High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Imaging Protocol and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Aneurysm Characteristics
3.2. Aneurysm Wall Enhancement and Relevant Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieuwkamp, D.J.; Setz, L.E.; Algra, A.; Linn, F.H.H.; de Rooij, N.K.; Rinkel, G.J. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, G.J.; Algra, A. Long-term outcomes of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshekhlee, A.; Mehta, S.; Edgell, R.C.; Vora, N.; Feen, E.; Mohammadi, A.; Kale, S.P.; Cruz-Flores, S. Hospital Mortality and Complications of Electively Clipped or Coiled Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm. Stroke 2010, 41, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greving, J.P.; Wermer, M.J.; Brown, R.D.; Morita, A.; Juvela, S.; Yonekura, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Torner, J.C.; Nakayama, T.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, C.; Jonzzon, S.; Winkler, E.A.; Raper, D.M.; Lawton, M.T.; Abla, A.A. Small Aneurysms with Low PHASES Scores Account for Most Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Cases. World Neurosurg. 2020, 139, e580–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.T.; Wendt, B.H.; Monarch, B.T.; Beaty, N.; Lin, L.-M.; Huang, J.; Coon, A.L.; Tamargo, R.J.; Colby, G. Small Aneurysms Account for the Majority and Increasing Percentage of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A 25-Year, Single Institution Study. Neurosurgery 2017, 83, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, D.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Qiao, Y.; Hess, C.P.; Hui, F.; Matouk, C.C.; Johnson, M.; Daemen, M.J.; Vossough, A.; Edjlali, M.; et al. Intracranial Vessel Wall MRI: Principles and Expert Consensus Recommendations of the American Society of Neuroradiology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 38, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edjlali, M.; Gentric, J.C.; Régent-Rodriguez, C.; Trystram, D.; Hassen, W.B.; Lion, S.; Nataf, F.; Raymond, J.; Wieben, O.; Turski, P.; et al. Does aneurysmal wall enhancement on vessel wall MRI help to distinguish stable from unstable intracranial aneurysms? Stroke 2014, 45, 3704–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edjlali, M.; Guédon, A.; Ben Hassen, W.; Boulouis, G.; Benzakoun, J.; Rodriguez-Régent, C.; Trystram, D.; Nataf, F.; Meder, J.