Characterization of the Fouling Layer on the Membrane Surface in a Membrane Bioreactor: Evolution of the Foulants’ Composition and Aggregation Ability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
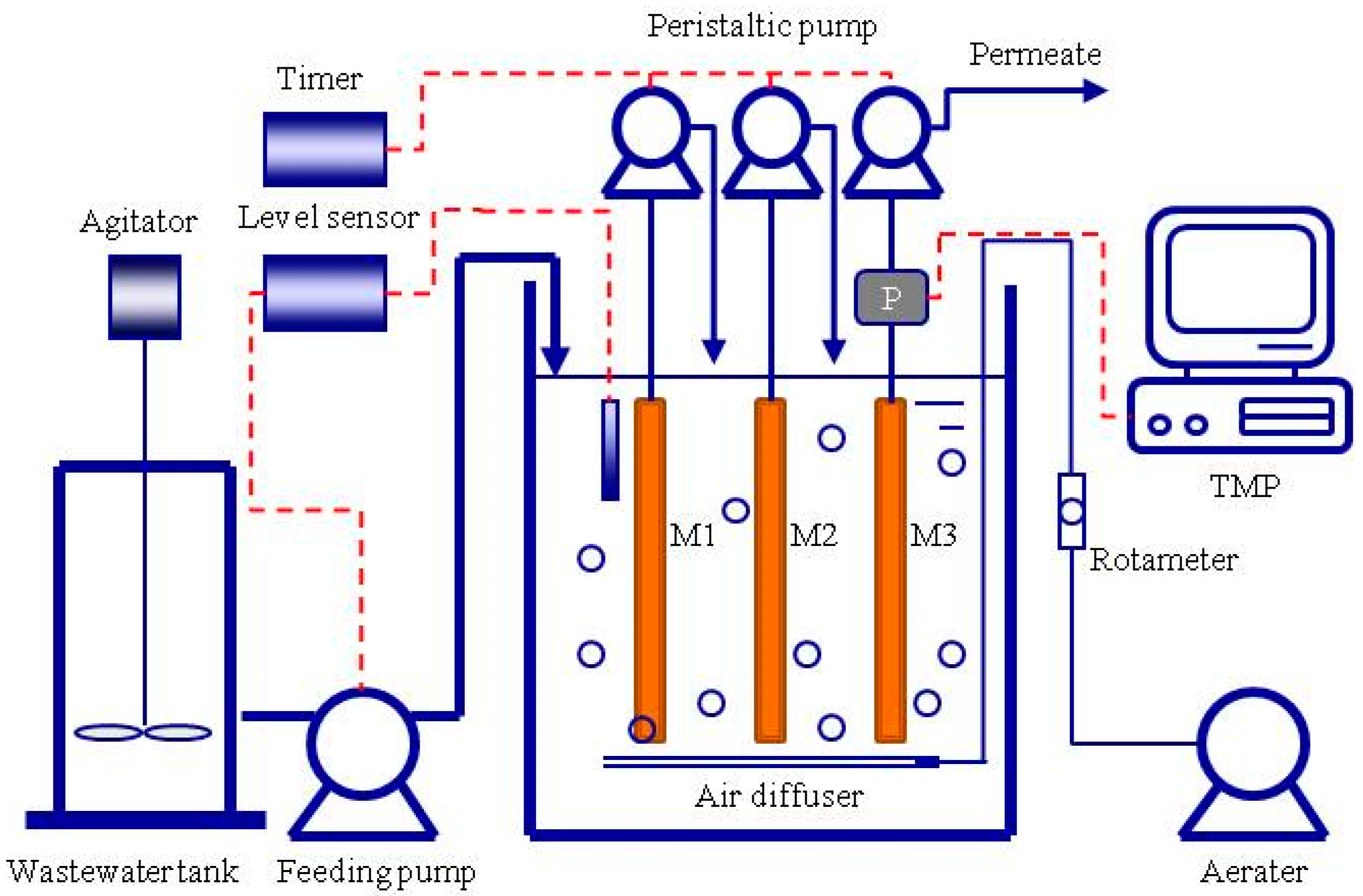
2.1. Experimental MBR Setup
2.2. Operation Conditions
2.3. Analytic Methods
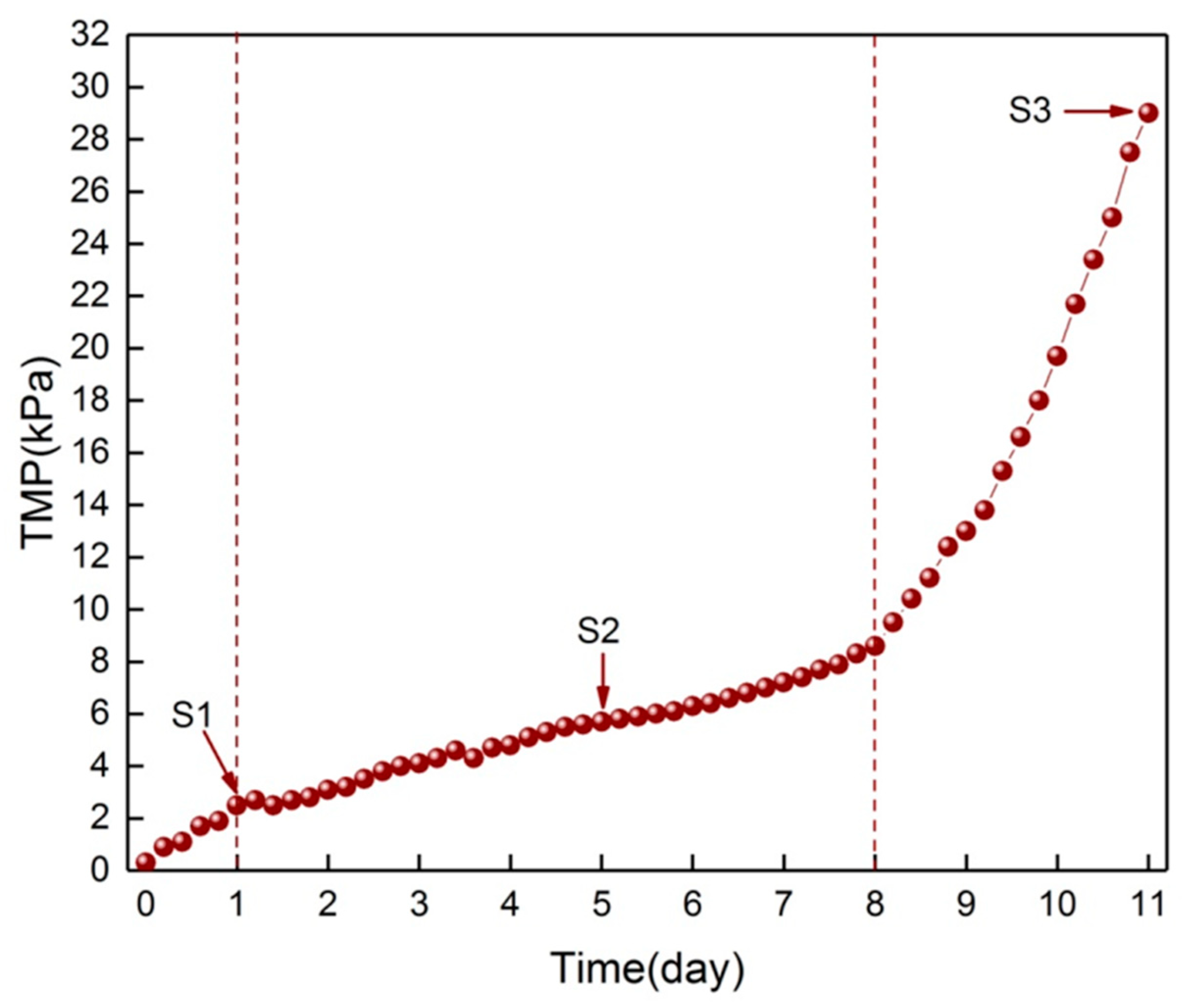
2.3.1. Sample Collection and Biofilm Treatment
2.3.2. EPS Extract and Determination
2.3.3. Aggregation Test
2.3.4. Other Analytic Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Change of Surface Morphology during the Three Phases
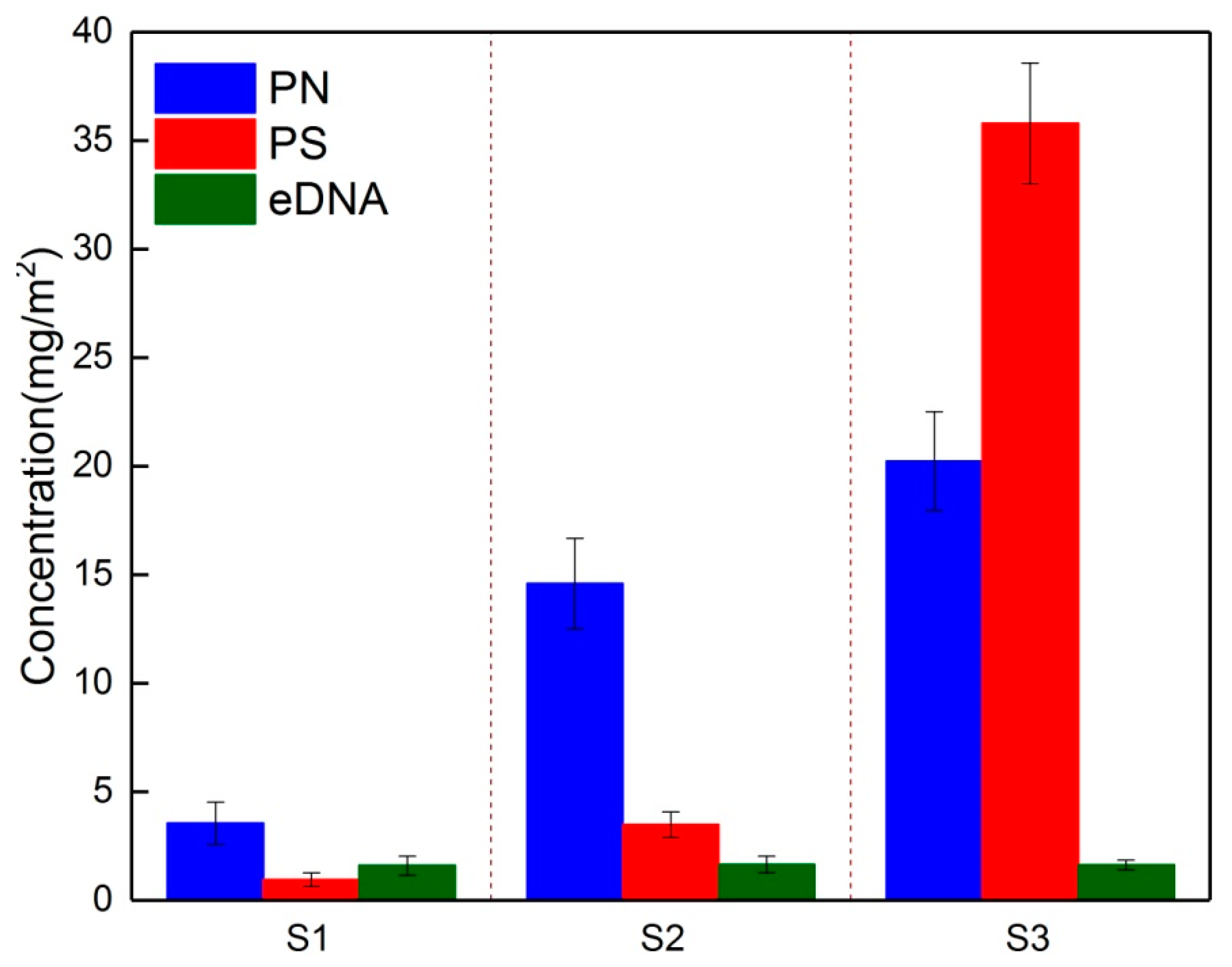
3.2. Temporal Dynamics of EPS Composition during Biofouling Layer Development
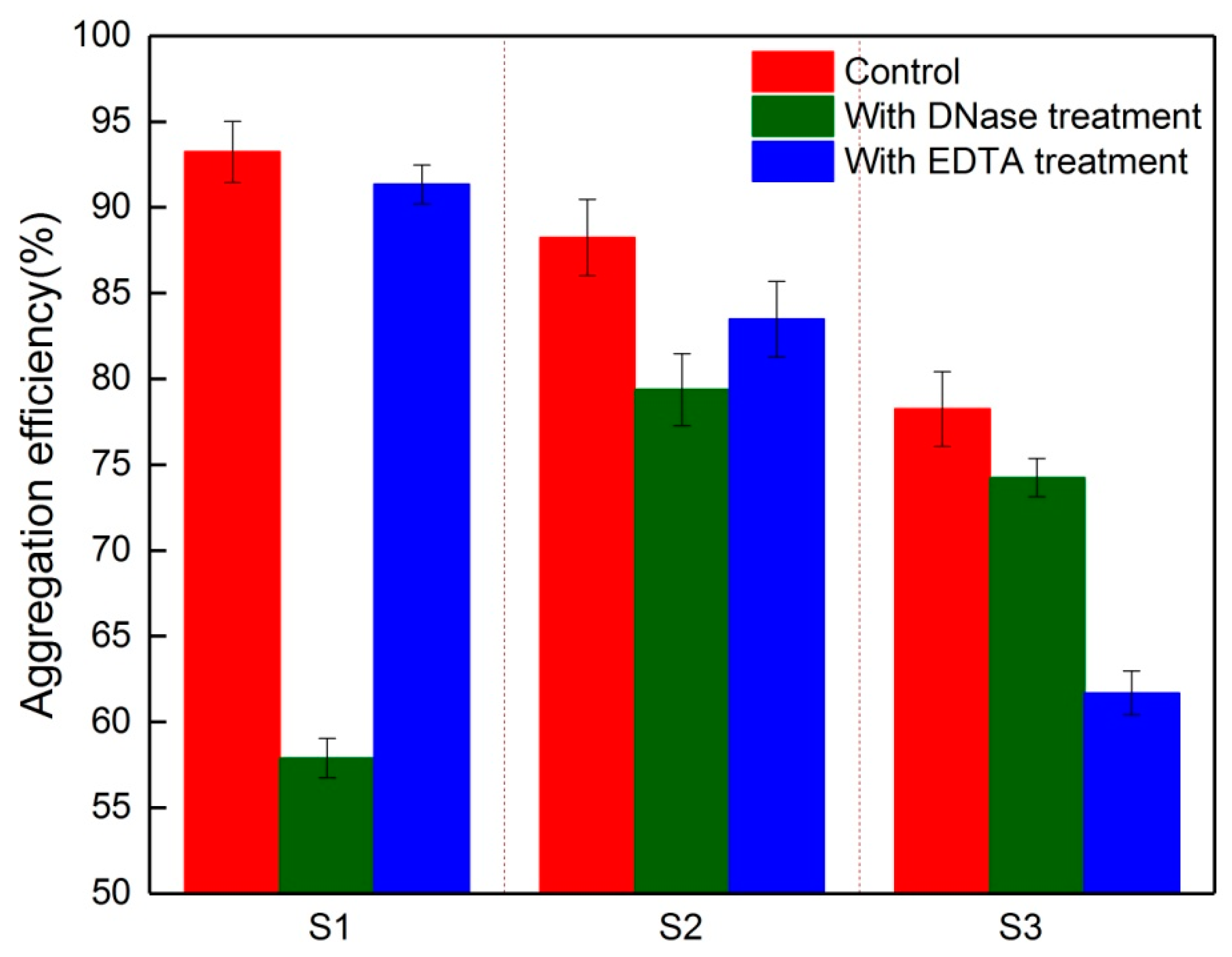
3.3. Key Component in EPS for the Aggregation Ability of Foulants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Y.; Su, X. Relation between the stability of activated sludge flocs and membrane fouling in MBR: Under different SRTs. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Song, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L. Fate of NaClO and membrane foulants during in-situ cleaning of membrane bioreactors: Combined effect on thermodynamic properties of sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 147, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Fu, Y.; Ren, N. Tracing biofouling to the structure of the microbial community and its metabolic products: A study of the three-stage MBR process. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6680–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Ahn, W.Y.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Li, S. Filtration capability and operational characteristics of dynamic membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, G.