Halloysite-Nanotube-Mediated High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ultrafiltration Membranes for Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
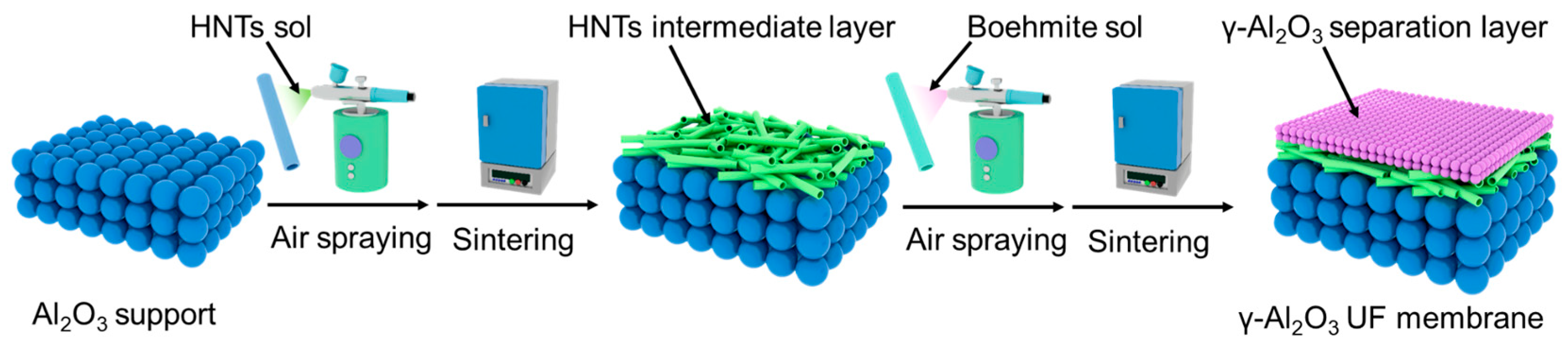
2.2. Preparation of the High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ceramic UF Membranes
2.2.1. Preparation of the HNTs Intermediate Layer
2.2.2. Preparation of the γ-Al2O3 UF Layer
2.3. Characterization of the Materials and Membranes
2.4. The CMP Waste Liquid Filtration Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical–Chemical Characterization of the HNTs
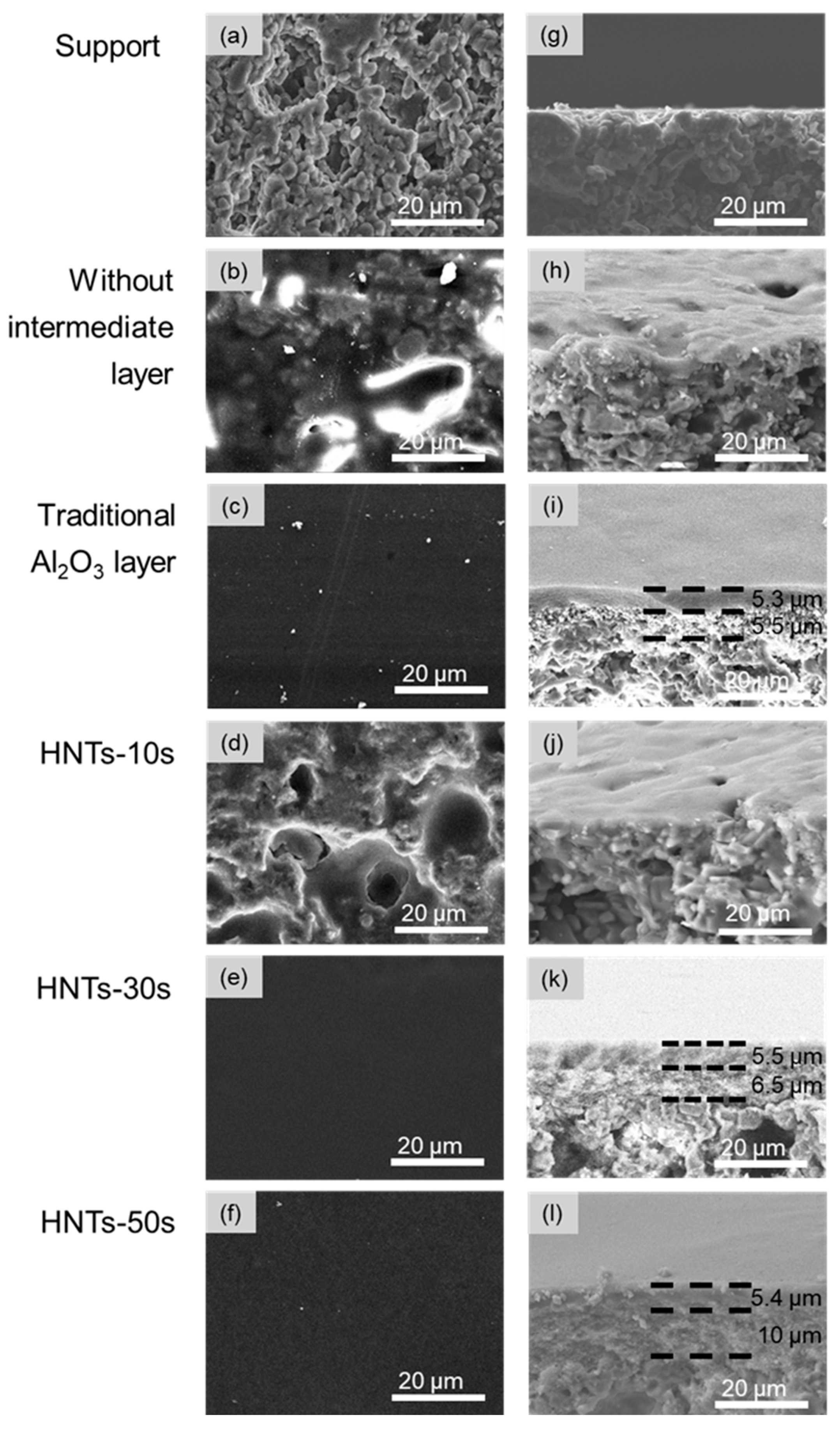
3.2. The Morphology and Characterization of the Properties of the High-Flux γ-Al2O3 UF Membranes
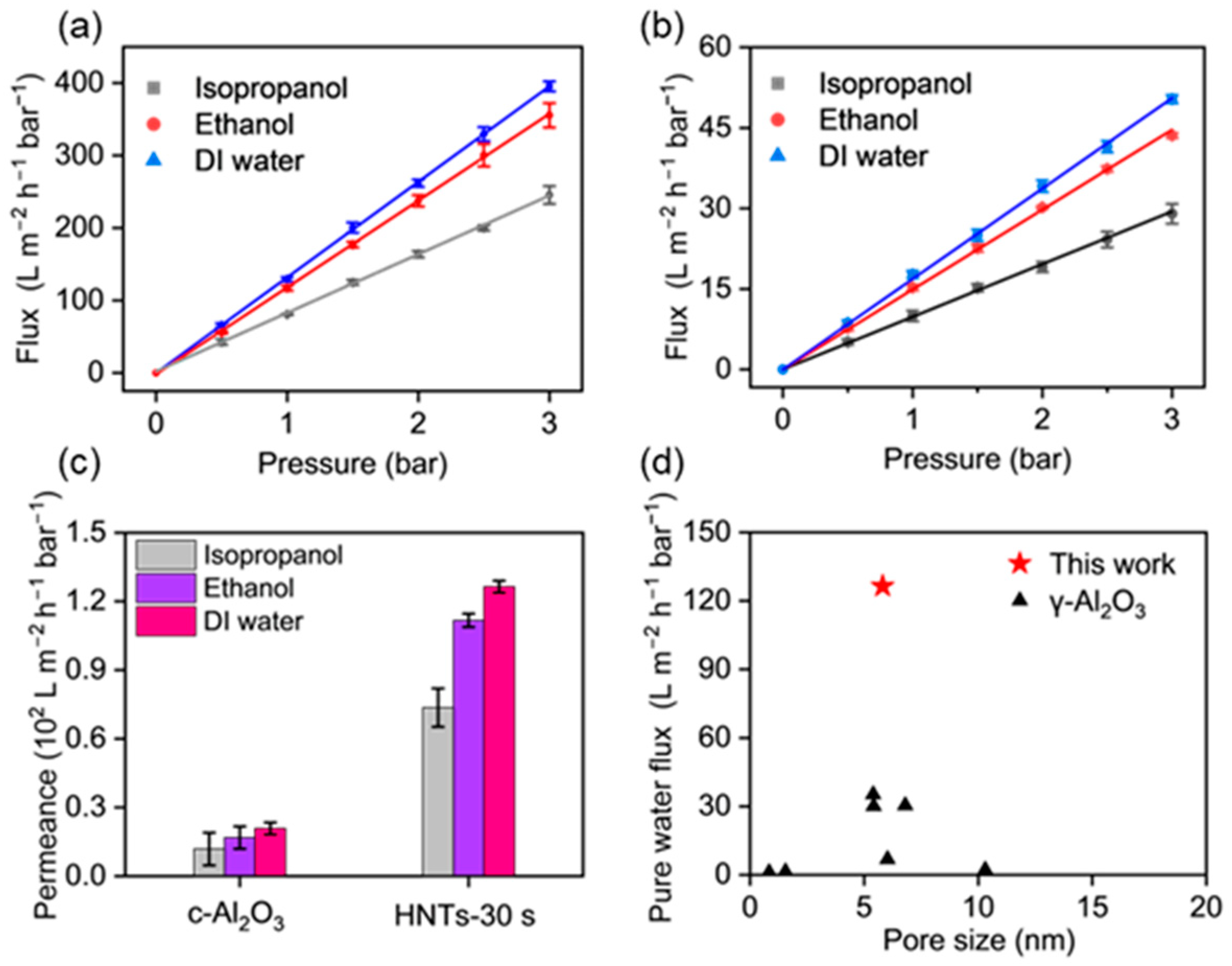
3.3. The Liquid Permeability of the HNTs-Mediated γ-Al2O3 UF Membranes
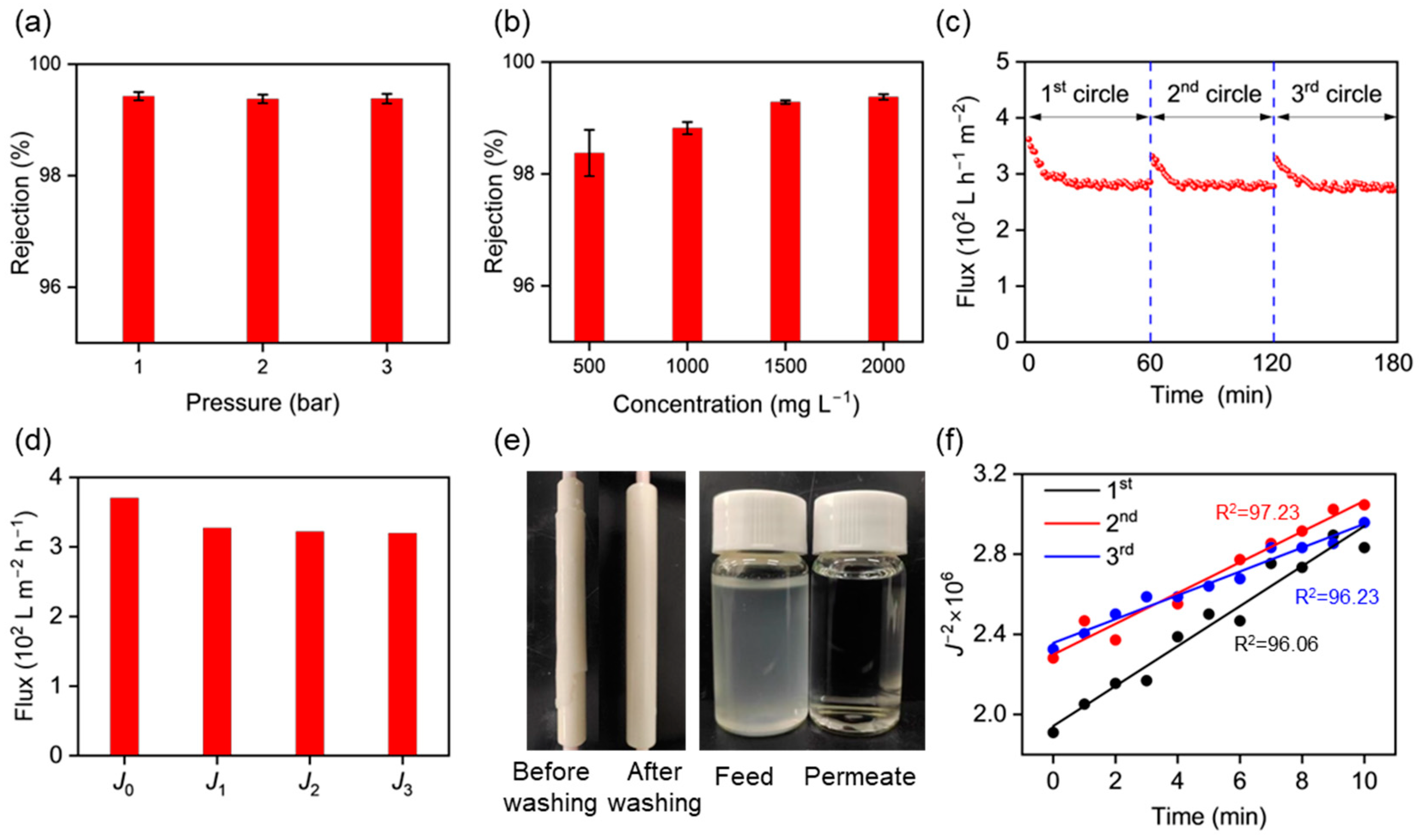
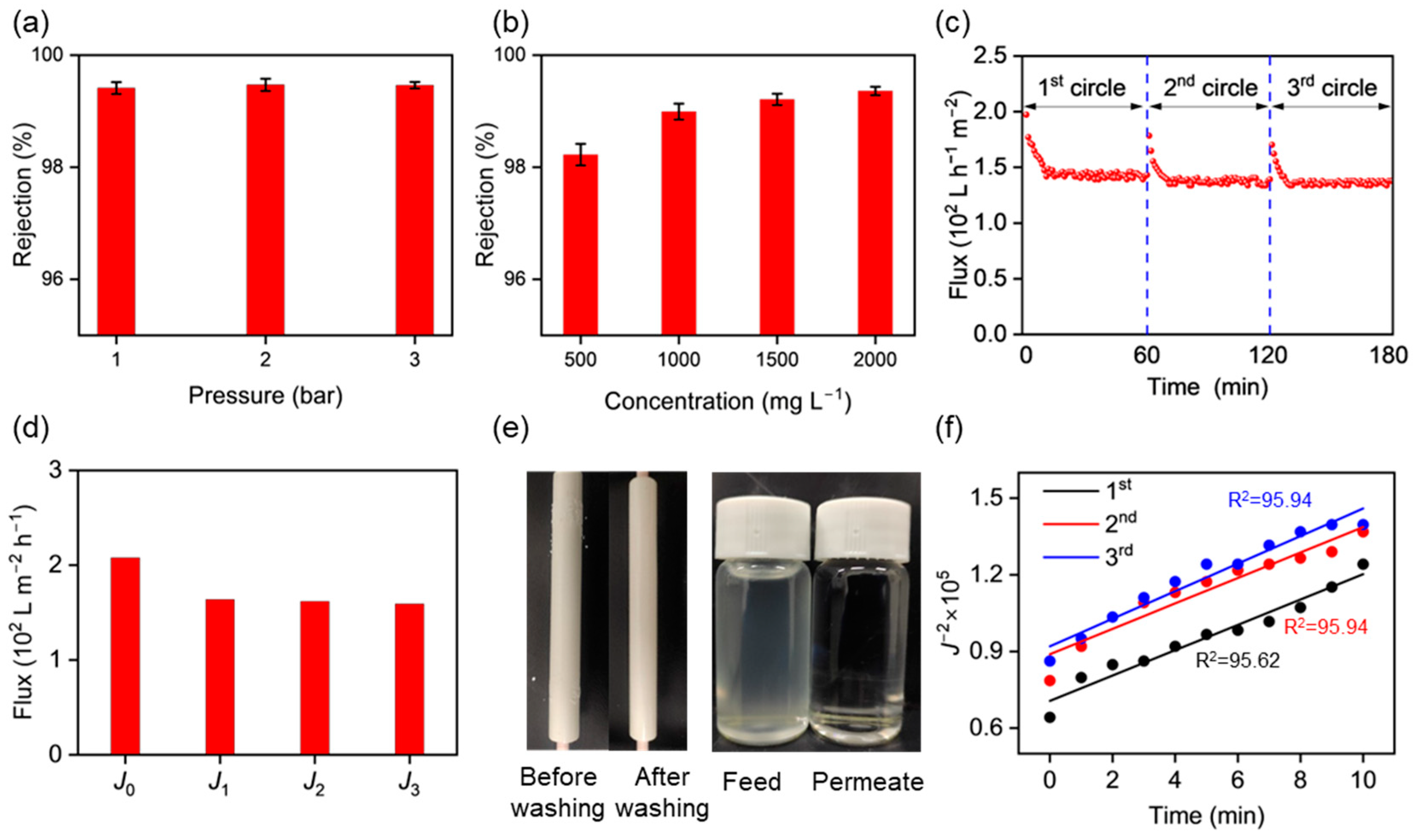
3.4. CMP Waste Liquid Treatment Using the γ-Al2O3 UF Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cha, M.; Boo, C.; Park, C. Simultaneous retention of organic and inorganic contaminants by a ceramic nanofiltration membrane for the treatment of semiconductor wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H. Approaches to Sustainability in Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP): A Review. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2021, 9, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Chemical and physical treatments of chemical mechanical polishing wastewater from semiconductor fabrication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 108, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Ren, L.-F.; Xia, L.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Investigation of fluoride and silica removal from semiconductor wastewaters with a clean coagulation-ultrafiltration process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teow, Y.H.; Chiah, Y.H.; Ho, K.C.; Mahmoudi, E. Treatment of semiconductor-industry wastewater with the application of ceramic membrane and polymeric membrane. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 33, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.-L.; Fane, A.G.; Krantz, W.B.; Lim, T.-T. Emergency water supply: A review of potential technologies and selection criteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3125–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Ceramic-based membranes for water and wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.; Ao, X.; Li, S. Ceramic nanocomposite membranes and membrane fouling: A review. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofs, B.; Ogier, J.; Vries, D.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Cornelissen, E.R. Comparison of ceramic and polymeric membrane permeability and fouling using surface water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Differential natural organic matter fouling of ceramic versus polymeric ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2014, 48, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Rapid removal of lactose for low-lactose milk by ceramic membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, F.; Coetsier, C.; Carretier, E.; Ennahali, M.; Laborie, B.; Serafino, C.; Bulgarelli, F.; Moulin, P. Retreatment of silicon slurry by membrane processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Shorney-Darby, H. What’s the Buzz About Ceramic Membranes? J. AWWA 2011, 103, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, S.M.; Gato-Trinidad, S.; Altaee, A. The application of pressure-driven ceramic membrane technology for the treatment of industrial wastewaters—A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusi, N.F.A.M.; Yusoff, M.H.M.; Seng, O.B.; Marzuki, M.S.; Abdullah, A.Z. Ultrafiltration based on various polymeric membranes for recovery of spent tungsten slurry for reuse in chemical mechanical polishing process. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohanessian, K.; Monnot, M.; Moulin, P.; Ferrasse, J.