-F.; Turski, P.; et al. Circumferential Thick Enhancement at Vessel Wall MRI Has High Specificity for Intracranial Aneurysm Instability. Radiology 2018, 289, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.-D.; Guan, S.-C.; Zhang, H.-Q. Wall enhancement on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging may predict an unsteady state of an intracranial saccular aneurysm. Neuroradiology 2016, 58, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebers, D.O.; Whisnant, J.P.; Huston, J.; Meissner, I.; Brown, R.D.; Piepgras, D.G.; Forbes, G.S.; Thielen, K.; Nichols, D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, F.; Morita, A.; Tominari, S.; Nakayama, T.; Shiokawa, Y.; Date, I.; Nozaki, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Kayama, T.; Arai, H. Rupture risk of small unruptured cerebral aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 132, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushige, T.; Shimonaga, K.; Mizoue, T.; Hosogai, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Ono, C.; Ishii, D.; Sakamoto, S.; Kurisu, K. Focal Aneurysm Wall Enhancement on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indicates Intraluminal Thrombus and the Rupture Point. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, e578–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; von der Brelie, C.; Trick, D.; Riedel, C.; Lindner, T.; Madjidyar, J.; Jansen, O.; Synowitz, M.; Flüh, C. Vessel Wall Enhancement in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: An Indicator for Higher Risk of Rupture? High-Resolution MR Imaging and Correlated Histologic Findings. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.S.; Zanaty, M.; Nakagawa, D.; Kung, D.K.; Jabbour, P.; Samaniego, E.A.; Hasan, D. Magnetic Resonance Vessel Wall Imaging in Human Intracranial Aneurysms. Stroke 2019, 50, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, K.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; An, Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, P.; Li, P.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Validation of Wall Enhancement as a New Imaging Biomarker of Unruptured Cerebral Aneurysm. Stroke 2019, 50, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulamo, R.; Frosen, J.; Hernesniemi, J.; Niemelä, M. Inflammatory changes in the aneurysm wall: A review. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2010, 2, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.; Kirino, T.; Hashi, K.; Aoki, N.; Fukuhara, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Nakayama, T.; Sakai, M.; Teramoto, A.; Tominari, S.; et al. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N. Eng. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2474–2482. [Google Scholar]
- Backes, D.; Hendrikse, J.; van der Schaaf, I.; Algra, A.; Lindgren, A.; Verweij, B.H.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Vergouwen, M.D.I. Determinants of Gadolinium-Enhancement of the Aneurysm Wall in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2017, 83, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qi, H.; Liu, A.; Lv, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Lu, B.; Lv, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Relationship between aneurysm wall enhancement and conventional risk factors in patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A black-blood MRI study. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2016, 22, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Karmonik, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J. Relationship Between Aneurysm Wall Enhancement in Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Rupture Risk of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2018, 84, E385–E391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa, J.A.; Zanaty, M.; Ishii, D.; Lu, Y.; Kung, D.K.; Starke, R.M.; Torner, J.C.; Jabbour, P.M.; Samaniego, E.A.; Hasan, D.M. Decreased contrast enhancement on high-resolution vessel wall imaging of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients taking aspirin. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, B.; Amidei, C.; Kongable, G.; Findlay, J.M.; Kassell, N.F.; Kelly, J.; Dai, L.; Karrison, T.G. The aspect ratio (dome/neck) of ruptured and unruptured aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindgren, A.E.; Koivisto, T.; Björkman, J.; Fraunberg, M.V.U.Z.; Helin, K.; Jääskeläinen, J.E.; Frösen, J. Irregular Shape of Intracranial Aneurysm Indicates Rupture Risk Irrespective of Size in a Population-Based Cohort. Stroke 2016, 47, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebral, J.; Sheridan, M.; Putman, C. Hemodynamics and Bleb Formation in Intracranial Aneurysms. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 31, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, N.; Flüh, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Voß, S.; Hille, G.; Trick, D.; Wodarg, F.; Synowitz, M.; Jansen, O.; Berg, P. Multimodal validation of focal enhancement in intracranial aneurysms as a surrogate marker for aneurysm instability. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.O.; Arana, V.T.; Rubbert, C.; Cornelius, J.F.; Fischer, I.; Bostelmann, R.; Mijderwijk, H.-J.; Turowski, B.; Steiger, H.-J.; May, R.; et al. Association between aneurysm hemodynamics and wall enhancement on 3D vessel wall MRI. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Qi, T.; He, S.; Li, Z.; Ou, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Huang, Z.; Liang, F. Low Wall Shear Stress Is Associated with Local Aneurysm Wall Enhancement on High-Resolution MR Vessel Wall Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebral, J.; Detmer, F.; Chung, B.J.; Choque-Velasquez, J.; Rezai, B.; Lehto, H.; Tulamo, R.; Hernesniemi, J.; Niemela, M.; Yu, A.; et al. Local Hemodynamic Conditions Associated with Focal Changes in the Intracranial Aneurysm Wall. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 510–516. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Guan, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Cheng, J. Clinical Significance of Circumferential Aneurysmal Wall Enhancement in Symptomatic Patients with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: A High-resolution MRI Study. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2017, 28, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.B.; Watase, H.; Sun, J.; Hippe, D.S.; Kim, L.; Levitt, M.; Sekhar, L.; Balu, N.; Hatsukami, T.; Yuan, C.; et al. Intracranial aneurysms at higher clinical risk for rupture demonstrate increased wall enhancement and thinning on multicontrast 3D vessel wall MRI. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matouk, C.C.; Mandell, D.M.; Günel, M.; Bulsara, K.R.; Malhotra, A.; Heber, R.; Johnson, M.H.; Mikulis, D.J.; Minja, F. Vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging identifies the site of rupture in patients with multiple intracranial aneurysms: Proof of principle. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergouwen, M.; Backes, D.; van der Schaaf, I.; Hendrikse, J.; Kleinloog, R.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G.J. Gadolinium Enhancement of the Aneurysm Wall in Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Aneurysm Instability: A Follow-Up Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Toossi, S.; Eisenmenger, L.; Faraji, F.; Ballweber, M.K.; Josephson, S.A.; Haraldsson, H.; Zhu, C.; Ahn, S.; Laub, G.; et al. Visualizing wall enhancement over time in unruptured intracranial aneurysms using 3D vessel wall imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, A.; Lehman, V.; Lanzino, G.; Brinjikji, W. Lack of Baseline Intracranial Aneurysm Wall Enhancement Predicts Future Stability: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Allinec, V.; Chatel, S.; Karakachoff, M.; Bourcereau, E.; Lamoureux, Z.; Gaignard, A.; Autrusseau, F.; Jouan, S.; Vion, A.-C.; Loirand, G.; et al. Prediction of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm Evolution: The UCAN Project. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa, J.A.; Zanaty, M.; Osorno-Cruz, C.; Ishii, D.; Bathla, G.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Hasan, D.M.; Samaniego, E.A. Objective quantification of contrast enhancement of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A high-resolution vessel wall imaging validation study. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodaka, S.; Endo, H.; Niizuma, K.; Fujimura, M.; Inoue, T.; Sato, K.; Sugiyama, S.-I.; Tominaga, T. Quantitative Assessment of Circumferential Enhancement along the Wall of Cerebral Aneurysms Using MR Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, B.M.W.; Leemans, E.L.; Coolen, B.F.; Peper, E.S.; Berg, R.V.D.; Marquering, H.A.; Slump, C.H.; Majoie, C.B.L.M. Insufficient slow-flow suppression mimicking aneurysm wall enhancement in magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging: A phantom study. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, V.; Brinjikji, W. Vessel Wall Imaging of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: Ready for Prime Time? Not so Fast! Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, E26–E29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.V.D. Intracranial aneurysm wall enhancement: Fact or fiction? Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
