Beneficial Effects of Opioid Rotation to Buprenorphine/Naloxone on Opioid Misuse, Craving, Mental Health, and Pain Control in Chronic Non-Cancer Pain Patients with Opioid Use Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
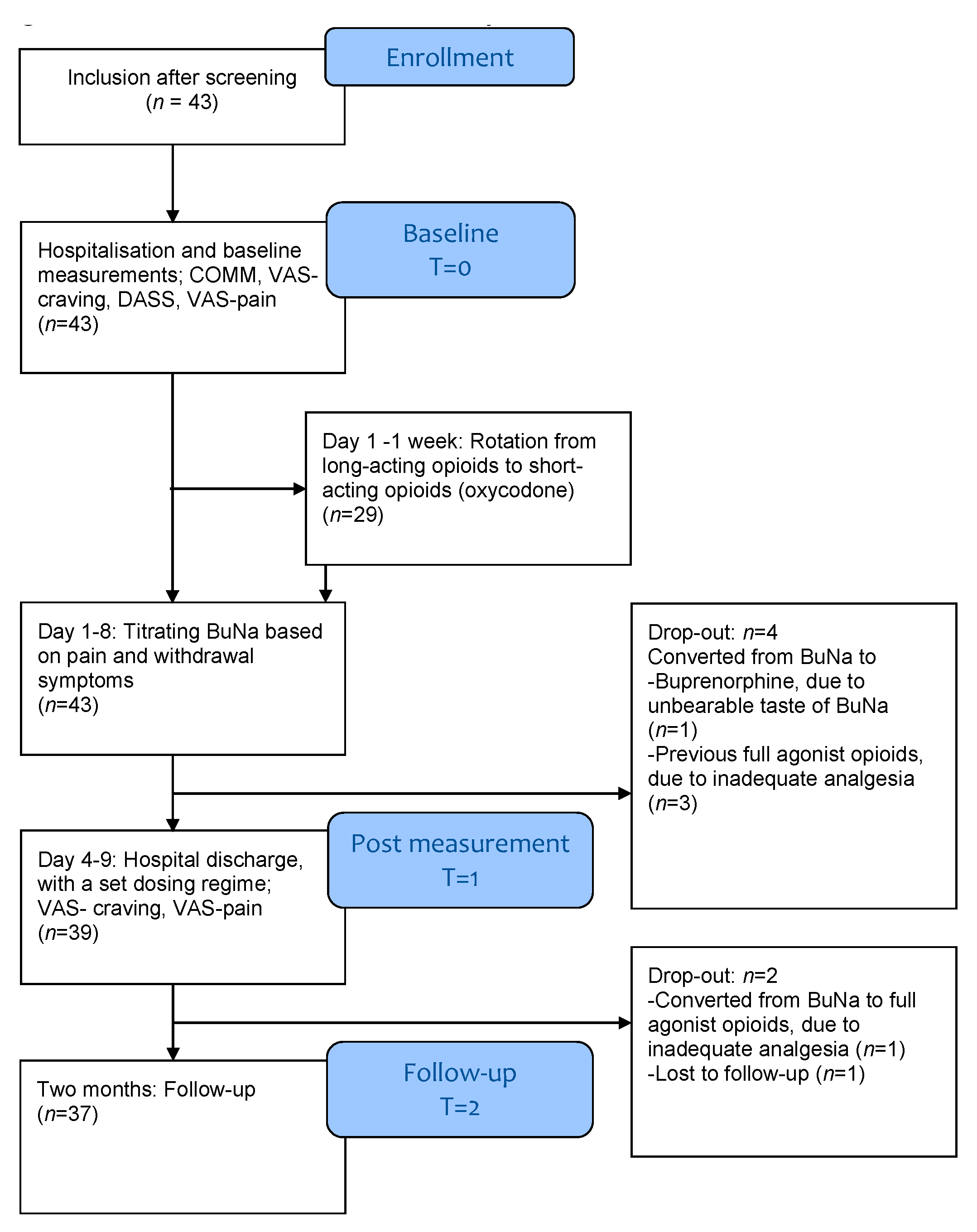
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Instruments
2.5. Opioid Misuse
2.6. Psychiatric Symptoms
2.7. Pain Assessment
2.8. Procedure
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- Primary outcomes:
- Secondary outcomes:
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, A.E.; Blackburn, N.A.; Des Jarlais, D.C.; Hagan, H. Past-year prevalence of prescription opioid misuse among those 11 to 30 years of age in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2017, 77, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, G.A.; Kramers, C.; van Dongen, R.T.; van den Brink, W.; Schellekens, A. Trends in use and misuse of opioids in the Netherlands: A retrospective, multi-source database study. Lancet Public Health 2019, 4, e498–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018 Annual Surveillance Report of Drug-Related Risks and Outcomes. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/pdf/pubs/2018-cdc-drug-surveillance-report.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Manchikanti, L.; Vallejo, R.; Manchikanti, K.N.; Benyamin, R.M.; Datta, S.; Christo, P.J. Effectiveness of long-term opioid therapy for chronic non-cancer pain. Pain Physician 2011, 14, E133–E156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trescot, A.M.; Glaser, S.E.; Hansen, H.; Benyamin, R.; Patel, S.; Manchikanti, L. Effectiveness of opioids in the treatment of chronic non-cancer pain. Pain Physician 2008, 11, S181–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.D.; Hollingworth, S.A.; Maravilla, J.C.; Connor, J.P.; Alati, R. Prescribed Dose of Opioids and Overdose: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Unintentional Prescription Opioid Overdose. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, D.; Haegerich, T.M.; Chou, R. CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/65/rr/rr6501e1.htm (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Baldini, A.; Von Korff, M.; Lin, E.H. A Review of Potential Adverse Effects of Long-Term Opioid Therapy: A Practitioner’s Guide. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2012, 14, PCC.11m01326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allegri, N.; Mennuni, S.; Rulli, E.; Vanacore, N.; Corli, O.; Floriani, I.; De Simone, I.; Allegri, M.; Govoni, S.; Vecchi, T.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Neuropsychological Effects of Long-Term Use of Opioids in Patients With Chronic Noncancer Pain. Pain Pract. 2019, 19, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijswijk, S.M.; van Beek, M.; Schoof, G.M.; Schene, A.H.; Steegers, M.; Schellekens, A.F. Iatrogenic opioid use disorder, chronic pain and psychiatric comorbidity: A systematic review. