Abstract
4-Nitroaniline (4NA) is a common organic pollutant that is released into the environment during the manufacture and processing of a wide variety of industrial products. This article describes the use of an emulsion liquid membrane process to remove 4NA from aqueous solutions using a type 1 facilitated transport mechanism. Optimization of the removal process was carried out by analyzing the efficiency of 4NA removal from the feed phase and the initial apparent feed/membrane fluxes and permeabilities under different experimental conditions. The kinetics of the removal process was analyzed using a simplified mass transfer model involving an empirical mass transfer coefficient calculated from experimental data, assuming that the concentrations of 4NA in the external aqueous phase and in the internal w/o emulsion are uniform. The results show that there is a very good fit between the experimental and model data and that the variation in the values of the overall mass transfer coefficients with the experimental conditions coincides with that of the removal efficiency mentioned above. The transport mechanism was studied by identifying the rate-controlling step of the removal process, using models described for adsorption processes, due to the strong parallelism between the transport mechanisms in adsorption and emulsion liquid membrane processes.
1. Introduction
The generation of potentially hazardous industrial effluents is an issue of growing concern today. Increasingly stringent environmental regulations require the development of technologies for the effective treatment of these industrial wastewaters containing hazardous pollutants. An investigation showed that 80% of streams in the USA contained organic pollutants [1]. Among these organic pollutants, nitroanilines constitute a group of compounds that have toxic effects on the environment and on human health [2].
4-Nitroaniline (4NA) is an aromatic amine widely used as an intermediate or precursor in the syntheses of azo dyes, pharmaceuticals, antioxidants, fuel additives, pesticides, corrosion inhibitors and oxidizing agents [2,3,4], being also present in some commonly used biosolid fertilizers [5,6]. Consequently, 4NA is discharged into the environment both directly in industrial effluents and through the application of such fertilizers, and indirectly, as a result of the degradation of some of the above mentioned compounds [7]. It is toxic through ingestion, inhalation, and contact with the skin, with a threshold limit value (TLV) of 0.001 kg/m3 [4]. Due to its non-biodegradability and environmental persistence, toxicity, carcinogenicity and mutagenesis, 4NA is considered as a toxic chemical by the USA Environmental Protection Agency and as a top-priority pollutant in China [8].
Therefore, the study of new technologies for the treatment of 4NA-contaminated water is a topic of great scientific interest. Several processes have been described for the removal of 4NA from water sources, including biodegradation [6,7,8,9], oxidation [10], reduction [11,12], adsorption [13,14,15], advanced oxidation processes [16,17,18,19] and pressure-driven membrane processes [20,21].
Liquid membrane separation processes have been applied as an effective tool for the removal of a wide variety of organic and inorganic compounds from aqueous solutions due to their ease of operation, high selectivity, combination of removal and recovery processes in a single step, low energy costs and simplicity of design [22]. A liquid membrane system consists of two miscible phases (feed and product phases) separated by a third immiscible phase (the membrane phase) [23]. According to their configuration, three groups of liquid membranes are usually considered: bulk, supported and emulsified. Emulsion liquid membranes are prepared by emulsifying the membrane and product phases and dispersing this emulsion in the feed phase, so that the membrane phase separates the product phase (encapsulated internal droplets) from the external feed phase [23].
To improve the effectiveness of the separation process, so-called facilitated transports are used to maximize the rate of extraction of the species to be separated and its release into the product phase, allowing the transport of the species against its concentration gradient [24]. In type 1 facilitation, a substance (stripping agent) is added to the product phase which reacts quantitatively with the diffusing species to produce a membrane-insoluble product, thereby reducing the concentration of that species to zero at the membrane/product interface and achieving a high concentration gradient of that species across the membrane phase [24].
This paper analyzes the efficiency, kinetics and mechanism of 4NA removal from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membranes using a type 1 facilitated transport mechanism occurring in a water-in-oil-in-water (w/o/w) emulsion consisting of an external feed aqueous phase containing 4NA, an internal aqueous product phase containing HCl as a stripping agent and a membrane phase composed of a solution of the surfactant Span 80 in kerosene as a solvent (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Type 1 facilitated transport of 4NA through emulsion liquid membranes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Kerosene and sorbitan monooleate (Span 80) were supplied by Sigma Aldrich, Steinheim (Germany). 4-Nitroaniline (98%) and HCl (37%) were obtained from Panreac, Darmstadt (Germany). All chemicals were used without any further purification. Deionized water was used for making all the aqueous solutions.
