Acidic Gases Separation from Gas Mixtures on the Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Providing the Facilitated and Solution-Diffusion Transport Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
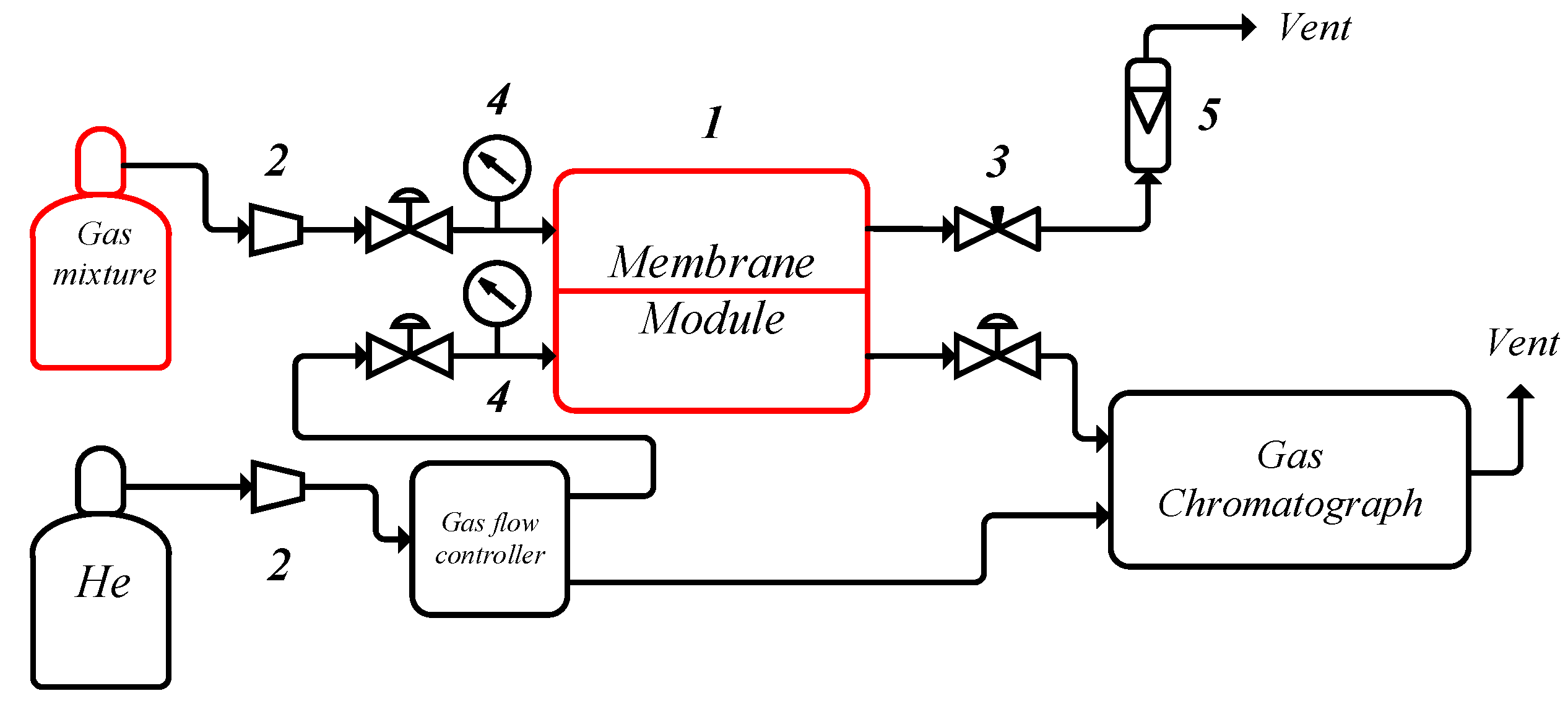
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
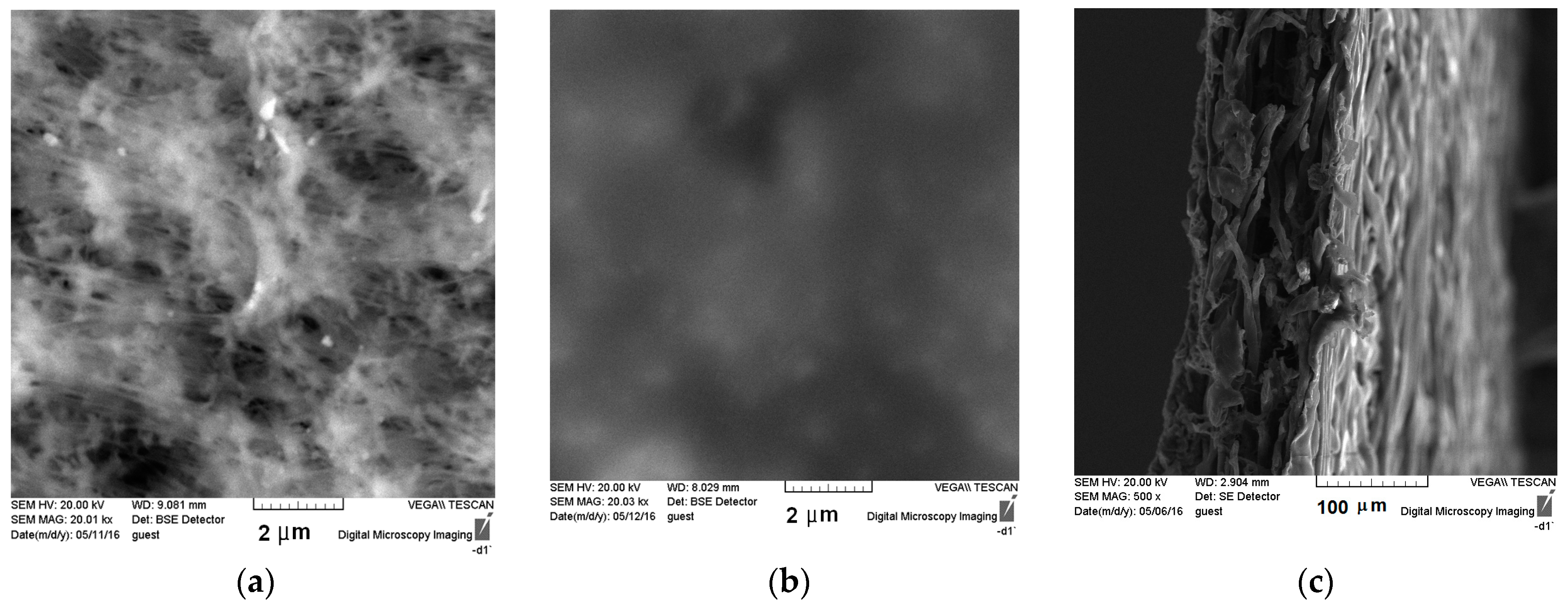
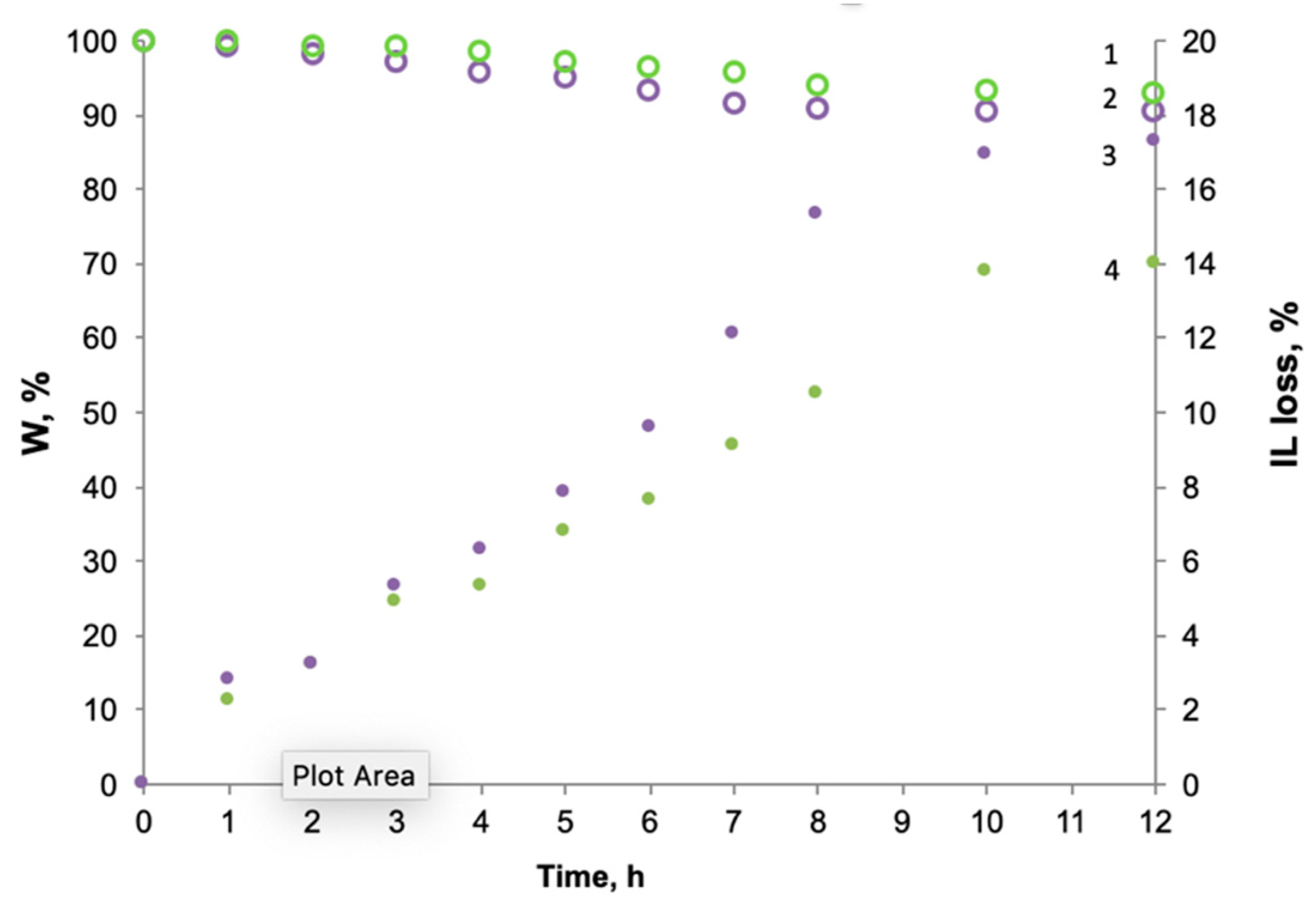
3.1. Membranes Characterization
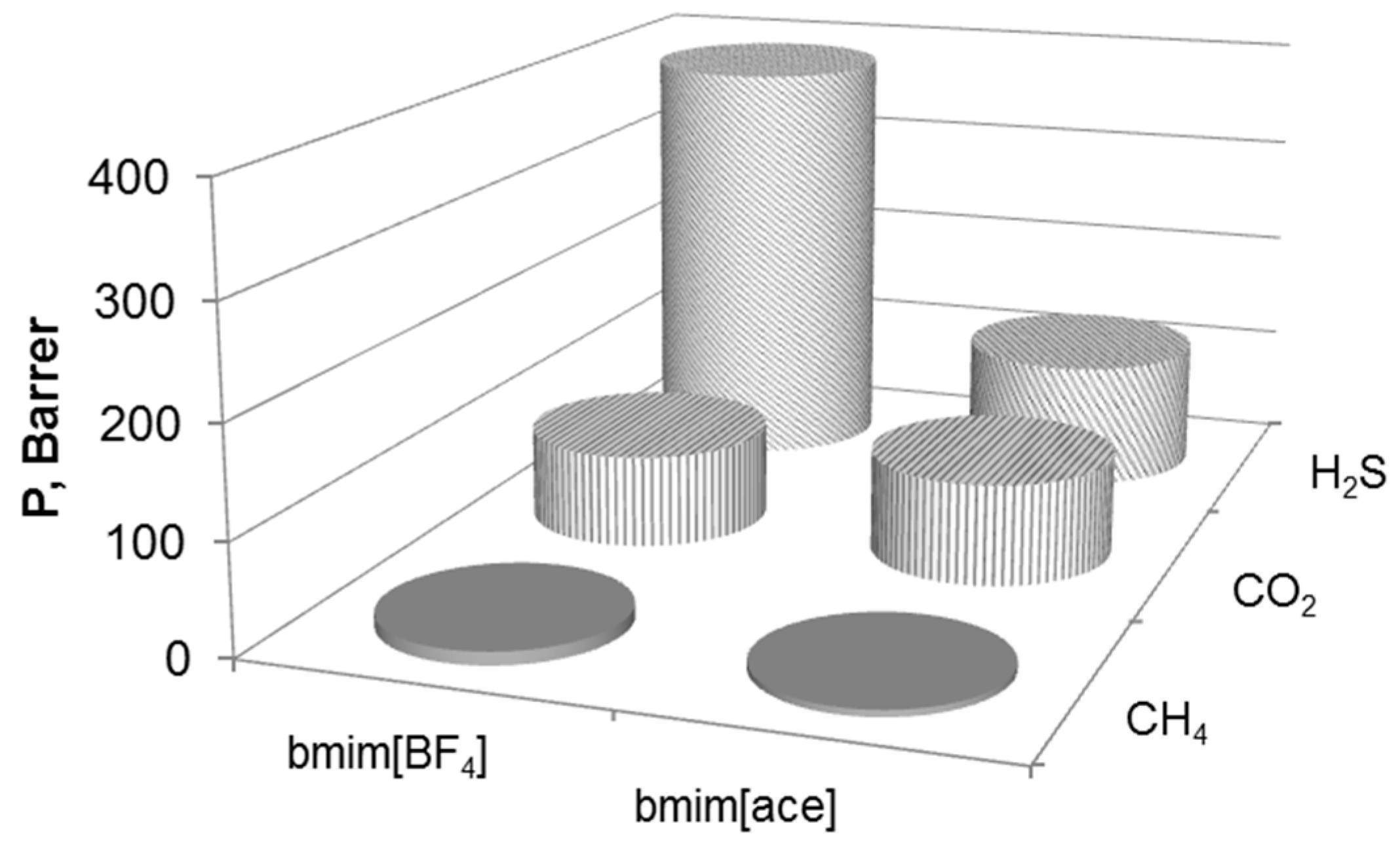
3.2. Single Gas Permeability
3.3. Mixed Gas Permeability
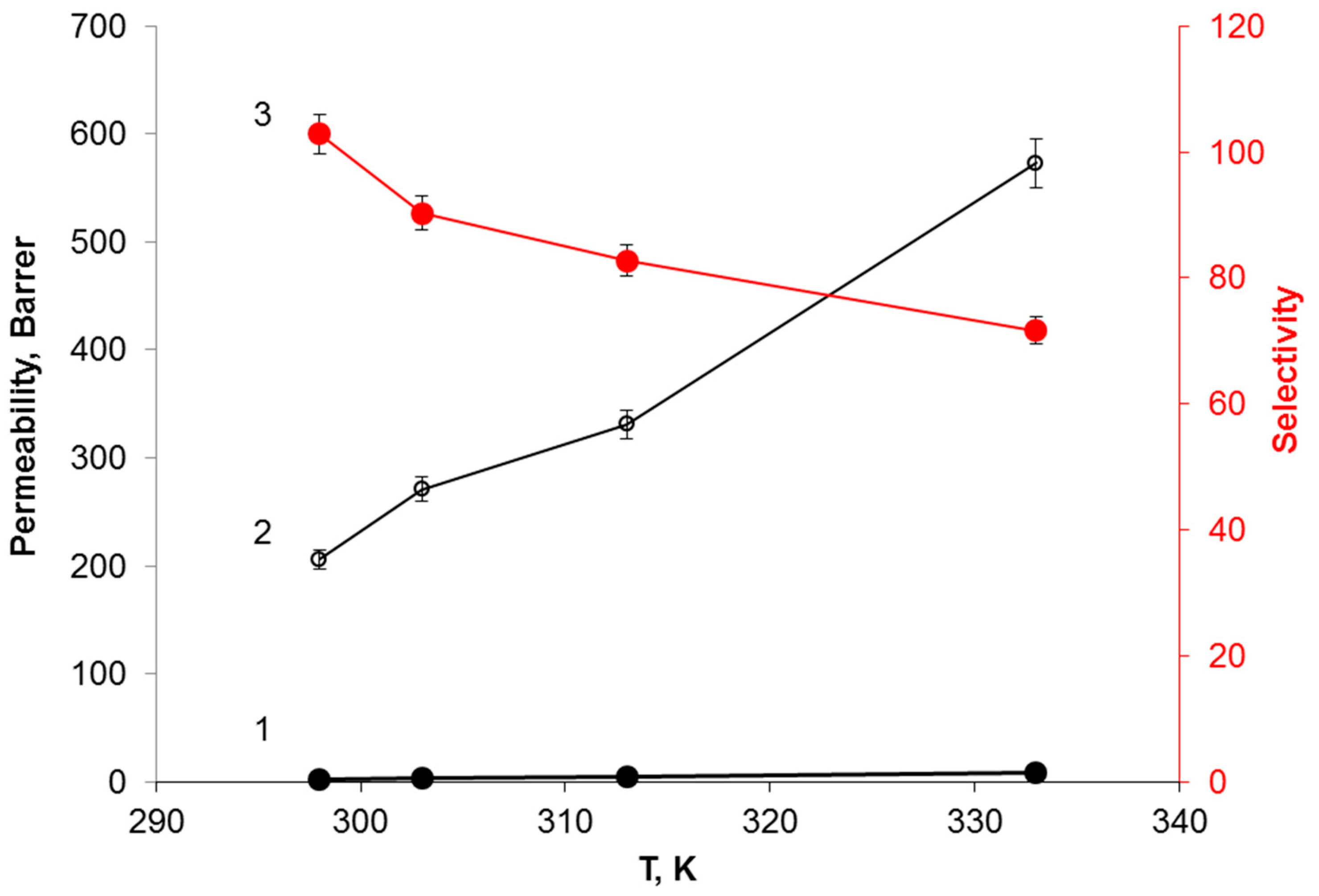
3.4. Effect of Temperature on the H2S Transport
3.5. SILMs Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SILM | supported ionic liquid membrane |
| bmim[OAc] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate |
| bmim[BF4] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| IL | ionic liquid |
| RTIL | room temperature ionic liquid |
| emim[BF4] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| emim[dca] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide |
| emim[CF3SO3] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate |
| C4mim[NTf2] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bistriflamide |
| DIP-C4mim[NTf2] | diisopropyl 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bistriflamide |
| FTM | facilitated transport membrane |
| PTFE | polytetrafluoroethylene |
| emim[OAc] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate |
| MFFK-1 | a flat sheet porous tetrafluoroethylene-vinylidene fluoride membrane with pore size equal to 150 nm |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| GCMS | gas chromatography mass-specrtometry |
| TCD | thermal conductivity detector |
| ppm | part per million, 10−4% |
References
- Arruebo, M.; Mallada, R.; Pina, M.P. Zeolite membranes: Synthesis, Characterization, Important applications and Recent advances. In Handbook of Membrane Separations: Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Biotechnological Applications; Pabby, A.K., Rizvi, S.S.H., Sastre, A.