Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
| Membrane | Permeability (barrer) | Ideal selectivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF [BMIM][DCA] | CO2 | 145 | CO2/N2 | 73 |
| N2 | 2 | CO2/O2 | 21 | |
| O2 | 7 | O2/N2 | 4 | |
| IJ [BMIM][DCA] [23] | CO2 | 120 | CO2/N2 | 10 |
| N2 | 12 | CO2/O2 | 5 | |
| O2 | 24 | O2/N2 | 2 | |
| Physical property | Physical property value |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.0555 g∙cm−3 (303.15 K) [32] |
| Viscosity | 24.4 ± 0.2 mPa∙s (303.15 K) [32] |
| Surface Tension | 48.6 ± 0.1 mN∙m−1 (303.15 K) [32] |
| CO2 solubility in IL | 0.015 mole fraction (0.113 MPa; 323.15 K) 0.024 mole fraction (0.177 MPa; 323.15 K) [29] |
| Equilibrium solubility in water | 12 g/L |
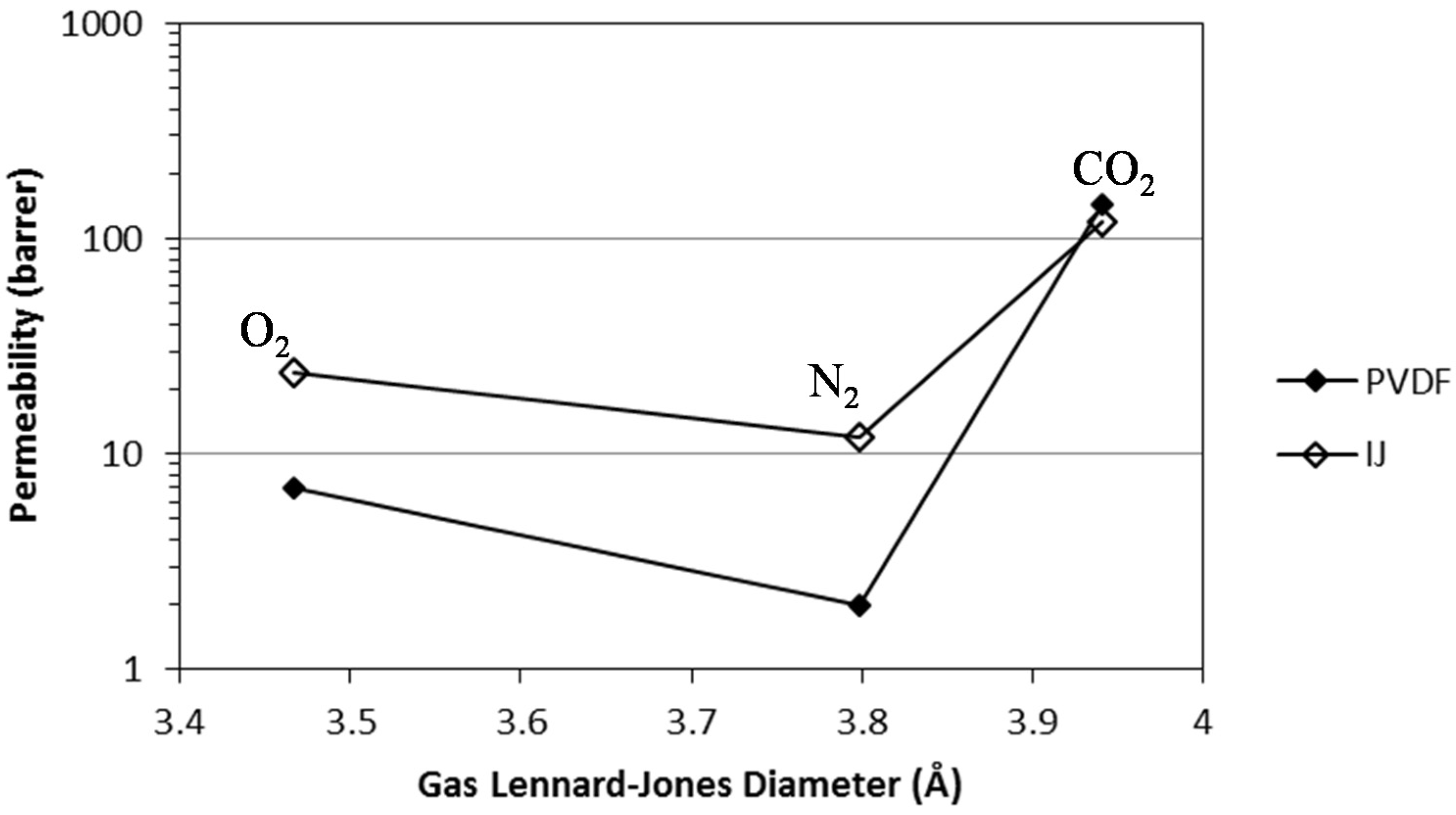
| RTIL | Ideal Selectivity CO2/N2 |
|---|---|
| [BMIM][DCA] | 73 |
| [BMIM][PF6] [4] | 23 |
| [BMIM][BF4] [4] | 35 |
| [BMIM][NTf2] [4] | 39 |
| [OMIM][PF6] [4] | 23 |
| [DMIM][BF4] [4] | 22 |
| Ionic Liquid | DCO2 (cm2/s) | DN2 (cm2/s) | DO2 (cm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [BMIM][DCA] | 6.97 × 10−6 | 8.00 × 10−6 | 1.05 × 10−5 |
| [BMIM][NTf2] | 3.94 × 10−6 | 4.52 × 10−6 | 5.70 × 10−6 |
3. Experimental Section

3.1. Preparation of Membranes
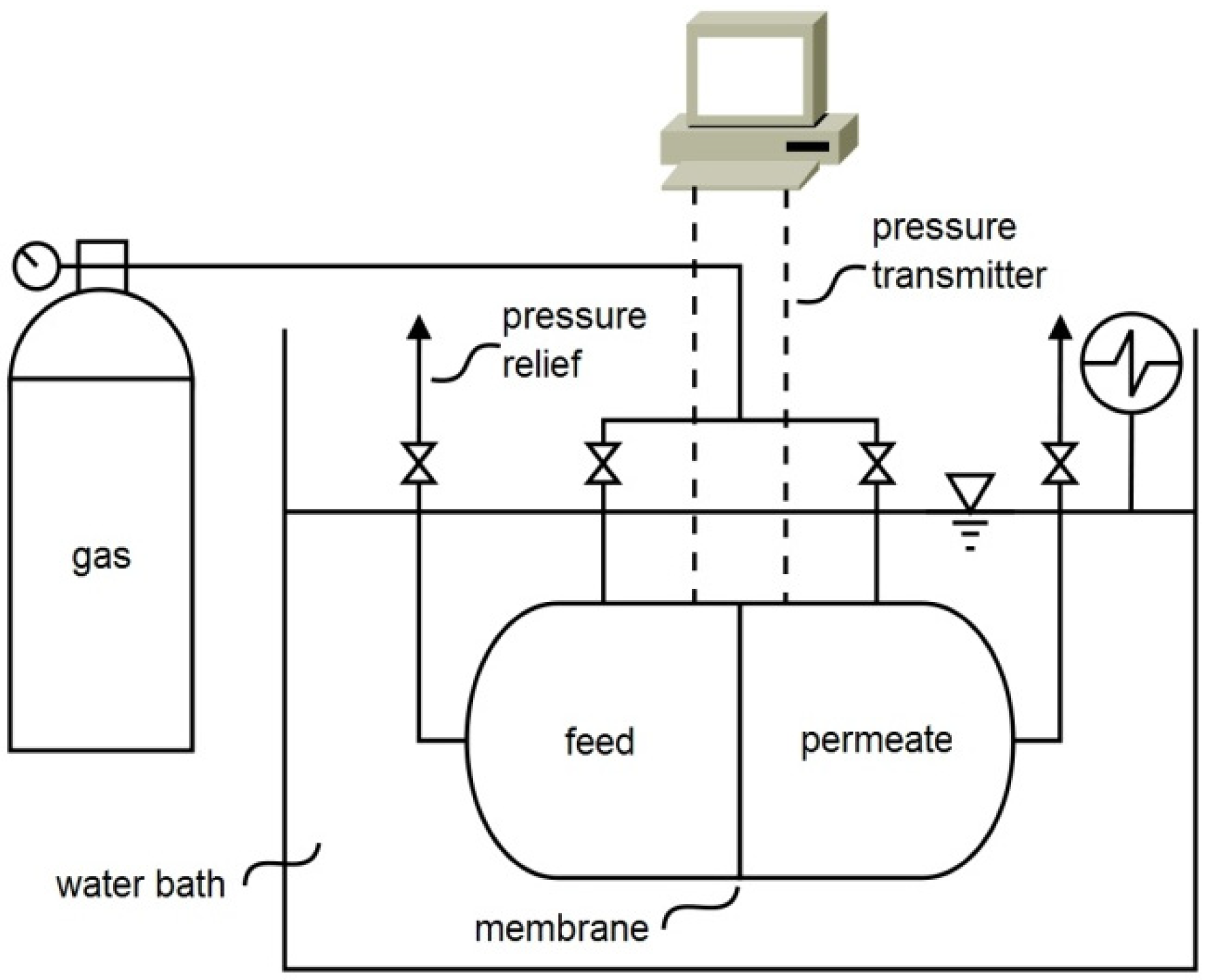
3.2. Single Gas Permeabilities
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bara, J.E.; Carlisle, T.K.; Gabriel, C.J.; Camper, D.; Finotello, A.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Guide to CO2 separations in imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Hashim, M.A.; Nabi, F. Ionic liquids in supported liquid membrane technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, L.J.; Godínez, C.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Sánchez-Segado, S.; Alguacil, F.J. Recent advances in supported ionic liquid membrane technology. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 376, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Crespo, J.G.; Coelhoso, I.M. Gas permeation studies in supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 357, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovazzo, P.; Kieft, J.; Finan, D.A.; Koval, C.; DuBois, D.; Noble, R. Gas separations using non-hexafluorophosphate [PF6]− anion supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 238, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltus, R.E.; Counce, R.M.; Culbertson, B.H.; Luo, H.; DePaoli, D.W.; Dai, S.; Duckworth, D.C. Examination of the potential of ionic liquids for gas separations. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, P.; Neves, L.A.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crfffespo, J.G.; Garea, A.; Irabien, A. Facilitated transport of CO2 and SO2 through Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs). Desalination 2009, 245, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.; Ferguson, L.; Scovazzo, P. Diffusivities of gases in room-temperature ionic liquids: Data and correlations obtained using a lag-time technique. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4815–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.A.; Nemestóthy, N.; Alves, V.D.; Cserjési, P.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Coelhoso, I.M. Separation of biohydrogen by supported ionic liquid membranes. Desalination 2009, 240, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Acetate based Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs) for CO2 separation: Influence of the temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojniak, S.D.; Khan, A.L.; Hollóczki, O.; Kirchner, B.; Vankelecom, I.F.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Separation of carbon dioxide from nitrogen or methane by Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes (SILMs): Influence of the cation charge of the ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 15131–15140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahurin, S.M.; Hillesheim, P.C.; Yeary, J.S.; Jiang, D.; Dai, S. High CO2 solubility, permeability and selectivity in ionic liquids with the tetracyanoborate anion. RSC Advances 2012, 2, 11813–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Aboudzadeh, M.A.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Mecerreyes, D.; Marrucho, I.M. Polymeric ionic liquids with mixtures of counter-anions: A new straightforward strategy for designing pyrrolidinium-based CO2 separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10403–10411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Baltus, R.E. Experimental measurement of the solubility and diffusivity of CO2 in room-temperature ionic liquids using a transient thin-liquid-film method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 8166–8175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condemarin, R.; Scovazzo, P. Gas permeabilities, solubilities, diffusivities, and diffusivity correlations for ammonium-based room temperature ionic liquids with comparison to imidazolium and phosphonium RTIL data. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserjési, P.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. Gas separation properties of supported liquid membranes prepared with unconventional ionic liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.; Scovazzo, P. Solubility, diffusivity, and permeability of gases in phosphonium-based room temperature ionic liquids: Data and correlations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.C.; Patinha, D.J.S.; Ferreira, R.; Garcia, H.; Silva Pereira, C.; Freire, C.S.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Cholinium-based Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes: A sustainable route for carbon dioxide separation. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, B.A.; Bara, J.E.; Gin, D.L.; Noble, R.D. Physically gelled ionic liquids: Solid membrane materials with liquid like CO2 gas transport. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3027–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, I.-N.; Yoo, S.; Park, S.-J.; Won, J. CO2 separation membranes using ion gels by self-assembly of a triblock copolymer in ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Friess, K.; Clarizia, G.; Schauer, J.; Izák, P. High ionic liquid content polymeric gel membranes: Preparation and performance. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.M.; Carvalho, T.; Neves, L.A.; Ruivo, R.M.; Vidinha, P.; Paiva, A.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Barreiros, S.; Simões, P.C. Development of Ion-Jelly® membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 106, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidinha, P.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Pinheiro, C.; Brás, A.R.; Carvalho, T.; Santos-Silva, T.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Romão, M.J.; Parola, J.; Dionisio, M.; et al. Ion jelly: A tailor-made conducting material for smart electrochemical devices. Chem. Commun. 2008, 44, 5842–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, A.F.R.; Baptista, A.C.; Carvalho, T.; Brogueira, P.; Lourenço, N.M.T.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Barreiros, S.; Vidinha, P.; Borges, J.P. Electrospinning of Ion Jelly fibers. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, T.; Vidinha, P.; Vieira, B.R.; Li, R.W.C.; Gruber, J. Ion Jelly: A novel sensing material for gas sensors and electronic noses. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.; Augusto, V.; Rocha, A.; Lourenco, N.M.T.; Correia, N.T.; Barreiros, S.; Vidinha, P.; Cabrita, E.J.; Dionísio, M. Ion Jelly conductive properties using dicyanamide-based ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 9445–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, T.M.; Carvalho, T.; Iwakura, D.C.; Braga, F.; Vieira, B.R.; Vidinha, P.; Gruber, J.; Torresi, R.M. All solid-state electrochromic device consisting of a water soluble viologen dissolved in gelatin-based ionogel. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2015, 132, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.; Obuskovic, G.; Jie, X.; Mulukutla, T.; Sirkar, K.K. Solubilities of CO2 and helium in an ionic liquid containing poly (amidoamine) dendrimer Gen 0. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10484–10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, J.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Maginn, E.J.; Brennecke, J.F. Anion effects on gas solubility in ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 6366–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindaratsamee, P.; Shimoyama, Y.; Morizaki, H.; Ito, A. Effects of temperature and anion species on CO2 permeability and CO2/N2 separation coefficient through ionic liquid membranes. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2011, 43, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, L.G.; Espel, J.R.; Onink, F.; Meindersma, G.W.; de Haan, A.B. Density, viscosity, and surface tension of synthesis grade imidazolium, pyridinium, and pyrrolidinium based room temperature ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussler, E.L. Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Couto, R.; Neves, L.; Simões, P.; Coelhoso, I. Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation. Membranes 2015, 5, 13-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5010013
Couto R, Neves L, Simões P, Coelhoso I. Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation. Membranes. 2015; 5(1):13-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleCouto, Ricardo, Luísa Neves, Pedro Simões, and Isabel Coelhoso. 2015. "Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation" Membranes 5, no. 1: 13-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5010013
APA StyleCouto, R., Neves, L., Simões, P., & Coelhoso, I. (2015). Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes and Ion-Jelly® Membranes with [BMIM][DCA]: Comparison of Its Performance for CO2 Separation. Membranes, 5(1), 13-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5010013









