Hemorrhoids Embolization: State of the Art and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Etiology
3. Clinical Presentation
4. Conservative Management
5. Arterial Anatomy
- Type II: the main trunk passes to the right, giving off branches to the left.
- Type III: the main trunk passes to the left supplying branches to the right and a MRA define a relevant contribution to the vascularization of the CCR.
- Type IV: trifurcation of the main trunk with supplying branches to both sides of the anal canal in some with a minor participation of MRA to the vascularization of the CCR (Figure 2).
- Type V: trifurcation of the main trunk with supplying branches to both sides of the rectum not reaching the anal canal with an MRA defining a main contribution to the supply of CCR.
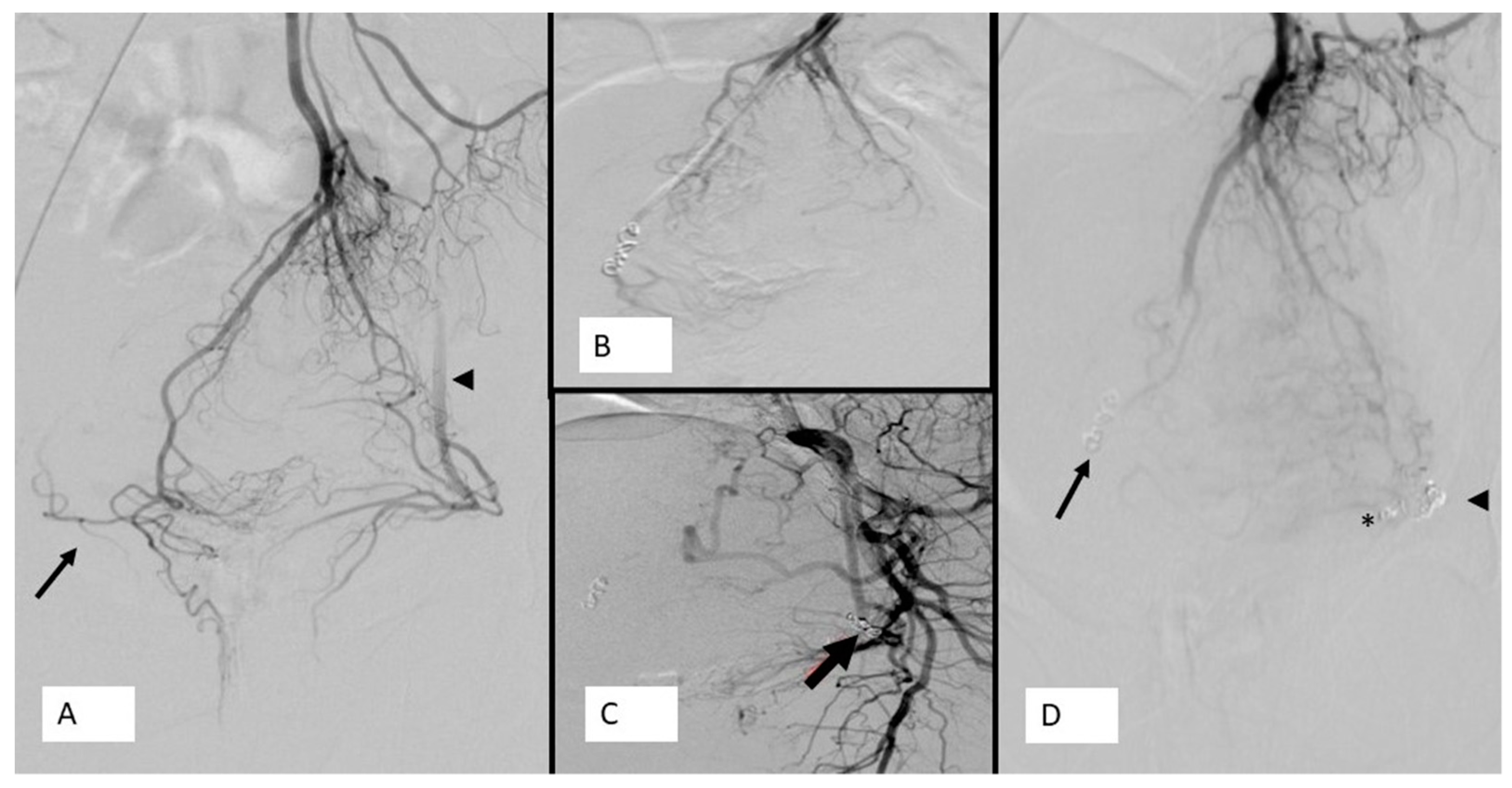
6. Embolization Agents
7. Clinical Indications
8. Hemorrhoid’s Embolization Outcome and Results
9. Futures Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, R.L.; Abcarian, H.; Davis, F.G.; Persky, V. Prevalence of Benign Anorectal Disease in a Randomly Selected Population. Dis. Colon Rectum 1995, 38, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.F.; Sonnenberg, A. The Prevalence of Hemorrhoids and Chronic Constipation. An epidemiologic study. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder, P.B.; Kamm, M.A.; Nicholls, R.; Phillips, R.K. Haemorrhoids: Pathology, Pathophysiology and Aetiology. Br. J. Surg. 1994, 81, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzner, F. The Corpus Cavernosum Recti. Dis. Colon Rectum 1964, 7, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakinic, J.; Poola, V.P. Hemorrhoids and Fistulas: New Solutions to Old Problems. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2014, 51, 98–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vidal, V.; Louis, G.; Bartoli, J.; Sielezneff, I. Embolization of the Hemorrhoidal Arteries (the Emborrhoid Technique): A new Concept and Challenge for Interventional Radiology. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2014, 95, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lestar, B.; Penninckx, F.; Kerremans, R. The Composition of Anal Basal Pressure: An In Vivo and In Vitro Study in Man. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 1989, 4, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurman, J.P.; Go, P.M.N.Y.H.; Bleys, R.L.A.W. Anatomical Branches of the Superior Rectal Artery in the Distal Rectum. Colorectal Dis. 2009, 11, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W.H.F. The Nature of Haemorrhoids. BJS 1975, 62, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, F.; Bodner, G.; Gruber, H.; Conrad, F.; Fritsch, H.; Margreiter, R.; Bonatti, H. The Vascular Nature of Hemorrhoids. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2006, 10, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheyer, M.; Antonietti, E.; Rollinger, G.; Mall, H.; Arnold, S. Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation. Am. J. Surg. 2006, 191, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, J.F.; Sonnenberg, A. Constipation is not a Risk Factor for Hemorrhoids: A Case-Control Study of Potential Etiological agents. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Riss, S.; Weiser, F.A.; Schwameis, K.; Riss, T.; Mittlböck, M.; Steiner, G.; Stift, A. The Prevalence of Hemorrhoids in Adults. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2011, 27, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunniss, P.J.; Mann, C.V. Classification of Internal Haemorrhoids: A Discussion Paper. Colorectal Dis. 2004, 6, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, F.M.; Sciaudone, G.; Canonico, S.; Selvaggi, F.; Pellino, G. Scoring System for Haemorrhoidal Disease. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2021, 16, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohsiriwat, V. Hemorrhoids: From Basic Pathophysiology to Clinical Management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tol, R.R.; Kleijnen, J.; Watson, A.J.M.; Jongen, J.; Altomare, D.F.; Qvist, N.; Higuero, T.; Muris, J.W.M.; Breukink, S.O. European Society of ColoProctology (ESCP): Guideline for Haemorrhoidal Disease. Colorectal Dis. 2020, 22, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilhim, T.; Pisco, J.M.; Tinto, H.R.; Fernandes, L.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Furtado, A.; Casal, D.; Duarte, M.; Pereira, J.; Oliveira, A.; et al. Prostatic Arterial Supply: Anatomic and Imaging Findings Relevant for Selective Arterial Embolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDio, P.L.; Diaz-Franco, C.; Schemainda, R.; Bezerra, A. Morphology of the Middle Rectal Arteries. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1986, 8, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, V.; Sapoval, M.; Sielezneff, Y.; De Parades, V.; Tradi, F.; Louis, G.; Bartoli, J.M.; Pellerin, O. Emborrhoid: A New Concept for the Treatment of Hemorrhoids with Arterial Embolization: The First 14 Cases. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 38, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharchenko, A.; Kaitoukov, Y.; Vinnik, Y.; Tradi, F.; Sapoval, M.; Sielezneff, I.; Galkin, E.; Vidal, V. Safety and Efficacy of Superior Rectal Artery Embolization with Particles and Metallic Coils for the Treatment of Hemorrhoids (Emborrhoid Technique). Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2016, 97, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradi, F.; Louis, G.; Giorgi, R.; Mege, D.; Bartoli, J.-M.; Sielezneff, I.; Vidal, V. Embolization of the Superior Rectal Arteries for Hemorrhoidal Disease: Prospective Results in 25 Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurazza, F.; Corvino, F.; Cavaglià, E.; Silvestre, M.; Cangiano, G.; Amodio, F.; De Magistris, G.; Niola, R. Emborrhoid in Patients with Portal Hypertension and Chronic Hemorrhoidal Bleeding: Preliminary Results in Five Cases with a New Coiling Release Fashion “Spaghetti Technique”. Radiol. Med. 2020, 125, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tawab, K.A.; Salem, A.A.; Khafagy, R. New Technique of Embolization of the Hemorrhoidal Arteries Using Embolization Particles Alone: Retrospective Results in 33 Patients. Arab. J. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 4, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükay, M.B.; Küçükay, F. Superior Rectal Artery Embolization with Tri-Acryl-Gelatin Particles: A Randomized Comparison of Particle Size. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, N.; Bonnet, B.; Pereira, H.; Pechmajou, L.; Pellerin, O.; Abed, A.; Del Giudice, C.; Dean, C.; Bouda, D.; De Parades, V.; et al. Mid-Term Results of Superior Rectal Artery and Coils for Hemorrhoidal Embolization with Particles Bleeding. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, N.; Sielezneff, I.; Sapoval, M.; Tradi, F.; Del Giudice, C.; Fathallah, N.; Pellerin, O.; Amouyal, G.; Pereira, H.; De Parades, V.; et al. Embolization of the Superior Rectal Arteries for Chronic Bleeding due to Haemorrhoidal Disease. Colorectal Dis. 2016, 19, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Burgos, A. Interventional Radiology should be Competitive-if Haemorrhoids are Arteriovenous Connections, It is now the Time for Liq-uids? Commentary on “Superior Rectal Artery Embolisation for Haemorrhoids: What do we Know so far?”. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, M.; De Nardi, P.; Marra, P.; Panzeri, M.; Brembilla, G.; Morelli, F.; Melchiorre, F.; DE Cobelli, F.; Del Maschio, A. Embolization of Superior Rectal Arteries for Transfusion Dependent Haemorrhoidal Bleeding in Severely Cardiopathic Patients: A New Field of Application of the “Emborrhoid” Technique. Tech. Coloproctol. 2018, 22, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiettini, D.; Graziosi, L.; Mosca, S.; Fischer, M.; Morelli, O.; Rebonato, A. Rectal Bleeding due to Ectopic Variceal Bleeding: The “Emborrhoid” Technique as a Bridge to TIPS Placement. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardi, P.; Maggi, G. Embolization of the Superior Rectal Artery: Another Management Option for Hemorrhoids. Tech. Coloproctol. 2020, 25, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Pt. Number | Country | Patient Selection | Embolic Agent | Median FU | Complication | Outcome (% of No/Unsatisfactory Clinical Success) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vidal 2014 | 14 | Goligher’s Grade II or IV | Coils | 6 months | none | 28% | |
| Zakharchenko 2016 | 40 | France | Goligher’s Grade I to III | Coils + PVA | 1 month | none | 6–17% |
| Moussa 2016 | 30 | France | Goligher’s Grade I to IV | Coils | 5 months | none | 28% |
| Tradi 2018 | 25 | France | Goligher’s Grade II or III | Coils | 12 months | none | 28% |
| Giurazza 2020 | 5 | Italy | portal hypertension and chronic hemorrhoidal bleeding | Colis | 3 months | none | 20% |
| Abd El Tawab 2020 | 33 | Egypt | Goligher’s Grade II or III | TAGp | 12 months | none | 3% |
| Moussa 2020 | 38 | France | Goligher’s Grade II or III | Coils + TAGp | 6 months | 15.00% | 34.00% |
| Küçükay 2021 | 42 | Turkey | Goligher’s Grade I or IV | TAGp | 12 months | 54% | 7% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebonato, A.; Maiettini, D.; Patriti, A.; Giurazza, F.; Tipaldi, M.A.; Piacentino, F.; Fontana, F.; Basile, A.; Venturini, M. Hemorrhoids Embolization: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163537
Rebonato A, Maiettini D, Patriti A, Giurazza F, Tipaldi MA, Piacentino F, Fontana F, Basile A, Venturini M. Hemorrhoids Embolization: State of the Art and Future Directions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163537
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebonato, Alberto, Daniele Maiettini, Alberto Patriti, Francesco Giurazza, Marcello Andrea Tipaldi, Filippo Piacentino, Federico Fontana, Antonio Basile, and Massimo Venturini. 2021. "Hemorrhoids Embolization: State of the Art and Future Directions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163537
APA StyleRebonato, A., Maiettini, D., Patriti, A., Giurazza, F., Tipaldi, M. A., Piacentino, F., Fontana, F., Basile, A., & Venturini, M. (2021). Hemorrhoids Embolization: State of the Art and Future Directions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163537






