Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using an HFO-PVDF Composite Adsorption Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of HFO-PVDF Membranes
2.3. Analysis and Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Membrane Filtration Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
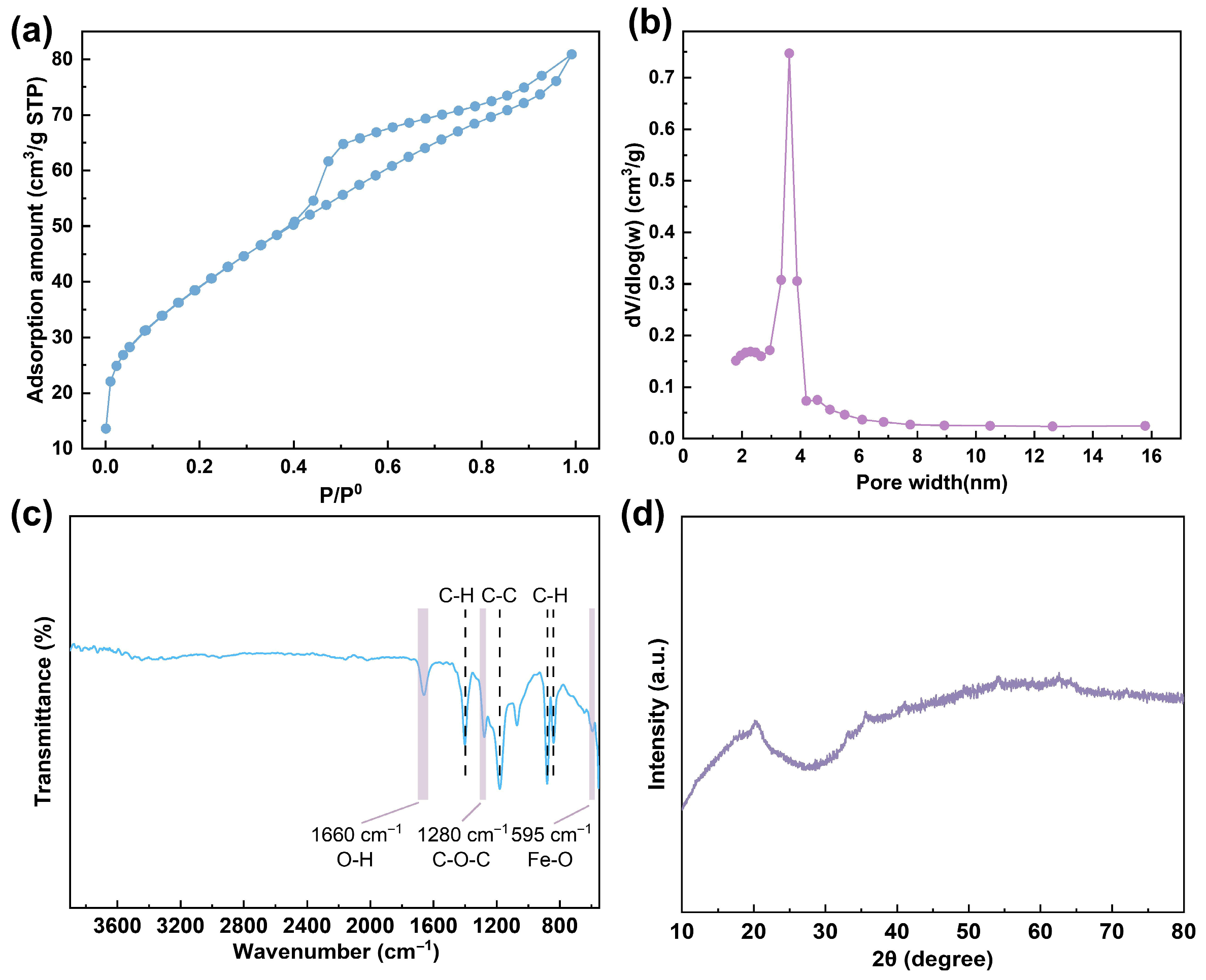
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the HFO-PVDF Membranes
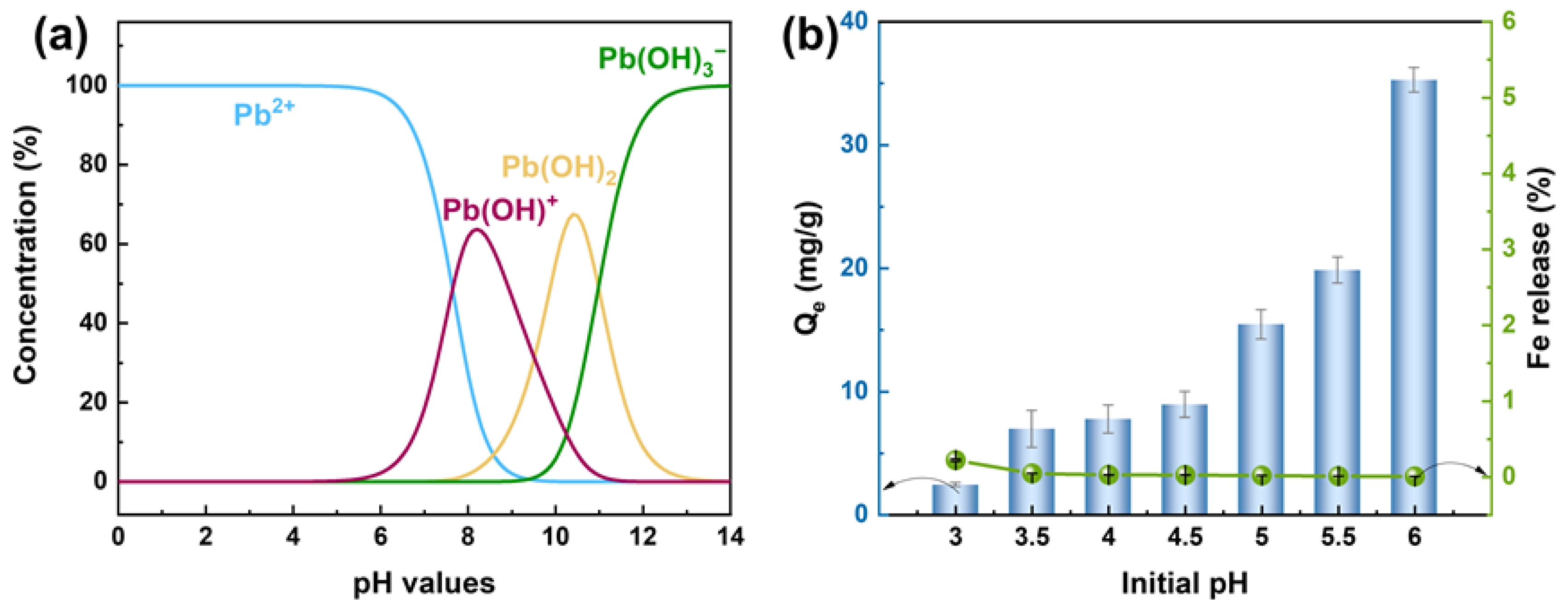
3.2. Effect of pH on Pb(II) Removal
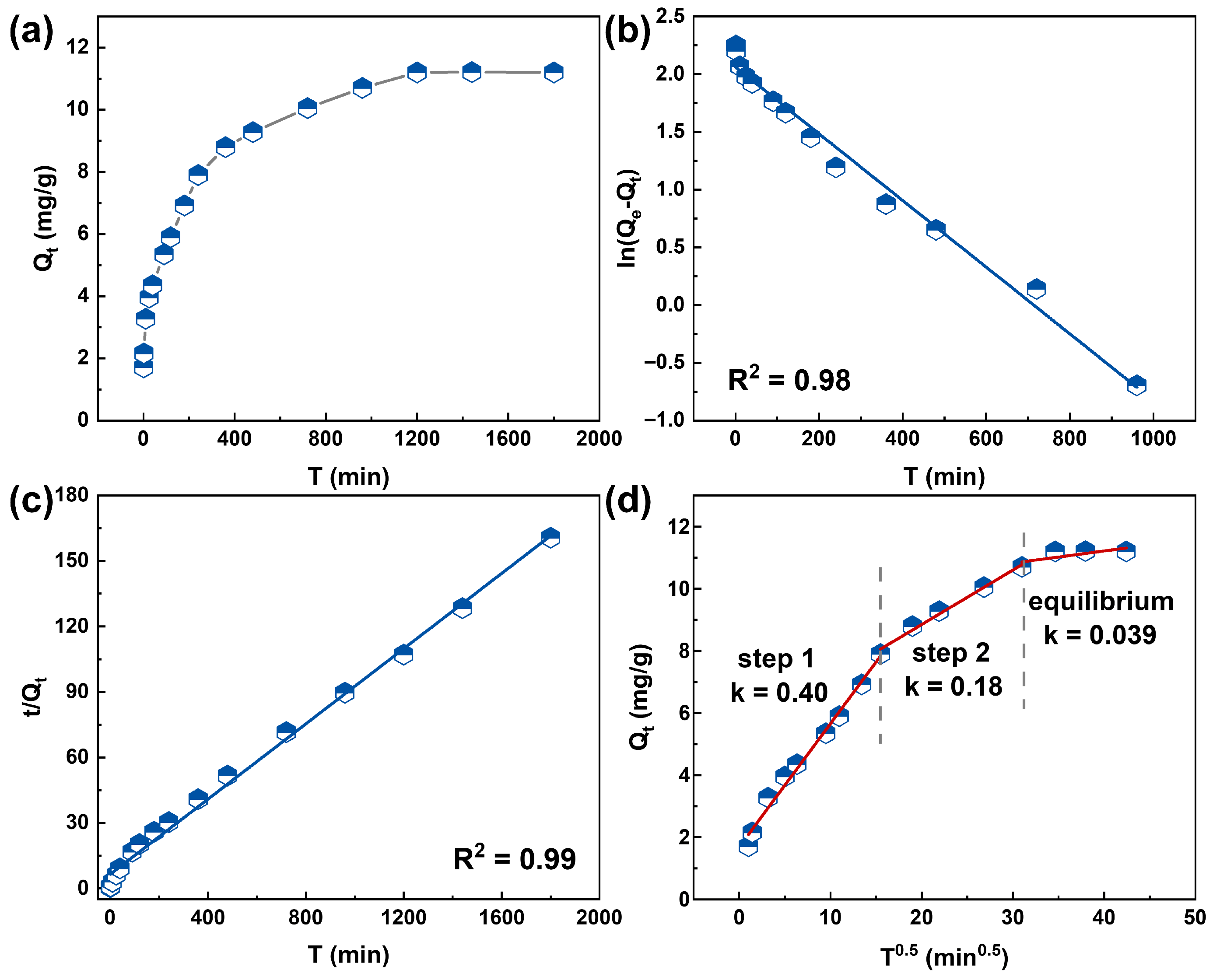
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
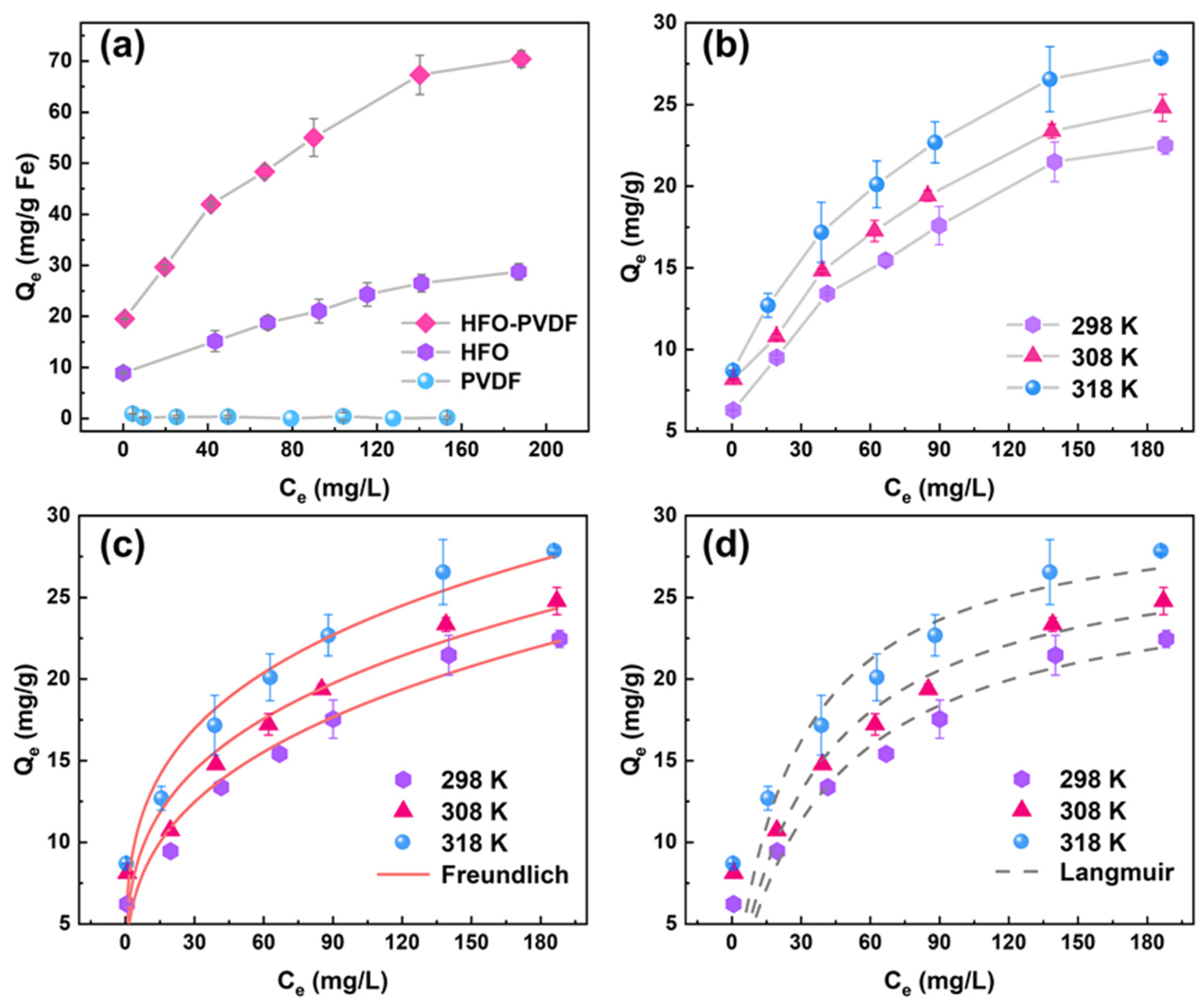
3.4. Adsorption Isotherm
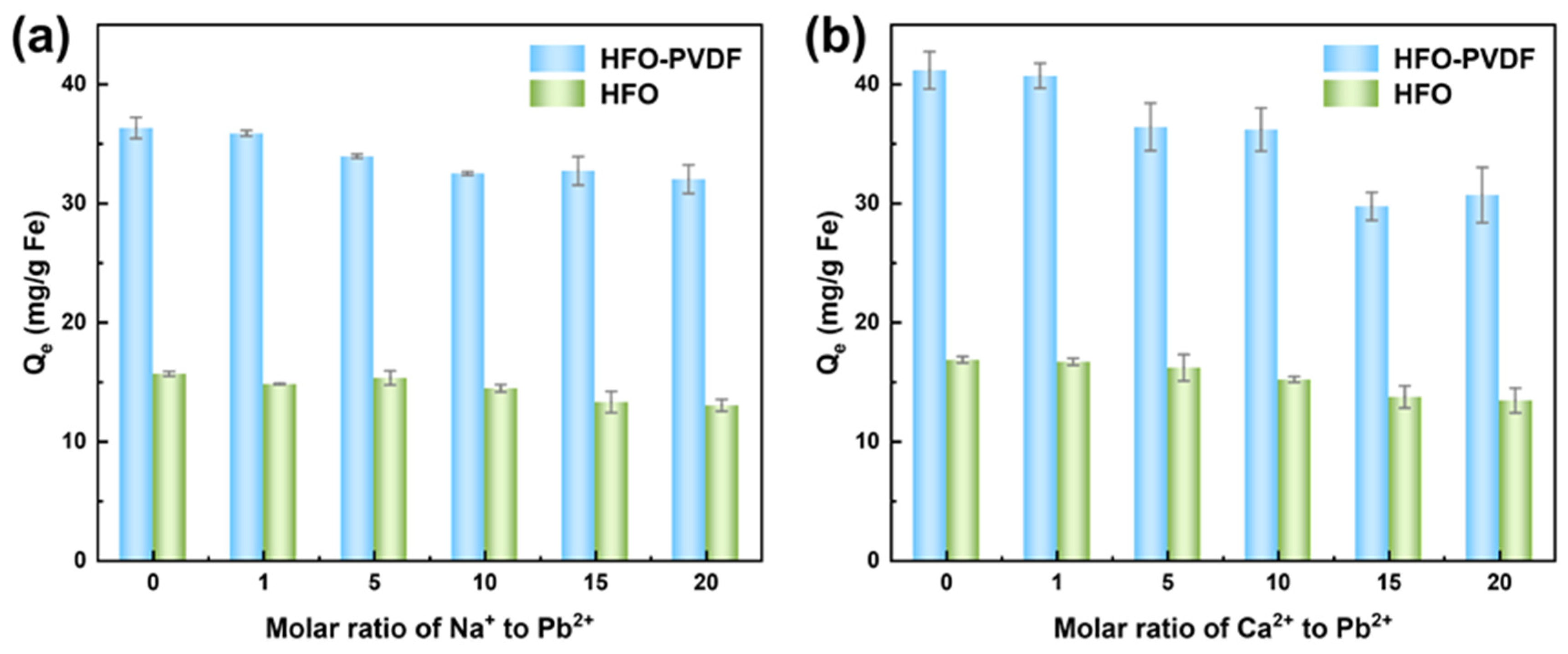
3.5. Effects of Coexisting Ions
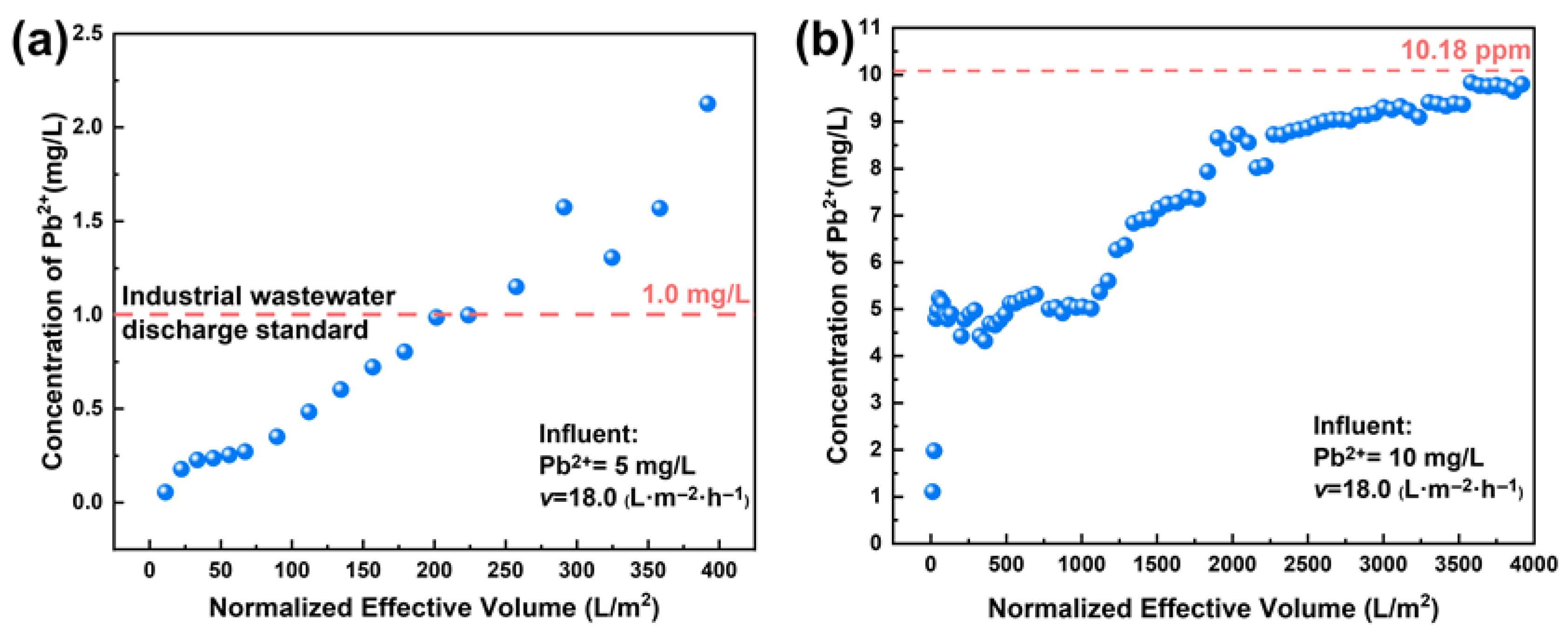
3.6. Dynamic Filtration
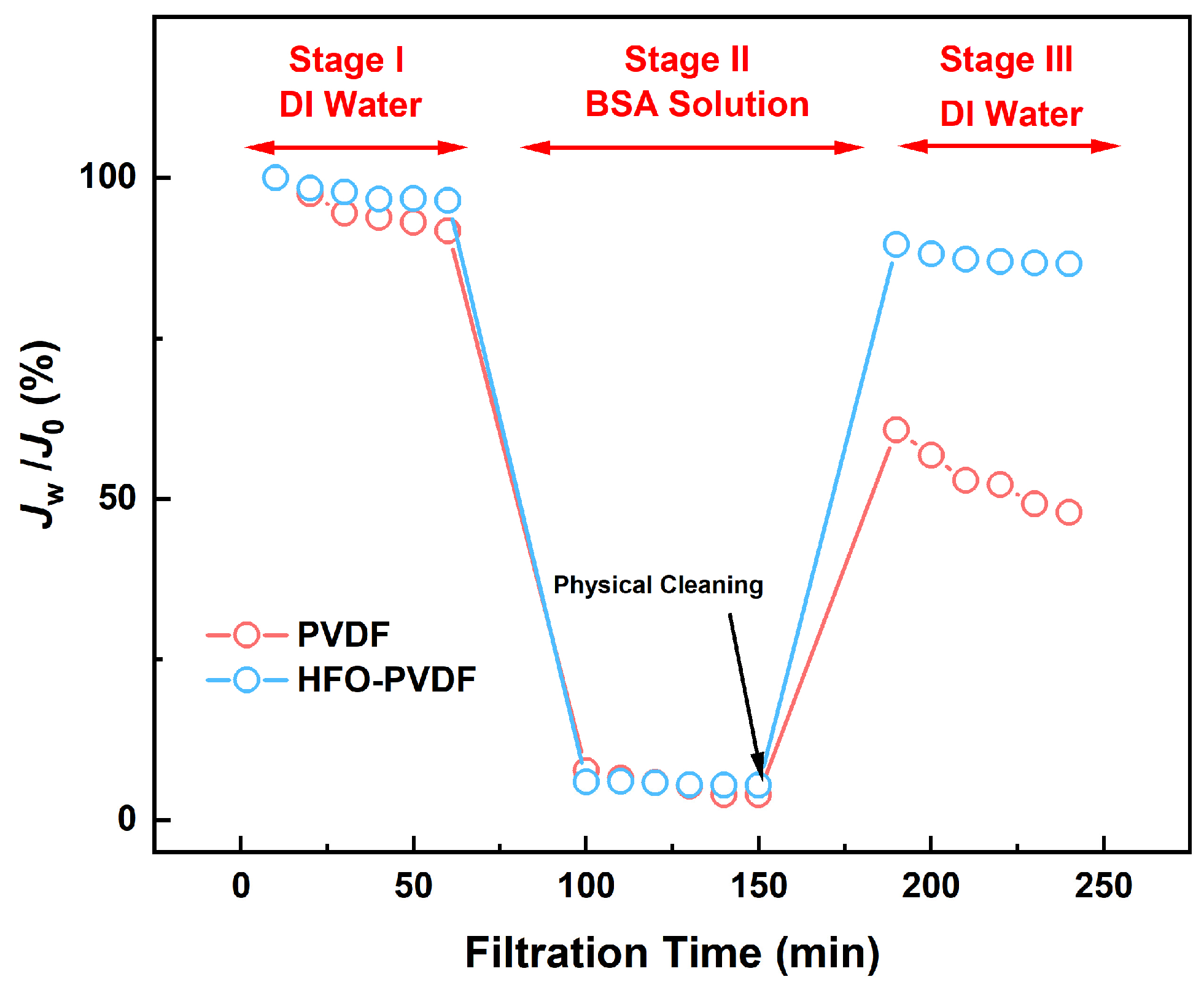
3.7. Antifouling Performance
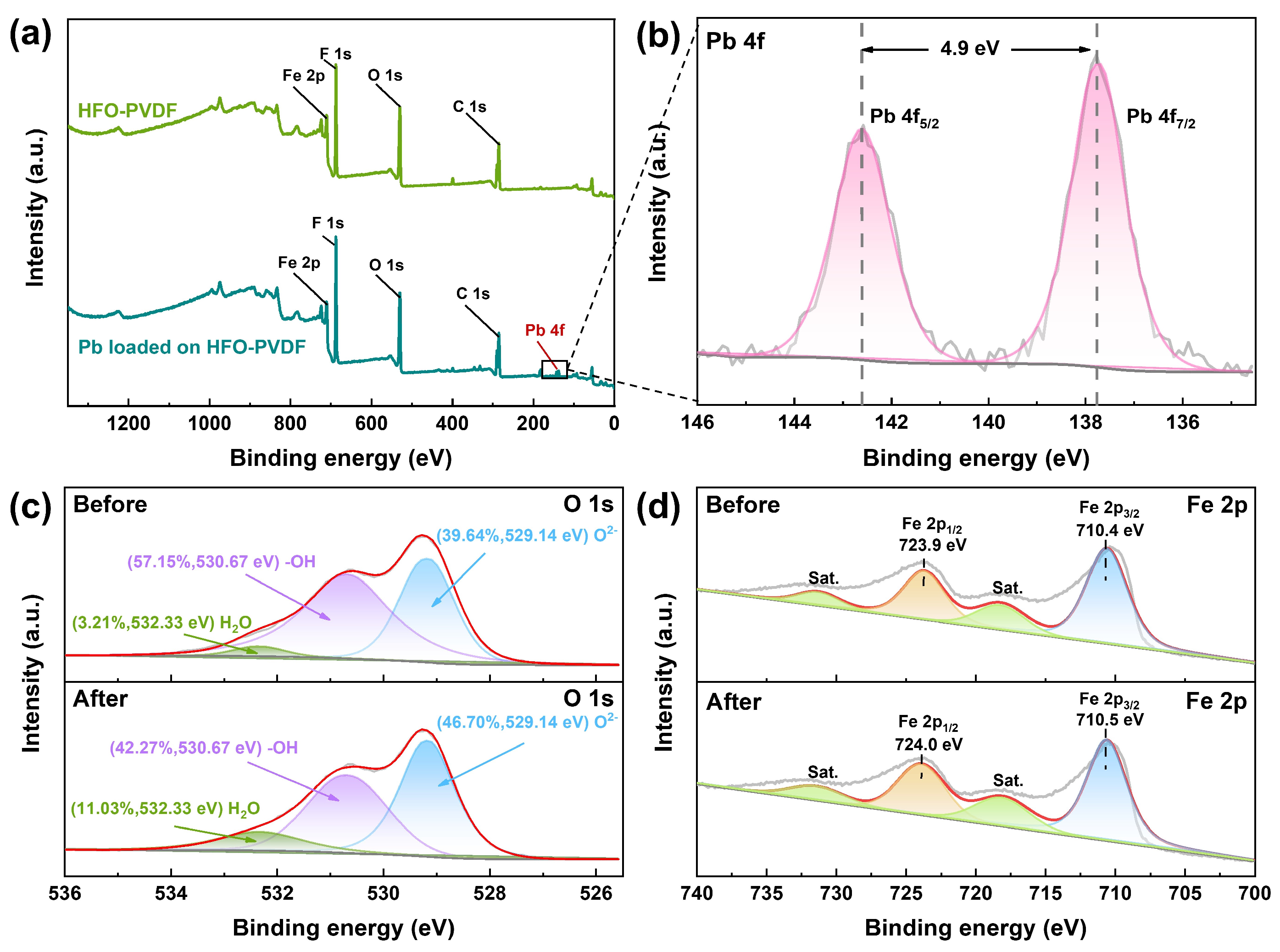
3.8. Adsorption Mechanism
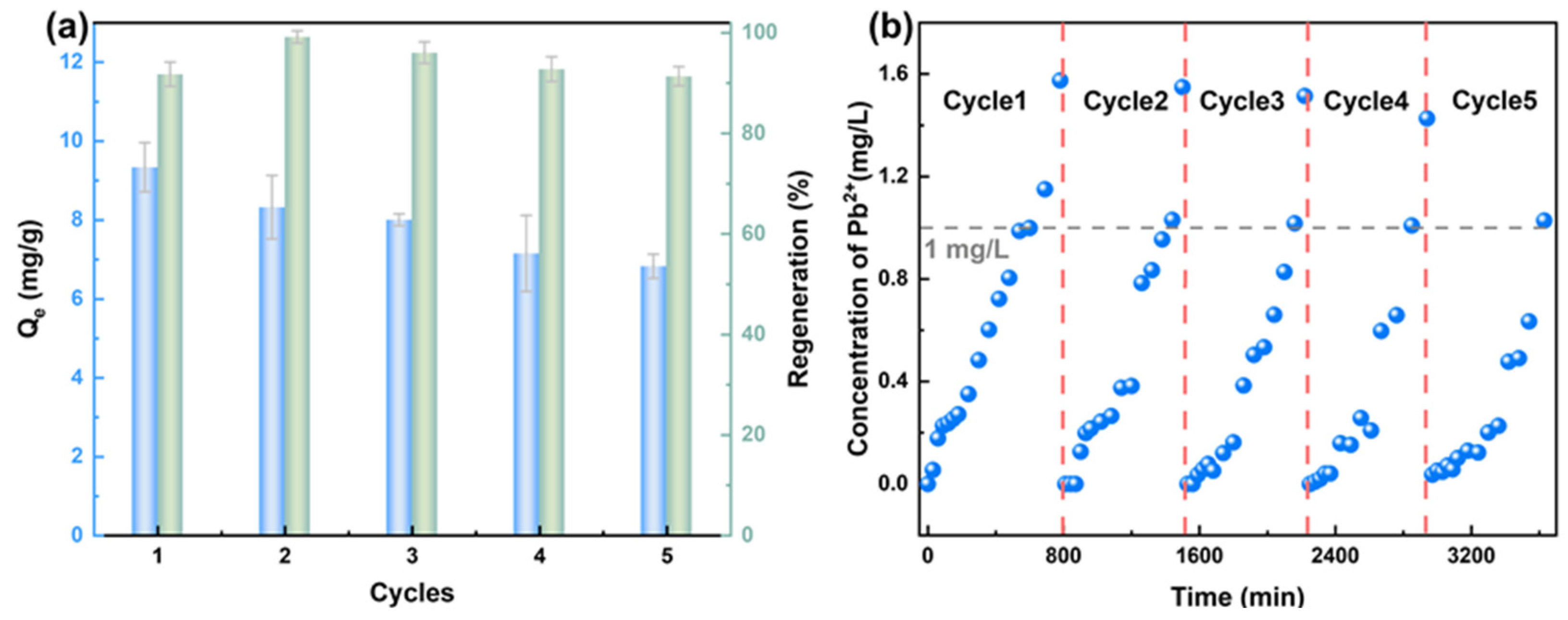
3.9. Evaluation of Practical Application Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, H.; Ni, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q. Remarkable ability of Pb(II) capture from water by self-assembled