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 269–323. ISBN 978-1-46-655556-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, S.; Smitha, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Separation of carbon dioxide from natural gas mixtures through polymeric membranes—A review. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2007, 36, 113–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillman, R.W. Economics of gas separation membranes. In Membrane Separations Technology. Principles and Applications; Noble, R.D., Stern, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 41–62. ISBN 978-0-44-481633-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, M.K.; Balsora, H.K.; Varshney, P. Progress and trends in CO2 capture/separation technologies: A review. Energy 2012, 46, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. Perspective on ionic liquids and ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovazzo, P.; Visser, A.E.; Davis, J.H.; Rogers, R.D.; Koval, C.A.; Du Bois, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Supported ionic liquid membranes and facilitated ionic liquid membranes. ACS Symp. Ser. 2002, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovazzo, P.; Kieft, J.; Finan, D.A.; Koval, C.A.; Du Bois, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Gas separations using non-hexafluorophosphate [PF6]-anion supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 238, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshina, A.I.; Petukhov, A.N.; Gumerova, O.R.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Nyuchev, A.V.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Solubility of H2S and CO2 in imidazolium-based ionic liquids with bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate anion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 130, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaloni, L.; Arif, A.; Ciftja, A.F.; Knuutila, H.K.; Deng, L. Development of Membrane Contactors Using Phase Change Solvents for CO2 Capture: Material Compatibility Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 13102–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, J.E.; Carlisle, T.K.; Gabriel, C.J.; Camper, D.; Finotello, A.