Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Their Role in ED
4. Calculators for CV Risk Estimation
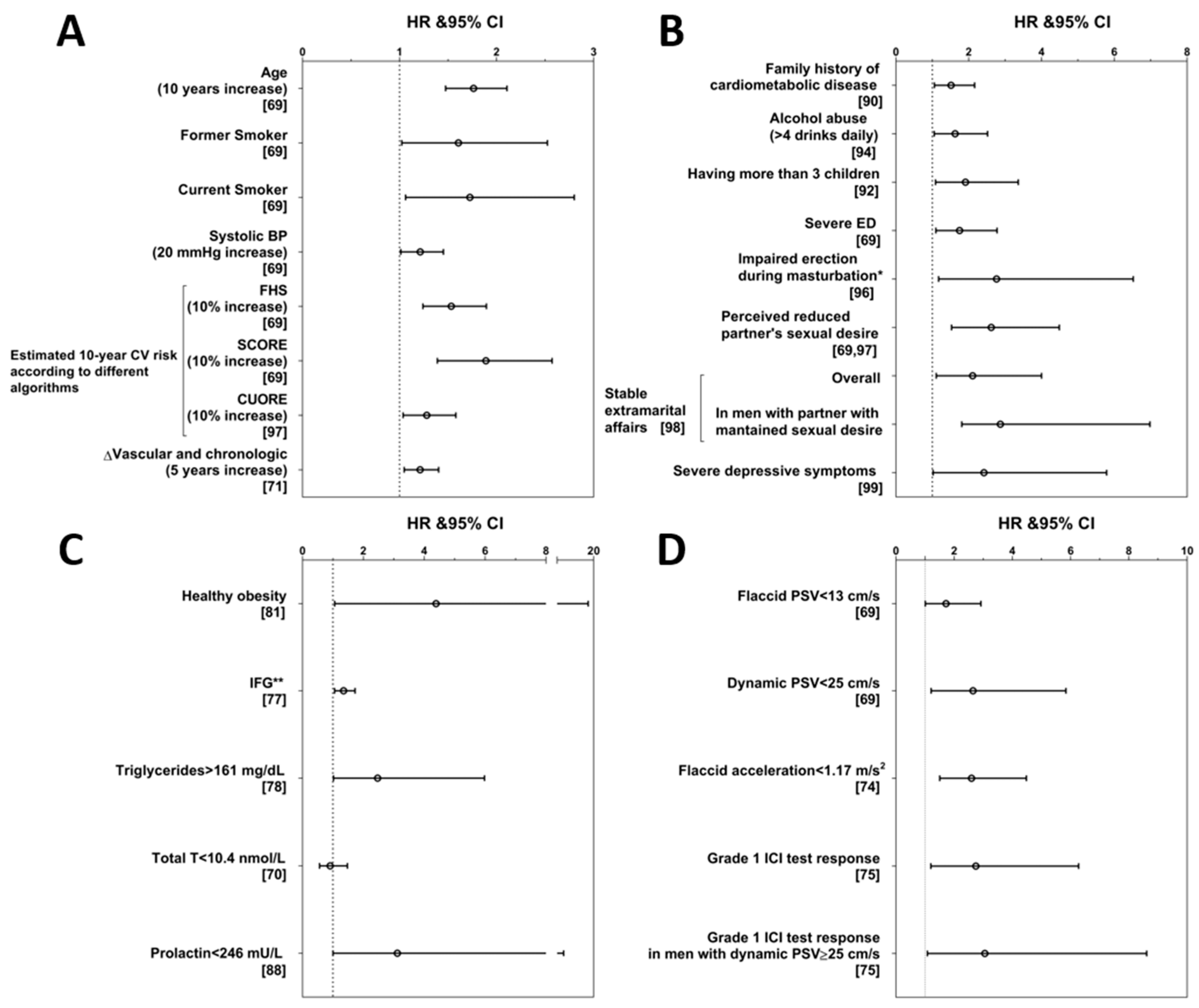
5. Beyond the Classical Risk Factors: Identifying ED Men at Higher CV Risk
5.1. Unconventional CV Risk Factors: Parameters Derived from Instrumental Assessment
5.2. Unconventional CV Risk Factors: Metabolic and Hormone Parameters
5.3. Unconventional CV Risk Factors: Personal History
5.4. Unconventional CV Risk Factors: Characteristics of ED and Sexual Life
6. From CV Risk Identification to CV Risk Modification
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- GBD Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCabe, M.P.; Sharlip, I.D.; Lewis, R.; Atalla, E.; Balon, R.; Fisher, A.D.; Laumann, E.; Lee, S.W.; Segraves, R.T. Incidence and Prevalence of Sexual Dysfunction in Women and Men: A Consensus Statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytaç, I.A.; McKinlay, J.B.; Krane, R.J. The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int. 1999, 84, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.; Sollie, S.; Challacombe, B.; Briggs, K.; Van Hemelrijck, M. The global prevalence of erectile dysfunction: A review. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montorsi, F.; Briganti, A.; Salonia, A.; Rigatti, P.; Margonato, A.; Macchi, A.; Galli, S.; Ravagnani, P.M.; Montorsi, P. Erectile Dysfunction Prevalence, Time of Onset and Association with Risk Factors in 300 Consecutive Patients with Acute Chest Pain and Angiographically Documented Coronary Artery Disease. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Maseroli, E.; Fralassi, N.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Low testosterone syndrome protects subjects with high cardiovascular risk burden from major adverse cardiovascular events. Andrology 2014, 2, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Hong, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yu, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Erectile Dysfunction Predicts Cardiovascular Events as an Independent Risk Factor: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sex. Med. 2019, 16, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montorsi, P.; Montorsi, F.; Schulman, C.C. Is erectile dysfunction the “tip of the lceberg” of a systemic vascular disorder? Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montorsi, P.; Ravagnani, P.M.; Galli, S.; Rotatori, F.; Briganti, A.; Salonia, A.; Rigatti, P.; Montorsi, F. The Artery Size Hypothesis: A Macrovascular Link between Erectile Dysfunction and Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, M. A dictionary of epidemiology. Rev. Española Salud Pública 2008, 82, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, C.; Johnson, A.D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S. 70-year legacy of the Framingham Heart Study. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawber, T.R.; Moore, F.E.; Mann, G.V. Coronary Heart Disease in the Framingham Study. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1957, 47, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.M.; Odell, P.M.; Wilson, P.W.; Kannel, W.B. Cardiovascular disease risk profiles. Am. Heart J. 1991, 121, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.A. Cardiovascular risk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, D.J.; Kannel, W.B. Patterns of coronary heart disease morbidity and mortality in the sexes: A 26-year follow-up of the Framingham population. Am. Heart J. 1986, 111, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.; Nam, B.-H.; D’Agostino, S.R.B.; Levy, D.; Murabito, J.M.; Wang, T.J.; Wilson, P.W.F.; O’Donnell, C.J. Parental Cardiovascular Disease as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease in Middle-aged Adults. JAMA 2004, 291, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmann, J.M.; Willis, B.L.; Ayers, C.R.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D. Association between family history and coronary heart disease death across long-term follow-up in men: The cooper center longitudinal study. Circulation 2012, 125, 3092–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivapalaratnam, S.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Trip, M.D.; Sandhu, M.S.; Luben, R.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Wareham, N.J.; Khaw, K.-T. Family history of premature coronary heart disease and risk prediction in the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Heart 2010, 96, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoit, B.D.; Gilpin, E.A.; Henning, H.; Maisel, A.A.; Dittrich, H.; Carlisle, J.; Ross, J. Myocardial infarction in young patients: An analysis by age subsets. Circulation 1986, 74, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamrozik, K. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002, 360, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J. Blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, and cardiovascular risks. US population data. