Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Results
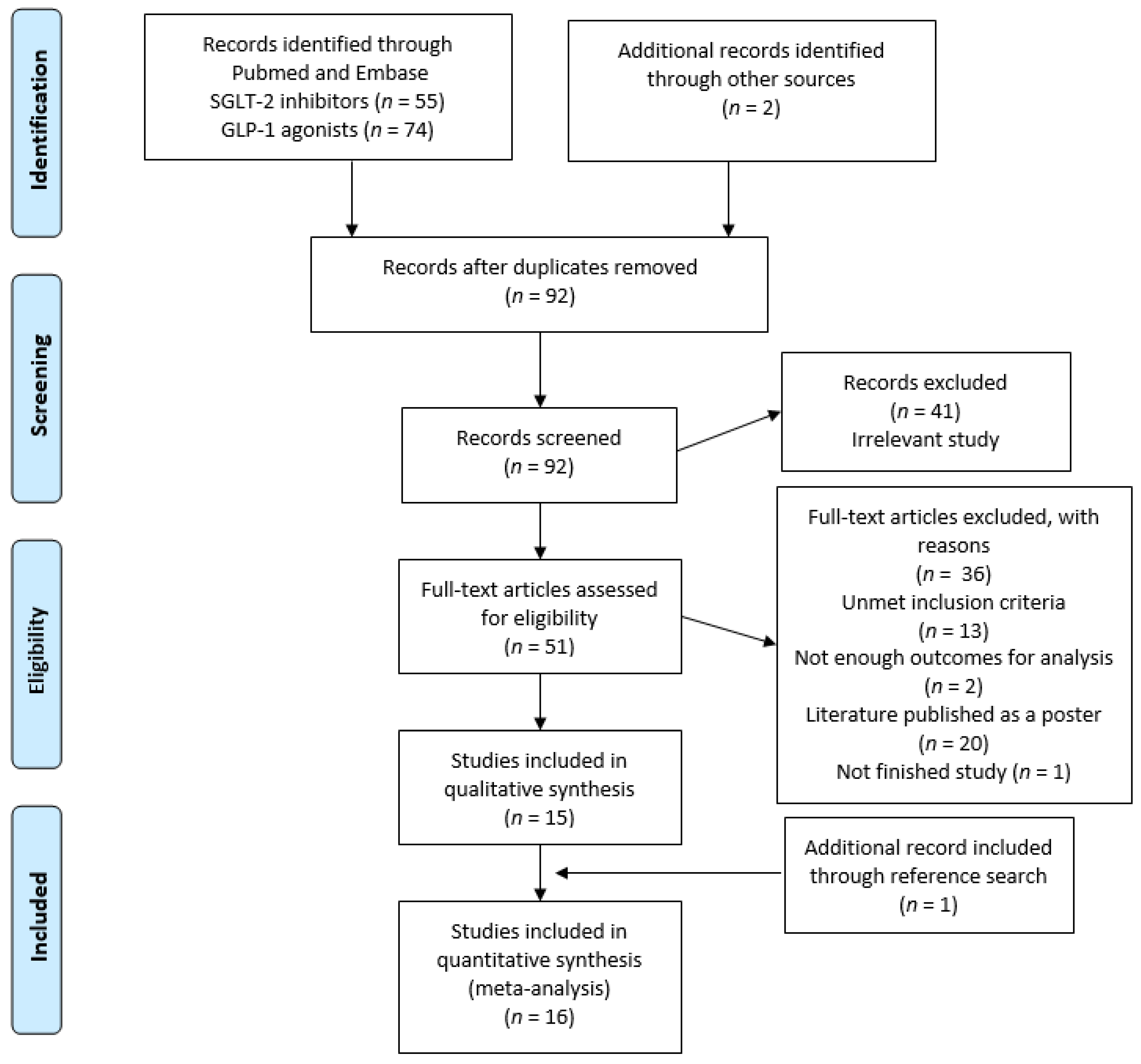
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Description
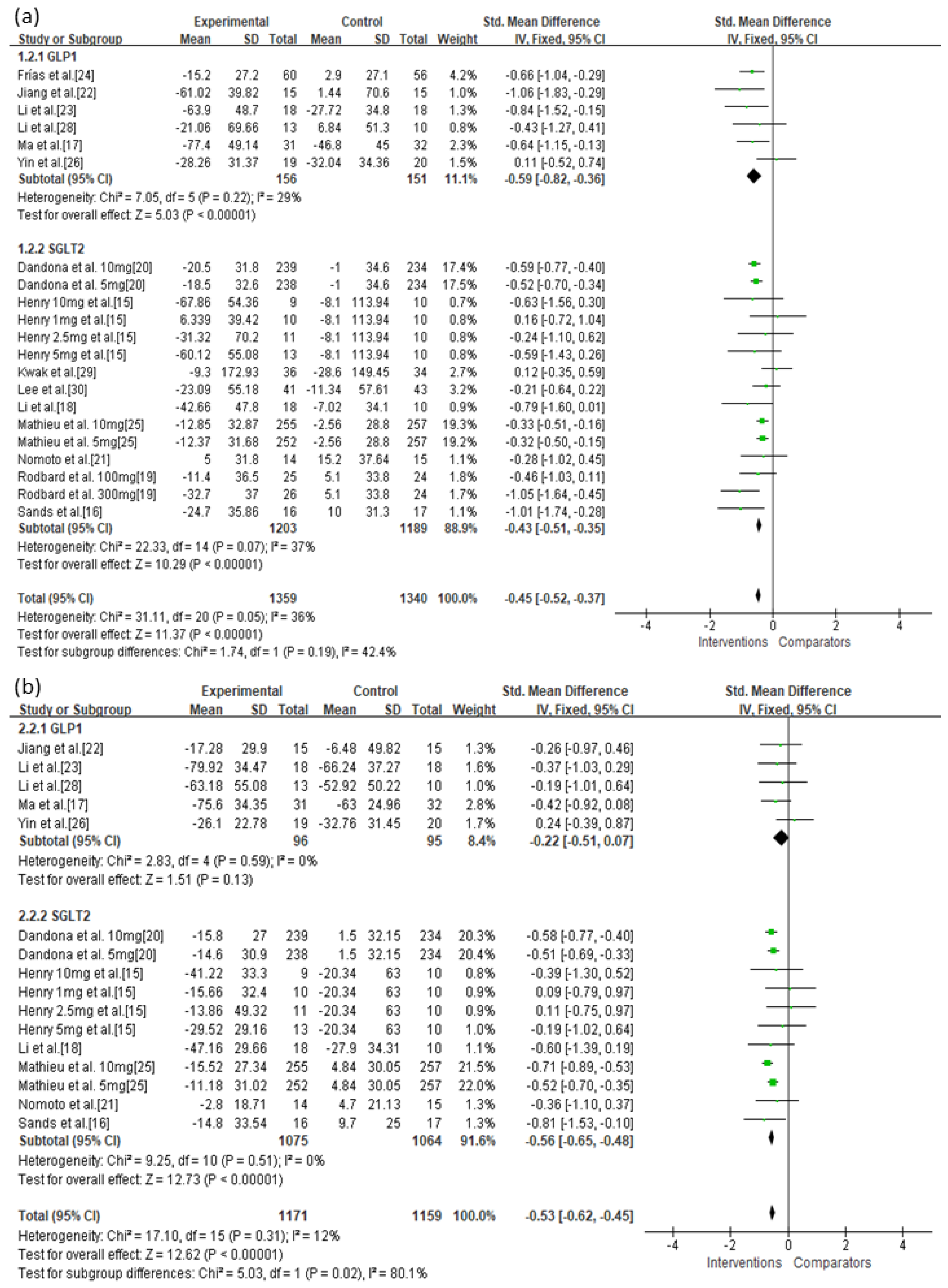
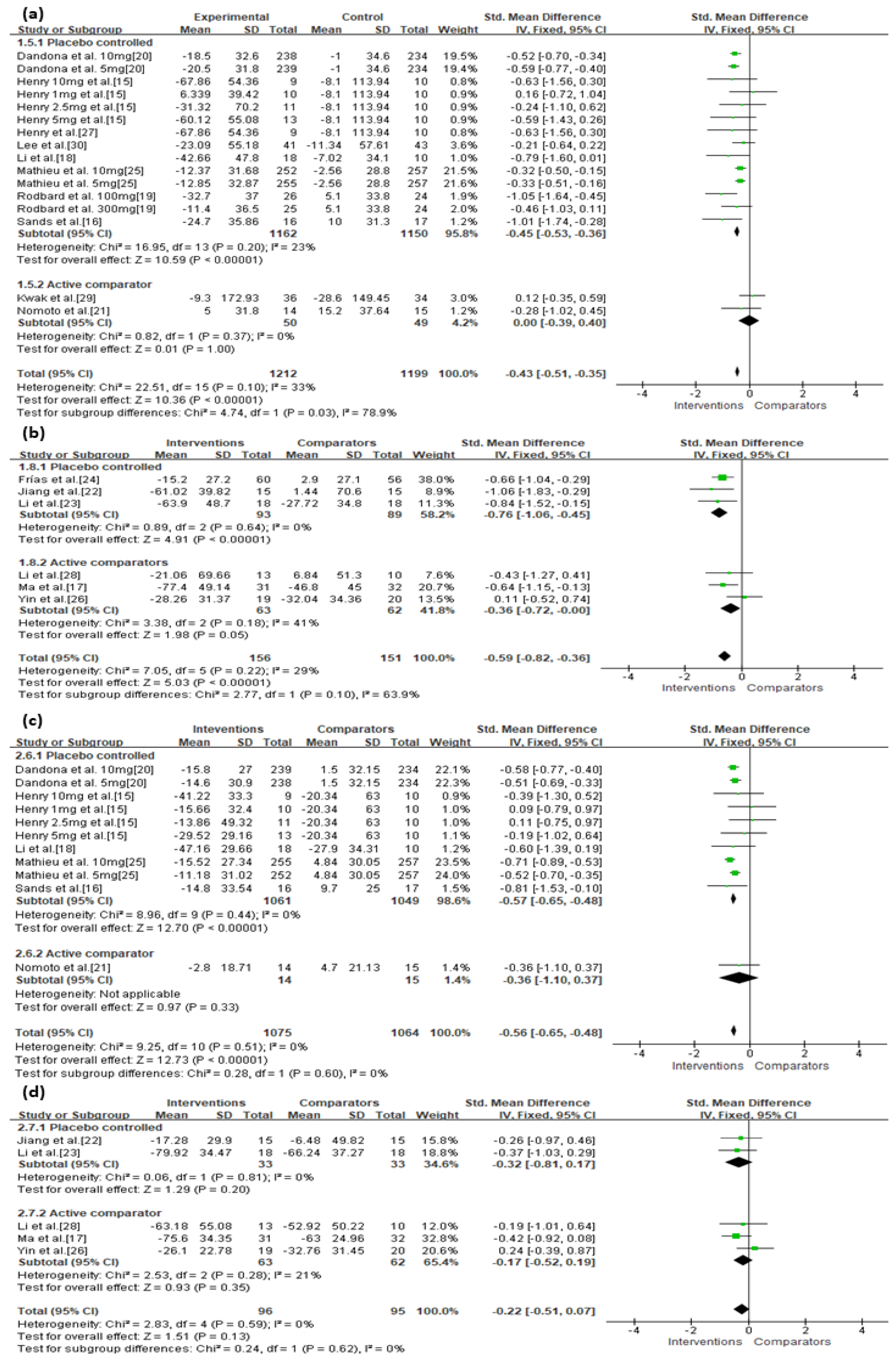
3.3. Primary Outcomes
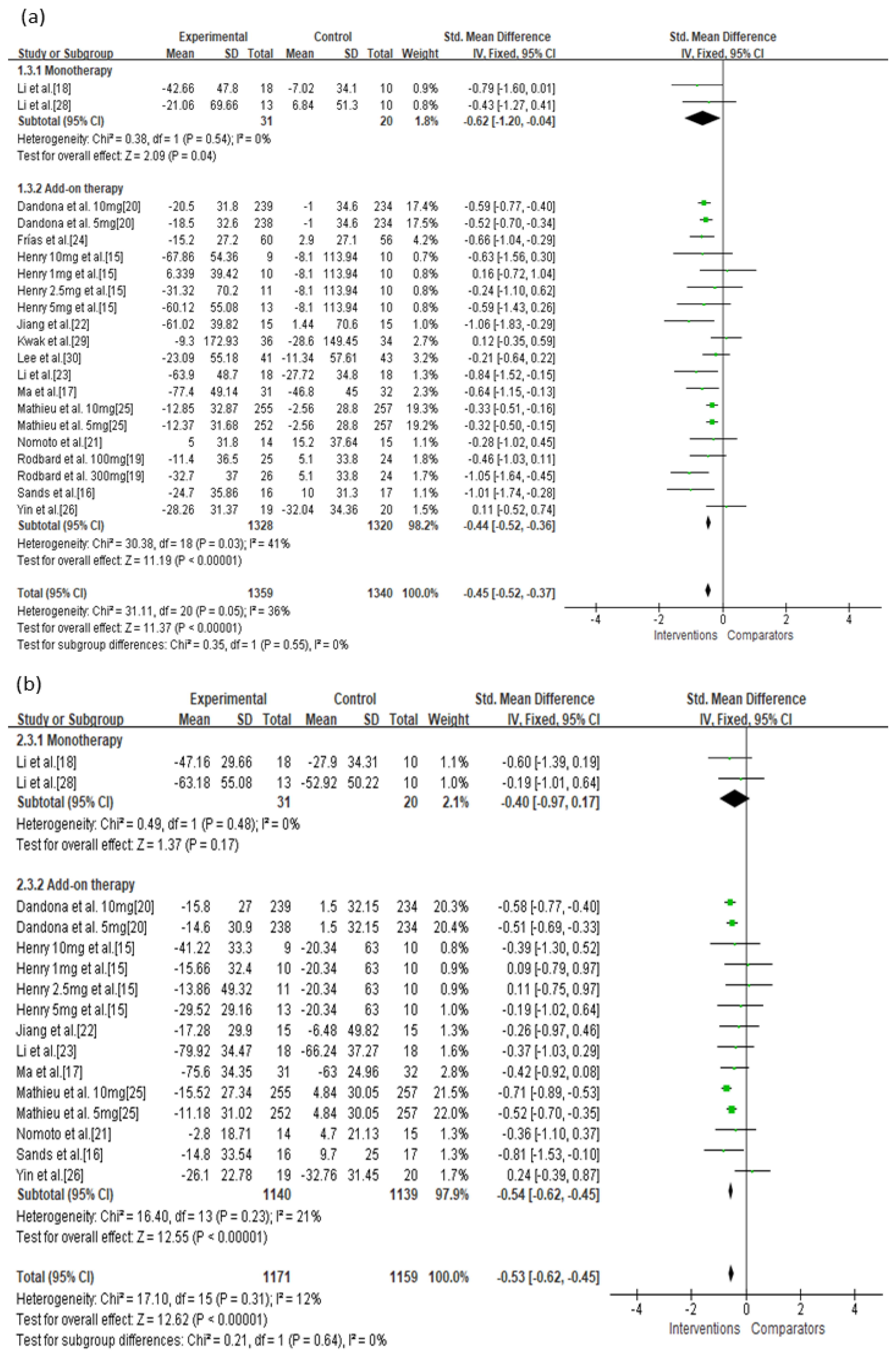
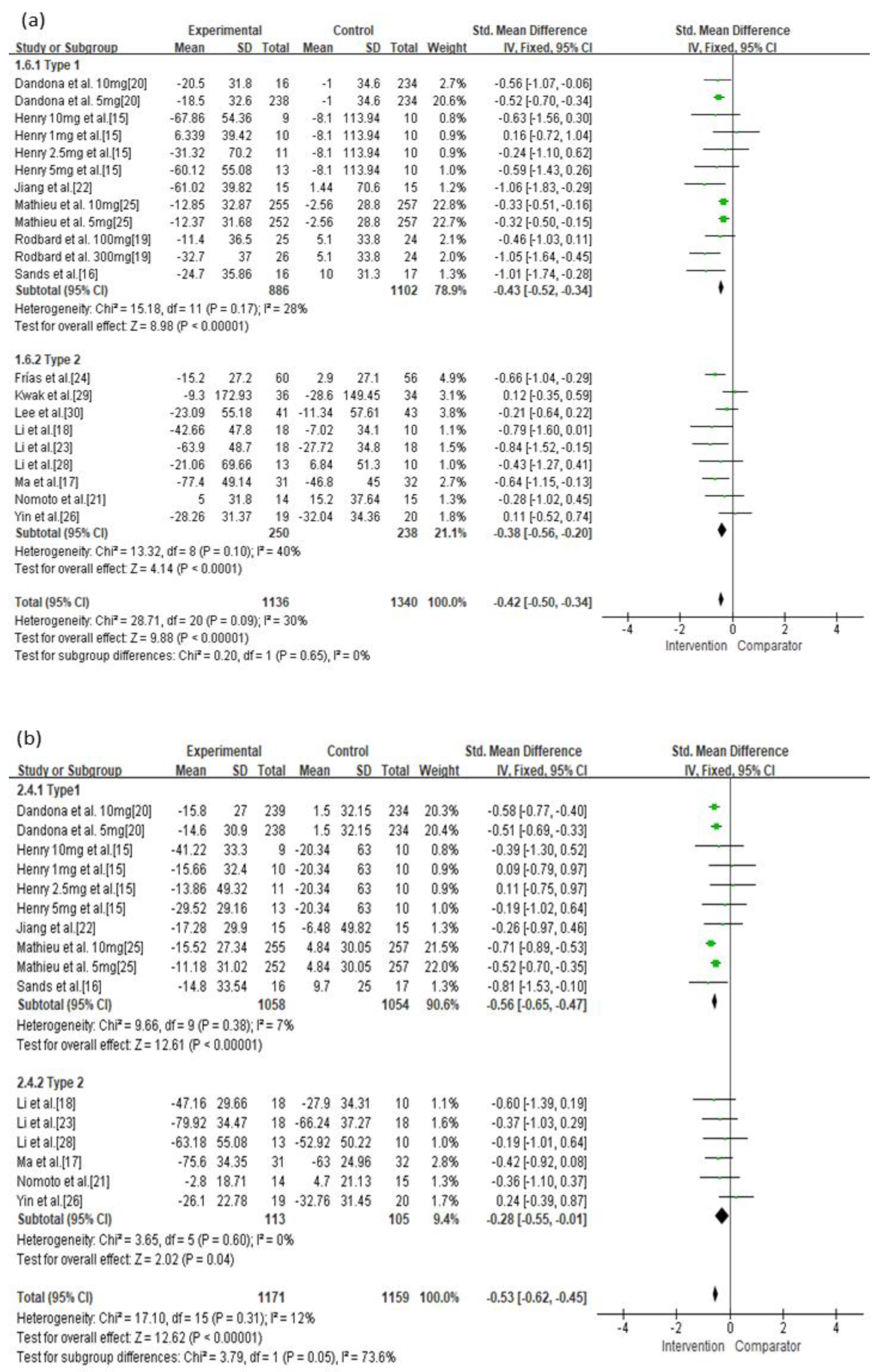
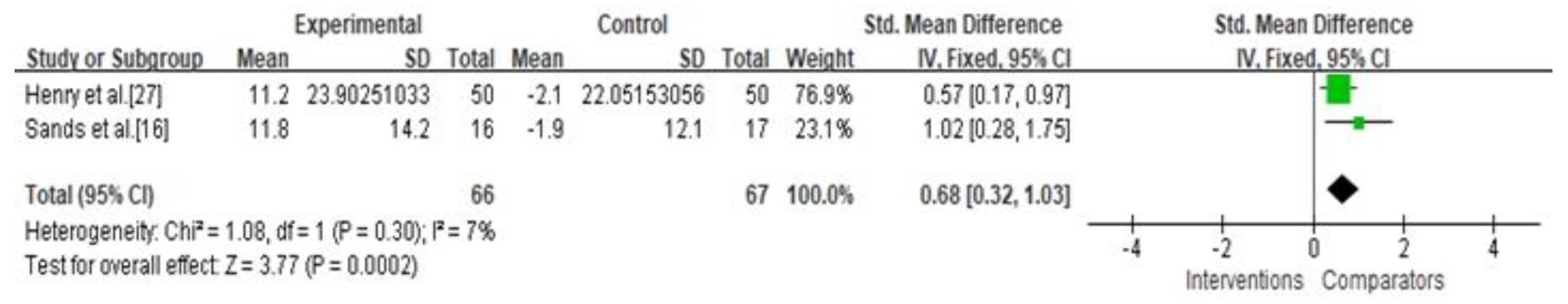
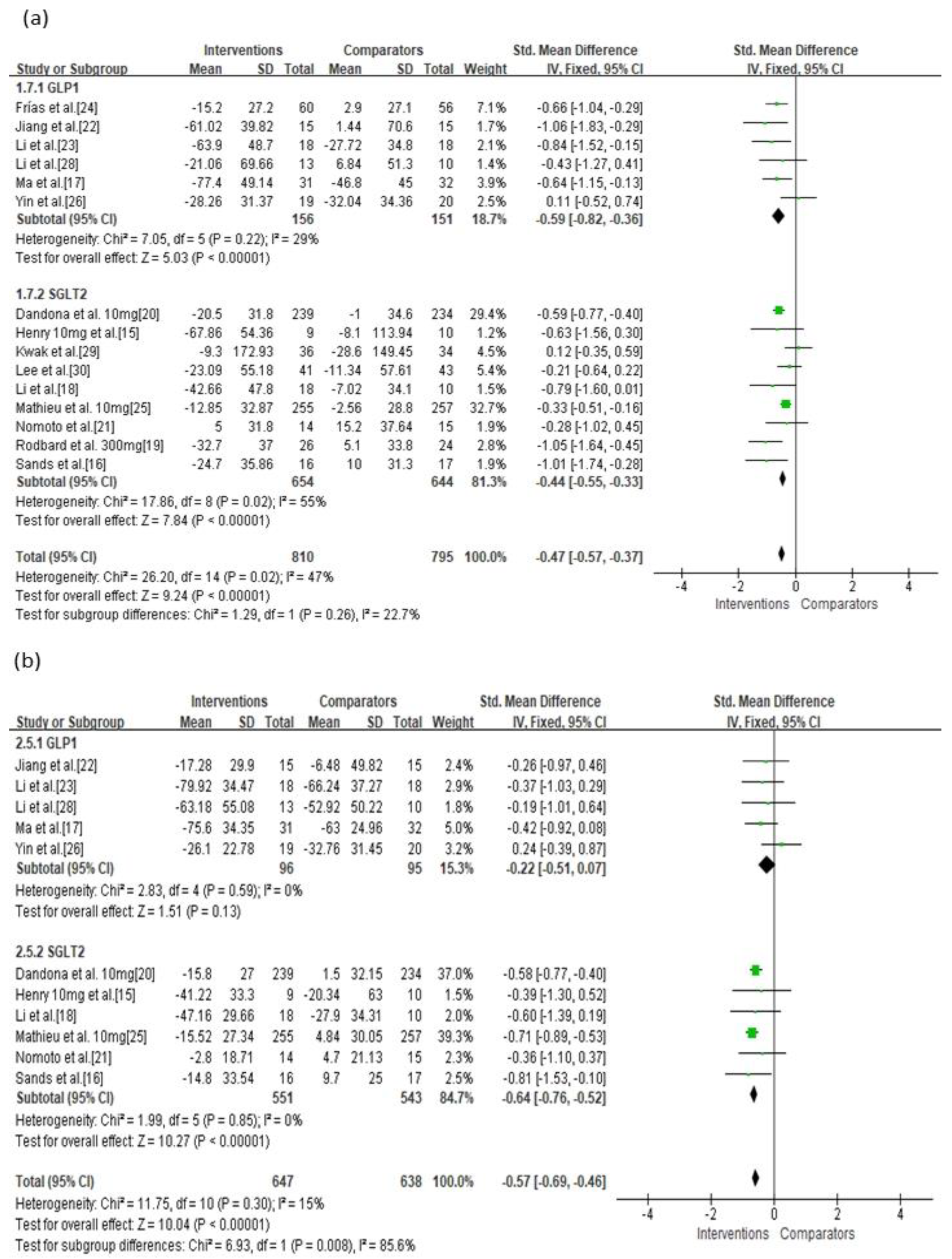
3.4. Secondary Outcomes
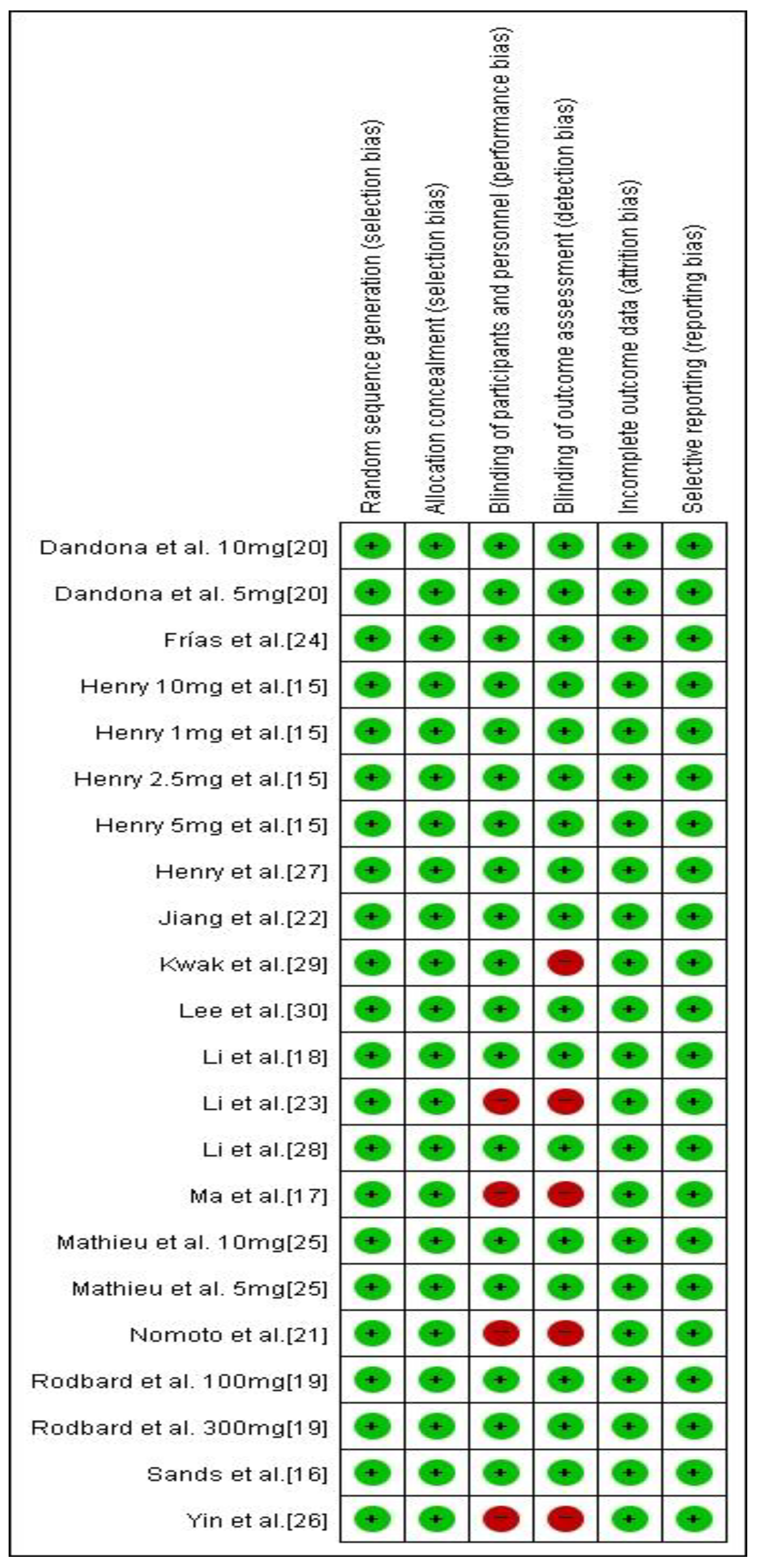
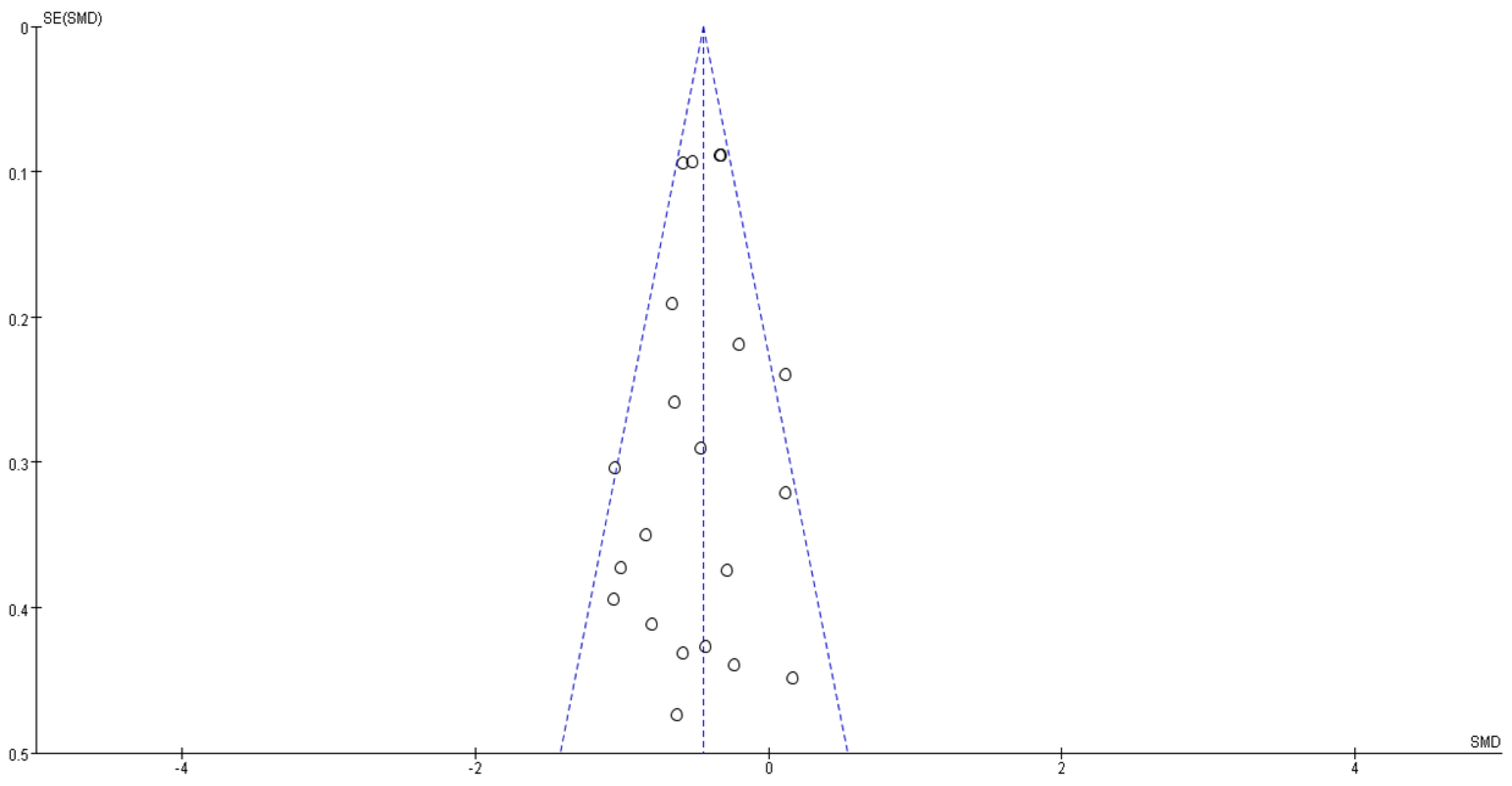
3.5. Risk of Bias and Level of Evidence
3.6. Meta-Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, S.L.; Roddick, A.J.; Aghar-Jaffar, R.; Shun-Shin, M.J.; Francis, D.; Oliver, N.; Meeran, K. Association between use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors with all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2018, 319, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A. Glucose variability and diabetic complications: Is it time to treat? Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Kim, J.H. Glycemic variability: How do we measure it and why is it important? Diabetes Metab. J. 2015, 39, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danne, T.; Nimri, R.; Battelino, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Close, K.L.; DeVries, J.H.; Garg, S.; Heinemann, L.; Hirsch, I.; Amiel, S.A.; et al. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makris, K.; Spanou, L. Is there a relationship between mean blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1572–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, R.; Montori, V.M. Glycemic control for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Our evolving faith in the face of evidence. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2016, 9, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, S.C.; Mavridis, D.; Nicolucci, A.; Johnson, D.W.; Tonelli, M.; Craig, J.C.; Maggo, J.; Gray, V.; De Berardis, G.; Ruospo, M.; et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2016, 316, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoulias, D.; Katsimardou, A.; Kalogirou, M.S.; Zografou, I.; Toumpourleka, M.; Imprialos, K.; Stavropoulos, K.; Stergiou, I.; Papadopoulos, C.; Doumas, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors as add-on therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes? A systematic review and meta-analysis of surrogate metabolic endpoints. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Zaccardi, F.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J.; Patsko, E.; Dhalwani, N.N.; Kloecker, D.E.; Ioannidou, E.; Gray, L.J. Efficacy and tolerability of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Service, F.J.; Molnar, G.D.; Rosevear, J.W.; Ackerman, E.; Gatewood, L.C.; Taylor, W.F. Mean amplitude of glycemic excursions, a measure of diabetic instability. Diabetes 1970, 19, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.; Altman, D.; Gotzsche, P.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balshem, H.; Helfand, M.; Schünemann, H.J.; Oxman, A.D.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Vist, G.E.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Meerpohl, J.; Norris, S.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, C.H.; Stark, P.C.; Berlin, J.A.; Landais, P.; Lau, J. Meta-regression detected associations between heterogeneous treatment effects and study-level, but not patient-level, factors. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Edelman, S.; Mudaliar, S.; Chalamandaris, A.G.; Kasichayanula, S.; Bogle, A.; Iqbal, N.; List, J.; Griffen, S.C. Exploring the potential of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in type 1 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sands, A.T.; Zambrowicz, B.P.; Rosenstock, J.; Lapuerta, P.; Bode, B.W.; Garg, S.K.; Buse, J.B.; Banks, P.; Heptulla, R.; Rendell, M.; et al. Sotagliflozin, a dual SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor, as adjunct therapy to insulin in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Yu, P.; Chen, L. Effect of liraglutide vs. NPH in combination with metformin on blood glucose fluctuations assessed using continuous glucose monitoring in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 53, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Gao, G.