Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap—A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, D.W.; Wang, B.-G.; Robb, G.L.; Reece, G.P.; Miller, M.J.; Evans, G.R.D.; Langstein, H.N.; Kroll, S.S. Effect of Obesity on Flap and Donor-Site Complications in Free Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.S.; Netscher, D.T. Complications of TRAM Flap Breast Reconstruction in Obese Patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1989, 84, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidenstuecker, K.; Munder, B.; Mahajan, A.L.; Richrath, P.; Behrendt, P.; Andree, C. Morbidity of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in Patients with Comorbid Conditions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczar, D.; Huayllani, M.T.; Forte, A.J.; Rinker, B. Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction in the Obese Patient Using Abdominal Flaps: Complication Profile and Patient Satisfaction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 84, S361–S363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harii, K.; Ohmori, K.; Sekiguchi, J. The free musculocutaneous flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1976, 57, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, T.; Huemer, G.M.; Wechselberger, G. The Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis Flap for Breast Reconstruction: Guidelines for Flap and Patient Selection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. The Transverse Myocutaneous Gracilis Free Flap: A Valuable Tissue Source in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, S.J.; Sandeen, S.N.; Bossert, R.P.; Perrone, A.; Ortiz, L.; Herrera, H. Gracilis Myocutaneous Free Flap in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craggs, B.; Vanmierlo, B.; Zeltzer, A.; Buyl, R.; Haentjens, P.; Hamdi, M. Donor-Site Morbidity following Harvest of the Transverse Myocutaneous Gracilis Flap for Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 682e–691e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pülzl, P.; Schoeller, T.; Kleewein, K.; Wechselberger, G. Donor-site morbidity of the transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap in autologous breast reconstruction: Short-term and long-term results. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 233e–242e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.R.; Officer, A.; De Carvalho, I.A.; Sadana, R.; Pot, A.M.; Michel, J.P.; Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; Epping-Jordan, J.E.; Peeters, G.G.; Mahanani, W.R.; et al. The World report on ageing and health: A policy framework for healthy ageing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Mojallal, A.; Bailey, S.H.; Trussler, A.; Saint-Cyr, M. The extended transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap: Vascular anatomy and clinical implications. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 67, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Neaman, K.C.; Armstrong, S.D.; Baca, M.E.; Albert, M.; Vander Woude, D.L.; Renucci, J.D. Outcomes of traditional cosmetic abdominoplasty in a community setting: A retrospective analysis of 1008 patients. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. März. 2013, 131, 403e–410e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechselberger, G.; Schwaiger, K. Transverse Upper Gracilis Flap in Breast Reconstruction. In Breast Reconstruction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Nahabedian, M.Y.; Momen, B. Lower Abdominal Bulge after Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap (DIEP) Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2005, 54, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondeel, P.; Boeckx, W.; Vanderstraeten, G.; Lysens, R.; Van Landuyt, K.; Tonnard, P.; Monstrey, S.; Matton, G. The fate of the oblique abdominal muscles after free TRAM flap surgery. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1997, 50, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.L.; Serletti, J.M. Outcome comparison between free and pedicled TRAM flap breast reconstruction in the obese patient. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 1954–1960; discussion 1961–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, J.A., 3rd.; Castaldo, E.T.; Nanney, L.B.; Wu, Y.C.; Donahue, R.; Wendel, J.J.; Hagan, K.F.; Shack, R.B. Autologous breast reconstruction: The Vanderbilt experience (1998 to 2005) of independent predictors of displeasing outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 207, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, O.; Chrysopoulo, M.; Nastala, C.; Ledoux, P.; Pisano, S. Abdominal wall stability and flap complications after deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: Does body mass index make a difference? Analysis of 418 patients and 639 flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 130, 21e–33e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-T.; Mun, G.-H. Effects of Obesity on Postoperative Complications After Breast Reconstruction Using Free Muscle-Sparing Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous, Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator, and Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palve, J.S.; Luukkaala, T.H.; Kääriäinen, M.T. Predictive risk factors of complications in different breast reconstruction methods. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 182, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.I.; Liu, J. Prospective Evaluation of Obese Patients Undergoing Autologous Abdominal Free Flap Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 120e–125e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, R.; Stalder, M.W.; Tessler, O.; Bartow, M.J.; Lam, J.; Patterson, C.; Wise, M.W.; Dupin, C.L.; Hilaire, H.S. Assessing Age as a Risk Factor for Complications in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 840e–846e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selber, J.C.; Bergey, M.; Sonnad, S.S.; Kovach, S.; Wu, L.; Serletti, J.M. Free Flap Breast Reconstruction in Advanced Age: Is It Safe? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.I.; Vaca, L.; DaLio, A.L.; Festekjian, J.H.; Crisera, C.A. Assessment of Advanced Age as a Risk Factor in Microvascular Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 67, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.; Flitcroft, K.; Brennan, M.; Spillane, A. Patterns and outcomes of breast reconstruction in older women—A systematic review of the literature. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2016, 42, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T.; Bauer, T.; Schwabegger, A.; Ninkovic, M.; Rainer, C.; Ninkovic, M. Surgical technique and clinical application of the transverse gracilismyocutaneous free flap. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2001, 54, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, M.B.; Zhong, T.; Mureau, M.A.; Hofer, S.O. Tug ‘O’ war: Challenges of transverse upper gracilis (TUG) myocutaneous free flap breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, F.; Dissaux, C.; Dupret-Bories, A.; Schohn, T.; Fiquet, C.; Bruant-Rodier, C. The transverse musculo-cutaneous gracilis flap for breast reconstruction: How to avoid complications. Microsurgery 2015, 36, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickl, S.; Nedomansky, J.; Radtke, C.; Haslik, W.; Schroegendorfer, K.F. Optimization of breast reconstruction results using TMG flap in 30 cases: Evaluation of several refinements addressing flap design, shaping techniques, and reduction of donor site morbidity. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Klettenheimer, A.; Küenzlen, L.; Kiehlmann, M.; Schlosshauer, T.; Djedovic, G.; Rieger, U.M. Outcome, complications, and body mass index correlation of horizontal and combined horizontal and vertical thigh lift: A 16-year single-center experience. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2019, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemerofsky, R.B.; Oliak, D.A.; Capella, J.F. Body Lift: An Account of 200 Consecutive Cases in the Massive Weight Loss Patient. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losco, L.; Roxo, A.C.; Roxo, C.W.; Torto, F.L.; Bolletta, A.; De Sire, A.; Aksoyler, D.; Ribuffo, D.; Cigna, E. Lower Body Lift After Bariatric Surgery: 323 Consecutive Cases Over 10-Year Experience. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 44, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, Z.M.; Cuadrado, D.; Sohn, V.; Wolcott, K.; Lesperance, K.; Carter, P.; Sebesta, J. Post-bariatric panniculectomy: Pre-panniculectomy body mass index impacts the complication profile. Am. J. Surg. 2007, 193, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranges, C.M.; Sisti, A. Medial Thigh Lift in the Massive Weight Loss Population: Outcomes and Complications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 273e–274e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
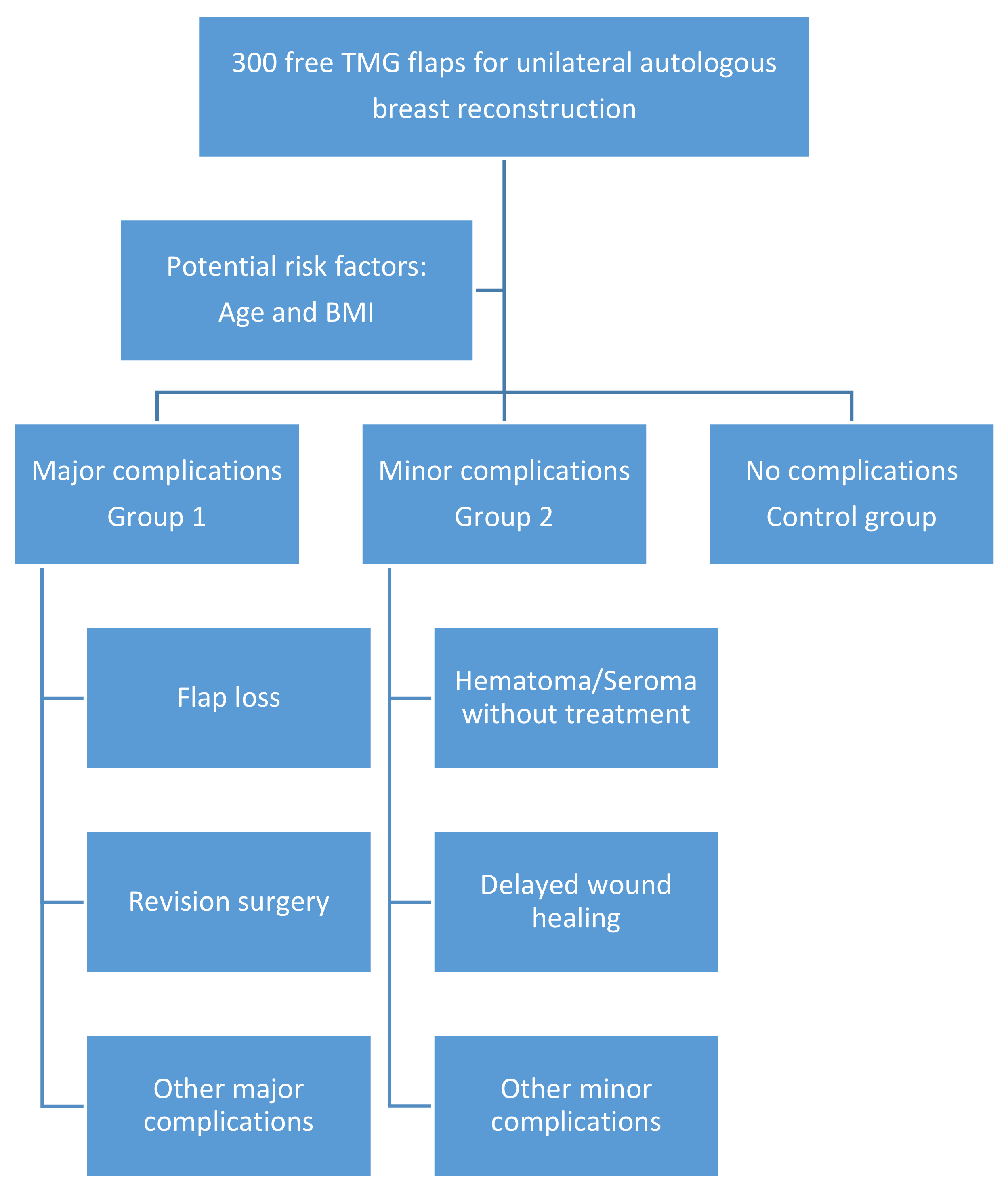


| Major complications | 1. Hematoma or flap insufficiency requiring surgical intervention |
| 2. Seroma requiring aspiration or surgery | |
| 3. Wound-healing problems (also flap or fat necrosis) requiring surgery | |
| 4. Infection requiring iv antibiotics | |
| 5. Deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism | |
| Minor complications | 1. Hematoma without treatment (+erythrocyte substitution with no other treatment necessary) |
