System Dynamics Modeling of Scale Formation in Membrane Distillation Systems for Seawater and RO Brine Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
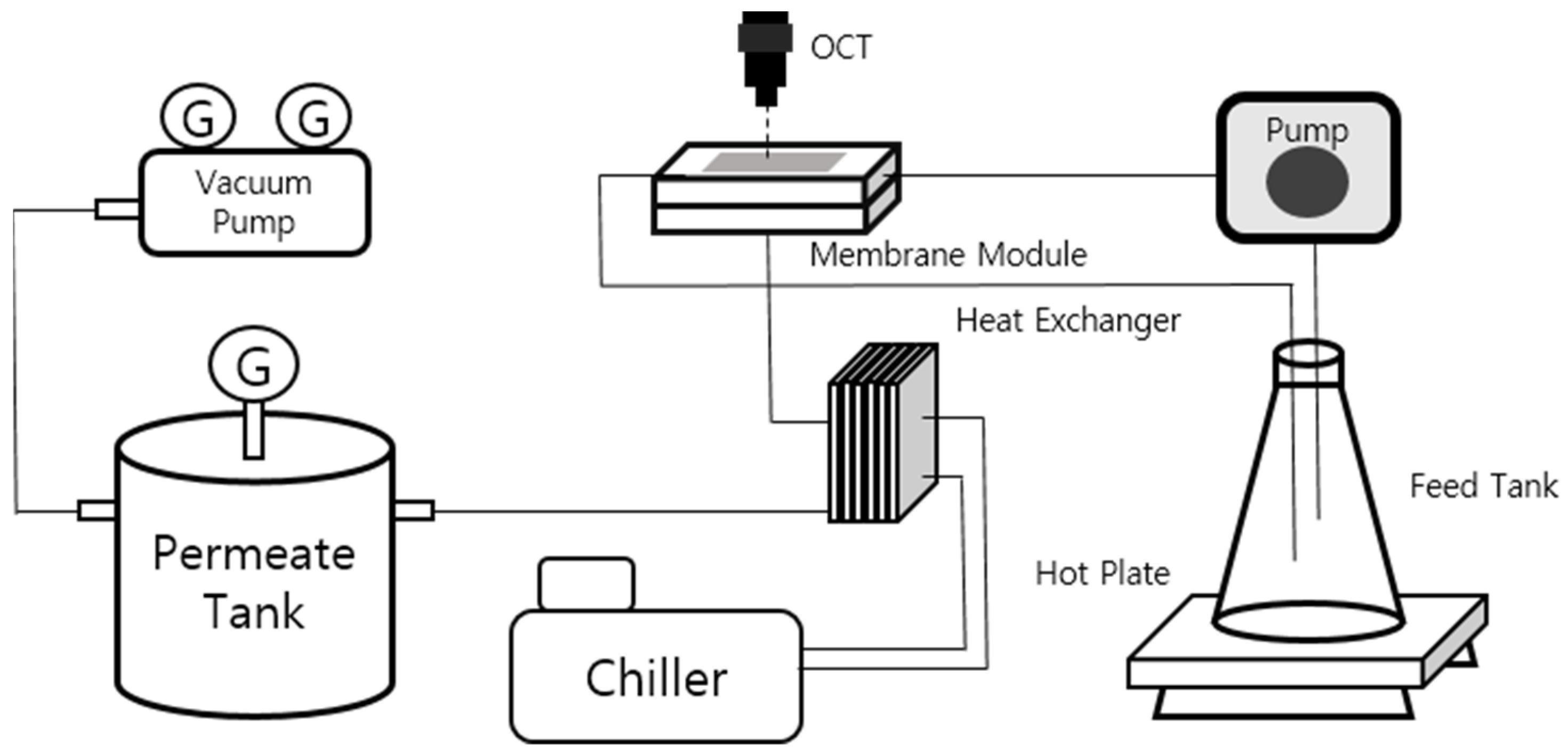
2.1. Laboratory VMD System
