Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked MXene-Nanocellulose Membrane for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ti3C2Tx Mxene Nanosheets
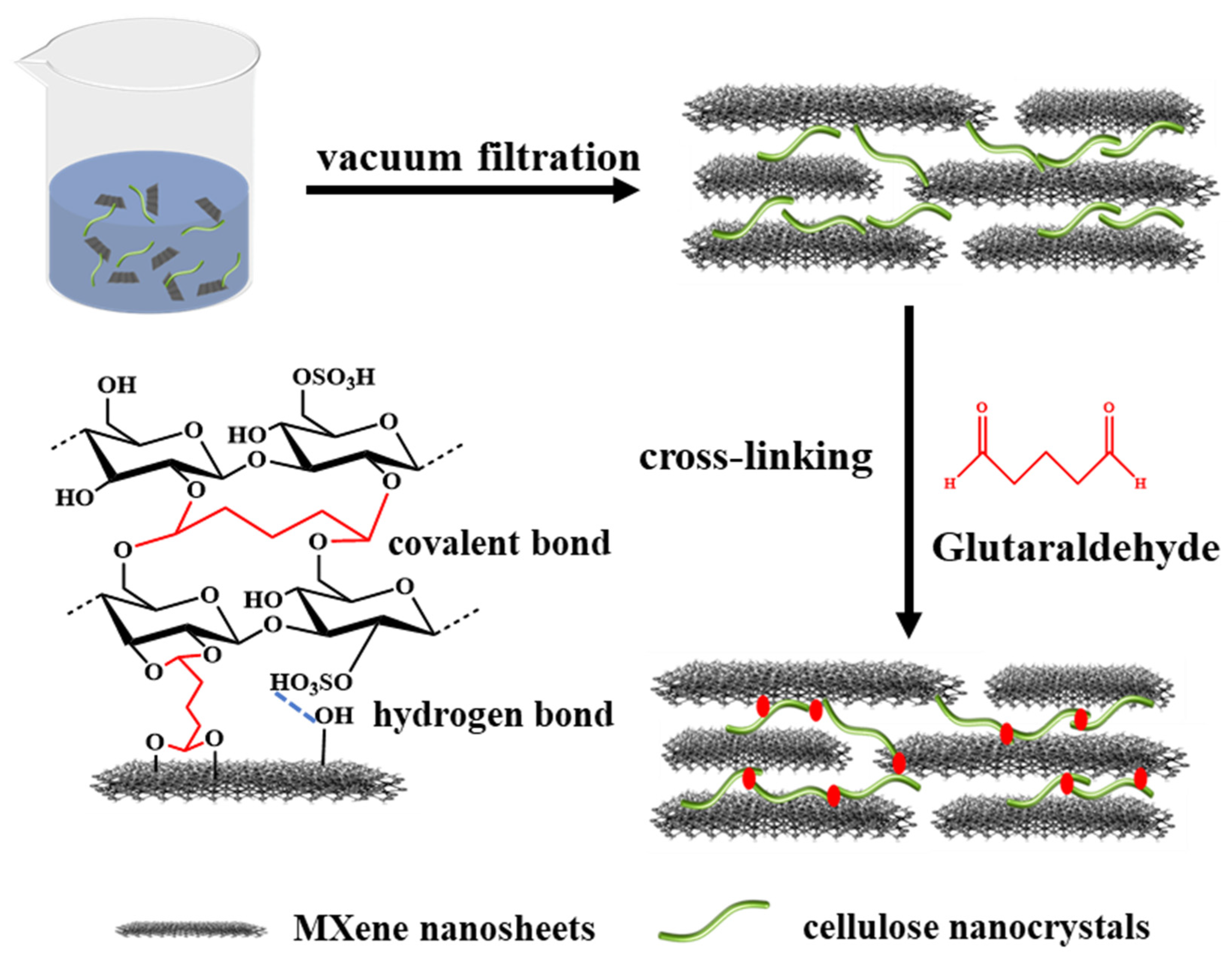
2.3. Fabrication of Mxene Membranes
2.4. Characterizations
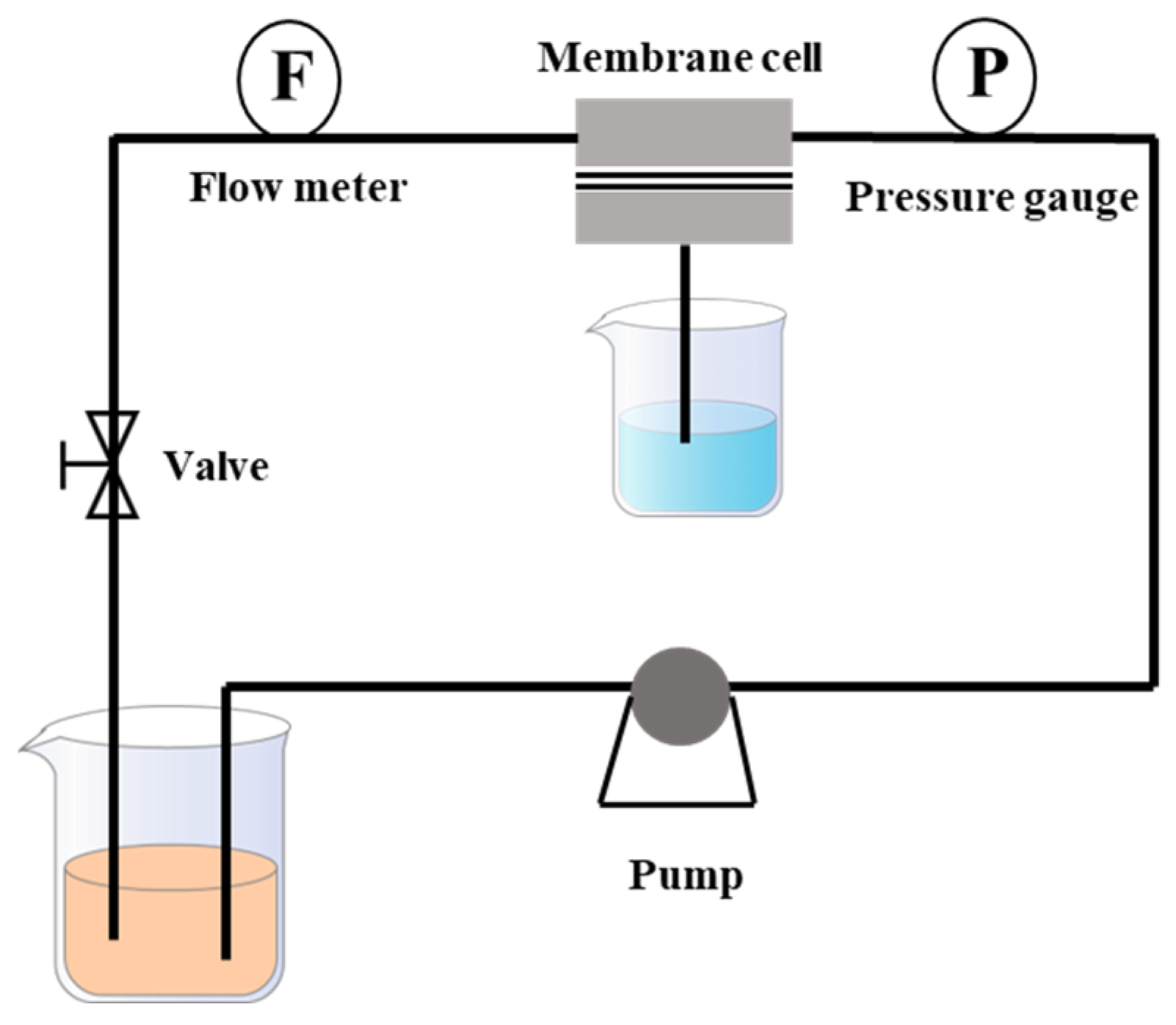
2.5. Membrane Filtration Performance
2.6. Water Uptake Analysis of Membranes
2.7. Calculations of Activation Energy (Ea) of Membranes
2.8. Membrane Stability Performance
2.9. Membrane Anti-Fouling Performance
3. Results
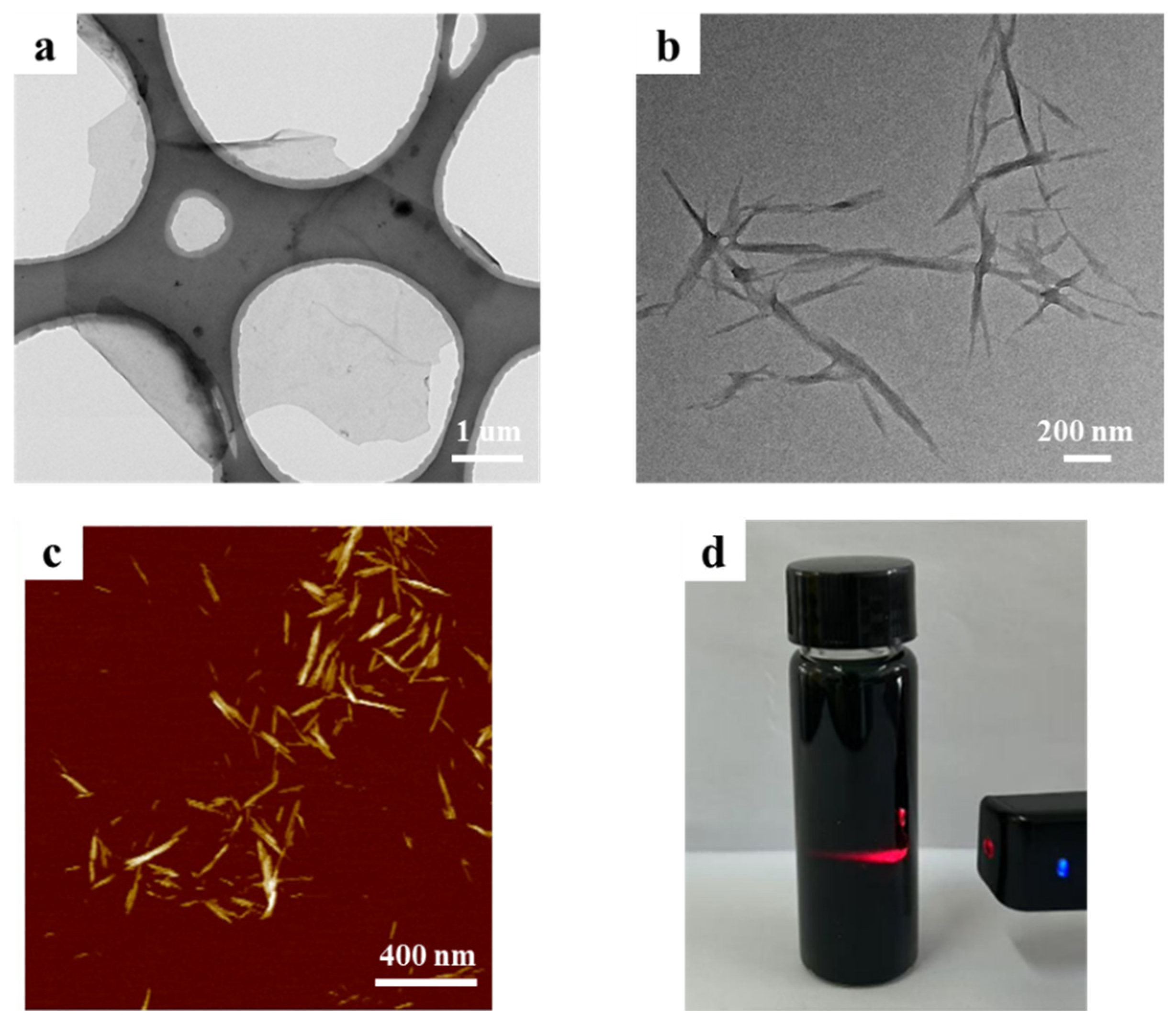
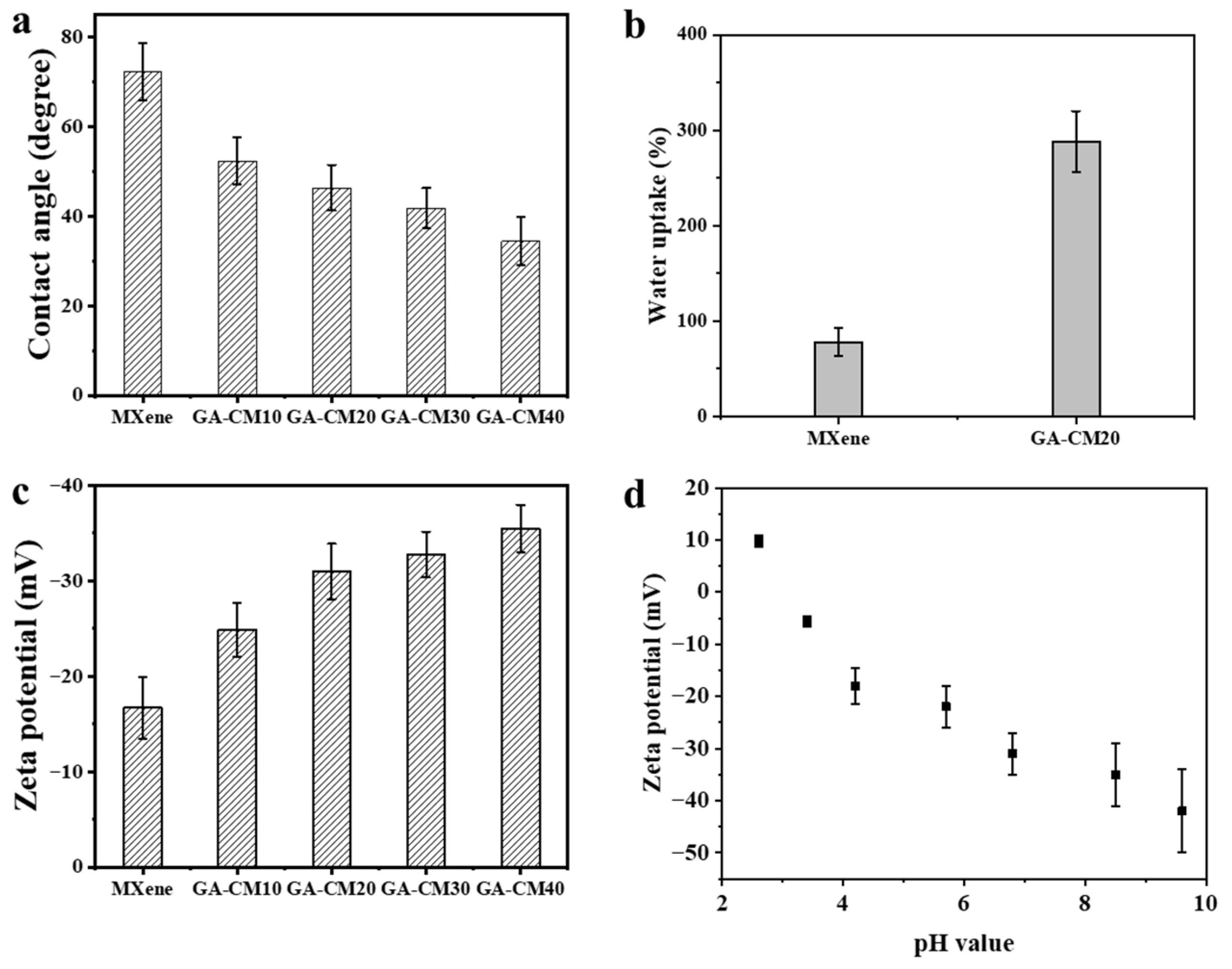
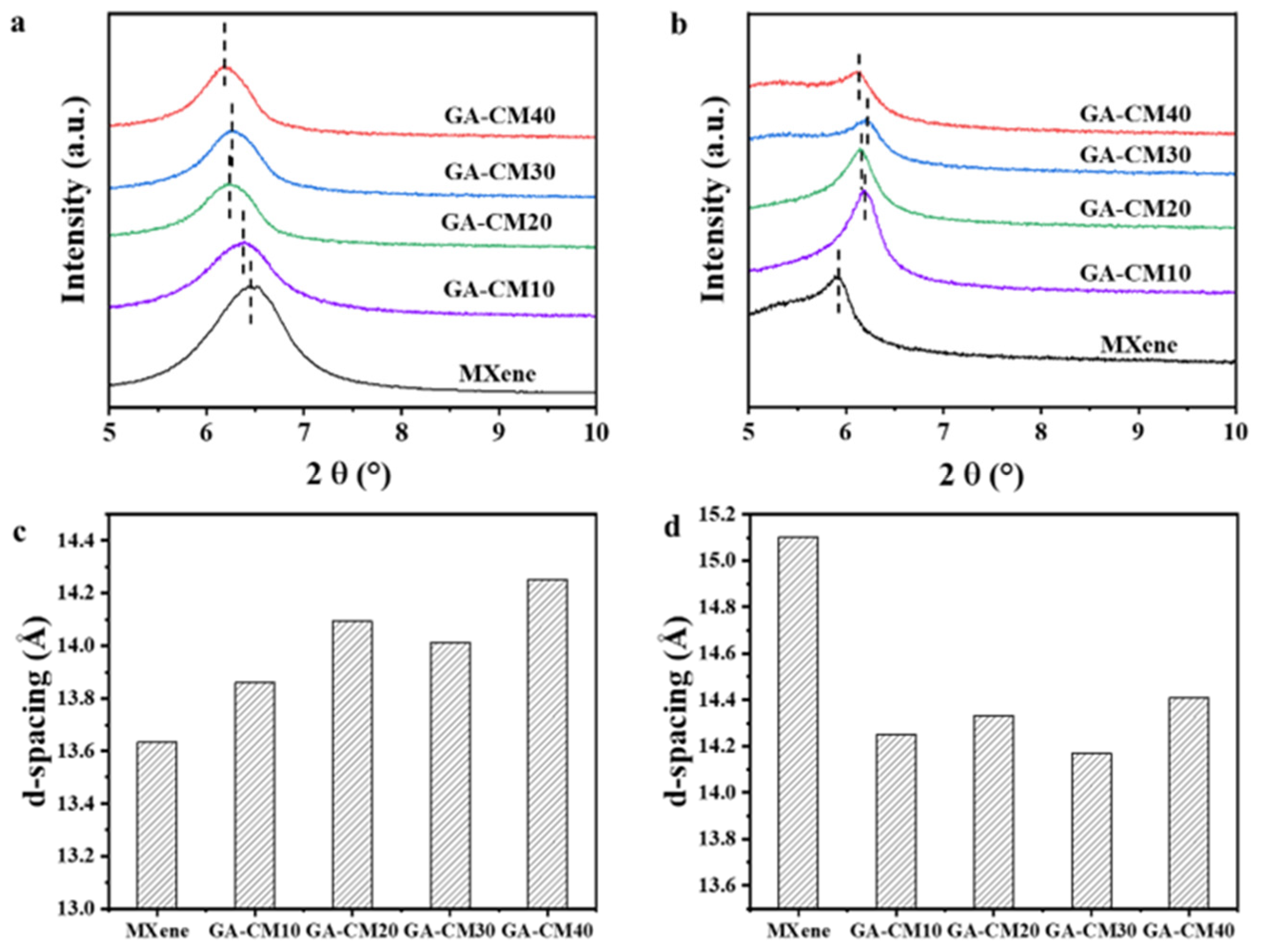
3.1. Characterization of Nanomaterial
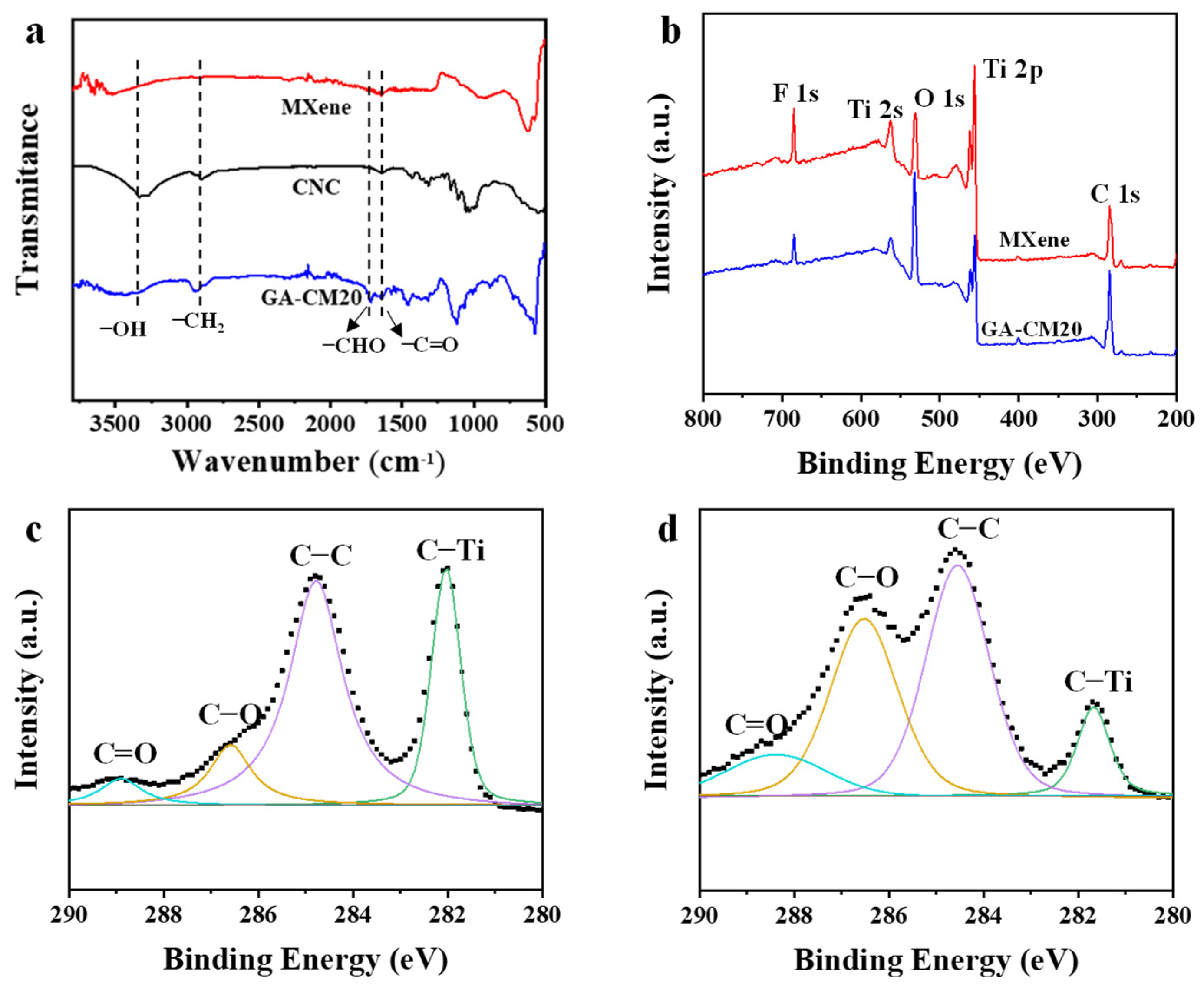
3.2. Characterization of Membranes
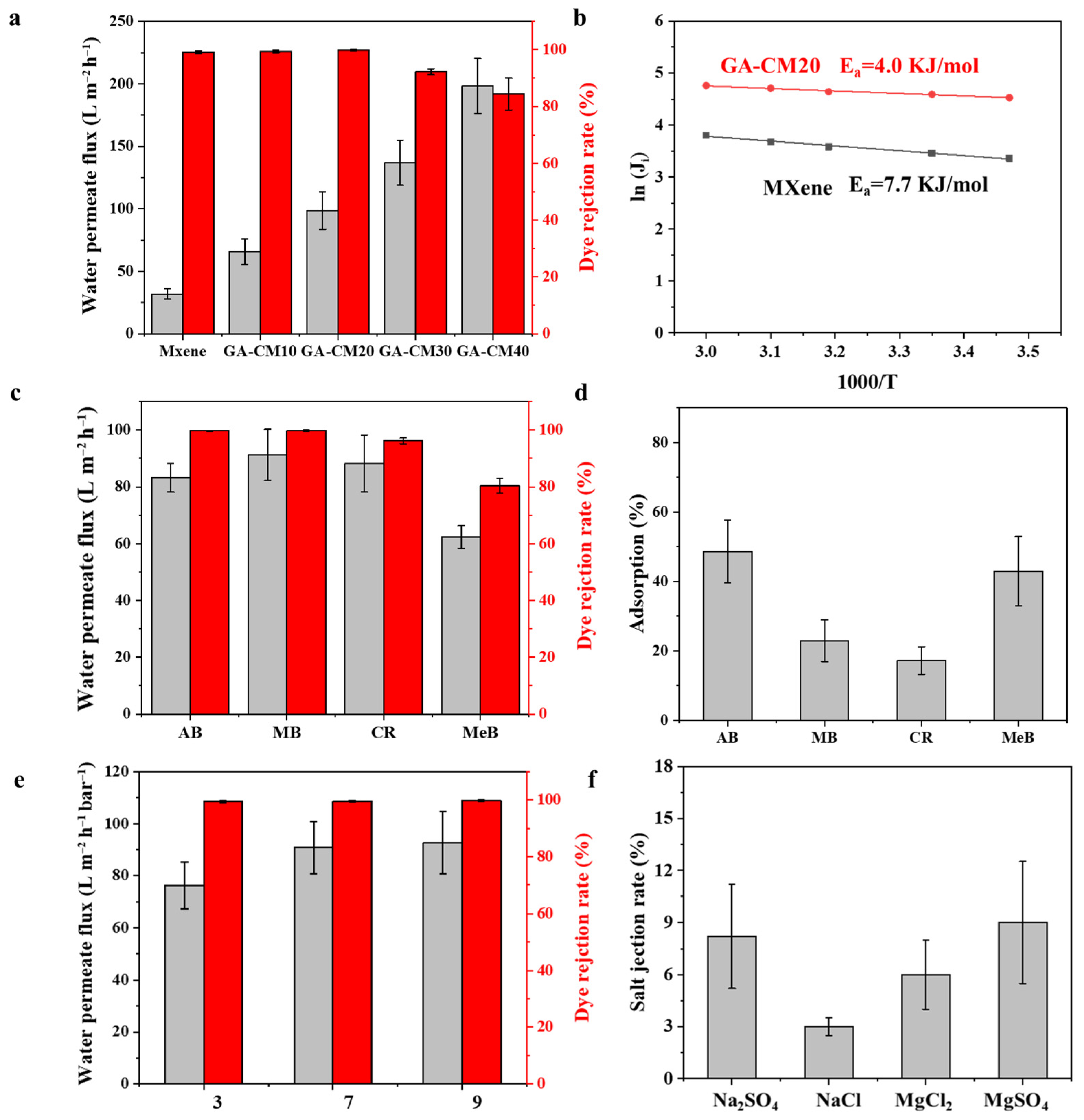
3.3. Separation Performance of Membranes
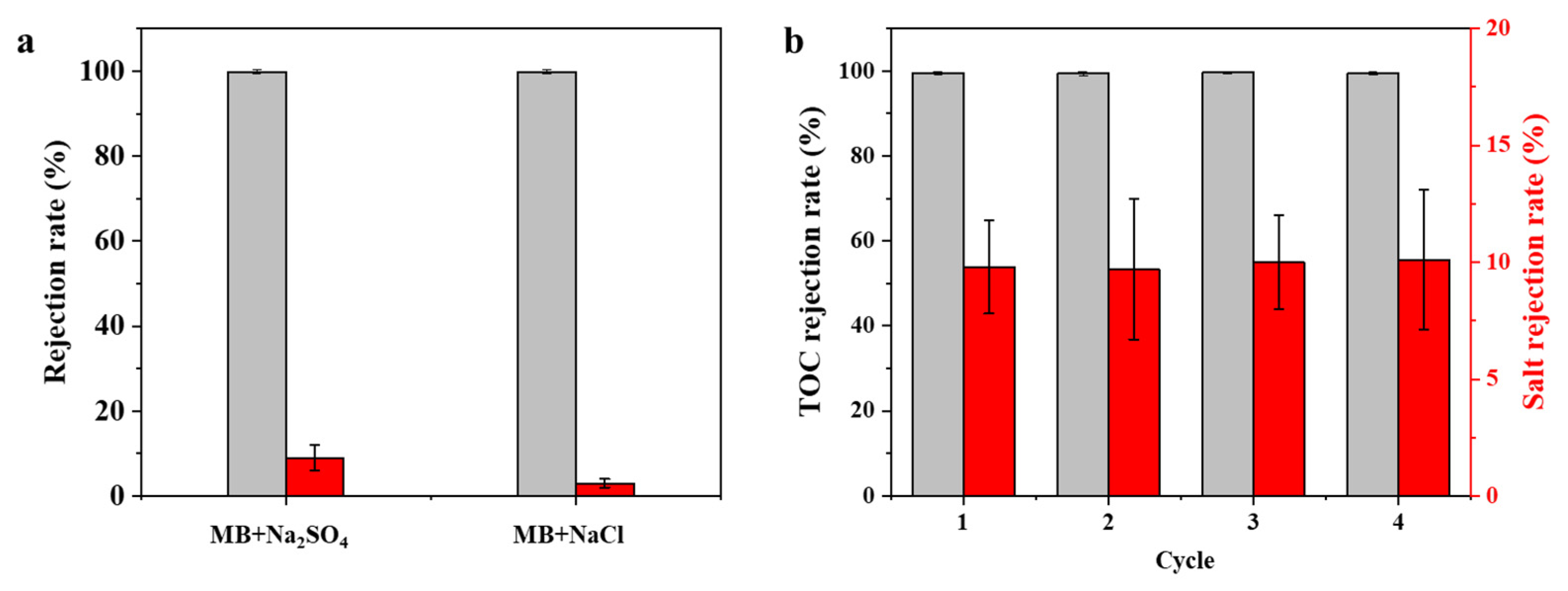
3.4. Long-Term Stability and Anti-Fouling Performance of Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MXene | carbides and nitrides |
| Ti3C2Tx | Titanium carbide |
| CNC | Cellulose nanocrystal |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| COF | Covalent organic framework |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| GA | Glutaraldehyde |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| AB | Alcian blue |
| MB | Methyl blue |
| CR | Congo red |
| MeB | Methylene blue |
| Tris-HCl | Tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane hydrochloride |
References