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2019, 59, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, C.Q.; Sullivan, M.D. The missing ‘P’ in pain management: How the current opioid epidemic highlights the need for psychiatric services in chronic pain care. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2014, 36, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.L.; Bennett, H.E.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; Hill, K.P.; Provost, S.E.; Weiss, R.D. Health-related quality of life among prescription opioid-dependent patients: Results from a multi-site study. Am. J. Addict. 2015, 24, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Z.; Sin, B.; Beckhusen, J.; Xia, D.; Khaimova, R.; Iliev, I. Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia in the Nonsurgical Setting: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 26, e397–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.; Smith, B.H.; Matthews, K. Evidence of opioid-induced hyperalgesia in clinical populations after chronic opioid exposure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, e114–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Els, C.; Jackson, T.D.; Kunyk, D.; Lappi, V.G.; Sonnenberg, B.; Hagtvedt, R.; Sharma, S.; Kolahdooz, F.; Straube, S. Adverse events associated with medium- and long-term use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: An overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 10, Cd012509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vowles, K.E.; McEntee, M.L.; Julnes, P.S.; Frohe, T.; Ney, J.P.; van der Goes, D.N. Rates of opioid misuse, abuse, and addiction in chronic pain: A systematic review and data synthesis. Pain 2015, 156, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, C.; Smith, B.H.; Matthews, K. Incidence of iatrogenic opioid dependence or abuse in patients with pain who were exposed to opioid analgesic therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speed, T.J.; Parekh, V.; Coe, W.; Antoine, D. Comorbid chronic pain and opioid use disorder: Literature review and potential treatment innovations. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2018, 30, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, A.D.; Jones, M.R.; Kaye, A.M.; Ripoll, J.G.; Galan, V.; Beakley, B.D.; Calixto, F.; Bolden, J.L.; Urman, R.D.; Manchikanti, L. Prescription Opioid Abuse in Chronic Pain: An Updated Review of Opioid Abuse Predictors and Strategies to Curb Opioid Abuse: Part 1. Pain Physician 2017, 20, S93–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Jones, M.R.; Kaye, A.M.; Ripoll, J.G.; Jones, D.E.; Galan, V.; Beakley, B.D.; Calixto, F.; Bolden, J.L.; Urman, R.D.; et al. Prescription Opioid Abuse in Chronic Pain: An Updated Review of Opioid Abuse Predictors and Strategies to Curb Opioid Abuse (Part 2). Pain Physician 2017, 20, S111–S133. