | 0 (0) | ||
| Surgical Index complication | ||||||
| POPF | 22 (39) | 3 (23) | 0.417 | 12 (38) | 13 (35) | 0.021 |
| PPH | 9 (16) | 6 (46) | 11 (34) | 4 (11) | ||
| Abdominal thrombosis | 7 (13) | 1 (8) | 3 (9) | 5 (14) | ||
| DGE | 7 (13) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 6 (16) | ||
| Anastomotic leakage * | 5 (9) | 1 (8) | 1 (3) | 5 (14) | ||
| Intraoperative complication | 1 (2) | 1 (8) | 2 (6) | 0 (0) | ||
| Others | 5 (9) | 1 (8) | 2 (6) | 4 (11) | ||
| Category of cause of death | ||||||
| Abdominal sepsis | 34 (61) | 9 (69) | 0.083 | 20 (63) | 23 (62) | 0.010 |
| Abdominal ischemia ** | 11 (20) | 1 (8) | 5 (16) | 7 (19) | ||
| Pulmonary sepsis | 8 (14) | 0 (0) | 1 (3) | 7 (19) | ||
| Hemorrhagic shock | 3 (5) | 3 (23) | 6 (19) | 0 (0) |
| Whipple/PPPD n = 68 | Left Pancreatectomy n = 14 | p-Value | Vascular Resection | p-Value | Multivisceral Resection | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes n = 22 | No n = 64 | Yes n = 28 | No n = 58 | |||||||
| Time to death (days) | 34 [1–126] | 30 [1–80] | 0.885 | 37 [1–146] | 33 [1–126] | 0.850 | 38 [1–146] | 33 [3–126] | 0.736 | |
| Classification of cause of death | ||||||||||
| Surgical | 58 (85) | 8 (57) | 0.026 | 20 (91) | 49 (77) | 0.217 | 22 (79) | 47 (81) | 1.000 | |
| Non-surgical | 10 (15) | 6 (43) | 2 (9) | 15 (23) | 6 (21) | 11 (19) | ||||
| Category of surgical index complication | ||||||||||
| Anastomotic | 38 (66) | 5 (63) | 0.374 | 9 (45) | 34 (69) | 0.012 | 13 (59) | 30 (64) | 1.000 | |
| Vascular | 14 (24) | 1 (13) | 10 (50) | 8 (16) | 6 (27) | 12(26) | ||||
| Other | 5 (9) | 1 (13) | 0 (0) | 6 (12) | 2 (9) | 4 (9) | ||||
| Intraoperative | 1 (2) | 1 (13) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) | ||||
| Surgical index complication | ||||||||||
| POPF | 24 (41) | 1 (13) | 0.002 | 6 (30) | 19 (39) | 0.141 | 5 (23) | 20 (43) | 0.001 | |
| PPH | 13 (22) | 0 (0) | 5 (25) | 10 (20) | 2 (9) | 13 (28) | ||||
| Abdominal thrombosis | 6 (10) | 1 (13) | 6 (30) | 2 (4) | 4 (18) | 4 (9) | ||||
| DGE | 7 (12) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 5 (10) | 2 (9) | 5 (11) | ||||
| Anastomotic leakage* | 2 (3) | 4 (50) | 0 (0) | 6 (12) | 6 (27) | 0 (0) | ||||
| Intraoperative complication | 1 (2) | 1 (13) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) | 1 (5) | 1 (2) | ||||
| Others | 5 (9) | 1 (13) | 0 (0) | 6 (12) | 2 (9) | 4 (9) | ||||
| Category of cause of death | ||||||||||
| Abdominal sepsis | 36 (62) | 7 (88) | 0.518 | 8 (40) | 35 (71) | 0.012 | 14 (64) | 19 (62) | 0.347 | |
| Abdominal ischemia** | 8 (14) | 1 (13) | 8 (40) | 4 (8) | 5 (23) | 7 (15) | ||||
| Pulmonary sepsis | 8 (14) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 6 (12) | 3 (14) | 5 (11) | ||||
| Hemorrhagic shock | 6 (10) | 0 (0) | 2 (10) | 4 (8) | 0 (0) | 6 (13) | ||||
| Standardized Questionnaire Items | Answer Options | Peer Reviewn/ N (%) | Online Re-Reviewn/ N (%) | Cohen’s Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All cases | ||||
| Classification of cause of death? | Surgical | 14/20 (70) | 13/20 (65) | 0.886 |
| Non-surgical | 6/20 (30) | 7/20 (35) | ||
| Potential of improvement? | Yes | 15/20 (75) | 13/20 (65) | 0.765 |
| No | 5/20 (25) | 7/20 (35) | ||
| Surgical cause of death | ||||
| Category of index complication? | Anastomotic | 7/14 (50) | 7/13 (54) | 0.714 |
| Vascular | 6/14 (43) | 6/13 (46) | ||
