Donor Site Morbidity in Unilateral and Bilateral Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis (TMG) Flap Breast Reconstruction: Sensation, Function, Aesthesis and Patient-Reported Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atisha, D.M.; Rushing, C.N.; Samsa, G.P.; Locklear, T.D.; Cox, C.E.; Shelley Hwang, E.; Zenn, M.R.; Pusic, A.L.; Abernethy, A.P. A national snapshot of satisfaction with breast cancer procedures. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, C.; Allen, R.J. The evolution of perforator flap breast reconstruction: Twenty years after the first DIEP flap. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 30, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.; Momeni, A.; von Fritschen, U.; Horch, R.; Stark, G.; Bannasch, H.; Harder, Y.; Heitmann, C.; Kremer, T.; Rieger, U.; et al. Brustrekonstruktion mit freien TRAM oder DIEP Lappen—Was ist zeitgemäßer Standard?: Konsensuspapier der Deutschen Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Mikrochirurgie der peripheren Nerven und Gefäße. Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast. Chir. 2018, 50, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, N.T.; Teotia, S.S. Consecutive 265 Profunda Artery Perforator Flaps: Refinements, Satisfaction, and Functional Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichman, K.E.; Tanna, N.; Broer, P.N.; Wilson, S.; Azhar, H.; Karp, N.S.; Choi, M.; Ahn, C.Y.; Levine, J.P.; Allen, R.J. Microsurgical breast reconstruction in thin patients: The impact of low body mass indices. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2015, 31, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegwart, L.C.; Fischer, S.; Diehm, Y.F.; Heil, J.M.; Hirche, C.; Kneser, U.; Kotsougiani-Fischer, D. The transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap for autologous breast reconstruction: Focus on donor site morbidity. Breast Cancer Tokyo Jpn. 2021, 28, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fansa, H.; Schirmer, S.; Warnecke, I.C.; Cervelli, A.; Frerichs, O. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis muscle flap: A fast and reliable method for breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, T.; Huemer, G.M.; Wechselberger, G. The transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap for breast reconstruction: Guidelines for flap and patient selection. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pülzl, P.; Schoeller, T.; Kleewein, K.; Wechselberger, G. Donor-site morbidity of the transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap in autologous breast reconstruction: Short-term and long-term results. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 233e–242e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craggs, B.; Vanmierlo, B.; Zeltzer, A.; Buyl, R.; Haentjens, P.; Hamdi, M. Donor-site morbidity following harvest of the transverse myocutaneous gracilis flap for breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 682e–691e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegwart, L.C.; Bolbos, A.; Tapking, C.; Seide, S.E.; Diehm, Y.; Fischer, S.; Kneser, U.; Kotsougiani-Fischer, D. Safety and donor site morbidity of the transverse musculocutaneous gracilis (TMG) flap in autologous breast reconstruction-A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 124, 492–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, G.; Tomaselli, F.; Monda, A.; Barone-Adesi, L.; Salgarello, M. Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap donor-site closure with cannula-assisted, limited undermining, and progressive high-tension sutures versus standard abdominoplasty: Complications, sensitivity, and cosmetic outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medical Research Council (MRC). MRC Muscle Scale. Available online: https://mrc.ukri.org/research/facilities-and-resources-for-researchers/mrc-scales/mrc-muscle-scale/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Binkley, J.M.; Stratford, P.W.; Lott, S.A.; Riddle, D.L. The Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS): Scale development, measurement properties, and clinical application. North American Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Research Network. Phys. Ther. 1999, 79, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klassen, A.F.; Cano, S.J.; Alderman, A.; Soldin, M.; Thoma, A.; Robson, S.; Kaur, M.; Papas, A.; Van Laeken, N.; Taylor, V.H.; et al. The BODY-Q: A Patient-Reported Outcome Instrument for Weight Loss and Body Contouring Treatments. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2016, 4, e679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pülzl, P.; Huemer, G.M.; Schoeller, T. Transverse musculocutaneous gracilis flap for treatment of capsular contracture in tertiary breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 74, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaiger, K.; Weitgasser, L.; Mahrhofer, M.; Bachleitner, K.; Abed, S.; Wimbauer, J.; Russe, E.; Schoeller, T.; Wechselberger, G. Age and Overweight