2.2. Procedure
The removal process involves four successive steps: 1—preparation of the primary water in oil emulsion, 2—removal of 4NA by contacting feed and primary emulsion to form the secondary emulsion (water-in-oil-in-water emulsion), 3—on samples taken for analysis, separation by decantation of the feed phase from the primary emulsion phase and 4—analysis of 4NA concentration in the feed phase to establish the efficiency of the removal process (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Schematic representation of steps involved in 4NA removal by emulsion liquid membranes.
The feed phase was formed by 0.1 g/L aqueous solution of 4-nitroaniline, the membrane phase consisted of solutions of the surfactant Span 80 in kerosene, at concentrations ranging from 0.5% to 5.0%, and the product phase comprised aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid ranging from 0.05 M to 0.50 M.
The primary water in oil emulsion (w/o) was prepared by mixing different volumes of the product phase (Vp) and of the membrane phase (Vm) by using a high-speed OMNI MIXER homogenizer (Omni International, Kennesaw, GA, USA), at 2700 rpm during 5 min. To prepare the water-in-oil-in-water emulsion (w/o/w) a volume of this primary emulsion (Vemul) was then gradually added to a volume of the external feed phase (Vf) in a glass cell equipped with a variable-speed propeller, stirring the mixture at a stirring rate ranging from 50 to 200 rpm. Vp/Vm volume ratios ranging from 0.7 to 1.0 were analyzed at a constant Vf/Vemul volume ratio of 2, while Vf/Vemul volume ratios ranging from 1 to 8 were analyzed at a constant Vp/Vm volume ratio of 1.
The duration of the experiments was 15 min, to ensure that in none of the studied experimental conditions there was a significant breakage of the emulsion globules; this should lead to an increase in the concentration of 4NA in the feed phase with time.
Samples of the secondary w/o/w emulsion were periodically taken and allowed to settle for 5 min to achieve separation of the feed phase and the primary w/o emulsion. A quantity of 1 mL of the feed phase was then analyzed, after the addition of 2 mL of 1 M HCl solution, by means of UV spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 243 nm using a UNICAM UV2 spectrophotometer (Unicam Limited, Cambridge, UK). The concentration of 4NA in the unknown sample was determined from the 4NA calibration curve. All the experiments were performed at room temperature and in duplicate. The results obtained showed a maximum deviation of 5%.
The typical experimental condition was: membrane phase 5% Span 80 in kerosene, product phase 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, stirring rate 200 rpm, Vf/Vemul volume ratio 2 and Vp/Vm volume ratio 1.
3. Results
3.1. Removal Efficiency
Removal percentage (RP), apparent initial flux (J) and apparent initial permeability (P) were used to study the efficiency of the 4NA removal process.
Percentage of 4NA removal from the feed phase (RP) was determined according to the Equation (1)
where Cf,0 and Cf,t are the initial and final (15 min) concentrations of 4NA in the external feed phase.
Initial apparent fluxes (J) and permeabilities (P) of 4NA through the feed/membrane interface were calculated from the slopes of the straight lines obtained when plotting, respectively, Cf and ln[Cf,t/(Cf,0] against time, during the first 3 minutes of the experiments, according to Equations (2) and (3) [25].
where Vemul is the volume of the primary emulsion, internal phase volume plus membrane volume, Vf in the volume of the external feed phase and t is the contact time. These equations are used assuming that the membrane area is proportional to the emulsion volume, that the release reaction, which takes place at the membrane/product interface, is very fast preventing the accumulation of solute in the membrane phase and that there is uniformity in the size of the emulsion droplets when the membrane preparation conditions are the same [25].
Figure 3 shows the values of the 4NA removal percentage, apparent initial flux and apparent initial permeability under the different experimental conditions studied.

Figure 3.
Removal percentage (RP), apparent initial flux (J) and apparent initial permeability (P) for 4NA removal by ELM under different experimental conditions.
The increase in HCl concentration in the product phase from 0.05 M to 0.50 M leads to an increase in 4NA removal as a consequence of the increase in the stripping driving force, which favors the diffusion of 4NA from the feed/membrane interface to the membrane/product interface leading to an increase in 4NA transport from the feed to the membrane phase [26].