metal-phenolic networks prepared with tannic acid and ferric ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Nguyen, E.P.; Panáček, D.; Šedajová, V.; Hrubý, V.; Rosati, G.; Silva, C.C.C.; Bakandritsos, A.; Otyepka, M.; Merkoçi, A. Metal-free cysteamine-functionalized graphene alleviates mutual interferences in heavy metal electrochemical detection. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Bao, T.; Yan, W.; Fang, D.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yin, G.; Wan, M.; Mao, C.; Shi, D. Nanomotor-based adsorbent for blood Lead(II) removal in vitro and in pig models. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Liao, Y. Preparation of Honeycomb-Structured Activated Carbon-Zeolite Composites from Modified Fly Ash and the Adsorptive Removal of Pb(II). ACS Omega 2022, 7, 9684–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, N.E.; Hamouda, R.A.; Mousa, I.E.; Abdel-Hamid, M.S.; Rabei, N.H. Biosorption optimization; characterization, immobilization and application of Gelidium amansii biomass for complete Pb(2+) removal from aqueous solutions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Phanlavong, P.; Zhao, X.; Peng, Q.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q. Efficient Heavy Metal Removal from Water by Polydopamine Confined ZrO2 Nanocrystals with Improvements in Nanoparticles Utilization and Ion Diffusion. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A.; Azari, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ansarpour, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, E.I.; Othmani, A.; Nnaji, C.C. A review on zeolites as cost-effective adsorbents for removal of heavy metals from aqueous environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 8061–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Eva, T. Removal of Heavy Metals during Primary Treatment of Municipal Wastewater and Possibilities of Enhanced Removal: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Kuang, J.; Yu, M.; Huang, Z.; Zou, Z.; Zhu, L. Facile preparation of MoS2@Kaolin composite by one-step hydrothermal method for efficient removal of Pb(II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.-H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, M.; He, Y.; Pan, B. Nanomaterials-enabled water and wastewater treatment. NanoImpact 2016, 3–4, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; He, F.; Wu, J.; Wan, W.; Gu, Y.; Gao, B. Rapid