Determining Accurate Pore Structures of Polypropylene Membrane for ECMO Using FE-SEM Under Optimized Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Observation of the Inner and Outer Surfaces of the Hollow Fiber Membrane Utilizing Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3. Sputter-Coating of Os or Au Particles on the Inner and Outer Surfaces of the Hollow Fiber Membrane
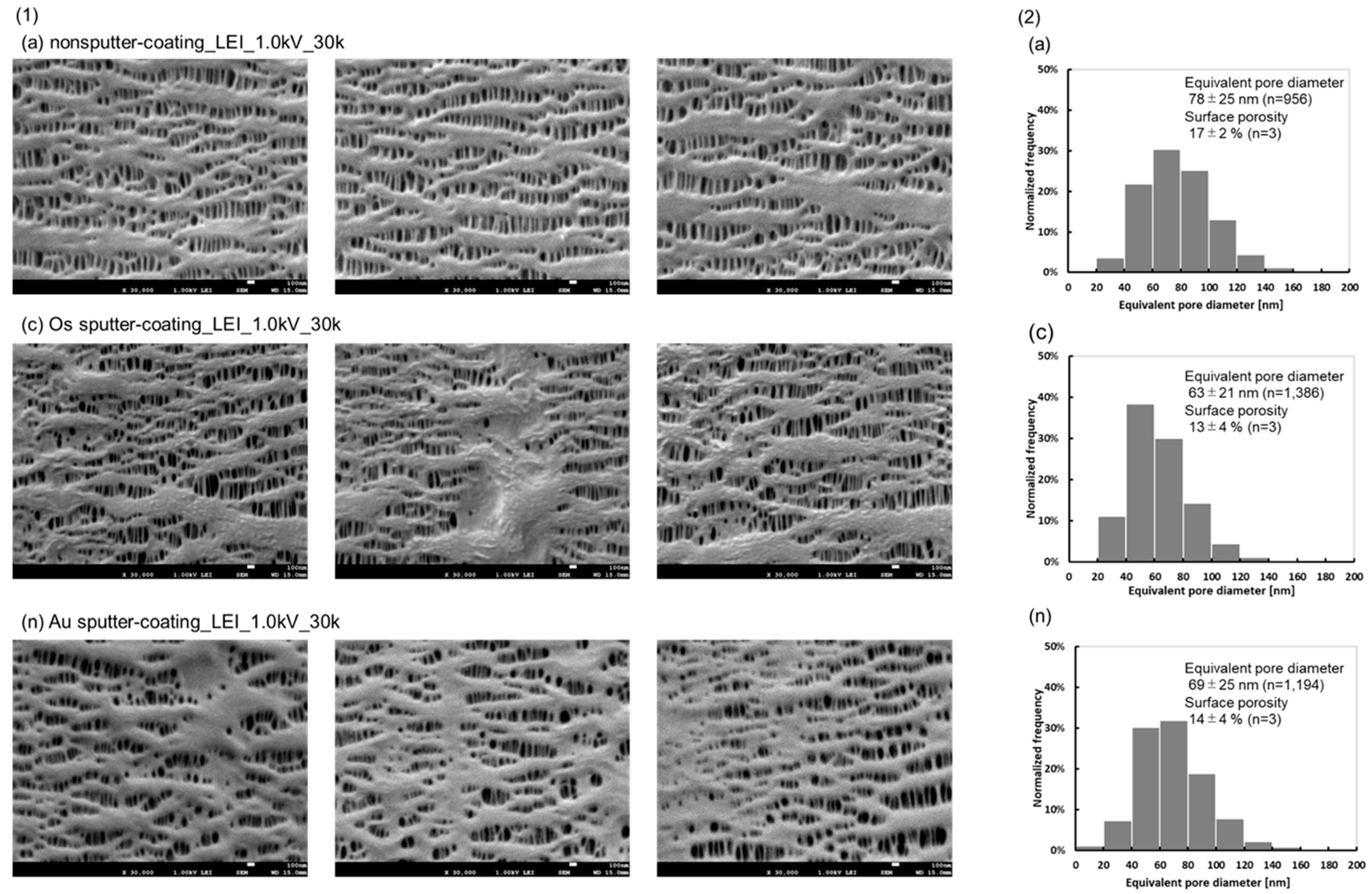
2.4. Determination of the Pore Diameter and Surface Porosity of the Hollow Fiber Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
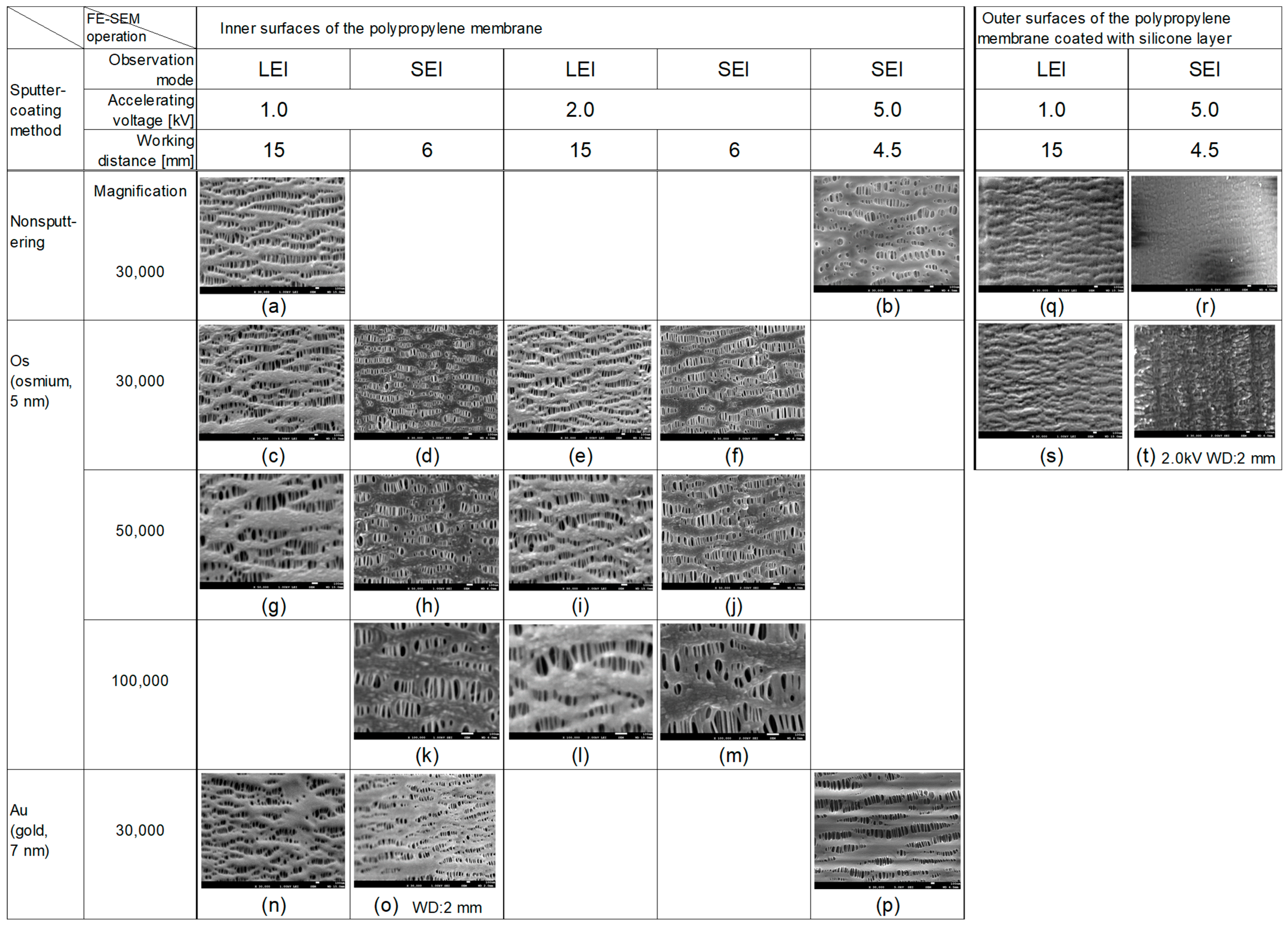
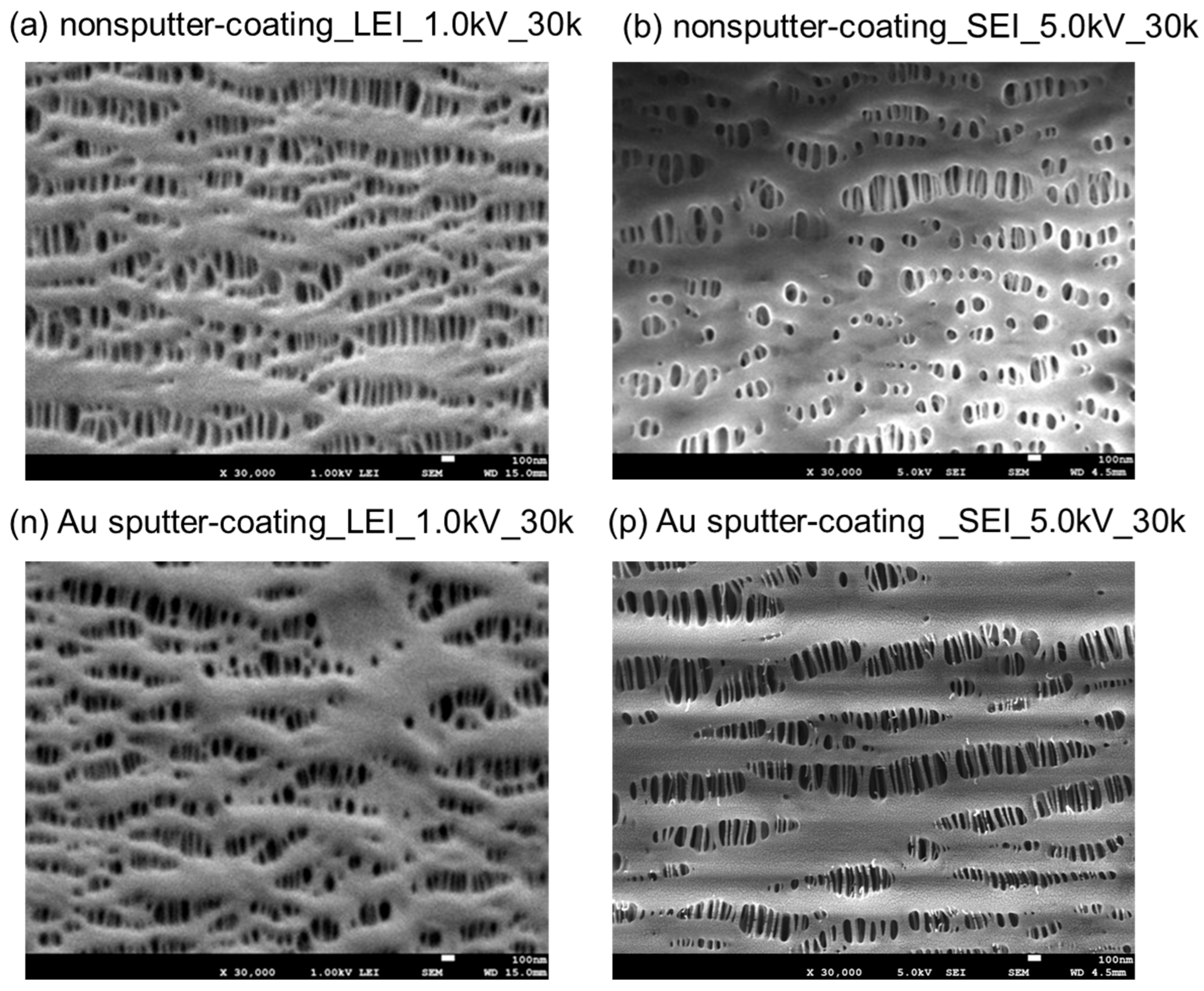
3.1. FE-SEM Images of the Inner Surfaces of the PP Membrane with the Different Sputter-Coating Methods and Observation Modes
3.2. Comparison of LEI and SEI Modes
3.3. Appropriate Accelerating Voltages in LEI and SEI Modes (Os Sputter-Coating)
3.4. Outer Surface of the Membrane Coated with Silicone Layer
3.5. Significance of This Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbaro, R.P.; MacLaren, G.; Boonstra, P.S.; Combes, A.; Agerstrand, C.; Annich, G.; Diaz, R.; Fan, E.; Hryniewicz, K.; Lorusso, R.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19: Evolving outcomes from the international Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Lancet 2021, 398, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arens, J.; Grottke, O.; Haverich, A.; Maier, L.S.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Wendel, H.P.; Rossaint, R. Toward a Long-Term Artificial Lung. ASAIO J. 2020, 50, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, D.; Katagiri, N.; Mizuno, T.; Tsukiya, T.; Takewa, Y.; Tatsumi, E. Preclinical biocompatibility study of ultra-compact durable ECMO system in chronic animal experiments for 2 weeks. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 23, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duy Nguyen, B.T.; Nguyen Thi, H.Y.; Nguyen Thi, B.P.; Kang, D.