Cardiovascular Events, Sleep Apnoea, and Pulmonary Hypertension in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Data from the French Health Insurance Database
Abstract
1. Introduction
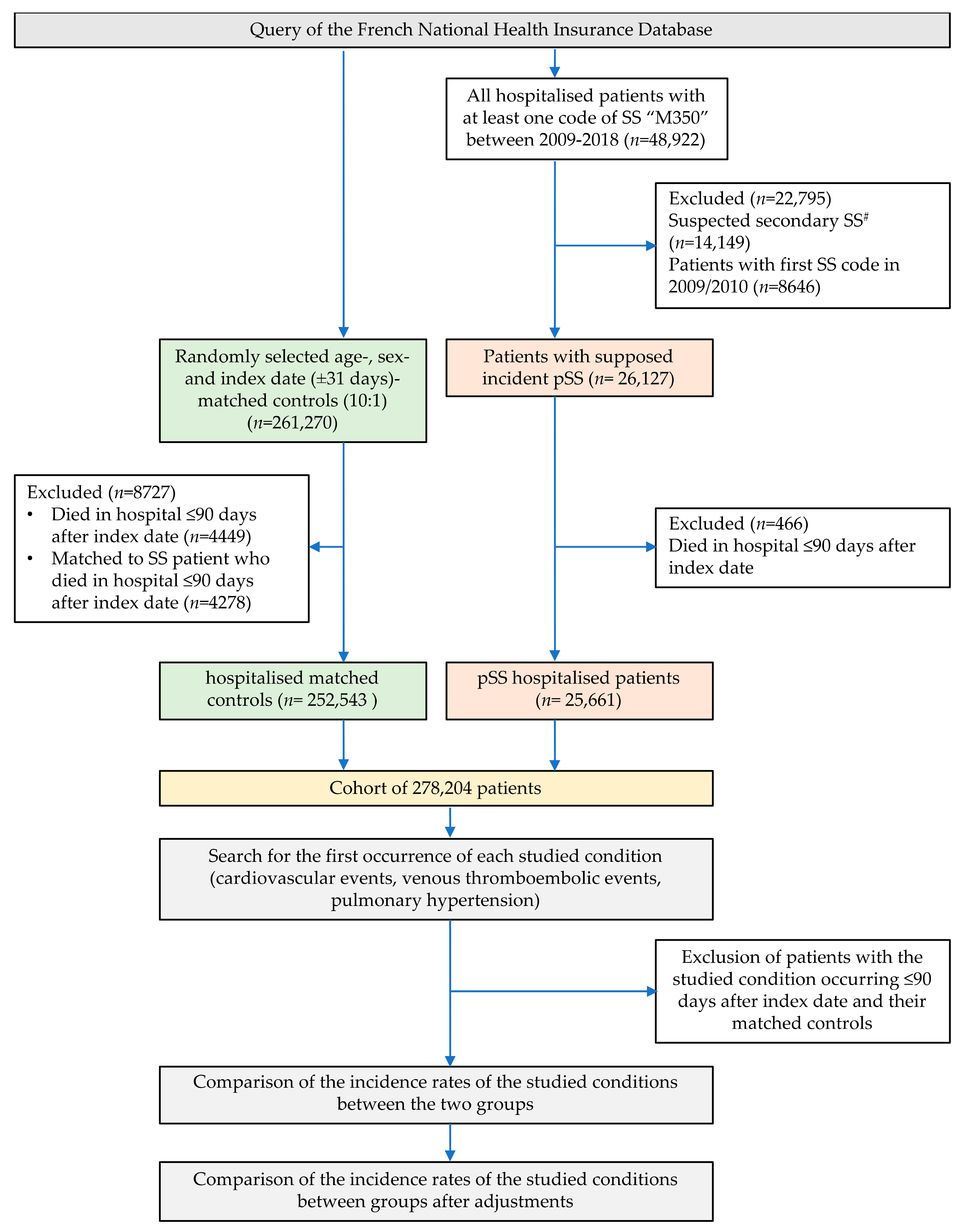
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Hospitalised Patients (pSS)
2.2. Control Group of Non-pSS Hospitalised Patients
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Past Medical History and Other Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Incidence of CVEs and SAS
3.3. Incidence of Venous Thromboembolic Events and Pulmonary Hypertension
3.4. Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pillemer, S.R.; Matteson, E.L.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Martens, P.B.; Melton, L.J.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Fox, P.C. Incidence of Physician-Diagnosed Primary Sjögren Syndrome in Residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabasakal, Y.; Kitapcioglu, G.; Turk, T.; Oder, G.; Durusoy, R.; Mete, N.; Egrilmez, S.; Akalin, T. The Prevalence of Sjögren’s Syndrome in Adult Women. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 35, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.J. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Lupus 2018, 27, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, G.; Servioli, L.; Nannini, C.; Berti, A.; Crowson, C.S.; Achenbach, S.J.; Matteson, E.L.; Cornec, D. Hospitalisation Rates among Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Population-Based Study, 1995–2016. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, K.; Dörner, T.; Redeker, I.; Karberg, K.; Marschall, U.; Zink, A.; Callhoff, J. Comorbidity and Health Care Utilisation in Persons with Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Claims Data Analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S126), 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, I.F.; Szanto, A.; Papp, G.; Zeher, M. Clinical Course, Prognosis, and Cause of Death in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 647507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, A.G.; Singh, S.; Matteson, E.L. Rate, Risk Factors and Causes of Mortality in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, E.; Baldini, C.; Ferro, F.; Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Cafaro, G.; Bombardieri, S.; Gerli, R.; Grossi, E. Application of Artificial Neural Network Analysis in the Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Novel Pathogenetic Scenario? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S118), 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, W.C.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Association between Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome, Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. S112), 190–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Liakouli, V.; Iacono, D.; Pantano, I.; Margiotta, D.P.E.; Navarini, L.; Destro Castaniti, G.M.; Maruotti, N.; Di Scala, G.; et al. Occurrence and Predictive Factors of High Blood Pressure, Type 2 Diabetes, and Metabolic Syndrome in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from a 3-Year, Multicentre, Prospective, Observational Study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrich, D.C.; van de Wetering, E.H.M.; Rennings, A.J.; Arts, E.E.; Meek, I.L.; den Broeder, A.A.; Fransen, J.; Popa, C.D. Younger Age and Female Gender Are Determinants of Underestimated Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuzot, C.; Letertre, S.; Daien, C.I.; Zerkowski, L.; Guilpain, P.; Terrier, B.; Fesler, P.; Roubille, C. Comorbidities and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)—Associated Vasculitis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltai, A.; Barnetche, T.; Daien, C.; Lukas, C.