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, M.; Treadwell, J.R.; Tregear, S.J.; Coates, V.H.; Wiffen, P.J.; Akafomo, C.; Schoelles, K.M. Long-term opioid management for chronic noncancer pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 1, CD006605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredheim, O.M.; Moksnes, K.; Borchgrevink, P.C.; Skurtveit, S. Opioid switching to methadone: A pharmacoepidemiological study from a national prescription database. Palliat. Med. 2012, 26, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.M.; Blondell, R.D.; Hoopsick, R.A.; Homish, G.G. Randomized clinical trial comparing buprenorphine/naloxone and methadone for the treatment of patients with failed back surgery syndrome and opioid addiction. J. Addict. Dis. 2019, 38, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, V.; Senderovich, H. Methadone in Pain Management: A Systematic Review. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2021, 22, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, P.; Karamouzian, M.; Kerr, T. Chronic pain and opioid misuse: A review of reviews. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2017, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolff, R.F.; Aune, D.; Truyers, C.; Hernandez, A.V.; Misso, K.; Riemsma, R.; Kleijnen, J. Systematic review of efficacy and safety of buprenorphine versus fentanyl or morphine in patients with chronic moderate to severe pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2012, 28, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daitch, D.; Daitch, J.; Novinson, D.; Frey, M.; Mitnick, C.; Pergolizzi, J., Jr. Conversion from high-dose full-opioid agonists to sublingual buprenorphine reduces pain scores and improves quality of life for chronic pain patients. Pain Med. (Malden Mass.) 2014, 15, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daitch, J.; Frey, M.E.; Silver, D.; Mitnick, C.; Daitch, D.; Pergolizzi, J., Jr. Conversion of chronic pain patients from full-opioid agonists to sublingual buprenorphine. Pain Physician 2012, 15, Es59–Es66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.; Sullivan, M.A.; Cohen, J.; Fugon, L.; Jones, J.D.; Vosburg, S.K.; Cooper, Z.D.; Manubay, J.M.; Mogali, S.; Comer, S.D. Buprenorphine/naloxone as a promising therapeutic option for opioid abusing patients with chronic pain: Reduction of pain, opioid withdrawal symptoms, and abuse liability of oral oxycodone. Pain 2013, 154, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pade, P.A.; Cardon, K.E.; Hoffman, R.M.; Geppert, C.M. Prescription opioid abuse, chronic pain, and primary care: A Co-occurring Disorders Clinic in the chronic disease model. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2012, 43, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, A.; Cruciani, R.A.; Strain, E.C.; Cleland, C.M.; Joseph, H.; Magura, S.; Marsch, L.A.; McNicholas, L.F.; Savage, S.R.; Sundaram, A.; et al. Sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone for chronic pain in at-risk patients: Development and pilot test of a clinical protocol. J. Opioid Manag. 2012, 8, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CADTH Rapid Response Reports. In Buprenorphine/Naloxone Versus Methadone for the Treatment of Opioid Dependence: A Review of Comparative Clinical Effectiveness, Cost-Effectiveness and Guidelines; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016.