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H.H.; Su, X.F.; Wu, J.D.; Ye, L.; Ma, J.H. Influence of dapagliflozin on glycemic variations in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 5347262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodbard, H.W.; Peters, A.L.; Slee, A.; Cao, A.; Traina, S.B.; Alba, M. The effect of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, on glycemic end points assessed by continuous glucose monitoring and patient-reported outcomes among people with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dandona, P.; Mathieu, C.; Phillip, M.; Hansen, L.; Griffen, S.C.; Tschöpe, D.; Thorén, F.; Xu, J.; Langkilde, A.M. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes (DEPICT-1): 24 week results from a multicentre, double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomoto, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Sugawara, H.; Ono, K.; Yanagiya, S.; Oita, M.; Nakamura, A.; Atsumi, T. A randomized controlled trial comparing the effects of dapagliflozin and DPP-4 inhibitors on glucose variability and metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on insulin. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.L.; Wang, S.Q.; Ding, B.; Zhu, J.; Jing, T.; Ye, L.; Lee, K.O.; Wu, J.D.; Ma, J.H. The effects of add-on exenatide to insulin on glycemic variability and hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Jiang, L.; Fu, L.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, D.; Su, X.F.; Wu, J.D.; Ye, L.; Ma, J.H. Exenatide add-on to continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy reduces bolus insulin doses in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled, open-label trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frías, J.P.; Nakhle, S.; Ruggles, J.A.; Zhuplatov, S.; Klein, E.; Zhou, R.; Strange, P. Exenatide once weekly improved 24-hour glucose control and reduced glycaemic variability in