2.2. Analysis of Membrane Surface
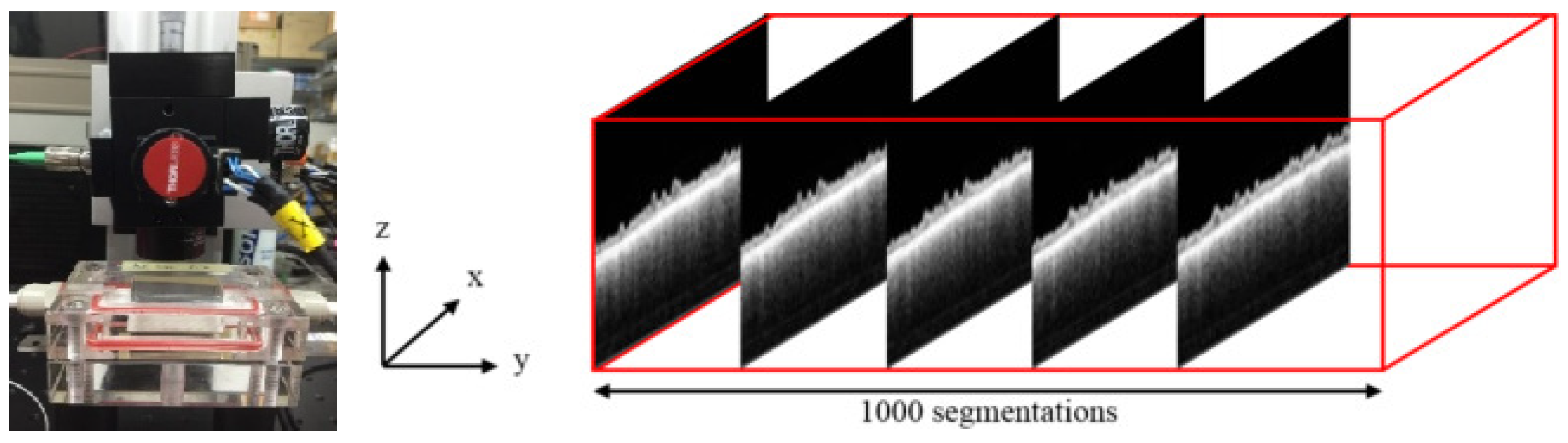
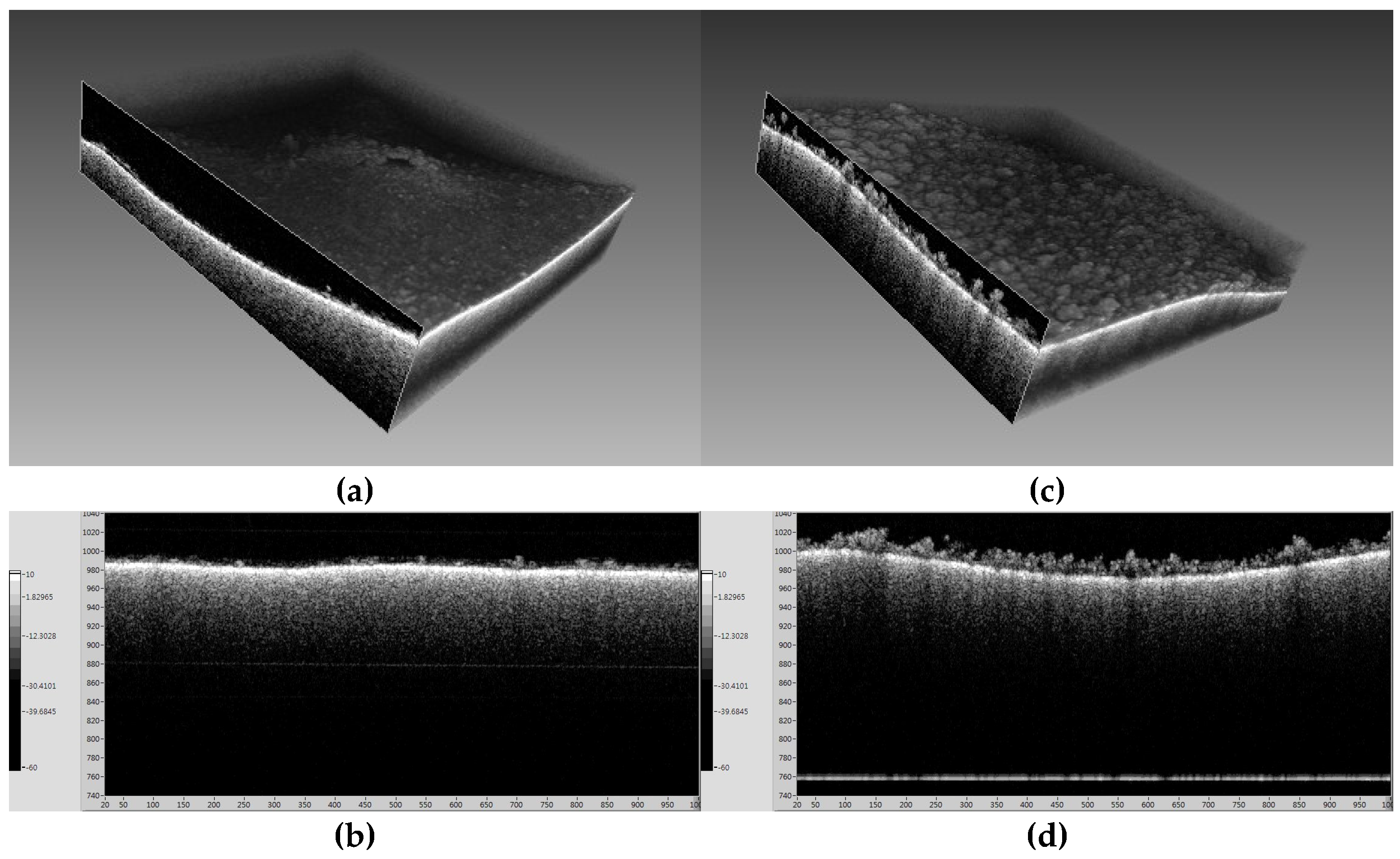
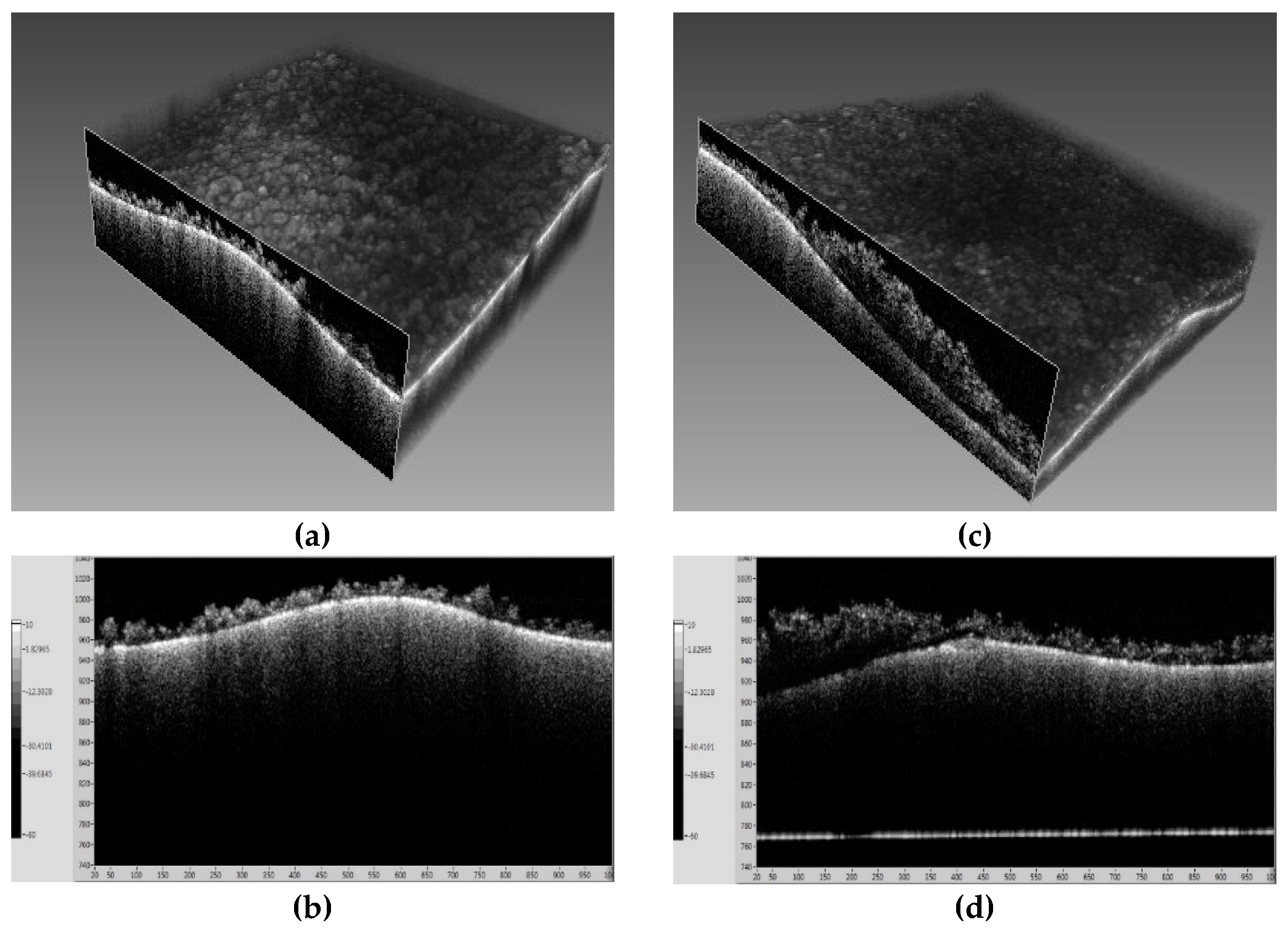
2.2.1. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
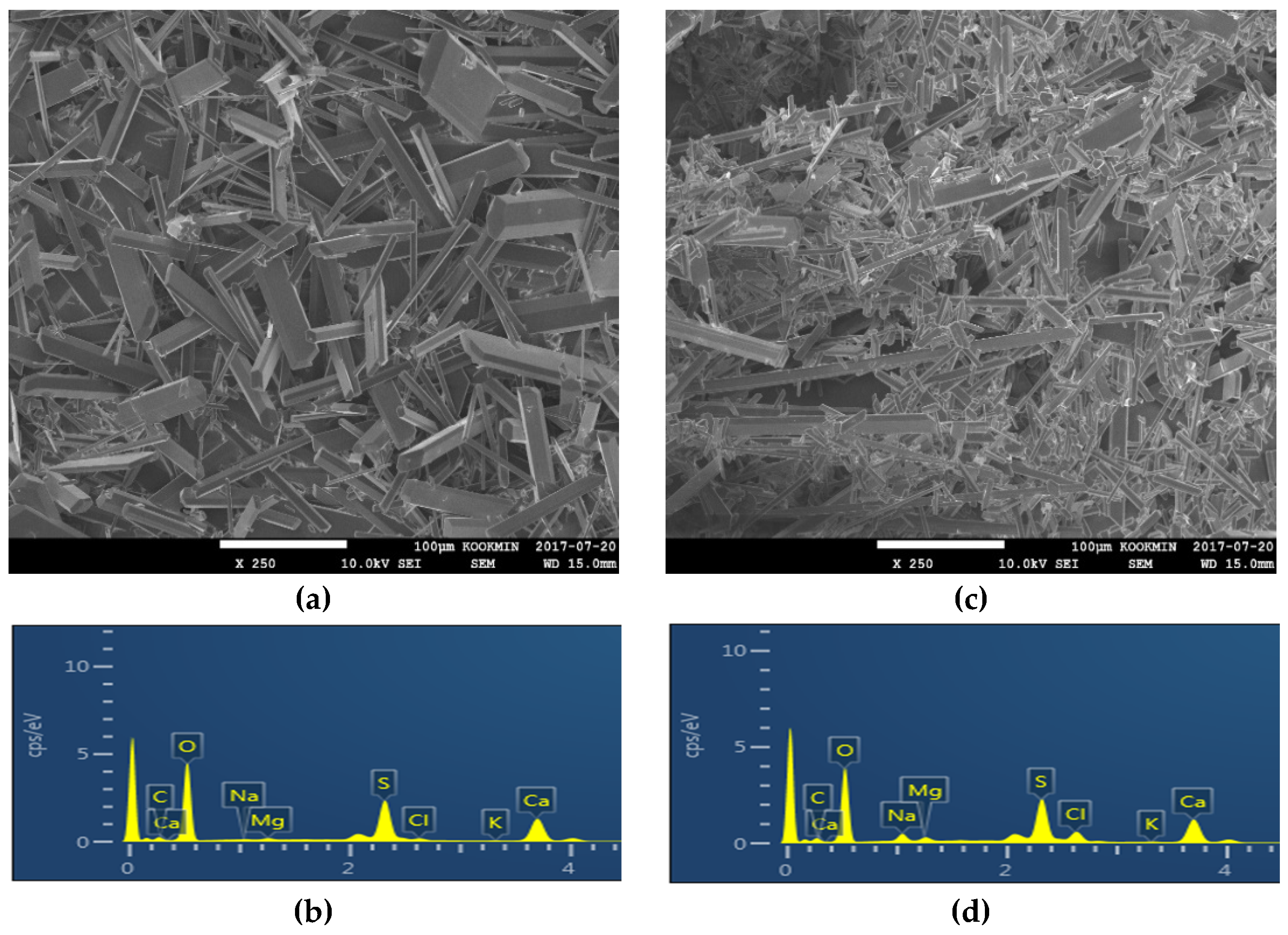