- Soyka, M. Treatment of opioid dependence with buprenorphine: Current update. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudala, P.J.; Bridge, T.P.; Herbert, S.; Williford, W.O.; Chiang, C.N.; Jones, K.; Collins, J.; Raisch, D.; Casadonte, P.; Goldsmith, R.J.; et al. Office-based treatment of opiate addiction with a sublingual-tablet formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, J.; Jahromi, M.S.; Ghahremani, D.; London, E.D. Single high-dose buprenorphine for opioid craving during withdrawal. Trials 2018, 19, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakko, J.; Alho, H.; Baldacchino, A.; Molina, R.; Nava, F.A.; Shaya, G. Craving in Opioid Use Disorder: From Neurobiology to Clinical Practice. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haight, B.R.; Learned, S.M.; Laffont, C.M.; Fudala, P.J.; Zhao, Y.; Garofalo, A.S.; Greenwald, M.K.; Nadipelli, V.R.; Ling, W.; Heidbreder, C. Efficacy and safety of a monthly buprenorphine depot injection for opioid use disorder: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Matthews, M.L.; Brick, D.; Nguyen, M.T.; Wasan, A.D.; Jamison, R.N.; Ellner, A.L.; Tishler, L.W.; Weiss, R.D. Implementation of a collaborative care management program with buprenorphine in primary care: A comparison between opioid-dependent patients and patients with chronic pain using opioids nonmedically. J. Opioid. Manag. 2014, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnelli, F.; Biondi, L.; Calabria, R.; Fiore, A.; Peluso, E.; Vonella, D.; Rota, A.G. Safety and efficacy of buprenorphine/naloxone in opioid-dependent patients: An Italian observational study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2010, 30 (Suppl. 1), 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.Y.; Chen, L.; Mao, J. Buprenorphine-naloxone therapy in pain management. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiang, C.N.; Hawks, R.L. Pharmacokinetics of the combination tablet of buprenorphine and naloxone. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2003, 70, S39–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, P.E.; Kieffer, B.L. Opioid receptors: Distinct roles in mood disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, P.P.; Bodkin, J.A. Opioidergic Agents as Antidepressants: Rationale and Promise. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peciña, M.; Karp, J.F.; Mathew, S.; Todtenkopf, M.S.; Ehrich, E.W.; Zubieta, J.K. Endogenous opioid system dysregulation in depression: Implications for new therapeutic approaches. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, J.F.; Butters, M.A.; Begley, A.E.; Miller, M.D.; Lenze, E.J.; Blumberger, D.M.; Mulsant, B.H.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd. Safety, tolerability, and clinical effect of low-dose buprenorphine for treatment-resistant depression in midlife and older adults. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e785–e793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, J.; Sefidfard Jahromi, M. Ultrarapid Influence of Buprenorphine on Major Depression in Opioid-Dependent Patients: A Double Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial. Subst. Use Misuse 2018, 53, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosten, T.R.; Morgan, C.; Kosten, T.A. Depressive symptoms during buprenorphine treatment of opioid abusers. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 1990, 7, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.J.; Bell, J.; Christie, M.J.; Mattick, R.P. Depressive symptoms during buprenorphine vs. methadone maintenance: Findings from a randomised, controlled trial in opioid dependence. Eur. Psychiatry 2004, 19, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, A.D.; Griffin, M.L.; McHugh, R.K.; Weiss, R.D. Depression history as a predictor of outcomes during buprenorphine-naloxone treatment of prescription opioid use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 213, 108122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Adavastro, G.; Canepa, G.; De Berardis, D.; Valchera, A.; Pompili, M.; Nasrallah, H.; Amore, M. The Efficacy of Buprenorphine in Major Depression, Treatment-Resistant Depression and Suicidal Behavior: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Association, A.P. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Bennett, M.I.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Finnerup, N.B.; First, M.B.; et al. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jong, C.A.J.; van Hoek, A.F.M.; Jongerhuis, M.; Fiers, M.; Ghijsen, L.C.J.L.; Gottmer, P.B.L.M.; Wijnen, A.P.M.J.; Joosten, E.A.G.; Vrasdonk, J.G.; Beentjes, F.J.C.; et al. Verantwoord Ontgiften Door Ambulante of Intramurale Detoxificatie. Available online: https://www.gerdierx.nl/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/detox.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Kampman, K.; Jarvis, M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) National Practice Guideline for the Use of Medications in the Treatment of Addiction Involving Opioid Use. J. Addict. Med. 2015, 9, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuldijk, D.; Giltay, E.J.; Carlier, I.V.; van Vliet, I.M.; van Hemert, A.M.; Zitman, F.G. A Validation Study of the Web Screening Questionnaire (WSQ) Compared With the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview-Plus (MINI-Plus). JMIR Ment. Health 2017, 4, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zandee, M.E.; de Jong, K. The inter-rater reliability of the MINI-Plus. Tijdschr. Psychiatr 2018, 60, 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Lecrubier, Y.; Sheehan, K.H.; Amorim, P.; Janavs, J.; Weiller, E.; Hergueta, T.; Baker, R.; Dunbar, G.C. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59 (Suppl. 20), 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer, E.C.; Rybin, D.; Saitz, R.; Samet, J.H.; Schwartz, S.L.; Butler, S.F.; Liebschutz, J.M. Identifying prescription opioid use disorder in primary care: Diagnostic characteristics of the Current Opioid Misuse Measure (COMM). Pain 2011, 152, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, S.F.; Budman, S.H.; Fanciullo, G.J.; Jamison, R.N. Cross validation of the current opioid misuse measure to monitor chronic pain patients on opioid therapy. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, S.F.; Budman, S.H.; Fernandez, K.C.; Houle, B.; Benoit, C.; Katz, N.; Jamison, R.N. Development and validation of the Current Opioid Misuse Measure. Pain 2007, 130, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleykamp, B.A.; De Santis, M.; Dworkin, R.H.; Huhn, A.S.; Kampman, K.M.; Montoya, I.D.; Preston, K.L.; Ramey, T.; Smith, S.M.; Turk, D.C.; et al. Craving and opioid use disorder: A scoping review. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2019, 205, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovibond, P.F.; Lovibond, S.H. The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, E.; Kaya, M. Depression, Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS): The Study of Validity and Reliability. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2016, 4, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.J.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.Z.; Park, S.H.; Tae, J.H.; Choi, S.S. Pain relief scale is more highly correlated with numerical rating scale than with visual analogue scale in chronic pain patients. Pain Physician 2015, 18, E195–E200. [Google Scholar]
