Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of MiR-379/656 MicroRNA Cluster in Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Annotation of Clustered miRNAs
2.2. Downloading and Preprocessing TCGA Data
2.3. Differential miRNA Expression Analysis in Breast Cancer
2.4. Logistic Regression Analysis of MiR-379/656 Expression
2.5. Cox (Proportional Hazards) Regression Analysis of MiR-379/656
2.6. Functional Enrichment Analysis of Validated Gene Targets of MiR-379/656
2.7. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MiR-379/656 Is the Most Significant Differentially Expressed Cluster in Breast Cancer
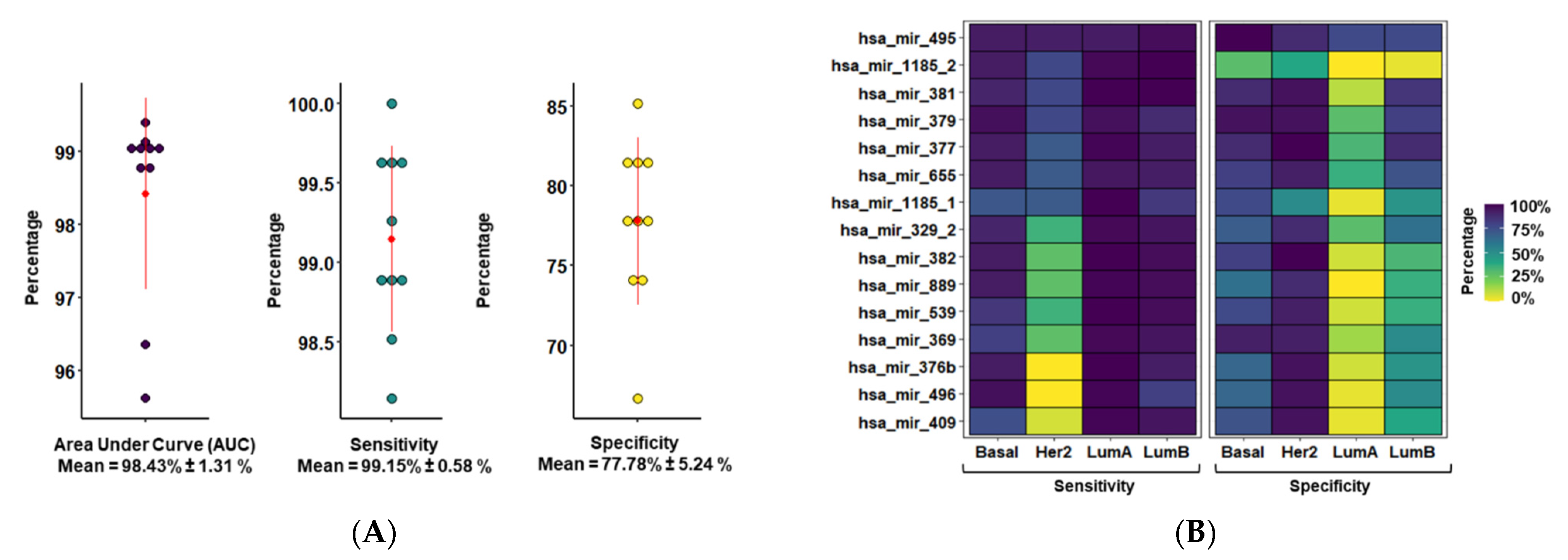
3.2. MiR-379/656 Accurately Classifies Tumor and Normal Samples—Especially Basal and Luminal B Subtypes
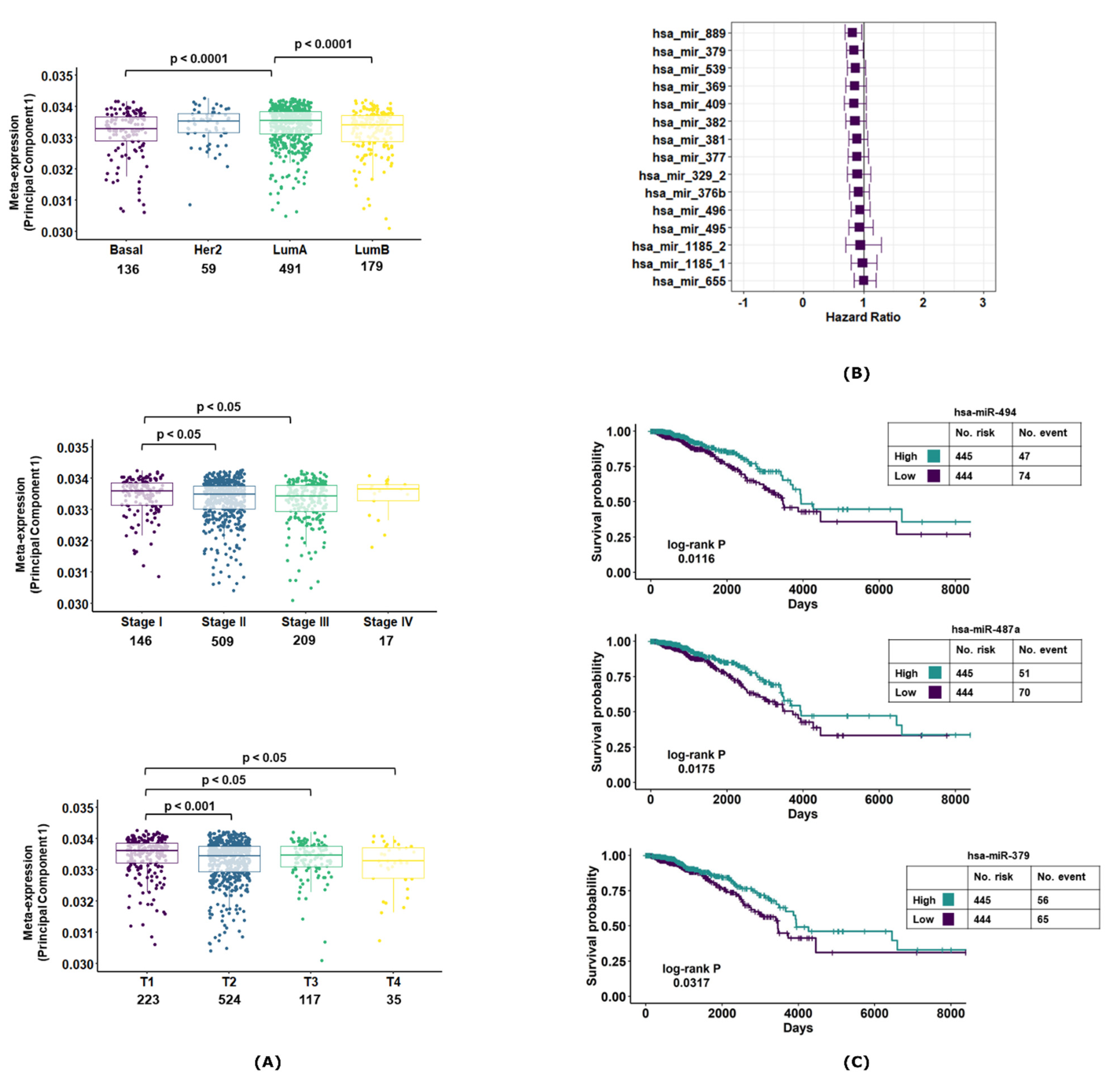
3.3. MiR-379/656 Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Breast Cancer
3.4. MiR-379/656 Target Genes Are Enriched for Cancer-Relevant Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C.S. OncomiRs: The discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammond, S.M. MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006, 16, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela, K.A.; Slack, J. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, Y.; Tay, F.C.; Lam, D.H.; Sandanaraj, E.; Tang, C.; Ang, B.-T.; Wang, S. Attenuated adenosine-to-inosine editing of microRNA-376a* promotes invasiveness of glioblastoma cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4059–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giovannetti, E.; Erozenci, A.; Smit, J.; Danesi, R.; Peters, G.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in anticancer drug resistance and implications for clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2012, 81, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummins, J.M.; Velculescu, V.E. Implications of micro-RNA profiling for cancer diagnosis. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6220–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takamizawa, J.; Konishi, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Osada, H.; Endoh, H.; Harano, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manterola, L.; Guruceaga, E.; Perez-Larraya, J.G.; González-Huarriz, M.; Jauregui, P.; Tejada, S.; Diez-Valle, R.; Segura, V.; Samprón, N.; Barrena, C.; et al. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X. Plasma-based microRNA signatures in early diagnosis of breast cancer. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marco, A.; Ninova, M.; Ronshaugen, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. Clusters of microRNAs emerge by new hairpins in existing transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7745–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, J.; Siepel, A.; Lai, E.C. Diverse modes of evolutionary emergence and flux of conserved microRNA clusters. RNA 2014, 20, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D152–D157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altuvia, Y.; Landgraf, P.; Lithwick, G.; Elefant, N.; Pfeffer, S.; Aravin, A.; Brownstein, M.J.; Tuschl, T.; Margalit, H. Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Young, A.G.; Winslow, M.M.; Lintault, L.; Meissner, A.; Erkeland, S.J.; Newman, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Stone, J.R.; et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17∼92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008, 132, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Yu, J.; Han, T.S.; Park, S.-Y.; Namkoong, B.; Kim, D.H.; Hur, K.; Yoo, M.-W.; Lee, H.-J.; Yang, H.-K.; et al. Functional links between clustered microRNAs: Suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, P.; He, S.; Liao, Q.; Kang, S.; Zhao, Y. Clustered microRNAs’ coordination in regulating protein-protein interaction network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Haubrock, M.; Cao, K.