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Combe, B.; Morel, J. Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Chen, P.-J.; Leu, H.-B.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, P.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, J.-W.; Chan, W.-L. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome and the Risk of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Nationwide Study. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2013, 29, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoloni, E.; Baldini, C.; Schillaci, G.; Quartuccio, L.; Priori, R.; Carubbi, F.; Bini, V.; Alunno, A.; Bombardieri, S.; Vita, S.D.; et al. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Burden in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Results of a Population-Based Multicentre Cohort Study. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luni, F.K.; Malik, S.A.; Khan, A.R.; Riaz, H.; Singh, H.; Federman, D.; Kanjwal, Y.; Dasa, O.; Khuder, S.; Kabour, A. Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease in Patients With Sjögren’s Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 354, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramagopalan, S.V.; Wotton, C.J.; Handel, A.E.; Yeates, D.; Goldacre, M.J. Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in People Admitted to Hospital with Selected Immune-Mediated Diseases: Record-Linkage Study. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-F.; Huang, J.-Y.; Chiou, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Wei, J.C.-C.; Dong, L.-L. Increased Risk of Coronary Heart Disease among Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, D.; Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.-Y.; Jais, X.; Simonneau, G.; Humbert, M. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Rare Complication of Primary Sjögren Syndrome: Report of 9 New Cases and Review of the Literature. Medicine 2007, 86, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofors, J.; Holmqvist, M.; Westermark, L.; Björk, A.; Kvarnström, M.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Magnusson Bucher, S.; Eriksson, P.; Theander, E.; Mandl, T.; et al. Concomitant Ro/SSA and La/SSB Antibodies Are Biomarkers for the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism and Cerebral Infarction in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Ko, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-A. Epidemiology and Mortality of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A National Cohort Study in Taiwan. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lai, J.; Tian, Z.; Song, H.; et al. Characteristics and Risk Factors of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Lee, D.S.; Fine, J.P. Introduction to the Analysis of Survival Data in the Presence of Competing Risks. Circulation 2016, 133, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudo, G.; Bocci, E.B.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Schillaci, G.; Wu, R.; Del Papa, N.; Vitali, C.; Delle Monache, F.; Marchesi, S.; Mannarino, E.; et al. Precocious Intima-Media Thickening in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3890–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerli, R.; Vaudo, G.; Bocci, E.B.; Schillaci, G.; Alunno, A.; Luccioli, F.; Hijazi, R.; Mannarino, E.; Shoenfeld, Y. Functional Impairment of the Arterial Wall in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Combined Action of Immunologic and Inflammatory Factors. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.C.