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Guide to CO2 separations in imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltus, R.E.; Counce, R.M.; Culbertson, B.H.; Luo, H.; De Paoli, D.W.; Dai, S.; Duckworth, D.C. Examination of the potential of ionic liquids for gas separations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovazzo, P.; Havard, D.; McShea, M.; Mixon, S.; Morgan, D. Long-term, continuous mixed-gas dry fed CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation performance and selectivities for room temperature ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Crespo, J.G.; Coelhoso, I.M. Gas permeation studies in supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iarikov, D.D.; Hacarlioglu, P.; Oyama, S.T. Supported room temperature ionic liquid membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althuluth, M.; Overbeek, J.P.; van Wees, H.J.; Zubeir, L.F.; Haije, W.G.; Berrouk, A.; Peters, C.J.; Kroon, M.C. Natural gas purification using supported ionic liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 484, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Khraisheh, M.; Atilhan, M.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; Qi, L.; Rooney, D. High-pressure CO2/N2 and CO2/CH4 separation using dense polysulfone-supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 36, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussler, E.L. Facilitated and Active Transport. In Polymeric Gas Separation Membranes, 1st ed.; Paul, D.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 273–300. ISBN 978-1-31-589678-6. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, R.D. Analysis of facilitated transport with fixed site carrier membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 50, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.D. Facilitated transport mechanism in fixed site carrier membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 60, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, R.D. Generalized microscopic mechanism of facilitated transport in fixed site carrier membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 75, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-J.; Li, B.; Hägg, M.