and highly selective removal of lead from water using graphene oxide-hydrated manganese oxide nanocomposites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 314, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Qiu, H.; Pan, B.; Nie, G.; Xiao, L.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S. Highly efficient removal of heavy metals by polymer-supported nanosized hydrated Fe(III) oxides: Behavior and XPS study. Water Res. 2010, 44, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.C.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, Q.X. Polymer-supported nanocomposites for environmental application: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Heavy metals removal using hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous ferric oxide: Synthesis, characterization, and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, N.; Yusof, N.; Shah, M.H.A.; Ikhsan, S.N.W.; Ng, Z.-C.; Maji, S.; Lau, W.J.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Ariga, K. Hydrous ferric oxide nanoparticles hosted porous polyethersulfone adsorptive membrane: Chromium (VI) adsorptive studies and its applicability for water/wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20386–20399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Xiao, L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, G. Metal-organic frameworks-based mixed matrix pervaporation membranes for recovery of organics. Adv. Membr. 2024, 4, 100092. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Japip, S.; Jiang, S.-D.; Chung, T.-S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D. Advanced Porous Materials in Mixed Matrix Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1802401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiong, D.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, X.; Ni, F.; Deng, S.; Shen, F.; Tian, D.; Long, L.; Luo, L. A novel homogenous in-situ generated ferrihydrite nanoparticles/polyethersulfone composite membrane for removal of lead from water: Development, characterization, performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, V.O.C.; Timóteo, L.; Duarte, L.A.N.; Bahú, J.O.; Munoz, F.L.; Silva, A.P.; Lodi, L.; Severino, P.; León-Pulido, J.; Souto, E.B. Properties, characterization and biomedical applications of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF): A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 