Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes
Abstract
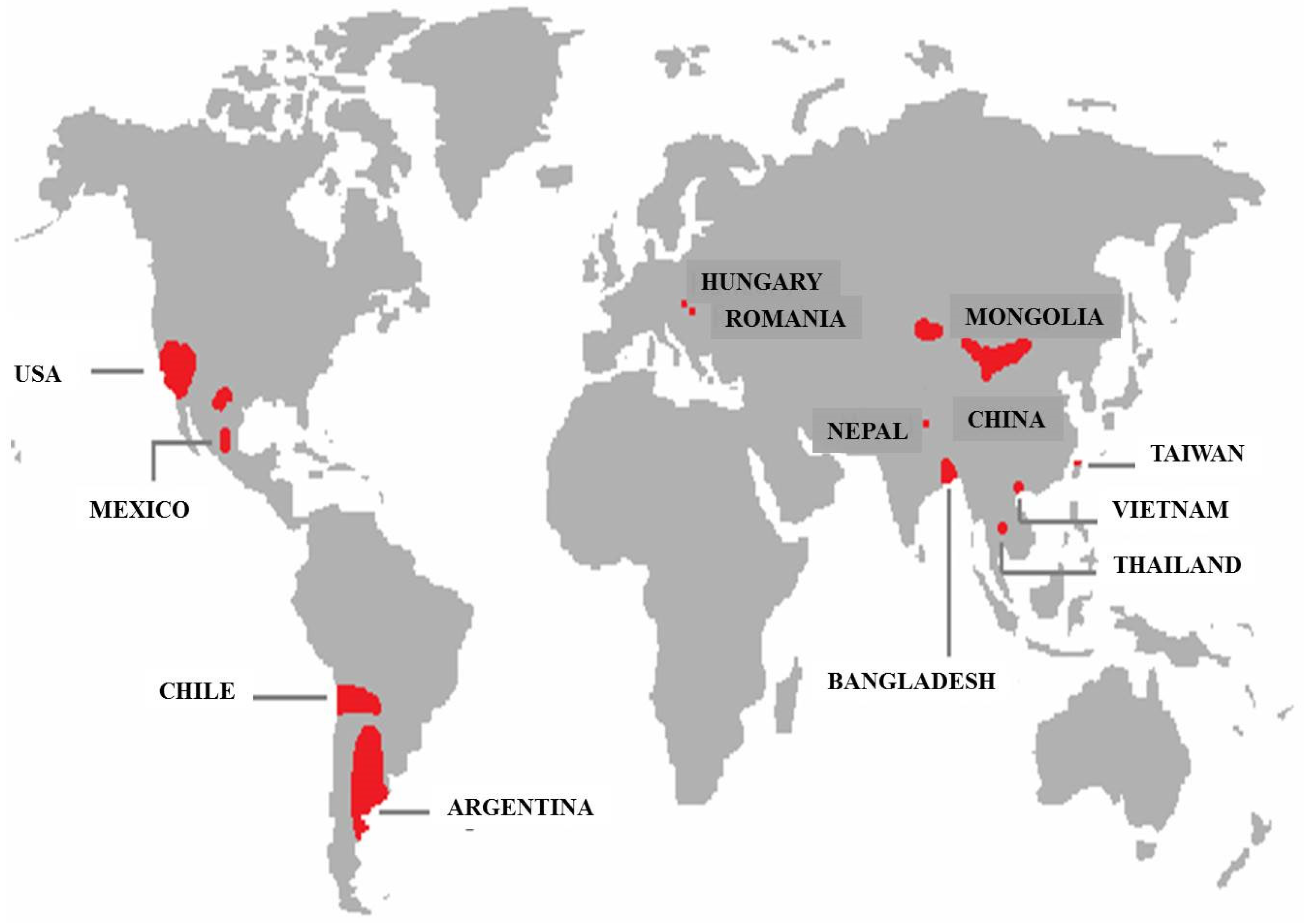
:1. Introduction
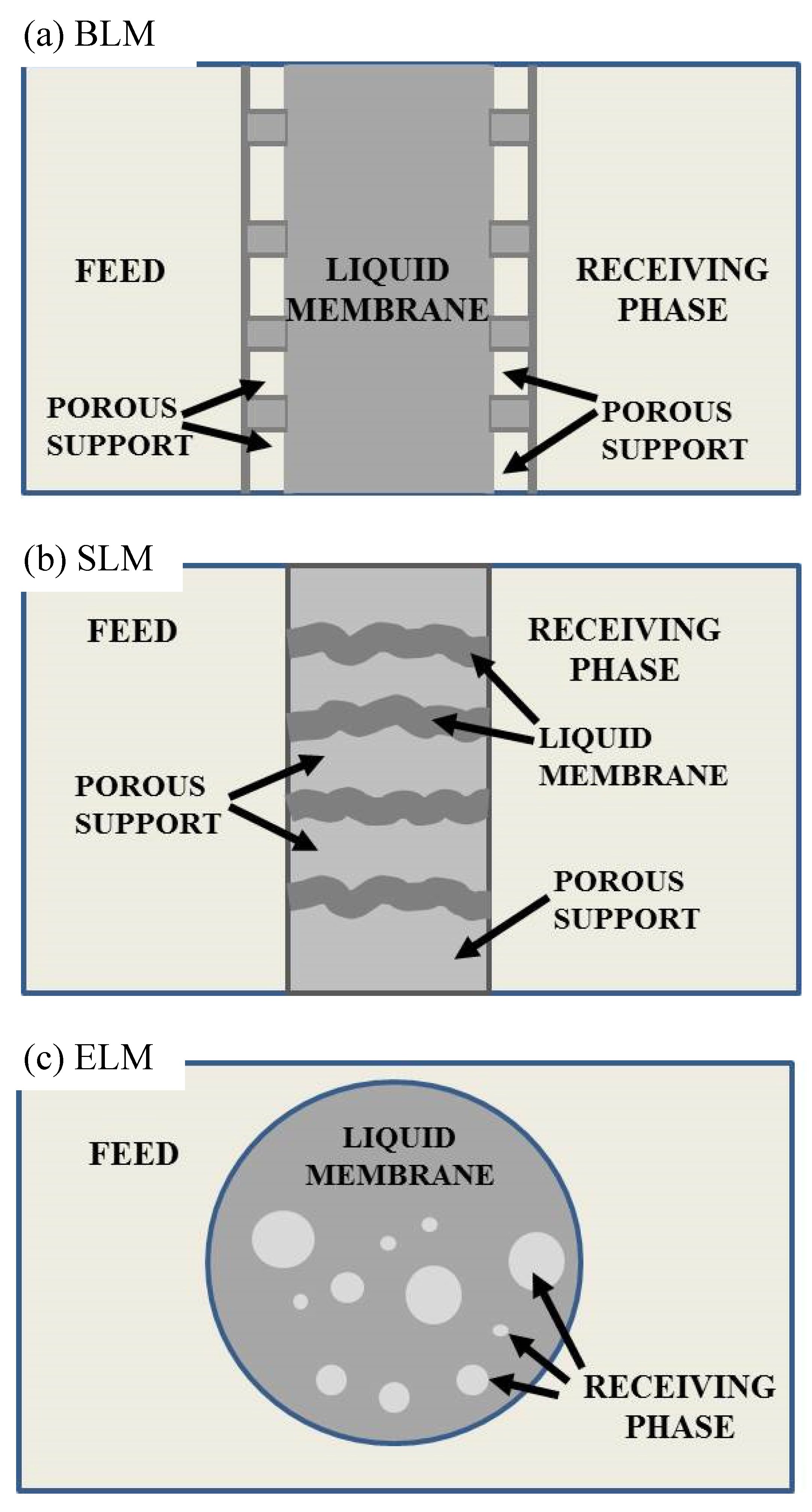
2. Liquid Membranes
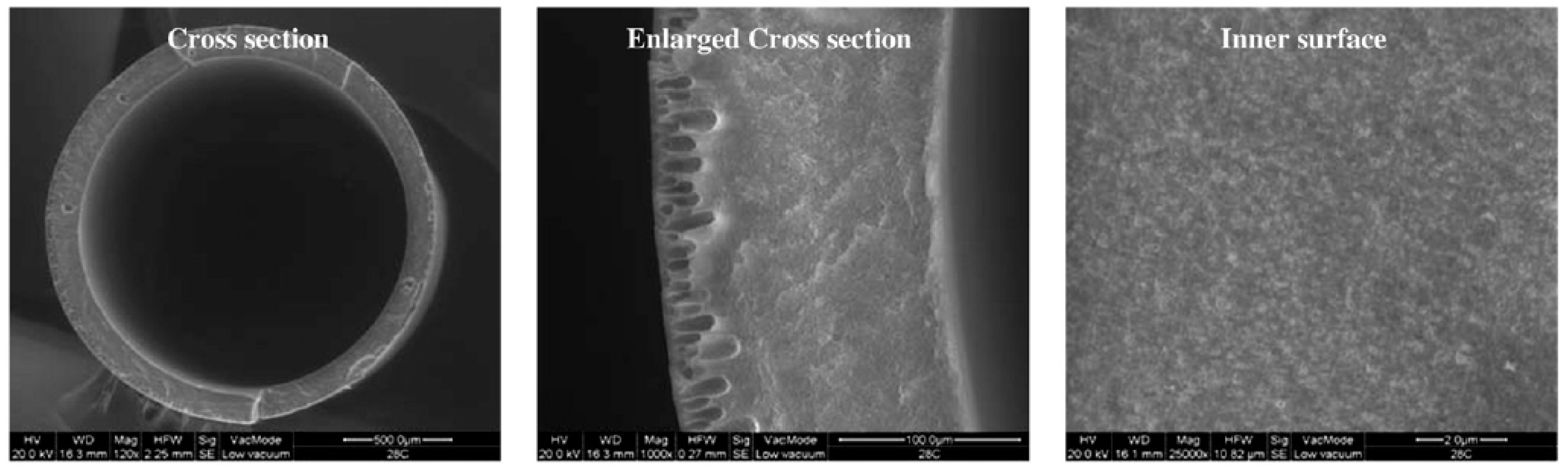
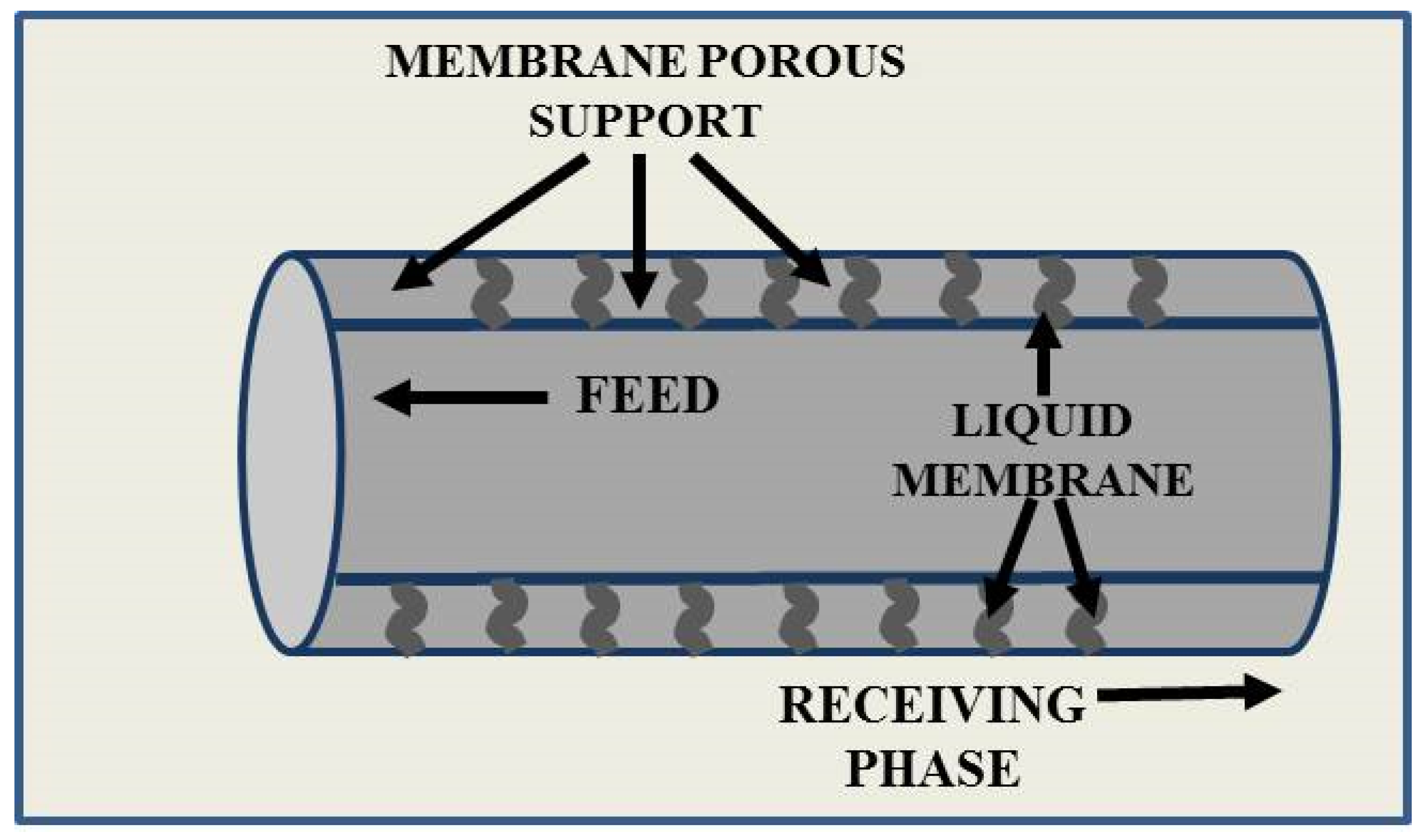
Liquid Membranes for Arsenic Removal
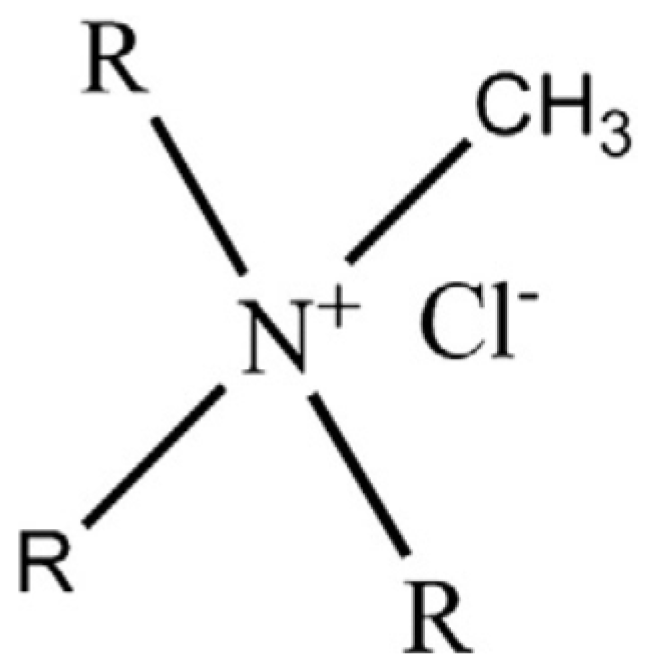
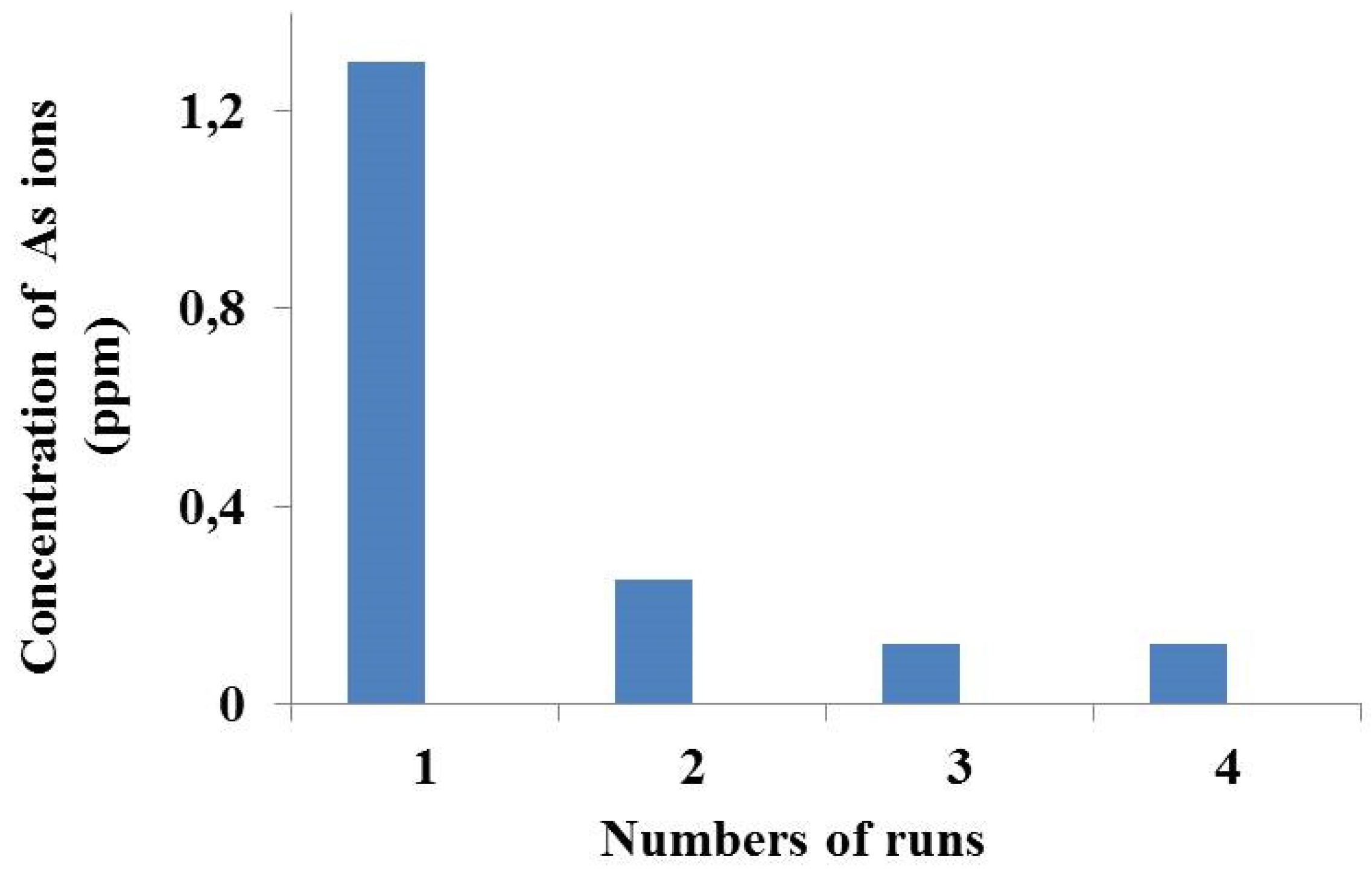
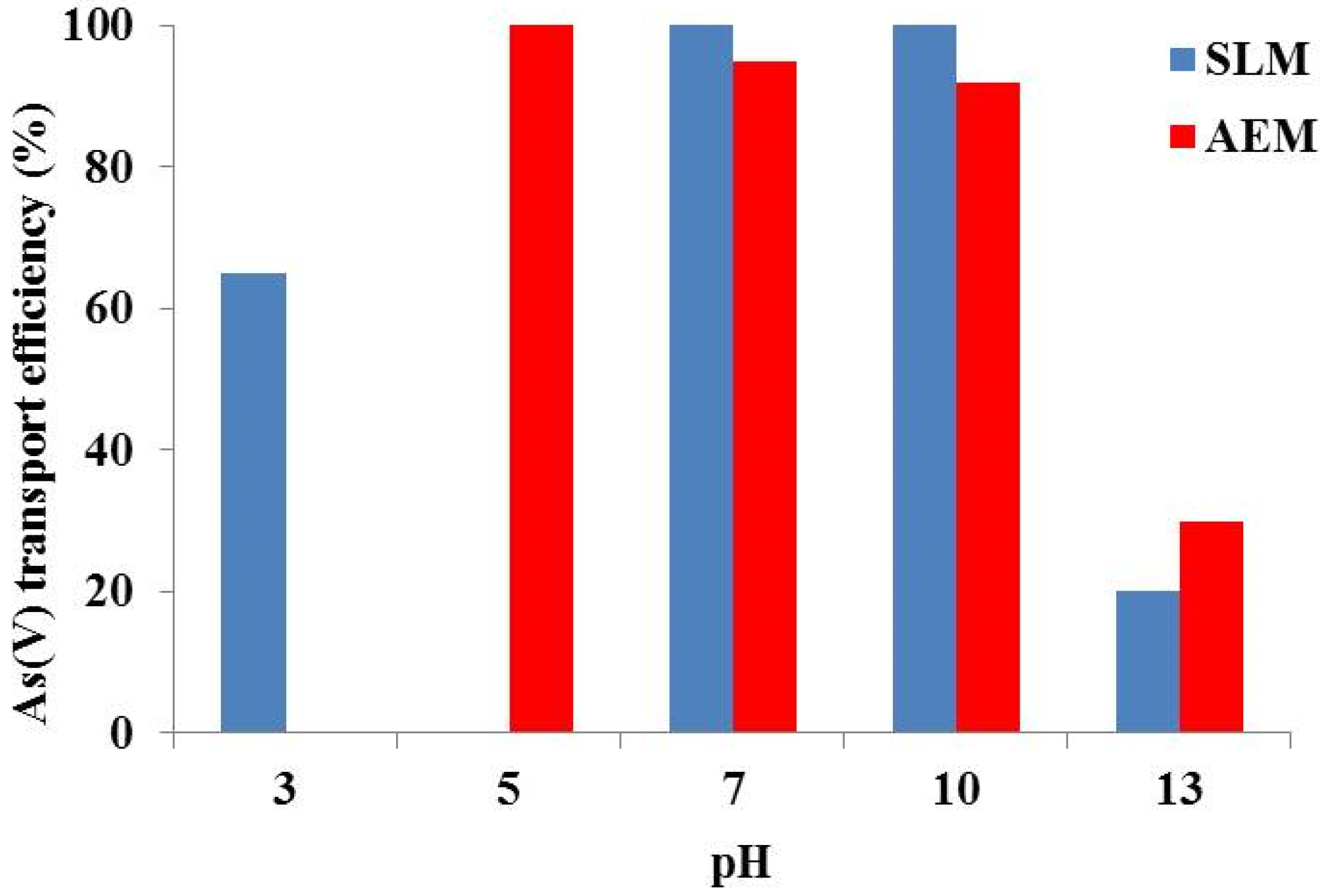

| Sulfuric acid concentration (mol/L) | % As(V) Extraction |
|---|---|
| ~0.25 | 20 |
| ~0.6 | 45 |
| ~1.0 | 85 |
| ~1.6 | 90 |
| ~2.0 | 65 |
| ~2.4 | 30 |