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, S.A.; Singhateh, Y.; Mackay, D.; Huxley, R.R.; Woodward, M. Total cholesterol as a risk factor for coronary heart disease and stroke in women compared with men: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, U.K.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F. Residual Cardiovascular Risk Despite Optimal LDL Cholesterol Reduction with Statins: The Evidence, Etiology, and Therapeutic Challenges. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2012, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Sarwar, N.; Perry, P. Emerging risk factors collaboration: Major Lipids, Apolipoproteins, and Risk of Vascular Disease. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S. Low HDL-C: A secondary target of dyslipidemia therapy. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Benn, M.; Schnohr, P.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A. Nonfasting Triglycerides and Risk of Myocardial Infarction, Ischemic Heart Disease, and Death in Men and Women. JAMA 2007, 298, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freiberg, J.J.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Jensen, J.S.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Nonfasting Triglycerides and Risk of Ischemic Stroke in the General Population. JAMA 2008, 300, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nordestgaard, B.G.; Varbo, A. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Nestel, P.J.; Simes, J.; Tonkin, A.M.; Pedersen, T.R.; Schwartz, G.G.; Olsson, A.G.; Colhoun, H.M.; Kronenberg, F.; et al. Baseline and on-statin treatment lipoprotein(a) levels for prediction of cardiovascular events: Individual patient-data meta-analysis of statin outcome trials. Lancet 2018, 392, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boerwinkle, E.; Leffert, C.C.; Lin, J.; Lackner, C.; Chiesa, G.; Hobbs, H.H. Apolipoprotein(a) gene accounts for greater than 90% of the variation in plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almdal, T.; Scharling, H.; Jensen, J.S.; Vestergaard, H. The independent effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on ischemic heart disease, stroke, and death: A population-based study of 13 000 men and women with 20 years of follow-up. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selvin, E.; Marinopoulos, S.; Berkenblit, G.; Rami, T.; Brancati, F.L.; Powe, N.R.; Golden, S.H. Meta-Analysis: Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cai, X.; Mai, W.; Li, M.; Hu, Y. Association between prediabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease and all cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 355, i5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakier, J.B. Smoking and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Med. 1992, 93, S8–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, E.; Hippe, M.; Schnohr, P.; Hein, H.O.; Vestbo, J. Smoking and risk of myocardial infarction in women and men: Longitudinal population study. BMJ 1998, 316, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, P.W.; Bozeman, S.R.; Burton, T.M.; Hoaglin, D.C.; Ben-Joseph, R.; Pashos, C.L. Prediction of First Events of Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke with Consideration of Adiposity. Circulation 2008, 118, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Jafar, T.H.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.; Matsushita, K.; Wen, C.P. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013, 382, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Hu, F.B.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Speizer, F.E.; Colditz, G.; Ascherio, A.; Rosner, B.; Spiegelman, D.; et al. The Effect of Fruit and Vegetable Intake on Risk for Coronary Heart Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.E.; Thompson, P.D.; Caspersen, C.J.; Kendrick, J.S. Physical activity and the incidence of coronary heart disease. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1987, 8, 253–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Glynn, R.J.; Hennekens, C.H. C-Reactive Protein Adds to the Predictive Value of Total and HDL Cholesterol in Determining Risk of First Myocardial Infarction. Circualtion 1998, 97, 2007–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yafi, F.A.; Jenkins, L.; Albersen, M.; Corona, G.; Isidori, A.M.; Goldfarb, S.; Maggi, M.; Nelson, C.J.; Parish, S.; Salonia, A.; et al. Erectile dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besiroglu, H.; Otunctemur, A.; Ozbek, E. The Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome, Its Components, and Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Sex. Med. 2015, 12, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, L.; Yang, L. Hypertension might be a risk factor for erectile dysfunction: A meta-analysis. Andrologia 2016, 49, e12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouidrat, Y.; Pizzol, D.; Cosco, T.; Thompson, T.; Carnaghi, M.; Bertoldo, A.; Solmi, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N. High prevalence of erectile dysfunction in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 145 studies. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tousoulis, D.; Kampoli, A.-M.; Papageorgiou, C.T.N.; Stefanadis, C. The Role of Nitric Oxide on Endothelial Function. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 10, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover-Páez, F.; Zavalza-Gómez, A.B. Endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Macera, C.A.; Davis, D.R.; Hornung, C.A.; Nankin, H.A.; Blair, S.N. Total Cholesterol and High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol as Important Predictors of Erectile Dysfunction. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 140, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Filippi, S.; Vignozzi, L.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Erectile dysfunction and central obesity: An Italian perspective. Asian J. Androl. 2014, 16, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.S.; Walter, E.E. Health-Related Lifestyle Factors and Sexual Dysfunction: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Research. J. Sex. Med. 2018, 15, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R.B.; Vasan, R.S.; Pencina, M.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Cobain, M.; Massaro, J.M.; Kannel, W.B. General cardiovascular risk profile for use in primary care: The Framingham heart study. Circulation 2008, 117, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conroy, R.M.; Pyörälä, K.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Sans, S.; Menotti, A.; De Backer, G.; De Bacquer, D.; Ducimetière, P.; Jousilahti, P.; Keil, U.; et al. Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in Europe: The SCORE project. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, G.; Cullen, P.; Schulte, H. Simple Scoring Scheme for Calculating the Risk of Acute Coronary Events Based on the 10-Year Follow-Up of the Prospective Cardiovascular Münster (PROCAM) Study. Circualtion 2002, 105, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C.; Vinogradova, Y.; Robson, J.; May, M.; Brindle, P. Derivation and validation of QRISK, a new cardiovascular disease risk score for the United Kingdom: Prospective open cohort study. BMJ 2007, 335, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C.; Vinogradova, Y.; Robson, J.; Minhas, R.; Sheikh, A.; Brindle, P. Predicting cardiovascular risk in England and Wales: Prospective derivation and validation of QRISK2. BMJ 2008, 336, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C.; Brindle, P. Development and validation of QRISK3 risk prediction algorithms to estimate future risk of cardiovascular disease: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2017, 357, j2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridker, P.M.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Cook, N.R. Development and validation of improved algorithms for the assessment of global cardiovascular risk in women: The Reynolds Risk Score. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 297, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JBS3 Board. Joint British Societies’ consensus recommendations for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (JBS3). Heart 2014, 100 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Paynter, N.P.; Rifai, N.; Gaziano, J.M.; Cook, N.R. C-reactive protein and parental history improve global cardiovascular risk prediction: The Reynolds risk score for men. Circulation 2008, 118, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmieri, L.; Panico, S.; Vanuzzo, D.; Ferrario, M.; Pilotto, L.; Sega, R.; Cesana, G.; Giampaoli, S.; Gruppo di Ricerca del Progetto CUORE. Evaluation of the global cardiovascular absolute risk: The Progetto CUORE individual score. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2004, 40, 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.T.; Corra, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menotti, A.; Puddu, P.E.; Lanti, M. Comparison of the Framingham risk function-based coronary chart with risk function from an Italian population study. Eur. Heart J. 2000, 21, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, M.T.; Dudina, A.L.; Graham, I.M. Value and Limitations of Existing Scores for the Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk. A Review for Clinicians. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasan, R.S.; Sullivan, L.M.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Sempos, C.T.; Sundström, J.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D.; D’Agostino, R.B. Relative importance of borderline and elevated levels of coronary heart disease risk factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; De Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, E1082–E1143. [Google Scholar]