metformin-treated participants with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, C.; Dandona, P.; Gillard, P.; Senior, P.A.; Hasslacher, C.; Araki, E.; Lind, M.; Bain, S.C.; Jabbour, S.; Arya, N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes-depict-2 study. Diabetes 2018, 67, A57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.T.; Bi, Y.; Li, P.; Shen, S.M.; Xiong, X.L.; Gao, L.J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Feng, W.H.; Zhu, D.L. Comparison of glycemic variability in Chinese T2DM patients treated with exenatide or insulin glargine: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henry, R.R.; Strange, P.; Zhou, R.; Pettus, J.; Shi, L.; Zhuplatov, S.B.; Mansfield, T.; Klein, D.; Katz, A. Effects of dapagliflozin on 24-hour glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Chen, M.; Jing, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, G.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; et al. A randomized study to compare the effects of once-weekly dulaglutide injection and once-daily glimepiride on glucose fluctuation of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A 26-week follow-up. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 6423987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.H.; Hwang, Y.C.; Won, J.C.; Bae, J.C.; Kim, H.J.; Suh, S.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H. Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin and dapagliflozin on glycaemic variability in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, open-label, active-controlled, 12-week study (STABLE II study). Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Min, K.W.; Lee, B.W.; Jeong, I.K.; Yoo, S.J.; Kwon, H.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Yoon, K.H. Effect of dapagliflozin as an add-on therapy to insulin on the glycemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DIVE): A multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 45, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, A.M.; Jacober, S.J. Relationship of glucose variability with glycated hemoglobin and daily mean glucose: A post hoc analysis of data from 5 phase 3 studies. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Risso, A.; Mercuri, F.; Quagliaro, L.; Damante, G.; Ceriello, A. Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E924–E930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, T.; Sueta, D.; Tabata, N.; Takashio, S.; Yamamoto, E.; Izumiya, Y.; Tsujita, K.; Kojima, S.; Kaikita, K.; Matsui, K.; et al. Effects of the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions and vascular endothelial dysfunction on cardiovascular events in nondiabetic patients with coronary artery disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumiller, J.J.; White, J.R.; Campbell, R.K. Sodium-glucose co-transport inhibitors: Progress and therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2010, 70, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Gastaldelli, A.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and the central/peripheral nervous system: Crosstalk in diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Fradkin, J.; Kernan, W.N.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; Rossing, P.; Tsapas, A.; Wexler, D.J.; Buse, J.B. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2669–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, T.; Shojima, N.; Noma, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as add-on therapy to insulin for type 1 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.; Dawed, A.Y.; Donnelly, L.A.; Nair, A.T.N.; Palmer, C.N.A.; Mohan, V.; Pearson, E.R. Efficacy of modern diabetes treatments DPP-4i, SGLT-2i, and GLP-1RA in White and Asian patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, E. Effect of DPP-IV Inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with T2DM: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Kim, E. Repositioning medication for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease to delay the onset and prevent progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 932–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Addendum. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020; 43(Suppl. 1):S111–S134. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1977–1978. [Google Scholar]
