Influence of the Ionic Liquid Type on the Gel Polymer Electrolytes Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| GPE name | PVdF-HFP/g | IL/g | ZnTf2/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVdF-HFP | 0.5 | 0 | 0 |
| IL-GPE | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0 |
| ZnTf2 GPE | 0.5 | 0 | 0.255 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 1 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.127 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 2 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.255 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 3 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.382 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 4 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.509 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 5 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.636 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 6 | 0.5 | 0.445 | 0.763 |
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Characterization of the Gel Polymer Electrolytes
2.1.1. XRD
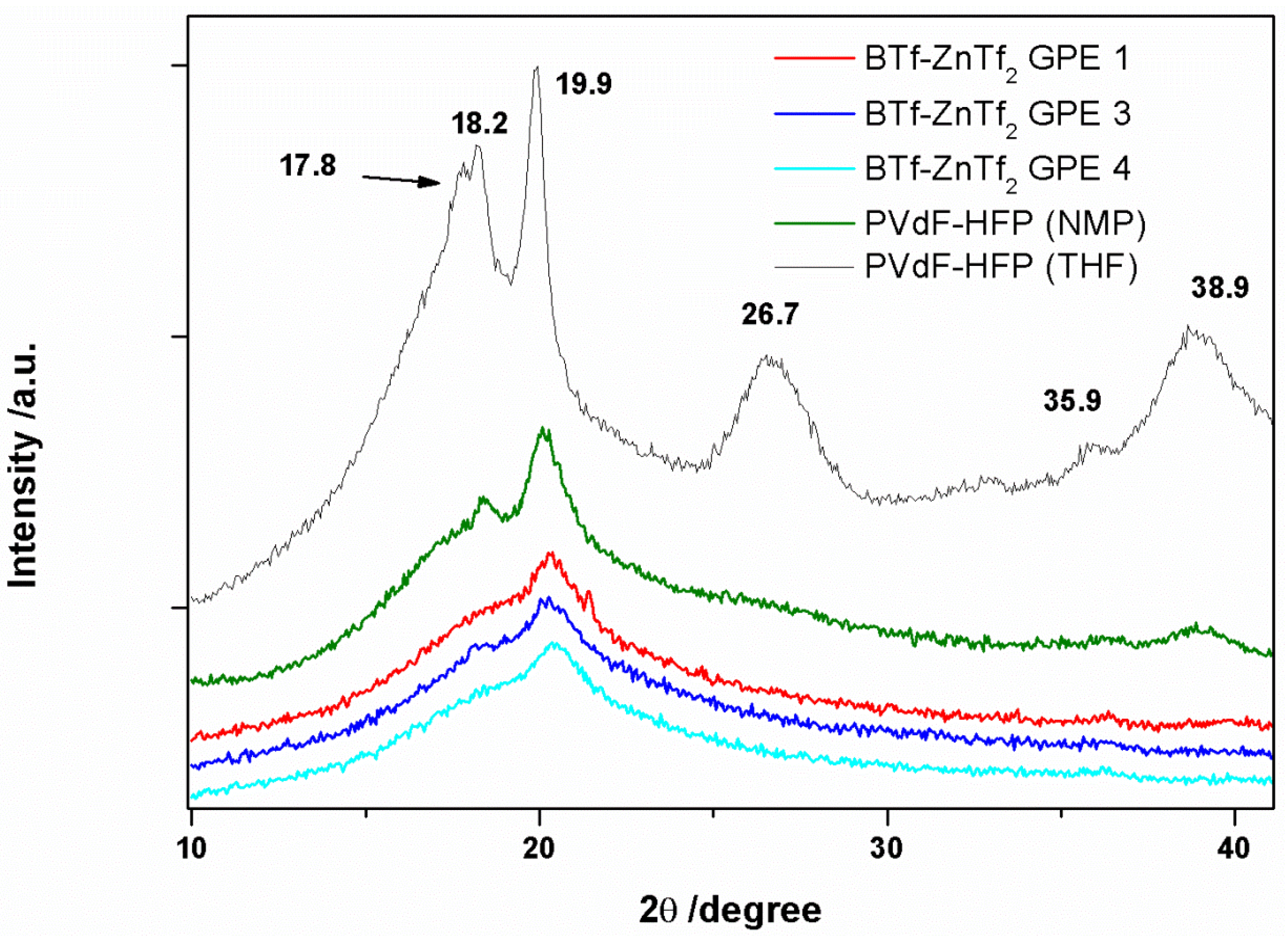
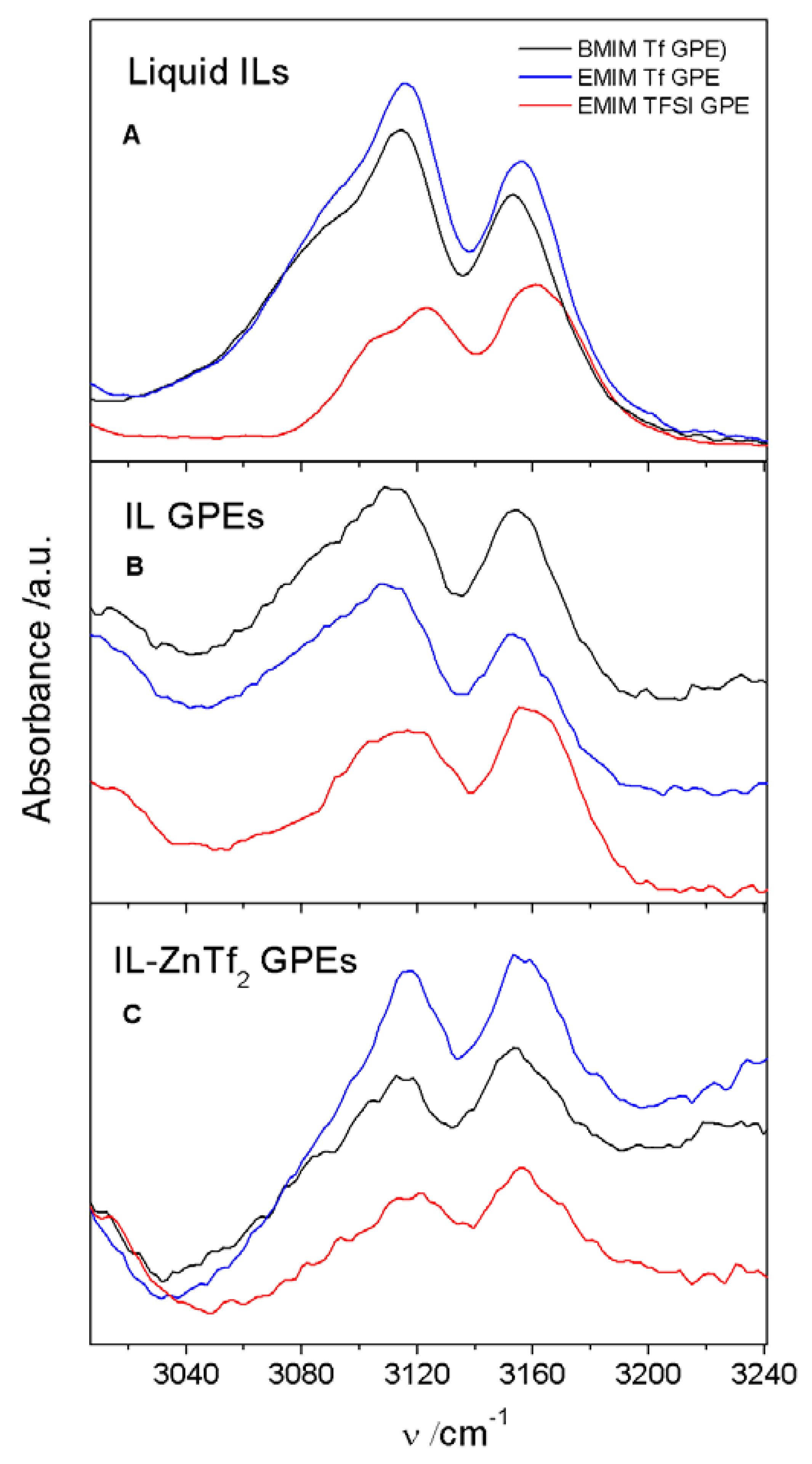
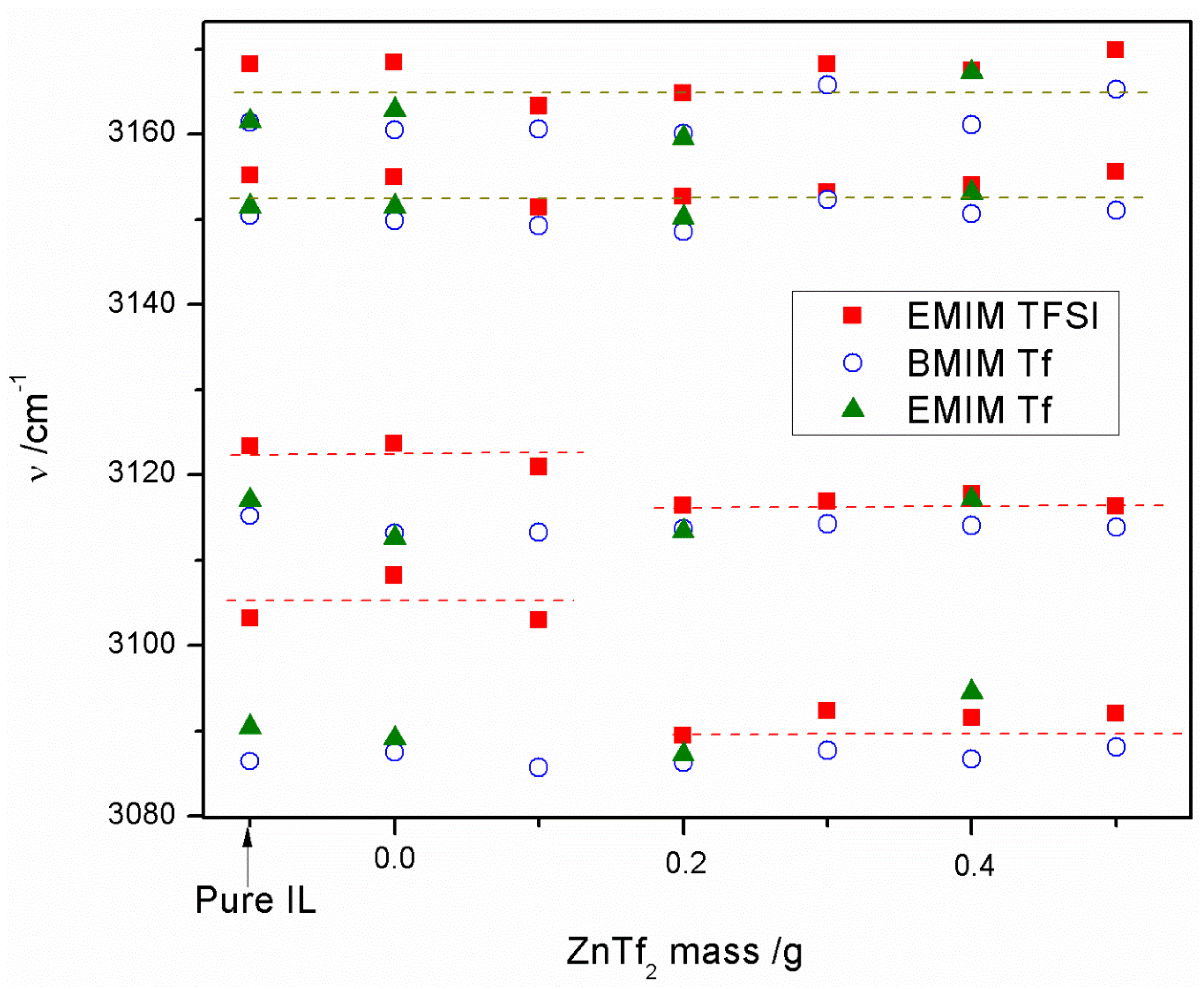
2.1.2. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
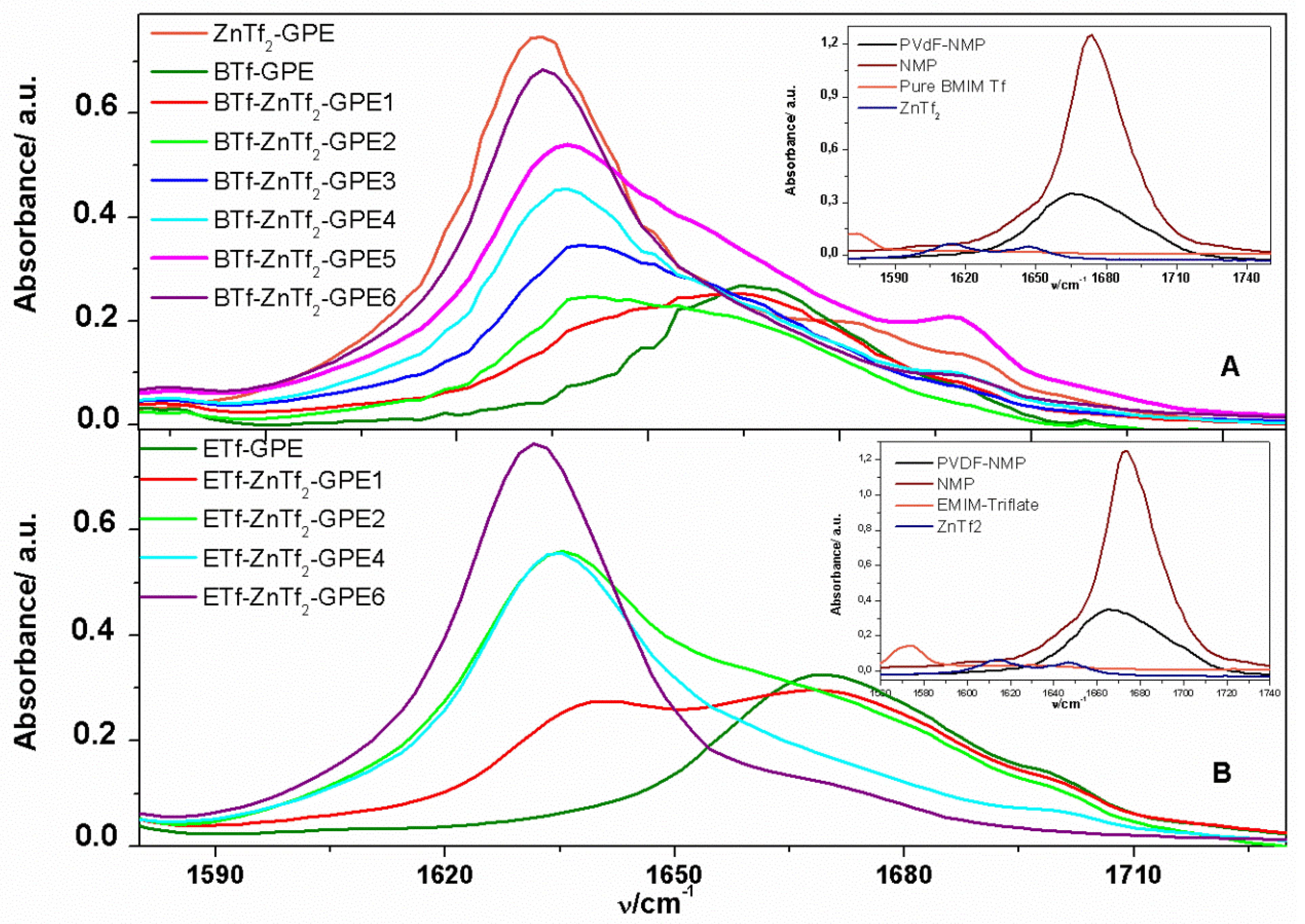
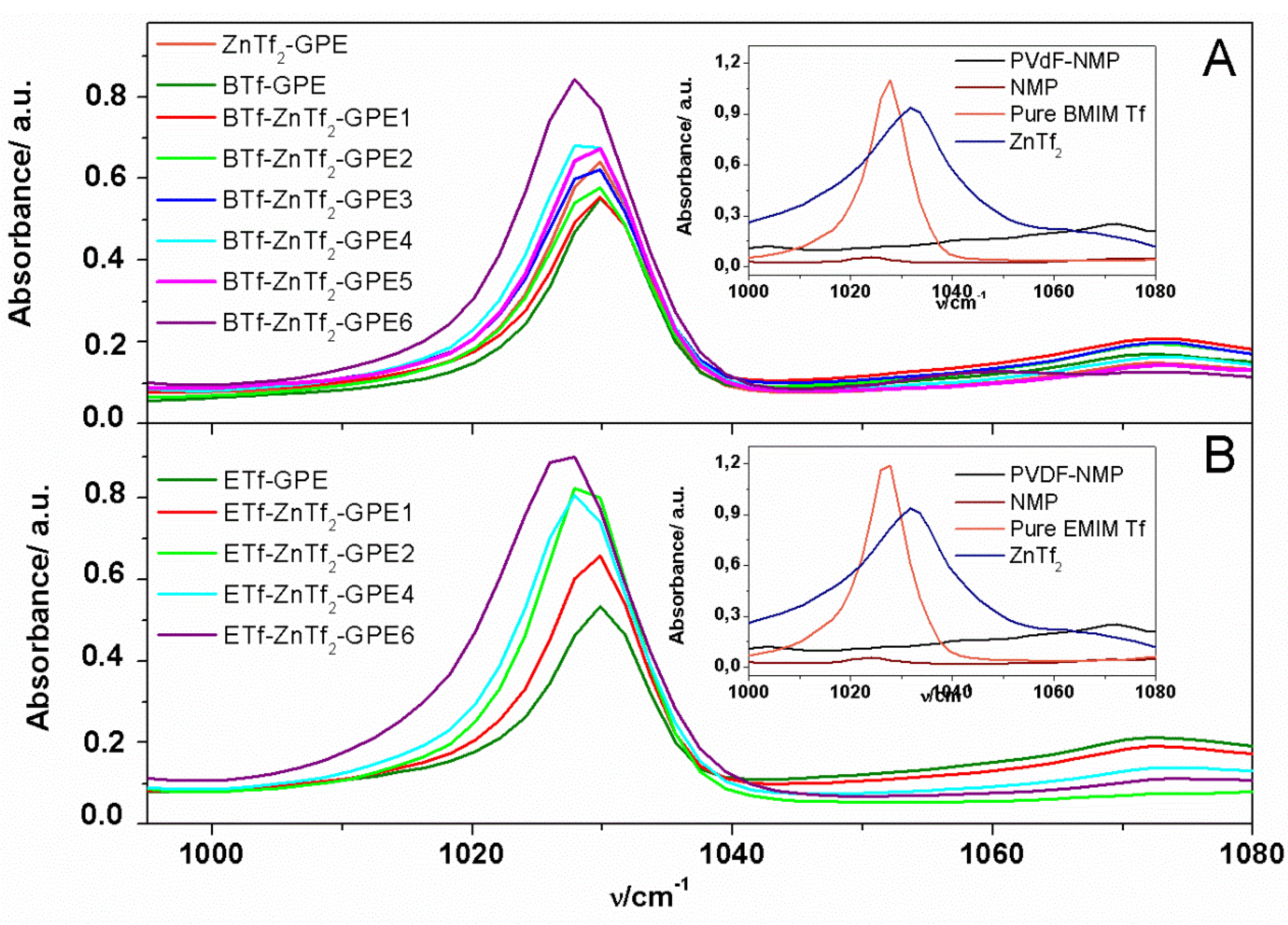
2.1.3. Thermal Analysis
| GPE name | EMIM TFSI | EMIM Tf | BMIM Tf | EMIM TFSI | EMIM Tf | BMIM Tf |
| Sample | Tg°C | σ(S cm−1)·10−3 | ||||
