Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnosis
3. Treatment
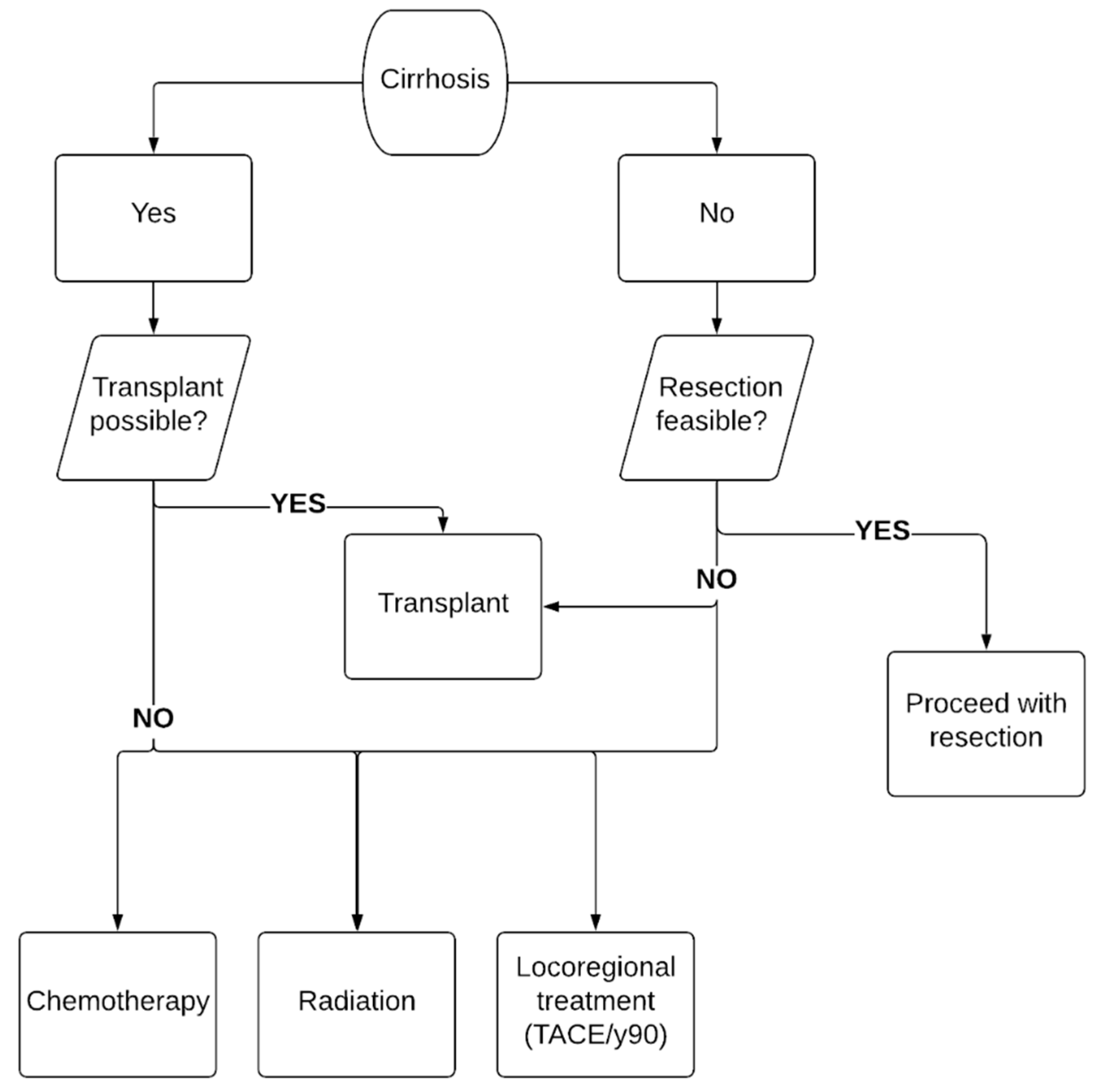
3.1. Surgical Resection
3.2. Liver Transplant
3.3. Locoregional Therapies
3.4. Chemotherapy
3.5. Adjuvant Chemotherapy
3.6. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
4. Advanced Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
5. Targeted Therapy
6. New Drugs on the Horizon
7. Radiation
7.1. Adjuvant Radiation
7.2. Definitive Radiation
7.3. Proton Beam Therapy
7.4. Brachytherapy (BT)
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saha, S.K.; Zhu, A.X.; Fuchs, C.S.; Brooks, G.A. Forty-Year Trends in Cholangiocarcinoma Incidence in the U.S.: Intrahepatic Disease on the Rise. Oncologist 2016, 21, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Floseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Macroscopic type and stage classification. J. Hepato Biliary Pancreat. Surg. 2003, 10, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakeeb, A.; Pitt, H.A.; Sohn, T.A.; Coleman, J.; Abrams, R.A.; Piantadosi, S.; Hruban, R.H.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L. Cholangiocarcinoma. A spectrum of intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal tumors. Ann. Surg. 1996, 224, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Borbath, I.; Khan, S.A.; Huguet, F.; Gruenberger, T.; Arnold, D. Biliary cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v28–v37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 2014, 383, 2168–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, T.M.; Graubard, B.I.; El–Serag, H.B.; Shaib, Y.H.; Hsing, A.W.; Davila, J.A.; McGlynn, K.A. Risk Factors for Intrahepatic and Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in the United States: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyson, G.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, K.W.; Angulo, P.; Pasha, T.M.; Egan, K.M.; Petz, J.; Lindor, K.D. Incidence and Risk Factors for Cholangiocarcinoma in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, M.; Kubo, S.; Tanaka, S.; Takemura, S.; Nishioka, T.; Hamano, G.; Ito, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ohsawa, M.; Shibata, T. The association between non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A hospital based case-control study. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, S.; Tovoli, F.; Mazzotta, A.; Vasuri, F.; Edeline, J.; Malvi, D.; Boudjema, K.; Renzulli, M.; Jeddou, H.; D’Errico, A.; et al. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis as a Risk Factor for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Its Prognostic Role. Cancers 2020, 12, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthiaume, E.P.; Wands, J. The Molecular Pathogenesis of Cholangiocarcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Toledano, M.; Taylor-Robinson, S. Epidemiology, risk factors, and pathogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma. HPB 2008, 10, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, K.N.; Gores, G.J. Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeOliveira, M.L.; Cunningham, S.C.; Cameron, J.L.; Kamangar, F.; Winter, J.M.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Choti, M.A.; Yeo, C.J.; Schulick, R.D. Cholangiocarcinoma: Thirty-one-year experience with 564 patients at a single institution. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Arai, Y.; Totoki, Y.; Shirota, T.; ElZawahry, A.; Kato, M.; Hama, N.; Hosoda, F.; Urushidate, T.; Ohashi, S.; et al. Genomic spectra of biliary tract cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Davidson, B.R.; Goldin, R.; Pereira, S.P.; Rosenberg, W.M.C.