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.3. Feed Solution
3. Model Development
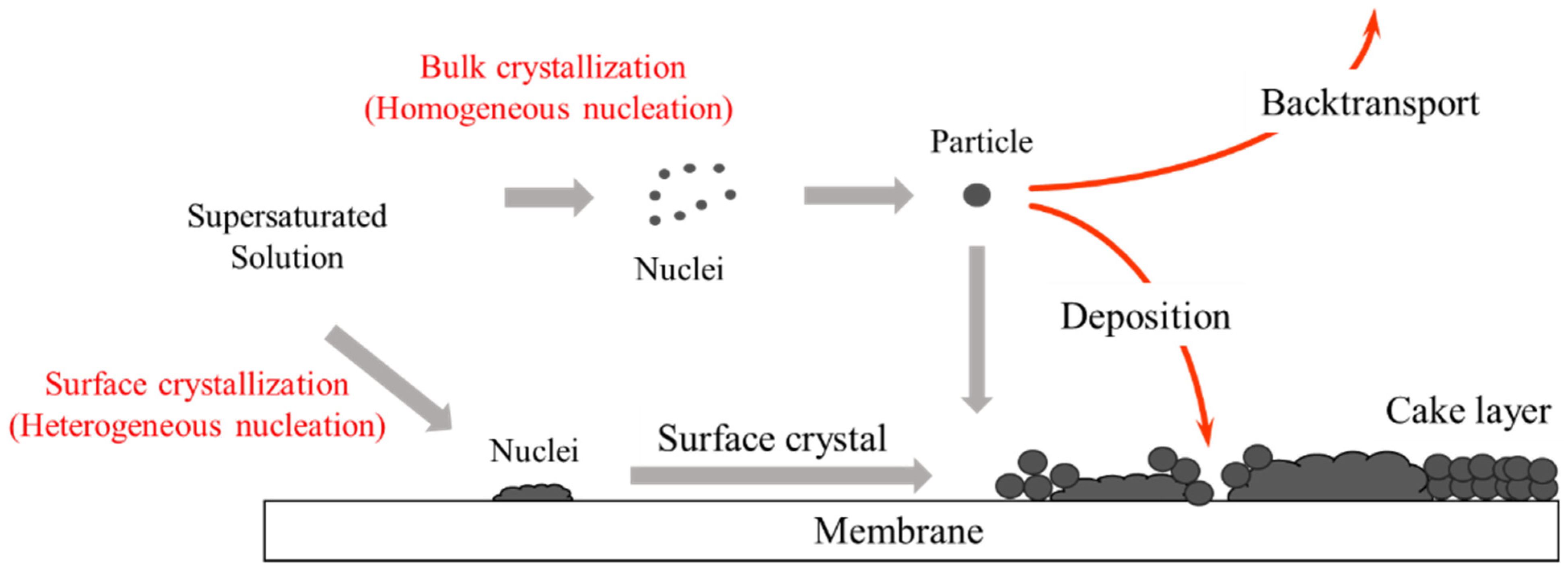
3.1. Mechanisms for the Scale Formation
3.2. Estimation of Wall Concentration
3.3. Induction Time and Crystal Growth Rate