| IL-GPE | −81.6 | −79.3 | −78.8 | 1.98 | 7.07 | 5.2 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 1 | −67.5 | −64.8 | −56.3 | 3.82 | 7.05 | 1.93 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 2 | −58.5 | −63.2 | −56.3 | 3.73 | 4.62 | 2.68 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 3 | −57.3 | – | −55.3 | 3.05 | – | 2.99 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 4 | −56.9 | −61.1 | −54.5 | 2.2 | 1.96 | 2.21 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 5 | −53.3 | – | −53.8 | 1.54 | – | 2.57 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 6 | −49.4 | −51.3 | −51.1 | 1.88 | 1.09 | 1.88 |
| GPE name | EMIM TFSI | EMIM Tf | BMIM Tf | EMIM TFSI | EMIM Tf | BMIM Tf |
| Sample | t+ | Ea(eV) | ||||
| IL-GPE | 0.098 | 0.42 | 0.19 | 0.041 | 0.024 | 0.03 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 1 | 0.296 | – | 0.42 | 0.027 | 0.026 | 0.026 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 2 | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.026 | 0.028 | 0.025 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 3 | 0.428 | – | 0.52 | 0.028 | – | 0.028 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 4 | 0.578 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.037 | 0.033 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 5 | 0.544 | – | – | 0.032 | – | 0.033 |
| IL-ZnTf2 GPE 6 | 0.575 | 0.52 | 0.48 | 0.027 | 0.038 | 0.031 |
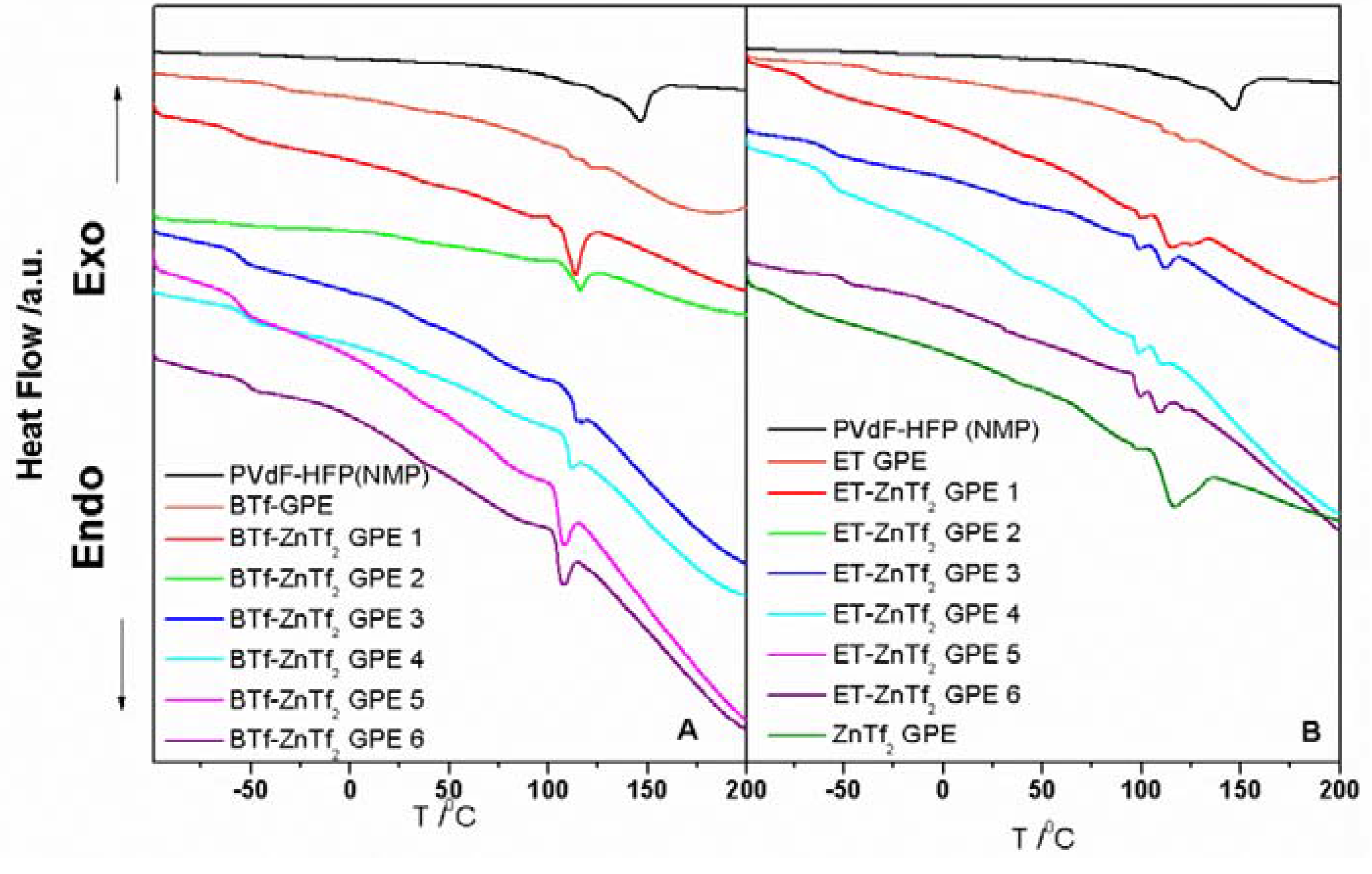
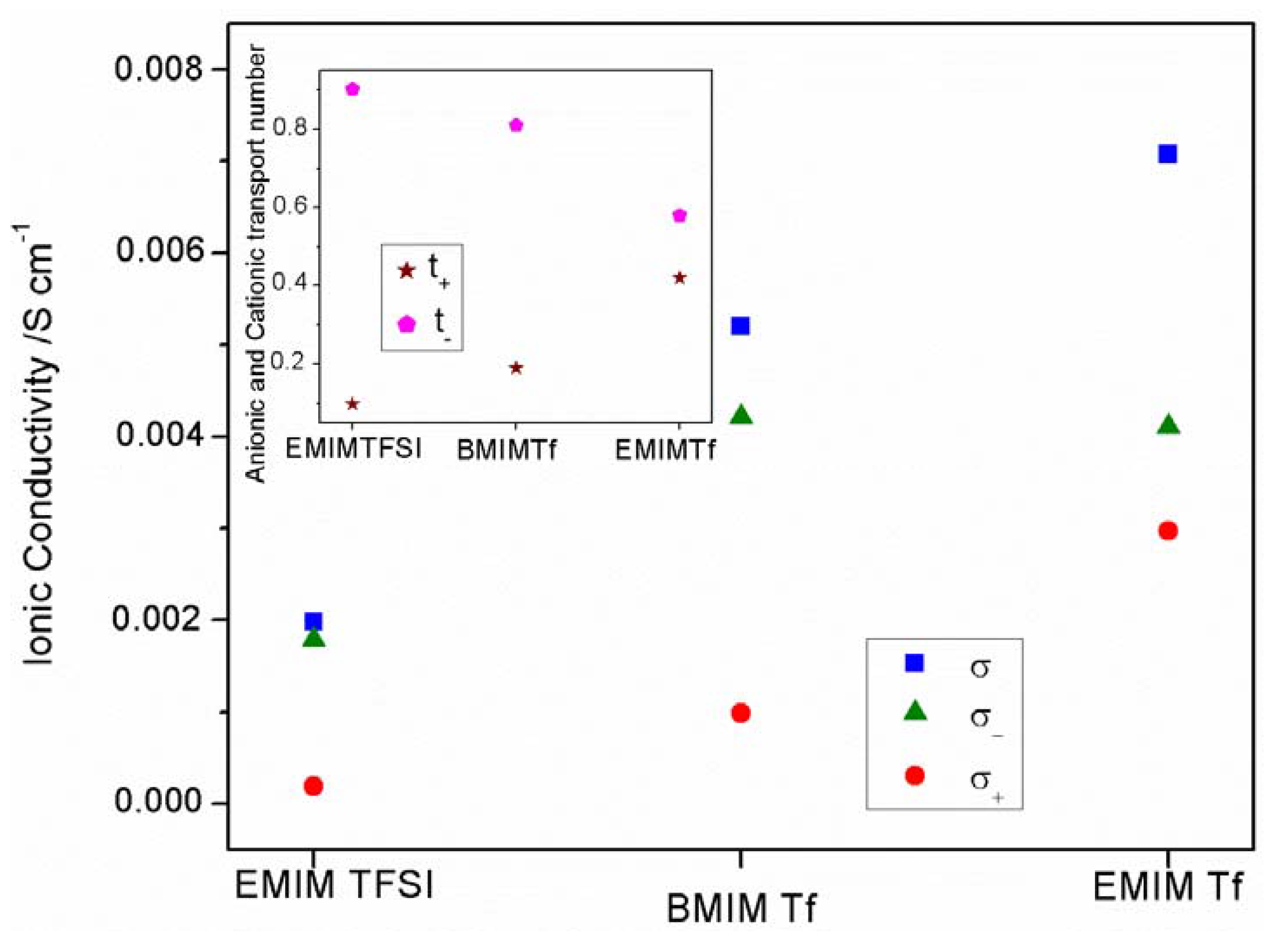
2.2. Electrical and Electrochemical Properties
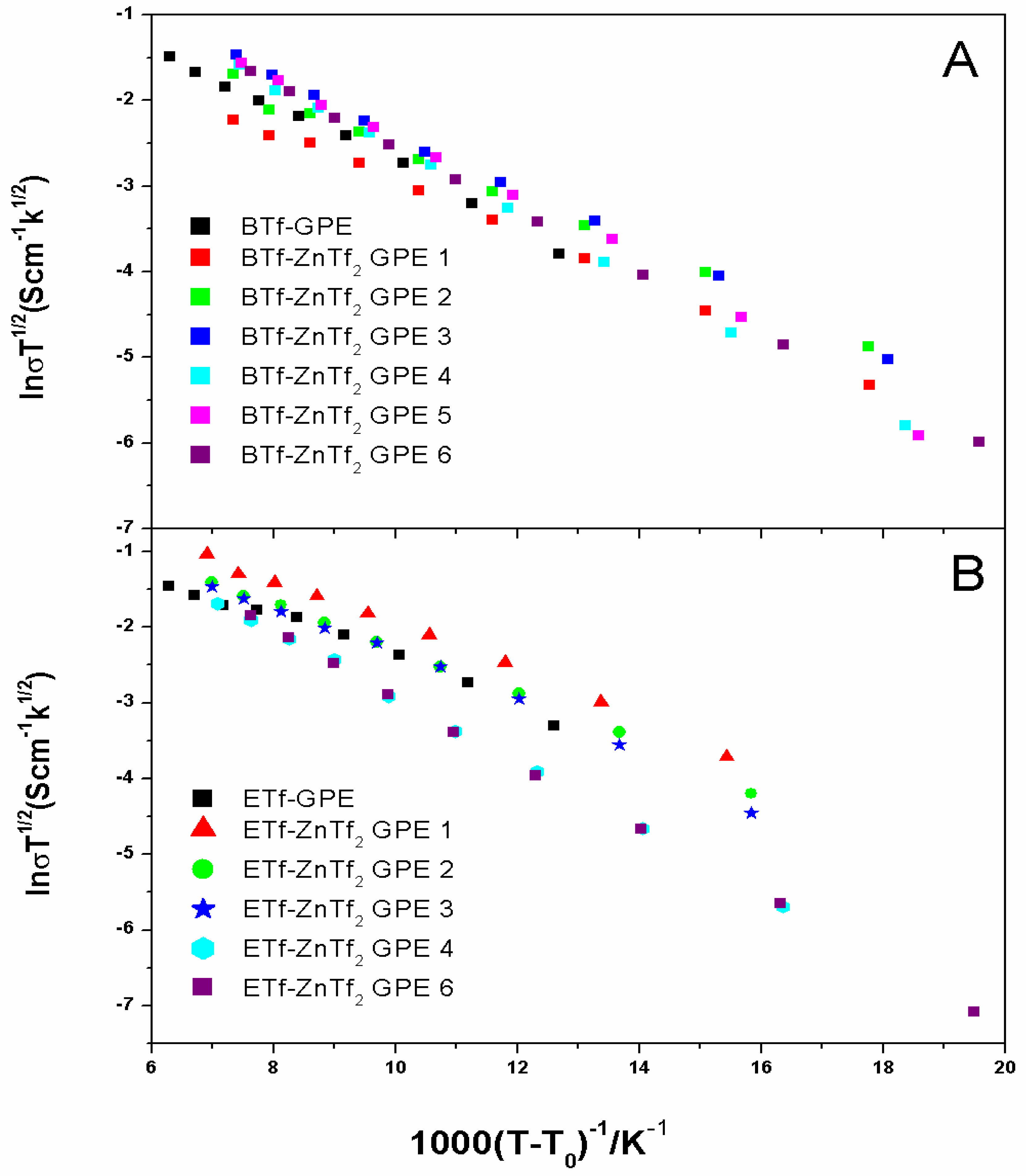
2.2.2. Transport Number
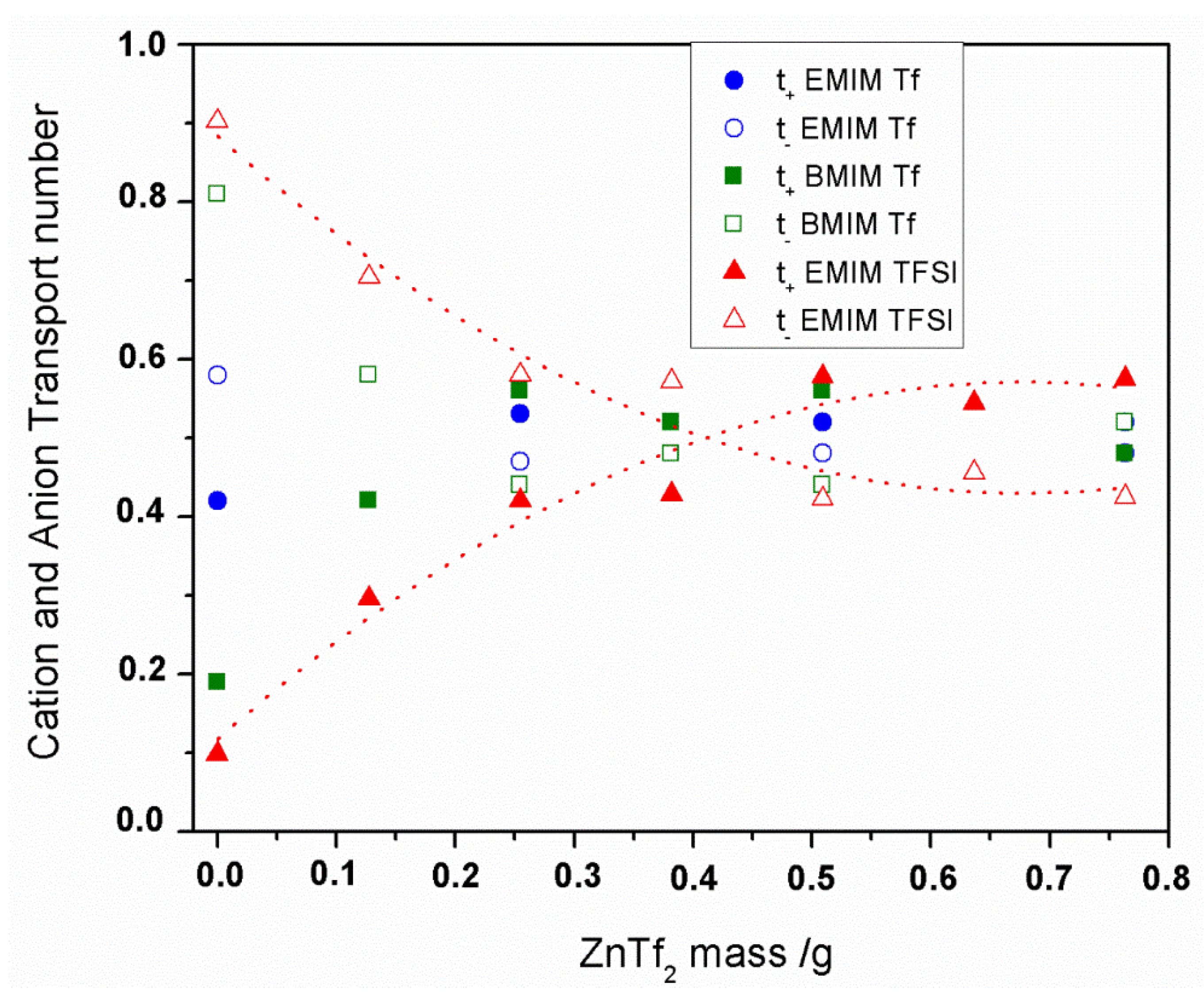
2.2.3. Cyclic Voltammetry
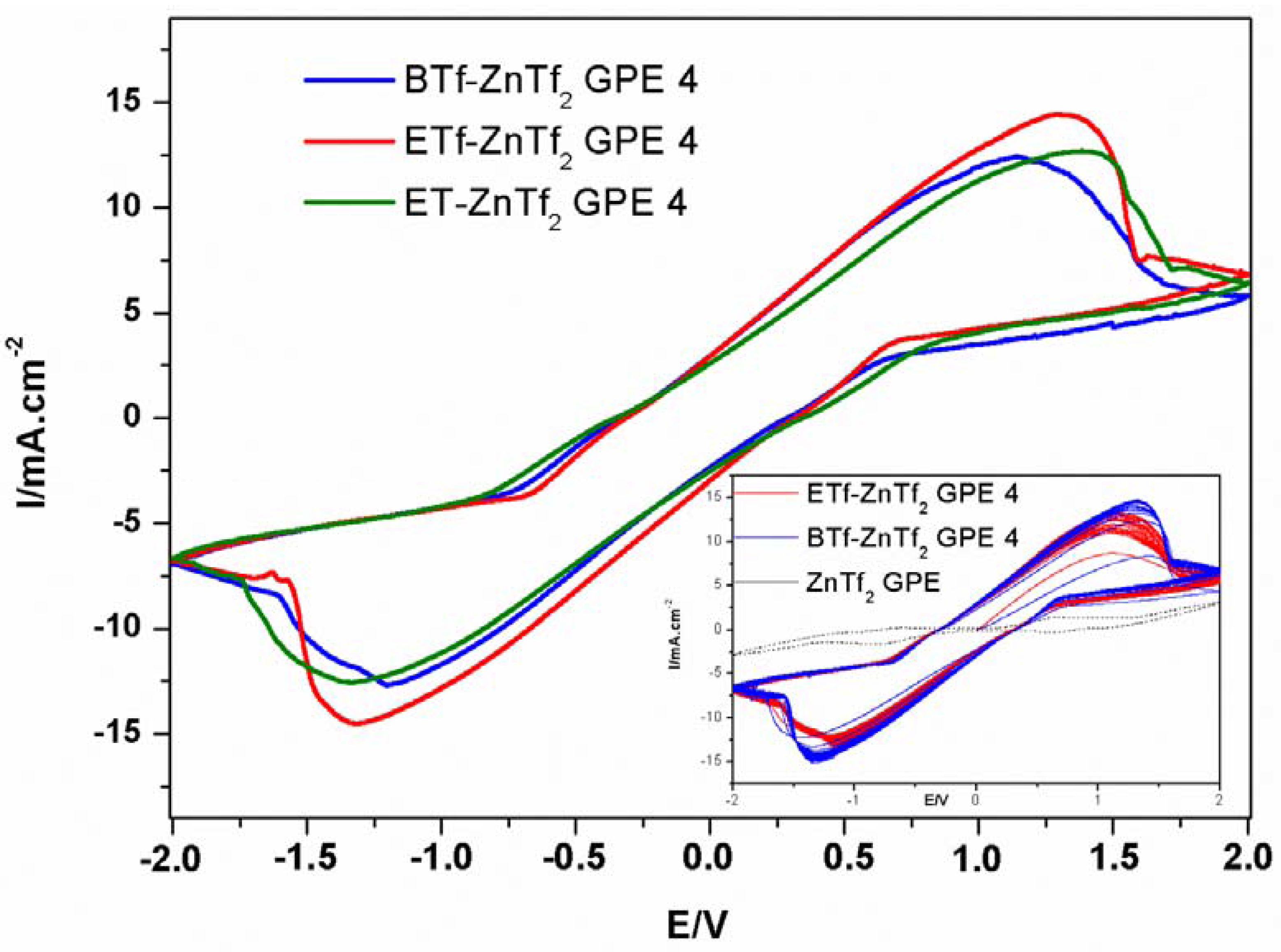
2.2.4. Zn/GPE/MnO2 Batteries