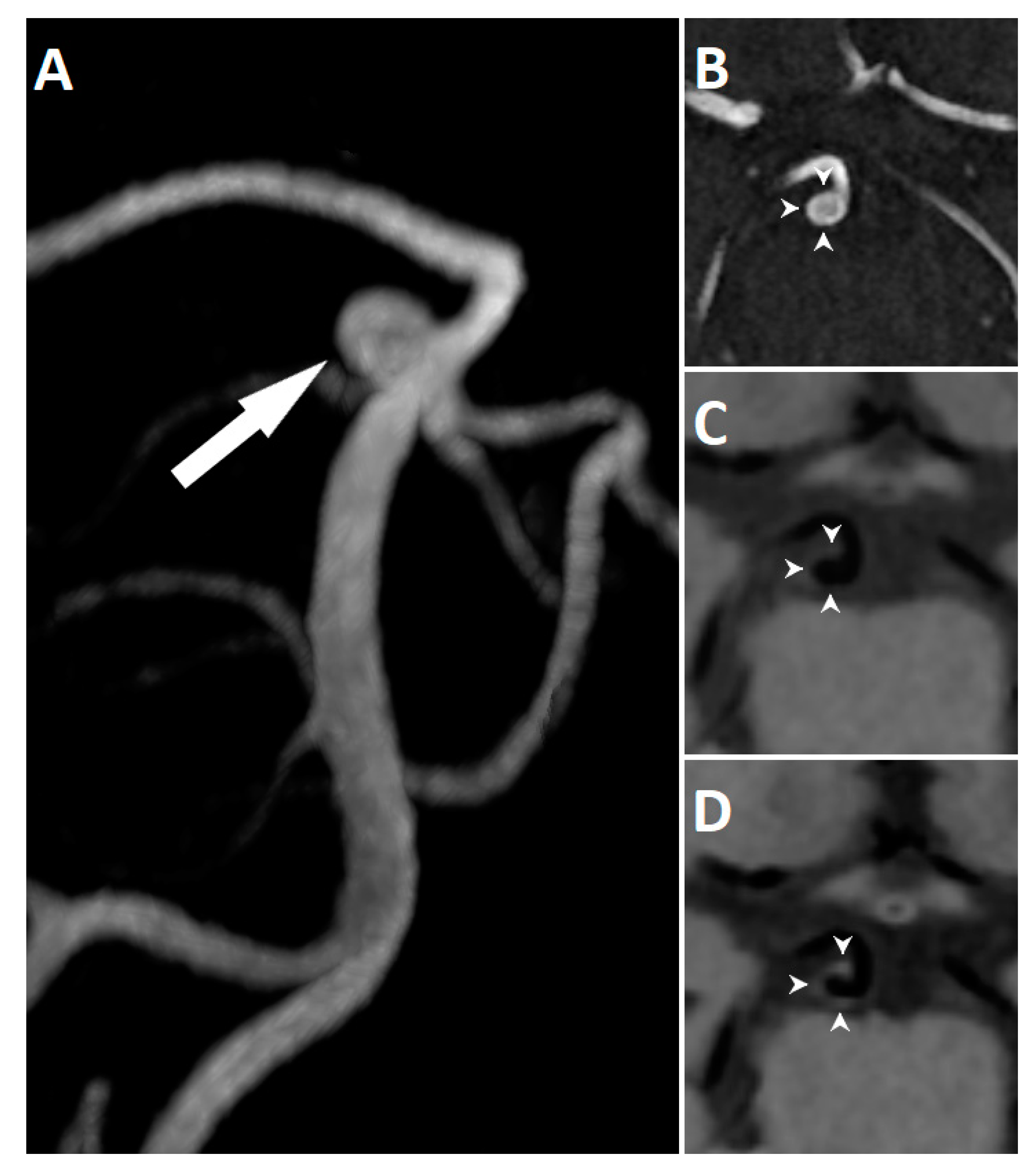
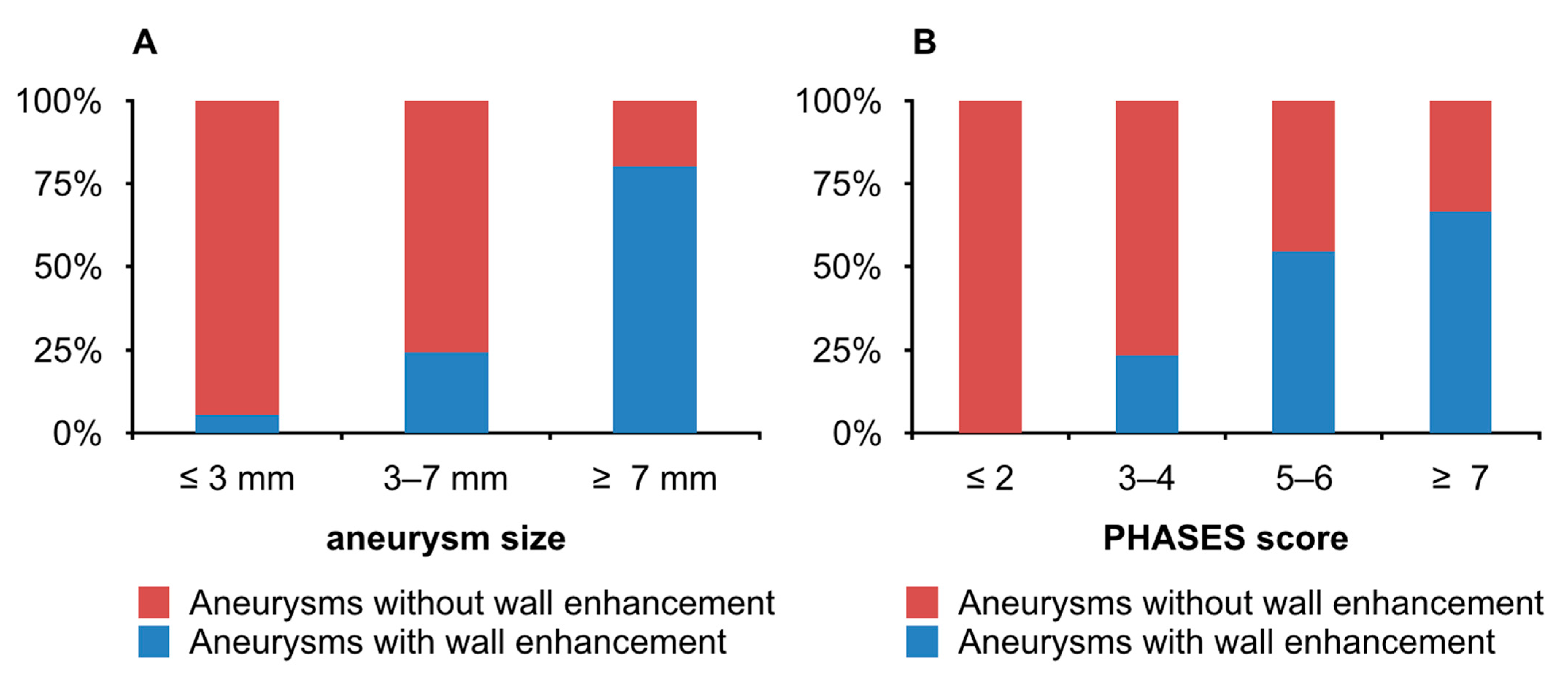
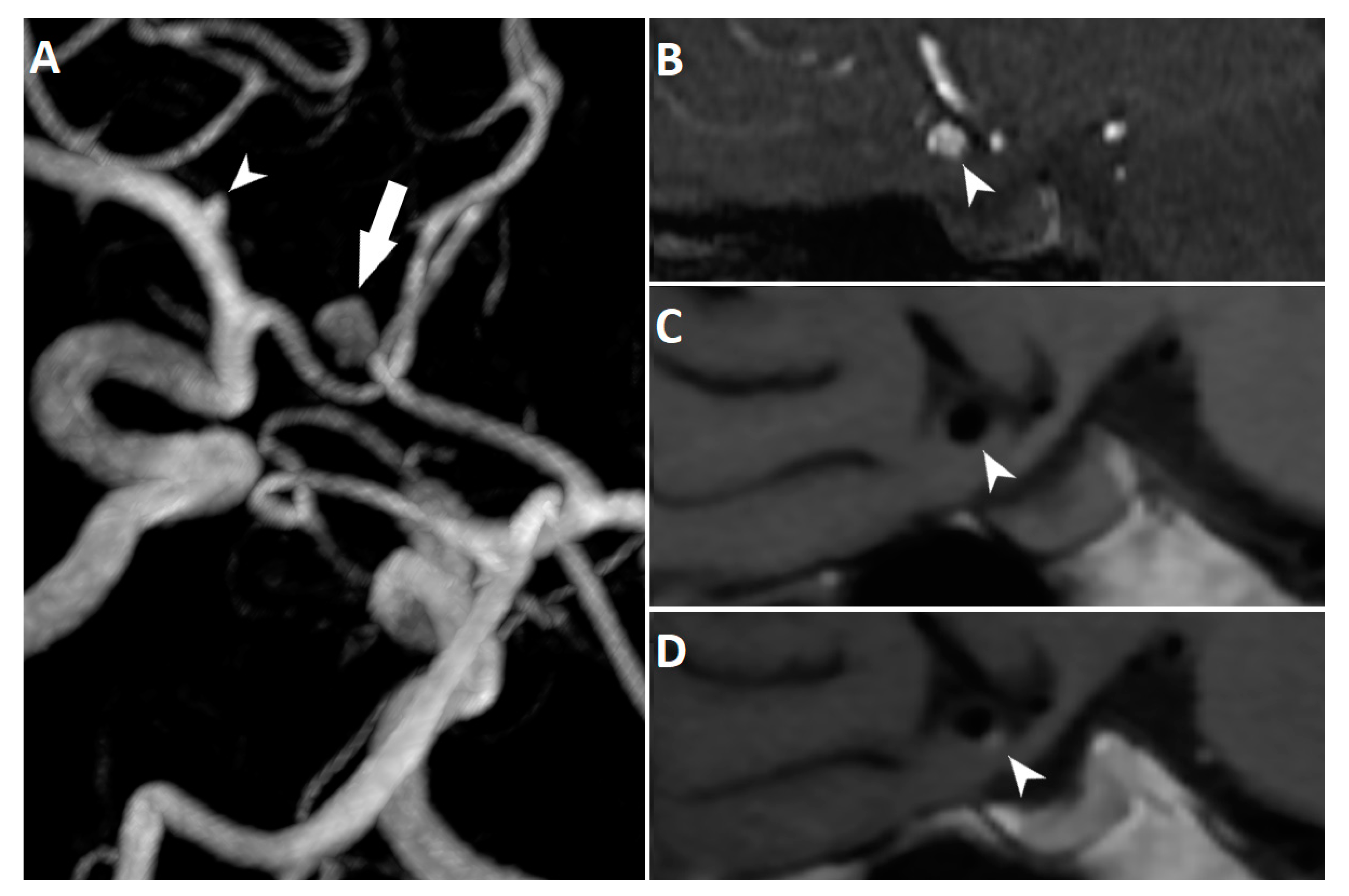
| Variable | AWE (n = 15) | Non-AWE (n = 49) | t/χ2 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age: M (SD) | 64.80 (6.03) | 58.22 (13.73) | −2.63 a | 0.011 |
| Sex: f/m | 15/0 | 40/9 | 1.87 b | 0.172 |
| Family history of IA: yes/no | 2/13 | 11/38 | 0.16 b | 0.688 |
| Prior SAH from another aneurysm: yes/no | 4/11 | 2/47 | 4.49 b | 0.034 |
| Smoking status: | ||||
| Current smoker: yes/no | 6/9 | 10/39 | 1.42 b | 0.233 |
| Previous smoker: yes/no | 7/8 | 17/32 | 0.28 b | 0.594 |
| Never smoked: yes/no | 2/13 | 22/27 | 3.63 b | 0.057 |
| Hypertension: yes/no | 10/5 | 24/25 | 0.82 b | 0.365 |
| Diabetes mellitus: yes/no | 1/14 | 8/41 | 0.27 b | 0.605 |
| Daily aspirin intake: yes/no | 2/13 | 12/37 | 0.31 b | 0.577 |
| PHASES: M (SD) | 5.13 (1.73) | 2.61 (1.88) | −4.63 a | 0.000 |
| PHASES: ≤ 2/3–4/5–6/≥ 7 | 0 */7/6 */2 | 20 */23/5 */1 | 15.18 c | 0.002 |
| Size: M (SD) | 5.79 (1.83) | 4.24 (1.36) | −3.55 a | 0.001 |
| Size: ≤ 3 mm/3–7 mm/≥ 7 mm | 1 */10/4 * | 17 */31/1 * | 12.14 c | 0.002 |
| Dome-to-neck ratio: M (SD) | 2.25 (0.83) | 1.72 (0.76) | −2.31 a | 0.024 |
| Dome-to-neck ratio: ≤ 2/> 2 | 6/9 | 39/10 | 6.83 b | 0.009 |
| Irregularity: yes/no | 8/7 | 6/43 | 9.07 b | 0.003 |
| Location: anterior/posterior circulation | 11/4 | 43/6 | 0.88 b | 0.347 |
| Multiple aneurysms: yes/no | 11/4 | 24/25 | 1.85 b | 0.173 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHASES | 2.34 | 1.33–4.16 | 0.003 |
| Irregularity | 7.95 | 1.54–41.01 | 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zwarzany, Ł.; Tyburski, E.; Poncyljusz, W. High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020225
Zwarzany Ł, Tyburski E, Poncyljusz W. High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleZwarzany, Łukasz, Ernest Tyburski, and Wojciech Poncyljusz. 2021. "High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020225
APA StyleZwarzany, Ł., Tyburski, E., & Poncyljusz, W. (2021). High-Resolution Vessel Wall Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Small Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10020225





