PCSK9 Levels and Metabolic Profiles in Elderly Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance under Statin Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
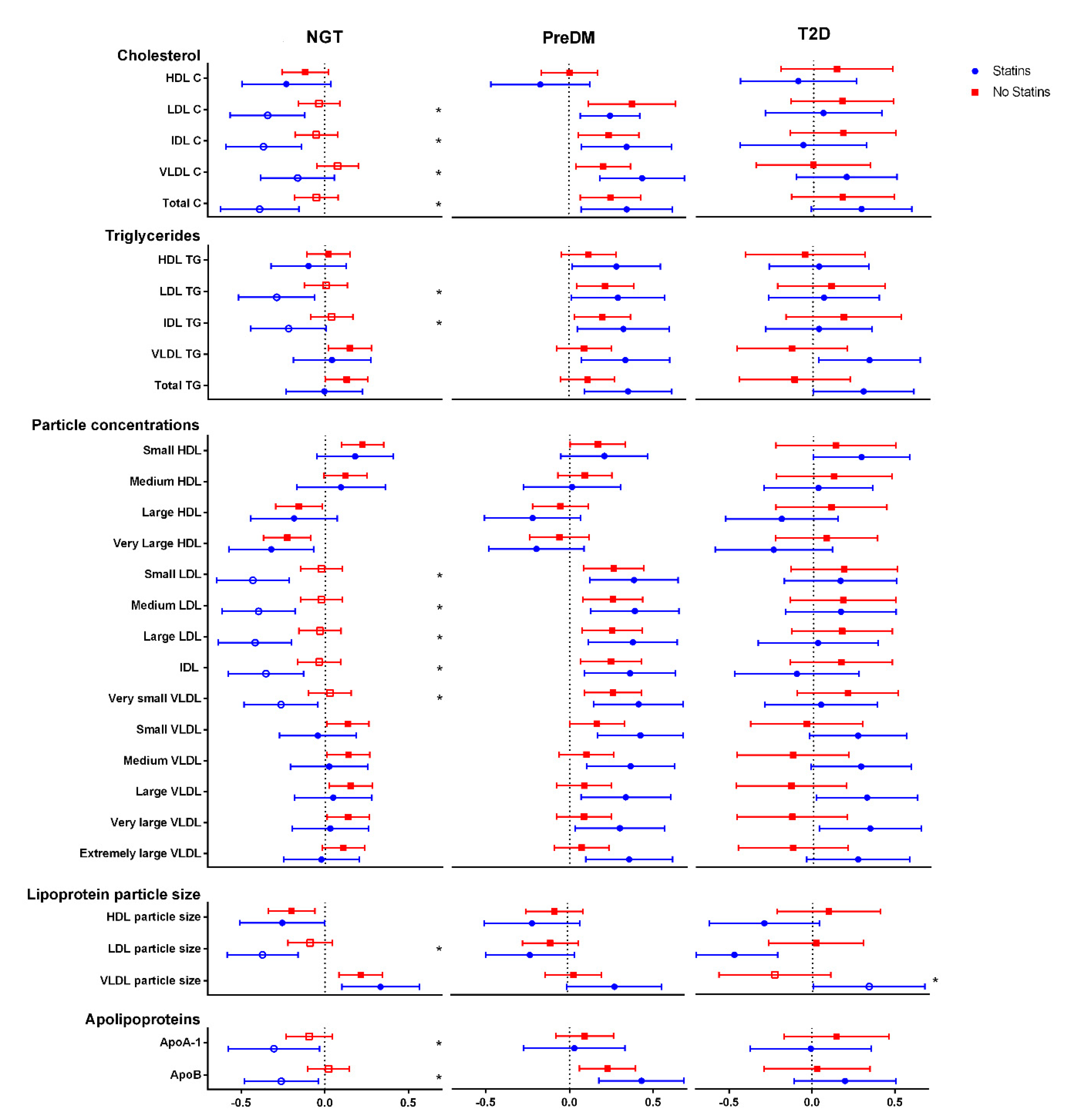
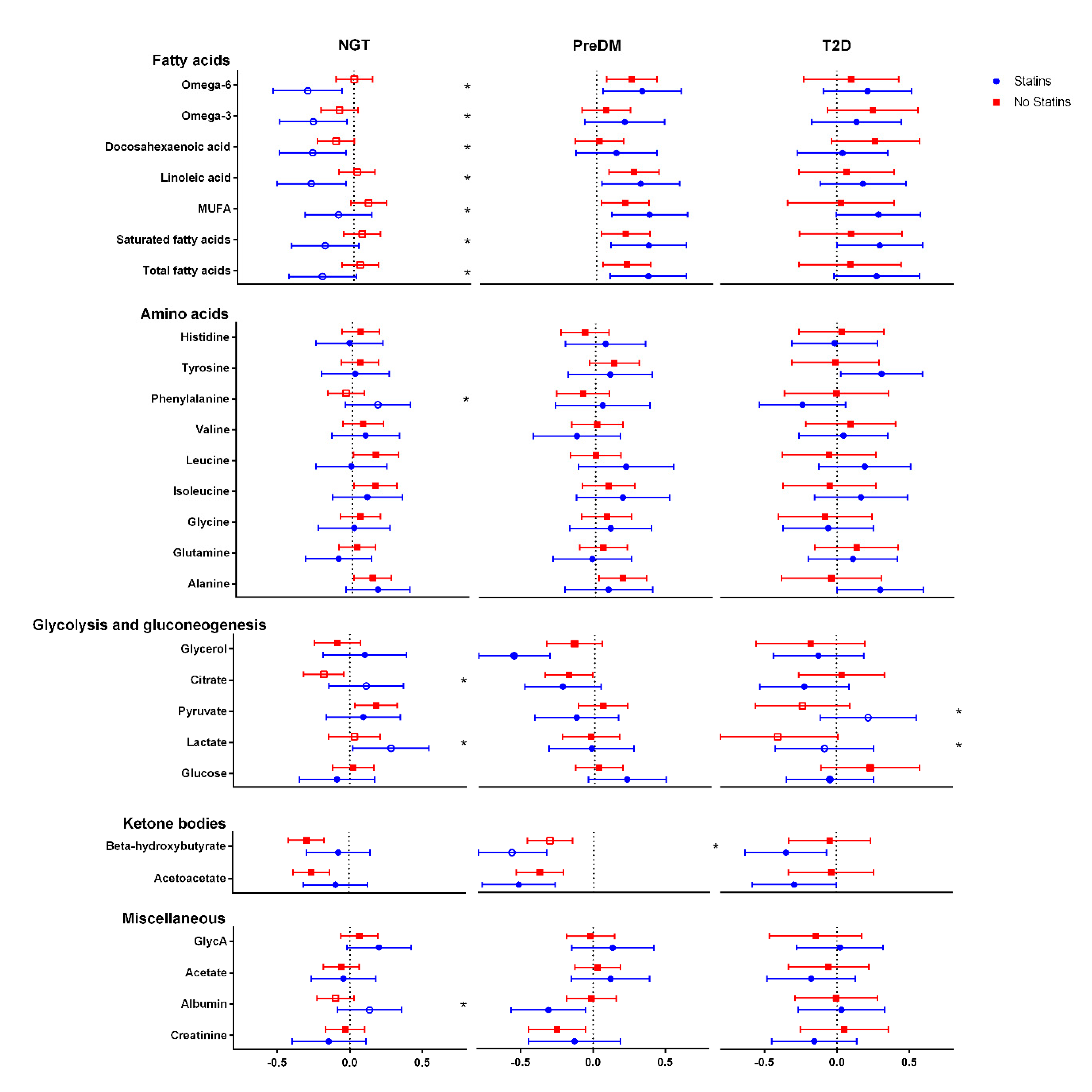
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidah, N.G.; Awan, Z.; Chrétien, M.; Mbikay, M. PCSK9. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabès, J.-P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; Cruaud, C.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Erlich, D.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, A.; Bianconi, V.; Gragnano, F.; Moscarella, E.; Fimiani, F.; Monda, E.; Scudiero, O.; Limongelli, G.; Pirro, M.; Calabrò, P. Beyond cholesterol metabolism: The pleiotropic effects of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9). Genetics, mutations, expression, and perspective for long-term inhibition. BioFactors 2020, 46, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Kotowski, I.K.; Graham, R.; Garcia, C.K.; Hobbs, H.H. Low LDL cholesterol in individuals of African descent resulting from frequent nonsense mutations in PCSK9. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Duprez, D.; Handelsman, Y.; Koren, M. Cardiovascular Outcomes and Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors: Current Data and Future Prospects. Vasc. Heal. Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi, A.A.; Banach, M.; Pirro, M.; Stein, E.A.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 and diabetes: Is there a link? Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakoski, S.G.; Lagace, T.A.; Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic and Metabolic Determinants of Plasma PCSK9 Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekaies, Y.; Baudin, B.; Kelbousi, S.; Sakly, M.; Attia, N. Plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 is associated with Lp(a) in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2015, 29, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, R.G.; Haley, R.W.; Willett, D.L.; Peshock, R.M.; Vaeth, P.C.; Leonard, D.; Basit, M.; Cooper, R.S.; Iannacchione, V.G.; A Visscher, W.; et al. The Dallas Heart Study: A population-based probability sample for the multidisciplinary study of ethnic differences in cardiovascular health. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B.; Duvillard, L.; Brindisi, M.C.; Gautier, E.; Krempf, M.; Costet, P.; Cariou, B. Lack of association between plasma PCSK9 and LDL-apoB100 catabolism in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2011, 219, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, M.; Troutt, J.; van Greevenbroek, M.; Ferreira, I.; Feskens, E.; van der Kallen, C.; Schaper, N.; Schalkwijk, C.; Konrad, R.; Stehouwer, C. Plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 is not altered in subjects with impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus, but its relationship with non-HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B may be modified by type 2 diabetes mellitus: The CODAM study. Atherosclerosis 2011, 217, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 37, S81–S90. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N. Prediabetes diagnosis and treatment: A review. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarretxe, D.; Girona, J.; Plana, N.; Cabré, A.; Ferré, R.; Amigó, N.; Guaita, S.; Mallol, R.; Heras, M.; Masana, L. Circulating PCSK9 in patients with type 2 diabetes and related metabolic disorders. Clínica Investig. Arterioscler. 2016, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colhoun, H.M.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Robinson, J.G.; Leiter, L.A.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Henry, R.R.; Cariou, B.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Pordy, R.; Merlet, L.; et al. No effect of PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab on the incidence of diabetes in a pooled analysis from 10 ODYSSEY Phase 3 studies. Eur. Hear. J. 2016, 37, 2981–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, L.S.F.; Campos, A.M.; Sposito, A.C. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Inhibitors and Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis with over 96,000 Patient-Years. Diabetes Care 2017, 41, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, N.; Tibolla, G.; Pirillo, A.; Cipollone, F.; Mezzetti, A.; Pacia, S.; Corsini, A.; Catapano, A.L. Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9) secreted by cultured smooth muscle cells reduces macrophages LDLR levels. Atherosclerosis 2012, 220, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.; Toth, P.; Fogacci, F.; Virdis, A.; Borghi, C. Improvement in arterial stiffness after short-term treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, B.; Montecucco, F.; Nanchen, D.; Carbone, F.; Klingenberg, R.; Vuilleumier, N.; Aghlmandi, S.; Heg, D.; Räber, L.; Auer, R.; et al. Prognostic value of PCSK9 levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Eur. Hear. J. 2016, 37, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.-G.; Xu, R.-X.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.-L.; Sun, J.; Li, J.-J. Relation of circulating PCSK9 concentration to fibrinogen in patients with stable coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, G.; Chamberland, A.; Wassef, H.; Davignon, J.; Seidah, N.G.; Bernier, L.; Prat, A. Statins UpregulatePCSK9, the Gene Encoding the Proprotein Convertase Neural Apoptosis-Regulated Convertase-1 Implicated in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careskey, H.E.; Davis, R.A.; Alborn, W.E.; Troutt, J.S.; Cao, G.; Konrad, R.J. Atorvastatin increases human serum levels of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayne, J.; Dewpura, T.; Raymond, A.; Cousins, M.; Chaplin, A.; A Lahey, K.; A LaHaye, S.; Mbikay, M.; Ooi, T.C.; Chrétien, M. Plasma PCSK9 levels are significantly modified by statins and fibrates in humans. Lipids Health Dis. 2008, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, K.A.; Leppäluoto, J.; Jokelainen, J.; Jämsä, T.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Herzig, K.-H. Effect of Physical Activity on Plasma PCSK9 in Subjects with High Risk for Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, C.; Del Turco, S.; Ragusa, R.; Lorenzoni, V.; De Graaf, M.; Basta, G.; Scholte, A.; De Caterina, R.; Neglia, D. Association of PCSK9 plasma levels with metabolic patterns and coronary atherosclerosis in patients with stable angina. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenbäck, V.; Mutt, S.J.; Leppäluoto, J.; Gagnon, D.D.; Mäkelä, K.A.; Jokelainen, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Herzig, K.-H. Association of Physical Activity With Telomere Length Among Elderly Adults—The Oulu Cohort 1945. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutt, S.J.; Jokelainen, J.; Sebert, S.; Auvinen, J.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Herzig, K.-H. Vitamin D Status and Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Older Subjects from Northern Finland (Latitude 65°North). