Usefulness of a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-Based Model for the Prediction of Functional Cure in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues: A Real-World Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Endpoint
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Serology and Virology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Patients Included in the Study
3.2. Comparison between Patients with or without HBsAg-Loss
3.3. Prediction of HBsAg-Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, W.K.; Lo, Y.R.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Yuen, M.F. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018, 392, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; Global Hepatitis Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, April 2017; Available online: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Ginzberg, D.; Wong, R.J.; Gish, R. Global HBV burden: Guesstimates and facts. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, N.; Corvino, A.R.; De Pascalis, S.; Signoriello, G.; Di Fiore, E.; Nienhaus, A.; Sagnelli, E.; Lamberti, M. The Long-Term Immunogenicity of Recombinant Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Vaccine: Contribution of Universal HBV Vaccination in Italy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zanetti, A.R.; Tanzi, E.; Romanò, L.; Grappasonni, I. Vaccination against hepatitis B: The Italian strategy. Vaccine 1993, 11, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Boemio, A.; Sagnelli, C.; Alessio, L.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Sagnelli, E.; Coppola, N. Hepatitis B virus burden in developing countries. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11941–11953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracco, G.M.; Evangelista, A.; Fagoonee, S.; Ciccone, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Rizzetto, M.; Pellicano, R.; Smedile, A. Etiology of chronic liver diseases in the Northwest of Italy, 1998 through 2014. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 8187–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnelli, E.; Stroffolini, T.; Sagnelli, C.; Morisco, F.; Coppola, N.; Smedile, A.; Pisaturo, M.; Colloredo, G.; Babudieri, S.; Licata, A.; et al. Influence of universal HBV vaccination on chronic HBV infection in Italy: Results of a cross-sectional multicenter study. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Pellicano, R.; Smedile, A. Chronic hepatitis B therapy: Available drugs and treatment guidelines. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2015, 61, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Collo, A.; Belci, P.; Fagoonee, S.; Loreti, L.; Gariglio, V.; Parise, R.; Magistroni, P.; Durazzo, M. Efficacy and safety of long-term entecavir therapy in a European population. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2018, 64, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroffolini, T.; Spadaro, A.; Di Marco, V.; Scifo, G.; Russello, M.; Montalto, G.; Bertino, G.; Surace, L.; Caroleo, B.; Foti, G.; et al. Current practice of chronic hepatitis B treatment in Southern Italy. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, e124–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cuomo, G.; Borghi, V.; Giuberti, T.; Andreone, P.; Massari, M.; Villa, E.; Pietrangelo, A.; Verucchi, G.; Levantesi, F.; Ferrari, C. What to start with in first line treatment of chronic hepatitis B patients: An Italian multicentre observational cohort, HBV-RER study group. Infez. Med. 2017, 25, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Olivero, A.; Ngatchou, D.; Saracco, G.M.; Smedile, A. Long-term results of chronic hepatitis B antiviral treatment with nucleos(t)ide analogues: A single center experience. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2019, 65, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornberg, M.; Wong, V.W.; Locarnini, S.; Brunetto, M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Chan, H.L. The role of quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen revisited. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P. HBsAg quantification to optimize treatment monitoring in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2015, 35, S82–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Moon, H.W.; Ko, S.Y.; Choe, W.H.; Kwon, S.Y. HBsAg level and clinical course in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleoside analogue: Five years of follow-up data. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peng, C.Y.; Lai, H.C.; Su, W.P.; Lin, C.H.; Chuang, P.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, C.H. Early hepatitis B surface antigen decline predicts treatment response to entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Chiu, Y.C.; Chiu, H.C.; Liu, W.C.; Cheng, P.N.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, T.T.; Wu, I.C. Clinical utility of hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B patients during long-term entecavir therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broquetas, T.; Garcia-Retortillo, M.; Hernandez, J.J.; Puigvehí, M.; Cañete, N.; Coll, S.; Cabrero, B.; Giménez, M.D.; Solà, R.; Carrión, J.A. Quantification of HBsAg to predict low levels and seroclearance in HBeAg-negative patients receiving nucleos(t)ide analogues. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Lee, D.M.; Kim, S.S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Cho, S.W. Correlation of serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with response to entecavir in naive patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Med. Virol. 2011, 83, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Touscoz, G.A.; Smedile, A.; Pellicano, R. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis: Key messages for clinicians. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2014, 124, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdino, E.; Ruggiero, T.; Proietti, A.; Milia, M.G.; Olivero, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Marietti, M.; Rizzetto, M.; Smedile, A.; Ghisetti, V. Quantification of hepatitis B surface antigen with the novel DiaSorin LIAISON XL Murex HBsAg Quant: Correlation with the ARCHITECT quantitative assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandoi, F.; Caviglia, G.P.; Pittaluga, F.; Abate, M.L.; Smedile, A.; Romagnoli, R.; Salizzoni, M. Prediction of occult hepatitis B virus infection in liver transplant donors through hepatitis B virus blood markers. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2014, 46, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carosi, G.; Rizzetto, M.; Alberti, A.; Cariti, G.; Colombo, M.; Craxì, A.; Filice, G.; Levrero, M.; Mazzotta, F.; Pastore, G.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Update of the recommendations from the 2007 Italian Workshop. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.M.; Liaw, Y.F. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during chronic HBV infection. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Wong, D.K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Reduction of hepatitis B surface antigen levels and hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving 10 years of nucleoside analogue therapy. Hepatology 2013, 58, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Seto, W.K.; Kopaniszen, M.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: Relationship to hepatitis B e-antigen seroclearance and hepatitis B e-antigen-negative hepatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S.; Kao, J.H. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict surface antigen loss in hepatitis B e antigen seroconverters. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striki, A.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Deutsch, M.; Kourikou, A.; Kontos, G.; Kranidioti, H.; Hadziyannis, E.; Papatheodoridis, G. Hepatitis B s antigen kinetics during treatment with nucleos(t)ides analogues in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Chen, E.Q.; Tao, C.M.; Zhou, T.Y.; Liao, J.; Zhang, D.M.; Wang, J.; Tang, H. Pronounced decline of serum HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B patients with long-term effective nucleos(t)ide analogs therapy. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, J.G.; Rijckborst, V.; Sonneveld, M.J.; Scherbeijn, S.M.; Boucher, C.A.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen differ between treatment with peginterferon and entecavir. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevaliez, S.; Hézode, C.; Bahrami, S.; Grare, M.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Long-term hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) kinetics during nucleoside/nucleotide analogue therapy: Finite treatment duration unlikely. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chiu, Y.C.; Lu, S.N.; Lee, C.M.; Wang, J.H.; Hu, T.H.; Hung, C.H. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels predict treatment response to nucleos(t)ide analogues. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7686–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, P.; Buti, M.; Krastev, Z.; de Man, R.A.; Zeuzem, S.; Lou, L.; Gaggar, A.; Flaherty, J.F.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; et al. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen loss in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszewicz, J.; Ho, H.; Markova, A.; Deterding, K.; Wursthorn, K.; Schulz, S.; Bock, C.T.; Tillmann, H.L.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) decrease and serum interferon-inducible protein-10 levels as predictive markers for HBsAg loss during treatment with nucleoside/nucleotide analogues. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoutendijk, R.; Bettina, E.; Hansen, B.E.; Van Vuuren, A.J.; Charles, A.B.; Boucher, C.A.B.; Janssen, H.L.A. Serum HBsAg decline during long-term potent nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B and prediction of HBsAg loss. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Hui, A.J.; Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Liu, K.S.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L. Treatment cessation of entecavir in Asian patients with hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B: A multicentre prospective study. Gut 2015, 64, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Carosi, G.; Greenbloom, S.; Mazur, W.; Nguyen, T.; Jeffers, L.; Brunetto, M.; Yu, S.; Llamoso, C. Quantification of HBsAg in nucleos(t)ide-naïve patients treated for chronic hepatitis B with entecavir with or without tenofovir in the BE-LOW study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, A. The Role of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen in Nucleos(t)ide Analogues Cessation Among Asian Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B: A Systematic Review. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