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Thillainayagam, A.V.; Thomas, H.C.; Thursz, M.R.; Wasan, H. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: Consensus document. Gut 2002, 51, vi1–vi9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimola, J.; Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Vilana, R.; De Lope, C.R.; Ayuso, C.; Bruix, J. Cholangiocarcinoma in cirrhosis: Absence of contrast washout in delayed phases by magnetic resonance imaging avoids misdiagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 50, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgrain, V. Staging cholangiocarcinoma by imaging studies. HPB 2008, 10, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Intrahepatic Mass-forming Cholangiocarcinoma: Enhancement Patterns on Gadoxetic Acid–enhanced MR Images. Radiology 2012, 264, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitenstein, S.; Apestegui, C.; Clavien, P.-A. Positron emission tomography (PET) for cholangiocarcinoma. HPB 2008, 10, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Yun, M.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.D. Usefulness of 18 F-FDG PET in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapisochin, G.; Fidelman, N.; Roberts, J.P.; Yao, F.Y. Mixed hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in patients undergoing transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Hong, J.C. Orthotopic liver transplantation in combination with neoadjuvant therapy: A new paradigm in the treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blechacz, B.; Komuta, M.; Roskams, T.; Gores, G.J. Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.H.; Harnois, D.M.; Klee, G.G.; LaRusso, N.F.; Gores, G.J. The utility of CA 19-9 in the diagnoses of cholangiocarcinoma in patients without primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Irisin alleviates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting excessive mitochondrial fission, promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and decreasing oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, K.; Cleary, S.P. A Review of Circulating Tumor DNA in Hepatobiliary Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Lamarca, A.; Goyal, L.; Barriuso, J.; Zhu, A.X. New Horizons for Precision Medicine in Biliary Tract Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettrich, T.J.; Schwerdel, D.; Dolnik, A.; Beuter, F.; Blätte, T.J.; Schmidt, S.A.; Stanescu-Siegmund, N.; Steinacker, J.; Marienfeld, R.; Kleger, A.; et al. Genotyping of circulating tumor DNA in cholangiocarcinoma reveals diagnostic and prognostic information. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, C.; Diamandis, E.P. Utility of circulating tumor DNA in cancer diagnostics with emphasis on early detection. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.C.C.; Coburn, N.G.; Baxter, N.N.; Kiss, A.; Law, C.H.L. Surgical Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma—A Population-Based Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 15, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.C.; Cassera, M.A.; Vetto, J.T.; Orloff, S.L.; Hansen, P.D.; Billingsley, K.G. Surgical treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Outcomes and predictive factors. HPB 2011, 13, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hyder, O.; Marques, H.; Pulitano, C.; Marsh, J.W.; Alexandrescu, S.; Bauer, T.W.; Gamblin, T.C.; Sotiropoulos, G.C.; Paul, A.; Barroso, E.; et al. A nomogram to predict long-term survival after resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: An Eastern and Western experience. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolverato, G.