-K.; Kim, J.F. The Roles of Membrane Technology in Artificial Organs: Current Challenges and Perspectives. Membranes 2021, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M. Evolutions of extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO): Perspectives for advanced hollow fiber membrane. J. Artif. Organs 2024, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Uemura, T.; Matsuda, W.; Sato, M.; Ishizuka, K.; Fukaya, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Nakamoto, T.; Ohmagari, N.; Katano, H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 leakage from the gas outlet port during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for COVID-19. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Furuya, T.; Sadano, K.; Tokumine, A.; Mori, T.; Saomoto, H.; Sakai, K. Electron microscopic confirmation of anisotropic pore characteristics for ECMO membranes theoretically validating the risk of SARS-CoV-2 permeation. Membranes 2021, 11, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, A.; Takasu, H. Introduction of ion milling system and its application. J. Surf. Finish. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 66, 581–585. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.; Sadano, K.; Maeda, T.; Murata, E.; Miyashita, N.; Tanaka, T.; Mori, T.; Saito, A.; Sakai, K. Characterization of anisotropic pore structure and dense selective layer of capillary membranes for long-term ECMO by cross-sectional ion-milling method. J. Artif. Organs 2024, 28, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeol Ltd. Available online: https://www.jeol.co.jp/products/scientific/sem/ (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Jeol Ltd. Available online: https://www.jeol.co.jp/words/semterms/20121024.022959.html#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Alqaheem, Y.; Alomair, A.A. Microscopy and spectroscopy