Are Not Contraindications for a Breast Reconstruction with a TMG-Flap-A Risk and Complication Analysis of a Retrospective Double Center Study Including 300 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, N.J.; Matloub, H.S.; Kolachalam, R.; Grunert, B.K.; Sanger, J.R. The transverse gracilis musculocutaneous flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1992, 29, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitgasser, L.; Schwaiger, K.; Medved, F.; Hamler, F.; Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. Bilateral Simultaneous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP- and TMG Flaps: Head to Head Comparison, Risk and Complication Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, M.B.; Zhong, T.; Mureau, M.A.M.; Hofer, S.O.P. Tug “O” war: Challenges of transverse upper gracilis (TUG) myocutaneous free flap breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechselberger, G.; Schoeller, T. The transverse myocutaneous gracilis free flap: A valuable tissue source in autologous breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, A.J.M.; Beugels, J.; Lataster, A.; Heuts, E.M.; Rozen, S.M.; Spiegel, A.J.; van der Hulst, R.R.W.J.; Tuinder, S.M.H. Comparing the sensation of common donor site regions for autologous breast reconstruction to that of a healthy breast. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2018, 71, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; LoTempio, M.M.; Granzow, J.W. Inferior Gluteal Perforator Flaps for Breast Reconstruction. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2006, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutinger, M.; Kuzbari, R.; Paternostro-Sluga, T.; Quittan, M.; Zauner-Dungl, A.; Worseg, A.; Todoroff, B.; Holle, J. Donor-site morbidity of the gracilis flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 95, 1240–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemans, S.A.; Kleipool, S.C.; Mulders, M.A.M.; Winkelhagen, J.; Schep, N.W.L.; Goslings, J.C.; Schepers, T. Normative data for the lower extremity functional scale (LEFS). Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, A.; Rassner, M.; Kiefer, J.; Bannasch, H.; Stark, G.B.; Eisenhardt, S.U. Donor-Site Morbidity of Free Muscle and Perforator Flaps: Comparison of the Gracilis Muscle Flap and the Anterolateral Thigh Flap. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2017, 33, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaffidi, M.; Vulpiani, M.C.; Vetrano, M.; Conforti, F.; Marchetti, M.R.; Bonifacino, A.; Marchetti, P.; Saraceni, V.M.; Ferretti, A. Early rehabilitation reduces the onset of complications in the upper limb following breast cancer surgery. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 48, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McNeely, M.L.; Campbell, K.; Ospina, M.; Rowe, B.H.; Dabbs, K.; Klassen, T.P.; Mackey, J.; Courneya, K. Exercise interventions for upper-limb dysfunction due to breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, CD005211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremp, M.; Wettstein, R.; Raffoul, W.; Schaefer, D.J.; Kalbermatten, D.F. Secret scar free gracilis flap. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2012, 28, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenblatt, N.; Gruenherz, L.; Farhadi, J. A systematic review of donor site aesthetic and complications after deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2019, 8, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enajat, M.; Smit, J.M.; Rozen, W.M.; Hartman, E.H.M.; Liss, A.; Kildal, M.; Audolfsson, T.; Acosta, R. Aesthetic refinements and reoperative procedures following 370 consecutive DIEP and SIEA flap breast reconstructions: Important considerations for patient consent. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2010, 34, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.; Klok, J.A.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opsomer, D.; Vyncke, T.; Ryx, M.; Stillaert, F.; Van Landuyt, K.; Blondeel, P. Comparing the Lumbar and SGAP Flaps to the DIEP Flap Using the BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 276e–282e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzano, S.; Marongiu, F.; Wade, R.; Figus, A. Optimizing DIEP Flap Insetting for Immediate Unilateral Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Cohort Study of Patient-Reported Aesthetic Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 261e–270e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

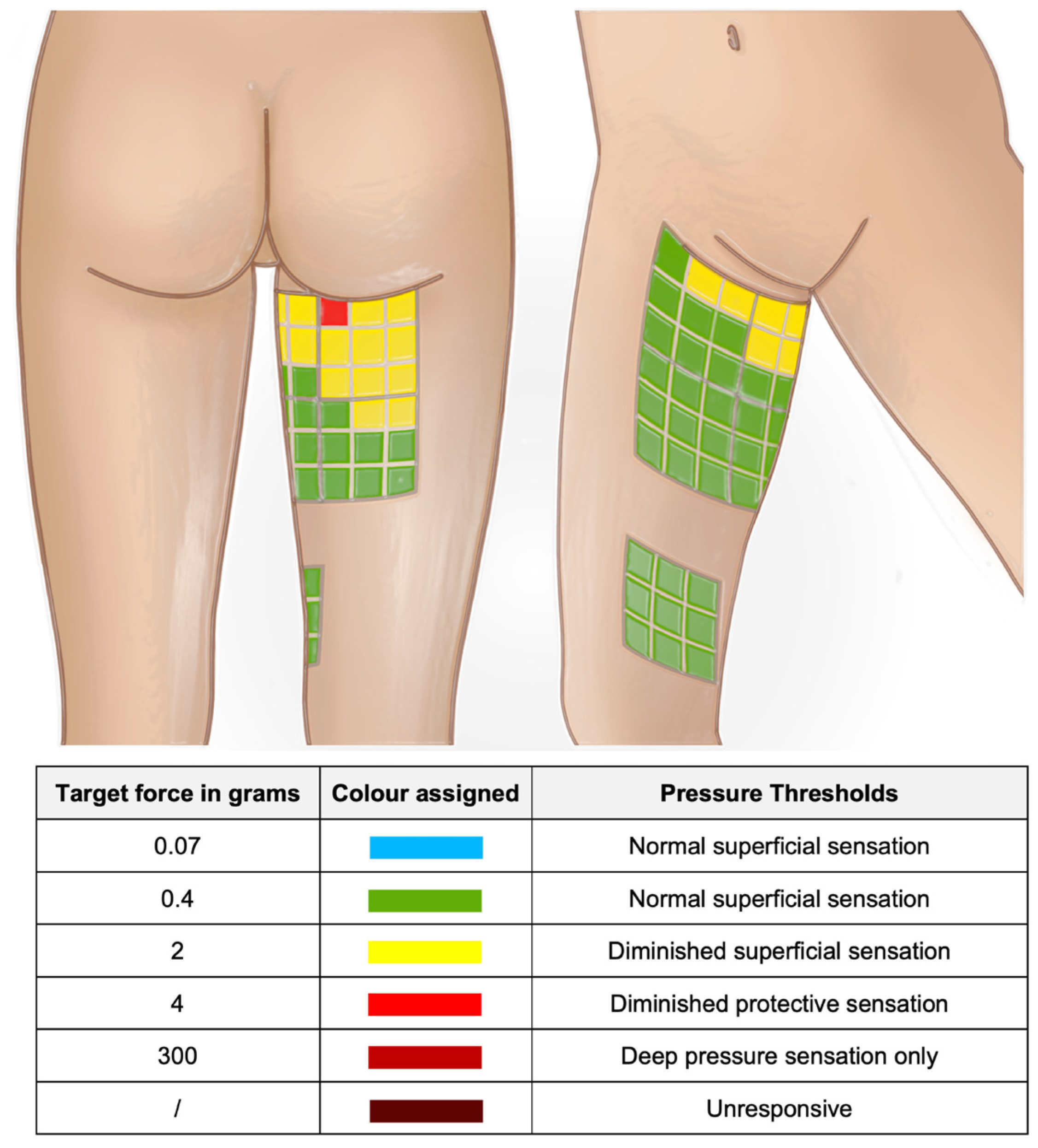

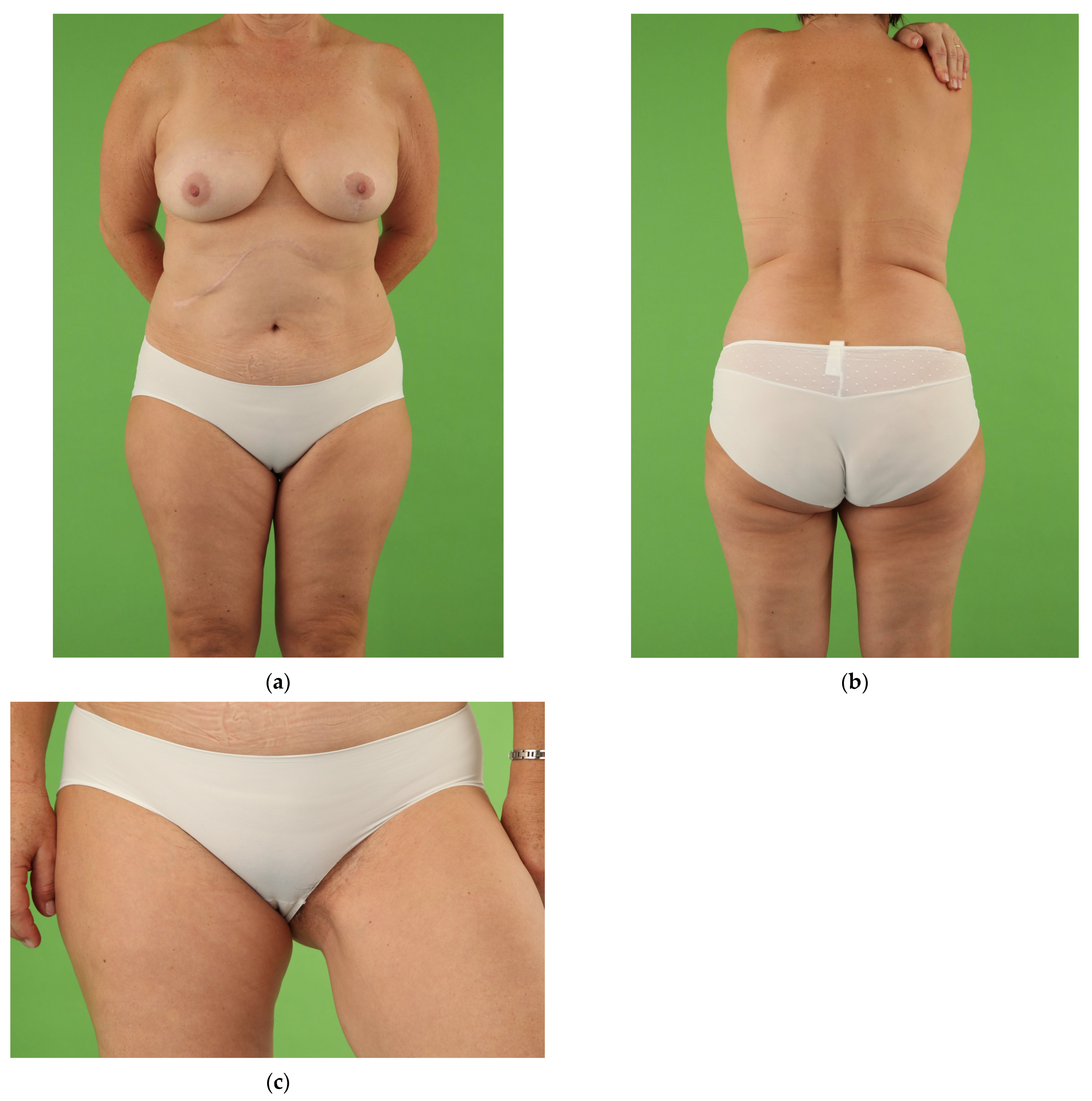
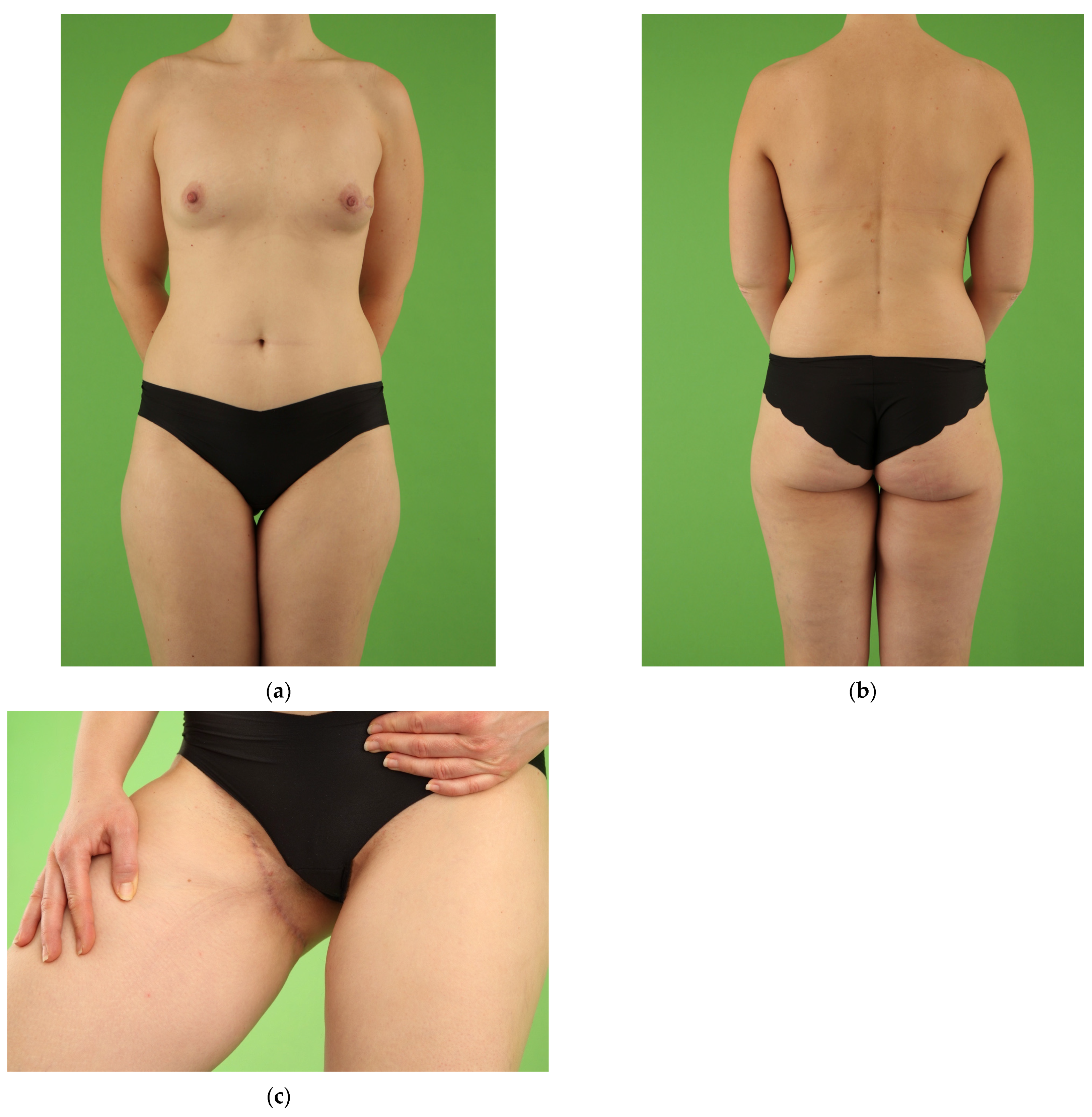
| UL Group | BL Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, N (%) | 17 (44.7%) | 21 (55.3%) | NA |
| TMG flaps, N (%) | 17 (28.8%) | 42 (71.2%) | NA |
| Age (years), Mean (SD) | 50.6 (11.7) | 48.6 (10.4) | 0.566 |
| BMI (kg/m2), Median (R) | 23.5 (20.7–32.8) | 24.7 (19.2–32.3) | 0.994 |
| Breast cancer, N (% of patients) | 14 (82.4%) | 16 (76.2%) | 0.708 |