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Kim, Y.; Alexandrescu, S.; Marques, H.P.; Lamelas, J.; Aldrighetti, L.; Gamblin, T.C.; Maithel, S.K.; Pulitano, C.; et al. The Impact of Surgical Margin Status on Long-Term Outcome After Resection for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, F.; Paschold, M.; Baumgart, J.; Hoppe-Lotichius, M.; Heinrich, S.; Lang, H. Surgical Resection for Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Surg. 2018, 43, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, K.Y.; Jung, J.C.; Heo, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, Y.I. What prognostic factors are important for resected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribero, D.; Pinna, A.D.; Guglielmi, A.; Ponti, A.; Nuzzo, G.; Giulini, S.M.; Aldrighetti, L.; Calise, F.; Gerunda, G.E.; Tomatis, M.; et al. Surgical Approach for Long-term Survival of Patients With Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Multi-institutional Analysis of 434 Patients. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieber, A.C.; Marino, I.R.; Iwatsuki, S.; Starzl, T.E. Cholangiocarcinoma in sclerosing cholangitis. The role of liver transplantation. Int. Surg. 1989, 74, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, C.G.; Penn, I.; James, L. Liver transplantation for cholangiocarcinoma: Results in 207 patients. Transplantation 2000, 69, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.C.; Jones, C.M.; Duffy, J.P.; Petrowsky, H.; Farmer, D.G.; French, S.; Finn, R.; Durazo, F.A.; Saab, S.; Tong, M.J.; et al. Comparative analysis of resection and liver transplantation for intrahepatic and hilar cholangiocarcinoma: A 24-year experience in a single center. Arch. Surg. 2011, 146, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.D.; Croome, K.P.; Musto, K.R.; Melendez, J.; Tranesh, G.; Nakhleh, R.; Taner, C.B.; Nguyen, J.H.; Patel, T.; Harnois, D.M. Liver transplantation for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2018, 24, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapisochin, G.; de Lope, C.R.; Gastaca, M.; de Urbina, J.O.; López-Andujar, R.; Palacios, F.; Ramos, E.; Fabregat, J.; Castroagudín, J.F.; Varo, E.; et al. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma or mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma in patients undergoing liver transplantation: A Spanish matched cohort multicenter study. Ann Surg. 2014, 259, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.; Harnois, D.M.; Sapisochin, G.; Dodge, J.L.; Lee, D.; Burns, J.M.; Sanchez, W.; Greig, P.D.; Grant, D.R.; et al. Validation of a Risk Estimation of Tumor Recurrence After Transplant (RETREAT) Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence After Liver Transplant. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunsford, K.E.; Javle, M.; Heyne, K.; Shroff, R.T.; Abdel-Wahab, R.; Gupta, N.; Mobley, C.M.; Saharia, A.; Victor, D.W.; Nguyen, D.T.; et al. Liver transplantation for locally advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma treated with neoadjuvant therapy: A prospective case-series. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, L.J.; Chapiro, J.; Geschwind, J.-F.H. Intra-arterial embolotherapy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Update and future prospects. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2017, 6, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann, U.; Kaths, J.; Heise, M.; Pitton, M.; Weinmann, A.; Hoppe-Lotichius, M.; Otto, G. Comparison of resection and transarterial chemoembolisation in the treatment of advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma—A single-center experience. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 39, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, R.; Dash, A. Availability of Yttrium-90 from Strontium-90: A Nuclear Medicine Perspective. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeze-Kuijpers, B.; Meerwaldt, J.; Lameris, J.; Van Blankenstein, M.; Van Putten, W.; Terpstra, O. The role of radiotherapy in the treatment of bile duct carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1990, 18, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adra, D.; Gill, R.; Axford, S.; Shi, X.; Kneteman, N.; Liau, S.-S. Treatment of unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with yttrium-90 radioembolization: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-González, Á.; Vilana, R.; Bianchi, L.; Ángeles, G.-C.; Rimola, J.; de Lope, C.R.; Ferrer, J.; Ayuso, C.; Da Fonseca, L.G.; Reig, M.; et al. Thermal Ablation for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma in Cirrhosis: Safety and Efficacy in Non-Surgical Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.-K.; Chou, Y.-H.; Chiang, J.-H.; Chang, C.-Y. Percutaneous Ultrasound-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Kaohsiung J. Med Sci. 2005, 21, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, J.; Yu, X.; Han, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, F.; Liang, P. Clinical and survival outcomes of percutaneous microwave ablation for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.P.; Vardanian, A.; Benjamin, E.; Watson, M.; Farmer, D.G.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Lipshutz, G.; Yersiz, H.; Lu, D.S.; Lassman, C.; et al. Liver transplantation criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma should be expanded: A 22-year experience with 467 patients at UCLA. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenhüner, A.R.; Seifert, H.; Bachmann, H.; Seifert, B.; Winder, T.; Feilchenfeldt, J.; Breitenstein, S.; Clavien, P.-A.; Stupp, R.; Knuth, A.; et al. Adjuvant treatment of resectable biliary tract cancer with cisplatin plus gemcitabine: A prospective single center phase II study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primrose, J.N.; Fox, R.P.; Palmer, D.H.; Malik, H.Z.; Prasad, R.; Mirza, D.; Anthony, A.; Corrie, P.; Falk, S.; Finch-Jones, M.; et al. Capecitabine compared with observation in resected biliary tract cancer (BILCAP): A randomised, controlled, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeline, J.; Benabdelghani, M.; Bertaut, A.; Watelet, J.; Hammel, P.; Joly, J.-P.; Boudjema, K.; Fartoux, L.; Bouhier-Leporrier, K.; Jouve, J.-L.; et al. Gemcitabine and Oxaliplatin Chemotherapy or Surveillance in Resected Biliary Tract Cancer (PRODIGE 12-ACCORD 18-UNICANCER GI): A Randomized Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, J.; Wasan, H.; Palmer, D.H.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Iveson, T.; Hughes, S.; Pereira, S.P.; et al. Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine versus Gemcitabine for Biliary Tract Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusaka, T.; Nakachi, K.; Fukutomi, A.; Mizuno, N.; Ohkawa, S.; Funakoshi, A.; Nagino, M.; Kondo, S.; Nagaoka, S.; Funai, J.; et al. Gemcitabine alone or in combination with cisplatin in patients with biliary tract cancer: A comparative multicentre study in Japan. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.W.; Oh, S.Y.; Jang, J.S.; Lee, M.; Sohn, B.; Yoon, S.; Choi, H.; et al. Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin versus gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for advanced biliary tract cancers: A multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase III, noninferiority trial. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, A.; Palemer, D.H.; Wasan, H.S.; Ross, P.J.; Ma, Y.T.; Arora, A.; Falk, S.; Gillmore, R.; Wadslet, J.; Patel, K.; et al. ABC-06|A randomised phase III, multi-centre, open-label study of active symptom control (ASC) alone or ASC with oxaliplatin/5-FU chemotherapy (ASC+mFOLFOX) for patients (pts) with locally advanced/metastatic biliary tract cancers (ABC) previously-treated with cisplatin/gemcitabine (CisGem) chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 15), 4003. [Google Scholar]
- Valle, J.W.; Wasan, H.; Lopes, A.; Backen, A.C.; Palmer, D.H.; Morris, K.; Duggan, M.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, D.A.; Corrie, P.; et al. Cediranib or placebo in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine chemotherapy for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer (ABC-03): A randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Sahai, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Vaccaro, G.; Melisi, D.; Al-Rajabi, R.; Paulson, A.S.; Borad, M.J.; Gallinson, D.; Murphy, A.G.; et al. Pemigatinib for previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Frega, G.; Ricci, A.D.; Palloni, A.; Abbati, F.; De Lorenzo, S.; Deserti, M.; Tavolari, S.; Brandi, G. Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. In Vivo 2020, 34, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Ikeda, M.; Sasaki, T.; Nagashima, F.; Mizuno, N.; Shimizu, S.; Ikezawa, H.; Hayata, N.; Nakajima, R.; Morizane, C. Phase 2 study of lenvatinib monotherapy as second-line treatment in unresectable biliary tract cancer: Primary analysis results. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Macarulla, T.; Javle, M.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Lubner, S.J.; Adeva, J.; Cleary, J.M.; Catenacci, D.V.; Borad, M.J.; Bridgewater, J.; et al. Ivosidenib in IDH1-mutant, chemotherapy-refractory cholangiocarcinoma (ClarIDHy): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piha-Paul, S.A.; Oh, D.; Ueno, M.; Malka, D.; Chung, H.C.; Nagrial, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Ros, W.; Italiano, A.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab for the treatment of advanced biliary cancer: Results from the KEYNOTE-158 and KEYNOTE-028 studies. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.D.; Chung, V.; Alese, O.B.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Li, D.; Al-Toubah, T.E.; Schell, M.J.; Zhou, J.-M.; Mahipal, A.; Kim, B.H.; et al. A Phase 2 Multi-institutional Study of Nivolumab for Patients With Advanced Refractory Biliary Tract Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgan, A.M.; Amir, E.; Walter, T.; Knox, J.J. Adjuvant Therapy in the Treatment of Biliary Tract Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akateh, C.; Ejaz, A.M.; Pawlik, T.M.; Cloyd, J.M. Neoadjuvant treatment strategies for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Xie, H.; Bin-Riaz, I.; Sharma, P.; Durani, U.; Goyal, G.; Borah, B.; Borad, M.J.; Smoot, R.L.; Roberts, L.R.; et al. Neoadjuvant vs. adjuvant chemotherapy for cholangiocarcinoma: A propensity score matched analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, B.; Gelli, M.; Pittau, G.; Allard, M.; Pereira, B.; Serji, B.; Vibert, E.; Castaing, D.; Adam, R.; Cherqui, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for initially unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BJS 2018, 105, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarca, A.; Ross, P.; Wasan, H.S.; Hubner, R.A.; McNamara, M.G.; Lopes, A.; Manoharan, P.; Palmer, D.; Bridgewater, J.; Valle, J.W. Advanced intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Post-hoc analysis of the ABC-01, -02 and -03 clinical trials. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 112, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Abbott, D.E.; Abrams, T.A.; Alberts, S.R.; Anaya, D.A.; Anders, R.; Are, C.; Brown, D.; Chang, D.T.; et al. Guidelines Insights: Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2019. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosele, F.; Remon, J.; Mateo, J.; Westphalen, C.; Barlesi, F.; Lolkema, M.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; Robson, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.; Borad, M.J. The rise of the FGFR inhibitor in advanced biliary cancer: The next cover of time magazine? J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Khawaja, M.R.; Dinardo, C.D.; Atkins, J.T.; Janku, F. Targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) in cancer. Discov. Med. 2016, 21, 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Shiao, M.-S.; Chiablaem, K.; Charoensawan, V.; Ngamphaiboon, N.; Jinawath, N. Emergence of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: How High-Throughput Technologies Expedite the Solutions for a Rare Cancer Type. Front. Genet. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.; Kim, D.; Yoo, C.; Kim, K.-P.; Jeong, J.H.; Chang, H.-M.; Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Song, T.J.; Hwang, S.; et al. Therapeutic relevance of targeted sequencing in management of patients with advanced biliary tract cancer: DNA damage repair gene mutations as a predictive biomarker. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, A.; Kapacee, Z.; Breeze, M.; Bell, C.; Belcher, D.; Staiger, H.; Taylor, C.; McNamara, M.G.; Hubner, R.A.; Valle, J.W. Molecular Profiling in Daily Clinical Practice: Practicalities in Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma and Other Biliary Tract Cancers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshidfar, F.; Zheng, S.; Gingras, M.-C.; Newton, Y.; Shih, J.; Robertson, A.G.; Hinoue, T.; Hoadley, K.A.; Gibb, E.A.; Roszik, J.; et al. Integrative Genomic Analysis of Cholangiocarcinoma Identifies Distinct IDH-Mutant Molecular Profiles. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2780–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardell, C.P.; Fujita, M.; Yamada, T.; Simbolo, M.; Fassan, M.; Karlic, R.; Polak, P.; Kim, J.; Hatanaka, Y.; Maejima, K.; et al. Genomic characterization of biliary tract cancers identifies driver genes and predisposing mutations. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bupathi, M.; Ahn, D.H.; Bekaii-Saab, T. Therapeutic options for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2017, 6, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzzenente, A.; Fassan, M.; Conci, S.; Simbolo, M.; Lawlor, R.T.; Pedrazzani, C.; Capelli, P.; D’Onofrio, M.; Iacono, C.; Scarpa, A.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma Heterogeneity Revealed by Multigene Mutational Profiling: Clinical and Prognostic Relevance in Surgically Resected Patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 23, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, J.; De Abreu, F.B.; Peterson, J.D.; Pipas, J.M.; Mody, K.; Amos, C.I.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Suriawinata, A.A. Molecular profiling of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using next generation sequencing. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.W.K.; Askan, G.; Daniel, T.D.; Lowery, M.; Klimstra, D.S.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Shia, J. Biliary carcinomas: Pathology and the role of DNA mismatch repair deficiency. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, M.G.; Seijo, S.; Yepes, I.; Achécar, L.; Catalina, M.V.; Ángeles, G.C.; Abraldes, J.G.; De La Peña, J.; Bañares, R.; Albillos, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anticoagulation on Patients With Cirrhosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kambadakone, A.R.; Muzikansky, A.; Zheng, H.; Clark, J.W.; Abrams, T.A.; Chan, J.A.; Enzinger, P.C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and bevacizumab in advanced biliary-tract cancers and correlation of changes in 18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET with clinical outcome: A phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churi, C.R.; Shroff, R.; Wang, Y.; Rashid, A.; Kang, H.C.; Weatherly, J.; Zuo, M.; Zinner, R.; Hong, D.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Mutation Profiling in Cholangiocarcinoma: Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, S.; Pilla, L.; Elvevi, A.; Longarini, R.; Rossi, R.E.; Bidoli, P.; Invernizzi, P. New and Emerging Systemic Therapeutic Options for Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, E.T.; Mitra, N.; Guo, M.; Metz, J.M. Radiation Therapy Is Associated With Improved Survival in the Adjuvant and Definitive Treatment of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, B.H.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, T.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, C.-M. Outcomes of concurrent chemoradiotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced-stage unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Krishnan, S.; Bhosale, P.R.; Javle, M.M.; Aloia, T.A.; Shroff, R.T.; Kaseb, A.O.; Bishop, A.; Swanick, C.W.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Ablative Radiotherapy Doses Lead to a Substantial Prolongation of Survival in Patients With Inoperable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Retrospective Dose Response Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.S.; Wo, J.Y.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ben-Josef, E.; McDonnell, E.I.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; Goyal, L.; et al. Multi-Institutional Phase II Study of High-Dose Hypofractionated Proton Beam Therapy in Patients With Localized, Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, A.; Mizumoto, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Abei, M.; Fukuda, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Sakae, T.; Tsuboi, K.; Okumura, T.; Sakurai, H. Proton beam therapy for unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 30, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Oikawa, H.; Onishi, H.; Kanesaka, N.; Tamamoto, T.; Kosugi, T.; Hatano, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. Impact of Intraluminal Brachytherapy on Survival Outcome for Radiation Therapy for Unresectable Biliary Tract Cancer: A Propensity-Score Matched-Pair Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 89, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
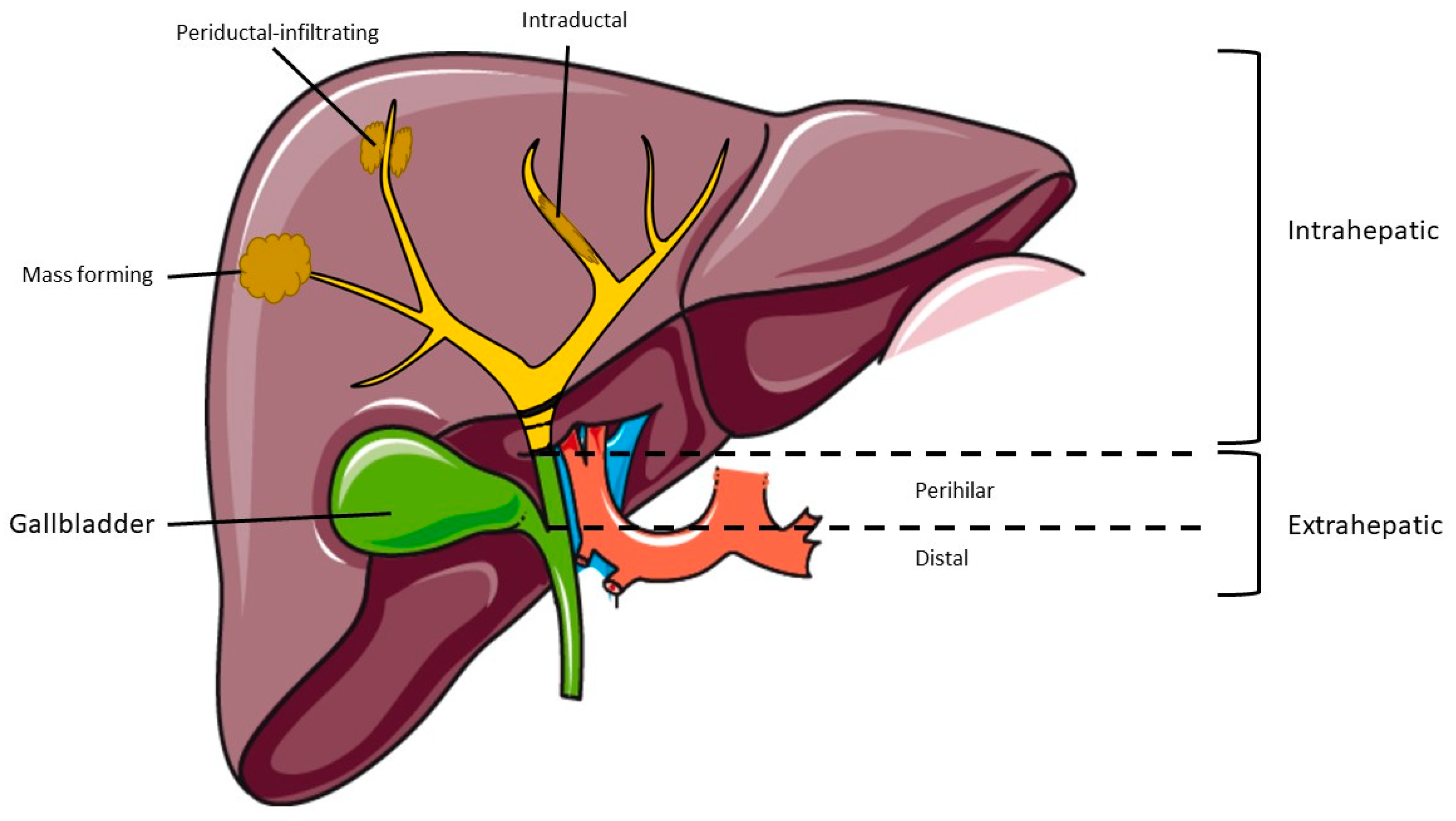
| Risk Factors for iCCA |
|---|
|
| Author, Year, Study | Patients, Country | Location of BTC | Treatment Arm | () |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADJUVANT THERAPY | ||||
| Siebenhüner, 2018 Phase 2 [56] | 30 Switzerland | Intrahepatic (57%) Extrahepatic (20%) Other (24%) | GC vs. gem | Median OS: no difference |
| Primrose, 2019 Phase 3 [57] | 447 UK | Intrahepatic (19%) Extrahepatic (64%) Other (17%) | Capecitabine vs. surveillance | Median OS: 51.1 vs. 36.4 HR for OS: 0.71 (0.55–0.92) (p = 0.010) Median RFS: 24.4 vs. 17.5 |