tech niques for characterization of polymeric membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of cross-sectional membrane samples for scanning electron microscopy characterizations using a new frozen section technique. Membranes 2023, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Z. Modification strategies to improve the membrane hemocompatibility in extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO). Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 847–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, C. Advanced hemocompatible polyethersulfone composite artificial lung membrane with efficient CO2/O2 exchange channel constructed by modified carbon nanotubes network. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 160, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-Q.; Jia, Z.-Q.; Peng, W.; Li, S.; Wen, J. Preparation of 4-methyl-1-pentene membranes via non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS). Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 178, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, Q.; Lin, H.; Liu, F. A novel poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) / polypropylene (PMP/PP) thin film composite (TFC) artificial lung membrane for enhanced gas transport and excellent hemo-compatibility. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 649, 120359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Feng, A.; Yu, L.; Wu, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. A novel tunable polypropylene hollow fiber membrane with gradient structure for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 693, 122325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H.; Nishitani, Y.; Kuwana, K.; Tahara, K.; Aoki, Y.; Osaki, S.; Hu, C. Development of new oxygenator with cyclosiloxane coated polypropylene hollow fiber. Jpn. J. Artif. Organs 1996, 25, 329–332. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Brickey, K.P.; Zydney, A.L.; Gomez, E.D. FIB-SEM tomography reveals the nanoscale 3D morphology of virus. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberge, H.; Moreau, P.; Couallier, E.; Abella, P. Determination of the key structural factors affecting permeability and selectivity of PAN and PES polymeric filtration membranes using 3D FIB/ SEM. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, P.C. Chapter 3 Slip flow, free molecule flow, and diffusional flow. In Flow of Gases Through Porous Media; Carman, P.C., Ed.; Butterworths Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1956; pp. 62–80. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukuda, M.; Nishite, Y.; Murata, E.; Namekawa, K.; Mori, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sakai, K. Determining Accurate Pore Structures of Polypropylene Membrane for ECMO Using FE-SEM Under Optimized Conditions. Membranes 2025, 15, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060174
Fukuda M, Nishite Y, Murata E, Namekawa K, Mori T, Tanaka T, Sakai K. Determining Accurate Pore Structures of Polypropylene Membrane for ECMO Using FE-SEM Under Optimized Conditions. Membranes. 2025; 15(6):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060174
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukuda, Makoto, Yoshiaki Nishite, Eri Murata, Koki Namekawa, Tomohiro Mori, Tsutomu Tanaka, and Kiyotaka Sakai. 2025. "Determining Accurate Pore Structures of Polypropylene Membrane for ECMO Using FE-SEM Under Optimized Conditions" Membranes 15, no. 6: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060174
APA StyleFukuda, M., Nishite, Y., Murata, E., Namekawa, K., Mori, T., Tanaka, T., & Sakai, K. (2025). Determining Accurate Pore Structures of Polypropylene Membrane for ECMO Using FE-SEM Under Optimized Conditions. Membranes, 15(6), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060174