- Ma, H.; Yu, L.; Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Shen, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Meng, J.; Miao, M.; Zhi, C. Graphene oxide composites for dye removal in textile, printing and dyeing wastewaters: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2025, 23, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuchiwal, S.; Gola, D.; Malik, A. Decolourization of textile effluent using native microbial consortium enriched from textile industry effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Shan, M.; Cheng, Q.; Wen, R.; Liu, S.; Zeng, H.; Yu, J.; Luo, J. Rapid pretreatment strategy to control nanofiltration membrane fouling in recycling of real textile wastewater: Comparison and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chi, M.; Eygen, G.V.; Guan, K.; Matsuyama, H. Comprehensive review of nanofiltration membranes for efficient resource recovery from textile wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Qi, H.; Hou, P.; Liu, K. Resource recovery from textile wastewater: Dye, salt, and water regeneration using solar-driven interfacial evaporation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.; Peng, H.; Li, K. High-performance loose nanofiltration membranes with excellent antifouling properties for dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 708, 123028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; et al. Preparation of a polysulfone loose nanofiltration membrane with gradient structure via hybrid-induced phase separation for the efficient separation of dyes/salts. Desalination 2025, 600, 118506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Jia, H.; Gao, F.; Wang, J. Insights into the performance gap in nanofiltration-based dye separation: Laboratory vs. factory perspectives. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 318, 122133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Sushkova, X.; Chepeleva, A.; Liamin, V.; Mikhailovskaya, O.; Kuzminova, A.; Semenov, K.