- Inman, B.A.; Sauver, J.L.S.; Jacobson, D.J.; McGree, M.E.; Nehra, A.; Lieber, M.M.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J. A Population-Based, Longitudinal Study of Erectile Dysfunction and Future Coronary Artery Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Boddi, V.; Cameron-Smith, M.; Lotti, F.; De Vita, G.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; et al. Male Sexuality and Cardiovascular Risk. A Cohort Study in Patients with Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Boddi, V.; Cameron-Smith, M.; Fisher, A.D.; De Vita, G.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; et al. Low Testosterone is Associated with an Increased Risk of MACE Lethality in Subjects with Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Vascular and Chronological Age in Men With Erectile Dysfunction: A Longitudinal Study. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikka, S.C.; Hellstrom, W.J.; Brock, G.; Morales, A.M. Standardization of Vascular Assessment of Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Fagioli, G.; Mannucci, E.; Romeo, A.; Rossi, M.; Lotti, F.; Sforza, A.; Morittu, S.; Chiarini, V.; Casella, G.; et al. Penile doppler ultrasound in patients with erectile dysfunction (ED): Role of peak systolic velocity measured in the flaccid state in predicting arteriogenic ED and silent coronary artery disease. J. Sex. Med. 2008, 5, 2623–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Lotti, F.; Aversa, A.; Bartolini, M.; Mancini, M.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Flaccid Penile Acceleration as a Marker of Cardiovascular Risk in Men without Classical Risk Factors. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Poor Response to Alprostadil ICI Test is Associated with Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction and Higher Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 3433–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, A.; Jackson, G.; Miner, M.; Billups, K.L.; Burnett, A.L.; Buvat, J.; Carson, C.C.; Cunningham, G.R.; Ganz, P.; Goldstein, I.; et al. The Princeton III Consensus Recommendations for the Management of Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2012, 87, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Balercia, G.; Lotti, F.; Sforza, A.; Monami, M.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Hormonal Association and Sexual Dysfunction in Patients with Impaired Fasting Glucose: A Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Study. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Cipriani, S.; Rastrelli, G.; Sforza, A.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. High Triglycerides Predicts Arteriogenic Erectile Dysfunction and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects With Sexual Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2016, 13, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, P.; Welsh, C.; Celis-Morales, C.A.; Brown, R.; Ho, F.K.; Ferguson, L.D.; Mark, P.B.; Lewsey, J.; Gray, S.R.; Lyall, D.M.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease: Prediction, attributable risk fraction, and estimating benefits from novel interventions. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, zwaa063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Rastrelli, G.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Is Metabolic Syndrome a Useless Category in Subjects with High Cardiovascular Risk? Results from a Cohort Study in Men with Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, F.; Rastrelli, G.; Maseroli, E.; Cipriani, S.; Guaraldi, F.; Krausz, C.; Reisman, Y.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M.; Corona, G. Impact of Metabolically Healthy Obesity in Patients with Andrological Problems. J. Sex. Med. 2019, 16, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Monami, M.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Body Mass Index Regulates Hypogonadism-Associated CV Risk: Results from a Cohort of Subjects with Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Monami, M.; Guay, A.; Buvat, J.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Hypogonadism as a risk factor for cardiovascular mortality in men: A meta-analytic study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araujo, A.B.; Dixon, J.M.; Suarez, E.A.; Murad, M.H.; Guey, L.T.; Wittert, G.A. Endogenous Testosterone and Mortality in Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salonia, A.; Rastrelli, G.; Hackett, G.; Seminara, S.B.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; Rey, R.A.; Hellstrom, W.J.G.; Palmert, M.R.; Corona, G.; Dohle, G.R.; et al. Paediatric and adult-onset male hypogonadism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Fisher, A.D.; Lotti, F.; Ricca, V.; Balercia, G.; Petrone, L.; Forti, G.; Maggi, M. Effect of Hyperprolactinemia in Male Patients Consulting for Sexual Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2007, 4, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Jannini, E.A.; Lotti, F.; Ricca, V.; Monami, M.; Boddi, V.; Bandini, E.; Balercia, G.; Forti, G.; et al. Hypoprolactinemia: A new clinical syndrome in patients with sexual dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2009, 6, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Boddi, V.; Monami, M.