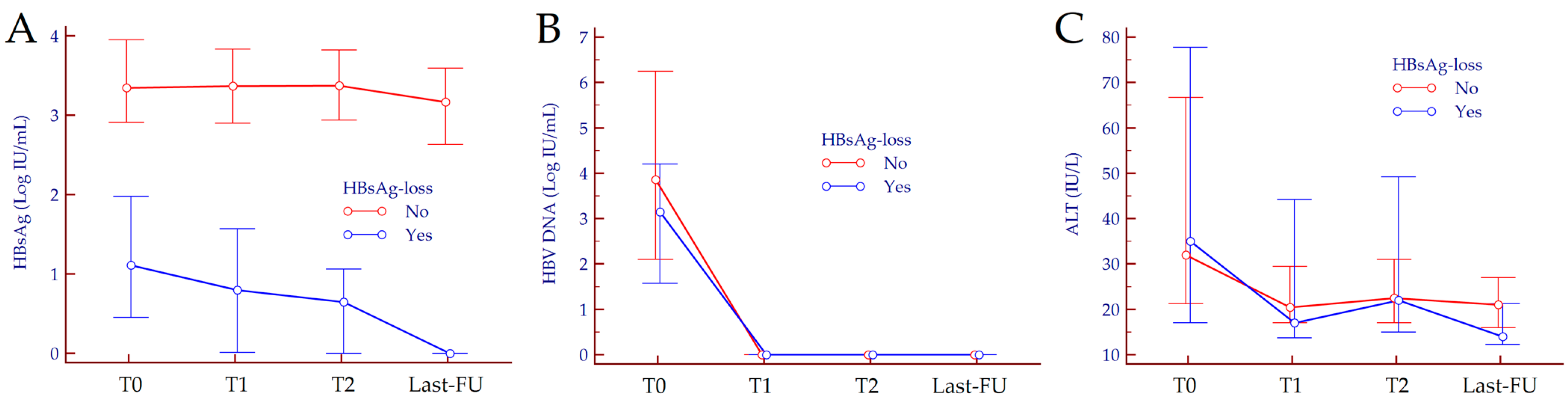

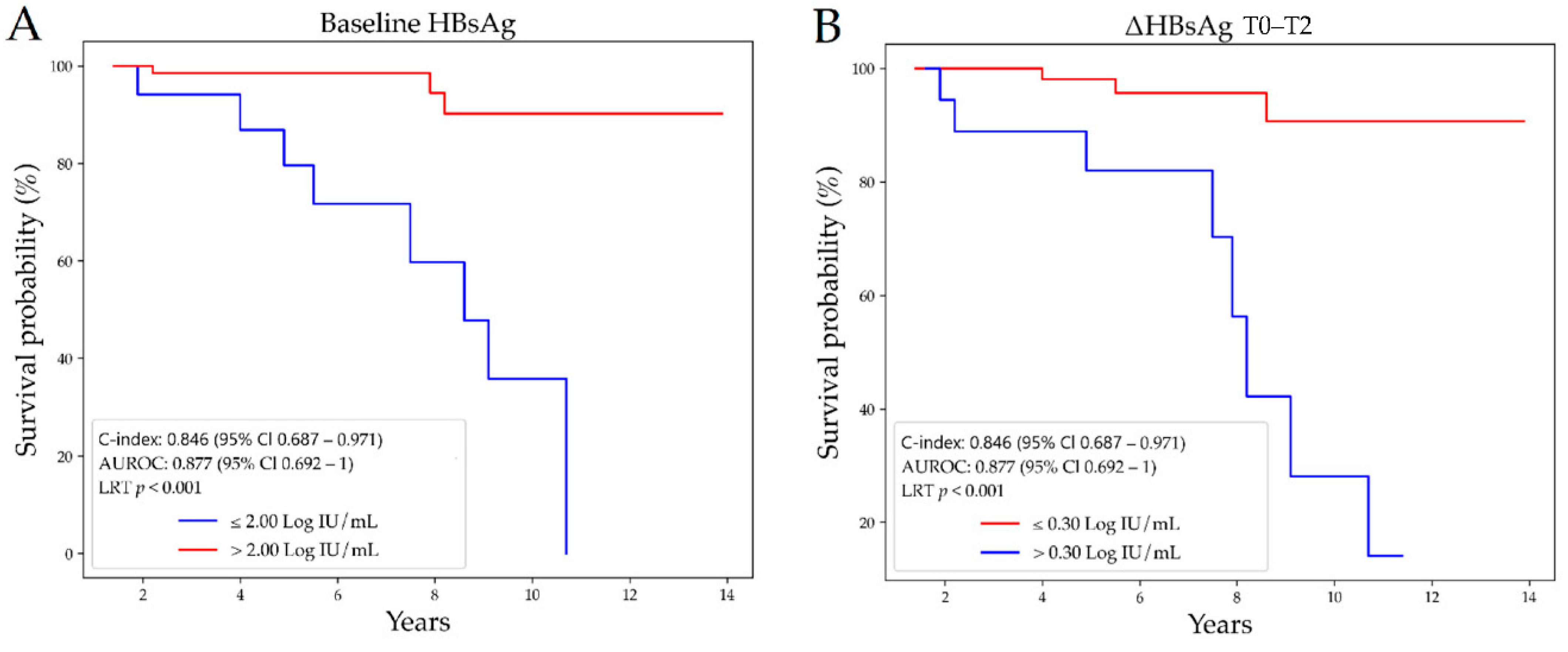
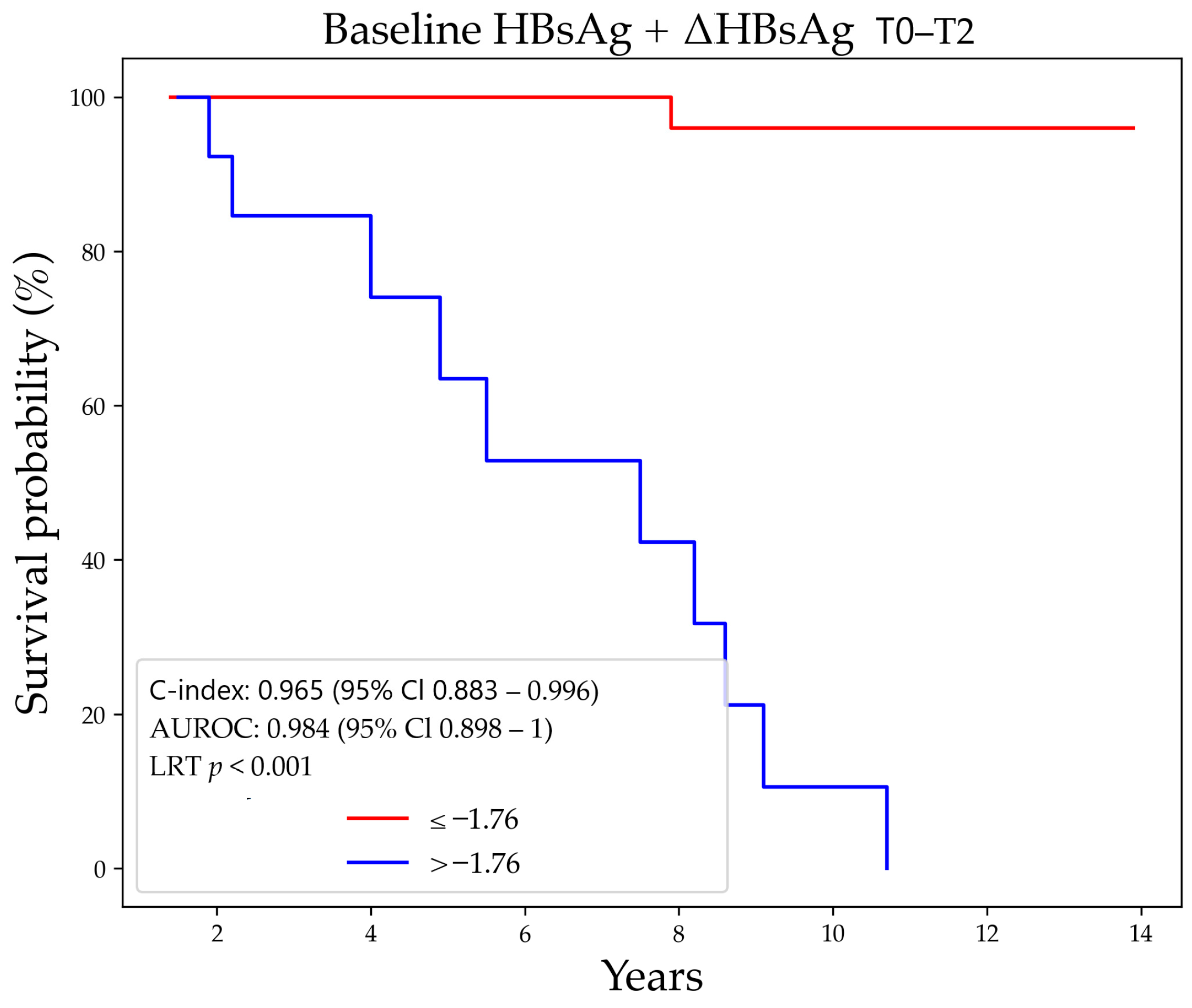
| Characteristics | Overall | No HBsAg-Loss | Functional Cure | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients, n | 101 | 90 | 11 | |
| Age (years), median (range) | 56 (32–79) | 57 (32–79) | 56 (32–72) | 0.624 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 69 (68%) | 62 (69%) | 7 (64%) | 0.739 |
| Nationality | ||||
| Italian, n (%) | 79 (78%) | 71 (79%) | 8 (73%) | 0.643 |
| East Europe, n (%) | 19 (19%) | 16 (18%) | 3 (27%) | |
| Other, n (%) A | 3 (3%) | 3 (3%) | 0 | |
| Risck factors for HBV infection | ||||
| Family exposure, n (%) | 46 (46%) | 42 (47%) | 4 (36%) | 0.75 |
| Sexual exposure, n (%) | 5 (5%) | 4 (4%) | 1 (9%) | 0.445 |
| Hospitalization, n (%) | 19 (19%) | 15 (17%) | 4 (36%) | 0.212 |
| Tattoo/Piercing, n (%) | 1 (<1%) | 1 (1%) | 0 | 1 |
| IVDU, n (%) | 1 (<1%) | 1 (1%) | 0 | 1 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Alcohol abuse, n (%) B | 7 (7%) | 6 (7%) | 1 (9%) | 0.566 |
| Obesity, n (%) C | 9 (9%) | 9 (10%) | 0 | 0.592 |
| T2DM, n (%) | 6 (6%) | 5 (6%) | 1 (9%) | 0.09 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 29 (29%) | 27 (30%) | 2 (18%) | 0.505 |
| Cirrhosis, n (%) | 18 (18%) | 15 (17%) | 3 (27%) | 0.408 |
| Ascites, n (%) | 1 (<1%) | 1 (1%) | 0 | 1 |
| Esophageal varices, n (%) | 6 (6%) | 5 (6%) | 1 (9%) | 0.509 |
| Serology | ||||
| HBsAg (Log IU/mL), median (IQR) | 3.25 (2.85–3.88) | 3.35 (2.91–3.95) | 1.11 (0.45–1.98) | <0.001 |
| HBV DNA (Log IU/mL), median (IQR) | 3.45 (1.91–5.63) | 3.86 (2.10–6.25) | 3.15 (1.57–4.21) | 0.13 |
| HBeAg+/anti-HBe+ | 15/86 | 14/74 | 10-1 | 1 |
| Biochemistry | ||||
| ALT (IU/L), median (IQR) | 34 (21–68) | 32 (21–67) | 35 (17–78) | 0.87 |
| AST (IU/L), median (IQR) | 29 (21–52) | 30 (21–53) | 24 (17–51) | 0.249 |
| γGT (IU/L), median (IQR) | 24 (16–39) | 24 (16–39) | 19 (11–47) | 0.33 |
| ALP (IU/L), median (IQR) | 65 (57–87) | 65 (57–83) | 81 (55–158) | 0.519 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.7 (0.6–0.9) | 0.7 (0.5–0.9) | 0.9 (0.7–1.3) | 0.077 |
| Albumin (g/L), median (IQR) | 4.5 (4.2–4.7) | 4.4 (4.1–4.7) | 4.5 (4.3–4.7) | 0.366 |
| Platelet count (x109/L), median (IQR) | 181 (133–227) | 185 (140–227) | 154 (111–225) | 0.235 |
| Previous IFN treatment, n (%) | 44 (44%) | 41 (46%) | 4 (36%) | 0.75 |
| Previous NAs treatment, n (%) | 61 (60%) | 53 (59%) | 8 (73%) | 0.519 |
| Duration of previous NAs (years), median (IQR) | 6 (3–10) | 6 (3–10) | 6 (1–12) | 0.602 |
| Biomarker | Timepoint | No HBsAg-Loss | Functional Cure | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg (Log IU/mL) | T0 | 3.46 (2.91–3.97) | 1.11 (0.45–1.98) | <0.001 |
