Seven-Channel Polyethersulfone Hollow-Fiber Membrane Preparation with Vapor-Induced Phase Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
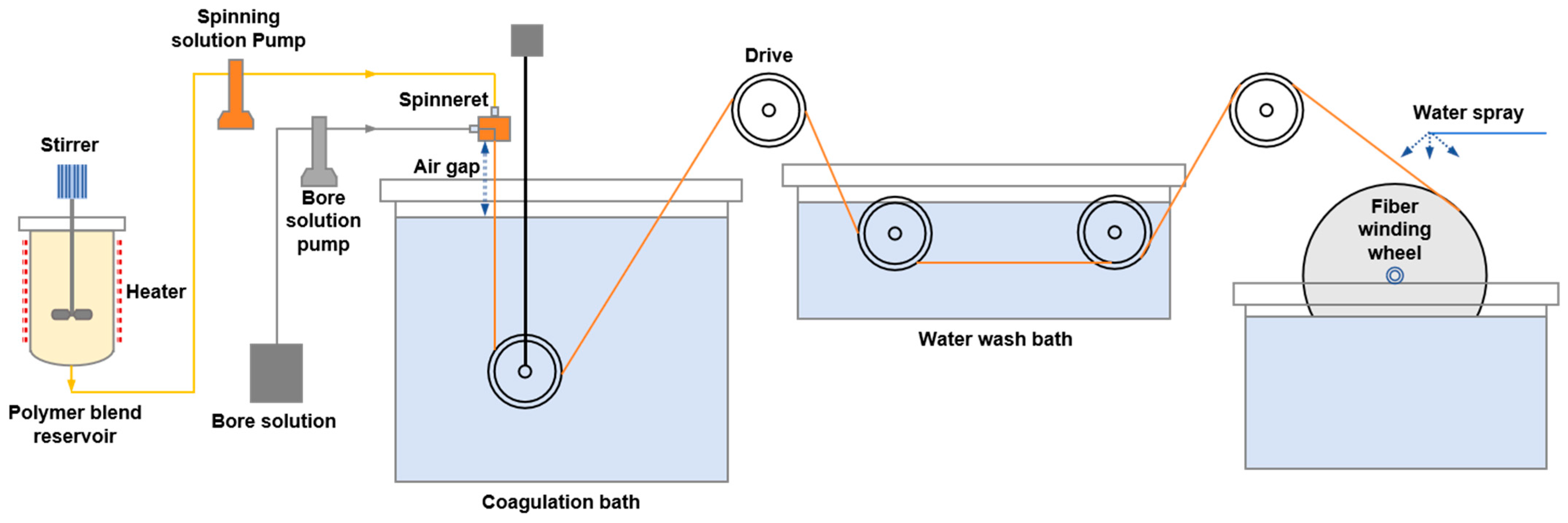
2.2. Preparation of Seven-Channel PES Hollow-Fiber Membrane
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Membrane Morphology and Structure
2.3.2. Infrared Spectral Analysis
2.3.3. Surface Contact Angle and Zeta Potential Test
2.3.4. Membrane Pore Size Distribution Analysis
2.3.5. Membrane Mechanical Performance Test
2.4. Membrane Performance Test
2.4.1. Pure Water Flux Tests
2.4.2. Membrane Filtration Performance Tests
2.4.3. Membrane Long-Term Filtration Performance Test
2.4.4. Water Quality Parameter Test
3. Results and Discussion
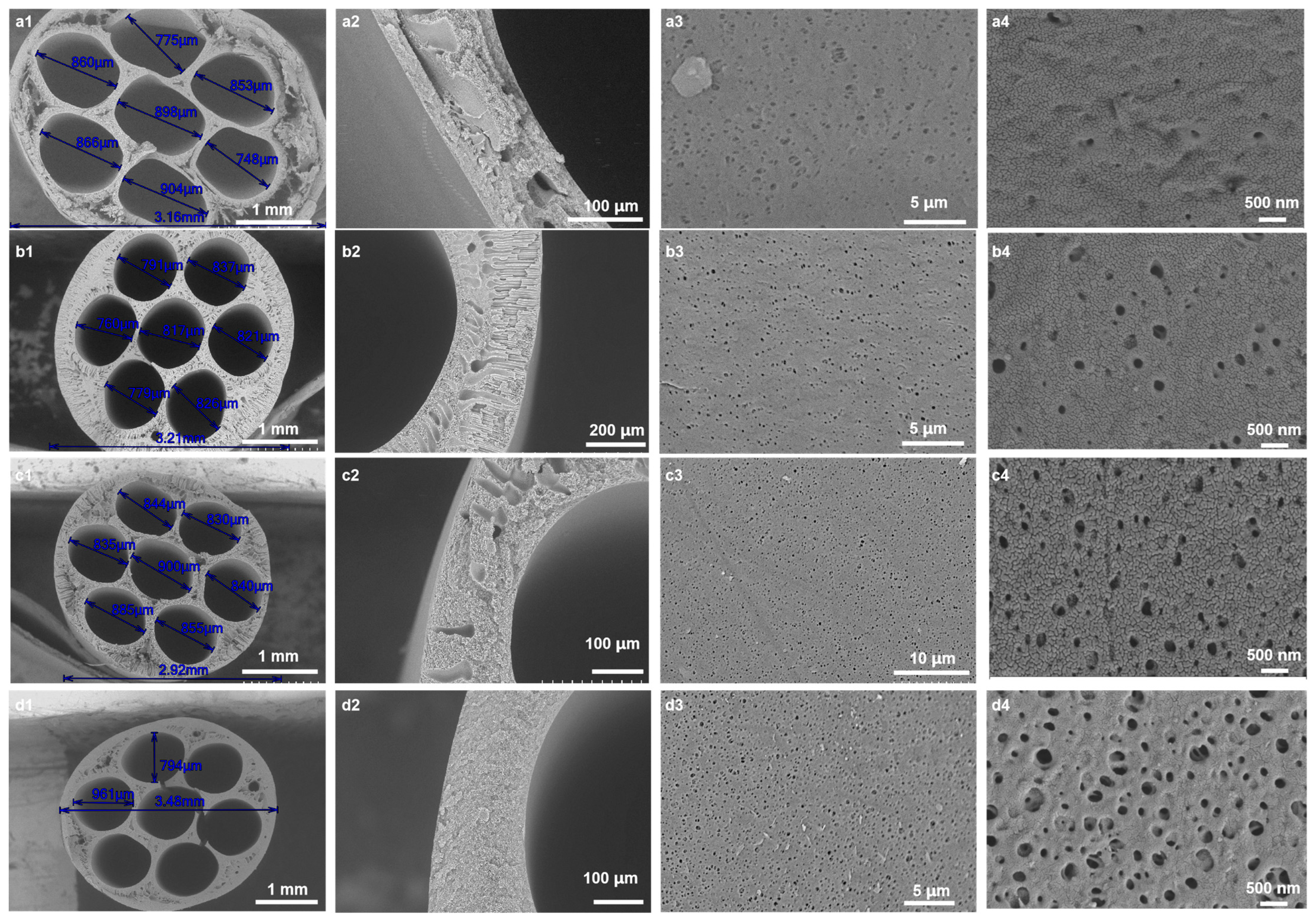
3.1. Influence of CGQD Mass Fraction on Membrane Microstructure and Performance
3.1.1. Microstructure of Membranes
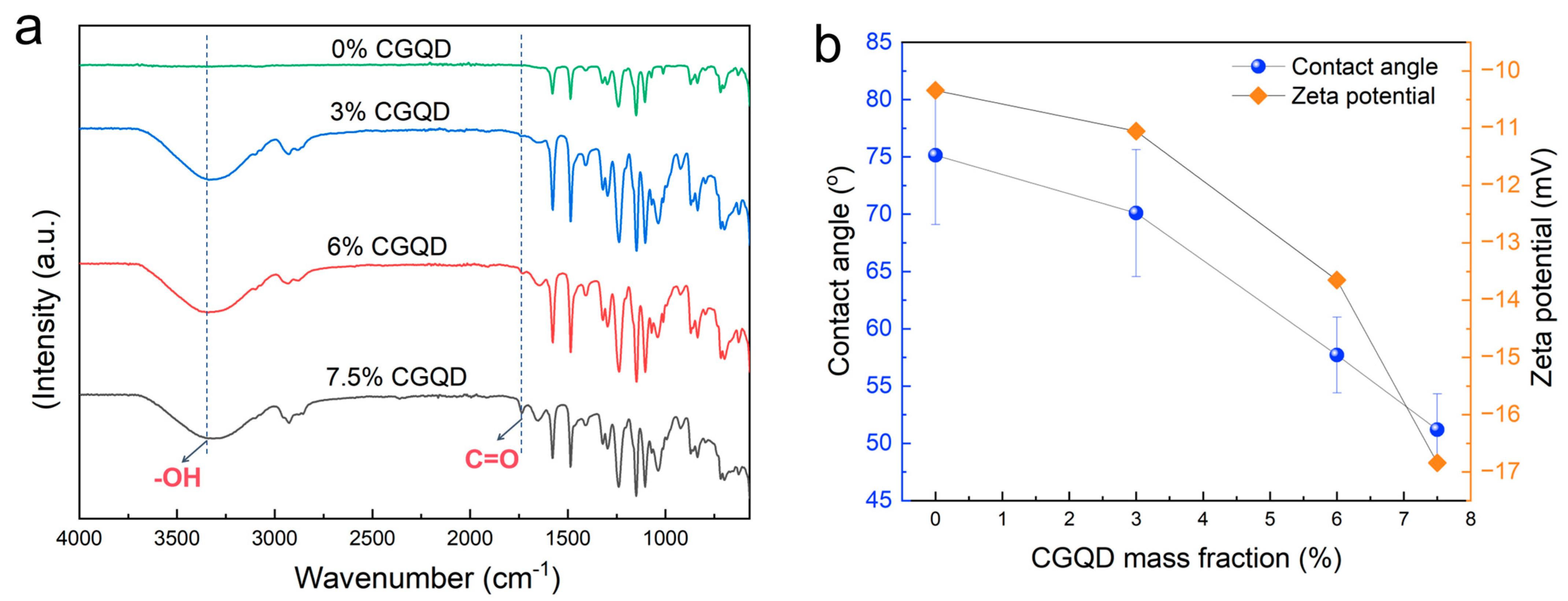
3.1.2. Chemical Composition, Water Contact Angle, and Zeta Potential
3.1.3. Pure Water Flux, BSA Rejection, and Mechanical Properties
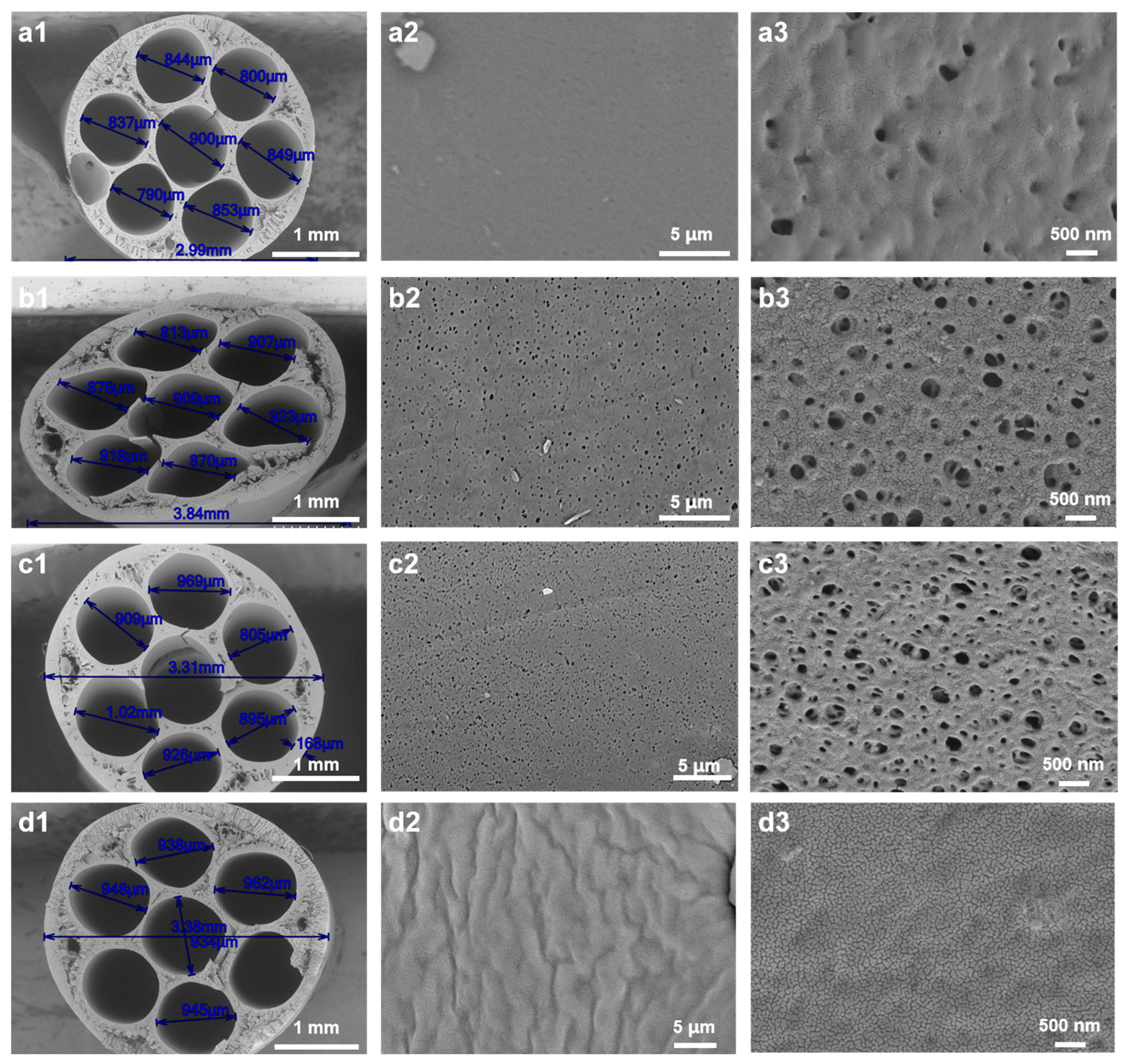
3.2. Influence of Air Gap and Relative Humidity on Membrane Microstructure
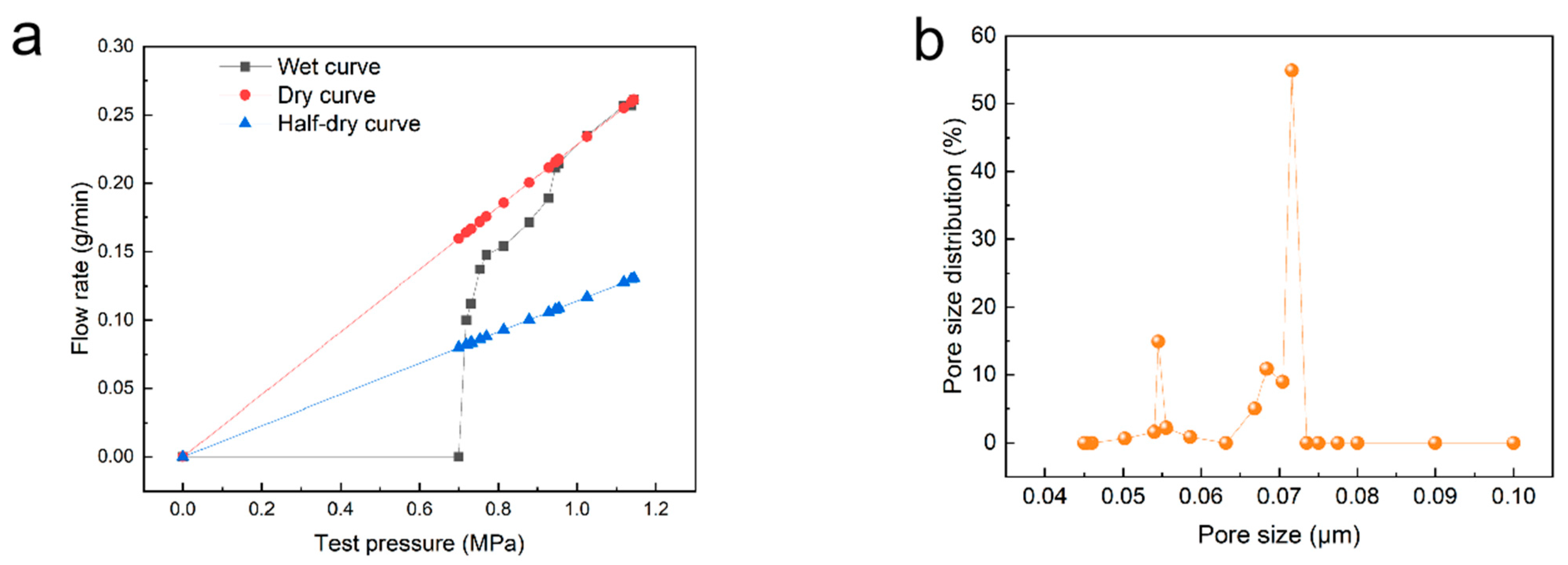
3.3. Membrane Pore Size and Pore Distribution
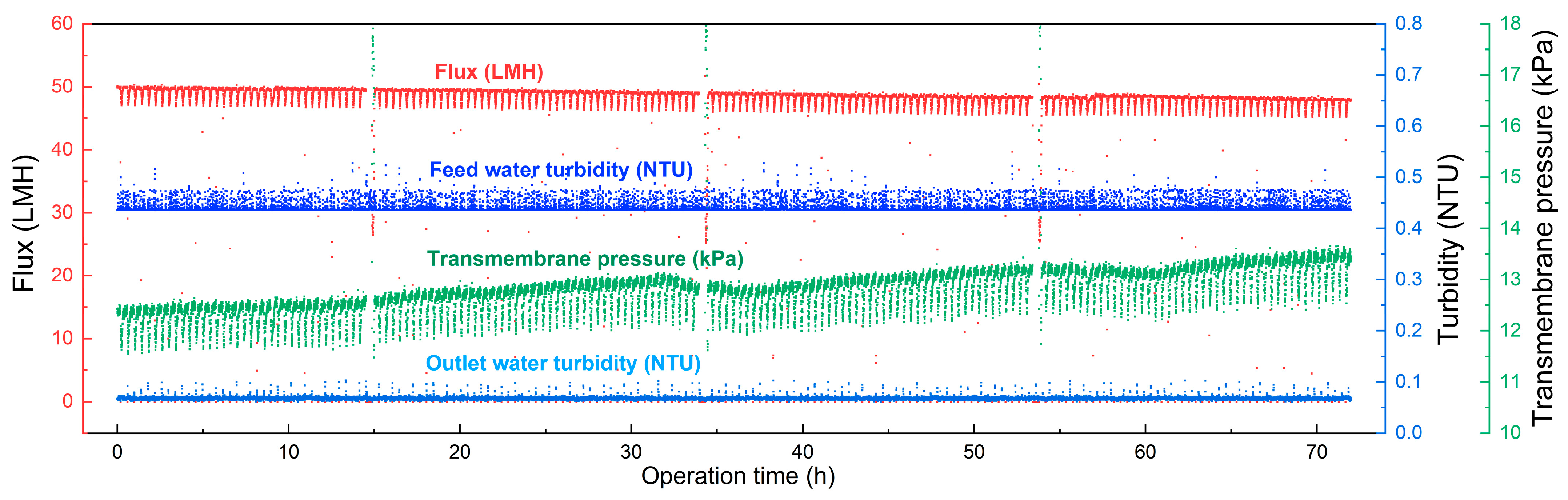