The 4NA removal increases as a surfactant concentration in the membrane phase increases from 0.5% to 5.0% due to the reduction in the interfacial tension between the phases resulting in smaller emulsion droplets that provide a larger mass transfer area, leading to an increase in 4NA transport [27].
The increase in the stirring speed from 50 to 200 rpm leads to an increase in 4NA removal due to the formation of smaller emulsion droplets, which provides a higher mass transfer area between the feed phase and the membrane phase, leading to an increase in the mass transfer rate [28].
The effect of the Vf/Vemul ratio on the 4NA removal was studied at a constant Vp/Vm ratio (Vp/Vm = 1). Increasing the Vf/Vemul ratio leads to an increase in the amount of 4NA that can be removed from the feed phase, but with no change in the amount of stripping agent in the product phase. This leads to an increase in the 4NA transport from the feed phase to the membrane phase that is manifested by an increase in flux and permeability (which is especially significant when the volume ratio increases from 1 to 2) and to a decrease in the removal percentage (the percentage of 4NA removed from the total 4NA present in the feed), which is especially significant at a volume ratio greater than 2, due to the significant increase in the number of 4NA molecules to be removed from the feed phase in comparison to the total number of 4NA molecules that can be effectively transported by a constant number of stripping agent molecules [29].
The effect of the Vp/Vm ratio on 4NA elimination was analyzed at a constant Vf/Vemul ratio (Vf/Vemul = 2). The increase in the internal volume of the aqueous phase produces two opposite effects. On the one hand, it generates an increase in emulsion viscosity, which leads to an increase in the emulsion droplet size which decreases the mass transfer area and results in a decrease in removal efficiency [30]. On the other hand, it produces an increased ratio between the amount of stripping agent in the permeate phase and the amount of 4NA in the feed phase, which increases the stripping driving force, delaying the accumulation of 4NA in the membrane phase, and resulting in an increase in the removal efficiency [26]. The total result of these two effects is a slight increase in 4NP flux, permeability and removal efficiency.
3.2. Removal Process Kinetics
Among the different models that have been proposed to describe the kinetics of the transport process in emulsion liquid membranes [31,32,33,34], we selected in this study the model of Lin et al. [34] because of its simplicity and ease of calculation. This model assumes that the 4NA concentrations are uniform in both the external aqueous phase and the primary water in oil emulsion and is represented by Equation (4) [34], which is valid for times shorter than the final time.
where Cemul,t and Cemul,tf are 4NA concentrations (mg/L) in the emulsion droplets at any time and at the final time (15 min), respectively, and k is the overall mass transfer coefficient (min−1).
4NA concentrations in the emulsion droplets (Cemul) and in the external feed aqueous solution (Cf) are related by the following material balance:
where Cf,0 and Cf,t are, respectively, the initial and time t concentrations of 4NA in the feed phase (mg/L), and Vf and Vemul are the volumes (mL) of the feed and the emulsion phases, respectively. 4NA concentrations (mg/L) in the emulsion droplets at the final time Cemul,tf were determined using Equation (5), Cf,t being the feed 4NA concentration at the final time (15 min).
Figure 4 shows the values of the representation against time of the experimental values of Y, ln[Cemul,tf/(Cemul,tf − Cemul,t)], and of those obtained by means of the model, under the different experimental conditions studied. A very good similarity between experimental and model values can be appreciated, which points to a good validity of the model.
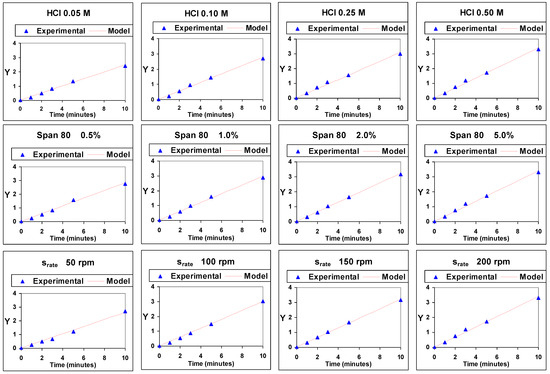

Figure 4.
Representation of experimental and model values of ln[Cemul,tf/(Cemul,tf − Cemul,t)] (Y) against time.
