Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, S.P.; Kakkar, R.; McCarthy, C.P.; Januzzi, J.L. Inflammation in Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1324–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirazi, L.F.; Bissett, J.; Romeo, F.M.J. Role of inflammation in heart failure. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, M.; Guralnik, J.M.; Longo, D.L.F.L. Interleukin-6 in aging and chronic disease: A magnificent pathway. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.S.; Packer, M.; Lo, K.H.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Willerson, J.T. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-α, in patients with moderate-to-severe heart failure: Results of the anti-TNF therapy against congestive heart failure (ATTACH. Circulation 2003, 107, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, D.L.; McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Swedberg, K.; Borer, J.S.; Colucci, W.S.; Djian, J.; Drexler, H.; Feldman, A.; Kober, L.; et al. Targeted anticytokine therapy in patients with chronic heart failure: Results of the Randomized Etanercept Worldwide Evaluation (RENEWAL). Circulation 2004, 109, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Tromp, J.; Ouwerkerk, W.; Devalaraja, M.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.S.; van der Hast, P.; Lang, C.C. The clinical significance of interleukin-6 in heart failure: Results from the BIOSTAT-CHF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.; Thuren, T.; Macfadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. GR on behalf of the CTG. Anti-inflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Libby, P.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Koening, W.; Shimokawa, H.; Everett, B.M.; Glynn, J.R. Modulation of the interleukin-6 signalling pathway and incidence rates of atherosclerotic events and all-cause mortality: Analyses from the Canakinumab Anti-Inflammatory Thrombosis Outcomes Study (CANTOS). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, Á.J.; García, M.; Sánchez, G.M.; Álvarez, L.M.; Herrero, V.A.; Herrero, P.P. MR-proadrenomedulina y copeptina como predictores de reconsulta precoz en insuficiencia cardiaca aguda. Emergencias 2018, 30, 358–359. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, K.; Tsutamoto, T.; Wada, A.; Mabuchi, N.; Hayashi, M.; Tsutsui, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Sawaki, M.; Fujii, M.; Matsumoto, T.K.M. High levels of plasma brain natriuretic peptide and interleukin-6 after optimized treatment for heart failure are independent risk factors for morbidity and mortality in patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1587–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzic-Mehmedbasic, A. Inflammatory cytokines as risk factors for mortality after acute cardiac events. Med. Arch. 2016, 70, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Warner, S.L.; Ahmad, T.; Amin, V.J.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Drazner, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Peterson, P.N.; et al. 2019 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Risk Assessment, Management, and Clinical Trajectory of Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1966–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkuma, T.; Jun, M.; Woodward, M.; Zoungas, S.; Cooper, M.E.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hamet, P.; Mancia, G.; Williams, B.; Welsh, P.; et al. Cardiac stress and inflammatory markers as predictors of heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: The ADVANCE trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.B.; Meigs, J.B.; Li, T.Y.; Rifai, N.M.J. Inflammatory markers and risk of developing type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes 2004, 53, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spranger, J.; Kroke, A.; Möhlig, M.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.M.; Ristow, M.; Boeing, H.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Inflammatory cytokines and the risk to develop type 2 diabetes: Results of the prospective population-based European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam Study. Diabetes 2003, 52, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, E.A.; Von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D.; MacDougall, I.C.P.P. Iron deficiency and heart failure: Diagnostic dilemmas and therapeutic perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Valore, E.V.; Territo, M.; Schiller, G.; Lichtenstein, A.G.T. Hepcidin, a putative mediator of anemia of inflammation, is a type II acute-phase protein. Blood 2003, 101, 2461–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, R.T., Jr. Advances in the anemia of chronic disease. Int. J. Hematol. 1999, 70, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.K.; Lee, J.K.; Chiang, F.T.; Yang, C.H.; Huang, S.W.; Hwang, J.J.; Lin, J.L.; Tseng, C.D.; Chen, J.J.T.C. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-? and interleukin-6 are associated with diastolic heart failure through downregulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, M.H.S. SERCA pump level is a critical determinant of Ca(2+)homeostasis and cardiac contractility. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanberg, J.S.; Rao, V.; Ahmad, T.; Chunara, Z.; Mahoney, D.; Jackson, K. Inflammation and cardio-renal interactions in heart failure: A potential role for interleukin-6. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 118, 6072–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Xu, H.; Davies, J.L.H.G. Increase of plasma IL-6 concentration with age in healthy subjects. Life Sci. 1992, 51, 1953–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershler, W.B.; Sun, W.H.; Binkley, N.; Gravenstein, S.; Volk, M.J.; Kamoske, G.; Klopp, R.G.; Roecker, E.B.; Daynes, R.A.; Weindruch, R. Interleukin-6 and aging: Blood levels and mononuclear cell production increase with advancing age and in vitro production is modifiable by dietary restriction. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1993, 12, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hager, K.; Machein, U.; Krieger, S.; Platt, D.; Seefried, G.B.J. Interleukin-6 and selected plasma proteins in healthy persons of different ages. Neurobiol. Aging 1994, 15, 771–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKane, W.R.; Khosla, S.; Peterson, J.M.; Egan, K.R.B. Circulating levels of cytokines that modulate bone resorption: Effects of age and menopause in women. J. Bone Min. Res. 1994, 9, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, D.M.; Binkley, N.; Checovich, M.; Havighurst, T.; Schilling, M.E.W. Elevated plasma levels of interleukin-6 in postmenopausal women do not correlate with bone density. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1995, 43, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.J.; Pieper, C.F.; Harris, T.; Rao, K.M.M.; Curie, M.S. The association of plasma IL-6 levels with functional disability in community-dwelling elderly. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1997, 52, M201–M208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Tracy, R.P.; Corti, M.C.; Wacholder, S.; Ettinger, W.H., Jr.; Heimovitz, H.; Cohen, H.J.; Wallace, R. Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am. J. Med. 1999, 106, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Corsi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Bartali, B.; Taub, D.D.; Gurlanik, J.M.; Longo, D.M. The origins of age-related proinflammatory state. Blood 2005, 105, 2294–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.F.P. Molecular mechanisms of aging-associated inflammation. Cancer Lett. 2006, 236, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, N.; Sansoni, P.; Girasole, G.; Vescovini, R.; Passeri, G.; Passeri, M.; Pedrazzoni, M. Serum interleukin-6, soluble interleukin-6 receptor and soluble gp130 exhibit different patterns of age- and menopause-related changes. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Meschi, T.; Lauretani, F.; Felis, G.; Franchi, F.; Pedrolli, C.; Barichella, M.; Benati, G.; Di Nuzzo, S.; Ceda, G.P.; et al. Nutrition and inflammation in older individuals: Focus on vitamin D, n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and whey proteins. Nutrients 2006, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: Depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, N.; Moghaddam, N.; Andrade, J.; Hawkins, N.; Krahn, A.; Deyell, M. Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, S47–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, T.T.; Dokainish, H.; Lakkis, N.M. Role of Inflammation in Initiation and Perpetuation of Atrial Fibrillation. A Systematic Review of the Published Data. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, N.; Miyasaka, Y.; Suwa, Y.; Harada, S.; Nakai, E.; Shiojima, I. Heart failure in atrial fibrillation: An update on clinical and echocardiographic implications. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I.; Teshima, Y.; Kondo, H.; Kaku, H.; Kira, S.; Ikebe, Y.; Saito, S.; Fukui, A.; Shinohara, T.; Yufu, K.; et al. Association of fibrotic remodeling and cytokines/chemokines content in epicardial adipose tissue with atrial myocardial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation. Hear Rhythm 2018, 15, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Bai, R.; Liu, N.; Li, N.; Schoenhagen, P.; Ma, C. Prognostic Significance of Left Ventricular Fibrosis Assessed by T1 Mapping in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (N = 78) | IL-6 Normal (N = 36) | IL-6 High (N = 42) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline characteristics | ||||
| Age in years—median (SD) | 79.2 ± 6.6 | 78.5 ± 5.3 | 79.8 ± 7.5 | 0.374 a |
| Sex female—n (%) | 46 (59) | 21 (58.3) | 25 (59.5) | 0.915 b |
| Smoking | 4 (5.1) | 2 (5.6) | 2 (4.8) | 0.874 b |
| Sedentary | 48 (61.5) | 21 (58.3) | 27 (64.3) | 0.590 b |
| Underlying cardiomyopathy | ||||
| Hypertensive cardiomyopathy | 32 (41.1) | 17 (47.2) | 15 (35.7) | 0.303 b |
| Ischemic cardiomyopathy | 17 (21.8) | 5 (13.9) | 12(28.6) | 0.117 b |
| Valvulopathy | 20 (25.6) | 10 (27.8) | 10 (23.8) | 0.689 b |
| Nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy | 6 (7.7) | 3 (8.3) | 3 (7.1) | 0.844 b |