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Maab, H.; Nunes, S.; Le-Clech, P.; Vrouwenvelder, J.; Saikaly, P.E. Temporal changes in extracellular polymeric substances on hydrophobic and hydrophilic membrane surfaces in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2016, 95, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Song, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H. New insights into the rapid formation of initial membrane fouling after in-situ cleaning in a membrane bioreactor. Process. Biochem. 2019, 78, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaeb, L.; Le-Clech, P.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ayoub, G.M.; Saikaly, P.E. Do biological-based strategies hold promise to biofouling control in MBR? Water Res. 2013, 47, 5447–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Sehar, S.; Manefield, M. The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Composition analysis of fractions of extracellular polymeric substances from an activated sludge culture and identification of dominant forces affecting microbial aggregation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Weng, X.; Yu, H.; Lin, H. Thermodynamic analysis of membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor and its implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic Fouling and Chemical Cleaning of Nanofiltration Membranes: Measurements and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Lu, Y. Identification of the change in fouling potential of soluble microbial products (SMP) in membrane bioreactor coupled with worm reactor. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Shao, L.; He, P. Enzyme disintegration with spatial resolution reveals different distributions of sludge extracellular polymer substances. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudan, C.; Filali, A.; Spérandio, M.; Girbal-Neuhauser, E. Multiple EPS interactions involved in the cohesion and structure of aerobic granules. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, J.Q.; Kong, X.J.; Lee, D.J. Fractional, biodegradable and spectral characteristics of extracted and fractionated sludge extracellular polymeric substances. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4387–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric Method for Determination of Sugars and Related Substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Boil. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Clinkenbeard, K.D.; Clarke, C.; Cudd, L.; Highlander, S.K.; Dabo, S.M. Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin induced apoptosis of bovine lymphocytes involves DNA fragmentation. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eboigbodin, K.E.; Biggs, C.A. Characterization of the Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced byEscherichia coliUsing Infrared Spectroscopic, Proteomic, and Aggregation Studies. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pembrey, R.S.; Marshall, K.C.; Schneider, R.P. Cell Surface Analysis Techniques: What Do Cell Preparation Protocols Do to Cell Surface Properties? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2877–2894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clescerl, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 12th ed. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health. 