Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Isolation and Culture
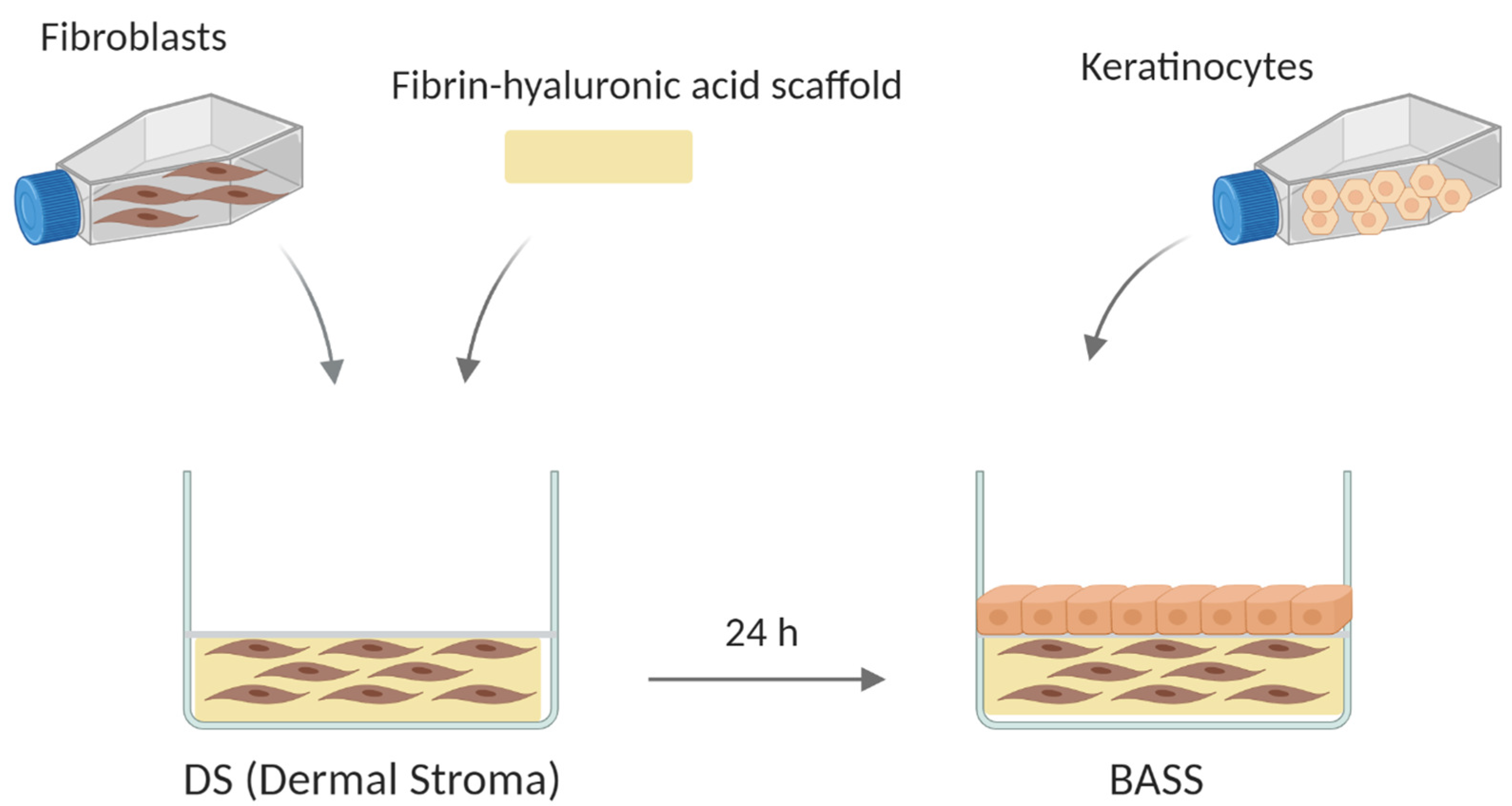
2.2. Bioengineered Artificial Skin Substitute (BASS) Manufacturing
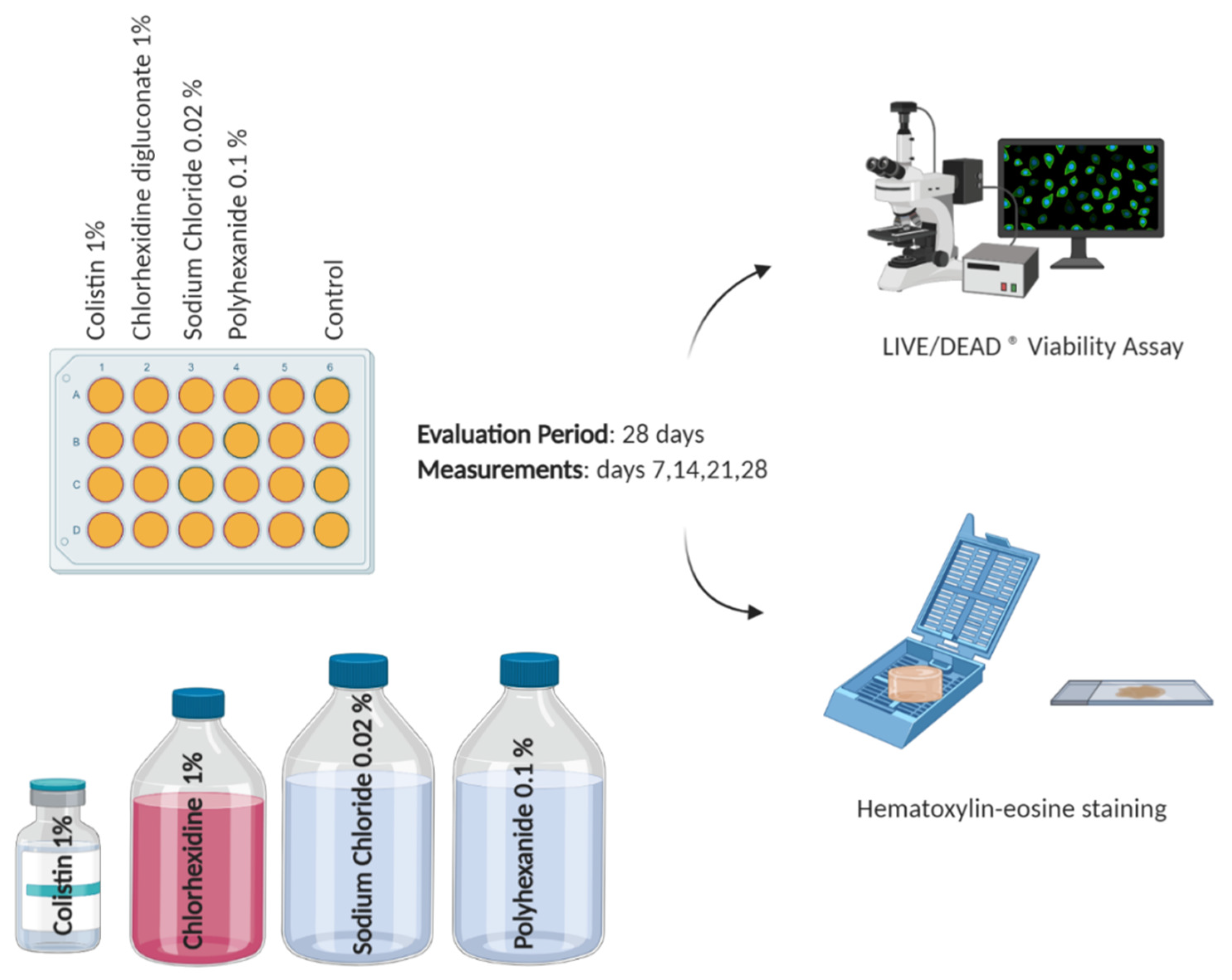
2.3. Antiseptic/Antibiotic Test
2.4. Viability Assay
2.5. Histological Analysis
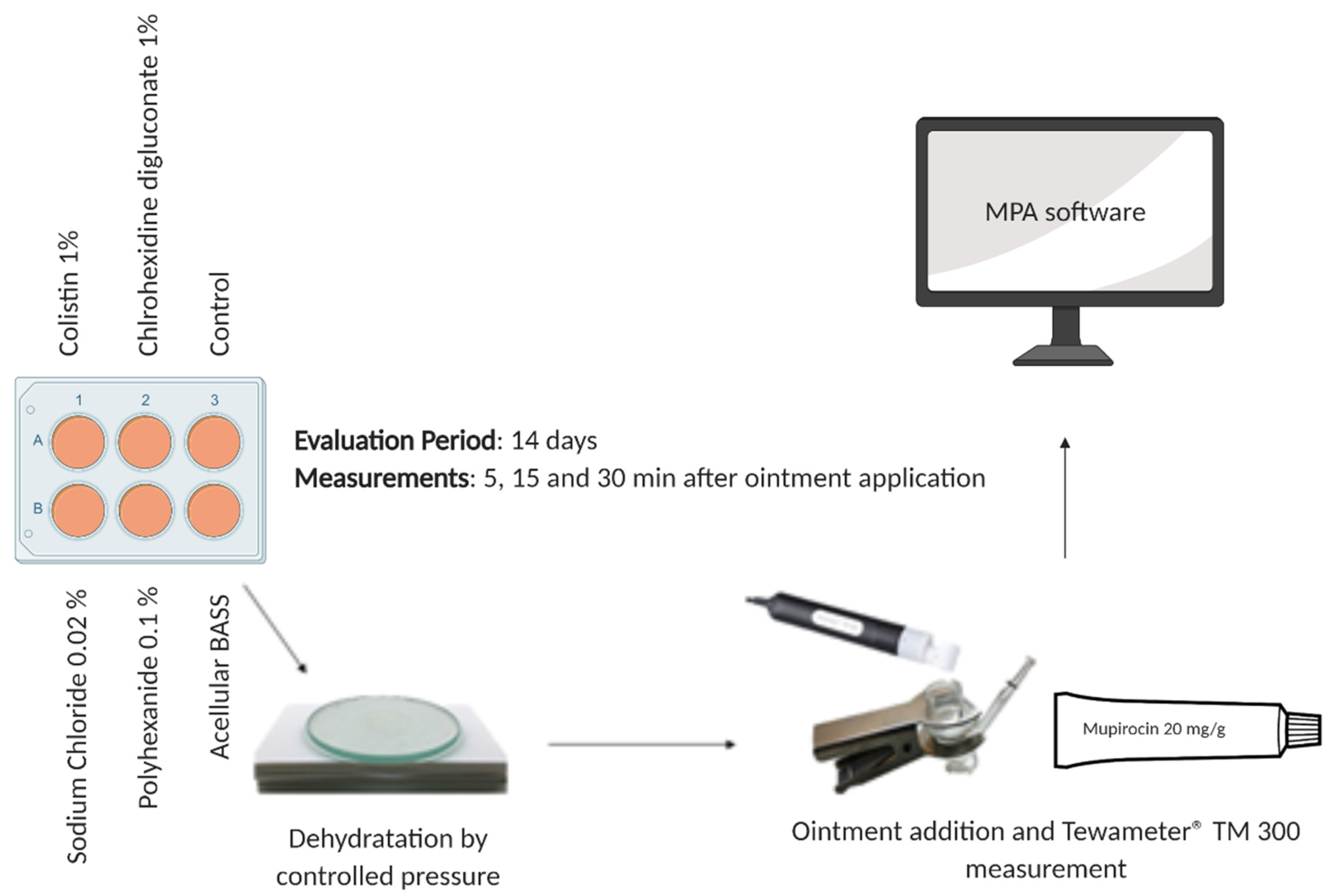
2.6. Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
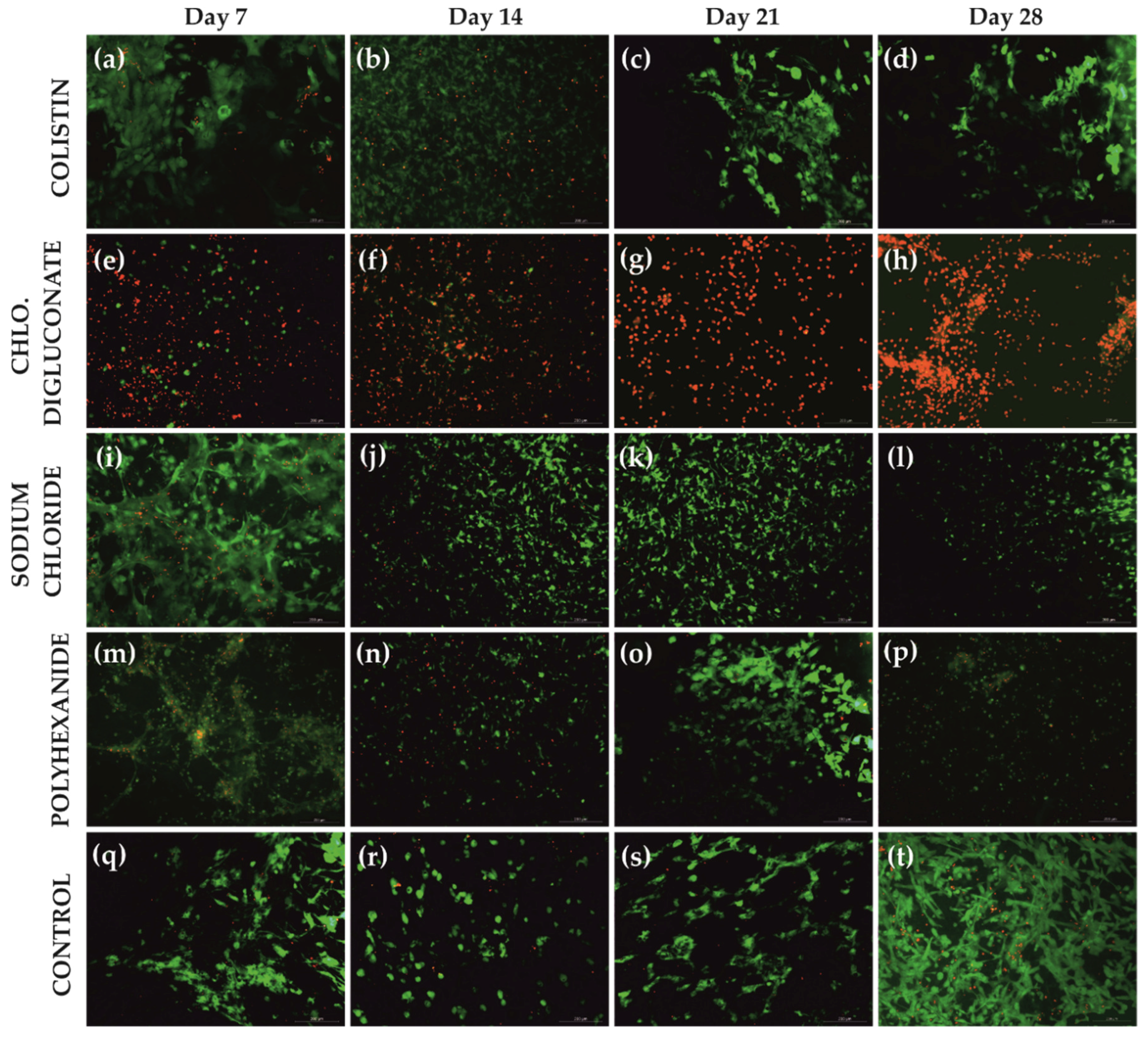
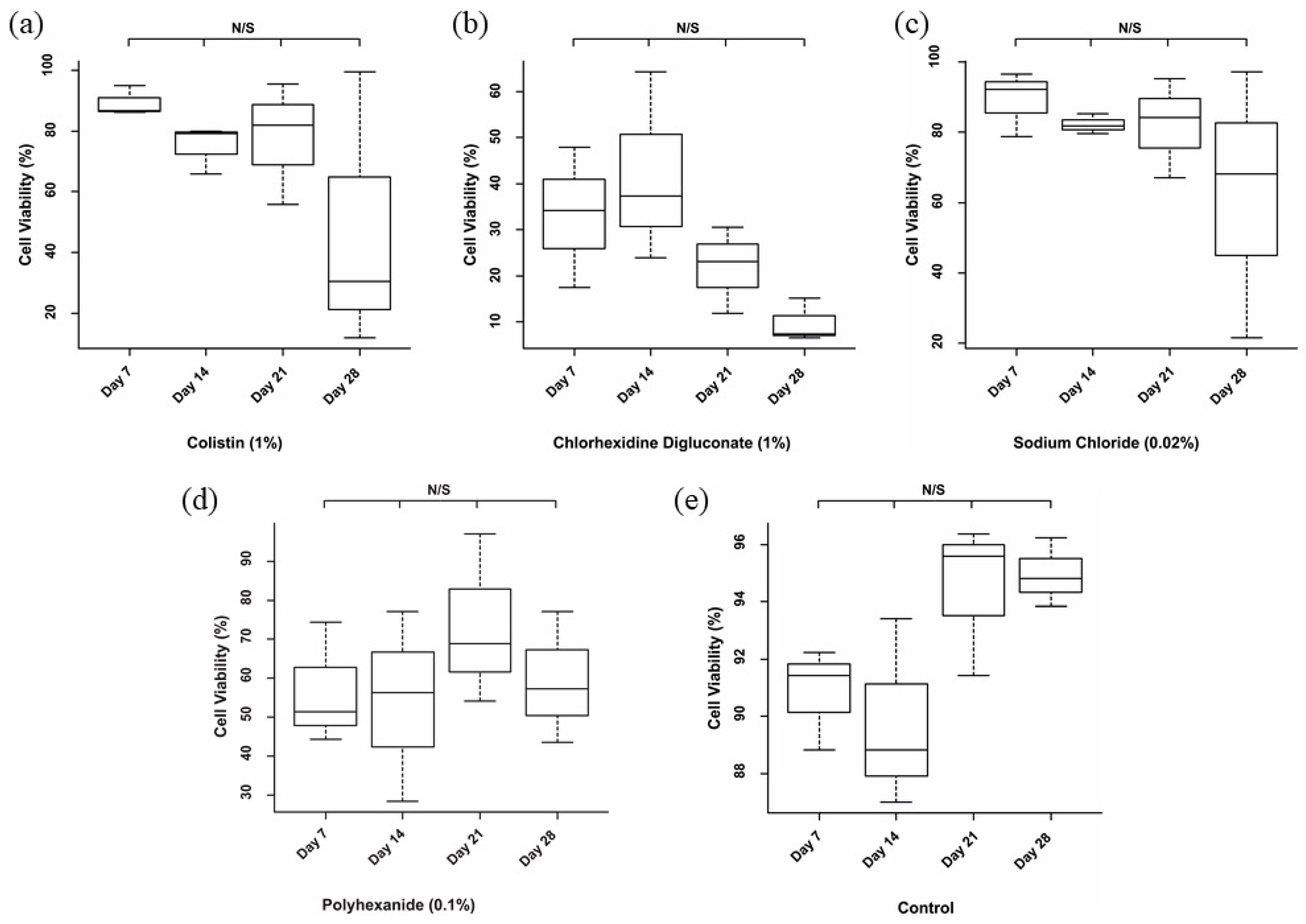
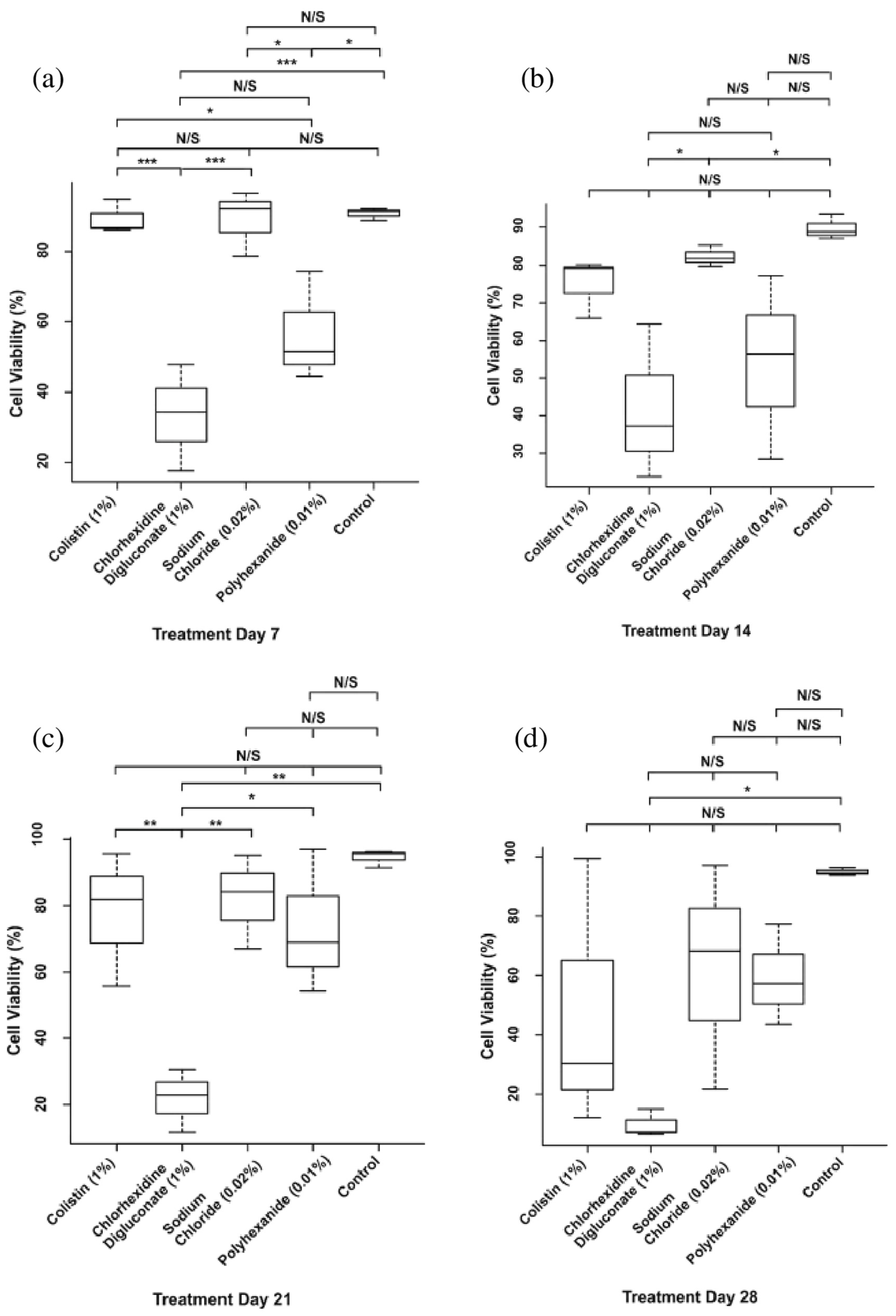
3.1. Chlorhexidine Digluconate Affects Cell Viability to a Greater Extent Compared to the Other Treatments
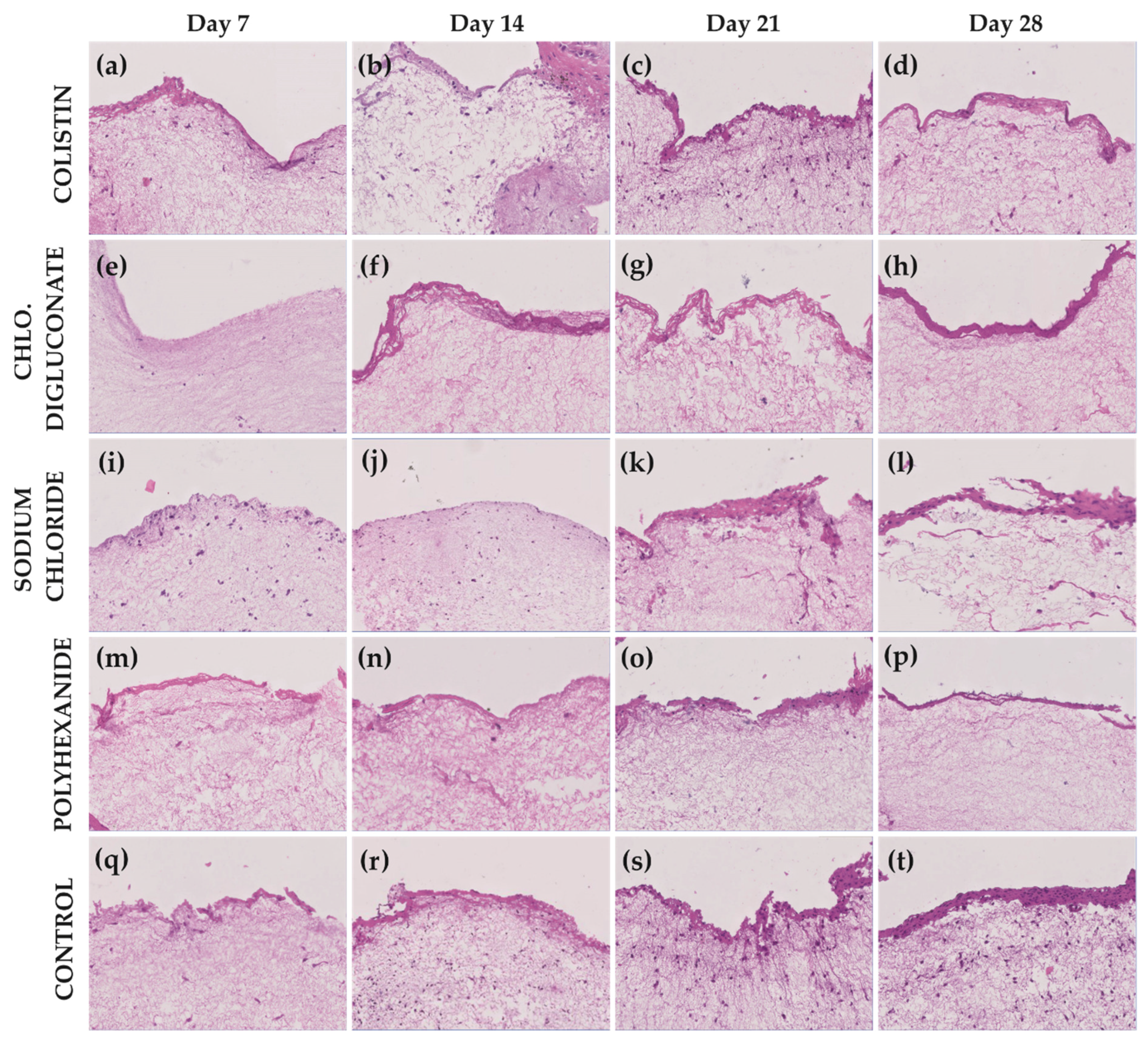
3.2. Chlorhexidine Digluconate and Polyhexanide Affect the Epithelium Integrity to a Greater Extent Compared to the Other Treatments
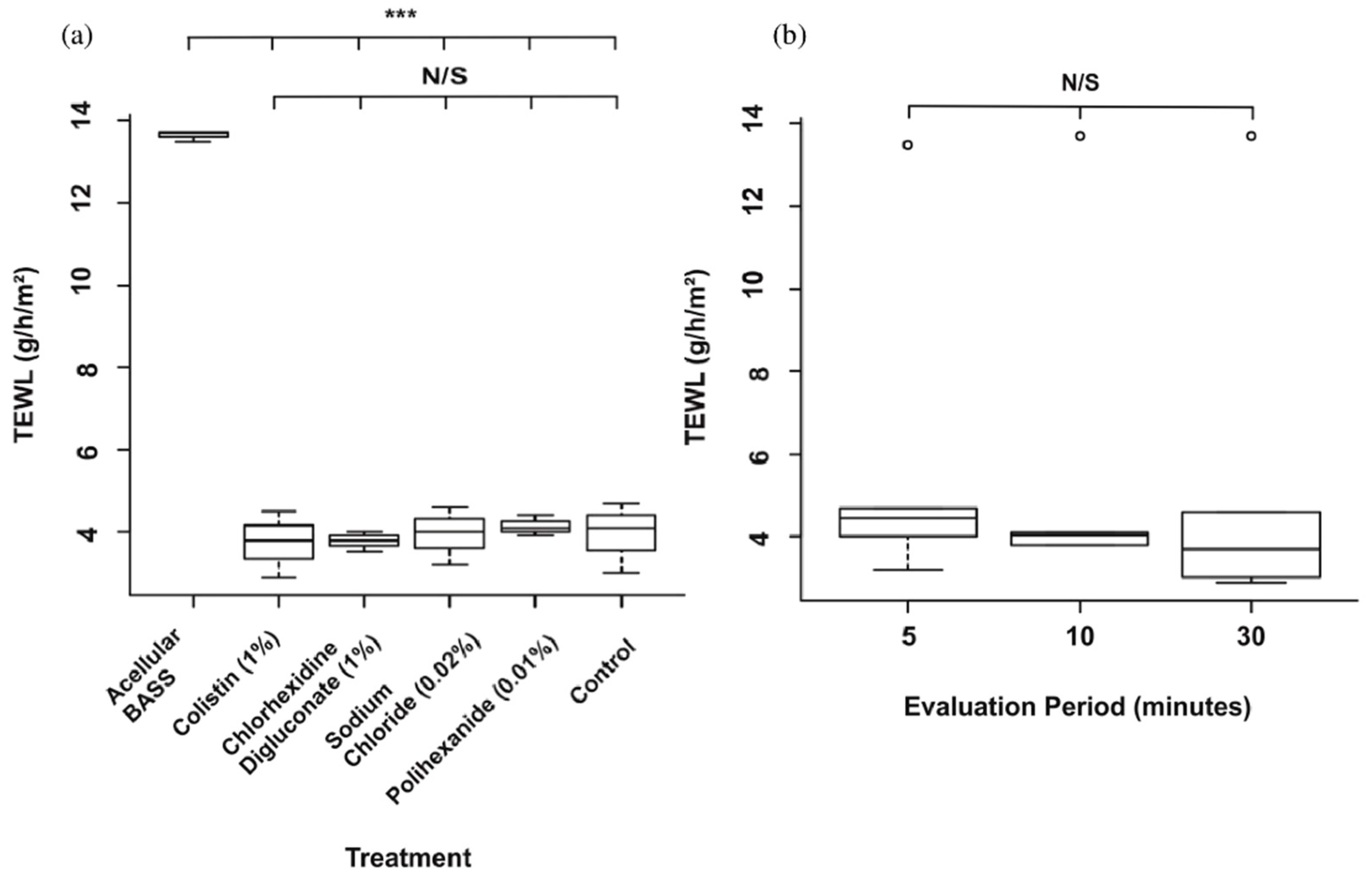
3.3. Skin Barrier Function Was Not Significantly Affected after the Antibiotic/Antiseptic Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vig, K.; Chaughari, A.; Tripathi, S.; Dixit, S.; Sahu, R.; Pillai, S.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Advances in skin regenation using tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, M.N.; Jeschke, M.G.; Amini-Nik, S. Methodologies in creating skin substitutes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3453–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Walsh, C.; Yue, D.; Dardik, A.; Cheema, U. Current advancements and strategies in tissue engineering for wound healing: A comprehensive review. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Sayed, P.; Hirt-Burri, N.; Roessingh, A.D.B.; Raffoul, W.; Applegate, L.A. Evolution of biological bandages as first cover for burn patients. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oualla-Bachiri, W.; Fernández-González, A.; Quiñones-Vico, M.I.; Arias-Santiago, S. From grafts to human bioengineered vascularized skin substitutes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Guerrero, J.J.; Carmona, G.; Correa, E.; Mata, R.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Alaminos, M.; Gacto, P.; Cuende, N. Transplant of tissue-engineered artificial autologous human skin in andalusia: An example of coordination and institutional collaboration. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 3047–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, A.G.; Giatsidis, G.; Orgill, D.P.; Halvorson, E.G. Skin substitutes and bioscaffolds: Temporary and permanent coverage. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.F.; Moreno, A.M.L.; Ramos, M.D.M.D.P.; García, A.R.; Ibáñez, O.E.; Porcel, N.F.; Calvo, J.G.; Arrabal, M.; López-Carmona, F.; Arias-Santiago, S. Optimization of human keratinocyte culture to develop an artificial human skin model: Cell alternatives as feeder layer of advanced therapies. Actual. MEDICA 2016, 101, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ścieżyńska, A.; Nogowska, A.; Sikorska, M.; Konys, J.; Karpińska, A.; Komorowski, M.; Ołdak, M.; Malejczyk, J. Isolation and culture of human primary keratinocytes—a methods review. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, L.E.; Minasian, R.A.; Caterson, E. Extracellular matrix and dermal fibroblast function in the healing wound. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.J.; Badylak, S.F. The use of biologic scaffolds in the treatment of chronic nonhealing wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.M.; Melrose, J. Proteoglycans in normal and healing skin. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 152–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Sánchez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Lizana-Moreno, O.E.-I.; Martinez-Lopez, A.J.; Guerrero-Calvo, N.; Fernández-Porcel, A.; Ruiz-García, A.; Ordoñez-Luque, V.; Carriel, S.A.-S. Hyaluronic acid biomaterial for human tissue-engineered skin substitutes: Preclinical comparative in vivo study of wound