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, A.-M.; Ahola, R.; Kulmala, J.; Hakonen, H.; Vähä-Ypyä, H.; Herzig, K.-H.; Auvinen, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Sievänen, H.; Tammelin, T.H.; et al. Measuring Physical Activity in Free-Living Conditions—Comparison of Three Accelerometry-Based Methods. Front. Physiol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Würtz, P.; Tukiainen, T.; Tynkkynen, T.; Laatikainen, R.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Viikari, J.; et al. High-throughput serum NMR metabonomics for cost-effective holistic studies on systemic metabolism. Analyst 2009, 134, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, T.; Mutt, S.J.; Jokelainen, J.; Saukkonen, A.-M.; Raza, G.S.; Karhu, T.; Härkönen, P.; Eckel, J.; Herzig, K.-H.; Rajala, U.; et al. Adipokines and inflammatory markers in elderly subjects with high risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Bellentani, S.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Passalacqua, M.; Castiglione, A.; Tiribelli, C. The Fatty Liver Index: A simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, B.J.; Petrides, F.; Tabet, F.; Bao, W.; Hovingh, G.K.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Ramin-Mangata, S.; Meilhac, O.; Demicco, D.; Rye, K.-A.; et al. Effect of atorvastatin, cholesterol ester transfer protein inhibition, and diabetes mellitus on circulating proprotein subtilisin kexin type 9 and lipoprotein(a) levels in patients at high cardiovascular risk. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilvo, M.; Simolin, H.; Metso, J.; Ruuth, M.; Öörni, K.; Jauhiainen, M.; Laaksonen, R.; Baruch, A. PCSK9 inhibition alters the lipidome of plasma and lipoprotein fractions. Atherosclerosis 2018, 269, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Pavlyha, M.; Ngai, C.; Thomas, T.; Holleran, S.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Karmally, W.; Nandakumar, R.; Fontanez, N.; Obunike, J.C.; et al. Effects of PCSK9 Inhibition With Alirocumab on Lipoprotein Metabolism in Healthy Humans. Circulation 2017, 135, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliz, E.; Kettunen, J.; Holmes, M.V.; Williams, C.O.; Boachie, C.; Wang, Q.; Männikkö, M.; Sebert, S.; Walters, R.; Lin, K.; et al. Metabolomic Consequences of Genetic Inhibition of PCSK9 Compared With Statin Treatment. Circulation 2018, 138, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakernaak, A.J.; Lambert, G.; Dullaart, R.P. Plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin–kexin type 9 is predominantly related to intermediate density lipoproteins. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.; Fabbrini, E.; Horton, J.D.; Korenblat, K.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S. Lack of a relationship between plasma PCSK9 concentrations and hepatic lipoprotein kinetics in obese people. Transl. Res. 2011, 158, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ai, D.; Chen, C.; Han, S.; Ganda, A.; Murphy, A.J.; Haeusler, R.; Thorp, E.; Accili, D.; Horton, J.D.; Tall, A.R. Regulation of hepatic LDL receptors by mTORC1 and PCSK9 in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbikay, M.; Sirois, F.; Mayne, J.; Wang, G.-S.; Chen, A.; Dewpura, T.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G.; Chretien, M.; Scott, F.W. PCSK9-deficient mice exhibit impaired glucose tolerance and pancreatic islet abnormalities. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Dalt, L.; Ruscica, M.; Bonacina, F.; Balzarotti, G.; Dhyani, A.; Di Cairano, E.; Baragetti, A.; Arnaboldi, L.; De Metrio, S.; Pellegatta, F.; et al. PCSK9 deficiency reduces insulin secretion and promotes glucose intolerance: The role of the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Eur. Hear. J. 2019, 40, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Murray, H.M.; Welsh, P.; Buckley, B.M.; De Craen, A.J.M.; Seshasai, S.R.K.; McMurray, J.J.; Freeman, D.J.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Statins and risk of incident diabetes: A collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet 2010, 375, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
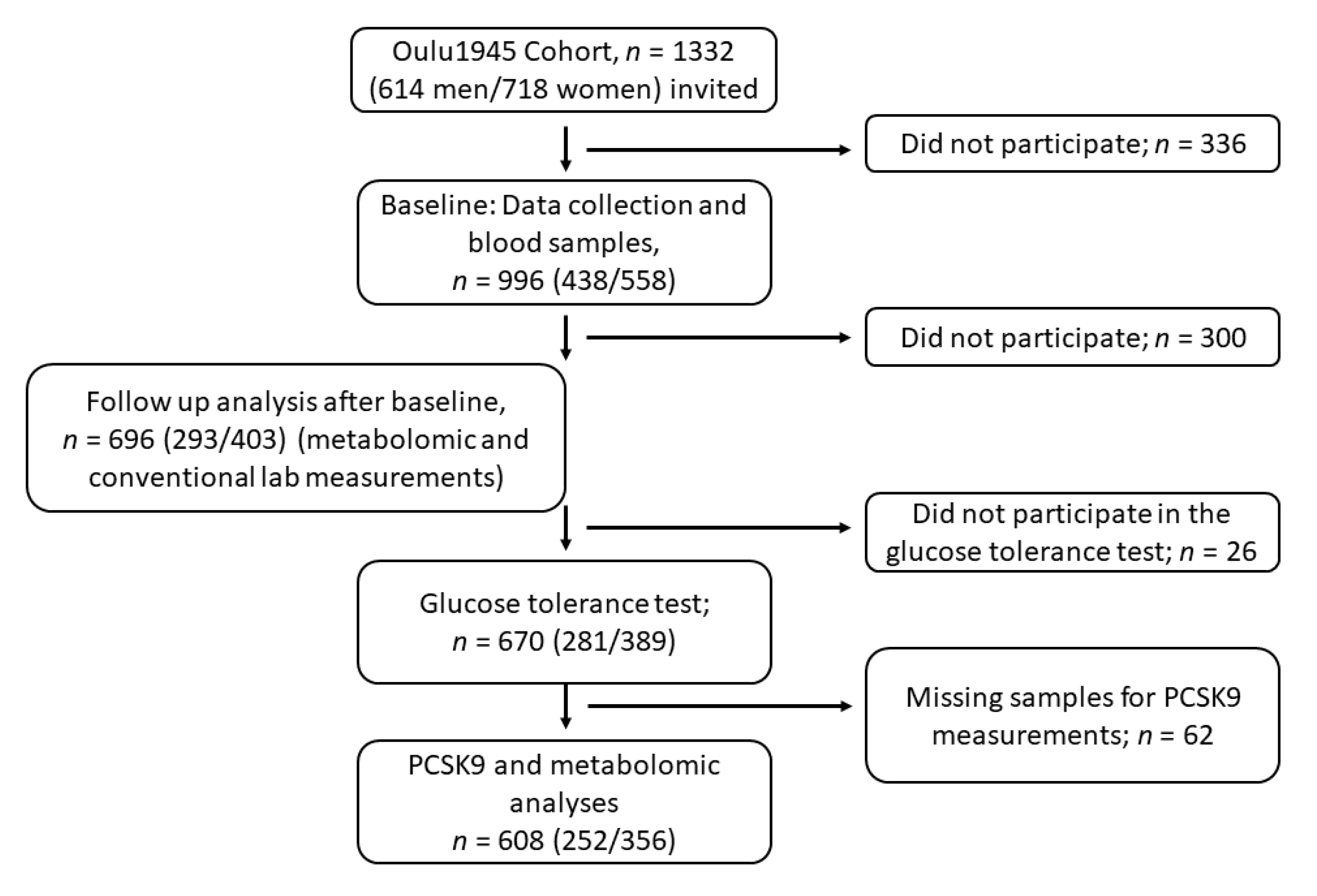
| Total | NGT | PreDM | DM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 670 | n = 348 | n = 217 | n = 105 | ||
| Age | 68.9 (0.55) | 68.9 (0.57) | 68.9 (0.52) | 68.8 (0.55) | 0.239 |
| Sex | 0.002 | ||||
| Men | 281 (41.9%) | 132 (37.9%) | 89 (41.0%) | 60 (57.1%) | |
| Women | 389 (58.1%) | 216 (62.1%) | 128 (59.0%) | 45 (42.9%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.6 (4.69) | 26.0 (3.75) | 28.6 (4.70) | 30.7 (5.31) | <0.001 |
