A Validated CFD Model for Gas Exchange in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: Incorporating the Bohr and Haldane Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Numerical Domain
2.2. Governing Equations, Boundary Conditions, and Simulation Settings
2.3. Oxygen Transport Simulations
2.4. Carbon Dioxide Transport Simulations
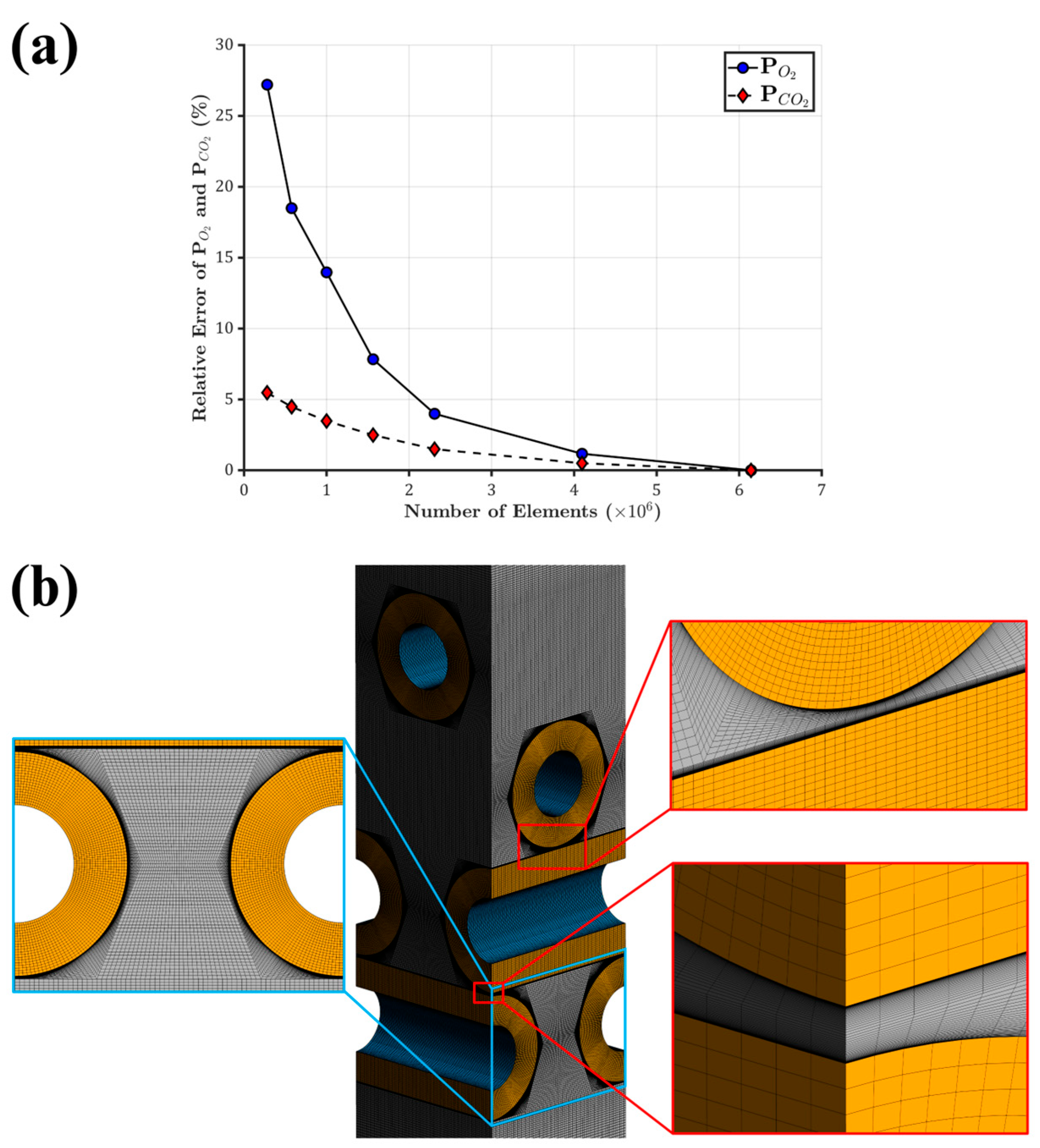
2.5. Mesh Sensitivity Study
3. Results
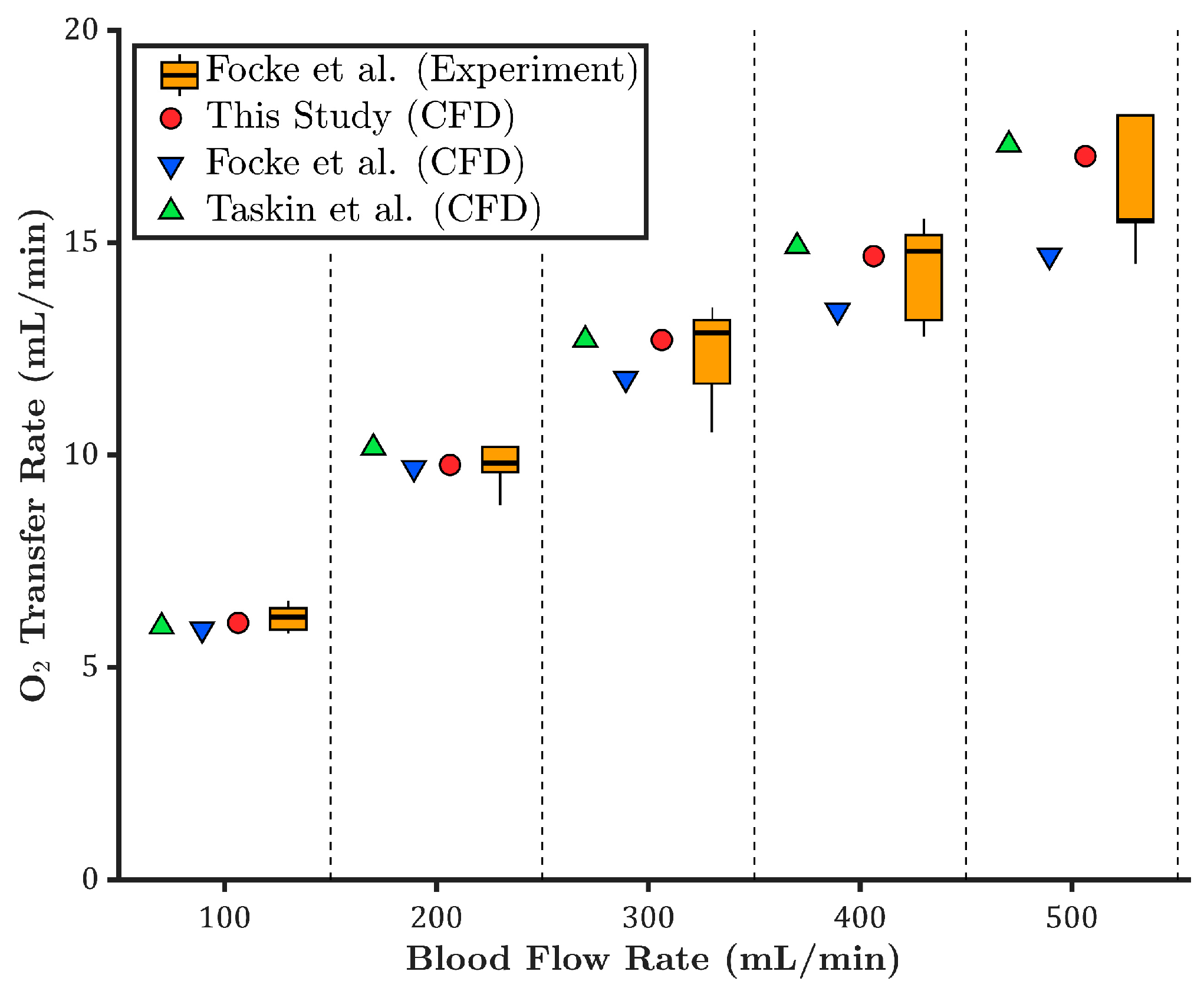
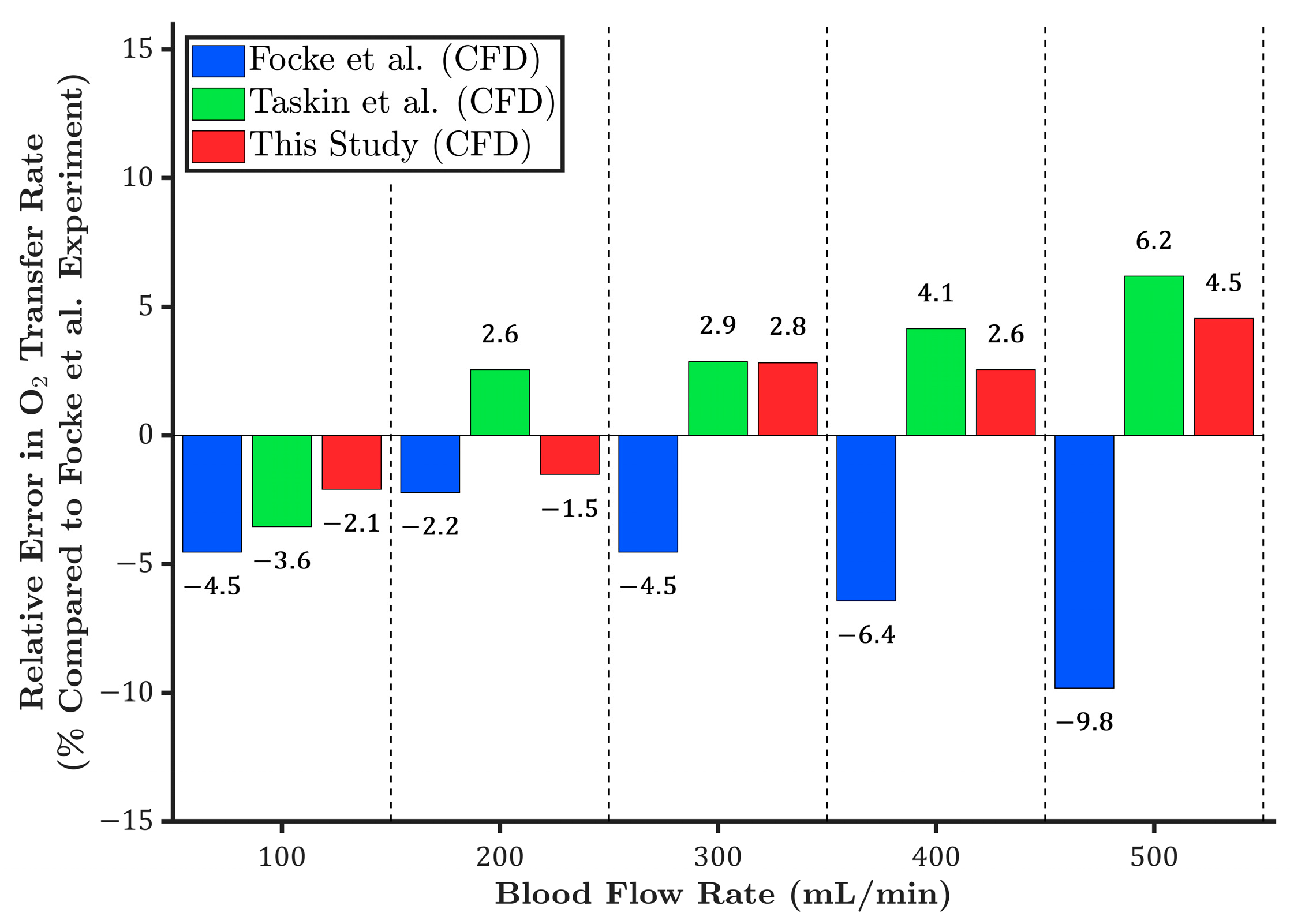
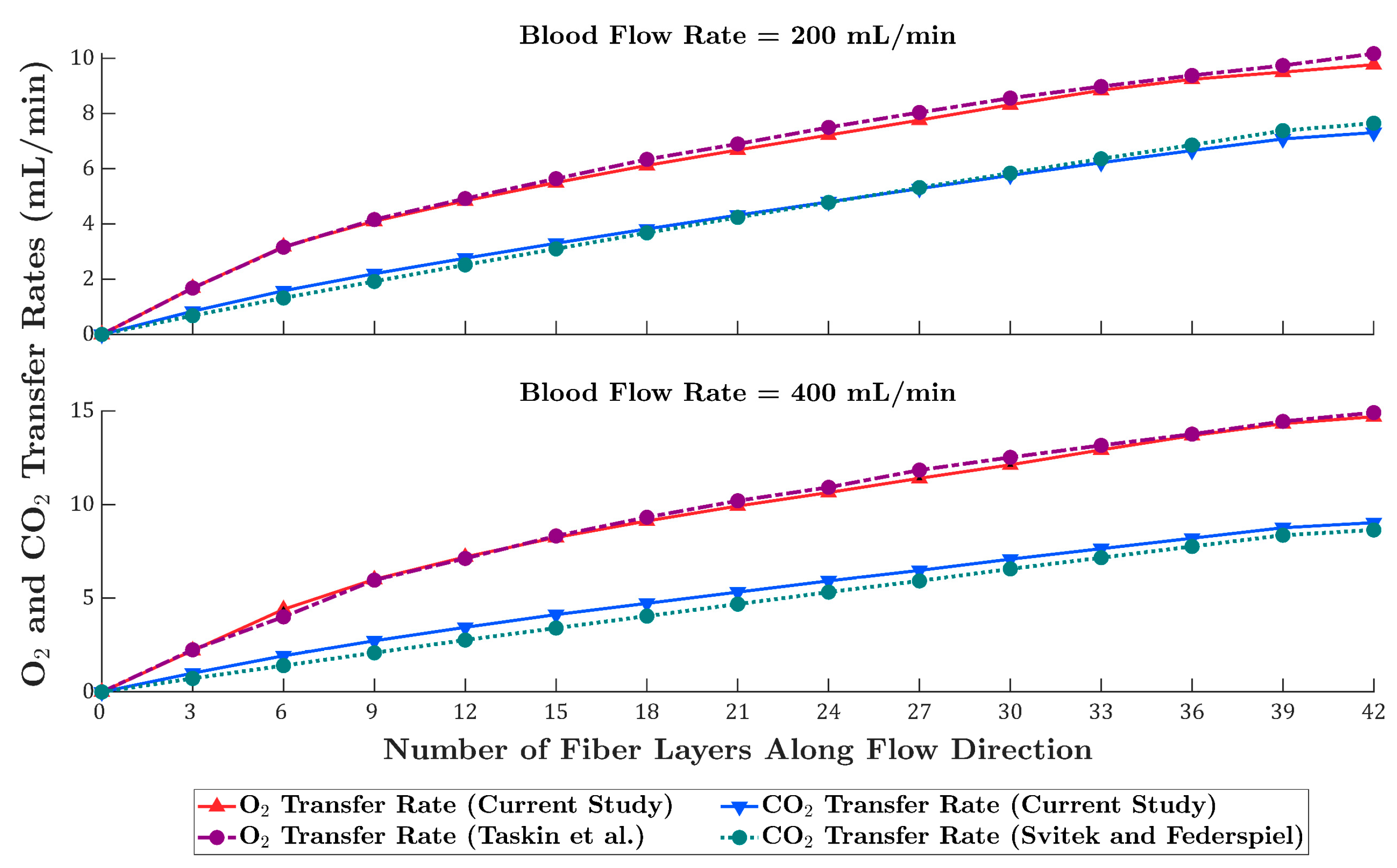
3.1. Oxygen Transfer Rate
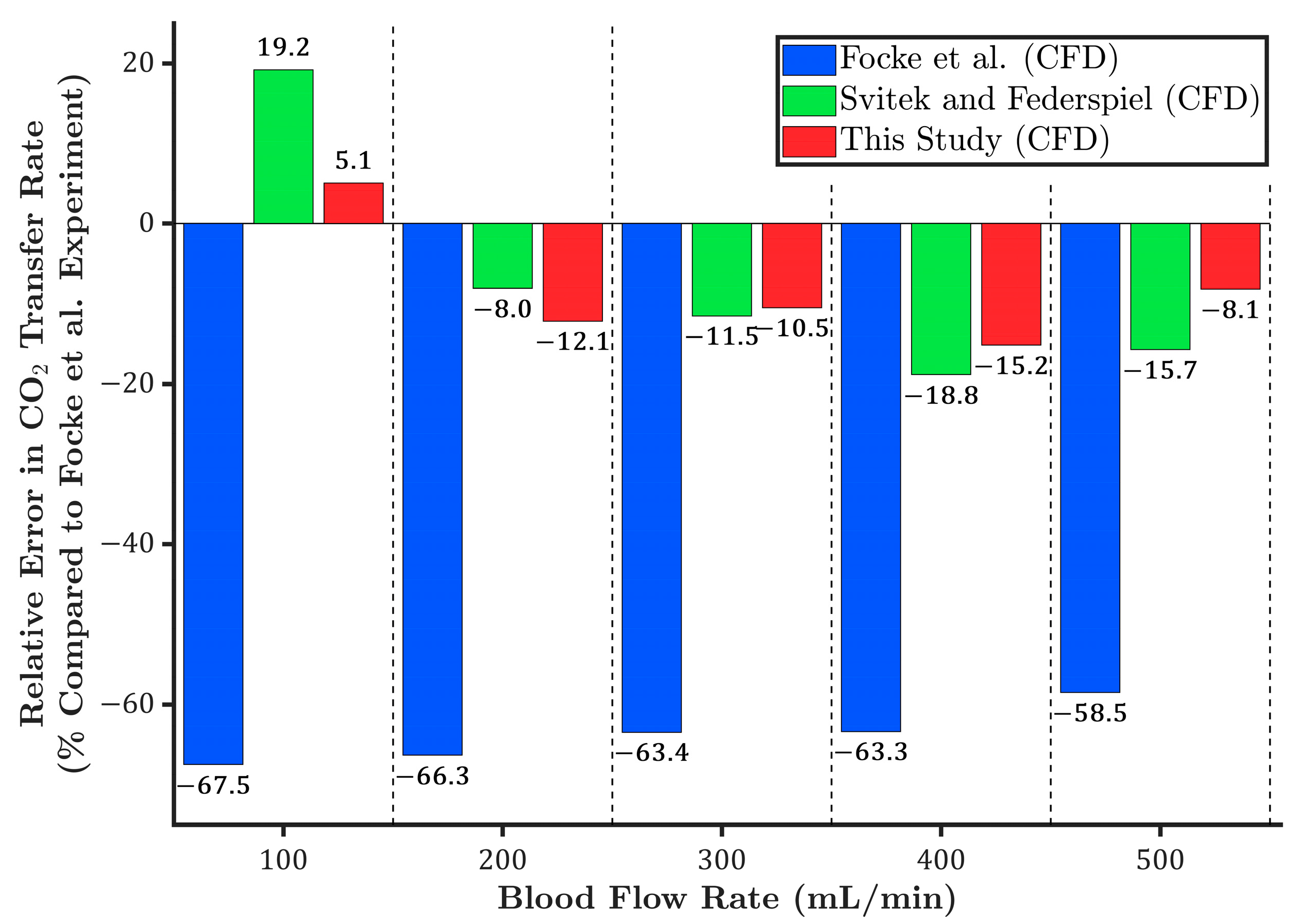
3.2. Carbon Dioxide Transfer Rate
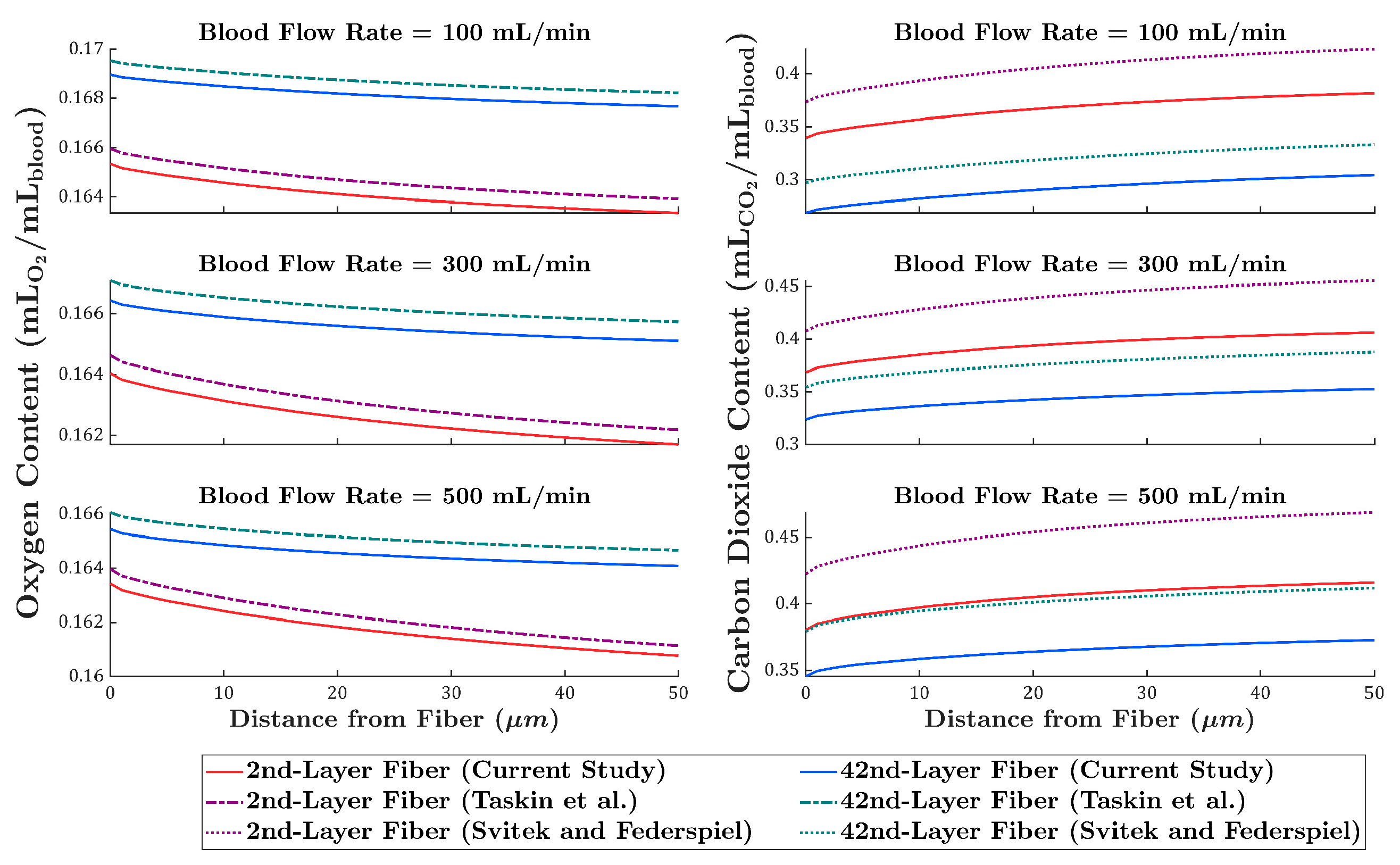
3.3. Comparison of Local Gas Transport Predictions with Existing Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Momtazmanesh, S.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Ghamari, S.-H.; Rad, E.M.; Rezaei, N.; Shobeiri, P.; Aali, A.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, Z.; Abdelmasseh, M. Global burden of chronic respiratory diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: An update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. E Clin. Med. 2023, 59, 101936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoul, M.; Bitton-Worms, K.; Adler, Z.; Saeed, A.; Cohen, O.; Bolotin, G. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)—A lifesaving technology. Review and single-center experience. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2019, 10, e0013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namendys-Silva, S.A. ECMO for ARDS due to COVID-19. Heart Lung 2020, 49, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, N.; Radjou, A.; Thuong, M. Hemolysis and plasma free hemoglobin during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: From clinical implications to laboratory details. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.R.; Murphree, C.R.; Zonies, D.; Meyer, A.D.; Mccarty, O.J.; Deloughery, T.G.; Shatzel, J.J. Thrombosis and bleeding in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) without anticoagulation: A systematic review. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Kostousov, V.; Teruya, J. Bleeding and thrombotic complications in the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. In Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann, M.; Lumlertgul, N. Acute kidney injury in ECMO patients. In Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine 2021; Vincent, J.-L., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Jujjavarapu, S.E.; Kumar, T.; Gupta, S. Computational Fluid Dynamics in Biomedical Engineering. In Computational Fluid Dynamics Applications in Bio and Biomedical Processes: Biotechnology Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 101–125. [Google Scholar]
- Estakhrposhti, S.H.M.; Xu, J.J.; Gföhler, M.; Harasek, M. Optimizing Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: A Multi-Objective Approach for Improved Gas Exchange and Reduced Blood Damage. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 731, 124228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke, J.M.; Bonke, P.-L.; Gendron, N.; Call, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Arens, J.; Neidlin, M. The influence of membrane fiber arrangement on gas exchange in blood oxygenators: A combined numerical and experimental analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 710, 123147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesler, A.; Rosen, M.; Schlanstein, P.C.; Wagner, G.; Groß-Hardt, S.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Arens, J. How computational modeling can help to predict gas transfer in artificial lungs early in the design process. ASAIO J. 2020, 66, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, M.E.; Fraser, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Micro-scale modeling of flow and oxygen transfer in hollow-fiber membrane bundle. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, G.; Bardón, R.G.; Dubini, G.; Pennati, G. CFD Two-Phase Blood Model Predicting the Hematocrit Heterogeneity Inside Fiber Bundles of Blood Oxygenators. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2025, 53, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, P.; Pekovits, M.; Yorov, T.; Haddadi, B.; Lukitsch, B.; Elenkov, M.; Janeczek, C.; Jordan, C.; Gfoehler, M.; Harasek, M. Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators. Membranes 2021, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askew, K.; Rizzo, J.; Fan, L.; He, G. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Sweep Gas Flow Rate-Dependent Carbon Dioxide Removal in Oxygenators. Fluids 2025, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, A.; Wang, L.; Deng, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, Y. Comparison of hemodynamic features and thrombosis risk of membrane oxygenators with different structures: A numerical study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 159, 106907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Xi, Y.; Sun, A.; Chen, Z.; Fan, Y. A comprehensive study of oxygenator gas transfer efficiency and thrombosis risk. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaesler, A.; Rosen, M.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Arens, J. Computational modeling of oxygen transfer in artificial lungs. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nolan, T.D.; Zhang, T.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Characterization of membrane blood oxygenation devices using computational fluid dynamics. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormes, M.; Borchardt, R.; Mager, I.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Behr, M.; Steinseifer, U. A validated CFD model to predict O2 and CO2 transfer within hollow fiber membrane oxygenators. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2011, 34, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasek, M.; Lukitsch, B.; Ecker, P.; Janeczek, C.; Elenkov, M.; Keck, T.; Haddadi, B.; Jordan, C.; Neudl, S.; Krenn, C. Fully resolved computational (CFD) and experimental analysis of pressure drop and blood gas transport in a hollow fibre membrane oxygenator module. Chem. Eng. 2019, 76, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J. Analysis of Low Reynolds Number Blood Flow in a Rectangular Microchannel Utilizing a Two-Phase Eulerian-Eulerian Model and Including a Steady State Oxygen-Hemoglobin Reaction Approximation. Master’s Thesis, The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bardón, R.G.; Passos, A.; Piergiovanni, M.; Balabani, S.; Pennati, G.; Dubini, G. Haematocrit heterogeneity in blood flows past microfluidic models of oxygenating fibre bundles. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 73, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svitek, R.G.; Federspiel, W.J. A mathematical model to predict CO2 removal in hollow fiber membrane oxygenators. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slyke, D.D.; Sendroy, J., Jr. Studies of gas and electrolyte equilibria in blood: XV. Line charts for graphic calculations by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, and for calculating plasma carbon dioxide content from whole blood content. J. Biol. Chem. 1928, 79, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, R.J.; Diller, K.R. Biotransport: Principles and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Teboul, J.-L.; Scheeren, T. Understanding the Haldane effect. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omecinski, K.S.; Federspiel, W.J. Improvement of a Mathematical Model to Predict CO2 Removal in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, L.B.; Mouzakis, F.L.; Kashefi, A.; Hima, F.; Spillner, J.W.; Mottaghy, K. Blood gas parameters and acid–base balance during extracorporeal lung support with oxygenators: Semi-empirical evaluation. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, G.R. Digital computer subroutine for the conversion of oxygen tension into saturation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1966, 21, 1375–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siggaard-Andersen, O.; Wimberley, P.D.; Fogh-Andersen, N.; Gøthgen, I.H. Measured and derived quantities with modern pH and blood gas equipment: Calculation algorithms with 54 equations. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1988, 48 (Suppl. S189), 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eash, H.J.; Jones, H.M.; Hattler, B.G.; Federspiel, W.J. Evaluation of plasma resistant hollow fiber membranes for artificial lungs. ASAIO J. 2004, 50, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Tanaka, R.; Sadano, K.; Tokumine, A.; Mori, T.; Saomoto, H.; Sakai, K. Insights into gradient and anisotropic pore structures of Capiox® gas exchange membranes for ECMO: Theoretically verifying SARS-CoV-2 permeability. Membranes 2022, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott Laboratories, AMG PMP Adult, Pediatric and Infant Oxygenators: Technical Brochure (Version 1.0). 2024. Available online: https://www.cardiovascular.abbott/CentriMag (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Hill, A.V. The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hemoglobin on its dissociation curves. J. Physiol. 1910, 40, iv–vii. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, L.J. Concerning the relationship between the strength of acids and their capacity to preserve neutrality. Am. J. Physiol. Leg. Content 1908, 21, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slyke, D.D. On the measurement of buffer values and on the relationship of buffer value to the dissociation constant of the buffer and the concentration and reaction of the buffer solution. J. Biol. Chem. 1922, 52, 525–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krbec, M.; Waldauf, P.; Zadek, F.; Brusatori, S.; Zanella, A.; Duška, F.; Langer, T. Non-carbonic buffer power of whole blood is increased in experimental metabolic acidosis: An in-vitro study. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1009378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, W.H.; Lacombe, E.; Rand, P.W.; Chatterjee, M. Solubility of carbon dioxide in serum from 15 to 38 °C. J. Appl. Physiol. 1963, 18, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.K.; Bassingthwaighte, J.B. Erratum to: Blood HbO2 and HbCO2 dissociation curves at varied O2, CO2, pH, 2,3-DPG and temperature levels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 1683–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHardy, G.J. The relationship between the differences in pressure and content of carbon dioxide in arterial and venous blood. Clin. Sci. 1967, 32, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.E.; Hall, M.E. Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood and tissue fluids. Guyton Hall Textb. Med. Physiol. 2016, 13, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.-Q.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Dahiya, A.; Soh, C.H.; Lin, K.C. Numerical modeling of pulsatile blood flow through a mini-oxygenator in artificial lungs. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Taskin, M.E.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. A quantitative comparison of mechanical blood damage parameters in rotary ventricular assist devices: Shear stress, exposure time and hemolysis index. J. Biomech. Eng. 2012, 134, 081002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxygen diffusion coefficient in blood | [12] | ||
| Oxygen solubility in blood | [12] | ||
| Oxyhemoglobin diffusion coefficient in blood | [18] | ||
| Oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin | [12] | ||
| Total hemoglobin concentration | [10] | ||
| Carbon dioxide diffusion coefficient in blood | [24] | ||
| Carbon dioxide solubility in blood | [29] | ||
| Carbaminohemoglobin diffusion coefficient in blood | |||
| Carbon dioxide-carrying capacity of hemoglobin | |||
| Bicarbonate diffusion coefficient in blood | [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monsefi Estakhrposhti, S.H.; Xu, J.; Gföhler, M.; Harasek, M. A Validated CFD Model for Gas Exchange in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: Incorporating the Bohr and Haldane Effects. Membranes 2025, 15, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090268
Monsefi Estakhrposhti SH, Xu J, Gföhler M, Harasek M. A Validated CFD Model for Gas Exchange in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: Incorporating the Bohr and Haldane Effects. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090268
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonsefi Estakhrposhti, Seyyed Hossein, Jingjing Xu, Margit Gföhler, and Michael Harasek. 2025. "A Validated CFD Model for Gas Exchange in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: Incorporating the Bohr and Haldane Effects" Membranes 15, no. 9: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090268
APA StyleMonsefi Estakhrposhti, S. H., Xu, J., Gföhler, M., & Harasek, M. (2025). A Validated CFD Model for Gas Exchange in Hollow Fiber Membrane Oxygenators: Incorporating the Bohr and Haldane Effects. Membranes, 15(9), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090268







