Selectivity of Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
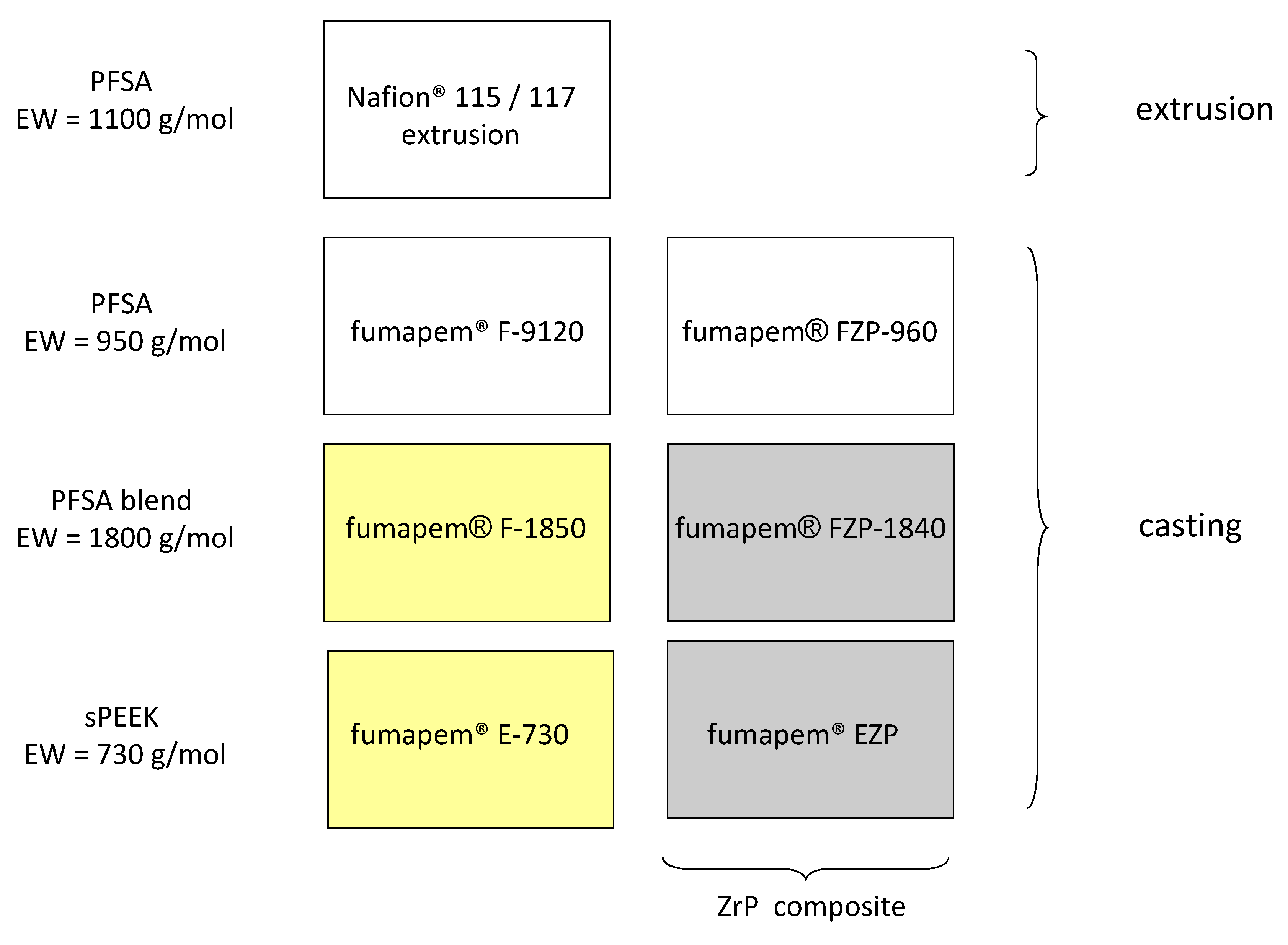
2.1. Membrane Characteristics
| Membrane Acronym | Unit | F-1850 | E-730 | FZP-960 | FX-7050 | N-115 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer Type | PFSA | sPEEK | PFSA-ZrP | PFSA Cross-Linked | PFSA | |
| Filler content | – | – | – | 10% | – | – |
| EW (theoretical) | g/mol | 1800 | 740 | 950 | 7000 | 1100 |
| IEC (exp.) | mmol/g | 0.50 | 1.35 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.9 |
| Thickness (dry) | µm | 50 | 30 | 60 | 50 | 125 |
| Solvent uptake in MeOH at 25 °C | Wt % | 30 | 38 | 115 | 33 | 54 |
| Length increase Δl in MeOH at 25 °C | % | 18 | 10 | 46 | 8 | 31 |
| Conductivity in H2O at T = 25 °C | mS·cm−1 | 58 | 16 | 23 | 56 | 62 |
2.2. Electrochemical Properties
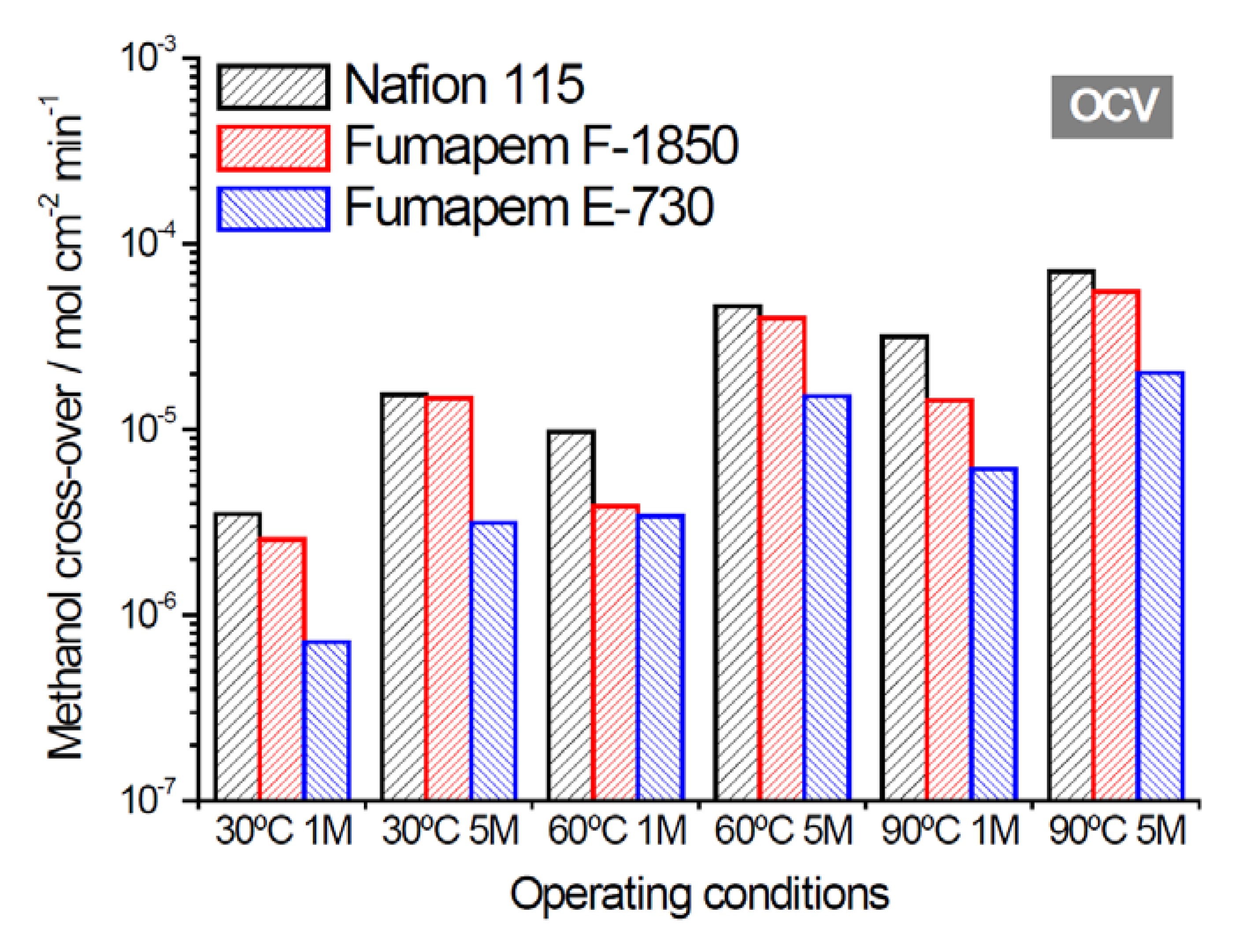
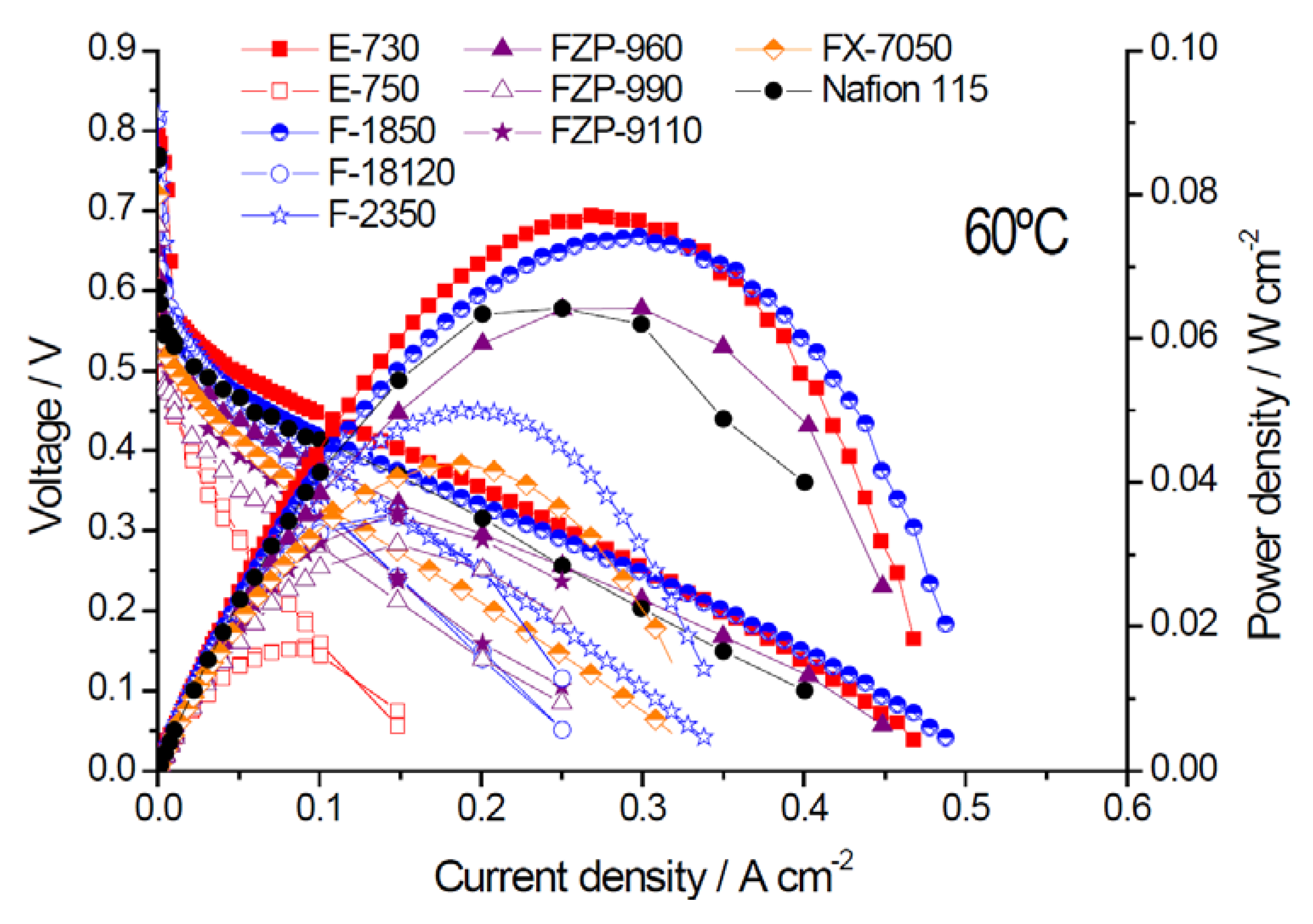
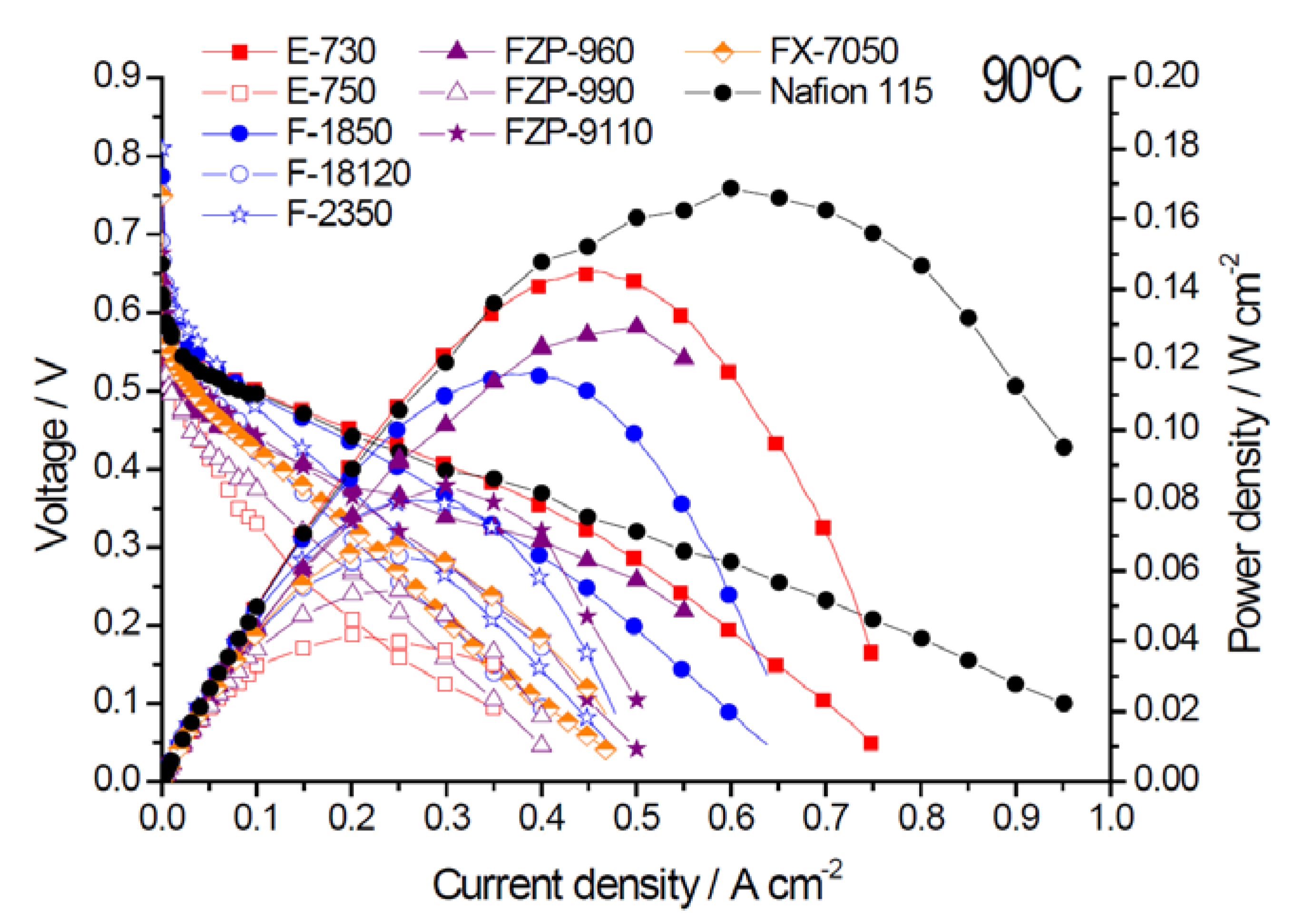
| Membrane Acronym | Units | E-730 | E-750 | F-1850 | F-18120 | F-2350 | FZP-960 | FZP-990 | FZP-9110 | FX-7050 | Nafion® 115 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer Type | s-PEEK | s-PEEK | PFSA | PFSA | PFSA | PFSA-ZrP | PFSA-ZrP | PFSA-ZrP | PFSA Cross-Linked | PFSA | |
| Equivalent weight | g/mol | 700 | 700 | 1800 | 1800 | 2300 | 950 | 950 | 950 | 7000 | 1100 |
| thickness | µm | 30 | 50 | 50 | 120 | 50 | 60 | 90 | 110 | 50 | 125 |
| Max. Power density | mW·cm−2 | 77 | 17 | 74 | 36 | 50 | 64 | 32 | 35 | 42 | 64 |
