Comparison of Ultrasound Descriptors of Abnormally Invasive Placenta (AIP) over the Course of the Second and Third Trimester—Is an Increase Verifiable?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
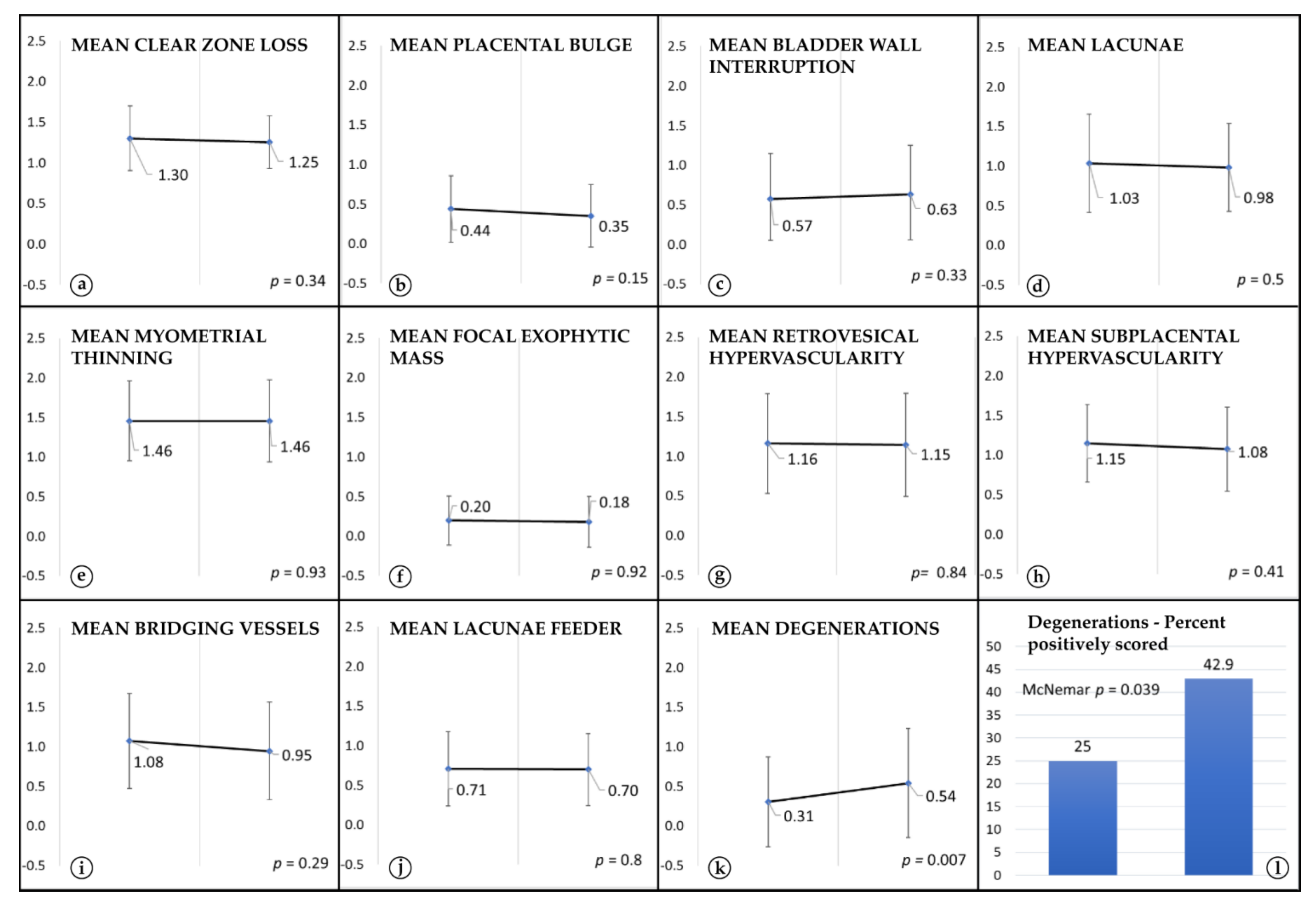
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thurn, L.; Lindqvist, P.G.; Jakobsson, M.; Colmorn, L.B.; Klungsoyr, K.; Bjarnadóttir, R.I.; Tapper, A.M.; Børdahl, P.E.; Gottvall, K.; Petersen, K.B.; et al. Abnormally invasive placenta—Prevalence, risk factors and antenatal suspicion: Results from a large population-based pregnancy cohort study in the Nordic countries. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 123, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Kocherginsky, M.; Hibbard, J.U. Abnormal placentation: Twenty-year analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 192, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauniaux, E.; Chantraine, F.; Silver, R.M.; Langhoff-Roos, J. FIGO Placenta Accreta Diagnosis and Management Expert Consensus Panel. FIGO consensus guidelines on placenta accreta spectrum disorders: Epidemiology. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 140, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantraine, F.; Braun, T.; Gonser, M.; Henrich, W.; Tutschek, B. Prenatal diagnosis of abnormally invasive placenta reduces ma-ternal peripartum hemorrhage and morbidity. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 92, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Alemdar, B.; van Beekhuizen, H.J.; Bertholdt, C.; Braun, T.; Calda, P.; Delorme, P.; Duvekot, J.J.; Gronbeck, L.; Kayem, G.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the manage-ment of abnormally invasive placenta: Recommendations from the International Society for Abnormally Invasive Placenta. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 220, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshkoli, T.; Weintraub, A.Y.; Sergienko, R.; Sheiner, E. Placenta accreta: Risk factors, perinatal outcomes, and consequences for subsequent births. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 208, 219.e1–219.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauniaux, E.; Collins, S.L.; Jurkovic, D.; Burton, G. Accreta placentation: A systematic review of prenatal ultrasound imaging and grading of villous invasiveness. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 215, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfirevic, Z.; Tang, A.-W.; Collins, S.L.; Robson, S.C.; Palacios-Jaraquemada, J. Ad-hoc International AIP Expert Group. Pro forma for ultrasound reporting in suspected abnormally invasive placenta (AIP): An international consensus. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 47, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, S.L.; Ashcroft, A.; Braun, T.; Calda, P.; Langhoff-Roos, J.; Morel, O.; Stefanovic, V.; Tutschek, B.; Chantraine, F. European Working Group on Abnormally Invasive Placenta (EW-AIP) Proposal for standardized ultrasound descriptors of abnormally invasive placenta (AIP). Proposal for standardized ultrasound descriptors of abnormally invasive placenta (AIP). Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 47, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Antonio, F.; Palacios-Jaraquemada, J.; Timor-Trisch, I.; Cali, G. Placenta accreta spectrum disorders: Prenatal diagnosis still lacks clinical correlation. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2018, 97, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jauniaux, E.R.M.; Alfirevic, Z.; Bhide, A.G.; Belfort, M.A.; Burton, G.J.; Collins, S.L.; Dornan, S.; Jurkovic, D.; Kayem, G.; Silver, R.; et al. Placenta Praevia and Placenta Accreta: Diagnosis and Management. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 126, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailit, J.L.; Grobman, W.A.; Rice, M.M.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.; Varner, M.; Leveno, K.J.; Iams, J.D.; Tita, A.; Saade, G.; et al. Morbidly Adherent Placenta Treatments and Outcomes. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buca, D.; Liberati, M.; Cali, G.; Forlani, F.; Caisutti, C.; Flacco, M.E.; Manzoli, L.; Familiari, A.; Scambia, G.; D’Antonio, F.; et al. Influence of prenatal diagnosis of abnormally invasive placenta on maternal outcome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, K.E.; Sellers, S.; Spark, P.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; Brocklehurst, P.; Knight, M. The management and outcomes of placenta accreta, increta, and percreta in the UK: A population-based descriptive study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2014, 121, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidesko, S.; Wainstock, T.; Sheiner, E.; Pariente, G. Long-Term Infectious Morbidity of Premature Infants: Is There a Critical Threshold? J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlembach, D.; Helmer, H.; Henrich, W.; Von Heymann, C.; Kainer, F.; Korte, W.; Kühnert, M.; Lier, H.; Maul, H.; Rath, W.; et al. Peripartum Haemorrhage, Diagnosis and Therapy. Guideline of the DGGG, OEGGG and SGGG (S2k Level, AWMF Registry No. 015/063, March 2016). Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2018, 78, 382–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jauniaux, E.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Langhoff-Roos, J.; Fox, K.A.; Collins, S.; Duncombe, G.; Klaritsch, P.; Chantraine, F.; Kingdom, J.; FIGO Placenta Accreta Diagnosis and Management Expert Consensus Panel; et al. FIGO classification for the clinical diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorders. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 146, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, M.; Vines, S.; Aquilina, J.; Wathen, N.; Harrington, K. Are Placental Lakes of any Clinical Significance? Placenta 2002, 23, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizot, M.L.; Schultz, R.; Nomura, R.M.Y.; Zugaib, M. Placental lakes on sonographic examination: Correlation with obstetric outcome and pathologic findings. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2005, 33, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauniaux, E.; Collins, S.; Burton, G.J. Placenta accreta spectrum: Pathophysiology and evidence-based anatomy for prenatal ul-trasound imaging. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 218, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedenhofen, B.; Musch, J. Cocor: A Comprehensive Solution for the Statistical Comparison of Correlations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauniaux, E.; Bhide, A.; Kennedy, A.; Woodward, P.; Hubinont, C.; Collins, S. FIGO consensus guidelines on placenta accreta spectrum disorders: Prenatal diagnosis and screening. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 140, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Tsui, W.-H. Unusual imaging findings of placenta accreta resulting in early hysterectomy in first tri-mester-Two case reports. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 55, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rac, M.W.F.; Moschos, E.; Wells, C.E.; McIntire, D.D.; Dashe, J.S.; Twickler, D.M. Sonographic Findings of Morbidly Adherent Placenta in the First Trimester. J. Ultrasound Med. 2015, 35, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Antonio, F.; Timor-Tritsch, I.E.; Palacios-Jaraquemada, J.; Monteagudo, A.; Buca, D.; Forlani, F.; Minneci, G.; Foti, F.; Manzoli, L.; Liberati, M.; et al. First-trimester detection of abnormally invasive placenta in high-risk women: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, R.M.; Barbour, K.D. Placenta accreta spectrum: Accreta, increta, and percreta. Obstet. Gynecol Clin. N. Am. 2015, 42, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalubinski, K.M.; Pils, S.; Klein, K.; Seemann, R.; Speiser, P.; Langer, M.; Ott, J. Prenatal sonography can predict degree of placental invasion. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antonio, F.; Iacovella, C.; Bhide, A. Prenatal identification of invasive placentation using ultrasound: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 42, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comstock, C.H.; Love, J.J.; Bronsteen, R.A.; Lee, W.; Vettraino, I.M.; Huang, R.R.; Lorenz, R.P. Sonographic detection of placenta accreta in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calì, G.; Timor-Trisch, I.E.; Palacios-Jaraquemada, J.; Monteaugudo, A.; Forlani, F.; Minneci, G.; Foti, F.; Buca, D.; Familiari, A.; Scambia, G.; et al. Changes in ultrasonography indicators of abnormally invasive placenta during pregnancy. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 140, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyall, F. Mechanisms regulating cytotrophoblast invasion in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2006, 46, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Calculated Scores & Values |
| “Severity of appearance”—mean estimate of severity for each US sign |
| “US-Score”—mean severity & number of positive signs per patient |
| Mean number of positively scored signs |
| “Probability-Score”—the reviewers subjective estimate of AIP probability & extent |
| Ultrasound Signs for US-Score Calculation and Reporting of Positively Scored Signs |
| Loss of clearzone |
