Lung Ultrasound to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Cohort and CLAD Definition
- BOS: A persistent decline in FEV1 of ≥20% compared to the average of the two best obtained post-LTx baseline values, where other causes of lung function decline were ruled out (e.g., infection, and pleural effusion).
- RAS: As stated above for BOS but with an additional decline in TLC of ≥10% compared to the best post-LTx baseline values and combined with persistent radiographic abnormalities including the presence of parenchymal with (PPFE pattern) or without pleural-based opacities.
2.4. Study Plan
2.5. LUS
2.5.1. Scanning Protocol and Equipment
2.5.2. Selected Outcome Variables
2.6. HRCT
2.6.1. Scanning Protocol
2.6.2. Selected Outcome Variables
- Honeycombing
- Tractions bronchiectasis
- Volume loss
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. LUS Findings
3.3. HRCT Findings
3.4. Diagnostic Accuracy of LUS
4. Discussion
4.1. LUS Findings
4.2. HRCT Findings
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
4.4. Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yusen, R.D.; Edwards, L.B.; Dipchand, A.I.; Goldfarb, S.B.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Levvey, B.J.; Lund, L.H.; Meiser, B.; Rossano, J.W.; Stehlik, J. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-Third Adult Lung and Heart-Lung Transplant Report-2016; Focus Theme: Primary Diagnostic Indications for Transplant. J. Hear. Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1170–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C.M.; Iversen, M.; Milman, N.; Zemtsovski, M.; Carlsen, J.; Steinbrüchel, D.; Mortensen, J.; Andersen, C.B. Outcome of Lung Transplanted Patients with Primary Graft Dysfunction. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2007, 31, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, C.M.; Iversen, M.; Carlsen, J.; Mortensen, J.; Andersen, C.B.; Steinbrüchel, D.; Scheike, T. Acute Cellular Rejection Is a Risk Factor for Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Independent of Post-Transplant Baseline Fev1. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2009, 28, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.H.; Møller, C.H.; Zemtsovski, M.; Ravn, J.; Perch, M.; Martinussen, T.; Carlsen, J.; Iversen, M. Donor Smoking and Older Age Increases Morbidity and Mortality after Lung Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2017, 49, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.C.; Raghu, G.; Verleden, G.M.; Corris, P.A.; Aurora, P.; Wilson, K.C.; Brozek, J.; Glanville, A.R. An International Ishlt/Ats/Ers Clinical Practice Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1479–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.J.; Diamond, J.M. Update in Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction. Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D. The Future of Lung Transplantation. Chest 2015, 147, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Hwang, D.M.; Haroon, A.; Wagnetz, D.; Chaparro, C.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; et al. Restrictive Allograft Syndrome (Ras): A Novel Form of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2011, 30, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, G.M.; Raghu, G.; Meyer, K.C.; Glanville, A.R.; Corris, P. A New Classification System for Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; de Jong, P.A.; Ruttens, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verschakelen, J.