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Prolactin levels independently predict major cardiovascular events in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 34, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. The role of prolactin in andrology: What is new? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Yannas, D.; Mucci, B.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. Family History for Cardio-Metabolic Diseases: A Predictor of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Men With Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2020, 17, 2370–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Black, S.; Wadsworth, M.E.J.; Kuh, D. Number of children and coronary heart disease risk factors in men and women from a British birth cohort. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2007, 114, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.D.; Rastrelli, G.; Bandini, E.; Corona, G.; Balzi, D.; Melani, C.; Monami, M.; Matta, V.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Metabolic and Cardiovascular Outcomes of Fatherhood: Results from a Cohort of Study in Subjects with Sexual Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukamal, K.; Lazo, M. Alcohol and cardiovascular disease. BMJ 2017, 356, j1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boddi, V.; Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Fisher, A.D.; Bandini, E.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Sforza, A.; Patussi, V.; Forti, G.; et al. Priapus is Happier with Venus than with Bacchus. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Monami, M.; Maseroli, E.; Jannini, E.A.; Balercia, G.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Frequency of sexual activity and cardiovascular risk in subjects with erectile dysfunction: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Andrology 2013, 1, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastrelli, G.; Boddi, V.; Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Impaired Masturbation-Induced Erections: A New Cardiovascular Risk Factor for Male Subjects with Sexual Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2013, 10, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastrelli, G.; Corona, G.; Fisher, A.D.; Silverii, A.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Two Unconventional Risk Factors for Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Subjects with Sexual Dysfunction: Low Education and Reported Partner’s Hypoactive Sexual Desire in Comparison with Conventional Risk Factors. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 3227–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.D.; Bandini, E.; Corona, G.; Monami, M.; Smith, M.C.; Melani, C.; Balzi, D.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Stable extramarital affairs are breaking the heart. Int. J. Androl. 2011, 35, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandini, E.; Fisher, A.D.; Corona, G.; Ricca, V.; Monami, M.; Boddi, V.; Balzi, D.; Melani, C.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; et al. Severe Depressive Symptoms and Cardiovascular Risk in Subjects with Erectile Dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G. Erectile dysfunction and coronary disease: Evaluating the link. Maturitas 2012, 72, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, C.C.; Manea, M.; Marcu, D.R.; Socea, B.; Spinu, A.D.; Bratu, O.G. The erectile dysfunction as a marker of cardio-vascular disease: A review. Acta Cardiol. 2020, 75, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D. Obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and sexual dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2005, 17, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, F.; Martedì, E.; Feola, G.; Marfella, R.; D’Armiento, M.; Giugliano, D. High Proportions of Erectile Dysfunction in Men With the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corona, G.; Forti, G.; Maggi, M. Why can patients with erectile dysfunction be considered lucky? The association with testosterone deficiency and metabolic syndrome. Aging Male 2008, 11, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Y.W.; Ng, E.M.L.; Ko, J.S.N.; Chen, R.Y.L. Physical activity and erectile dysfunction: Meta-analysis of population-based studies. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006, 19, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbild, H.; Larsen, C.M.; Graugaard, C.; Josefsson, K.A. Physical Activity to Improve Erectile Function: A Systematic Review of Intervention Studies. Sex. Med. 2018, 6, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meldrum, D.R.; Gambone, J.C.; Morris, M.A.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Ignarro, L.J. Lifestyle and metabolic approaches to maximizing erectile and vascular health. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2011, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Francescomarino, S.; Sciartilli, A.; Di Valerio, V.; Di Baldassarre, A.; Gallina, S. The Effect of Physical Exercise on Endothelial Function. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Conraads, V.M. Endothelial progenitor cells in vascular health: Focus on lifestyle. Microvasc. Res. 2010, 79, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Marfella, R.; Ciotola, M.; Di Palo, C.; Giugliano, F.; Giugliano, G.; D’Armiento, M.; D’Andrea, F.; Giugliano, D. Effect of a Mediterranean-style diet on endothelial dysfunction and markers of vascular inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: A randomized trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 292, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, K.; Ciotola, M.; Giugliano, F.; De Sio, M.; Giugliano, G.; D’Armiento, M.; Giugliano, D. Mediterranean diet improves erectile function in subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006, 18, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Caputo, M.; Castaldo, F.; Improta, M.R.; Giugliano, D.; Esposito, K. Effects of Mediterranean diet on sexual function in people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: The MÈDITA trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.; Piantadosi, C.; Duncan, R.; Worthley, S.G.; Jenkins, A.; Noakes, M.; Worthley, M.I.; Lange, K.; Wittert, G.A. Comparing Effects of a Low-energy Diet and a High-protein Low-fat Diet on Sexual and Endothelial Function, Urinary Tract Symptoms, and Inflammation in Obese Diabetic Men. J. Sex. Med. 2011, 8, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.; Ling, P.-S.; Tan, J.; Teo, A.; Ng, H.-L.; Chen, R.Y.-T.; Tay, T.-L.; Tan, E.; Cheong, M. Comparing the effects of meal replacements with reduced-fat diet on weight, sexual and endothelial function, testosterone and quality of life in obese Asian men. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2013, 26, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Morelli, A.; Sarchielli, E.; Cipriani, S.; Vignozzi, L.; Maggi, M. Treatment of Functional Hypogonadism Besides Pharmacological Substitution. World J. Mens Health 2020, 38, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, F.; Di Palo, C.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; D’Andrea, F.; D’Armiento, M.; Giugliano, D. Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wing, R.R.; Rosen, R.C.; Fava, J.L.; Bahnson, J.; Brancati, F.; Gendrano, I.N.C.; Kitabchi, A.; Schneider, S.H.; Wadden, T.A. Effects of Weight Loss Intervention on Erectile Function in Older Men with Type 2 Diabetes in the Look AHEAD Trial. J. Sex. Med. 2010, 7, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karaca, F.C.; Taş, T. Early Effect of Metabolic Surgery on Erectile Function and Ejaculation: A Pilot Study of Obese Men with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Obes. Surg. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleid, M.; Muneer, A.; Renshaw, S.; George, J.; Jenkinson, A.D.; Adamo, M.; Elkalaawy, M.; Batterham, R.L.; Ralph, D.J.; Hashemi, M.; et al. Early Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Urogenital Function in Morbidly Obese Men. J. Sex. Med. 2017, 14, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Aranda, G.B.; De Hollanda, A.; Flores, L.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Vidal, J. Weight loss is a major contributor to improved sexual function after bariatric surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groutz, A.; Gordon, D.; Schachter, P.; Amir, H.; Shimonov, M. Effects of bariatric surgery on male lower urinary tract symptoms and sexual function. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 36, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, S.K.; Bae, W.J.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, H.J.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, T.-K.; Kim, S.W. Bariatric Surgery Improves the Cavernosal Neuronal, Vasorelaxation, and Contraction Mechanisms for Erectile Dysfunction As Result of Amelioration of Glucose Homeostasis in a Diabetic Rat Model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, L.; Pin, Z.; Jianzhong, D.; Xiaodong, H.; Haoyong, Y.; Yuqian, B.; Hongwei, Z. Significant Improvement of Erectile Function after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery in Obese Chinese Men with Erectile Dysfunction. Obes. Surg. 2014, 25, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, A.T.; Perez, J.B.; Heatley, G.J. Cessation of Smoking Rapidly Decreases Erectile Dysfunction. Endocr. Pract. 1998, 4, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sighinolfi, M.; Mofferdin, A.; De Stefani, S.; Micali, S.; Cicero, A.; Bianchi, G. Immediate Improvement in Penile Hemodynamics after Cessation of Smoking: Previous Results. Urology 2007, 69, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Leung, D.Y.; Abdullah, A.S.; Lo, S.S.; Yip, A.W.; Kok, W.