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Modification approaches of polyphenylene oxide membranes to enhance nanofiltration performance. Membranes 2023, 13, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jin, P.; Croes, T.; Volodine, A.; Yuan, S.; Van der Bruggen, B. Sugar-based membranes for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 619, 118786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Li, H.; Wen, C.; Tian, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; Li, Z. 2D biomimetic membranes constructed by charge assembly and hydrogen bonding for precise ion separation. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2419496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.E.; Goh, K.; Zhang, C.; Yang, E.; Yıldırım, C.; Chuah, C.Y.; Ahunbay, M.G.; Lee, J.; Tantekin-Ersolmaz, Ş.B.; Chen, Y.; et al. MXene materials for designing advanced separation membranes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chang, R.; Qu, H.; Xu, J.; Ma, J. Designing heterogeneous MOF-on-MOF membrane with hierarchical pores for effective water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 658, 120737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, B.; Liang, W.; VahidMohammadi, A.; Karnik, R.; Noy, A.; Wanunu, M. High permeability sub-nanometre sieve composite MoS2 membranes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Sun, J.; He, Y.; Wu, B.; Ge, L.; Pan, J. Ultrathin zwitterionic COF membranes from colloidal 2D-COF towards precise molecular sieving. Water Res. 2025, 274, 123073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, A.; Sonu; Awan, H.T.A.; Singh, K.; Gaurav; Walvekar, R.; Zhao, Z.; Kaushik, A.; Khalid, M.; Chaudhary, V. Emergence of MXene and MXene–polymer hybrid membranes as future- environmental remediation strategies. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Li, R.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nie, L.; Li, Z. Hybrid lignin-intercalated MXene membranes for enhanced water purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 376, 134122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, F.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. MXene nanosheet stacks with tunable nanochannels for efficient molecular separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 132070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Tang, J.; Qin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H. Surface charge modification on 2d nanofluidic membrane for regulating ion transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2208959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Malankowska, M.; Marschall Thostrup, T.; DeMartini, M.; Khajavi, P.; Guo, H.; Storm Pedersen, L.; Pinelo, M. Comparison of 2D and 3D materials on membrane modification for improved pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 285, 119638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, F.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Additive-mediated intercalation and surface modification of MXenes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 2972–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Tian, M.; Zheng, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Ion sieving by a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx alginate lamellar membrane with stable interlayer spacing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Feng, X. Mechanically strong MXene/Kevlar nanofiber composite membranes as high-performance nanofluidic osmotic power generators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B.; Zhang, X. Two-dimensional MXene membranes with biomimetic sub-nanochannels for enhanced cation sieving. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, G.; Liu, Z.-Q. Self-assembly enabled nano-intercalation for stable high-performance MXene membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xu, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ji, W.; Nian, P.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y. Amino acid-bonded Ti3C2Tx MXene nanofiltration membranes with superior antifouling property for enhanced water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 693, 122384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Yang, J. Covalently bridged MXene/COF hybrid membrane toward efficient dye separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 349, 127908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhao, D.L.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Kong, N.; Han, L.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Tang, C.; Chung, T.-S. Titanium oxide nanotubes intercalated two-dimensional MXene composite membrane with exceptional antifouling and self-cleaning properties for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Shen, Z.; Xia, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Metal-polyphenol cross-linked titanium carbide membranes with stable interlayer spacing for efficient wastewater treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yao, Y.; Ju, J.; Yuan, H.; Tan, Y. Green, Cross-Linked, Curcumin-loaded