-B. Novel fixed-site–carrier polyvinylamine membrane for carbon dioxide capture. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 4326–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zou, J.; Ho, W.S. Carbon dioxide capture using a CO2-selective facilitated transport membrane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Kim, T.-J.; Hägg, M.-B. Facilitated transport of CO2 in novel PVAm/PVA blend membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Hägg, M.-B. A feasibility study of CO2 capture from flue gas by a facilitated transport membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 359, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ho, W.S. Steric hindrance effect on amine demonstrated in solid polymer membranes for CO2 transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Appleby, J.B.; Pez, G.P. New facilitated transport membranes for the separation of carbon dioxide from hydrogen and methane. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 104, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
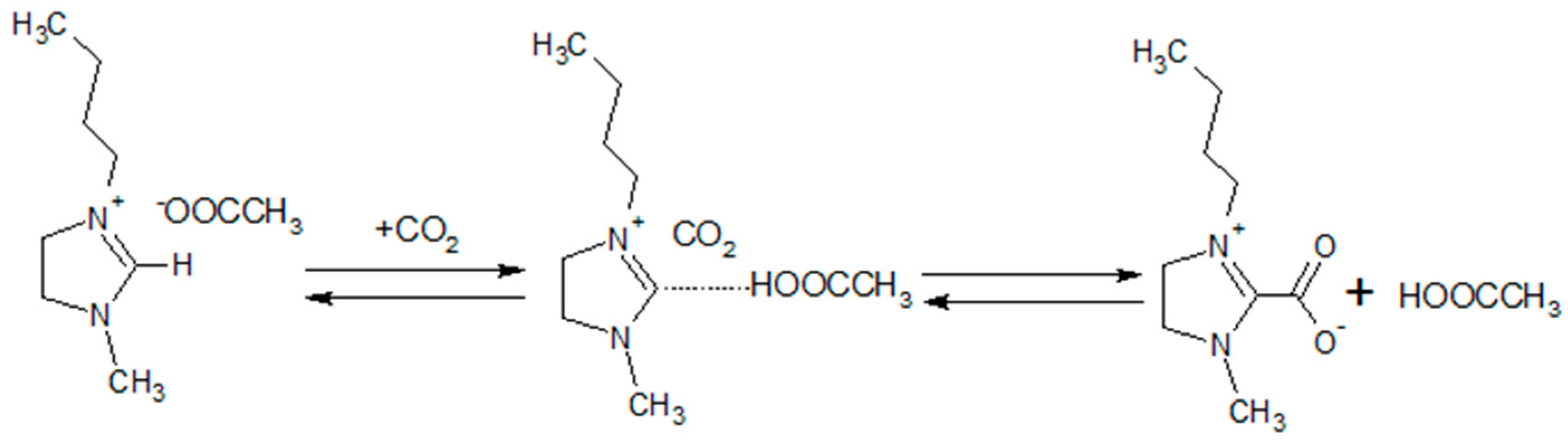
- Hanioka, S.; Maruyama, T.; Sotani, T.; Teramoto, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Nakashima, K.; Hanaki, M.; Kubota, F.; Goto, M. CO2 separation facilitated by task-specific ionic liquids using a supported liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 314, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Yoshizawa, M.; Ohno, H. Room temperature ionic liquids from 20 natural amino acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2398–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Lv, X. Supported absorption of CO2 by tetrabutylphosphonium amino acid ionic liquids. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurkan, B.E.; de la Fuente, J.C.; Mindrup, E.M.; Ficke, L.E.; Goodrich, B.F.; Price, E.A.; Schneider, W.F.; Brennecke, J.F. Equimolar CO2 absorption by anion-functionalized ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2116–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, S.; Kamio, E.; Ishigami, T.; Matsuyama, H. Amino acid ionic liquid-based facilitated transport membranes for CO2 separation. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6903–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ding, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X. Ionic Liquid Co-catalyzed Artificial Photosynthesis of CO. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Acetate based Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs) for CO2 separation: Influence of the temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurau, G.; Rodrguez, H.; Kelley, S.P.; Janiczek, P.; Kalb, R.S.; Rogers, R.D. Demonstration of chemisorption of carbon dioxide in 1,3-dialkylimidazolium acetate ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 12024–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maginn, E.J. Design and Evaluation of Ionic Liquids as Novel CO2 Absorbents; DOE Report (Award Number: DE-FG26–04NT42122); University of Norte Dame: Norte Dame, IN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Albo, J.; Tsuru, T. Thin Ionic Liquid Membranes Based on Inorganic Supports with Different Pore Sizes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Densities and Viscosities of 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate ± Molecular Solvent Binary Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 2056–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogolitsyn, K.G.; Skrebets, T.E.; Makhova, T.A. Physicochemical properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2009, 79, 659–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshina, A.I.; Gumerova, O.R.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Sazanova, T.S.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Nyuchev, A.V.; Razov, E.N.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Permeability and selectivity of acid gases in supported conventional and novel imidazolium-based ionic liquid membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán Sánchez, L.M.; Meindersma, G.W.; de Haan, A.B. Solvent Properties of Functionalized Ionic Liquids for CO2 Absorption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2007, 85, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshina, A.; Davletbaeva, I.; Grebenschikova, E.; Sazanova, T.; Petukhov, A.; Atlaskin, A.; Razov, E.; Zaripov, I.; Martins, C.; Neves, L.; et al. The Effect of Microporous Polymeric Support Modification on Surface and Gas Transport Properties of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes. Membranes 2015, 6, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; He, G.; Nie, F.