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Association between Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome, Arterial Stiffness, and Subclinical Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezis Demirci, M.; Karabulut, G.; Gungor, O.; Celtik, A.; Ok, E.; Kabasakal, Y. Is There an Increased Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome? Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Luo, J.; Wei, T.; Qin, W.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Risk of Cardiovascular Involvement in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Cohort Study. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2019, 44, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartoloni, E.; Alunno, A.; Valentini, V.; Valentini, E.; La Paglia, G.M.C.; Leone, M.C.; Cafaro, G.; Marcucci, E.; Bonifacio, A.F.; Luccioli, F.; et al. The Prevalence and Relevance of Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36 (Suppl. S112), 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Juarez, M.; Toms, T.E.; de Pablo, P.; Mitchell, S.; Bowman, S.; Nightingale, P.; Price, E.J.; Griffiths, B.; Hunter, J.; Gupta, M.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Women with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: United Kingdom Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Registry Results. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoloni, E.; Baldini, C.; De Vita, S.; Priori, R.; Giacomelli, R.; Bini, V.; Gerli, R. Interplay of Anti-SSA/SSB Status and Hypertension in Determining Cardiovascular Risk in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-C.; Chen, W.-S.; Chang, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-H.; Chang, C.-C. Risk of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Sjögren Syndrome and Behçet’s Disease: A Nationwide, Population-Based Cohort Study. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, Z.A.; Hlavac, M.; Rischmueller, M.; Heraganahally, S.S.; Hilditch, C.J.; Lester, S.; Catcheside, P.G.; Antic, N.A.; Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; McEvoy, R.D. Sleep Disordered Breathing in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Group Controlled Study. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-C.; Hsu, C.-W.; Lu, M.-C.; Koo, M. Increased Risks of Psychiatric Disorders in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome-a Secondary Cohort Analysis of Nationwide, Population-Based Health Claim Data. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilditch, C.J.; McEvoy, R.D.; George, K.E.; Thompson, C.C.; Ryan, M.K.; Rischmueller, M.; Catcheside, P.G. Upper Airway Surface Tension but Not Upper Airway Collapsibility Is Elevated in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Sleep 2008, 31, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Gairy, K.; Knight, C.; Anthony, P.; Hoskin, B. Burden of Illness among Subgroups of Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome and Systemic Involvement. Rheumatology 2020, 39, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, P.; Kong, X.; Duan, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Association between Comorbidities and Extraglandular Manifestations in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic Definitions and Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, D.; Tian, Z.; Wei, W.; Zuo, X.; et al. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Multicentre Cohort Study from China. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Gladue, H.; Channick, R.; Chung, L.; Distler, O.; Furst, D.E.; Hachulla, E.; Humbert, M.; Langleben, D.; Mathai, S.C.; et al. Recommendations for Screening and Detection of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. The Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor Inhibitors, Methotrexate, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Corticosteroids on Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubille, C.; Coffy, A.; Rincheval, N.; Dougados, M.; Flipo, R.