| @ 60 °C | |||||||||||
| Rs (EIS) | Ω cm2 | 0.20 | 0.62 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.085 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| @ 60 °C | |||||||||||
| Crossover current | mA·cm−2 | 48 | 106 | 120 | 100 | 88 | 128 | 135 | 208 | 186 | 195 |
| @ 60 °C | |||||||||||
| Max. Power density | mW·cm−2 | 145 | 42 | 116 | 64 | 80 | 129 | 55 | 84 | 67 | 167 |
| @ 90 °C | |||||||||||
| Rs (EIS) | Ω cm2 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.14 |
| @ 90 °C | |||||||||||
| Crossover current | mA·cm−2 | 74 | 185 | 193 | 123 | 121 | 153 | 162 | 245 | 260 | 380 |
| @ 90 °C |
2.3. Membrane Selectivity

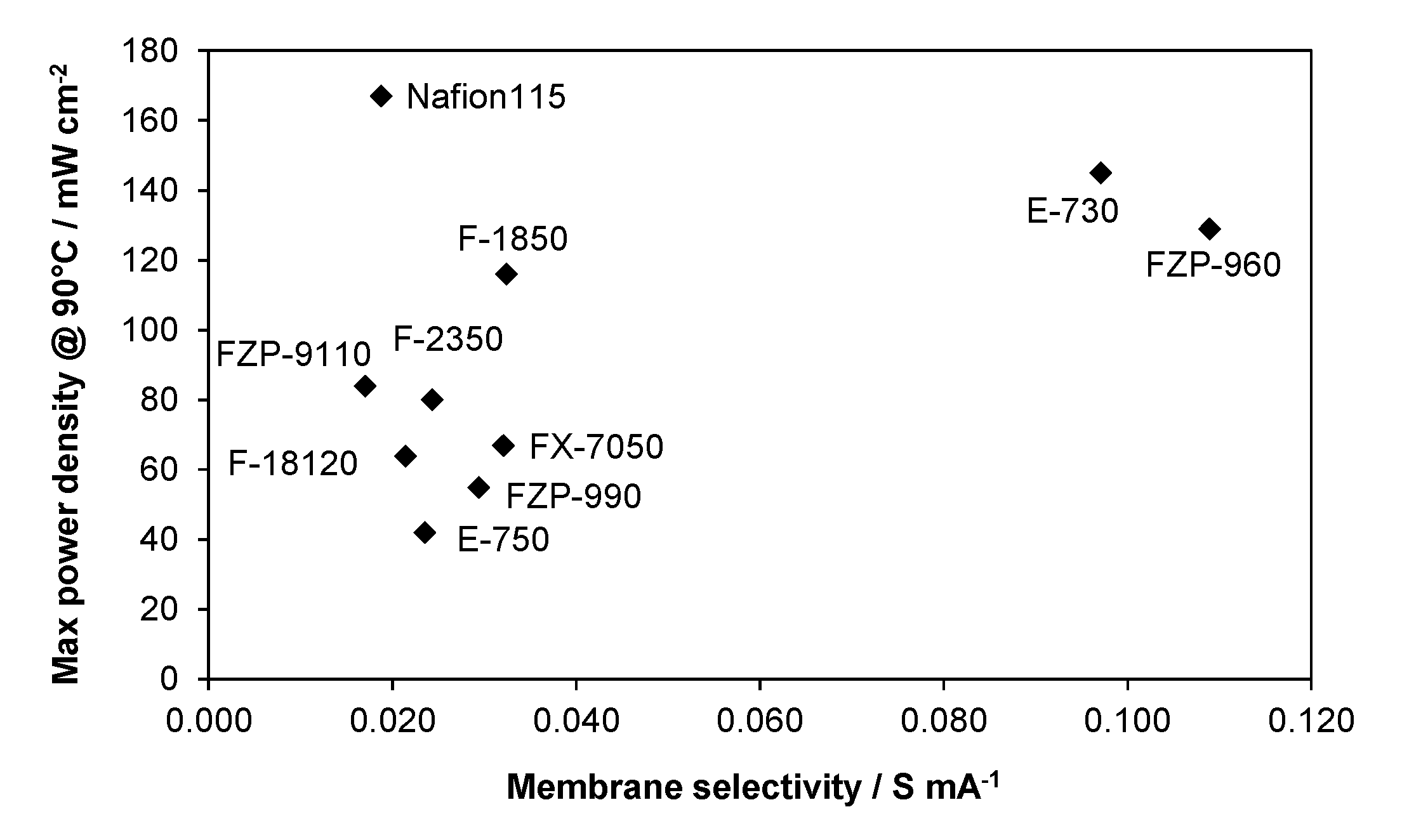
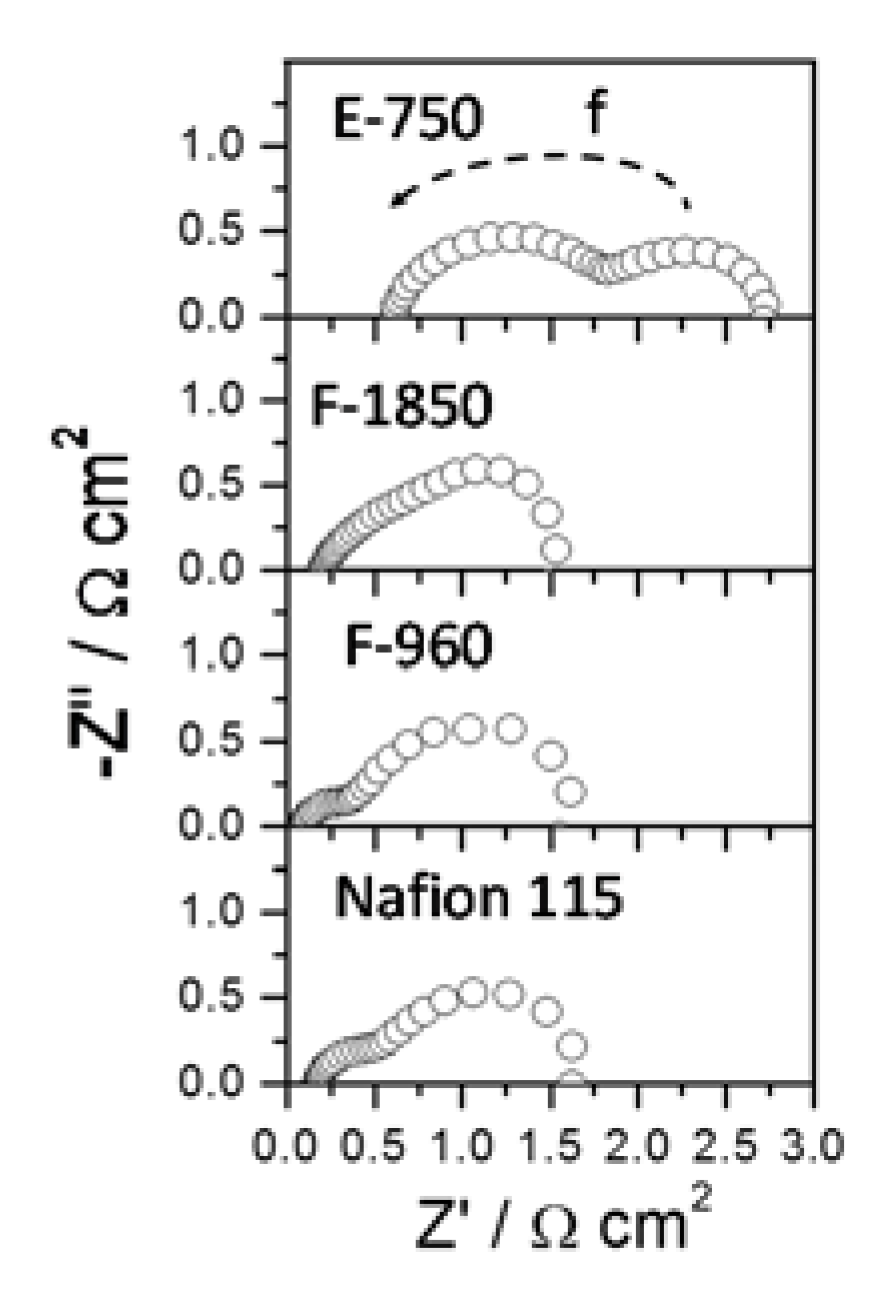
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aricò, A.S.; Srinivasan, S.; Antonucci, V. DMFCs: From fundamental aspects to technology development. Fuel Cells 2001, 2, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neburchilov, V.; Martin, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. A review of polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 169, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; Antonucci, V. Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: History, Status and Perspectives. In Electrocatalysis of Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: From Fundamentals to Applications; Zhang, T.J., Liu, H.S., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Z.; Khatun, S.; Akins, D.; Adam, Y.; Suarez, S. A