- -
- Internal phase: 2 M KOH;
- -
- Membrane phase: 6% (v/v) L113A and 4% (v/v) liquid paraffin;
- -
- External phase: 4 mg/L As(III) and 7 M HCl;
- -
- Phase ratio: 2 oil/ 3 internal and 1 emulsion/5 water;
- -
- Agitation speed: 400 rotations/minute;
- -
- Extraction time: 10 minutes
| Sonication time (minutes) | Mean droplet diameter (μm) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2.3 |
| 3 | 1.9 |
| 4 | 1.7 |
| 7 | 3.7 |
| Span 80 concentration (vol %) | Extraction time (minutes) | As(V) in the feed phase (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 37 |
| 2 | 6 | 45 |
| 2 | 9 | 47 |
| 4 | 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 6 | 19 |
| 4 | 9 | 21 |
| 5 | 3 | 20 |
| 5 | 6 | 26 |
| 5 | 9 | 34 |
| 7 | 3 | 34 |
| 7 | 6 | 36 |
| 7 | 9 | 42 |
3. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MINERALS.NET: THE MINERAL & GEMSTONE KINGDOM. Available online: http://www.minerals.net/mineral/orpiment.aspx (accessed on 7 December 2014).
- Jain, C.K.; Ali, I. Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res. 2000, 34, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Saha, A. Metabolism and toxicity of arsenic: A human carcinogen. Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, J.M. Ecotoxicology of arsenic in the marine environment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 5, 917–927. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, R.; Hug, S.J.; Inauen, J.; Khan, N.I.; Mosler, H.J.; Yang, H. Enhancing arsenic mitigation in Bangladesh: Findings from institutional, psychological, and technical investigations. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Lingas, E.O.; Rahman, M. Contamination of drinking-water by arsenic in Bangladesh: A public health emergency. Bull. World Health Organ. 2000, 9, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Chavan, K.; García, V.; Jimeno, G.; Albo, J.; Marathe, K.V.; Yadav, G.D.; Irabien, A. Arsenic Removal from Natural Waters by Adsorption or Ion Exchange: An Environmental Sustainability Assessment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, J.; Bringas, E.; Ortiz, I. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as new adsorption materials for arsenic removal from polluted waters. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Han, B.; Zimbron, J.; Shen, Z.; Karim, M.N. Arsenic removal by coagulation and filtration: comparison of groundwaters from the United States and Bangladesh. Desalination 2004, 169, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenial, Ü.; Bulut, G.; Sirkeci, A.A. Arsenic Removal by Adsorptive Flotation Methods. CLEAN—Soil, Air, Water 2014, 42, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/drink/index.cfm (accessed on 7 December 2014).
- EPA UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/lawsregs/rulesregs/sdwa/arsenic/regulations.cfm (accessed on 10 December 2014).