| Cor pulmonale | 3 (3.8) | 1 (2.8) | 2 (4,8) | 0.65 b |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Arterial hypertension | 78(100) | 36 (46) | 42 (54) | 0.521 b |
| Diabetes mellitus | 42 (53.8) | 15 (41.7) | 27 (64.3) | 0.046b |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 51 (65.4) | 19 (52.8) | 32 (76.2) | 0.030b |
| Metabolic syndrome | 24 (30.8) | 8 (22.2) | 16 (38.1) | 0.130 b |
| Atrial fibrillation | 56 (71.8) | 30 (83.3) | 26 (61.9) | 0.036b |
| Chronic renal failure | 31 (39.7) | 15 (41.7) | 16 (38.1) | 0.748 b |
| Anemia | 31 (39.7) | 9 (25) | 22 (52.4) | 0.014b |
| Obesity (BMI >30) | 17 (21.8) | 9 (25) | 8 (19) | 0.526 b |
| Functional evaluation | ||||
| Pfeiffer Test | ||||
| 0-2 mistakes | 73 (93.6) | 33 (91.7) | 40 (95.2) | 0.465 b |
| >2 mistakes | 5 (6.4) | 3 (8.3) | 2 (4.8) | |
| Nutritional evaluation (MNA Test) | ||||
| Normal (≥24 points) | 52 (66.7) | 25 (75.8) | 27 (67.5) | 0.438 b |
| At risk of malnutrition or established malnutrition (<24 points) | 21 (26.9) | 8 (24.2) | 13 (32.5) | |
| Frailty (Barber >1) | 71 (91) | 32 (88.9) | 39 (92.9) | 0.541 b |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| Left ventricular hypertrophy | 47 (60.3) | 21 (58.3) | 26 (61.9) | 0.648 b |
| Preserved LVEF (≥50%) | 50 (64.1) | 20 (55.6) | 30 (71.4) | 0.145b |
| Reduced LVEF (<50%) | 28(35.8) | 16 (44.4) | 12 (28.6) | 0.163 d |
| Vital parameters | ||||
| SBP (mmHg) | 136 ± 21 | 136 ± 19 | 135 ± 23 | 0.230 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 68 ± 10 | 70 ± 9 | 66 ± 10 | 0.697 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 78 ± 16 | 77 ± 17 | 78 ± 16 | 0.582 |
| Blood results | ||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dl) | 12.7 ± 1.9 | 13.2 ± 2.3 | 12.3 ±2.1 | <0.001 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 175 ± 289 | 147 ± 223 | 194 ± 322 | 0.108 c |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 1.28 ± 0.65 | 1.08 ± 0.57 | 1.35 ± 0.69 | 0.024 |
| CKD-EPI glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/m2) | 46 ± 26 | 59.95 ± 35 | 43.6 ± 19 | 0.007 |
| Microalbuminuria (mg/L) | 16.9 ± 60.7 | 15.9 ± 25.8 | 17.6 ± 99 | 0.451 c |
| HbA1c (%) | 6 ± 1 | 6 ± 1 | 6.3 ± 1 | 0.108 c |
| NT-ProBNP (pg/mL) | 1613 ± 2297 | 1244 ± 2780 | 1990 ± 4019 | 0.061 c |
| Usual treatment | ||||
| Beta Blockers | 52 (66.7) | 21 (58.3) | 31 (73.8) | 0.148 b |
| Furosemide | 65 (83.3) | 31 (86.1) | 34 (81) | 0.542 b |
| Chlorthalidone | 6 (7.7) | 5 (13.9) | 1 (2.4) | 0.057 b |
| Spironolactone/Eplerenone | 33 (42.3) | 13 (36.1) | 20 (47.6) | 0.305 b |