| Genetic predisposition to breast cancer, N (% of patients) | |||
| Total | 4 (23.5%) | 18 (85.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Breast cancer | 2 (11.7%) | 12 (57.1%) | NA |
| No breast cancer | 2 (11.7%) | 6 (28.6%) | NA |
| Risk Factors, N (% of patients) | |||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.8%) | 0.999 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) | 2 (11.8%) | 4 (19.0%) | 0.672 |
| Active smoker | 3 (17.6%) | 4 (19.0%) | 0.999 |
| Preoperative chemotherapy | 9 (52.9%) | 11 (52.4%) | 0.744 |
| Preoperative radiotherapy | 8 (47.1%) | 11 (52.4%) | 0.744 |
| Indication for reconstruction, N (% of breasts) | |||
| Therapeutic mastectomy | 14 (82.4%) | 16 (38.1%) | 0.002 * |
| Prophylactic mastectomy | 2 (11.8%) | 26 (61.9%) | <0.001 * |
| Breast aplasia | 1 (5.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.288 |
| Follow-up (months), Median ® | 34 (4–117) | 54 (24–144) | 0.081 |
| UL Group | BL Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, N (%) | 17 (44.7%) | 21 (55.3%) | NA |
| Donor sites, N (%) | 17 (28.8%) | 42 (71.2%) | NA |
| Hip adduction strength, N (% donor legs) | |||
| MRC 1–3 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.999 |
| MRC 4 | 3 (17.6%) | 1 (2.4%) | 0.068 |
| MRC 5 | 14 (82.4%) | 41 (97.6%) | 0.068 |
| Hip mobility (degree), Median (R) | |||
| Adduction | 25 (15–35) | 25 (15–40) | 0.903 |
| Abduction | 30 (20–45) | 30 (20–45) | 0.435 |
| Impairment of hip mobility, N (% of patients) | |||
| Adduction | 1 (5.9%) | 1 (4.8%) | 0.999 |
| Abduction | 2 (11.8%) | 2 (9.5%) | 0.999 |
| UL Group | BL Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor sites, N (%) | 17 (28.8%) | 42 (71.2%) | NA |
| Aesthetic refinements donor site, N (% of donor thighs) | |||
| Total | 7 (41.1%) | 10 (23.8%) | 0.182 |
| Scar correction | 1(5.9%) | 5 (11.9%) | 0.662 |
| Dog ear excision | 0 (0%) | 5 (11.9%) | 0.308 |
| Contour alignment donor thigh | 2 (11.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.079 |
| Contralateral thigh alignment | 4 (23.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.005 * |
| Unilateral Group | Bilateral Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor sites, N (%) | 17 (28.8%) | 42 (71.2%) | NA |
| Scar length (cm), Mean (SD) | 21.3 (3.8) | 22.9 (3.1) | 0.891 |
| Scar position to the groin (cm), Median (R) | 1.0 (0.2–3.5) | 1.0 (0.3–4.5) | 0.329 |
| Thigh circumference (cm), Mean (SD) | |||
| Proximal thigh | |||
| Donor leg vs. contralateral leg | |||