-H.; Barca, C.; Soric, A.; Boutin, O. Dead-end and crossflow ultrafiltration process modelling: Application on chemical mechanical polishing wastewaters. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 158, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaş-Alkan, A.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z. Solvent recovery from photolithography wastes using cellulose ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 647, 120261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, B.K.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Preparation and characterization of low cost ceramic membranes for micro-filtration applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 42, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.Z.X.; Liu, H. High-flux ceramic membranes with a nanomesh of metal oxide nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 5000–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayati, B.; Bayat, Y.; Charchi, N.; Ejtemaei, M.; Babaluo, A.A.; Haghighi, M.; Drioli, E. Preparation of Crack-Free Nanocomposite Ceramic Membrane Intermediate Layers on α-alumina Tubular Supports. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Ng, T.C.A.; Bao, Y.; Ng, H.Y.; Tan, S.C.; Wang, J. Developing better ceramic membranes for water and wastewater Treatment: Where microstructure integrates with chemistry and functionalities. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Huang, W.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Jin, W.; Fan, Y. Fabrication of Supported Mesoporous TiO2 Membranes: Matching the Assembled and Interparticle Pores for an Improved Ultrafiltration Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.B.; Zhu, H.Y.; Gao, X.P.; Liu, J.W.; Zheng, Z.F. High-Performance Ceramic Membranes with a Separation Layer of Metal Oxide Nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zou, D.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Efficient strategies for engineering high-permeance SiC ceramic membranes for gas/solid filtration: Prefilling method. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 695, 122496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zhou, J.-E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, G. Hydrophilic modification of Al2O3 microfiltration membrane with nano-sized γ-Al2O3 coating. Desalination 2010, 262, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Boo, C.; Song, I.-H.; Park, C. Investigating the potential of ammonium retention by graphene oxide ceramic nanofiltration membranes for the treatment of semiconductor wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; So, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, C. Mxene-based ceramic nanofiltration membranes for selective separation of primary contaminants in semiconductor wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihama, S.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Yoshizuka, K. Separation of tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide using an MFI-type zeolite-coated membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Qiu, M.; Chen, X.; Drioli, E.; Fan, Y. One step co-sintering process for low-cost fly ash based ceramic microfiltration membrane in oil-in-water emulsion treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gu, Q.; Ng, T.C.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, J. Hierarchically porous interlayer for highly permeable and fouling-resistant ceramic membranes in water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Joshi, A.; Wei, W.B.; Zhao, Y.F.; Lvov, Y. Enlargement of Halloysite Clay Nanotube Lumen by Selective Etching of Aluminum Oxide. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7216–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Mohwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Controlled release of Protective Agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S.; Grylewicz, A.; Zgrzebnicki, M.; Darowna, D.; Czyzewski, A. Investigations on the Properties and Performance of Mixed-Matrix Polyethersulfone Membranes Modified with Halloysite Nanotubes. Polymers 