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; Vos, R. Functional and Computed Tomographic Evolution and Survival of Restrictive Allograft Syndrome after Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, R.; Verleden, S.E.; Verleden, G.M. Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Evolving Practice. Curr. Opin. Organ Transpl. 2015, 20, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, E.; Sato, M.; Saito, T.; Wagnetz, U.; Roberts, H.C.; Chaparro, C.; Waddell, T.K.; Singer, L.G.; Hutcheon, M.A.; Keshavjee, S.; et al. Restrictive Allograft Syndrome Post Lung Transplantation Is Characterized by Pleuroparenchymal Fibroelastosis. Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, A.R.; Verleden, G.M.; Todd, J.L.; Benden, C.; Calabrese, F.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Levine, D.; Meloni, F.; Palmer, S.M.; et al. Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Definition and Update of Restrictive Allograft Syndrome—A Consensus Report from the Pulmonary Council of the Ishlt. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verleden, G.M.; Glanville, A.R.; Lease, E.D.; Fisher, A.J.; Calabrese, F.; Corris, P.A.; Ensor, C.R.; Gottlieb, J.; Hachem, R.R.; Lama, V.; et al. Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Definition, Diagnostic Criteria, and Approaches to Treatment—A Consensus Report from the Pulmonary Council of the Ishlt. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corris, P.A.; Ryan, V.A.; Small, T.; Lordan, J.; Fisher, A.J.; Meachery, G.; Johnson, G.; Ward, C. A Randomised Controlled Trial of Azithromycin Therapy in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome (Bos) Post Lung Transplantation. Thorax 2015, 70, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleden, S.E.; Todd, J.L.; Sato, M.; Palmer, S.M.; Martinu, T.; Pavlisko, E.N.; Vos, R.; Neyrinck, A.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Saito, T.; et al. Impact of Clad Phenotype on Survival after Lung Retransplantation: A Multicenter Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensted, K.; McKenzie, J.; Havryk, A.; Plit, M.; Ben-Menachem, E. Lung Ultrasound after Transbronchial Biopsy for Pneumothorax Screening in Post-Lung Transplant Patients. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2018, 25, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, U.; Schiefer, J.; Mühlbacher, J.; Bernardi, M.H.; Ortner, C.M.; Jaksch, P. High Altitude Trekking after Lung Transplantation: A Prospective Study Using Lung Ultrasound to Detect Comets Tails for Interstitial Pulmonary Edema in Lung Transplant Recipients and Healthy Volunteers. Transpl. Int. 2018, 31, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsen, J.R.; Schultz, H.H.L.; Henriksen, D.P.; Iversen, M.; Kalhauge, A.; Carlsen, J.; Perch, M.; Graumann, O.; Laursen, C.B. Lung Ultrasound in the Assessment of Pulmonary Complications after Lung Transplantation. Ultraschall Der Med. 2020, 41, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droneau, S.; Noel-Savina, E.; Plat, G.; Murris-Espin, M.; Leborgne-Krams, A.; Brouchet, L.; Dahan, M.; Didier, A. Use of Ultrasonography for Lung Transplant Recipients on Postoperative Care. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, A.; Kroegel, C. Transthoracic Sonography of Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease: The Role of Comet Tail Artifacts. J. Ultrasound Med. 2003, 22, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli, G.; Elbarbary, M.; Blaivas, M.; Lichtenstein, D.A.; Mathis, G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Melniker, L.; Gargani, L.; Noble, V.E.; Via, G.; et al. International Evidence-Based Recommendations for Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, L. Interstitial Syndrome. In Thoracic Ultrasund [ERS Monograph]; Laursen, C.B., Rahman, N.M., Volpicelli, G., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barskova, T.; Gargani, L.; Guiducci, S.; Randone, S.B.; Bruni, C.; Carnesecchi, G.; Conforti, M.L.; Porta, F.; Pignone, A.; Caramella, D.; et al. Lung Ultrasound for the Screening of Interstitial Lung Disease in Very Early Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.A.; Makhlouf, H.A. B-Lines: Transthoracic Chest Ultrasound Signs Useful in Assessment of Interstitial Lung Diseases. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2014, 9, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Pallisa-Nuñez, E.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Castella-Fierro, E.; Simeon-Aznar, C.P.; Fonollosa-Pla, V.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Pleural Irregularity, a New Ultrasound Sign for the Study of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis and Antisynthetase Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. 91), S136–S141. [Google Scholar]
- Laursen, C.B.; Clive, A.; Hallifax, R.; Pietersen, P.I.; Asciak, R.; Davidsen, J.R.; Bhatnagar, R.; Bedawi, E.O.; Jacobsen, N.; Coleman, C.; et al. European Respiratory Society Statement on Thoracic Ultrasound. Eur. Respir. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, J.R.; Laursen, C.B.; Bendstrup, E.; Schultz, H.H.L. Lung Ultrasound—A Novel Diagnostic Tool to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction? Ultrasound Int. Open 2017, 3, E117–E119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burton, C.M.; Milman, N.; Carlsen, J.; Arendrup, H.; Eliasen, K.; Andersen, C.B.; Iversen, M. The Copenhagen National Lung Transplant Group: Survival after Single Lung, Double Lung, and Heart-Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2005, 24, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, T.K.; Møller, C.H.; Davidsen, J.R.; Schultz HH, L.; Bredahl, P.; Ravn, J.; Olsen, P.S.; Bendstrup, E.; Perch, M. The First 25 Years of Lung Transplantations in Denmark. Ugeskr. Laeger 2019, 181, V09180624. [Google Scholar]
- Davidsen, J.R.; Bendstrup, E.; Henriksen, D.P.; Graumann, O.; Laursen, C.B. Lung Ultrasound Has Limited Diagnostic Value in Rare Cystic Lung Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2017, 4, 1330111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lichtenstein, D.; Mezière, G. A Lung Ultrasound Sign Allowing Bedside Distinction between Pulmonary Edema and Copd: The Comet-Tail Artifact. Intensive Care Med. 1998, 24, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, R.C.; Schnoy, N.; Schönfeld, N.; Grassot, A.; Loddenkemper, R.; Lode, H.; Kaiser, D.; Krumhaar, D.; Felix, R. High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Tomography (Hr-Mrt) of the Pleura and Thoracic Wall: Normal Findings and Pathological Changes. Rofo: Fortschr. Auf Dem Geb. Der Röntgenstrahlen Und Der Nukl. 1995, 162, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaati, E.; Jensen, C.; Kofoed, K.F.; Iversen, M.; Steffensen, I.; Nielsen, M.B. Primary Graft Dysfunction; Possible Evaluation by High Resolution Computed Tomography, and Suggestions for a Scoring System. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 9, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmaati, E.O.; Steffensen, I.; Jensen, C.; Kofoed, K.F.; Mortensen, J.; Nielsen, M.B.; Iversen, M. Radiological Patterns of Primary Graft Dysfunction after Lung Transplantation Evaluated by 64-Multi-Slice Computed Tomography: A Descriptive Study. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 14, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Hansell, D.M. Hrct of Fibrosing Lung Disease. Respirology 2015, 20, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Wells, A.U.; Clerisme-Beaty, E.; Collard, H.R.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Inoue, Y.; Le Maulf, F.; Richeldi, L.; et al. Design of the Pf-Ild Trial: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase Iii Trial of Nintedanib in Patients with Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2017, 4, e000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Doveri, M.; D’Errico, L.; Frassi, F.; Bazzichi, M.L.; Sedie, A.D.; Scali, M.C.; Monti, S.; Mondillo, S.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. Ultrasound Lung Comets in Systemic Sclerosis: A Chest Sonography Hallmark of Pulmonary Interstitial Fibrosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardella, M.; Gutierrez, M.; Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Ariani, A.; Bertolazzi, C.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W. Ultrasound in the Assessment of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Connective Tissue Disorders: Correlation with High-Resolution Computed Tomography. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, P.; Dass, C.; Kumaran, M.; Simpson, S. High-Resolution Ct Findings of Obstructive and Restrictive Phenotypes of Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: More Than Just Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, W13–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Salazar, P.; Saito, T.; Binnie, M.; Brock, K.; Yasufuku, K.; Azad, S.; Keshavjee, S.; Martinu, T.; Paul, N. Quantitative Chest Ct for Subtyping Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction and Its Association with Survival. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, D.; Benden, C.; Corris, P.A.; Dark, J.H.; Davis, R.D.; Keshavjee, S.; Lederer, D.J.; Mulligan, M.J.; Patterson, G.A.; Singer, L.G.; et al. A Consensus Document for the Selection of Lung Transplant Candidates: 2014—An Update from the Pulmonary Transplantation Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongodi, S.; Bouhemad, B.; Orlando, A.; Stella, A.; Tavazzi, G.; Via, G.; Iotti ABraschi, A.; Mojoli, F. Modified Lung Ultrasound Score for Assessing and Monitoring Pulmonary Aeration. Ultraschall Der Med. 2017, 38, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Sloth, E.; Lassen, A.T.; Davidsen, J.R.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Henriksen, D.P.; Madsen, P.H.; Rasmussen, F. Does Point-of-Care Ultrasonography Cause Discomfort in Patients Admitted with Respiratory Symptoms? Scand. J. TraumaResusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

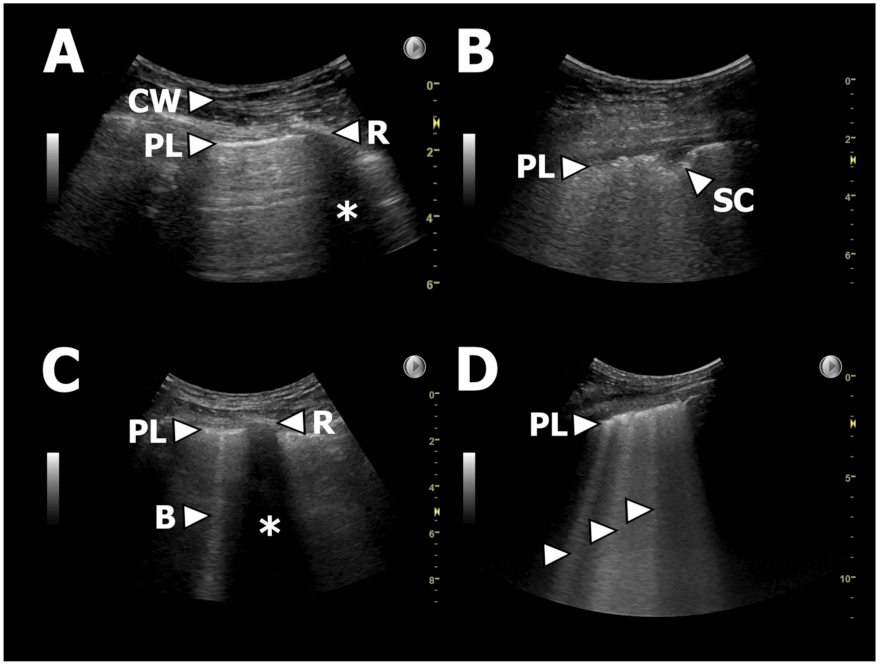
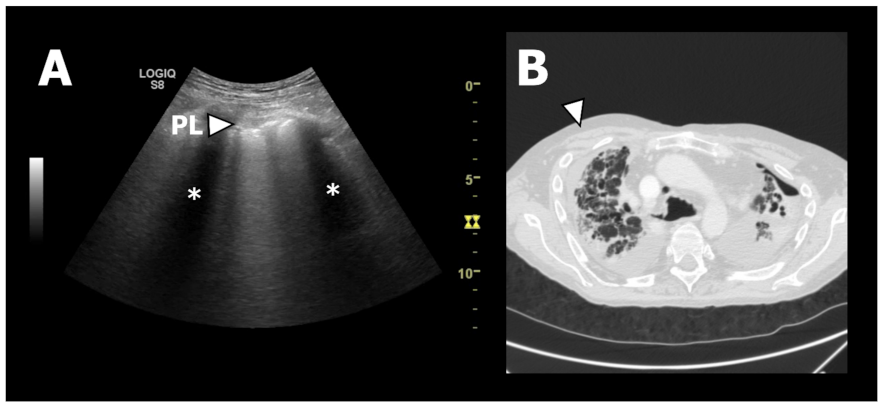
| Characteristic | BOS | RAS | All CLAD |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 19) | (n = 6) | (n = 25) | |
| Age, median (IQR) | 54 (37 to 57) | 51 (33 to 58) | 54 (37 to 57) |
| Female | 6 (32%) | 1 (17%) | 7 (28%) |
| Years post-LTx to CLAD (IQR) | 2.6 (1.8 to 7.2) | 4.9 (3.1 to 7.6) | 3.1 (2.1 to 7.2) |
| Underlying lung disease | |||
| A1AD emphysema | 4 (21%) | 2 (33%) | 6 (24%) |
| COPD emphysema | 5 (26%) | 1 (17%) | 6 (24%) |
| IPF | 1 (5%) | 0 | 1 (4%) |
| NSIP | 3 (16%) | 0 | 3 (12%) |
| Sarcoidosis | 0 | 1 (17%) | 1 (4%) |
| PAH | 0 | 1 (17%) | 1 (4%) |
| Anti-syntethase syndrome | 1 (5%) | 0 | 1 (4%) |
| CF | 5 (26%) | 1 (17%) | 6 (24%) |
| re-LT | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pre-LTX smoking status | |||