konjac glucomannan/cellulose nanocrystal nanofiber membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 5003–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Afolabi, M.A.; Xiao, D.; Chen, Y. Incorporation of cellulose nanocrystals into graphene oxide membranes for efficient antibiotic removal at high nutrient recovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14102–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbey-Unal, B.; Balcik, C.; Yuan, S.; Van der Bruggen, B. Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals-incorporated dense Janus membranes for enhanced desalination and oily saline wastewater treatment via membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Ding, A.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Application of cellulose nanocrystals in water treatment membranes: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. High-performance and stable two-dimensional MXene-polyethyleneimine composite lamellar membranes for molecular separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10237–10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Su, Y.; Cao, L.; Yu, Q.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, K.; He, M.; Jiang, Z. Metal-coordinated sub-10 nm membranes for water purification. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, P.; Li, P.; Ji, Y.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Designing biomimic two-dimensional ionic transport channels for efficient ion sieving. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5209–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L. Enhanced flux and fouling resistance forward osmosis membrane based on a hydrogel/MOF hybrid selective layer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, Z.; Rastgar, M.; Mohseni, M.; Firouzjaei, M.D.; Dilokekunakul, W.; Anasori, B.; Vecitis, C.D.; Keller, R.; Wessling, M.; Elliott, M.; et al. Electro-conductive Ti3C2 MXene multilayered membranes: Dye removal and antifouling performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liao, S.; Qi, F.; Liu, R.; Xiao, T.; Hu, J.; Li, K.; Wang, R.; Min, Y. Direct deposition of two-dimensional MXene nanosheets on commercially available filter for fast and efficient dye removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J. MXene nanosheet tailored bioinspired modification of a nanofiltration membrane for dye/salt separation. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Héraly, F.; Chang, J.; Khorsand Kheirabad, A.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. A transport channel-regulated MXene membrane via organic phosphonic acids for efficient water permeation. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 6245–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.-Y.; Fan, T.-T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.-H.; Lin, J.-H.; Long, Y.-Z. High performance GO/MXene/PPS composite filtration membrane for dye wastewater treatment under harsh environmental conditions. Compos. Commun. 2022, 29, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Membrane | MXene Loading (mg) | CNC Loading (mg) | CNC/MXene Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MXene | 1.0 | 0 | 0 |
| GA-CM10 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 10 |
| GA-CM20 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 20 |
| GA-CM30 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 30 |