| Myometrial thinning |
| Abnormal placental lacunae |
| Placental bulge |
| Focal exophytic mass |
| Uterovesical hypervascularity |
| Subplacental hypervascularity |
| Bridging vessels |
| Placental lacunae feeder vessels |
| Estimates of AIP Probability & Extent |
| Raters’ estimate of AIP probability |
| Raters’ estimate of AIP extent |
| Sample Size n = 37 | Mean | 95% CI for Mean | Median | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal age yrs | 33.8 | 32.1–35.5 | 34.4 | 23.7 | 43.2 |
| Delivery week | 34.2 | 33.3–35.0 | 34.7 | 26.3 | 37.4 |
| Delivery before week 37 + 0 n (%) | 34 (91.9) | ||||
| Delivery before week 34 + 0 n (%) | 11 (29.7) | ||||
| Final diagnosis | |||||
| placenta accreta n (%) | 10 (27.0) | ||||
| placenta increta n (%) | 8 (21.6) | ||||
| placenta percreta n (%) | 19 (54.4) | ||||
| Week of pregnancy | |||||
| US-Scan 1 | 24.6 | 23.1–26.1 | 25.4 | 13.4 | 32.1 |
| US-Scan 2 | 32.3 | 31.5–33.2 | 33.1 | 25.1 | 35.4 |
| Mean Ultrasound-Score | Mean Number of Positive Signs | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| US-Scan 1 | US-Scan 2 | US-Scan | US-Scan | |||||||
| Rater | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p |
| 1 | 8.3 | 4.18 | 8.6 | 3.84 | 0.35 | 6.3 | 2.50 | 6.5 | 2.18 | 0.35 |
| 2 | 8.5 | 4.74 | 8.4 | 4.79 | 0.19 | 5.9 | 2.68 | 5.9 | 2.85 | 0.19 |
| 3 | 8.1 | 4.77 | 7.6 | 5.04 | 0.41 | 5.7 | 2.76 | 5.3 | 3.04 | 0.33 |
| 4 | 8.2 | 3.20 | 8.8 | 3.62 | 0.54 | 6.2 | 1.99 | 6.4 | 2.06 | 0.52 |
| 5 | 9.3 | 5.22 | 8.9 | 5.21 | 0.50 | 6.2 | 2.67 | 5.9 | 2.56 | 0.433 |
| Mean of 5 Raters | 8.5 | 3.66 | 8.4 | 3.89 | 0.79 | 6.1 | 2.06 | 5.9 | 2.16 | 0.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorczyca, M.E.; Springer, S.; Pateisky, P.; Ott, J.; Ulm, B.; Chalubinski, K. Comparison of Ultrasound Descriptors of Abnormally Invasive Placenta (AIP) over the Course of the Second and Third Trimester—Is an Increase Verifiable? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214960
Gorczyca ME, Springer S, Pateisky P, Ott J, Ulm B, Chalubinski K. Comparison of Ultrasound Descriptors of Abnormally Invasive Placenta (AIP) over the Course of the Second and Third Trimester—Is an Increase Verifiable? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(21):4960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214960
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorczyca, Monika E., Stephanie Springer, Petra Pateisky, Johannes Ott, Barbara Ulm, and Kinga Chalubinski. 2021. "Comparison of Ultrasound Descriptors of Abnormally Invasive Placenta (AIP) over the Course of the Second and Third Trimester—Is an Increase Verifiable?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 21: 4960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214960
APA StyleGorczyca, M. E., Springer, S., Pateisky, P., Ott, J., Ulm, B., & Chalubinski, K. (2021). Comparison of Ultrasound Descriptors of Abnormally Invasive Placenta (AIP) over the Course of the Second and Third Trimester—Is an Increase Verifiable? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(21), 4960. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10214960