3.4. Solution Method
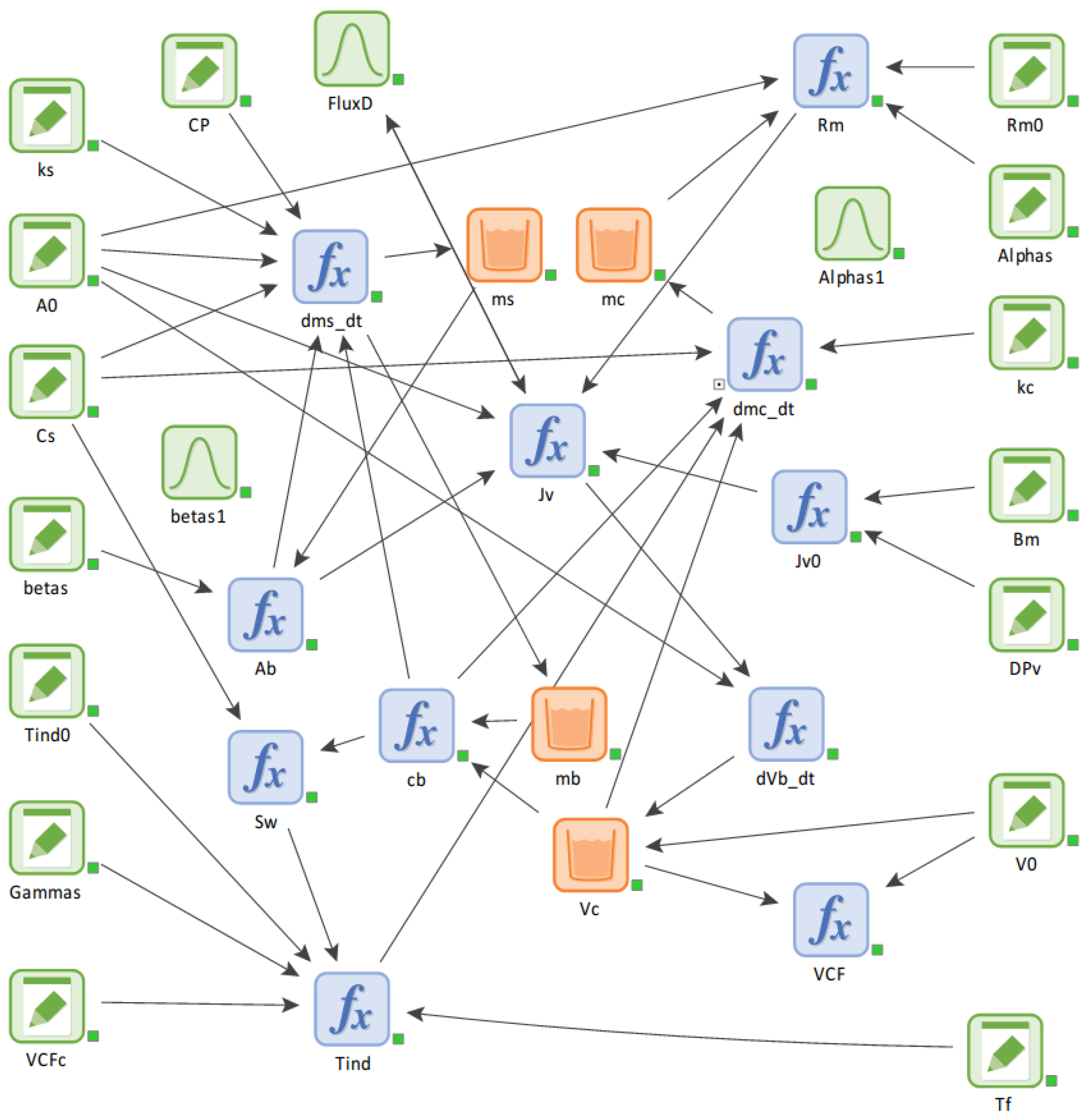
3.5. Procedures of System Dynamics Modeling
4. Results and Discussion
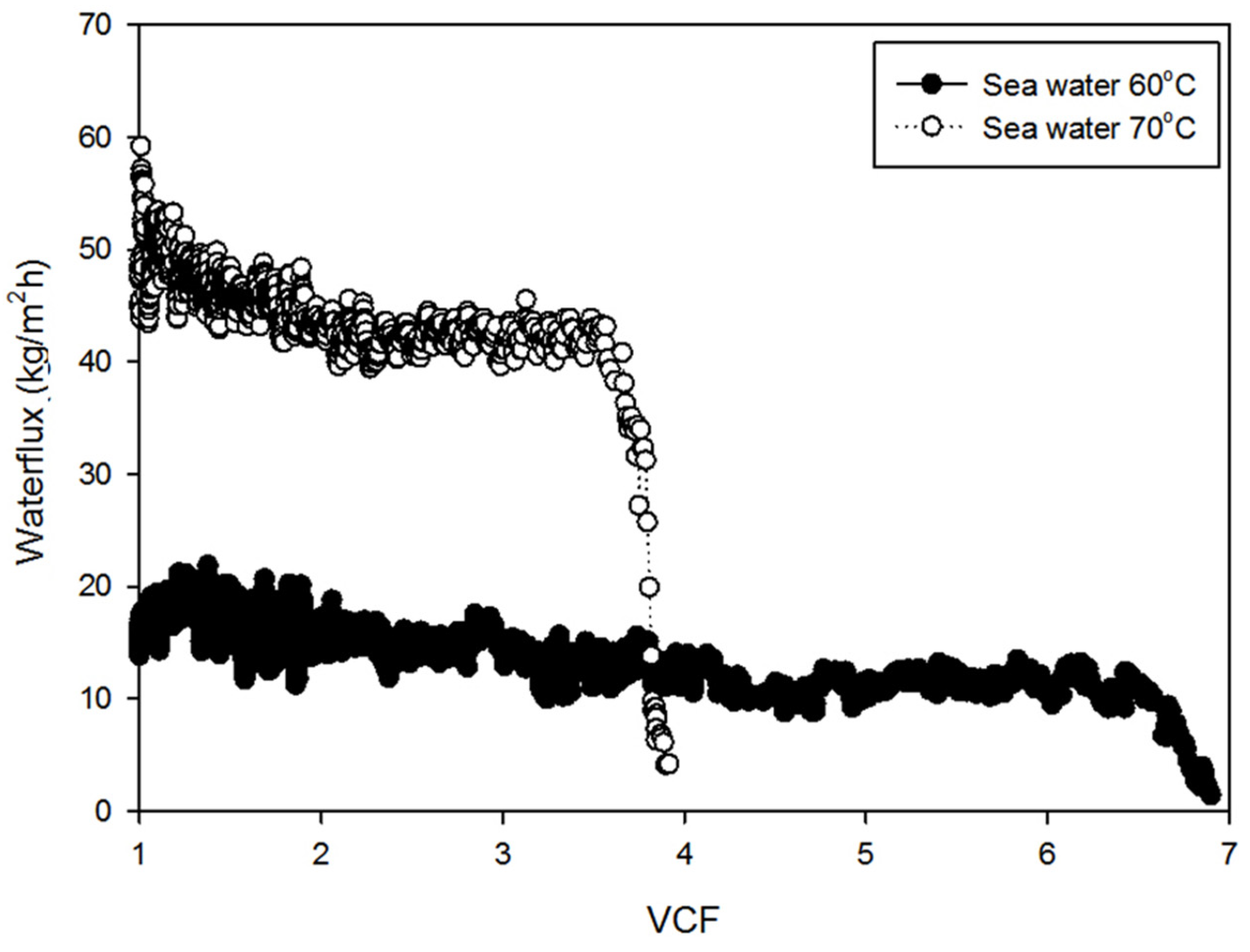
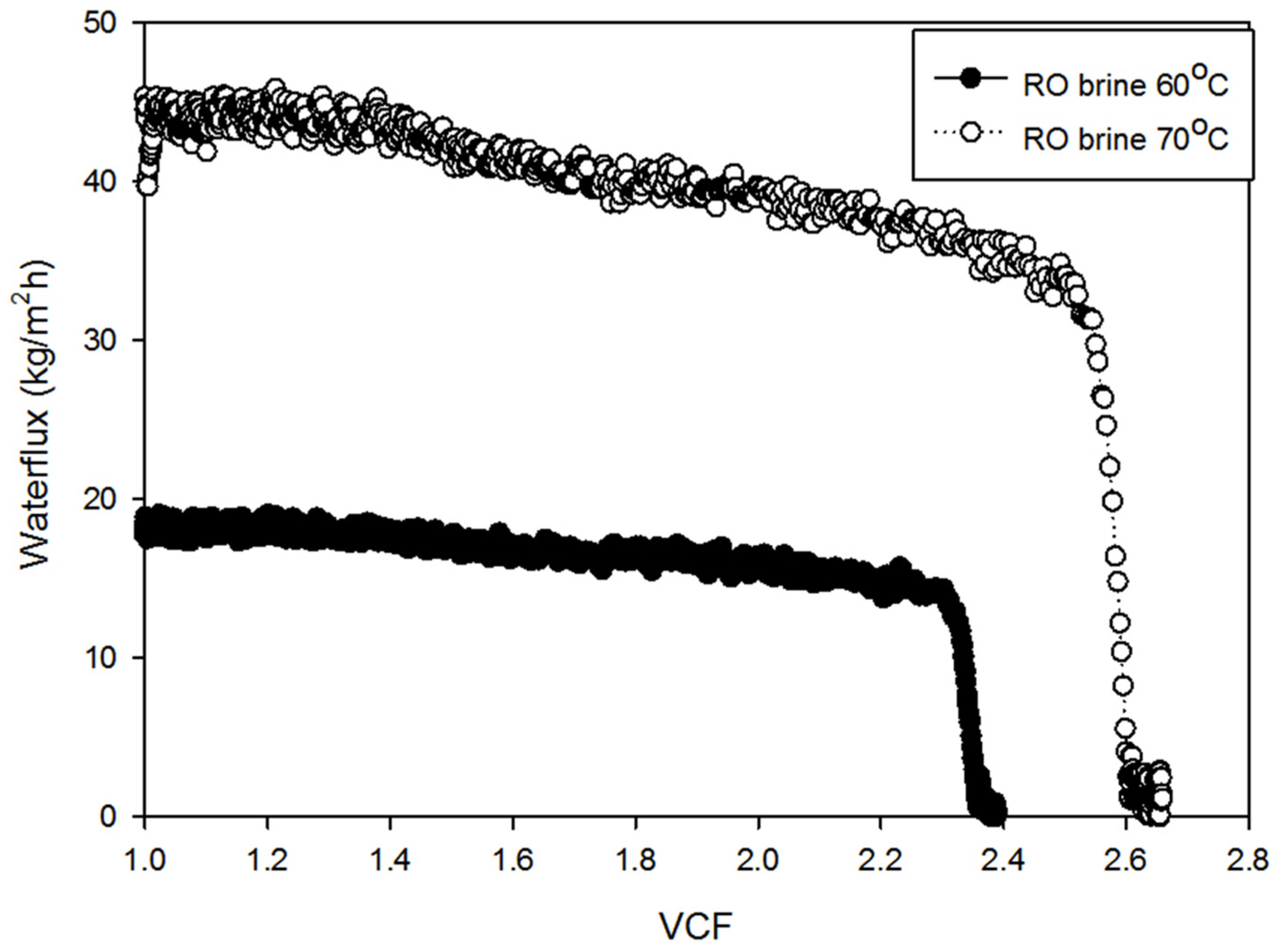