- DeVries, J.H. Glucose variability: Where it is important and how to measure it. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1405–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, G.; Saba, F.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Diabetic ketoacidosis with SGLT2 inhibitors. BMJ 2020, 371, m4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study Name | Publication Year | Therapy Regimen | Diabetes Type | Intervention | Comparator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henry et al. [15] | 2015 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Dapagliflozin and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Sands et al. [16] | 2015 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Sotagliflozin and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Ma et al. [17] | 2015 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Liraglutide and metformin | Insulin and metformin |
| Li et al. [18] | 2016 | Monotherapy | Type 2 | Dapagliflozin | Placebo |
| Rodbard et al. [19] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Canagliflozin and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Dandona et al. [20] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Dapagliflozin and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Nomoto et al. [21] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Dapagliflozin and insulin | DPP-IV and insulin |
| Jiang et al. [22] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Exenatide and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Li et al. [23] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Exenatide and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Frías et al. [24] | 2017 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Exenatide and metformin | Placebo and metformin |
| Mathieu et al. [25] | 2018 | Add-on therapy | Type 1 | Dapagliflozin and insulin | Placebo and insulin |
| Yin et al. [26] | 2018 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Exenatide and metformin | Insulin and metformin |
| Henry et al. [27] | 2018 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Dapagliflozin and insulin or metformin | Placebo and insulin or metformin |
| Li et al. [28] | 2019 | Monotherapy | Type 2 | Dulaglutide | Glimepiride |
| Kwak et al. [29] | 2020 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Dapagliflozin and metformin | Gemigliptin and metformin |
| Lee et al. [30] | 2020 | Add-on therapy | Type 2 | Dapagliflozin and insulin and/or OADs | Placebo and insulin and/or OADs |
| Outcome | Limitation | Inconsistency | Indirection | Imprecision | Publication Bias | Standard Mean Difference | Quality of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAGE | |||||||
| GLP-1 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.59 (−0.82, −0.36) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.43 (−0.51, −0.35) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Monotherapy | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.62 (−1.20, −0.04) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
| Add-on therapy | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.44 (−0.52, −0.36) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Type 1 | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.43 (−0.52, −0.34) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
| Type 2 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.38 (−0.56, −0.20) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 vs. Placebo a | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.45 (−0.53, −0.36) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
| GLP-1 vs. Placebo b | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.76 (−1.06, −0.45) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 vs. Active c | Very serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | 0.00 (−0.39, 0.40) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low |
| GLP-1 vs. Active d | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.36 (−0.72, −0.00) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| MBG | |||||||
| GLP-1 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.22 (−0.51, 0.07) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.56 (−0.65, −0.48) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Monotherapy | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.40 (−0.97, 0.17) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Add-on therapy | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.54 (−0.62, −0.45) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Type 1 | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.56 (−0.65, −0.47) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
| Type 2 | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.28 (−0.55, −0.01) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 vs. Placebo a | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.57 (−0.65, −0.48) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
| GLP-1 vs. Placebo b | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.32 (−0.81, 0.17) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| SGLT-2 vs. Active c | Very serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.36 (−1.10, 0.37) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low |
| GLP-1 vs. Active d | Serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | −0.17 (−0.52, 0.19) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate |
| Percentage of time maintaining euglycemia | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Not serious | Undetected | 0.68 (0.32, 1.03) | ⊕⊕⊕⊕ High |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Park, S.-e.; Kim, E.-Y. Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184078
Lee H, Park S-e, Kim E-Y. Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184078
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Heeyoung, Se-eun Park, and Eun-Young Kim. 2021. "Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184078
APA StyleLee, H., Park, S.-e., & Kim, E.-Y. (2021). Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4078. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184078