1998, 56, 684. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Mei, R.; Chen, J.; Hong, H. A novel approach for quantitative evaluation of the physicochemical interactions between rough membrane surface and sludge foulants in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, X.; Wang, B.; Song, L. Calcium ion on membrane in membrane bioreactor at high salt shock. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shen, L.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Yu, G. Influences of fractal dimension of membrane surface on interfacial interactions related to membrane fouling in a membrane bioreactor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 500, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torti, A.; Lever, M.A.; Jørgensen, B.B. Originfouling reduction and bioflocculation promotion, dynamics, and implications of extracellular DNA pools in marine sediments. Mar. Genom. 2015, 24, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, C.; Akçelik, N.; Akçelik, M. The Role of Extracellular DNA in Salmonella Biofilms. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 2018, 33, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, F.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Gu, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y. Influence of pH on heavy metal speciation and removal from wastewater using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Halogenated organics generated during online chemical cleaning of MBR: An emerging threat to water supply and public health. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 656, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item | Virgin Membrane | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average roughness (nm) | 37.35 ± 2.76 | 38.54 ± 1.25 | 71.27 ± 10.73 | 53.28 ± 3.65 |
| Fractal dimension (Df) | 2.35 | 2.25 | 2.33 | 2.31 |
| Item | S1 | S2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential (mV) | −23.3 | −18.7 | −14.8 |
| Hydrophobicity (%) | 82.3 | 88.1 | 56.3 |
| Ca2+ content (mg/g SS) | 1.3 | 4.7 | 23.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Li, R.; Song, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, L.; Zhang, H. Characterization of the Fouling Layer on the Membrane Surface in a Membrane Bioreactor: Evolution of the Foulants’ Composition and Aggregation Ability. Membranes 2019, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070085
Yan L, Li R, Song Y, Jia Y, Li Z, Song L, Zhang H. Characterization of the Fouling Layer on the Membrane Surface in a Membrane Bioreactor: Evolution of the Foulants’ Composition and Aggregation Ability. Membranes. 2019; 9(7):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070085
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Linlin, Ruixue Li, Yu Song, Yanping Jia, Zheng Li, Lianfa Song, and Haifeng Zhang. 2019. "Characterization of the Fouling Layer on the Membrane Surface in a Membrane Bioreactor: Evolution of the Foulants’ Composition and Aggregation Ability" Membranes 9, no. 7: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070085
APA StyleYan, L., Li, R., Song, Y., Jia, Y., Li, Z., Song, L., & Zhang, H. (2019). Characterization of the Fouling Layer on the Membrane Surface in a Membrane Bioreactor: Evolution of the Foulants’ Composition and Aggregation Ability. Membranes, 9(7), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9070085