study of the effect of heat-treatment on the morphology of Nafion ionomer dispersion for use in the passive direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). Membranes 2012, 2, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houchins, C.; Kleen, G.J.; Spendelow, J.S.; Kopasz, J.; Peterson, D.; Garland, N.L.; Ho, D.L.; Marcinkoski, J.; Martin, K.E.; Tyler, R.; et al. U.S. DOE progress towards developing low-cost, high performance, durable polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications. Membranes 2012, 2, 855–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicotera, I.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V. NMR and electrochemical investigation of the transport properties of methanol and water in Nafion and clay-nanocomposites membranes for DMFCs. Membranes 2012, 2, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, T.S. Performance characterization of passive direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, F.; Baglio, V.; Staiti, P.; Antonucci, V.; Arico’, A.S. Performance analysis of polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabd, Y.A.; Napadensky, E.; Sloan, J.M.; Crawford, D.M.; Walker, C.W. Triblock copolymer ionomer membranes Part I. Methanol and proton transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 217, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telfah, A.; Majer, G.; Kreuer, K.D.; Schuster, M.; Maier, J. Formation and mobility of protonic charge carriers in methyl sulfonic acid-water mixtures: A model for sulfonic acid based ionomers at low degree of hydration. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, V.; Kreuer, K.D.; Schuster, M.; Merkle, R.; Maier, J. On the swelling properties of proton conducting membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D.; Paddison, S.J.; Spohr, E.; Schuster, M. Transport in proton conductors for fuel-cell applications: Simulations, elementary reactions, and phenomenology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4637–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.C.; Peck, D.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lim, S.; Jung, D.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, D.Y. Dynamic response and long-term stability of a small direct methanol fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4080–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; di Blasi, A.; Creti, P.; Antonucci, P.L.; Antonucci, V. Influence of the acid-base characteristics of inorganic fillers on the high temperature performance of composite membranes in direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2003, 161, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Guiver, M.D.; Pivovar, B.S. High performance nitrile copolymers for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 321, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Manthiram, A.; Guiver, M.D.; Liu, B. High performance direct methanol fuel cells based on acid-base blend membranes containing benzotriazole. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.; Zhang, W.; Ullrich, A.; Tang, C.M.; Hein, M.; Gogel, V.; Frey, T.; Jorissen, L. Synthesis and characterization of polyaryl blend membranes having different composition, different covalent and/or ionical cross-linking density, and their application to DMFC. Desalination 2002, 147, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Nam, W.H.; Chung, D.Y.; Park, I.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Song, J.C.; Sung, Y.E. Enhanced Methanol Tolerance of Highly Pd rich Pd-Pt Cathode Electrocatalysts in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 164, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Stassi, A.; D’Urso, C.; Sebastián, D.; Baglio, V. Synthesis of Pd3Co1@Pt/C core-shell catalysts for methanol-tolerant cathodes of direct methanol fuel cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 10679–10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Li, L.; Tang, J.K.; Bauer, B.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.R.; Taillades-Jacquin, M.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J.; Lebedeva, N.; et al. Development of covalently cross-linked and composite perfluorosulfonic acid membranes. ECS Trans. 2009, 25, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Gatto, I.; Stassi, A.; Baglio, V.; Carbone, A.; Passalacqua, E.; Aricò, A.S.; Schuster, M.; Bauer, B. Optimization of perfluorosulphonic ionomer amount in gas diffusion electrodes for PEMFC operation under automotive conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 165, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.; Jones, D.J.; Rozière, J.; Tchicaya, L.; Alberti, G.; Casciola, M.; Massinelli, L.; Peraio, A.; Besse, S.; Ramunni, E. Electrochemical characterisation of sulfonated polyetherketone membranes. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2000, 3, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, G.; Casciola, M.; Capitani, D.; Donnadio, A.; Narducci, R.; Pica, M.; Sganappa, M. Novel Nafion-zirconium phosphate nanocomposite membranes with enhanced stability of proton conductivity at medium temperature and high relative humidity. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 8125–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranesi, B.; Hou, H.; Polini, R.; Sgreccia, E.; Alberti, G.; Narducci, R.; Knauth, P.; di Vona, M.L. Cross-linking of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) by thermal treatment: How does the reaction occur? Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, G.A.; Piga, M.; Lavina, S.; Navarra, M.A.; D’Epifanio, A.; Scrosati, B.; Noto, V.D. Characterization of sulfated-zirconia/Nafion® composite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 198, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, F.; Baglio, V.; di Blasi, O.; Staiti, P.