| 2. Seroma without treatment | |
| 3. Delayed wound healing | |
| 4. Cellulitis (also fat necrosis) treated with oral antibiotics without hospitalization |
| Patient Characteristics | Number | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cases included | 300 | 100 | |
| Age, years | |||
| Median | 48.0 | ||
| SD | 10.6 | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | |||
| Mean | 22.9 | ||
| SD | 3.0 | ||
| Radiotherapy | |||
| Yes | 116 | 38.7 | |
| No | 183 | 61.0 | |
| Unknown | 1 | 0.3 | |
| Hormone therapy | |||
| Yes | 120 | 40.0 | |
| No | 180 | 60.0 | |
| Unknown | 0 | ||
| Minor complications | 70 | 23.3 | |
| Major complications | 83 | 27.6 | |
| No complications | 153 | 51.0 | |
| Revision needed | 78 | 26.0 |
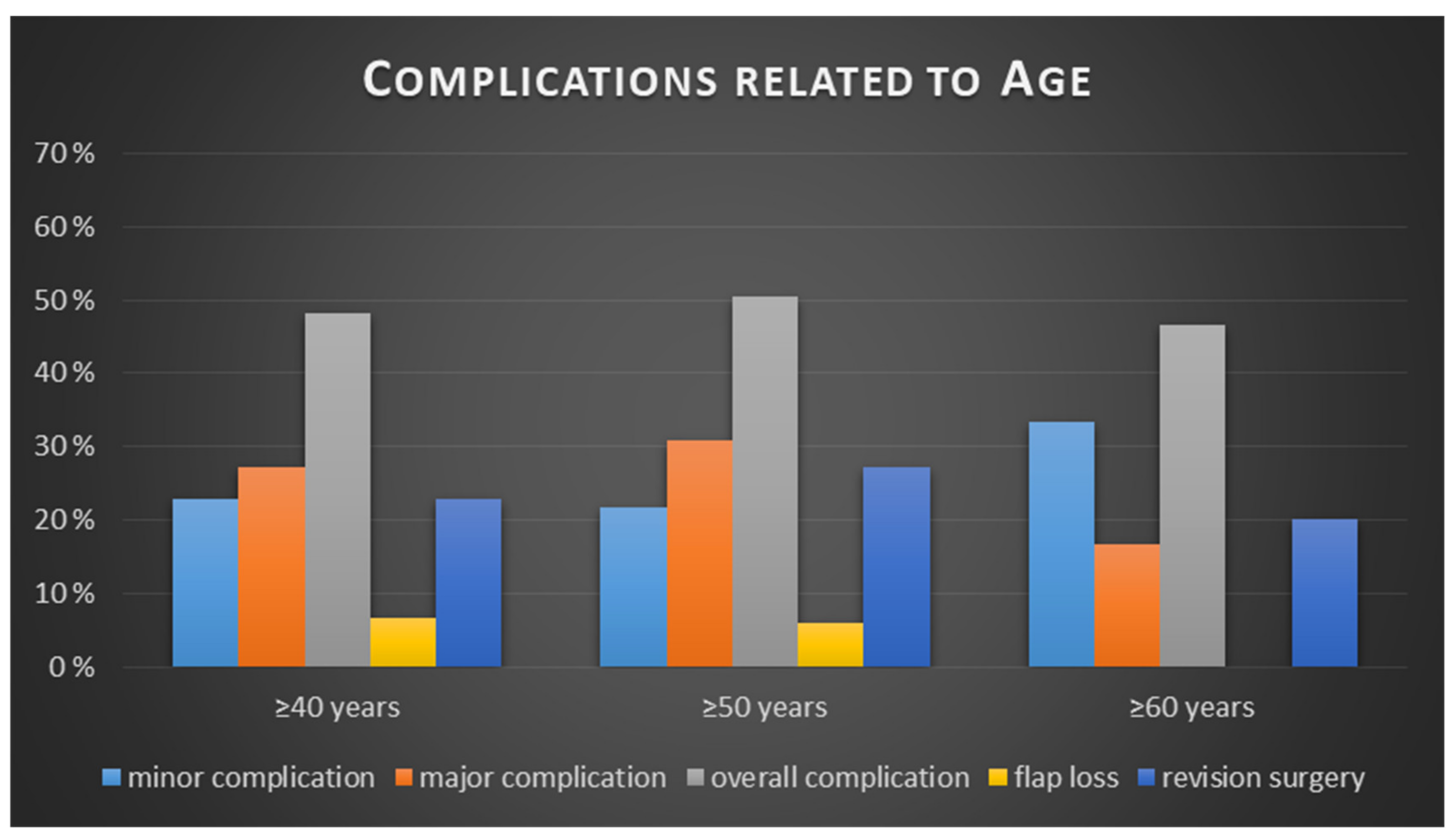
| <40 Years | ≥40 Years | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor complication | 18 (25.00%) | 52 (22.81%) | p = 0.644 |
| No complication | 35 | 118 | |
| Relative risk for minor complication for ≥ 40: 0.91 | |||
| Major complication | 21 (29.17%) | 62 (27.19%) | p = 0.676 |
| No complication | 35 | 118 | |
| Relative risk for major complication for ≥40: 0.93 | |||
| All complications | 37 (51.39%) | 110 (48.25%) | p = 0.642 |
| No complication | 35 | 118 | |
| Relative risk for any complication for ≥ 40: 0.94 | |||
| Flap loss | 4 (5.56%) | 15 (6.58%) | p = 0.756 |
| No flap loss | 68 | 213 | |
| Relative risk for flap loss for ≥40: 1.18 | |||
| Revision surgery | 20 (27.78%) | 52 (22.81%) | p = 0.389 |
| No revision surgery | 52 | 176 | |
| Relative risk for revision surgery for ≥40: 0.82 | |||
| <50 years | ≥50 years | ||
| Minor complication | 41 (24.55%) | 29 (21.80%) | p = 0.811 |
| No complication | 87 | 66 | |
| Relative risk for minor complication for ≥ 50: 0.89 | |||
| Major complication | 42 (25.15%) | 41 (30.83%) | p = 0.356 |
| No complication | 87 | 66 | |
| Relative risk for major complication for ≥ 50: 1.23 | |||
| All complications | 80 (47.90%) | 67 (50.38%) | p = 0.671 |
| No complication | 87 | 66 | |
| Relative risk for any complication for ≥ 50: 1.05 | |||
| Flap loss | 11 (6.59%) | 8 (6.02%) | p = 0.839 |
| No flap loss | 156 | 125 | |
| Relative risk for flap loss for ≥ 50: 0.91 | |||
| Revision surgery | 36 (21.56%) | 36 (27.07%) | p = 0.267 |
| No revision surgery | 131 | 97 | |
| Relative risk for revision surgery for ≥50: 1.26 | |||
| <60 years | ≥60 years | ||
| Minor complication | 60 (22.22%) | 10 (33.33%) | p = 0.408 |
| No complication | 137 | 16 | |
| Relative risk for minor complication for ≥ 60: 1.50 | |||
| Major complication | 78 (28.89%) | 5 (16.67%) | p = 0.253 |
| No complication | 137 | 16 | |
| Relative risk for major complication for ≥ 60: 0.58 | |||
| All complications | 133 (49.26%) | 14 (46.67%) | p = 0.788 |
| No complication | 137 | 16 | |
| Relative risk for any complication for ≥ 60: 0.95 | |||
| Flap loss | 19 (7.04%) | 0 (0.00%) | p = 0.133 |
| No flap loss | 251 | 30 | |
| Relative risk for flap loss for ≥ 60: 0.0 | |||
| Revision surgery | 66 (24.44%) | 6 (20.00%) | p = 0.589 |
| No revision surgery | 204 | 24 | |
| Relative risk for revision surgery for ≥60: 0.82 | |||
