Factors Affecting Mass Transport Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Membranes for Tissue Engineering Bioreactors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Water and Protein Flux
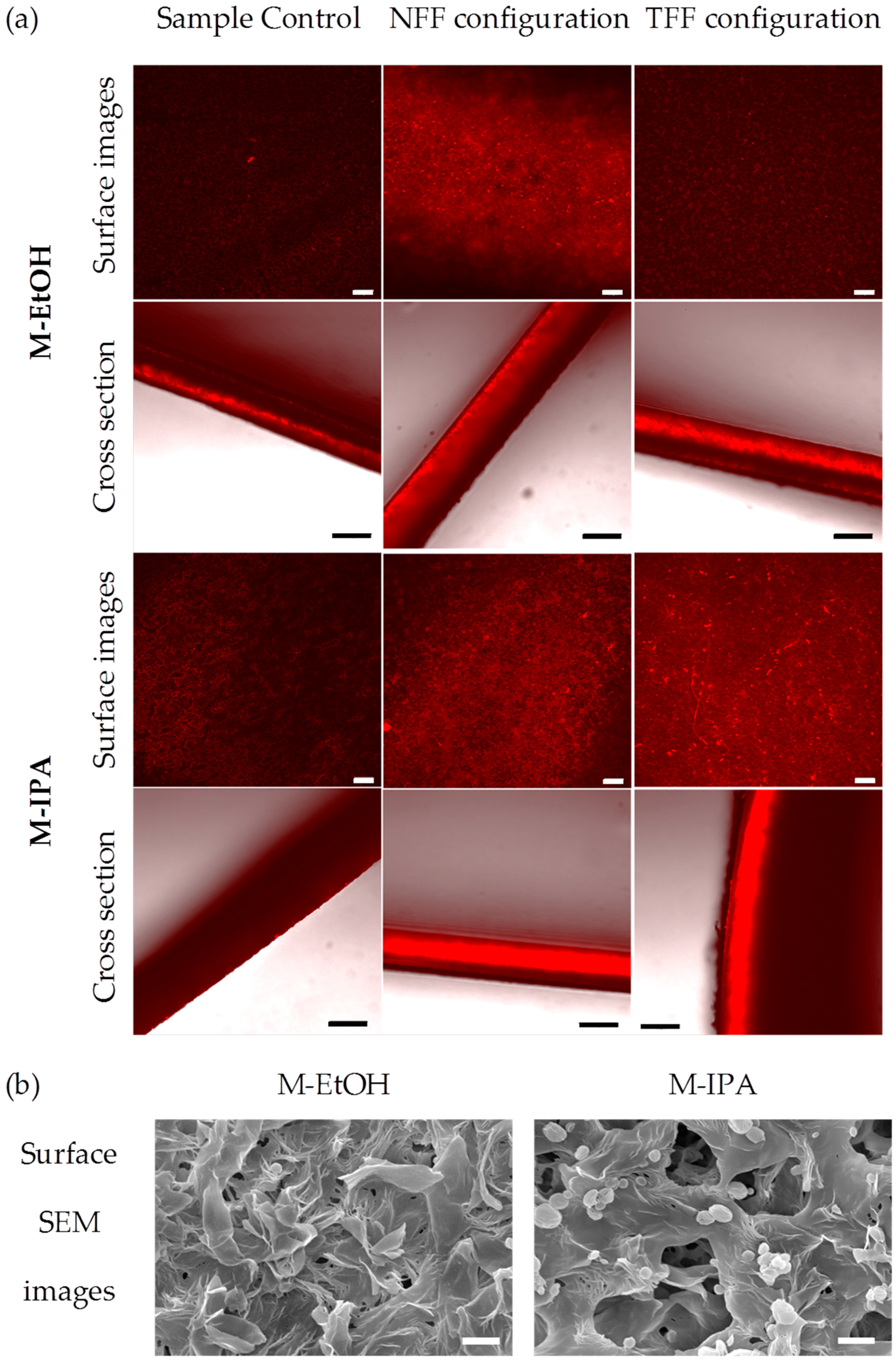
2.3. Membrane Morphology (Physical Characterization)
2.4. Statistical Data Treatment
3. Results
3.1. Protein Fouling
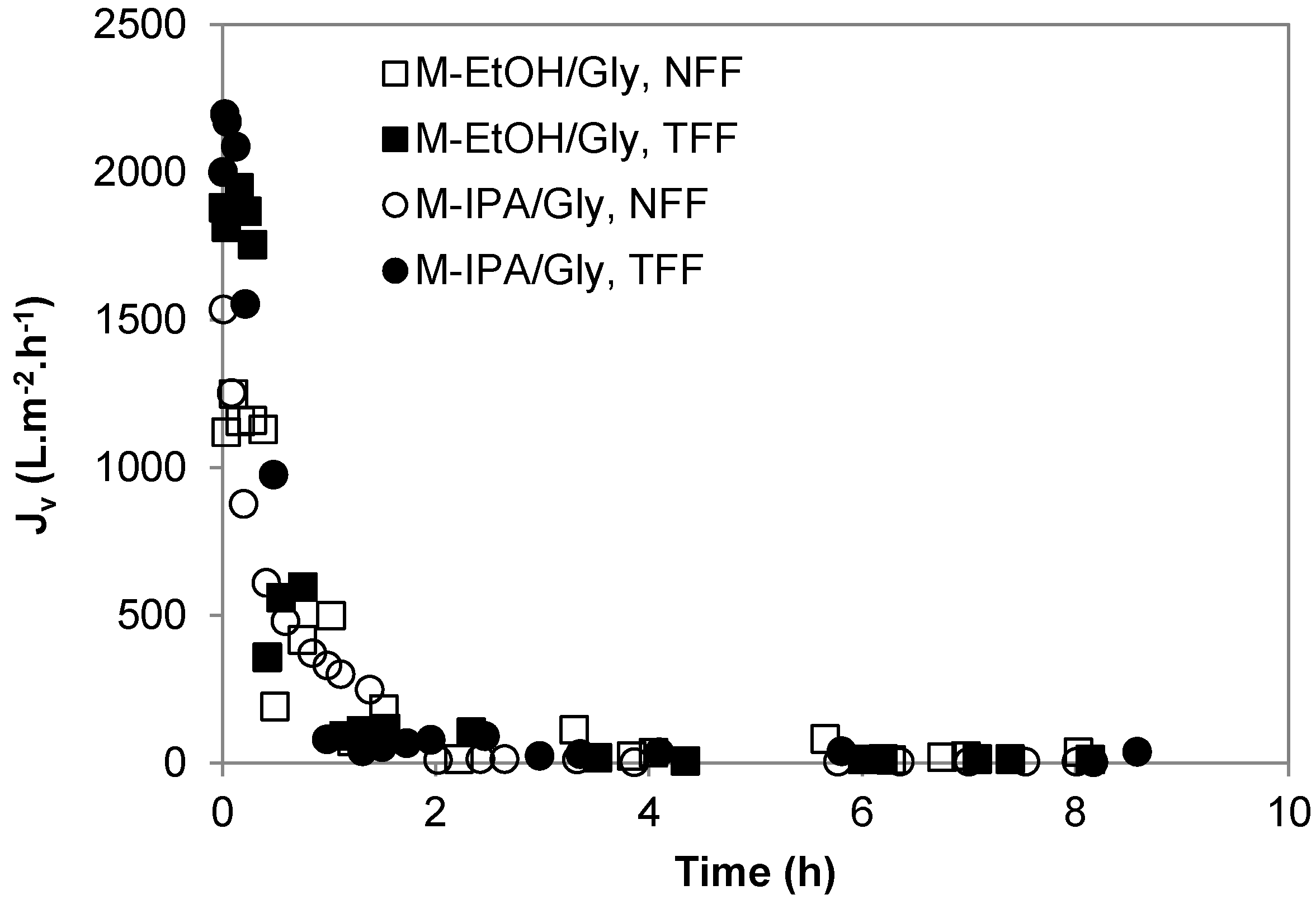
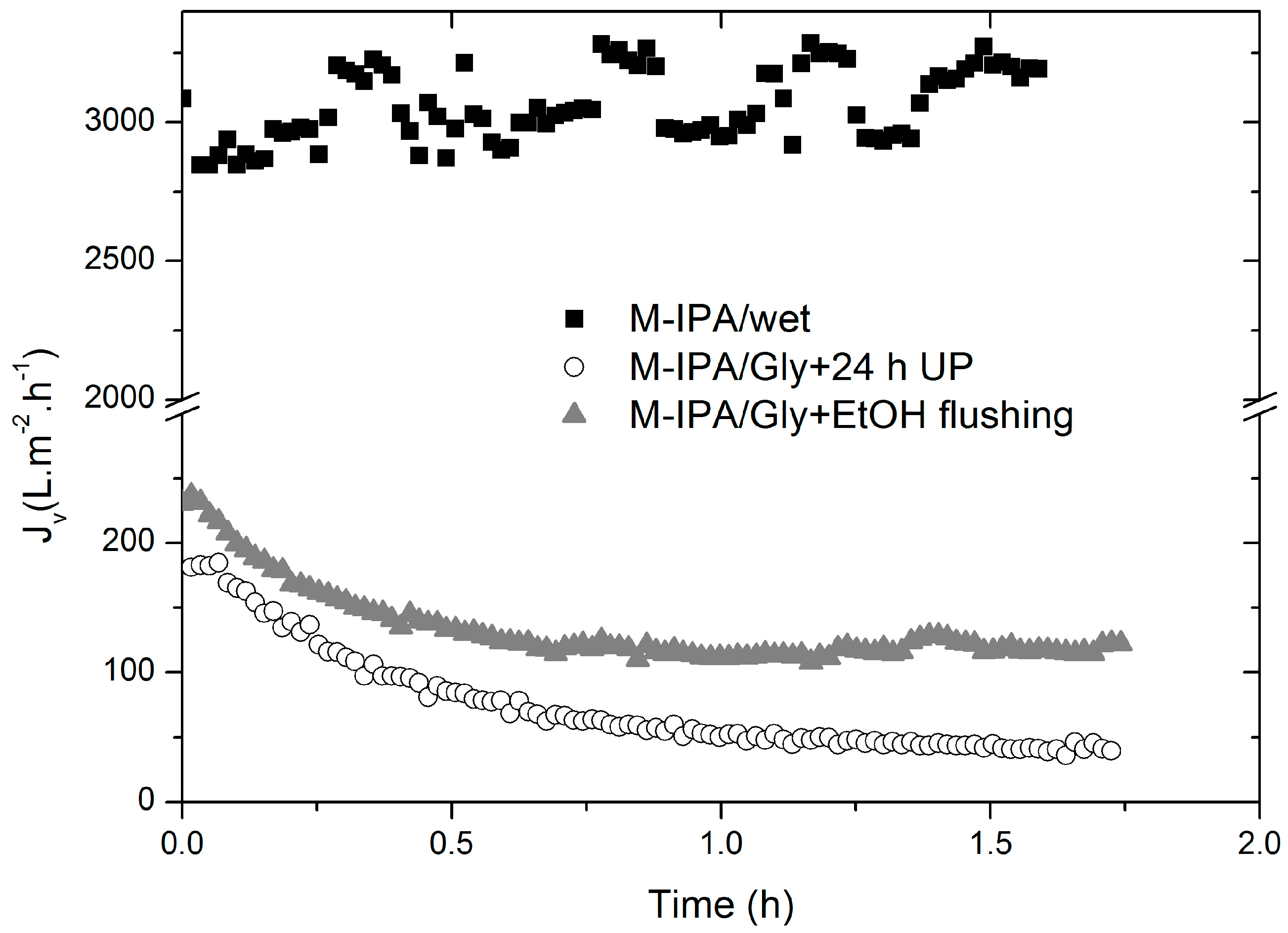
3.2. Transient Membrane Compaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ginai, M.; Elsby, R.; Hewitt, C.J.; Surry, D.; Fenner, K.; Coopman, K. The use of bioreactors as in vitro models in pharmaceutical research. Drug Discovery Today 2013, 18, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bartolo, L.; Leindlein, A.; Hofmann, D.; Bader, A.; de Grey, A.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Bio-hybrid organs and tissues for patient therapy: A future vision for 2030. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2012, 51, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N. Perspectives on engineering organs in vitro: overcoming oxygen supply limitations. J. Chem. Eng. Res. Stud. 2014, 1, E3. [Google Scholar]
- Diban, N.; Stamatialis, D. Polymeric hollow fiber membranes for bioartificial organs and tissue engineering applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.; Vermette, P. Bioreactors for tissue mass culture: Design, characterization, and recent advances. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7481–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi-nik, N.; Amoabediny, G.; Pouran, B.; Tabesh, H.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Haghighipour, N.; Khatibi, N.; Anisi, F. Engineering Parameters in Bioreactor’s Design: A Critical Aspect in Tissue Engineering. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2013, 762132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botchwey, E.A.; Dupree, M.A.; Pollack, S.R.; Levine, E.M.; Laurencin, C.T. Tissue engineered bone: Measurement of nutrient transport in three-dimensional matrices. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.—Part A 2003, 67, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, B.J.; Devarapalli, M.; Madihally, S.V. Flow dynamics in bioreactors containing tissue engineering scaffolds. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisi, F.; Salehi-Nik, N.; Amoabediny, G.; Pouran, B.; Haghighipour, N.; Zandieh-Doulabi, B. Applying shear stress to endothelial cells in a new perfusion chamber: hydrodynamic analysis. J. Artif. Organs 2014, 17, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, M.M.; Raimondi, M.T.; Pietrabissa, R. A multiphysics 3D model of tissue growth under interstitial perfusion in a tissue-engineering bioreactor. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2013, 12, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drioli, E.; De Bartolo, L. Membrane bioreactor for cell tissues and organoids. Artif. Organs 2006, 30, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, E.; De Bartolo, L.; Barbieri, G.; Rende, M.; Giorno, L.; Morelli, S.; Drioli, E. Diffusive and convective transport through hollow fiber membranes for liver cell culture. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 117, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bartolo, L.; Salerno, S.; Curcio, E.; Piscioneri, A.; Rende, M.; Morelli, S.; Tasselli, F.; Bader, A.; Drioli, E. Human hepatocyte functions in a crossed hollow fiber membrane bioreactor. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diban, N.; Haimi, S.; Bolhuis-Versteeg, L.; Teixeira, S.; Miettinen, S.; Poot, A.; Grijpma, D.; Stamatialis, D. Hollow fibers of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and poly(ε-caprolactone) blends for vascular tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6450–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.; Piscioneri, A.; Salerno, S.; Tasselli, F.; Di Vito, A.; Giusi, G.; Canonaco, M.; Drioli, E.; De Bartolo, L. PAN hollow fiber membranes elicit functional hippocampal neuronal network. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghello, G.; Parker, D.J.; Ainsworth, B.J.; Perera, S.P.; Chaudhuri, J.B.; Ellis, M.J.; De Bank, P.A. Fabrication and characterization of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/polyvinyl alcohol blended hollow fibre membranes for tissue engineering applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tomlins, P.E.; Coombes, A.G.A.; Rides, M. On the determination of Darcy permeability coefficients for a microporous tissue scaffold. Tissue Eng. Part C. Methods 2010, 16, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohonak, D.M.; Zydney, A.L. Compaction and permeability effects with virus filtration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.M.; Gekas, V.; Trägårdh, G. Study of membrane compaction and its influence on ultrafiltration water permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diban, N.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Remuzgo-Martinez, S.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Poly (ε-caprolactone) films with favourable properties for neural cell growth. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diban, N.; Stamatialis, D.F. Functional polymer scaffolds for blood vessel tissue engineering. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 309–310, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, H.; Ellis, M.J.; Perera, S.P.; Chaudhur, J.B. Effects of common sterilization methods on the structure and properties of poly(D,L lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettahalli, N.M.S.; Steg, H.; Wessling, M.; Stamatialis, D. Development of poly(l-lactic acid) hollow fiber membranes for artificial vasculature in tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiLeo, A.J.; Allegrezza, A.E.; Builder, S.E. High resolution removal of virus from protein solutions using a membrane of unique structure. Nat. Biotechnol. 1992, 10, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-J.; Chiang, Y.-C. Comparisons of membrane fouling and separation efficiency in protein/polysaccharide cross-flow microfiltration using membranes with different morphologies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 125, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, A.; Jönsson, A.