3.4. Membrane Long-Term Filtration Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Chapter 1—Introduction. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Chung, T.-S., Feng, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, N.; Widjojo, N.; Sukitpaneenit, P.; Teoh, M.M.; Lipscomb, G.G.; Chung, T.-S.; Lai, J.-Y. Evolution of polymeric hollow fibers as sustainable technologies: Past, present, and future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1401–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, J.O.; Brandstätter, R.; Spruck, M.; Koch, M.; Penner, S.; Rupprich, M. Parameter Screening of PVDF/PVP Multi-Channel Capillary Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Han, M.; Chen, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, G. Membrane fouling control in ultrafiltration technology for drinking water production: A review. Desalination 2011, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Yuan, X.; Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhao, S. Reduction of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by the Pretreatment Removal of Emerging Pollutants: A Review. Membranes 2023, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Ulbricht, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, X. Progress in alumina ceramic membranes for water purification: Status and prospects. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Recent progress in polymeric hollow-fibre membrane preparation and applications. Membr. Technol. 2016, 2016, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xue, J.; Ran, F.; Sun, S. Modification of polyethersulfone membranes—A review of methods. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 76–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.-S. Chapter 14—Design and fabrication of lotus root-like multibore hollow fiber membrane for direct contact membrane distillation. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Chung, T.-S., Feng, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 291–314. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.-S. Design and fabrication of lotus-root-like multi-bore hollow fiber membrane for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Han, G.; Chung, T.-S. Novel thin-film composite tri-bore hollow fiber membrane fabrication for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu-Rashid, K.A.; Czolkoss, W. Pilot Tests of Multibore UF Membrane at Addur SWRO Desalination Plant, Bahrain. Desalination 2007, 203, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Venault, A.; Lai, J.-Y. Chapter 2—Fundamentals of nonsolvent-induced phase separation. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Chung, T.-S., Feng, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 13–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tasselli, F.; Jansen, J.C.; Sidari, F.; Drioli, E. Morphology and transport property control of modified poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEKWC) hollow fiber membranes prepared from PEEKWC/PVP blends: Influence of the relative humidity in the air gap. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 255, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.A.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Wang, D.M.; Deratani, A.