| Never smoker | 9 (47%) | 3 (50%) | 12 (48%) |
| Previous smoker | 10 (53%) | 3 (50%) | 13 (52%) |
| Co-morbities | |||
| GERD | 6 (32%) | 2 (33%) | 8 (32%) |
| Immunosuppressive medication | |||
| Corticosteroids | 18 (95%) | 6 (100%) | 24 (96%) |
| AZA | 8 (42%) | 4 (67%) | 12 (48%) |
| MMF | 5 (26%) | 2 (33%) | 7 (28%) |
| Ciclosporine | 14 (74%) | 3 (50%) | 17 (68%) |
| Tacrolimus | 5 (26%) | 3 (50%) | 8 (32%) |
| Everolimus | 4 (21%) | 0 | 4 (16%) |
| CLAD staging | |||
| CLAD 0 (FEV1 > 80%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CLAD 1 (FEV1 > 65–80%) | 1 (5%) | 1 (17%) | 2 (8%) |
| CLAD 2 (FEV1 > 50–65%) | 3 (16%) | 1 (17%) | 4 (16%) |
| CLAD 3 (FEV1 > 35–50%) | 8 (42%) | 2 (33%) | 10 (40%) |
| CLAD 4 (FEV1 < 35%) | 7 (37%) | 2 (33%) | 9 (36%) |
| Change from best post-LTX, median (IQR) | |||
| FEV1, L | −1.77 (−1.96 to −1.20) | −1.76 (−2.15 to −1.36) | −1.77 (−1.99 to −1.34) |
| FEV1, percent | −49 (−68 to −38) | −48 (−48 to −35) | −48 (−60 to −35) |
| FVC, L | −0.95 (−1.37 to −0.43) | −2.08 (−2.31 to −1.69) | −1.12 (−1.87 to −0.52) |
| FVC, percent | −22 (−36 to −16) | −45 (−50 to −34) | −24 (−45 to −19) |
| TLC, L | 0.02 (−0.30 to 0.69) | −2.45 (−3.20 to −2.00) | −0.07 (−1.33 to 0.30) |
| TLC, percent | 0 (−4 to 7) | −38 (−53 to −32) | −1 (−15 to 6) |
| Bronchial stenosis | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | No (%) | |
| Pleural thickening | ||||||||||||||
| All | 4 (16) | 3 (12) | 6 (24) | 5 (20) | 8 (32) | 9 (36) | 6 (24) | 7 (28) | 7 (28) | 7 (28) | 6 (24) | 9 (36) | 7 (28) | 7 (28) |
| BOS | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 2 (11) | 4 (21) | 3 (16) | 0 (0) | 2 (11) | 1 (5) | 3 (16) | 1 (5) | 5 (26) | 2 (11) | 2 (11) |
| RAS | 4 (67) | 2 (33) | 4 (67) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) |
| Lung sliding | ||||||||||||||
| All | 24 (96) | 20 (80) | 22 (88) | 25 (100) | 24 (96) | 22 (88) | 21 (84) | 24 (96) | 23 (92) | 24 (96) | 23 (92) | 24 (96) | 23 (92) | 17 (68) |
| BOS | 19 (100) | 17 (89) | 17 (89) | 19 (100) | 18 (95) | 17 (89) | 17 (89) | 19 (100) | 17 (89) | 18 (95) | 18 (95) | 18 (95) | 18 (95) | 15 (79) |
| RAS | 5 (83) | 3 (50) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 2 (33) |
| >=3 B-lines | ||||||||||||||
| All | 2 (8) | 3 (12) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 3 (12) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 2 (8) | 2 (8) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) |
| BOS | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| RAS | 2 (33) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) |
| Consolidation | ||||||||||||||
| All | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| BOS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| RAS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| RU Central | RU Peri-Pheral | RM Central | RM Peri-Pheral | RL Central | RL Peri-Pheral | LU Central | LU Peri-Pheral | LL Central | LL Peri-Pheral | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground glass opacity | All | 9 (36) | 12 (48) | 8 (32) | 11 (44) | 8 (32) | 10 (40) | 9 (36) | 10 (40) | 9 (36) | 8 (32) |
| BOS | 5 (26) | 7 (37) | 5 (26) | 7 (37) | 5 (26) | 6 (32) | 5 (26) | 6 (32) | 6 (32) | 5 (26) | |
| RAS | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | 4 (67) | 4 (67) | 3 (50) | 3 (50) | |
| Consolidation | All | 6 (24) | 7 (28) | 5 (20) | 8 (32) | 4 (16) | 7 (28) | 7 (28) | 9 (36) | 4 (16) | 6 (24) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 2 (11) | 3 (16) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | |
| RAS | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 6 (100) | 3 (50) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | |
| Septal thickening | All | 7 (28) | 14 (56) | 8 (32) | 12 (48) | 8 (32) | 11 (44) | 6 (24) | 13 (52) | 9 (36) | 11 (44) |
| BOS | 2 (11) | 8 (42) | 3 (16) | 7 (37) | 3 (16) | 5 (26) | 2 (11) | 8 (42) | 3 (16) | 5 (26) | |
| RAS | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | |
| Reticulation | All | 7 (28) | 11 (44) | 7 (28) | 11 (44) | 7 (28) | 10 (40) | 7 (28) | 11 (44) | 7 (28) | 9 (36) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 5 (26) | 1 (5) | 5 (26) | 1 (5) | 4 (21) | 1 (5) | 5 (26) | 1 (5) | 3 (16) | |
| RAS | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | |
| Noduli | All | 1 (4) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| RAS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Mosaic attenuation | All | 9 (36) | 10 (40) | 10 (40) | 10 (40) | 11 (44) | 12 (48) | 10 (40) | 10 (40) | 11 (44) | 12 (48) |
| BOS | 8 (42) | 9 (47) | 9 (47) | 9 (47) | 10 (53) | 11 (58) | 9 (47) | 9 (47) | 10 (53) | 11 (58) | |
| RAS | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | 1 (17) | |
| Tree-in-bud | All | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 1 (4) |
| BOS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | |
| RAS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Bronchiectasis | All | 20 (80) | 16 (64) | 18 (72) | 16 (64) | 17 (68) | 16 (64) | 19 (76) | 16 (64) | 18 (72) | 16 (64) |
| BOS | 14 (74) | 12 (63) | 13 (68) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 13 (68) | 12 (63) | 13 (68) | 12 (63) | |
| RAS | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | |
| Peribronchial thickening | All | 15 (60) | 15 (60) | 16 (64) | 14 (56) | 14 (56) | 14 (56) | 14 (56) | 16 (64) | 14 (56) | 15 (60) |
| BOS | 13 (68) | 13 (68) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | |
| RAS | 2 (33) | 2 (33) | 4 (67) | 2 (33) | 2 (33) | 2 (33) | 2 (33) | 4 (67) | 2 (33) | 3 (50) | |
| Air trapping | All | 12 (48) | 12 (48) | 13 (52) | 13 (52) | 13 (52) | 13 (52) | 12 (48) | 12 (48) | 13 (52) | 13 (52) |
| BOS | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 13 (68) | 13 (68) | 13 (68) | 13 (68) | 12 (63) | 12 (63) | 13 (68) | 13 (68) | |
| RAS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Pleural thickening | All | - | 11 (44) | 11 (44) | - | 12 (48) | - | 14 (56) | - | 11 (44) | |
| BOS | - | 5 (26) | 5 (26) | - | 6 (32) | - | 8 (42) | - | 5 (26) | ||
| RAS | - | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | - | 6 (100) | - | 6 (100) | - | 6 (100) | ||
| Honeycombing | All | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| BOS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| RAS | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Traction bronchiectasis | All | 7 (28) | 6 (24) | 5 (20) | 5 (20) | 5 (20) | 5 (20) | 6 (24) | 7 (28) | 6 (24) | 7 (28) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 2 (11) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | |
| RAS | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 4 (67) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | |
| Volume loss | All | 7 (28) | 7 (28) | 5 (20) | 5 (20) | 4 (16) | 5 (20) | 6 (24) | 8 (32) | 4 (16) | 5 (20) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | |
| RAS | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 4 (67) | 4 (67) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 3 (50) | 4 (67) | |
| Fibrosis | All | 7 (28) | 6 (24) | 6 (24) | 7 (28) | 5 (20) | 8 (32) | 8 (32) | 9 (36) | 7 (28) | 8 (32) |
| BOS | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | 2 (11) | 2 (11) | 3 (16) | 2 (11) | 3 (16) | |