4.1. Experimental Results and Flux Decline Analysis
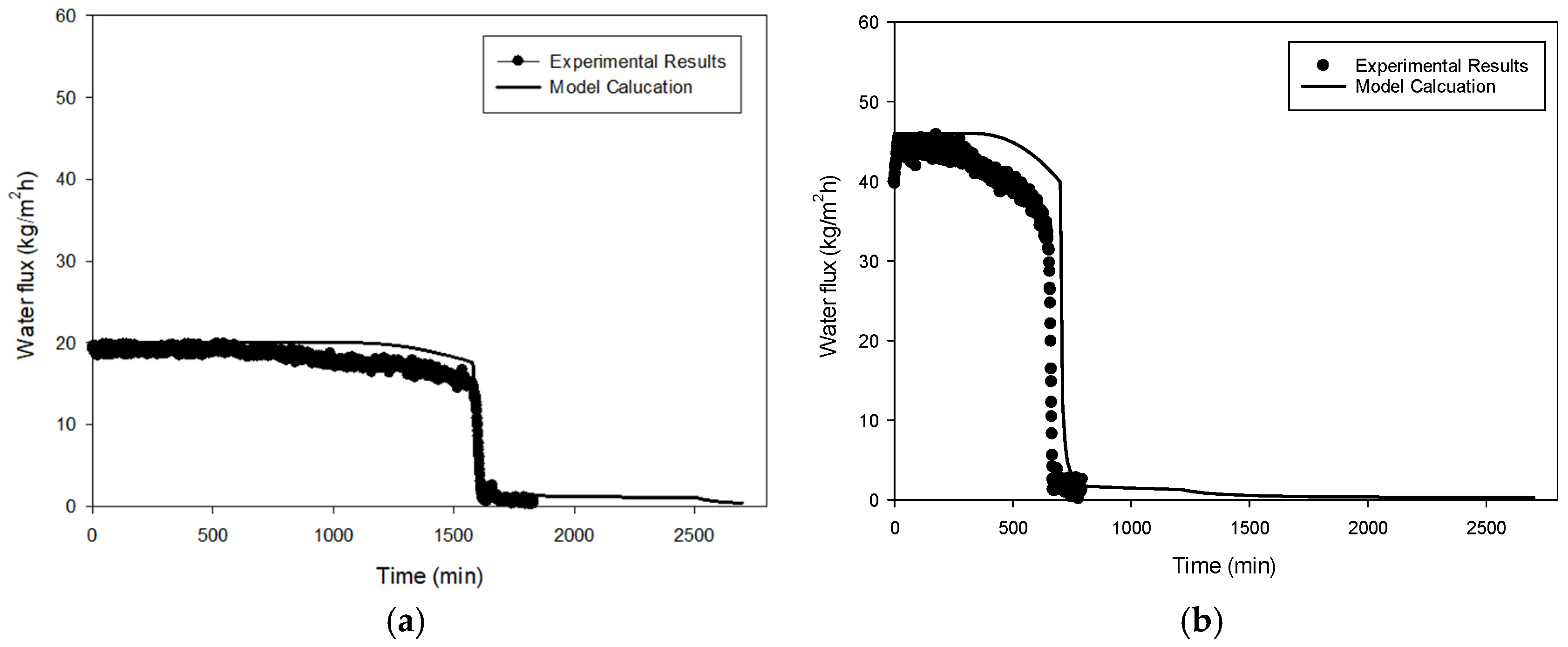
4.2. Comparison of Model Calculations with Experimental Results
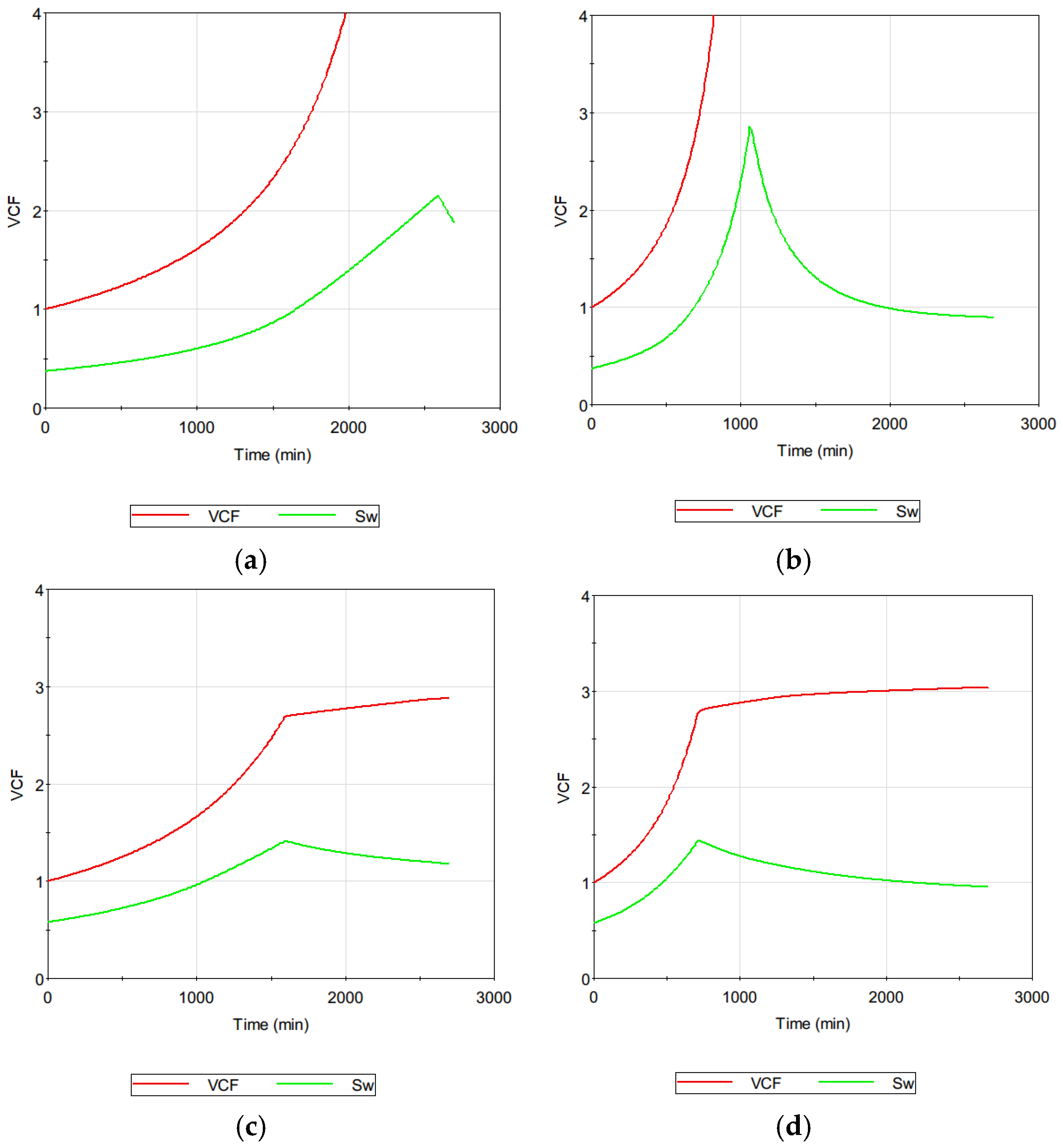
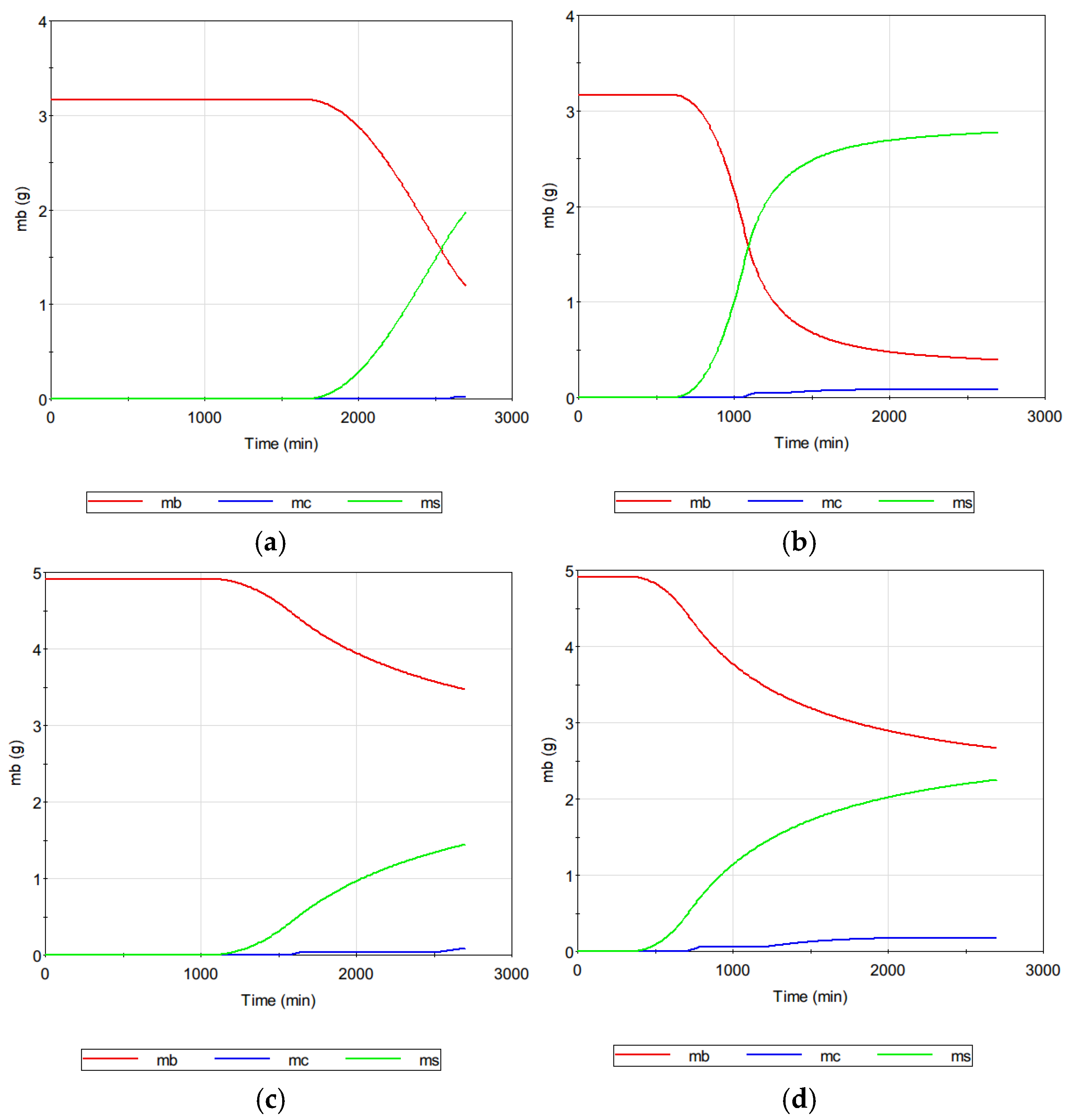
4.3. Theoretical Analysis of Scale Formation in MD System
5. Conclusions
- The experimental results indicate that the flux decline in MD systems is controlled by two primary mechanisms: surface crystal formation on the membrane surface and bulk crystal formation in the solution phase. The initial decrease in flux is linked to surface crystal formation on the membrane, whereas the later and more significant flux drop is caused by bulk crystal formation occurring in the solution.