In another way, Figure 5 shows the values of the overall mass transfer coefficient under those different experimental conditions. It can be observed that the variation in the overall mass transfer coefficients with the variation in different experimental conditions studied coincides with that of the 4NA removal efficiency analyzed above. That is, the increase in HCl concentration in the product, surfactant concentration in the membrane phase, stirring rate of the secondary w/o/w emulsion, and Vp/Vm ratio lead to an increase in the value of the overall mass transfer coefficient, while the increase in the Vf/Vemul leads to its decrease.

Figure 5.
Overall mass transfer coefficients of 4NA removal under different studied experimental conditions.
3.3. Transport Mechanism
The mechanism of 4NA transport through an emulsion liquid membrane by a type 1 facilitated transport includes four steps (Figure 6a) [31]:

Figure 6.
Transport mechanisms in emulsion liquid membrane (a) and adsorption processes (b).
- 4NA diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed aqueous phase at feed/membrane interface.
- 4NA solubilization into the membrane phase.
- 4NA diffusion through the membrane phase to the membrane/product interface.
- At the membrane/product interface, reaction of 4NA with the striping agent (HCl) present in the product phase to form a membrane phase insoluble product (4NAH+Cl−].
As the solubilization and reaction steps are much faster than those of the diffusion, the transport in a type 1-facilitated emulsion liquid membrane process will be governed by diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed aqueous phase at the membrane/phase interface or by diffusion through the membrane phase.
This elementary transport mechanism is very similar to that of the adsorption of an adsorbate (we will refer to the 4NA) onto an adsorbent, which includes three basic steps (Figure 6b) [35]:
- External diffusion (film diffusion), transport of the adsorbate (4NA) from the bulk phase to the external surface of the adsorbent.
- Intraparticle diffusion (pore diffusion), transport of the adsorbate (4NA) from the external surface into the pores.
- Surface reaction, which is the attachment of the adsorbate to the internal surface of the adsorbent.
As indicated above, the reaction step is much faster than the diffusion steps, so transport in an adsorption process will be governed by either external diffusion or intraparticle diffusion.
This great parallelism between the mechanisms associated with the transport in both adsorption and type 1 emulsion liquid membrane processes makes it possible to assimilate the external diffusion and the intraparticle diffusion of the adsorption process with the diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed aqueous phase at the feed/membrane interface and the membrane–phase diffusion, respectively, of the emulsion liquid membrane process.
In order to establish the extent of an adsorption process, the parameter adsorption capacity is often used, which is usually defined, for both at any time t (qt) or at the final time or equilibrium (qe), as the amount of adsorbate retained per unit mass of adsorbent (mg/g) [35], according to Equations (6) and (7).
where C0, Ct and Ce were, respectively, the initial, time t and equilibrium adsorbate concentrations in the solution (mg/L), V the volume of the adsorbate solution (L) and m the mass of the adsorbent (g).
These parameters have been defined in the case of emulsion liquid membranes [36] as the amount of compound removed from the feed phase per volume unit of emulsion phase (mg/L), according to Equations (8) and (9).
where Cf,e is the equilibrium concentration (at 15 min) of 4NA in the feed phase (mg/L).
Accordingly, the amounts of 4NA removed from the feed phase per volume unit of the emulsion phase, at any time t (qt), and at 15 min (qe), were estimated from Equations (8) and (9).
Therefore, the mechanism of type 1-facilitated transport of 4NA through an emulsion liquid membrane was analyzed by means of two models developed for adsorption processes, the Weber and Morris intraparticle diffusion model and the Boyd model.
The Weber and Morris intraparticle diffusion model [37] is usually expressed according to Equation (10):
where kintp (mg/g·h1/2) is the rate constant of the intraparticle diffusion (membrane diffusion in the case of ELM)) and Ci represents the effect of the external diffusion (diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed phase in the case of ELM). The value of these parameters is obtained from the slope and the intercept when qt plotted against t1/2. If this representation is linear and passes through the origin, intraparticle diffusion is the only step that controls the rate of the process, but if the representation shows multilinearity, both external diffusion and intraparticle diffusion are involved in controlling the rate of the process.
When the latter occurs, the Boyd kinetic model [38] allows us to establish which of the two steps is the one that mainly controls the rate of the process. This model is described by the equation:
If the plot of B·t versus time is a straight line passing through the origin, the transport process is mainly controlled by intraparticle diffusion; otherwise, it is mainly controlled by external diffusion.