| Other | 1/14 (7) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Intraoperative | 0/14 (0) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Index complication? | POPF | 6/14 (43) | 4/13 (31) | 0.492 |
| PPH | 3/14 (21) | 2/13 (15) | ||
| Abdominal thrombosis | 3/14 (21) | 4/13 (31) | ||
| DGE | 0/14 (0) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Anastomotic leakage * | 1/14 (7) | 3/13 (23) | ||
| Intraoperative complication | 0/14 (0) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Other | 1/14 (7) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Category of cause of death? | Abdominal sepsis | 9/14 (64) | 8/13 (6) | 0.694 |
| Abdominal ischemia ** | 5/14 (36) | 4/13 (31) | ||
| Pulmonary sepsis | 0/14 (0) | 0/13 (0) | ||
| Hemorrhagic shock | 0/14 (0) | 1/13 (8) | ||
| Non-surgical cause of death | ||||
| Index complication? | Myocardial infarction | 1/6 (17) | 1/7 (14) | 0.793 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 2/6 (33) | 2/7 (29) | ||
| Cerebral infarction | 1/6 (17) | 1/7 (14) | ||
| Heart insufficiency | 1/6 (17) | 2/7 (29) | ||
| Hypoxia | 1/6 (17) | 1/7 (14) | ||
| Standardized Questionnaire Items | Answer Options | Fleiss’ Kappa |
|---|---|---|
| All cases (n = 20) | ||
| Classification of cause of death? | Surgical | 0.724 |
| Non-surgical | ||
| Potential of improvement? | Yes | 0.262 |
| No | ||
| Surgical cause of death (n = 13) | ||
| Category of index complication? | Anastomotic | 0.455 |
| Vascular | ||
| Other | ||
| Intraoperative | ||
| Index complication? | POPF | 0.424 |
| PPH | ||
| Abdominal thrombosis | ||
| DGE | ||
| Anastomotic leakage * | ||
| Intraoperative complication | ||
| Others | ||
| Category of cause of death? | Abdominal sepsis | 0.533 |
| Abdominal ischemia ** | ||
| Pulmonary sepsis | ||
| Hemorrhagic shock | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunner, M.; Mücke, F.; Langheinrich, M.; Struller, F.; Rückert, F.; Welsch, T.; Distler, M.; Kersting, S.; Weber, G.F.; Grützmann, R.; et al. Proposal of a Standardized Questionnaire to Structure Clinical Peer Reviews of Mortality and Failure of Rescue in Pancreatic Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061281
Brunner M, Mücke F, Langheinrich M, Struller F, Rückert F, Welsch T, Distler M, Kersting S, Weber GF, Grützmann R, et al. Proposal of a Standardized Questionnaire to Structure Clinical Peer Reviews of Mortality and Failure of Rescue in Pancreatic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(6):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061281
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunner, Maximilian, Franziska Mücke, Melanie Langheinrich, Florian Struller, Felix Rückert, Thilo Welsch, Marius Distler, Stephan Kersting, Georg F. Weber, Robert Grützmann, and et al. 2021. "Proposal of a Standardized Questionnaire to Structure Clinical Peer Reviews of Mortality and Failure of Rescue in Pancreatic Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 6: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061281
APA StyleBrunner, M., Mücke, F., Langheinrich, M., Struller, F., Rückert, F., Welsch, T., Distler, M., Kersting, S., Weber, G. F., Grützmann, R., & Krautz, C. (2021). Proposal of a Standardized Questionnaire to Structure Clinical Peer Reviews of Mortality and Failure of Rescue in Pancreatic Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(6), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061281