-M.; Ho, S.-Y.; Lam, T.-H. Smoking-Cessation and Adherence Intervention Among Chinese Patients with Erectile Dysfunction. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2010, 39, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harte, C.B.; Meston, C.M. Association between smoking cessation and sexual health in men. BJU Int. 2011, 109, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Fan, W.; Li, G.; Tam, T. Predictors for erectile dysfunction among diabetics. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 71, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Chai, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.; Paick, J.-S.; Kim, S.W. Investigation of the Effects of the Level of Glycemic Control on Erectile Function and Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Diabetic Rats. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin, S.K.; Kashyap, S.R. Effects of metformin on weight loss: Potential mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes. Obes. 2014, 21, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Cañete, M.D.; Caballero-Villarraso, J.; Hoyos, R.; Latorre, M.; Vázquez-Cobela, R.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Maldonado, J.; Bueno, G.; Leis, R.; et al. Metformin for Obesity in Prepubertal and Pubertal Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20164285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saisho, Y. Metformin and Inflammation: Its Potential Beyond Glucose-lowering Effect. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.W. Obesity and Erectile Dysfunction: From Bench to Clinical Implication. World J. Mens Health 2019, 37, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignozzi, L.; Filippi, S.; Comeglio, P.; Cellai, I.; Morelli, A.; Rastrelli, G.; Maneschi, E.; Mannucci, E.; Maggi, M. Metformin In Vitro and In Vivo Increases Adenosine Signaling in Rabbit Corpora Cavernosa. J. Sex. Med. 2014, 11, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Valzacchi, G.J.; Costanzo, P.R.; Finger, L.A.; Layus, A.O.; Gueglio, G.M.; Litwak, L.E.; Knoblovits, P. Addition of Metformin to Sildenafil Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction in Eugonadal Nondiabetic Men With Insulin Resistance. A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind Pilot Study. J. Androl. 2011, 33, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Isidori, A.M.; Aversa, A.; Bonomi, M.; Ferlin, A.; Foresta, C.; La Vignera, S.; Maggi, M.; Pivonello, R.; Vignozzi, L.; et al. Male and female sexual dysfunction in diabetic subjects: Focus on new antihyperglycemic drugs. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Ma, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Liraglutide Ameliorates Erectile Dysfunction via Regulating Oxidative Stress, the RhoA/ROCK Pathway and Autophagy in Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagulli, V.A.; Carbone, M.D.; Ramunni, M.I.; Licchelli, B.; De Pergola, G.; Sabbà, C.; Guastamacchia, E.; Triggiani, V. Adding liraglutide to lifestyle changes, metformin and testosterone therapy boosts erectile function in diabetic obese men with overt hypogonadism. Andrology 2015, 3, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaly, R.; Gorny, D.; Compagnie, S.; Mayoux, E.; Bernabe, J.; Alexandre, L.; Giuliano, F.; Behr-Roussel, D. The Favorable Effect of Empagliflozin on Erectile Function in an Experimental Model of Type 2 Diabetes. J. Sex. Med. 2018, 15, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Shih, C.-M.; Tsao, N.-W.; Lin, Y.-W.; Huang, P.-H.; Wu, S.-C.; Lee, A.-W.; Kao, Y.-T.; Chang, N.-C.; Nakagami, H.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor improves neovascularization by increasing circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harmar, A.J.; Fahrenkrug, J.; Gozes, I.; Laburthe, M.; May, V.; Pisegna, J.R.; Vaudry, D.; Vaudry, H.; Waschek, J.A.; Said, S.I. Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: IUPHAR Review 1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsubara, J.; Sugiyama, S.; Sugamura, K.; Nakamura, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Akiyama, E.; Kurokawa, H.; Nozaki, T.; Ohba, K.; Konishi, M.; et al. A Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Des-Fluoro-Sitagliptin, Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formation in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Ho, D.-R.; Lin, J.-H.; Huang, K.-T.; Chen, C.-S.; Shi, C.-S. Dietary Modification Is Associated with Normalization of Penile Hemodynamics in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Sex. Med. 2019, 16, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwon, O.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Paick, J.-S.; Kim, S.W. Chronic administration of atorvastatin could partially ameliorate erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, F.; Shan, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, J.; Shen, W.; Dai, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; et al. Simvastatin alleviated diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats by enhancing AMPK pathway-induced autophagy. Andrology 2020, 8, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Framingham Risk Score 2008 [53] | SCORE [54] | PROCAM [55] | QRISK1 [56], 2 [57], and 3 [58] | JBS3 Risk Calculator [59] | Reynolds [60,61] | CUORE [62] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort type | General population; US | Mainly general population, some occupational cohorts; EU | Healthy employees; Germany | Healthy general practice attendees; England/Wales | Healthy general practice attendees; England/Wales | Health professionals; US | General population; Italy |