| Donor leg vs. donor leg | 59.5 ± 3.9 vs. 61.9 ± 4.6 | 0.118 | |
| Mid-thigh | 59.3 ± 6.3 vs. 60.5 ± 6.4 | 0.558 | |
| Donor leg vs. contralateral leg | |||
| Donor leg vs. donor leg | 55.6 ± 4.6 vs. 56.4 ± 4.6 | 0.597 | |
| Lower thigh | 55.3 ± 4.8 vs. 56.3 ± 4.9 | 0.481 | |
| Donor leg vs. contralateral leg | 0.597 | ||
| Donor leg vs. donor leg | 49.5 ± 4.7 vs. 49.6 ± 4.9 | 48.4 ± 4.3 vs. 49.4 ± 4.4 | 0.453 |
| Unilateral Group | Bilateral Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, N (%) | 17 (44.7%) | 21 (55.3%) | NA |
| LEFS (points), Median (R) | s | 78.5 (47–80) | 0.120 |
| BODY-Q Inner Thigh * (points), Median (R) | 66 (33–100) | 66 (0–100) | 0.487 |
| BODY-Q Scar ** (points), Median (R) | 65 (18–100) | 66 (0–100) | 0.791 |
| BODY-Q Sexuality *** (points), Median (R) | 47 (0–86) | 49 (0–75) | 0.902 |
| Pain, N (%) | |||
| at rest | 0 (0%) | 3 (14.2%) | 0.238 |
| during movement | 6 (35.3%) | 8 (38.1%) | 0.858 |
| Labial spreading, N (%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (4.8%) | 0.576 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siegwart, L.C.; Bolbos, A.; Haug, V.F.; Diehm, Y.F.; Kneser, U.; Kotsougiani-Fischer, D. Donor Site Morbidity in Unilateral and Bilateral Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis (TMG) Flap Breast Reconstruction: Sensation, Function, Aesthesis and Patient-Reported Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215066
Siegwart LC, Bolbos A, Haug VF, Diehm YF, Kneser U, Kotsougiani-Fischer D. Donor Site Morbidity in Unilateral and Bilateral Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis (TMG) Flap Breast Reconstruction: Sensation, Function, Aesthesis and Patient-Reported Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiegwart, Laura Cosima, Anca Bolbos, Valentin Felix Haug, Yannick Fabian Diehm, Ulrich Kneser, and Dimitra Kotsougiani-Fischer. 2021. "Donor Site Morbidity in Unilateral and Bilateral Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis (TMG) Flap Breast Reconstruction: Sensation, Function, Aesthesis and Patient-Reported Outcomes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215066
APA StyleSiegwart, L. C., Bolbos, A., Haug, V. F., Diehm, Y. F., Kneser, U., & Kotsougiani-Fischer, D. (2021). Donor Site Morbidity in Unilateral and Bilateral Transverse Musculocutaneous Gracilis (TMG) Flap Breast Reconstruction: Sensation, Function, Aesthesis and Patient-Reported Outcomes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 5066. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215066