14185–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, L. Recent Advances in Polyvinylidene Fluoride with Multifunctional Properties in Nanogenerators. Small 2025, 21, e2412476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Da, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Hu, K.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y. Enhanced biofouling resistance of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes using crayfish shell biochar with calcium species. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.-C.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Zhang, W.-M.; Zhang, Q.-X. Critical review in adsorption kinetic models. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. A 2009, 10, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Pan, B. Mesoporous polyacrylonitrile membrane with ultrahigh loading of well-dispersed Fe2O3 nanoparticles: A powerful phosphate scavenger Enabling inhibition of microbial regrowth in Treated Water. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostergren, J.D.; Bargar, J.R.; Brown, G.E.; Parks, G.A. Combined EXAFS and FTIR investigation of sulfate and carbonate effects on Pb(II) sorption to goethite (alpha-FeOOH). J. Synchrotron Radiat. 1999, 6, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masibi, E.G.; Makhetha, T.A.; Moutloali, R.M. Effect of the Incorporation of ZIF-8@GO into the Thin-Film Membrane on Salt Rejection and BSA Fouling. Membranes 2022, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Nie, D.; Wang, W.; Xu, Q.; Nie, G. Fabrication of a MoS2@PAN composite membrane for efficient removal of toxic Cr(VI). Desalination 2025, 600, 118460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, A.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y. Unique Lead Adsorption Behavior of Activated Hydroxyl Group in Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4113–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | KF (g/L) | 1/n | R2 | |
| 298 | 26.73 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 4.23 | 0.04 | 0.95 |
| 308 | 28.63 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 5.45 | 0.29 | 0.93 |
| 318 | 30.66 | 0.02 | 0.76 | 6.88 | 0.27 | 0.96 |
| T (K) | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (kJ/(mol∙K) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | −10.48 | 0.056 | 16.19 |
| 308 | −13.96 | ||
| 318 | −18.19 |
| Membrane Types | Rt | Rr | Rir | FRR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 95.71 | 47.90 | 47.81 | 52.19 |
| HFO-PVDF | 94.39 | 84.14 | 10.25 | 89.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, S.; Xu, Q.; Liu, M.-L.; Zou, D.; Nie, G. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using an HFO-PVDF Composite Adsorption Membrane. Membranes 2025, 15, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090264
Lu S, Xu Q, Liu M-L, Zou D, Nie G. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using an HFO-PVDF Composite Adsorption Membrane. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090264
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Shuhang, Qianhui Xu, Mei-Ling Liu, Dong Zou, and Guangze Nie. 2025. "Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using an HFO-PVDF Composite Adsorption Membrane" Membranes 15, no. 9: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090264
APA StyleLu, S., Xu, Q., Liu, M.-L., Zou, D., & Nie, G. (2025). Efficient Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using an HFO-PVDF Composite Adsorption Membrane. Membranes, 15(9), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090264