- Thong, I.S.K.; Jensen, M.P.; Miró, J.; Tan, G. The validity of pain intensity measures: What do the NRS, VAS, VRS, and FPS-R measure? Scand. J. Pain 2018, 18, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W.; Charuvastra, C.; Collins, J.F.; Batki, S.; Brown, L.S., Jr.; Kintaudi, P.; Wesson, D.R.; McNicholas, L.; Tusel, D.J.; Malkerneker, U.; et al. Buprenorphine maintenance treatment of opiate dependence: A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. Addiction 1998, 93, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoorob, R.; Kowalchuk, A.; Mejia de Grubb, M. Buprenorphine Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.A.; Scott, L.J. Buprenorphine/Naloxone (Zubsolv(®)): A Review in Opioid Dependence. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Gray, F.; Sheng, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Ling, W.; Li, W.; et al. Treatment of opioid dependence with buprenorphine/naloxone sublingual tablets: A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Asia-Pac. Psychiatry 2019, 11, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, R.; Shao, L.; Qiu, Z. Major Depressive Disorder and Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists. Transl. Perioper. Pain Med. 2016, 1, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, E.P.; Mitchell, B.G.; Shorter, D.I.; Kosten, T.; Domingo, C.B.; Walder, A.M. Buprenorphine for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder. Am. J. Addict. 2019, 28, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalanne, L.; Ayranci, G.; Filliol, D.; Gavériaux-Ruff, C.; Befort, K.; Kieffer, B.L.; Lutz, P.E. Kappa opioid receptor antagonism and chronic antidepressant treatment have beneficial activities on social interactions and grooming deficits during heroin abstinence. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Tunis, J.; Parry, C.; Tallarida, R.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Synergistic antidepressant-like effects between a kappa opioid antagonist (LY2444296) and a delta opioid agonist (ADL5859) in the mouse forced swim test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 781, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, S.; Mavrikaki, M.M.; Lintz, T.; Puttick, D.; Roberts, E.; Rosen, H.; Carroll, F.I.; Carlezon, W.A.; Chartoff, E.H. Behavioral Pharmacology of Novel Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonists in Rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.D. Depression Effects on Long-term Prescription Opioid Use, Abuse, and Addiction. Clin. J. Pain 2018, 34, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenkovich, K.; Chockalingam, R.; Scherrer, J.F.; Panagopoulos, V.N.; Lustman, P.J.; Ray, J.M.; Freedland, K.E.; Svrakic, D.M. Prescription Opioid Analgesics Increase Risk of Major Depression: New Evidence, Plausible Neurobiological Mechanisms and Management to Achieve Depression Prophylaxis. Mo. Med. 2014, 111, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer, J.F.; Svrakic, D.M.; Freedland, K.E.; Chrusciel, T.; Balasubramanian, S.; Bucholz, K.K.; Lawler, E.V.; Lustman, P.J. Prescription opioid analgesics increase the risk of depression. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramasubbu, C.; Gupta, A. Pharmacological treatment of opioid-induced hyperalgesia: A review of the evidence. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2011, 25, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, I.K.; Pillarisetti, S. Buprenorphine—An attractive opioid with underutilized potential in treatment of chronic pain. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berna, C.; Kulich, R.J.; Rathmell, J.P. Tapering Long-term Opioid Therapy in Chronic Noncancer Pain: Evidence and Recommendations for Everyday Practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 828–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, K.; Jia, P.; Bhargava, S.; Zhang, Y.; Reza, T.; Peng, Y.B.; Wang, G.G. Opioid tapering in patients with prescription opioid use disorder: A retrospective study. Scand. J. Pain 2017, 17, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgierska, A.E.; Burzinski, C.A.; Cox, J.; Kloke, J.; Stegner, A.; Cook, D.B.; Singles, J.; Mirgain, S.; Coe, C.L.; Bačkonja, M. Mindfulness Meditation and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Intervention Reduces Pain Severity and Sensitivity in Opioid-Treated Chronic Low Back Pain: Pilot Findings from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 1865–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoerl, R.; Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Weisberg, J. Chronic Pain and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: An Integrative Review. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2016, 38, 596–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, L.; Hempel, S.; Ewing, B.A.; Apaydin, E.; Xenakis, L.; Newberry, S.; Colaiaco, B.; Maher, A.R.; Shanman, R.M.; Sorbero, M.E.; et al. Mindfulness Meditation for Chronic Pain: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Behav. Med. 2017, 51, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tripp, C.C.; Rak, E.; Burker, E. A Review of Effective Treatments for Patients With Co-Occurring Chronic Pain and Opioid Addiction. VISTAS Online 2017, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
| Total (n = 37) | |
|---|---|
| Marital status | |
| Single | 8 (21.6%) |
| Cohabitating | 29 (78.4%) |
| Education ‡ | |
| Low | 3 (8.1%) |
| Middle | 25 (66.7%) |
| High | 9 (24.3%) |
| Employment † | 10 (27.0%) |
| Substance use § | |
| Nicotine | 14 (37.8%) |
| Alcohol | 15 (40.5%) |
| Drugs | 10 (27.0%) |
| Type of pain ‡‡ | |
| Nociceptive | 20 (54.1%) |
| Neuropathic | 13 (35.1%) |
| Idiopathic | 4 (10.8%) |
| Type of opioid †† | |
| Oxycodone | 28 (75.7%) |
| Methadone | 6 (15.8%) |
| Fentanyl | 10 (27.0%) |
| Other | 9 (24.3%) |
| Multiple opioids | 14 (37.8%) |
| Other analgesics †† | |
| Paracetamol | 21 (56.8%) |
| NSAID | 4 (10.8%) |
| Antidepressant | 10 (27.0%) |
| GABA/glutamatergic (e.g., pregabalin) | 15 (40.5%) |
| Other medication †† | |
| Sedatives | 10 (27.0%) |
| Psychotropics | 12 (32.4%) |
| Gastrointestinal | 21 (56.8%) |
| Laxatives | 14 (37.8%) |
| Cardiac | 9 (24.3%) |
| Pulmonary | 6 (16.2%) |
| Baseline; Mean (±SE; 95% CI; Z-Score) | Discharge; Mean (±SE; 95% CI; Z-Score) | Follow-up; Mean (±SE; 95% CI; Z-Score) | F-Value (df) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMM | 17.1 ± 1.40 (14.3–19.9; 0.504) | - | 6.7 ± 1.45 (3.8–9.6; −0.539) | 36.50 (35.61) | 0.000 * |
| VAS-craving | 39.3 ± 4.23 (30.5–48.2; 0.590) | 21.4 ± 4.34 (12.7–30.0; −0.016) | 5.3 ± 4.34 (−3.4–13.9; −0.557) | 26.42 (70.75) | 0.000 * |
| DASS | 12.1 ± 1.17 (9.8–14.5; 0.296) | - | 6.6 ± 1.19 (4.2–9.0; −0.341) | 56.32 (173.49) | 0.000 * |
| VAS-pain | 51.3 ± 4.53 (41.6–59.6; 0.267) | 41.7 ± 4.42 (33.0–50.5; −0.057) | 37.2 ± 4.42 (28.5–46.0; −0.222) | 3.28 (70.11) | 0.044 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schellekens, A.F.A.; Veldman, S.E.; Suranto, E.S.D.; van Rijswijk, S.M.; van der Wal, S.E.I.; Schene, A.H.; van Beek, M.H.C.T. Beneficial Effects of Opioid Rotation to Buprenorphine/Naloxone on Opioid Misuse, Craving, Mental Health, and Pain Control in Chronic Non-Cancer Pain Patients with Opioid Use Disorder. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163727
Schellekens AFA, Veldman SE, Suranto ESD, van Rijswijk SM, van der Wal SEI, Schene AH, van Beek MHCT. Beneficial Effects of Opioid Rotation to Buprenorphine/Naloxone on Opioid Misuse, Craving, Mental Health, and Pain Control in Chronic Non-Cancer Pain Patients with Opioid Use Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163727
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchellekens, Arnt F. A., Stijn E. Veldman, Eka S. D. Suranto, Steffie M. van Rijswijk, Selina E. I. van der Wal, Aart H. Schene, and Marleen H. C. T. van Beek. 2021. "Beneficial Effects of Opioid Rotation to Buprenorphine/Naloxone on Opioid Misuse, Craving, Mental Health, and Pain Control in Chronic Non-Cancer Pain Patients with Opioid Use Disorder" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163727
APA StyleSchellekens, A. F. A., Veldman, S. E., Suranto, E. S. D., van Rijswijk, S. M., van der Wal, S. E. I., Schene, A. H., & van Beek, M. H. C. T. (2021). Beneficial Effects of Opioid Rotation to Buprenorphine/Naloxone on Opioid Misuse, Craving, Mental Health, and Pain Control in Chronic Non-Cancer Pain Patients with Opioid Use Disorder. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163727