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Liu, H. Membrane liquid loss mechanism of supported ionic liquid membrane for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 411–412, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Ferguson, L.; Scovazzo, P. Diffusivities of Gases in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Data and Correlations Obtained Using a Lag-Time Technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4815–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemin, J.; Costa Gomes, M.F.; Husson, P.; Majer, V. Solubility of carbon dioxide, ethane, methane, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, argon, and carbon monoxide in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate between temperatures 283K and 343K and at pressures close to atmospheric. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2006, 38, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, A.H.; Rahmati-Rostami, M.; Ghotbi, C.; Hosseini-Jenab, M.; Ahmadi, A.N. Solubility of H2S in Ionic Liquids [bmim][PF6], [bmim][BF4], and [bmim][Tf2N]. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tu, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, K.; Hu, X.; Wu, Y.; MacFarlane, D.R. Selective separation of H2S and CO2 from CH4 by supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflett, M.B.; Kasprzak, D.J.; Junk, C.P.; Yokozeki, A. Phase behavior of {carbon dioxide+[bmim][Ac]} mixtures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2008, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Cai, D.-N.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-T.; Hu, X.-B.; Zhang, Z.-B. Thermodynamic validation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium carboxylates as task-specific ionic liquids for H2S absorption. AIChE J. 2012, 59, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.I.; Kim, B.S.; Byun, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.W.; Lee, J.M. Preparation of supported ionic liquid membranes (SILMs) for the removal of acidic gases from crude natural gas. Desalination 2009, 236, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, I.V.; Murav’ev, D.V. Fine gas purification to remove slightly penetrating impurities using a membrane module with a feed reservoir. Dokl. Chem. 2006, 411, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, I.V.; Belyaev, E.S. Deep gas cleaning of highly permeating impurities using a membrane module with a feed tank. Pet. Chem. 2011, 51, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ionic Liquid | Density, kg/m3 | Viscosity 103, Pa·s | Water Content, ppm |
|---|---|---|---|
| bmim[BF4] | 1200.7 a | 110.3 | 1679 |
| bmim[OAc] | 1055.0 | 343.3 b | 1713 |
| IL | Contact Angle, ° | Surface Tension, N/m | Capillary Pressure, bar |
|---|---|---|---|
| bmim[BF4] | 44 ± 0.8 | 44.8 × 10−3 a | 8.6 |
| bmim[OAc] | 49 ± 0.7 | 37.6 × 10−3 b | 6.6 |
| Gas | P 10−15 (mol·m/m2·s·Pa) a | D 10−11 (m2/s) | Scalc 10−5 (mol/m3·Pa) | Slit 10−5 (mol/m3·Pa) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | 5.0 | 45.02 | 1.11 | 3.15 | [45] |
| CO2 | 35.2 | 47.07 | 7.47 | 43.80 | [45] |
| H2S | 160.0 | 46.63 | 91.62 | 107.8 | [46] |
| CH4 | 2.5 | 11.10 | 2.26 | 2.04 | this work |
| IL | Support | Permeability, Barrer | Selectivity | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | CO2 | H2S | CO2/CH4 | H2S/CH4 | |||
| bmim[OAc] | MFFK-1 | 6.0 ± 0.3 | 92.0 ± 3.0 | 115.0 ± 3.0 | 15.0 ± 0.4 | 19.0 ± 0.6 | this work (pure gases) |
| bmim[OAc] | MFFK-1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 186.1 ± 5.7 | 205.8 ± 6.2 | 96.9 ± 2.9 | 102.9 ± 3.1 | this work (binary mixture) |
| bmim[OAc] | MFFK-1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 100.3 ± 3.0 | 110.4 ± 3.3 | 96.5 ± 2.9 | 106.2 ± 3.2 | this work (ternary mixture) |
| bmim[BF4] | MFFK-1 | 12.0 ± 0.3 | 84.0 ± 2.0 | 383.0 ± 12.0 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 32.0 ± 1.0 | this work (pure gases) |