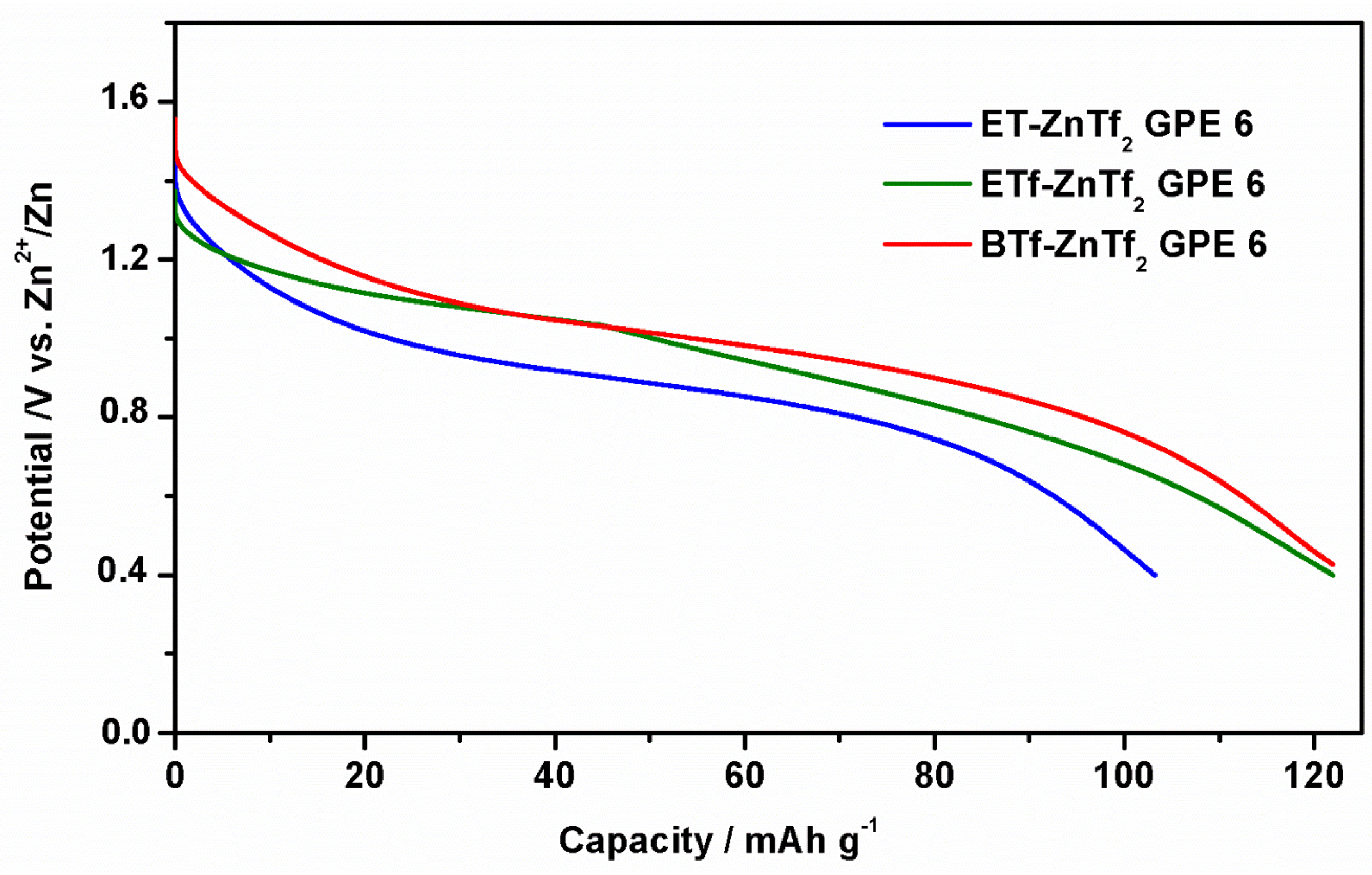
2.3. Conductivity and ATR-FTIR Analysis of the IL-Based GPEs with and without ZnTf2
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrosati, B. Applications of Electroactive Polymers; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, A.M. Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafur, J.P.; Fernandez Romero, A.J. Electrical and spectroscopic characterization of PVdF-HFP and TFSI—Ionic liquids-based gel polymer electrolyte membranes. Influence of ZnTf2 salt. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Sampath, S. Electrochemical characterization of poly(vinylidenefluoride)-zinc triflate gel polymer electrolyte and its application in solid-state zinc batteries. Solid State Ionics 2003, 160, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wan, C.C. Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 77, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbrent, S.; Plestil, J.; Hlavata, D.; Lindgren, J.; Tegenfeldt, J.; Wendsjö, Å. Crystallinity and morphology of PVdF-HFP-based gel electrolytes. Polymer 2001, 42, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, S.S. Conductivity behaviour of polymer gel electrolytes: Role of polymer. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2003, 26, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gosselink, D.; Doan, T.N.L.; Sadhu, M.; Cheang, H.-J.; Chen, P. Polymer electrolytes for lithium/sulfur batteries. Membranes 2012, 2, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataollahi, N.; Ahmad, A.; Hamzah, H.; Rahman, M.Y.A.; Mohamed, N.S. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-HFP/MG49 based polymer blend electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 6693–6703. [Google Scholar]