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajdak, A.; Skoczylas, N.; Szymanek, A.; Lutynski, M.; Sakiewicz, P. Sorption of CO(2) and CH(4) on Raw and Calcined Halloysite-Structural and Pore Characterization Study. Materials 2020, 13, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: Recent research advances and future prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112–113, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthai, W.; Kanezashi, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Tsuru, T. Nanofiltration performance of SiO2-ZrO2 membranes in aqueous solutions at high temperatures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 168, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Park, J. Evaluation of permeable pore sizes of macroporous materials using a modified gas permeation method. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuru, T.; Takata, Y.; Kondo, H.; Hirano, F.; Yoshioka, T.; Asaeda, M. Characterization of sol–gel derived membranes and zeolite membranes by nanopermporometry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abejón, S.B.I.R.; Puthai, W.; Nagasawa, H.; Tsuru, T. Evaluation of non-commercial ceramic SiO2-ZrO2 and organosilica BTESE membranes in a highly oxidative medium: Performance in hydrogen peroxide. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisaha, W.P.S.; Kanezashia, M.; Nagasawaa, H.; Tsurua, T. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of TiO2-ZrO2 nanofiltration membranes fired at different temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrini, L.; Toja, R.M.; Conconi, M.S.; Requejo, F.G.; Rendtorff, N.M. Halloysite nanotube and its firing products: Structural characterization of halloysite, metahalloysite, spinel type silicoaluminate and mullite. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2019, 234, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgut, E.; Cinar, M.; Terzi, M.; Unver, I.K.; Yildirim, Y.; Ozdemir, O. Evaluation of Different Dispersants on the Dispersion/Sedimentation Behavior of Halloysite, Kaolinite, and Quartz Suspensions in the Enrichment of Halloysite Ore by Mechanical Dispersion. Minerals 2022, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, X.; He, R.R.; Liu, Z.; Lvov, Y.R.; Liu, M. The Horizons of Medical Mineralogy: Structure-Bioactivity Relationship and Biomedical Applications of Halloysite Nanoclay. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 20001–20026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierchala, M.K.; Kadumudi, F.B.; Mehrali, M.; Zsurzsan, T.G.; Kempen, P.J.; Serdeczny, M.P.; Spangenberg, J.; Andresen, T.L.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A. Soft Electronic Materials with Combinatorial Properties Generated via Mussel-Inspired Chemistry and Halloysite Nanotube Reinforcement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9531–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setter, O.P.; Movsowitz, A.; Goldberg, S.; Segal, E. Antibody-Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes for Targeting Bacterial Cells. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 4094–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Park, Y.-I.; Nam, S.E. Effect of coating and surface modification on water and organic solvent nanofiltration using ceramic hollow fiber membrane. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 34020–34027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Guo, W.; Xiao, H. Preparation of γ-Al2O3 membranes for ultrafiltration by reverse micelles-mediated sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22783–22792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Chen, X.; Drioli, E.; Ke, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Facile co-sintering process to fabricate sustainable antifouling silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-enhanced tight ceramic ultrafiltration membranes for protein separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Ni, S.; Yao, H.; Hu, C.; Low, Z.-X.N.; Zhong, Z. Co-sintering of ceramic ultrafiltration membrane with gradient pore structures for separation of dye/salt wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Qiu, M.