| bmim[BF4] | MFFK-1 | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 68.9 ± 2.1 | 128.6 ± 3.9 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 23.4 ± 0.7 | this work (binary mixture) |
| bmim[BF4] | MFFK-1 | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 70.0 ± 2 | 142.0 ± 3.0 | 8.0 ± 0.2 | 16.4 ± 0.5 | this work (ternary mixture) |
| bmim[OAc] | PVDF | 37.2 | 443 | 5279 | 11.9 | 142 | [47] (pure gases) |
| bmim[BF4] | PVDF | 92.4 | 1056 | 3708 | 3.5 | 40 | [47] (pure gases) |
| bmim[BF4] | PVDF | 4 | 180 | 1100 | 6 | 260 | [50] (pure gases) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhmetshina, A.I.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Mechergui, A.; Otvagina, K.V.; Razov, E.N.; Mochalova, A.E.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Acidic Gases Separation from Gas Mixtures on the Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Providing the Facilitated and Solution-Diffusion Transport Mechanisms. Membranes 2019, 9, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010009
Akhmetshina AI, Yanbikov NR, Atlaskin AA, Trubyanov MM, Mechergui A, Otvagina KV, Razov EN, Mochalova AE, Vorotyntsev IV. Acidic Gases Separation from Gas Mixtures on the Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Providing the Facilitated and Solution-Diffusion Transport Mechanisms. Membranes. 2019; 9(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhmetshina, Alsu I., Nail R. Yanbikov, Artem A. Atlaskin, Maxim M. Trubyanov, Amal Mechergui, Ksenia V. Otvagina, Evgeny N. Razov, Alla E. Mochalova, and Ilya V. Vorotyntsev. 2019. "Acidic Gases Separation from Gas Mixtures on the Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Providing the Facilitated and Solution-Diffusion Transport Mechanisms" Membranes 9, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010009
APA StyleAkhmetshina, A. I., Yanbikov, N. R., Atlaskin, A. A., Trubyanov, M. M., Mechergui, A., Otvagina, K. V., Razov, E. N., Mochalova, A. E., & Vorotyntsev, I. V. (2019). Acidic Gases Separation from Gas Mixtures on the Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes Providing the Facilitated and Solution-Diffusion Transport Mechanisms. Membranes, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010009