| <25 BMI (kg/m2) | ≥25 BMI (kg/m2) | Total, p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor complication | 56 (24.24%) | 14 (20.29%) | p = 0.708 |
| No complication | 119 | 34 | |
| Relative risk for minor complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25: 0.84 | |||
| Major complication | 61 (26.41%) | 22 (31.88%) | p = 0.460 |
| No complication | 119 | 34 | |
| Relative risk for major complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25: 1.21 | |||
| All complications | 112 (48.48%) | 35 (50.72%) | p = 0.744 |
| No complication | 119 | 34 | |
| Relative risk for any complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25: 1.05 | |||
| Flap loss | 14 (6.06%) | 5 (7.25%) | p = 0.723 |
| No flap loss | 217 | 64 | |
| Relative risk for flap loss for patients with BMI ≥ 25: 1.20 | |||
| Revision surgery | 54 (23.38%) | 18 (26.09%) | p = 0.644 |
| No revision surgery | 177 | 51 | |
| Relative risk for revision surgery for patients with BMI ≥ 25: 1.12 | |||
| <25 BMI (kg/m2) and < 50 Years | ≥25 BMI (kg/m2) and ≥ 50 Years | Total, p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor complication | 34 (26.77%) | 7 (24.14%) | p = 0.931 |
| No complication | 66 | 13 | |
| Relative risk for minor complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25 and over 50: 0.90 | |||
| Major complication | 29 (22.83%) | 9 (31.03%) | p = 0.349 |
| No complication | 66 | 13 | |
| Relative risk for major complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25 and over 50: 1.36 | |||
| All complications | 61 (48.03%) | 16 (55.17%) | p = 0.488 |
| No complication | 66 | 13 | |
| Relative risk for any complication for patients with BMI ≥ 25 and over 50: 1.15 | |||
| Flap loss | 8 (6.30%) | 2 (6.90%) | p = 0.906 |
| No flap loss | 119 | 27 | |
| Relative risk for flap loss for patients with BMI ≥ 25 and over 50: 1.10 | |||
| Revision surgery | 25 (19.69%) | 7 (24.14%) | p = 0.592 |
| No revision surgery | 102 | 22 | |
| Relative risk for revision surgery for patients with BMI ≥ 25 and over 50: 1.23 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwaiger, K.; Weitgasser, L.; Mahrhofer, M.; Bachleitner, K.; Abed, S.; Wimbauer, J.; Russe, E.; Schoeller, T.; Wechselberger, G. Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap—A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050926
Schwaiger K, Weitgasser L, Mahrhofer M, Bachleitner K, Abed S, Wimbauer J, Russe E, Schoeller T, Wechselberger G. Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap—A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050926
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwaiger, Karl, Laurenz Weitgasser, Maximilian Mahrhofer, Kathrin Bachleitner, Selim Abed, Julia Wimbauer, Elisabeth Russe, Thomas Schoeller, and Gottfried Wechselberger. 2021. "Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap—A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050926
APA StyleSchwaiger, K., Weitgasser, L., Mahrhofer, M., Bachleitner, K., Abed, S., Wimbauer, J., Russe, E., Schoeller, T., & Wechselberger, G. (2021). Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap—A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10050926