- Chernyak, Y. Dielectric constant, dipole moment, and solubility parameters of some cyclic acid esters. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Oh, S.M. Importance of donor number in determining solvating ability of polymers and transport properties in gel-type polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Huang, H.; Xue, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, F. A Vibrational spectroscopic study on the interaction between lithium salt and ethylene carbonate plasticizer for PAN-based electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Huang, H.; Xue, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, F. Infrared spectroscopic study of the interaction between lithium salt LiClO4 and the plasticizer ethylene carbonate in the polyacrylonitrile-based electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 1996, 85, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Romero, A.J.; Tafur, J.P. Interaction between Zn2+ cations and n-methyl-2-pyrrolidone in ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolytes for Zn/batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, A.; Kariyawasam, L.; Dutta, P.; Banerjee, S. Enhancement of lithium ion mobility in ionic liquid electrolytes in presence of additives. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 25343–25351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, J.J.; Khalfan, A.; Greenbaum, S.G. Li ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquid/PVDF-HFP blends. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A1048–A1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.K.; Kumar, A. Ionic transport properties of PVDF-HFP-MMT intercalated nanocomposite electrolytes based on ionic liquid, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide. Ionics 2013, 19, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.; Somers, A.; Torriero, A.A.J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Howlett, P.C.; Forsyth, M. Discharge behaviour and interfacial properties of a magnesium battery incorporating trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium based ionic liquid electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Henderson, W.A.; Passerini, S. Ionic liquids to the rescue? Overcoming the ionic conductivity limitations of polymer electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.T.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Alessandrini, F.; Passerini, S. Solvent-free, PYR1ATFSI ionic liquid-based ternary polymer electrolyte systems. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Appetecchi, G.B.; Carewska, M.; Joost, M.; Balducci, A.; Winter, M.; Passerini, S. UV cross-linked, lithium-conducting ternary polymer electrolytes containing ionic liquids. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6130–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libo, L.; Jiajia, W.; Peixia, Y.; Shaowen, G.; Heng, W.; Xiuchun, Y.; Xuwei, M.; Shuo, Y.; Baohua, W. Preparation and characterization of gel polymer electrolytes containing N-butyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide ionic liquid for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Hou, J.