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A.S. Solid polymer electrolyte based on sulfonated polysulfone membranes and acidic silica for direct methanol fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2012, 216, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aricò, A.S.; Baglio, V.; di Blasi, A.; Modica, E.; Antonucci, P.L.; Antonucci, V. Analysis of the high-temperature methanol oxidation behaviour at carbon-supported Pt-Ru catalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 557, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Stassi, A.; Baglio, V.; Aricò, A.S.; Capitanio, F.; Tavares, A.C. Investigation of carbon-supported Pt and PtCo catalysts for oxygen reduction in direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4844–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, V.; Stassi, A.; Matera, F.V.; Kim, H.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A.S. AC-impedance investigation of different MEA configurations for passive-mode DMFC mini-stack applications. Fuel Cells 2010, 10, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scipioni, R.; Gazzoli, D.; Teocoli, F.; Palumbo, O.; Paolone, A.; Ibris, N.; Brutti, S.; Navarra, M.A. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite polymer membranes containing functionalized SnO2 additives. Membranes 2014, 4, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titvinidze, G.; Kreuer, K.D.; Schuster, M.; de Araujo, C.C.; Melchior, J.P.; Meyer, W.H. Proton conducting phase-separated multiblock copolymers with sulfonated poly(phenylene sulfone) blocks for electrochemical applications: Preparation, morphology, hydration behavior, and transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4456–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aricò, A.S.; Sebastian, D.; Schuster, M.; Bauer, B.; D'Urso, C.; Lufrano, F.; Baglio, V. Selectivity of Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Membranes. Membranes 2015, 5, 793-809. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040793
Aricò AS, Sebastian D, Schuster M, Bauer B, D'Urso C, Lufrano F, Baglio V. Selectivity of Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Membranes. Membranes. 2015; 5(4):793-809. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040793
Chicago/Turabian StyleAricò, Antonino S., David Sebastian, Michael Schuster, Bernd Bauer, Claudia D'Urso, Francesco Lufrano, and Vincenzo Baglio. 2015. "Selectivity of Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Membranes" Membranes 5, no. 4: 793-809. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040793
APA StyleAricò, A. S., Sebastian, D., Schuster, M., Bauer, B., D'Urso, C., Lufrano, F., & Baglio, V. (2015). Selectivity of Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Membranes. Membranes, 5(4), 793-809. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040793