-M.; Daurès, J.-P.; Combe, B. Ten-Year Analysis of the Risk of Severe Outcomes Related to Low-Dose Glucocorticoids in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 3738–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubille, C.; Fesler, P.; Combe, B. Shifting from a Rheumatologic Point of View toward Patient-Centered Care in Rheumatoid Arthritis with an Integrated Management of Comorbidities. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. Evidence-Based Recommendations for the Management of Comorbidities in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis, and Psoriatic Arthritis: Expert Opinion of the Canadian Dermatology-Rheumatology Comorbidity Initiative. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Tzioufas, A.G. Cardio-Rheumatology: Two Collaborating Disciplines to Deal with the Enhanced Cardiovascular Risk in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 18, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kwong, J.S.-W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Tian, H.; et al. Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine Are Associated with Reduced Cardiovascular Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-H.; Wang, Y.-H.; Pan, L.-F.; Wei, J.C.-C. Cardiovascular Protection of Hydroxychloroquine in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Patients (n = 25,661) | Matched Controls (n = 252,543) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | % of pSS Patients | Number of Matched Patients | % of Matched Patients | Comparison (p Value) | |
| Sex (female) (n, %) | 22,489 | 87.66% | 224,887 | 87.65% | 0.995 |
| Low socio-economic status (n, %) | 1224 | 4.77% | 8482 | 3.31% | <0.001 |
| Age (mean, SD) (years) | 60.2 | ±16.3 | 60.0 | ±16.3 | 0.075 * |
| Number of hospitalisations before index date (mean, SD) | 3.7 | ±9.0 | 0.21 | ±1.1 | <0.001 * |
| Annual rate of hospitalisations before index date (n, %) | |||||
| ≤0.25 per year | 10,245 | 39.93% | 244107 | 95.15% | <0.001 |
| Between 0.25 and 0.5 per year | 5959 | 23.23% | 8679 | 3.38% | . |
| Between 0.5 and 1 per year | 5430 | 21.16% | 2807 | 1.09% | . |
| Between 1 and 5 per year | 3704 | 14.44% | 908 | 0.35% | . |
| More than 5 per year | 318 | 1.24% | 59 | 0.02% | . |
| Deaths (incidence a, 95%CI) | 14.4 | (13.7–15.2) | 10.5 | (10.3–10.7) | <0.001 |
| Follow-up time after index date (median, (IQR), years) | 3.96 | (1.96–5.96) | 3.96 | (1.96–6.04) | 0.003 * |
| Past medical history mentioned in previous hospitalisations (used as adjustment covariates) | |||||
| Cardiovascular risk factors or associated reported during a hospitalisation | |||||
| Hypertension | 274 | 1.07% | 876 | 0.35% | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 656 | 2.56% | 2818 | 1.12% | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 294 | 1.15% | 1393 | 0.55% | <0.001 |
| Sleep apnoea syndrome | 560 | 2.18% | 1461 | 0.58% | <0.001 |
| All cardiovascular diseases b | 1361 | 5.30% | 8281 | 3.28% | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 251 | 0.98% | 450 | 0.18% | <0.001 |
| Dialysis | 83 | 0.32% | 214 | 0.08% | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular events | |||||
| Ischemic heart disease | 871 | 3.39% | 5174 | 2.05% | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 356 | 1.39% | 2304 | 0.91% | <0.001 |
| All venous thromboembolic events c | 155 | 0.60% | 515 | 0.20% | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 127 | 0.49% | 65 | 0.03% | <0.001 |