| ACE inhibitors/Angiotensin II Antagonist | 23 (29.5) | 13 (36.1) | 10 (23.8) | 0.235 b |
| Statins | 52 (66.7) | 23 (63.9) | 29 (69) | 0.63 b |
| Anticoagulation | 56 (71.8) | 31 (86.1) | 25 (59.5) | 0.009b |
| Follow-up | ||||
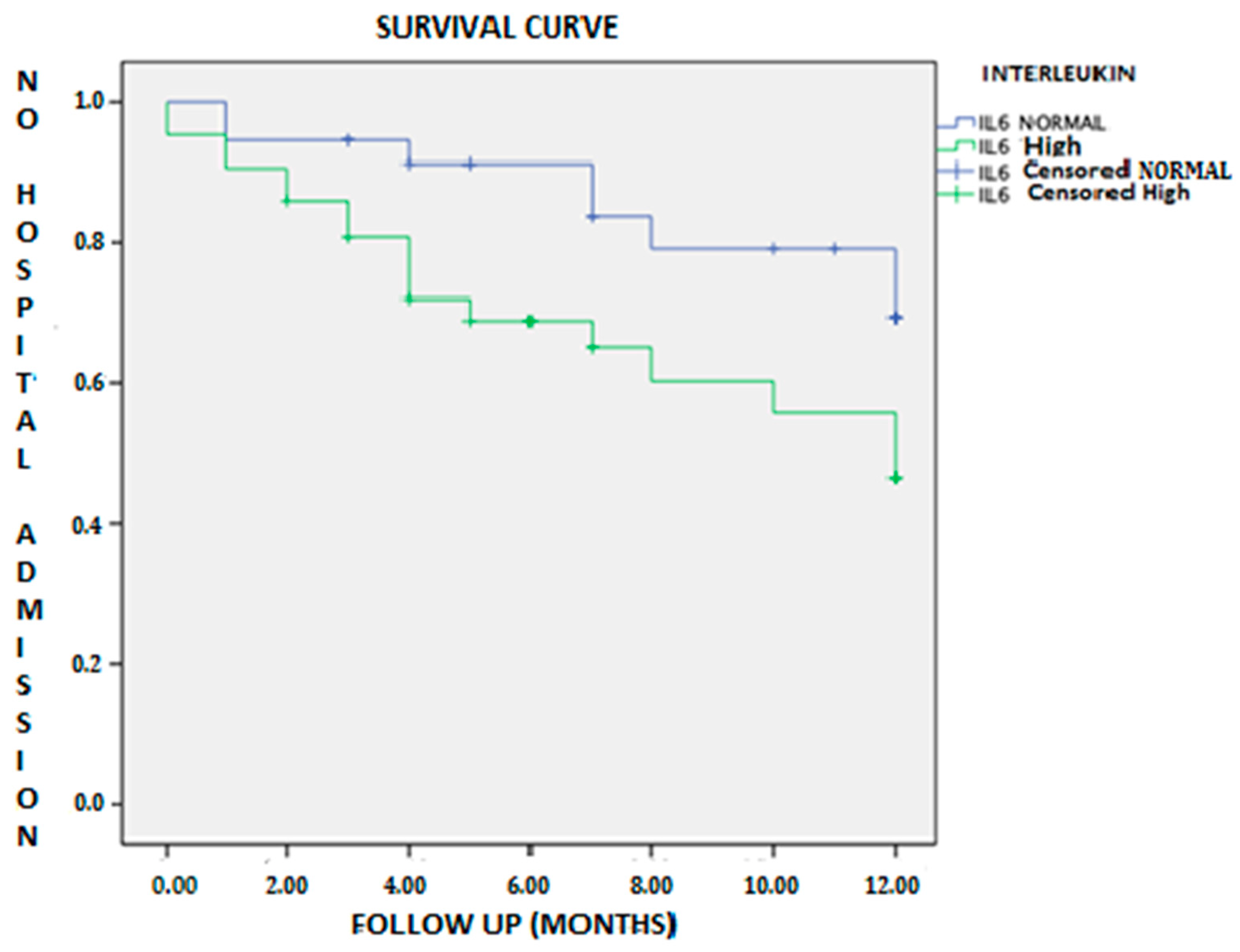
| Event (combined) | 40 (51.3) | 15 (41.7) | 25 (59.5) | 0.116 b |
| HF hospitalization | 25 (32.1) | 8 (22.2) | 17 (40.5) | 0.069d |
| Visit to ED for HF | 13 (16.7) | 4 (11.1) | 9 (21.4) | 0.223 b |
| Visit to Day Care Hospital for HF | 11 (14.1) | 6 (16.7) | 5 (11.9) | 0.547 b |
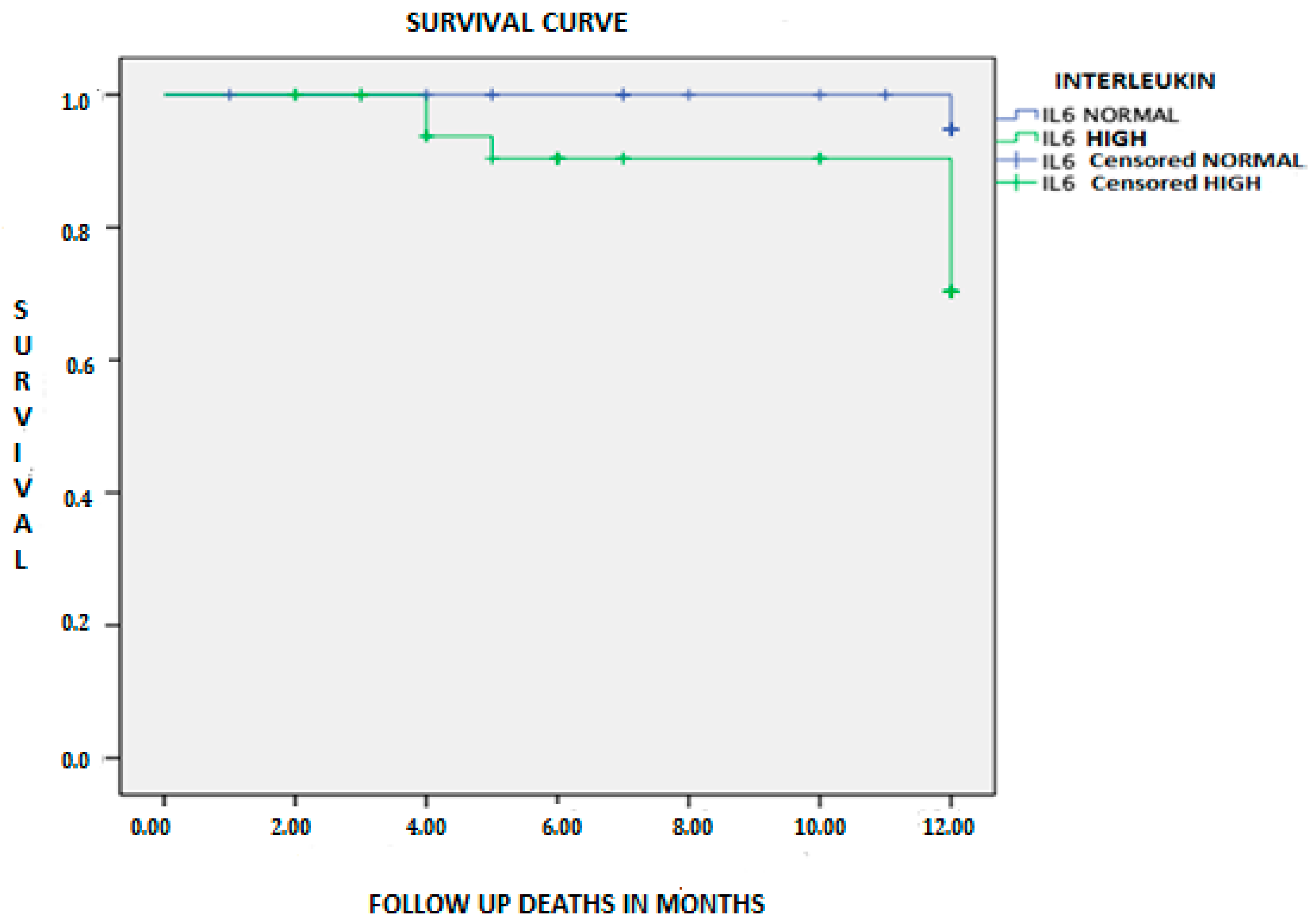
| Mortality from any cause | 8 (10.3) | 1 (2.8) | 7 (16.7) | 0.044b |
| Multivariable OR (95%CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Atrial fibrillation | 1.240 (0.332–4.626) | 0.749 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.41 (0.128–01.134) | 0.134 |
| Anemia | 3.513 (1.163–10.607) | 0.026 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 0.565 (0.177–1.802) | 0.335 |
| GFR CKD EPI | 0.963 (0.936–0.991) | 0.009 |
| Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|
| Factors Associated with Mortality | OR (95%CI) | p |
| Age | 1.131 (0.992–1.290) | 0.066 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction | 0.207 (0.018–2.393) | 0.207 |
| IL-6 levels | 1.037 (1.000–1.074) | 0.048 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Povar-Echeverría, M.; Auquilla-Clavijo, P.E.; Andrès, E.; Martin-Sánchez, F.J.; Laguna-Calle, M.V.; Calvo-Elías, A.E.; Lorenzo-Villalba, N.; Méndez-Bailón, M. Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030504
Povar-Echeverría M, Auquilla-Clavijo PE, Andrès E, Martin-Sánchez FJ, Laguna-Calle MV, Calvo-Elías AE, Lorenzo-Villalba N, Méndez-Bailón M. Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(3):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030504
Chicago/Turabian StylePovar-Echeverría, Marina, Pablo Esteban Auquilla-Clavijo, Emmanuel Andrès, Francisco Javier Martin-Sánchez, María Victoria Laguna-Calle, Alberto Elpidio Calvo-Elías, Noel Lorenzo-Villalba, and Manuel Méndez-Bailón. 2021. "Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 3: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030504
APA StylePovar-Echeverría, M., Auquilla-Clavijo, P. E., Andrès, E., Martin-Sánchez, F. J., Laguna-Calle, M. V., Calvo-Elías, A. E., Lorenzo-Villalba, N., & Méndez-Bailón, M. (2021). Interleukin-6 Could Be a Potential Prognostic Factor in Ambulatory Elderly Patients with Stable Heart Failure: Results from a Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(3), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030504