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y. One-step preparation of high-performance bilayer α-alumina ultrafiltration membranes via co-sintering process. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Membrane Code | Intermediate Layer | Spray-Coating Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Support | - | - |
| c-Al2O3 | α-Al2O3 | - |
| HNTs-10s | HNTs | 10 |
| HNTs-30s | HNTs | 30 |
| HNTs-50s | HNTs | 50 |
| HNTs-70s | HNTs | 70 |
| HNTs-90s | HNTs | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, S.; Chen, D.; Guo, Z.; Li, Q.; Wen, M.; Wang, J.; Guo, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; et al. Halloysite-Nanotube-Mediated High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ultrafiltration Membranes for Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2025, 15, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050130
Geng S, Chen D, Guo Z, Li Q, Wen M, Wang J, Guo K, Wang J, Wang Y, Yu L, et al. Halloysite-Nanotube-Mediated High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ultrafiltration Membranes for Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment. Membranes. 2025; 15(5):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Shining, Dazhi Chen, Zhenghua Guo, Qian Li, Manyu Wen, Jiahui Wang, Kaidi Guo, Jing Wang, Yu Wang, Liang Yu, and et al. 2025. "Halloysite-Nanotube-Mediated High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ultrafiltration Membranes for Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment" Membranes 15, no. 5: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050130
APA StyleGeng, S., Chen, D., Guo, Z., Li, Q., Wen, M., Wang, J., Guo, K., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Yu, L., Li, X., & Li, X. (2025). Halloysite-Nanotube-Mediated High-Flux γ-Al2O3 Ultrafiltration Membranes for Semiconductor Wastewater Treatment. Membranes, 15(5), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15050130