The results are presented in Figure 7. As this figure shows that Weber–Morris model representations are not linear over the entire time range, 4NA transport from the feed phase to the product phase is controlled by both the diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed aqueous phase at the feed/membrane interface and the diffusion through the membrane phase.

Figure 7.
Weber–Morris and Boyd model representations of 4NA type 1-facilitated transport through ELM.
As Boyd model representations are not fully linear and they do not pass through the origin, it can be concluded that the rate of 4NA type 1-facilitated transport through emulsion liquid membranes is mainly controlled by 4NA diffusion through the stagnant film of the feed aqueous phase at the feed/membrane interface.
4. Conclusions
The removal of 4NA from aqueous solutions by emulsion liquid membranes using a type 1-facilitated transport mechanism was studied in this paper. In order to optimize the removal process, the efficiency of 4NA removal from the feed phase and the initial apparent feed/membrane fluxes and permeabilities were studied under different experimental conditions. The removal of 4NA increased by increasing the HCl concentration in the internal aqueous phase from 0.05 M to 0.50 M, by increasing the surfactant concentration in the membrane phase from 0.5% to 5.0%, by increasing the stirring speed from 50 to 200 rpm, by increasing the permeate/membrane volume ratio from 0.7 to 1, and by decreasing the feed/emulsion volume ratio from 8 to 1.
The kinetics of the removal process were analyzed using a simplified mass transfer model involving an empirical mass transfer coefficient calculated from experimental data. The results show a very good fit between the experimental and model data and that the values of the overall mass transfer coefficient with the experimental conditions coincide with those of the removal efficiency mentioned above.
Due to the great parallelism between the transport mechanisms of adsorption and emulsion liquid membrane processes, the mechanism of the type 1-facilitated transport of 4NA through ELM was studied by identifying the rate-controlling step of the process using models described for adsorption processes. The results show that there is more than one rate-controlling step in the removal process, with diffusion through the boundary layer at the feed/membrane interface being the main rate-controlling step in the removal of 4NA from aqueous solutions by type 1-facilitated transport.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.L., A.M.H. and B.M.; methodology, G.L., M.G. and E,G.; validation, G.L., A.M.H., M.G., E.G. and B.M.; formal analysis, G.L., A.M.H. and M.G.; investigation, G.L., M.G. and E.G.; resources, G.L., A.M.H., M.G., E.G. and B.M.; data curation, G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L., A.M.H. and M.G.; writing—review and editing, G.L., E.G. and B.M.; visualization, G.L. and B.M; supervision, G.L., A.M.H. and B.M.; project administration, G.L., A.M.H. and E.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the fact that they are part of a much larger study that is still underway.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kolpin, D.; Furlong, E.; Meyer, M.; Thurman, E.M.; Zaugg, S.; Barber, L.; Buxton, H. Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, and Other Organic Wastewater Contaminants in U.S. Streams, 1999–2000: A National Reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghash-Hamed, S.; Arsalani, N.; Mousavi, S.B. Facile fabrication of CuFe2O4 coated with carbon quantum dots nanocomposite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst toward the reduction of nitroaniline compounds for management of aquatic resources. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2023, 443, 114822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Sun, S.P.; Fan, M.H.; Guo, H.Q.; Qiao, L.P.; Sun, R.X. A kinetic study on the degradation of p-nitroaniline by Fenton oxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wang, M.; Pu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Xiong, T. Transient and steady-state photolysis of p-nitroaniline in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.R. Organic contaminants in sewage sludge (biosolids) and their significance for agricultural recycling. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 4005–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silambarasan, S.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation of 4-nitroaniline by plant-growth promoting Acinetobacter sp. AVLB2 and toxicological analysis of its biodegradation metabolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Crowley, D.E. Biodegradation potential of pure and mixed bacterial cultures for removal of 4-nitroaniline from textile dye wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Enhanced treatment of nitroaniline-containing wastewater by a membrane aerated biofilm reactor: Simultaneous nitroaniline degradation and nitrogen removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silambarasan, S.; Cornejo, P.; Vangnai, A.S. Biodegradation of 4-nitroaniline by novel isolate Bacillus sp. strain AVPP64 in the presence of pesticides. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Park, K.S.; Nam, Y.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, C.H. Hydrothermal decomposition and oxidation of p-nitroaniline in supercritical water. J. Hazard. Mater. 