healing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2414–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Jahromi, M.; Sahandi, P.; Masoud, S.; Basri, M.; Sahandi, K.; Ghamarypour, A.; Aref, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: Preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 123, 33–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zieger, M.A.J.; Campana, G.; Tholpady, S.; Ziaie, B.; Sood, R.; Ochoa, M.; Rahimi, R. Skin regeneration using dermal substrates that contain autologous cells and silver nanoparticles to promote antibacterial activity: In vitro studies. Mil. Med. 2017, 182, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Norman, G.; Christie, J.; Liu, Z.; Mj, W.; Jm, J.; Hudson, T.; Edwards, J.; Dp, M.; Ia, H.; Jc, D. Antiseptics for burns (Review). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, 1–236. [Google Scholar]
- Barajas-Nava, L.A.; Lopez-Alcalde, J.; Roque i Figuls, M.; Solà, I.; Bonfill Cosp, X. Antibiotic prophylaxis for preventing burn wound infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, E.; Dominguez, C. Mechanisms underlying chlorhexidine-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol. Vitr. 2001, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Werner, J.; Kirsch, T.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Virk, M. Cytotoxicity evaluation of chlorhexidine gluconate on human fibroblasts, myoblasts, and osteoblasts. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2018, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, A.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.; Rossi, R. The relationship between skin function, barrier properties, and body-dependent factors. Ski. Res. Technol. 2017, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Sayed, P.; Tornay, D.; Hirt-Burri, N.; Roessingh, A.D.B.; Raffoul, W.; Applegate, L.A. Implications of chlorhexidine use in burn units for wound healing. Burn. 2020, 46, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivathasan, N.; Goodfellow, P.B. Skin cleansers: The risks of chlorhexidine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 51, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, D.S.; Topp, R.; Boykin, R.E.; Schultz, G.; Yang, Q. Efficacy and safety of a novel skin cleansing formulation versus chlorhexidine gluconate. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2018, 46, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskey, C.J.; Deshpande, A. Effect of chlorhexidine bathing in preventing infections and reducing skin burden and environmental contamination: A review of the literature. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2016, 44, e17–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivathasan, N.; Sivathasan, N.; Vijayarajan, L. Chlorhexidine’s complications. J. Perioper. Pract. 