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Lee, K.R.; Lai, J.Y. Morphology control of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes via water vapor induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-J. Effect of propionic acid in the casting solution on the characteristics of phase inversion polysulfone membranes. Desalination 1999, 121, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laninovic, V. Relationship between type of nonsolvent additive and properties of polyethersulfone membranes. Desalination 2005, 186, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.B.; Wu, H.; Shen, J.L.; Cao, L.; He, X.Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.Z.; Xu, M.Z.; Mao, X.L.; et al. Control of Edge/in-Plane Interactions toward Robust, Highly Proton Conductive Graphene Oxide Membranes. ACS NANO 2019, 13, 10366–10375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, A.H.; Sofer, Z.; Bouša, D.; Ulbrich, P.; Bonanni, A.; Pumera, M. Carboxylic Carbon Quantum Dots as a Fluorescent Sensing Platform for DNA Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Salih, H.A.; Simone, S.; Zablouk, M.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Poly(ether sulfone) (PES) hollow-fiber membranes prepared from various spinning parameters. Desalination 2014, 345, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Calvo, J.I.; Prádanos, P.; Tejerina, F. Pore size distributions in microporous membranes. A critical analysis of the bubble point extended method. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 112, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Q. Preparation of polysulfone membranes via vapor-induced phase separation and simulation of direct-contact membrane distillation by measuring hydrophobic layer thickness. Desalination 2013, 316, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Kuo, C.Y.; Wang, D.M.; Lai, J.Y.; Deratani, A.; Pochat, C.; Bouyer, D. Interplay of mass transfer, phase separation, and membrane morphology in vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 338, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | CPES | CCGQDs | Cwater | CTEG | CDMAc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | |||||
| a | 18 | 0 | 1.5 | 20 | 60.5 |
| b | 18 | 3 | 1.5 | 20 | 57.5 |
| c | 18 | 6 | 1.5 | 20 | 54.5 |
| d | 18 | 7.5 | 1.5 | 20 | 53 |
| Cwater (wt%) | CDMAc (wt%) | CTEG (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| 55 | 20 | 25 |
| Process Conditions | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Feed tank operating temperature (°C) | 40 |
| Bore solution tank operating temperature (°C) | 25 |
| Gear pump operating temperature (°C) | 40 |
| Spinning solution Flux (mL/min) | 12 |
| Bore solution Flux (mL/min) | 35 |
| Coagulation bath | Tap water |
| Temperature of the coagulation bath (°C) | 25 |
| Air gap (cm) | 7.5–15 |
| Air gap temperature (°C) | 25 |
| Air gap relative humidity (%) | 50–99% |
| ID | Air Gap (cm) | Relative Humidity (%) | Air Exposure Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 5(a1–a3) | 7.5 | 50 | 0.75 |