| T1 | 3.39 (2.90–3.92) | 0.80 (0.01–1.57) | <0.001 | |
| T2 | 3.40 (2.95–3.89) | 0.65 (0.01–1.06) | <0.001 | |
| Last-FU | 3.21 (2.63–3.78) | 0 (0–0) | <0.001 | |
| HBV DNA (Log IU/mL) | T0 | 3.86 (2.10–6.25) | 3.15 (1.57–4.21) | 0.130 |
| T1 | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.273 | |
| T2 | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 0.386 | |
| Last-FU | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) | 1.000 | |
| ALT (IU/L) | T0 | 30 (20–67) | 35 (17–78) | 0.985 |
| T1 | 22 (17–31) | 17 (14–44) | 0.445 | |
| T2 | 23 (17–31) | 22 (15–49) | 0.815 | |
| Last-FU | 21 (16–28) | 14 (12–21) | 0.038 |
| Biomarker | Time Interval | No HBsAg-Loss | Functional Cure | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔHBsAg (Log IU/mL) | T0–T1 | 0.02 (−0.02–0.10) | 0.19 (−0.04–0.37) | 0.082 |
| T1–T2 | 0.02 (−0.01–0.09) | 0.15 (0–0.27) | 0.117 | |
| T0–T2 | 0.05 (−0.04–0.13) | 0.38 (0.11–0.80) | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caviglia, G.P.; Troshina, Y.; Garro, E.; Gesualdo, M.; Aneli, S.; Birolo, G.; Pittaluga, F.; Cavallo, R.; Saracco, G.M.; Ciancio, A. Usefulness of a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-Based Model for the Prediction of Functional Cure in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues: A Real-World Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153308
Caviglia GP, Troshina Y, Garro E, Gesualdo M, Aneli S, Birolo G, Pittaluga F, Cavallo R, Saracco GM, Ciancio A. Usefulness of a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-Based Model for the Prediction of Functional Cure in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues: A Real-World Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153308
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaviglia, Gian Paolo, Yulia Troshina, Enrico Garro, Marcantonio Gesualdo, Serena Aneli, Giovanni Birolo, Fabrizia Pittaluga, Rossana Cavallo, Giorgio Maria Saracco, and Alessia Ciancio. 2021. "Usefulness of a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-Based Model for the Prediction of Functional Cure in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues: A Real-World Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153308
APA StyleCaviglia, G. P., Troshina, Y., Garro, E., Gesualdo, M., Aneli, S., Birolo, G., Pittaluga, F., Cavallo, R., Saracco, G. M., & Ciancio, A. (2021). Usefulness of a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen-Based Model for the Prediction of Functional Cure in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Treated with Nucleos(t)ide Analogues: A Real-World Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3308. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153308