2010, 20, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bever, G.J.; Brodie, F.L.; Hwang, D.G. Corneal Injury from Presurgical Chlorhexidine Skin Preparation. World Neurosurg. 2016, 96, 610.e1–610.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedner, R.; Schopf, E. Inhibition of wound healing by antiseptics. Br. J. Dermatol. 1986, 115, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, J.A.; Layon, A.J.; Nappo, R.; Richards, W.T.; Mozingo, D.W. Hospital-acquired infections and thermally injured patients: Chlorhexidine gluconate baths work. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2014, 42, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guth, K.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Fabian, E.; Landsiedel, R.; Van Ravenzwaay, B. Suitability of skin integrity tests for dermal absorption studies in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Torre, R.S.-D.; Fernández-González, A.; Quiñones-Vico, M.I.; Montero-Vilchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S. Bioengineered skin intended as in vitro model for pharmacosmetics, skin disease study and environmental skin impact analysis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.-V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin barrier function in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis: Transepidermal water loss and temperature as useful tools to assess disease severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzlaff, F.; Kostka, K.-H.; Lehr, C.-M.; Schaefer, U.F. TEWL measurements as a routine method for evaluating the integrity of epidermis sheets in static Franz type diffusion cells in vitro. Limitations shown by transport data testing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, H.; Brown, S.; Danby, S.; Flohr, C. Research techniques made simple: Transepidermal water loss measurement as a research tool. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2295–2300.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebilcock, K.; Heylings, J.; Wilks, M. In vitro tape stripping as a model for in vivo skin stripping. Toxicol. Vitr. 1994, 8, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Nikolaev, V.; Kröger, M.; Zoschke, C.; Darvin, M.E.; Witzel, C.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Meinke, M.C. Barrier-disrupted skin: Quantitative analysis of tape and cyanoacrylate stripping efficiency by multiphoton tomography. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | Day 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colistin | 89.35% | 75.03% | 77.7% | 47.34% |
| Chlorhexidine digluconate | 33.16% | 41.86% | 21.81% | 9.69% |
| Sodium chloride | 89.15% | 82.18% | 82.08% | 62.34% |
| Polyhexanide | 56.66% | 53.99% | 73.37% | 59.41% |
| Control | 90.83% | 89.76% | 94.47% | 94.96% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quiñones-Vico, M.I.; Fernández-González, A.; Pérez-Castejón, E.; Montero-Vílchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S. Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040642
Quiñones-Vico MI, Fernández-González A, Pérez-Castejón E, Montero-Vílchez T, Arias-Santiago S. Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(4):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040642
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuiñones-Vico, María I., Ana Fernández-González, Elena Pérez-Castejón, Trinidad Montero-Vílchez, and Salvador Arias-Santiago. 2021. "Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 4: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040642
APA StyleQuiñones-Vico, M. I., Fernández-González, A., Pérez-Castejón, E., Montero-Vílchez, T., & Arias-Santiago, S. (2021). Cytotoxicity and Epidermal Barrier Function Evaluation of Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use in an Artificial Autologous Skin Model. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(4), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040642