- Mamtaz, R.; Bache, D.H. Low-Cost Separation of Arsenic from Water: With Special Reference to Bangladesh. Water Environ. J. 2000, 14, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.F.; Gavis, J. A review of the arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res. 1972, 6, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, M.D. DDT and the Insect Problem. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1947, 37, 468–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekel, M.R. Removal of arsenic in drinking water treatment. In Arsenic in the Environment; Nriagu, J.O., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kartinen, E.O., Jr.; Martin, C.J. An overview of arsenic removal processes. Desalination 1995, 103, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, S. Removal of arsenic from water. J. Jpn. Society Water Environ. 1997, 20, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Z. Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto iron oxide/activated carbon magnetic composite. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.G.; Gong, X.J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.R.; Fan, W.B. Adsorption characteristics of arsenic from micro-polluted water by an innovative coal-based mesoporous activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 165, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, F.; Erto, A.; Lancia, A.; Musmarra, D. A descriptive model for metallic ions adsorption from aqueous solutions onto activated carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, M.-C. An overview of arsenic removal by pressure-driven membrane processes. Desalination 2005, 172, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Hoinkis, J. Review of membrane processes for arsenic removal from drinking water. In the Global Arsenic Problem, Challenges for Safe Water Production; Kabay, N., Bundschuh, J., Hendry, B., Bryjak, M., Yoshizuka, K., Bhattacharya, P., Anaç, S., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2010; Chapter 10; pp. 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.T.; Mozumder, M.S.I.; Figoli, A.; Islam, M.A.; Drioli, E. Arsenic removal by conventional and membrane technology: An overview. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2007, 14, 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, P.; Bhowmick, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Figoli, A.; Van der Bruggen, B. Remediation of inorganic arsenic in groundwater for safe water supply: A critical assessment of technological solutions. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, T.; Bhattacherjee, C.; Bhattacherjee, S. Removal of Arsenic Using Membrane Technology: A Review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Hoinkis, J.; Drioli, E. Arsenic removal by traditional and innovative membrane technologies. In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Metals and Related Substances in Drinking Water, Kristianstad, Sweden, 13–15 October 2010; IWA PUBLISHING: London, UK, 2011; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Bey, S.; Criscuoli, A.; Figoli, A.; Leopold, A.; Simone, S.; Benamor, M.; Drioli, E. Removal of As(V) by PVDF hollow fibers membrane contactors using Aliquat-336 as extractant. Desalination 2010, 264, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuoli, A.; Galizia, A.; Drioli, E. Arsenic Oxidation by Membrane Contactors. In Water Treatment Technologies for the Removal of High-Toxicity Pollutants; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2010; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C: Environmental Security; pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Figoli, A.; Sager, W.F.C.; Mulder, M.H.V. Facilitated oxygen transport in liquid membranes: Review and new concepts. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 181, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A. Liquid Membrane in Gas Separations. In Liquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater Treatment; Kislik, V.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, T.; Talebi, A. Green Liquid Membrane: Development and Challenges. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Parhi, P.K. Supported Liquid Membrane Principle and Its Practices: A Short Review. J. Chem. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarca, G.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Facilitated-transport supported ionic liquid membranes for the simultaneous recovery of hydrogen and carbon monoxide from nitrogen-enriched gas mixtures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, R.; Argurio, P.; Poerio, T. Studies of various solid membrane supports to prepare stable sandwich liquid membranes and testing copper(II) removal from aqueous media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Tsukube, H. (Eds.) Liquid membranes: Chemical Applications. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990.
- Bartsch, R.A.; Way, J.D. (Eds.) Chemical separation with Liquid Membranes. ACS Symposium Series 642; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Kislik, V.S. (Ed.) Liquid membranes. Pronciples and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater Treatment. Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2010.
- Ajwani, P.; Lokwani, L.; Sharma, U. Bulk Liquid Membrane Transport of Alkali Metal Cations Using Non Cyclic Ionophores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India Section A: Phys. Sci. 2012, 82, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocherginsky, N.M.; Yang, Q. Big Carrousel mechanism of copper removal from ammoniacal wastewater through supported liquid membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 54, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Kusumastuti, A.; Derek, C.J.C.; Ooi, B.S. Emulsion liquid membrane for heavy metal removal: An overview on emulsion stabilization and destabilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fei, D.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, J. Studies on the extraction of chromium(III) by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, R.; Argurio, P.; Poerio, T. Flux enhancement of stagnant sandwich compared to supported liquid membrane systems in the removal of Gemfibrozil from waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylton, K.; Mitra, S. A microfluidic hollow fiber membrane extractor for arsenic(V) detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, P.; Alguacil, F.J. Removal of arsenic from copper electrolytes by solvent extraction with tributylphosphate. Can. Metall. Q. 1996, 35, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lourdes Ballinas, M.; De San Miguel, E.R.; De Jesus Rodriguez, M.T.; Silva, O.; Munoz, M.; De Gyves, J. Arsenic(V) removal with polymer inclusion membranes from sulfuric acid media using DBBP as carrier. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangtumrong, S.; Ramakul, P.; Satayaprasert, C.; Lothongkum, A.W. Purely separation of mixture of mercury and arsenic via hollow fiber supported liquid membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2007, 5, 751–756. [Google Scholar]
- Lothongkum, A.W.; Suren, S.; Chaturabul, S.; Thamphiphit, N.; Pancharoen, U. Simultaneous removal of arsenic and mercury from natural-gas-co-produced water from the Gulf of Thailand using synergistic extractant via HFSLM. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancharoen, U.; Poonkuma, W.; Lothongkum, A.W. Treatment of arsenic ions from produced water through hollow fiber supported liquid membrane. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 482, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thailand Regulatory Discharge Standards 2. Ministry of Industry: Bangkok, Thailand, 1996.