| Normal | 201 (30.3%) | 140 (40.8%) | 49 (22.6%) | 12 (11.5%) | |
| Overweight | 293 (44.1%) | 162 (47.2%) | 94 (43.3%) | 37 (35.6%) | |
| Obese | 170 (25.6%) | 41 (12.0%) | 74 (34.1%) | 55 (52.9%) | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 94.0 (13.7) | 88.9 (11.5) | 97.0 (12.8) | 105 (14.0) | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 5.75 (1.03) | 5.31 (0.41) | 5.88 (0.55) | 7.02 (1.85) | <0.001 |
| Fasting insulin (pmol/L) | 15.4 (17.0) | 11.3 (5.62) | 16.1 (9.42) | 27.8 (37.3) | <0.001 |
| HOMA2-B | 109 (42.0) | 108 (33.7) | 112 (42.9) | 106 (62.1) | 0.406 |
| HOMA2-S | 71.7 (39.9) | 82.4 (38.7) | 63.2 (38.4) | 52.3 (35.8) | <0.001 |
| HOMA2-IR | 1.91 (1.36) | 1.48 (0.71) | 2.12 (1.20) | 2.98 (2.42) | <0.001 |
| DP (mmHg) | 85.6 (9.73) | 84.1 (9.50) | 88.1 (9.44) | 85.2 (10.1) | <0.001 |
| SP (mmHg) | 144 (17.7) | 141 (17.2) | 148 (18.0) | 147 (16.6) | <0.001 |
| Daily steps | 8869 (3696) | 9283 (3613) | 8499 (3686) | 8118 (3885) | 0.024 |
| Physical activity questionaires | <0.001 | ||||
| Non-active a | 153 (23.3%) | 62 (18.1%) | 46 (21.4%) | 45 (44.6%) | |
| Active b | 505 (76.7%) | 280 (81.9%) | 169 (78.6%) | 56 (55.4%) | |
| Smoking: | 0.001 | ||||
| Current | 81 (12.4%) | 39 (11.4%) | 20 (9.5%) | 22 (21.8%) | |
| Former (>6 months earlier) | 225 (34.4%) | 107 (31.2%) | 75 (35.5%) | 43 (42.6%) | |
| Never | 349 (53.2%) | 197 (57.4%) | 116 (55.0%) | 36 (35.6%) | |
| Alcohol (g/d) | 1.85 (4.61) | 1.23 (2.29) | 2.80 (7.11) | 1.99 (3.37) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.33 (1.22) | 5.44 (1.15) | 5.51 (1.18) | 4.60 (1.26) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.65 (0.46) | 1.74 (0.46) | 1.61 (0.43) | 1.40 (0.38) | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.27 (0.81) | 1.07 (0.42) | 1.42 (0.70) | 1.63 (1.53) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (mmol/L) | 40.6 (5.87) | 38.9 (3.45) | 40.2 (4.00) | 47.1 (9.95) | <0.001 |
| FLI | 45.6 (28.9) | 33.2 (23.9) | 54.5 (28.0) | 68.0 (25.9) | <0.001 |
| h-CRP (mg/L) | 3.49 (9.47) | 2.30 (4.42) | 4.49 (12.7) | 5.36 (13.0) | 0.002 |
| Analyte | No Statin (n = 427) | Statin Medication (n = 181) | Total (n = 608) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCSK9 (ng/mL) | NGT | 251.6 (77.0) | 326.3 (136.1) | 270.6 (100.7) | <0.001 |
| PreDM | 248.5 (70.5) | 331.9 (74.3) | 271.4 (80.6) | <0.001 | |