| Other covariates | |||||
| Interstitial pneumonitis or lung fibrosis | 695 | 2,71% | 154 | 0.06% | <0.001 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 442 | 1.72% | 1202 | 0.48% | <0.001 |
| Neuro-psychiatric disorders d | 667 | 2.60% | 2529 | 0.99% | <0.001 |
| pSS Patients | Matched Controls | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incident Cases # | Py | Incidence # | CI | Incident Cases # | Py | Incidence # | CI | Crude HR | Crude CI | Crude p Value | aHR | Adjusted CI | Adjusted p Value | |
| Cardiovascular events | ||||||||||||||
| Ischemic heart disease | 535 | 98611 | 5.43 | (4.97–5.89) | 3723 | 967246 | 3.85 | (3.73–3.97) | 1.39 | (1.27–1.52) | 0.000 | 1.20 | (1.06–1.34) | 0.003 |
| Stroke | 227 | 101241 | 2.24 | (1.95–2.53) | 2159 | 1000199 | 2.16 | (2.07–2.25) | 1.01 | (0.88–1.16) | 0.845 | 1.05 | (0.88–1.25) | 0.606 |
| Heart failure | 486 | 100321 | 4.84 | (4.41–5.27) | 3339 | 991590 | 3.37 | (3.26–3.48) | 1.42 | (1.29–1.56) | 0.000 | 1.05 | (0.92–1.19) | 0.497 |
| Cardiovascular risk factors | ||||||||||||||
| Hypertension | 137 | 101508 | 1.35 | (1.12–1.58) | 807 | 1008796 | 0.8 | (0.74–0.86) | 1.71 | (1.42–2.05) | 0.000 | 1.39 | (1.07–1.80) | 0.014 |
| Sleep apnoea syndrome | 438 | 99839 | 4.39 | (3.98–4.8) | 1645 | 995874 | 1.65 | (1.57–1.73) | 2.66 | (2.39–2.95) | 0.000 | 1.97 | (1.70–2.28) | <0.001 |
| Venous thromboembolic events | ||||||||||||||
| Pulmonary embolism | 131 | 101747 | 1.29 | (1.07–1.51) | 887 | 1011218 | 0.88 | (0.82–0.94) | 1.45 | (1.21–1.75) | 0.000 | 1.10 | (0.86–1.41) | 0.460 |
| All vein thromboses | 214 | 101027 | 2.12 | (1.84–2.4) | 1400 | 1002691 | 1.4 | (1.33–1.47) | 1.50 | (1.30–1.73) | 0.000 | 1.04 | (0.85–1.27) | 0.701 |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 72 | 102319 | 0.70 | (0.54–0.86) | 126 | 1019457 | 0.12 | (0.10–0.14) | 5.72 | (4.27–7.68) | 0.000 | 3.32 | (2.10–5.25) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goulabchand, R.; Roubille, C.; Montani, D.; Fesler, P.; Bourdin, A.; Malafaye, N.; Morel, J.; Arnaud, E.; Lattuca, B.; Barateau, L.; et al. Cardiovascular Events, Sleep Apnoea, and Pulmonary Hypertension in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Data from the French Health Insurance Database. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215115
Goulabchand R, Roubille C, Montani D, Fesler P, Bourdin A, Malafaye N, Morel J, Arnaud E, Lattuca B, Barateau L, et al. Cardiovascular Events, Sleep Apnoea, and Pulmonary Hypertension in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Data from the French Health Insurance Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):5115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215115
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoulabchand, Radjiv, Camille Roubille, David Montani, Pierre Fesler, Arnaud Bourdin, Nicolas Malafaye, Jacques Morel, Erik Arnaud, Benoit Lattuca, Lucie Barateau, and et al. 2021. "Cardiovascular Events, Sleep Apnoea, and Pulmonary Hypertension in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Data from the French Health Insurance Database" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 5115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215115
APA StyleGoulabchand, R., Roubille, C., Montani, D., Fesler, P., Bourdin, A., Malafaye, N., Morel, J., Arnaud, E., Lattuca, B., Barateau, L., Guilpain, P., & Mura, T. (2021). Cardiovascular Events, Sleep Apnoea, and Pulmonary Hypertension in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Data from the French Health Insurance Database. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 5115. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215115