| Cohort size (% men) | 8491 (47%) | 205,178 (57%) | 26,975 (68%) | QRISK1: 1.28 million (50%) QRISK2: 2.29 million (50%) QRISK3: 2.92 million (50%) | 2.29 million (50%) | 35,332 (40%) | 20,647 (37%) |
| Age range (years) | 30–75 | 40–65 | 20–75 | QRISK1 and 2: 35–74 QRISK3: 25–84 | 35–74 | 45–80 | 35–69 |
| Endpoint assessed | 10-yr risk of CVD events (CHD death, myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency or angina, coronary revascularization, stroke/TIA, PAD, heart failure) | 10-yr risk of CVD mortality (including CHD, arrhythmia, heart failure, stroke, aortic aneurysm, and PAD) | Two different scores: 10-yr risk of CHD 10-yr risk of stroke | 10-yr risk of CVD events (CHD death, myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency or angina, coronary revascularization, stroke/TIA, PAD) | 10-yr and lifetime risk of CVD events (CHD death, myocardial infarction, coronary insufficiency or angina, coronary revascularization, stroke/TIA, PAD); Effect of risk factor optimization; Heart age; CVD-free life-expectancy | 10-yr risk of CVD events/mortality (myocardial infarction, stroke, coronary revascularization) | 10-yr risk of CVD events (myocardial infarction, stroke) |
| Variables included | Sex, age, total cholesterol (mg/dL), HDL cholesterol (mg/dL), SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), diabetes (yes or no), hypertensive treatment (yes or no) | Sex, age, total cholesterol (mg/dL) or total cholesterol/ HDL cholesterol ratio, SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no) High- and low-risk countries version Most diabetic patients considered high-risk regardless of other factor | Sex, age, LDL cholesterol (mg/dL), HDL cholesterol (mg/dL), SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), diabetes (yes or no), | QRISK1: Sex, age, total cholesterol/ HDL cholesterol ratio, SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), hypertensive treatment (yes or no), area-based index of poverty, family history of premature CVD in first degree relative (yes or no), BMI (kg/m2) QRISK2: also includes ethnicity, diabetes (yes or no), rheumatoid arthritis, chronic renal disease, and atrial fibrillation QRISK3: migraine, medications (corticosteroids and atypical antipsychotics), systemic lupus erythematosus, severe mental illness, SBP variability, erectile dysfunction | Sex, age, total cholesterol/ HDL cholesterol ratio, SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), hypertensive treatment (yes or no), area-based index of poverty, family history of premature CVD in first degree relative (yes or no), BMI (kg/m2), ethnicity, diabetes (yes or no), rheumatoid arthritis, chronic renal disease, and atrial fibrillation | Sex, age, total cholesterol (mg/dL), HDL cholesterol (mg/dL), SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), hs-CRP (mg/L), HbA1C if diabetic (percent), parental history of premature CVD (yes or no) | Sex, age, total cholesterol (mg/dL), HDL cholesterol (mg/dL), SBP (mmHg), current smoking (yes or no), diabetes (yes or no) |
| Important variables excluded | Family history of, CVD, BMI | Diabetes, Family history of CVD, BMI, Hypertensive treatment | Family history of CVD, BMI, Hypertensive treatment | None | None | BMI, Hypertensive treatment | Family history of CVD, BMI, Hypertensive treatment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yannas, D.; Frizza, F.; Vignozzi, L.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M.; Rastrelli, G. Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102221
Yannas D, Frizza F, Vignozzi L, Corona G, Maggi M, Rastrelli G. Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(10):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102221
Chicago/Turabian StyleYannas, Dimitri, Francesca Frizza, Linda Vignozzi, Giovanni Corona, Mario Maggi, and Giulia Rastrelli. 2021. "Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 10: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102221
APA StyleYannas, D., Frizza, F., Vignozzi, L., Corona, G., Maggi, M., & Rastrelli, G. (2021). Erectile Dysfunction Is a Hallmark of Cardiovascular Disease: Unavoidable Matter of Fact or Opportunity to Improve Men’s Health? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(10), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10102221