-S.; Zacchi, G. Transmission of BSA during cross-flow microfiltration: influence of pH and salt concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 223, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güell, C.; Davis, R.H. Membrane fouling during microfiltration of protein mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 119, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.; Davis, R.H. Protein fouling of surface-modified polymeric microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 116, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A. The effect of protein–protein and protein–membrane interactions on membrane fouling in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna, M.; Piscitelli, F.; Mangiacapra, P.; Buonocore, G.G. Study of the combined effect of both clay and glycerol plasticizer on the properties of chitosan films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakhiew, W.; Devahastin, S.; Soponronnarit, S. Effects of drying methods and plasticizer concentration on some physical and mechanical properties of edible chitosan films. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, P.C.; Ramesh, M.N.; Tharanathan, R.N. Effect of plasticizers and fatty acids on mechanical and permeability characteristics of chitosan films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.T.; Zydney, A.L. Mechanisms for BSA fouling during microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-C.; Zydney, A.L. A Combined Pore Blockage and Cake Filtration Model for Protein Fouling during Microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, T.; Niegelhell, K.; Nagaraj, C.; Reishofer, D.; Spirk, S.; Olschewski, A.; Stana Kleinschek, K.; Kargl, R. Interaction of Tissue Engineering Substrates with Serum Proteins and Its Influence on Human Primary Endothelial Cells. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khampieng, T.; Yamassatien, V.; Ekabutr, P.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Protein adsorption and cell behaviors on polycaprolactone film: The effect of surface topography. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2017, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Room T and BSA Solution pH ~ 5 | 37 °C, BSA Solution pH 7.2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-EtOH/Gly, NFF | M-EtOH/Gly, TFF | M-IPA/Gly, NFF | M-IPA/Gly, TFF | M-IPA/Gly, TFF | |
| KT, s.s. (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) for CWF | 209 ± 27 | 160 ± 77 | 309 ± 90 | 218 ± 33 | 244 ± 50 |
| KT, s.s. (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) for BSA solution | 99 ± 14 * | 165 ± 82 | 46 ± 14 * | 116 ± 50 * | 110 ± 30 * |
| TBSA (%) | 98 ± 3 | 91 ± 11 | 93 ± 6 | 91 ± 10 | 76 ± 3 |
| Mean Flow Pore Size, MFP (µm) | 0.72 ± 0.17 | 0.74 ± 0.17 | |||
| Bubble Point Pore Size, BPP (µm) | 1.06 ± 0.39 | 0.97 ± 0.26 | |||
| Smallest Pore Size, SP (µm) | 0.53 ± 0.20 | 0.58 ± 0.17 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diban, N.; Gómez-Ruiz, B.; Lázaro-Díez, M.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Factors Affecting Mass Transport Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Membranes for Tissue Engineering Bioreactors. Membranes 2018, 8, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030051
Diban N, Gómez-Ruiz B, Lázaro-Díez M, Ramos-Vivas J, Ortiz I, Urtiaga A. Factors Affecting Mass Transport Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Membranes for Tissue Engineering Bioreactors. Membranes. 2018; 8(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiban, Nazely, Beatriz Gómez-Ruiz, María Lázaro-Díez, Jose Ramos-Vivas, Inmaculada Ortiz, and Ane Urtiaga. 2018. "Factors Affecting Mass Transport Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Membranes for Tissue Engineering Bioreactors" Membranes 8, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030051
APA StyleDiban, N., Gómez-Ruiz, B., Lázaro-Díez, M., Ramos-Vivas, J., Ortiz, I., & Urtiaga, A. (2018). Factors Affecting Mass Transport Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Membranes for Tissue Engineering Bioreactors. Membranes, 8(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030051