| T2D | 275.5 (215.1) | 315.6 (85.5) | 295.3 (164.7) | <0.001 | |
| p-value | 0.258 | 0.751 | 0.131 | ||
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | NGT | 1.7 (0.5) | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.6 (0.5) | <0.001 |
| PreDM | 1.7 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.5) | 1.6 (0.5) | <0.001 | |
| T2D | 1.4 (0.6) | 1.0 (0.3) | 1.2 (0.5) | <0.001 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| VLDL-C (mmol/L) | NGT | 0.6 (0.2) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.6 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| PreDM | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.2) | <0.001 | |
| T2D | 0.7 (0.4) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.6 (0.3) | 0.001 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | 0.298 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mäkelä, K.A.; Jokelainen, J.; Stenbäck, V.; Auvinen, J.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Tulppo, M.; Leppäluoto, J.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Herzig, K.-H. PCSK9 Levels and Metabolic Profiles in Elderly Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance under Statin Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050994
Mäkelä KA, Jokelainen J, Stenbäck V, Auvinen J, Järvelin M-R, Tulppo M, Leppäluoto J, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Herzig K-H. PCSK9 Levels and Metabolic Profiles in Elderly Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance under Statin Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050994
Chicago/Turabian StyleMäkelä, Kari A., Jari Jokelainen, Ville Stenbäck, Juha Auvinen, Marjo-Riitta Järvelin, Mikko Tulppo, Juhani Leppäluoto, Sirkka Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, and Karl-Heinz Herzig. 2021. "PCSK9 Levels and Metabolic Profiles in Elderly Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance under Statin Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050994
APA StyleMäkelä, K. A., Jokelainen, J., Stenbäck, V., Auvinen, J., Järvelin, M.-R., Tulppo, M., Leppäluoto, J., Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S., & Herzig, K.-H. (2021). PCSK9 Levels and Metabolic Profiles in Elderly Subjects with Different Glucose Tolerance under Statin Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050994