- Prapasawat, T.; Ramakul, P.; Satayaprasert, C.; Pancharoen, U.; Lothongkum, A.W. Separation of As(III) and As(V) by hollow fiber supported liquid membrane based on the mass transfer theory. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafu, L.D.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. The simultaneous stripping of arsenic and selenium from wastewaters using hollow-fibre supported liquid membranes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8865–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güell, R.; Fontàs, C.; Salvadó, V.; Anticó, E. Modelling of liquid–liquid extraction and liquid membrane separation of arsenic species in environmental matrices. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güell, R.; Fontàs, C.; Anticó, E.; Salvadó, V.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Transport and separationof arsenate and arsenite from aqueous media by supported liquid and anion-exchange membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Perez, M.E.; Reyes-Aguilera, J.A.; Saucedo, T.I.; Gonzalez, M.P.; Navarro, R.; AvilaRodriguez, M. Study of As(V) transfer through a supported liquid membrane impregnated with trioctylphosphine oxide (Cyanex 921). J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chen, W.-C.; Yang, F.-R.; Chen, J.-H.; Lin, J.-C. Separation of galliumand arsenic in wafer grinding extraction solution using a supported liquid membrane that contains PC88A as a carrier. J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2005, 40, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, D.Y.; Alamos, L.; Mex, N. Separation of metals by supported liquid membranes. US 5,114,579, 19 May 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Kiani, S.; Razavi, M.; Hemati, F.A.; Abbasi, B. Extraction of Arsenic(V) from Water Using Emulsion Liquid Membrane. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ping, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y. Emulsion liquid membrane separation of As(III) and As(V). Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 363, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargari, A.; Kaghazchi, T.; Soleimani, M. Role of emulsifier in the extraction of gold (III) ions from aqueous solutions using the emulsion liquid membrane technique. Desalination 2004, 162, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, S.; Mousavi, S.M. Ultrasound assisted preparation of water in oil emulsions and their application in arsenic (V) removal from water in an emulsion liquid membrane process. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.G.; Pandit, A.B. Ultrasound emulsification: effect of ultrasonic and physicochemical properties on dispersed phase volume and droplet size. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2008, 15, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, M.; Solans, C.; González, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Properties of water-in-oil (W/O) nano-emulsions prepared by a low-energy emulsification method. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 324, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocherginsky, N.M.; Yang, Q.; Seelam, L. Recent advances in supported liquid membrane technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Takeuchi, H. Transport of copper through a supported liquid membrane. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1985, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesi, P.R. Lifetime of supported liquid membranes: The influence of interfacial properties, chemical composition and water transport on the long-term stability of the membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 31, 117–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesi, P.R. Separation of metal species by supported liquid membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1984, 19, 857–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.F.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.G.D. Instability mechanisms of supported liquid membranes in phenol transport process. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Takahashi, K.; Goto, W. Some observations on the stability of supported liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 34, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.F.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.G.D. Effect of surface-tension gradients on stability of supported liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.F.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.G.D.; Schofield, R.W. Critical displacement pressure of a supported liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 75, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozol, J.F.; Casas, J.; Sastre, A. Stability of flat sheet supported liquid membranes in the transport of radionuclides from reprocessing concentrate solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 82, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, R.; De Bartolo, L.; Drioli, E. Coupled transport of amino-acids through a supported liquid membrane. 1. Experimental optimization. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarizia, R.; Horwitz, E.P.; Rickert, P.G.; Hodgson, K.M. Application of supported liquid membranes for removal of uranium from groundwater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Fane, A.G.; Bi, J.; Griesser, H.J. Stabilization of supported liquid membranes by plasma polymerization surface coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 168, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kemperman, A.J.B.; Damink, B.; Van Den Boomgaard, T.; Strathmann, H. Stabilization of supported liquid membranes by gelation with PVC. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neplenbroek, A.M.; Bargeman, D.; Smolders, C.A. The stability of supported liquid membranes. Desalination 1990, 79, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marino, T.; Figoli, A. Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes. Membranes 2015, 5, 150-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020150
Marino T, Figoli A. Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes. Membranes. 2015; 5(2):150-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarino, Tiziana, and Alberto Figoli. 2015. "Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes" Membranes 5, no. 2: 150-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020150
APA StyleMarino, T., & Figoli, A. (2015). Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes. Membranes, 5(2), 150-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020150