- The system dynamics model was developed by incorporating complex interactions among variables and parameters. Despite inherent experimental variability and random errors, the model demonstrated strong predictive capabilities by accurately reproducing the observed trends in experimental flux decline. This suggests that the model is robust and reliable for predicting fouling behavior in MD systems.
- One of the strengths of the model is its ability to provide detailed information on hidden variables such as the supersaturation ratio (Sw), mass of dissolved solutes (mb), surface crystal mass (ms), and cake crystal mass (mc). These variables are challenging to measure directly in experimental settings but are crucial for understanding the underlying fouling mechanisms. Such insights are expected to guide the development of more effective fouling-control strategies for MD applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, S. World’s largest desalination plant begins operating in Israel. Membr. Technol. 2005, 2005, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Chen, H.-L.; Gao, C.-J. Progress and prospects of seawater desalination in China. Desalination 2005, 182, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S. Japan’s largest sea-water desalination plant uses Nitto Denko membranes. Membr. Technol. 2005, 2005, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.; El-Manharawy, S. Economics of seawater RO desalination in the Red Sea region, Egypt. Part 1. A case study. Desalination 2003, 153, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avlonitis, S.; Kouroumbas, K.; Vlachakis, N. Energy consumption and membrane replacement cost for seawater RO desalination plants. Desalination 2003, 157, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegler, K.S.; El-Sayed, Y.M. The energetics of desalination processes. Desalination 2001, 134, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutaz, I.S. A comparative study of RO and MSF desalination plants. Desalination 1996, 106, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termpiyakul, P.; Jiraratananon, R.; Srisurichan, S. Heat and mass transfer characteristics of a direct contact membrane distillation process for desalination. Desalination 2005, 177, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Wang, J.; Hou, D.; Yin, Z.; Luan, Z. Effect of microwave irradiation on vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Duke, M.; Xie, Z.; Gray, S. Performance of asymmetric hollow fibre membranes in membrane distillation under various configurations and vacuum enhancement. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, A.; Dufour, V.; Al Marzooqi, F.; Al Kaabi, M.; Hasan, S. Brine management methods: Recent innovations and current status. Desalination 2017, 407, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervov, A.G. Scale Formation Prognosis and Cleaning Procedure Schedules in Reverse-Osmosis Systems Operation. Desalination 1991, 83, 77–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-H. Analysis of CaSO4 scale formation mechanism in various nanofiltration modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 163, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L. Fouling process of membrane distillation for seawater desalination: An especial focus on the thermal-effect and concentrating-effect during biofouling. Desalination 2020, 485, 114457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, M.C.V.; Blanco, S.; García, J.L.; Rodríguez, E.B. Analysis of membrane pore blocking models adapted to crossflow ultrafiltration in the ultrafiltration of PEG. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C.-H. Effect of operating conditions on CaSO4 scale formation mechanism in nanofiltration for water softening. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3854–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-J.; Choung, Y.-K.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.-S.; Hwang, T.-M.; Kim, J.H. Scale formation in reverse osmosis desalination: Model development. Desalination 2009, 238, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepetsanis, P.G.; Koutsoukos, P.G. Precipitation of calcium sulfate dihydrate at constant calcium activity. J. Cryst. Growth 1989, 98, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troup, D.H.; Richardson, J.A. Scale nucleation on a heat transfer surface and its prevention. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1978, 2, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Fouling in direct contact membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, J.; Hasson, D. Calcium sulfate fouling of reverse osmosis membranes, Flux decline mechanism. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1987, 42, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, W. Insights into the wetting phenomenon induced by scaling of calcium sulfate in membrane distillation. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, J. A study on optimal schedule of membrane cleaning and replacement for spiral-wound SWRO system. Desalination 2017, 404, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S. Application of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) to Analyze Membrane Fouling Under Intermittent Operation. Membranes 2023, 13, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, L.M.; Dumée, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.-d.; Duke, M.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in Membrane Distillation for Water Desalination and Purification Applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Payo, M.C.; Izquierdo-Gil, M.A.; Fernández-Pineda, C. Air gap membrane distillation of aqueous alcohol solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 169, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.D.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R.A. Critical review of system dynamics modelling applications for water resources planning and management. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2021, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.M.; Simonovic, S.P.; Hartford, D.N.D. Using system dynamics simulation for assessment of hydropower system safety. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7148–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshianlamouki, E.; Masia, S.; Karimi, P.; van der Zaag, P.; Sušnik, J. A system dynamics model to quantify the impacts of restoration measures on the water-energy-food nexus in the Urmia lake Basin, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Guan, K.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Cysteamine-crosslinked graphene oxide membrane with enhanced hydrogen separation property. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzotzi, C.; Pahiadaki, T.; Yiantsios, S.; Karabelas, A.; Andritsos, N. A study of CaCO3 scale formation and inhibition in RO and NF membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, G. Evaluating the Potential of Scaling Due to Calcium Compounds in Hydrometallurgical Processes; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hasson, D.; Drak, A.; Semiat, R. Interception of CaSO4 scaling on RO membranes at various water recovery levels. Desalination 2001, 139, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, M.; Borden, J.; Hasson, D. Flux decline due to gypsum precipitation on RO membranes. Desalination 1992, 86, 187–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Sea Water | RO Bine |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.1 | 7.6 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 35,045 | 54,400 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 20,069 | 32,600 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 2699 | 5050 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 1495 | 6100 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 465 | 1760 |
| Sodium (mg/L) | 10,899 | 17,330 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, Y.; Koo, J.; Lee, S. System Dynamics Modeling of Scale Formation in Membrane Distillation Systems for Seawater and RO Brine Treatment. Membranes 2024, 14, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120252
Shin Y, Koo J, Lee S. System Dynamics Modeling of Scale Formation in Membrane Distillation Systems for Seawater and RO Brine Treatment. Membranes. 2024; 14(12):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120252
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Yonghyun, Jaewuk Koo, and Sangho Lee. 2024. "System Dynamics Modeling of Scale Formation in Membrane Distillation Systems for Seawater and RO Brine Treatment" Membranes 14, no. 12: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120252
APA StyleShin, Y., Koo, J., & Lee, S. (2024). System Dynamics Modeling of Scale Formation in Membrane Distillation Systems for Seawater and RO Brine Treatment. Membranes, 14(12), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14120252