| Edeline, 2019 Phase 3 [58] | 196 France | Intrahepatic (44%) Extrahepatic (36%) Other (20%) | GEMOX vs. surveillance | Median OS: no difference Median RFS: no difference |
| THERAPEUTIC | ||||
| Valle, 2010 Phase 3 [59] | 410 UK | CCA * (59%) Other (41%) | GC vs. gem | Median OS: 11.7 vs. 8.1 HR for OS: 0.64 (0.52–0.80) (p < 0.001) Median PFS 8.0 vs. 5.0 (p < 0.001) |
| Okusaka, 2010 Phase 2 [60] | 83 Japan | Intrahepatic (34%) Extrahepatic (23%) Other (43%) | GC vs. gem | Median OS: 11.2 vs. 7.7 Median PFS: 6.8 vs. 3.7 HR for PFS: 0.66 (0.41–1.05) (p = 0.077) |
| Kim, 2019 Phase 3 [61] | 222 South Korea | CCA * (73%) Other (27%) | XELOX vs. GEMOX | Median OS: no difference ORR: no difference |
| Lamarca, 2019 Phase 3 [62] | 162 UK | Intrahepatic (44%) Extrahepatic (28%) Other (28%) | Oxaliplatin + 5-FU + symptom control vs. symptom control | Median OS: 6.2 vs. 5.3 HR for OS: 0.69 (0.50–0.97) (p = 0.031) |
| TARGETED THERAPY | ||||
| Valle, 2015 Phase 2 [63] | 124 UK | Intrahepatic (23%) Extrahepatic (39%) Other (38%) | Cediranib (anti-VEGF) + GC vs. GC | Median PFS: no difference |
| Abou-Alfa, 2020 Phase 2 [64] | 146 Global | Intrahepatic (89%) Extrahepatic (8%) Other (3%) | Pemigatinib (anti-FGFR) + with or without FGF fusion/rearrangement | Median OS: 21.1 vs. 4.0 OR: 35.5% vs. 0% Median PFS: 6.9 vs. 1.7 |
| Rizzo, 2020 Retrospective study [65] | 450 Global | Intrahepatic (64%) Extrahepatic (18%) Other (18%) | EGFR inhibitor + gem vs. gem | Median OS: no difference Median PFS: no difference ORR: no difference |
| Ueno, 2020 Phase 2 [66] | 26 Japan | Intrahepatic (23%) Extrahepatic (31%) Other (46%) | Lenvatinib (anti-VEGF) | Median OS: 7.36 ORR: 11.5% (3.2–27.2) Median PFS: 3.19 |
| Abou-Alfa, 2020 Phase 3 [67] | 185 Global | Intrahepatic (92%) Extrahepatic (3%) Other (5%) | Ivosideninb (IDH1 inhibitor) vs. placebo | Median PFS: 2.7 vs. 1.4 (p < 0.001) HR for PFS: 0.37 (0.25–0.54) (p < 0.0001) Median OS: no difference |
| IMMUNOTHERAPY | ||||
| Piha-Paul, 2020 Phase 1b, 2 [68] | 104 (phase 2) 24 (phase 1b) Global | Pembrolizumab (anti-PD1) | KEYNOTE-158 (phase 2) Median OS: 7.4 Median PFS: 2.0 KEYNOTE-028 (phase 1b) Median OS: 5.7 Median PFS: 1.8 | |
| Kim, 2020 Phase 2 [69] | 54 USA | Intrahepatic (59%) Extrahepatic (9%) Other (32%) | Nivolumab (anti-PD1) | Median OS: 14.24 Median PFS: 3.68 ORR: 22% |
| Molecular Target | Frequency of Mutations (%) | Targeted Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Cell cycle regulation | ||
| TP53 | 12–43 [79,80] | p53 activators |
| CDKN2A | 10–47 [81,82] | CDK 4/6 inhibitors |
| Epigenetic modification | ||
| IDH1/2 | 3–36 [83,84] | IDH inhibitors |
| BAP1 | 4–32 [82,83] | PARP/ATM inhibitors |
| Chromatin remodeling | ||
| ARID1A | 5–27 [81,82] | EZH2, HDAC, DNMT inhibitors |
| PBRM1 | 6–21 [79,83] | |
| Kinase signaling | ||
| KRAS | 3–47 [79,85] | KRAS inhibitors |
| BRAF | 1–45 [81,86] | BRAF inhibitors |
| EGFR | 10–32 [84] | EGFR inhibitors |
| FGFR1/2/3 | 5–50 [17,84] | FGFR inhibitors |
| PIK3CA | 5–13 [82,83] | mTOR inhibitors |
| c-MET | 20–60 [84] | MET inhibitors |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kodali, S.; Shetty, A.; Shekhar, S.; Victor, D.W.; Ghobrial, R.M. Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112368
Kodali S, Shetty A, Shekhar S, Victor DW, Ghobrial RM. Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112368
Chicago/Turabian StyleKodali, Sudha, Akshay Shetty, Soumya Shekhar, David W. Victor, and Rafik M. Ghobrial. 2021. "Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112368
APA StyleKodali, S., Shetty, A., Shekhar, S., Victor, D. W., & Ghobrial, R. M. (2021). Management of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112368