| Figure 5(b1–b3) | 7.5 | 99 | 0.75 |
| Figure 5(c1–c3) | 10 | 99 | 1 |
| Figure 5(d1–d3) | 15 | 99 | 1.5 |
| Operation Time | Feed Water TOC (mg/L) | Outlet Water TOC (mg/L) | TOC Rejection Rate (%) | Transmembrane Pressure Increase (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day1 | 1.12 | 0.92 | 17.8 | 0.617 |
| Day2 | 1.19 | 1.01 | 15.1 | 0.315 |
| Day3 | 1.30 | 1.02 | 21.6 | 0.389 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Huang, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X. Seven-Channel Polyethersulfone Hollow-Fiber Membrane Preparation with Vapor-Induced Phase Separation. Membranes 2025, 15, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060175
Wang X, Hao Z, Huang R, Huang Y, Zhang H, Hao X. Seven-Channel Polyethersulfone Hollow-Fiber Membrane Preparation with Vapor-Induced Phase Separation. Membranes. 2025; 15(6):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060175
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoyao, Zhiyuan Hao, Rui Huang, Yajing Huang, Huiqun Zhang, and Xiujuan Hao. 2025. "Seven-Channel Polyethersulfone Hollow-Fiber Membrane Preparation with Vapor-Induced Phase Separation" Membranes 15, no. 6: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060175
APA StyleWang, X., Hao, Z., Huang, R., Huang, Y., Zhang, H., & Hao, X. (2025). Seven-Channel Polyethersulfone Hollow-Fiber Membrane Preparation with Vapor-Induced Phase Separation. Membranes, 15(6), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060175