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; An, M.; Li, N. Gel polymer electrolyte based on polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene and ionic liquid for lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafur, J.P.; Abad, J.; Román, E.; Fernández Romero, A.J. Charge storage mechanism of MnO2 cathodes in Zn/MnO2 batteries using ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 60, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Sabin, K.C.; Chen, X. Ionic liquid–solid polymer electrolyte blends for supercapacitor applications. Polym. Bull. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Ye, H.; Huang, J. Novel zinc ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquids. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.C.; Evans, J.W.; Wright, P.K. Direct write dispenser printing of a zinc microbattery with an ionic liquid gel electrolyte. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolwijk, N.A.; Kösters, J.; Wiencierz, M.; Schönhoff, M. On the extraction of ion association data and transference numbers from ionic diffusivity and conductivity data in polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 102, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Montazami, R. Ionic liquid-doped gel polymer electrolyte for flexible lithium-ion polymer batteries. Materials 2015, 8, 2735–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterly, D.M.; Love, B.J. Phase transformation to β-poly(vinylidene fluoride) by milling. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.H.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. Preparation and properties PVDF based BATIO3 containing nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, R.P.; Khakhar, D.V.; Misra, A. Phase transformation and enhancement of toughness in polyvinylidene fluoride by onium salts. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, Y.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, E. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, T.; Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Piaggio, P. Characterization of PVDF Membranes by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Sampath, S. Spectroscopic characterization of a gel polymer electrolyte of zinc triflate and polyacrylonitrile. Polymer 2004, 45, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, R. Development of ion conducting polymer gel electrolyte membranes based on polymer PVDF-HFP, BMIMTFSI ionic liquid and the Li-salt with improved electrical, thermal and structural properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7305–7318. [Google Scholar]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Meakin, P.; Bishop, A.; McNaughton, D.; Rosalie, J.M.; Forsyth, M. Ftir study of ion-pairing effects in plasticized polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 2333–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, H.L.; Marsa, B. Ionic properties of non-aqueous liquid and PVDF-based gel electrolytes containing a cesium thiolate/disulfide redox couple. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Vincent, C.A.; Bruce, P.G. Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 1987, 28, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.G.; Evans, J.; Vincent, C.A. Conductivity and transference number measurements on polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 1988, 28, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plancha, M.J.; Rangel, C.M.; Sequeira, C.A.C.; Lumiar, P. Cation mobility in poly(ethylene oxide) solid electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 442, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Lin, T.P.; Chang, F.C. Ionic conductivity enhancement of the plasticized PMMA/LiClO4 polymer nano composite electrolyte containing clay. Polymer 2002, 43, 5281–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tafur, J.P.; Santos, F.; Romero, A.J.F. Influence of the Ionic Liquid Type on the Gel Polymer Electrolytes Properties. Membranes 2015, 5, 752-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040752
Tafur JP, Santos F, Romero AJF. Influence of the Ionic Liquid Type on the Gel Polymer Electrolytes Properties. Membranes. 2015; 5(4):752-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040752
Chicago/Turabian StyleTafur, Juan P., Florencio Santos, and Antonio J. Fernández Romero. 2015. "Influence of the Ionic Liquid Type on the Gel Polymer Electrolytes Properties" Membranes 5, no. 4: 752-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040752
APA StyleTafur, J. P., Santos, F., & Romero, A. J. F. (2015). Influence of the Ionic Liquid Type on the Gel Polymer Electrolytes Properties. Membranes, 5(4), 752-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040752