| GA-CM40 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 40 |
| Membrane | Water Permeate Flux (LMH/bar) | Dye Rejection Rate | FRR | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-CM20 | 90.8 | MB: 99.6% CR: 97.2% | BSA 96% | This work |
| MCE/MXene | 44.97 | MeB: 100.0% | N * | [39] |
| MXene/PEI/TMC | 38.2 | CR: 99.7% | N * | [40] |
| MXene/enzymatic hydrolysis lignin | 61.22 | MB:78.5% | Methylene blue 90.33% | [17] |
| MXene/PEI | 20.9 | CR: 99.42% | N * | [18] |
| MXene/phytic acid | 510 | CR:99.7% | N * | [41] |
| GO/MXene-PPS | 52.8 | MB:99.9% | Methyl blue 85% | [42] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Qiu, M. Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked MXene-Nanocellulose Membrane for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation. Membranes 2025, 15, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100287
Zhang Y, Qiu M. Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked MXene-Nanocellulose Membrane for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation. Membranes. 2025; 15(10):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100287
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, and Ming Qiu. 2025. "Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked MXene-Nanocellulose Membrane for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation" Membranes 15, no. 10: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100287
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Qiu, M. (2025). Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked MXene-Nanocellulose Membrane for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation. Membranes, 15(10), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15100287