1997, 56, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Seleim, S.M.; Abouelanwar, M.E. Behavior of surface coated zirconium silicate-nanopolyaniline with nano zerovalent copper (ZrSiO4@NPANI@nZVCu) toward catalytic reduction of nitroanilines. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulizar, Y.; Apriandanu, D.O.B.; Zahra, Z.A. SiO2/NiFe2O4 nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization and their catalytic activity for 4-nitroaniline reduction. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 261, 124243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wen, R.; Wei, D.; Wu, D. Effects of the steric hindrance of micropores in the hyper-cross-linked polymeric adsorbent on the adsorption of p-nitroaniline in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A. Adsorption of nitroaniline onto high surface area nanographene. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senlik, K.; Gezici, O.; Guven, I.; Pekacar, A.I. Adsorption of nitroaniline positional isomers on humic acid-incorporated monolithic cryogel discs: Application of ligand-exchange concept. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandrabal, B.; Tikker, P.; Preis, S. Oxidation of Aqueous p-Nitroaniline by Pulsed Corona Discharge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbulekshmi, N.L.; Subramanian, E. Nano CuO immobilized fly ash zeolite Fenton-like catalyst for oxidative degradation of p-nitrophenol and p-nitroaniline. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.Q.; Zhou, R. Kinetic modeling and efficiency of sulfate radical-based oxidation to remove p-nitroaniline from wastewater by persulfate/Fe3O4 nanoparticles process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Gharaghani, M.A.; Dehdarirad, A.; Khatami, M.; Ahmadian, M.; Heidari, M.R.; Mahdizadeh, H. ZnO nanoparticles immobilized on the surface of stones to study the removal efficiency of 4-nitroaniline by the hybrid advanced oxidation process (UV/ZnO/O3). J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.M.; León, G.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Gómez, E.; Giner, C. Behaviour of RO90 membrane on the removal of 4-nitrophenol and4-nitroaniline by low pressure reverse osmosis. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.M.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Gómez, E.; León, G.; Cascales, E. Influence of Physicochemical Parameters of Organic Solutes on the Retention and Flux in a Nanofiltration Process. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, F.; Torkaman, R.; Moosavian, M.A.; Zaheri, P. Optimization of extraction conditions using central composite design for the removal of Co (II) from chloride solution by supported liquid membrane. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislik, V.S. Introduction, General Description, Definitions and Classification. Overview. In Liquid Membranes. Principles and Applications in Chemical Separation and Wastewater Treatment, 1st ed.; Kislik, V.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- León, G. Facilitated transport. In Encyclopedia of Membranes, 1st ed.; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 763–764. [Google Scholar]
- Kedari, C.S.; Pandit, S.S.; Parikh, K.J.; Tripathi, S.C. Removal of 241Am from aqueous nitrate solutions by liquid surfactant membrane containing 2-ethylhexyl phosphonic acid mono 2-ethylhexyl ester as ion carrier. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, S.; Bhattacharya, P.K.; Verma, N. Removal of aniline from aqueous solution in a mixed flow reactor using emulsion liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, I.; Altas, L. A fast and effective method for ammonium removal: Emulsion Liquid Membrane. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebizadeh, P.; Javanshir, S.; Ahmadi, A. Zinc extraction from a bioleaching solution by emulsion liquid membrane technique. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Mahajani, V.V. Application of liquid emulsion membrane (LEM) process for enrichment of Molybdenum from aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 201, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Atiya, M.A. Application of emulsion and Pickering emulsion liquid membrane technique for wastewater treatment: An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36184–36204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Kun, S.C. A general mass transfer model for liquid surfactant membrane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.S.; Hatton, T.A.; Lightfoot, E.N.; Li, N.N. Batch extraction with liquid surfactant membranes: A diffusion controlled model. AIChE J. 1982, 28, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Sakai, T.; Yamagawa, K.; Ohsuga, M.; Miyake, Y. Extraction of phenol and cresol by liquid surfactant membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1983, 18, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Pan, C.L.; Leu, H.G. Equilibrium and mass transfer characteristics of 2-chlorophenol ramoval from aqueous solutions by liquid membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 87, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León, G.; Gómez, E.; Miguel, B.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Guzmán, M.A. Feasibility of Adsorption Kinetic Models to Study Carrier-Mediated Transport of Heavy Metal Ions in Emulsion Liquid Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, G.E.; Adamson, A.W.; Myers, L.S. The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II. Kinetics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1947, 69, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).