-M.; Hua, X.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Wingender, E.; Li, J. Regulatory coordination of clustered microRNAs based on microRNA-transcription factor regulatory network. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Zeller, K.I.; Dang, C.V.; Mendell, J.T. c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005, 435, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, H.; Seto, M. A microRNA cluster as a target of genomic amplification in malignant lymphoma. Leukemia 2005, 19, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrakis, K.J.; Wolfe, A.L.; Oricchio, E.; Palomero, T.; de Keersmaecker, K.; McJunkin, K.; Zuber, J.; James, T.; Khan, A.A.; Leslie, C.S.; et al. Genome-wide RNA-mediated interference screen identifies miR-19 targets in Notch-induced T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mestdagh, P.; Boström, A.-K.; Impens, F.; Fredlund, E.; Van Peer, G.; De Antonellis, P.; von Stedingk, K.; Ghesquière, B.; Schulte, S.; Dews, M.; et al. The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, P.; Han, Y.-C.; Betel, D.; Yao, E.; Squatrito, M.; Ogrodowski, P.; de Stanchina, E.; D’Andrea, A.; Sander, C.; Ventura, A. Genetic dissection of the miR-17~92 cluster of microRNAs in Myc-induced B-cell lymphomas. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2806–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendell, J.T. miRiad roles for the miR-17-92 cluster in development and disease. Cell 2008, 133, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stinson, S.; Lackner, M.R.; Adai, A.T.; Yu, N.; Kim, H.-J.; O’Brien, C.; Spoerke, J.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Boyd, Z.; Januario, T.; et al. miR-221/222 targeting of trichorhinophalangeal 1 (TRPS1) promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, pt5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Luo, X.; Gu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Fei, J. Systematic analysis of berberine-induced signaling pathway between miRNA clusters and mRNAs and identification of mir-99a∼125b cluster function by seed-targeting inhibitors in multiple myeloma cells. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glazov, E.A.; McWilliam, S.; Barris, W.C.; Dalrymple, B.P. Origin, evolution, and biological role of miRNA cluster in DLK-DIO3 genomic region in placental mammals. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Rocha, S.T.; Edwards, C.A.; Ito, M.; Ogata, T.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Genomic imprinting at the mammalian Dlk1-Dio3 domain. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Aich, M.; Kumar, A.; Sengupta, S.; Bajad, P.; Dhapola, P.; Paul, D.; Narta, K.; Purkrait, S.; Mehani, B.; et al. Novel internal regulators and candidate miRNAs within miR-379/miR-656 miRNA cluster can alter cellular phenotype of human glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laddha, S.V.; Nayak, S.; Paul, D.; Reddy, R.; Sharma, C.; Jha, P.; Hariharan, M.; Agrawal, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Sarkar, C.; et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals downregulation of miR-379/miR-656 cluster in human cancers. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zehavi, L.; Avraham, R.; Barzilai, A.; Bar-Ilan, D.; Navon, R.; Sidi, Y.; Avni, D.; Leibowitz-Amit, R. Silencing of a large microRNA cluster on human chromosome 14q32 in melanoma: Biological effects of mir-376a and mir-376c on insulin growth factor 1 receptor. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haller, F.; von Heydebreck, A.; Zhang, J.D.; Gunawan, B.; Langer, C.; Ramadori, G.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, O. Localization- and mutation-dependent microRNA (miRNA) expression signatures in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs), with a cluster of co-expressed miRNAs located at 14q32.31. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Volinia, S.; Bonome, T.; Calin, G.A.; Greshock, J.; Yang, N.; Liu, C.-G.; Giannakakis, A.; Alexiou, P.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Genomic and epigenetic alterations deregulate microRNA expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7004–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uppal, A.; Wightman, S.C.; Mallon, S.; Oshima, G.; Pitroda, S.P.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Darga, T.E.; Huang, L.; Andrade, J.; et al. 14q32-encoded microRNAs mediate an oligometastatic phenotype. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3540–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantini, L.; Bertoli, G.; Cava, C.; Dubois, T.; Zinovyev, A.; Caselle, M.; Castiglioni, I.; Barillot, E.; Martignetti, L. Identification of microRNA clusters cooperatively acting on epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, M.; Lucchetta, M.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Bontempi, G.; Chen, X.; Noushmehr, H.; Colaprico, A.; Papaleo, E. New functionalities in the TCGAbiolinks package for the study and integration of cancer data from GDC and GTEx. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthikeyan, M. Expression Normalization Workflow: Gene Expression Normalization Workflow, R package version 1.18.0; R Foundation For Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- UCSC Xena. Available online: https://xena.ucsc.edu (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, M. Caret: Classification and Regression Training. R Package Version 6.0-86. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: A More Scalable Alternative to Venn and Euler Diagrams for Visualizing Intersecting Sets. R Package Version 1.4.0. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=UpSetR (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Therneau, T. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R Package Version 3.2-7. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-387-98784-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Kosinski, M.; Biecek, P. Survminer: Drawing Survival Curves Using “ggplot2”. R Package Version 0.4.8. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survminer (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- miRTarBase 7.0. Available online: http://mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/ (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research, Version=2.0.9; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Pedersen, T.L. Ggraph: An Implementation of Grammar of Graphics for Graphs and Networks. R Package Version 2.0.3. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggraph (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Pedersen, T.L. Tidygraph: A Tidy API for Graph Manipulation. R Package Version 1.2.0. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidygraph (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Yu, G.; He, Q.-Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor package for reactome pathway analysis and visualization. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, W. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olive, V.; Li, Q.; He, L. mir-17-92: A polycistronic oncomir with pleiotropic functions. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.-L.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.-X.; Wu, H.-M.; Lei, F.-Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, X. Downregulated miR-495 Inhibits the G1-S Phase Transition by Targeting Bmi-1 in Breast Cancer. Medicine 2015, 94, e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.-X.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Chen, X.-Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-L. Lnc RNA SNHG20 participated in proliferation, invasion, and migration of breast cancer cells via miR-495. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7971–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, D.; Tian, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Demethylation of miR-495 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and promotes apoptosis by targeting STAT-3 in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3581–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Brougham, C.L.; Ryan, J.; Sahrudin, A.; O’Neill, G.; Wall, D.; Curran, C.; Newell, J.; Kerin, M.J.; Dwyer, R.M. miR-379 regulates cyclin B1 expression and is decreased in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.-B.; Hu, S.-L.; Zang, R.-K.; Su, Y.; Liang, Y.-C.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-487a promotes proliferation of esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting p62 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.-M.; Xiao, S.; Lei, X.; Yang, H.; Fang, F.; Yang, L.-Y. miRNA-487a Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herranz, H.; Cohen, S.M. MicroRNAs and gene regulatory networks: Managing the impact of noise in biological systems. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelinic, P.; Shaw, P. Loss of imprinting and cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leick, M.B.; Shoff, C.J.; Wang, E.C.; Congress, J.L.; Gallicano, G.I. Loss of imprinting of IGF2 and the epigenetic progenitor model of cancer. Am. J. Stem Cells 2012, 1, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kagami, M.; Sekita, Y.; Nishimura, G.; Irie, M.; Kato, F.; Okada, M.; Yamamori, S.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakayama, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Deletions and epimutations affecting the human 14q32.2 imprinted region in individuals with paternal and maternal upd(14)-like phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtfeld, M.; Apostolou, E.; Akutsu, H.; Fukuda, A.; Follett, P.; Natesan, S.; Kono, T.; Shioda, T.; Hochedlinger, K. Aberrant silencing of imprinted genes on chromosome 12qF1 in mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2010, 465, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kameswaran, V.; Bramswig, N.C.; McKenna, L.B.; Penn, M.; Schug, J.; Hand, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Choi, I.; Vourekas, A.; Won, K.-J.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of the DLK1-MEG3 microRNA cluster in human type 2 diabetic islets. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molina-Pinelo, S.; Salinas, A.; Moreno-Mata, N.; Ferrer, I.; Suarez, R.; Andrés-León, E.; Rodríguez-Paredes, M.; Gutekunst, J.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Camps, C.; et al. Impact of DLK1-DIO3 imprinted cluster hypomethylation in smoker patients with lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4395–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vallinas, M.; Rodríguez-Paredes, M.; Albrecht, M.; Sticht, C.; Stichel, D.; Gutekunst, J.; Pitea, A.; Sass, S.; Sánchez-Rivera, F.J.; Lorenzo-Bermejo, J.; et al. Epigenetically Regulated Chromosome 14q32 miRNA Cluster Induces Metastasis and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lal, M.; Ansari, A.H.; Agrawal, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of MiR-379/656 MicroRNA Cluster in Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184071
Lal M, Ansari AH, Agrawal A, Mukhopadhyay A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of MiR-379/656 MicroRNA Cluster in Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184071
Chicago/Turabian StyleLal, Megha, Asgar Hussain Ansari, Anurag Agrawal, and Arijit Mukhopadhyay. 2021. "Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of MiR-379/656 MicroRNA Cluster in Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184071
APA StyleLal, M., Ansari, A. H., Agrawal, A., & Mukhopadhyay, A. (2021). Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of MiR-379/656 MicroRNA Cluster in Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184071