| RAS | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 6 (100) | 5 (83) | 5 (83) |
| TP | FP | FN | TN | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | N | N | N | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) | % (95% CI) | |
| Parenchyma | ||||||||
| >=2 zones/lung | ||||||||
| IS | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| IS (R/L1 + 4 + 7) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| IS (R/L1 + 7) | 0 | 0 | 6 | 19 | 0 (0–46) | 100 (82–100) | - | 76 (55–91) |
| IS (R/L1 + 4) | 0 | 0 | 6 | 19 | 0 (0–46) | 100 (82–100) | - | 76 (55–91) |
| IS (R/L4 + 7) | 0 | 0 | 6 | 19 | 0 (0–46) | 100 (82–100) | - | 76 (55–91) |
| >=1 zones/lung | ||||||||
| IS (R/L1 + 4 + 7) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| IS (R/L1 + 7) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| IS (R/L1 + 4) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| IS (R/L4 + 7) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| Pleura | ||||||||
| Thickening (R/L1 + 2 + 3 + 4) | 1 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 17 (0–64) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (3–100) | 79 (58–93) |
| Thickening (R/L1 + 4 + 7) | 2 | 0 | 4 | 19 | 33 (4–78) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (16–100) | 83 (61–95) |
| Thickening (R/L1 + 4) | 3 | 0 | 3 | 19 | 50 (12–88) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (29–100) | 86 (65–97) |
| Thickening (R/L1 + 7) | 3 | 0 | 3 | 19 | 50 (12–88) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (29–100) | 86 (65–97) |
| Thickening (R/L4 + 7) | 2 | 0 | 4 | 19 | 33 (4–78) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (16–100) | 83 (61–95) |
| Thickening (R/L1) | 4 | 0 | 2 | 19 | 67 (22–96) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (40–100) | 90 (70–99) |
| Thickening (R/L4) | 3 | 1 | 3 | 18 | 50 (12–88) | 95 (74–100) | 75 (19–99) | 86 (64–97) |
| Thickening (R/L7) | 5 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 83 (36–100) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (48–100) | 95 (75–100) |
| Thickening (R/L1 or R/L7) | 6 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 100 (54–100) | 100 (82–100) | 100 (54–100) | 100 (82–100) |
| Thickening a.m. IS | 4 | 3 | 2 | 16 | 67 (22–96) | 84 (60–97) | 57 (18–90) | 89 (65–99) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davidsen, J.R.; Laursen, C.B.; Højlund, M.; Lund, T.K.; Jeschke, K.N.; Iversen, M.; Kalhauge, A.; Bendstrup, E.; Carlsen, J.; Perch, M.; et al. Lung Ultrasound to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. A Prospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051078
Davidsen JR, Laursen CB, Højlund M, Lund TK, Jeschke KN, Iversen M, Kalhauge A, Bendstrup E, Carlsen J, Perch M, et al. Lung Ultrasound to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051078
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavidsen, Jesper Rømhild, Christian B. Laursen, Mikkel Højlund, Thomas Kromann Lund, Klaus Nielsen Jeschke, Martin Iversen, Anna Kalhauge, Elisabeth Bendstrup, Jørn Carlsen, Michael Perch, and et al. 2021. "Lung Ultrasound to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. A Prospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051078
APA StyleDavidsen, J. R., Laursen, C. B., Højlund, M., Lund, T. K., Jeschke, K. N., Iversen, M., Kalhauge, A., Bendstrup, E., Carlsen, J., Perch, M., Henriksen, D. P., & Schultz, H. H. L. (2021). Lung Ultrasound to Phenotype Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction in Lung Transplant Recipients. A Prospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051078







