Pathway for Water Transport through Breathable Nanocomposite Membranes of PEBAX with Ionic Liquid [C12C1im]Cl
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Simulation Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation and Breathability Tests
2.3. Simulation Methods
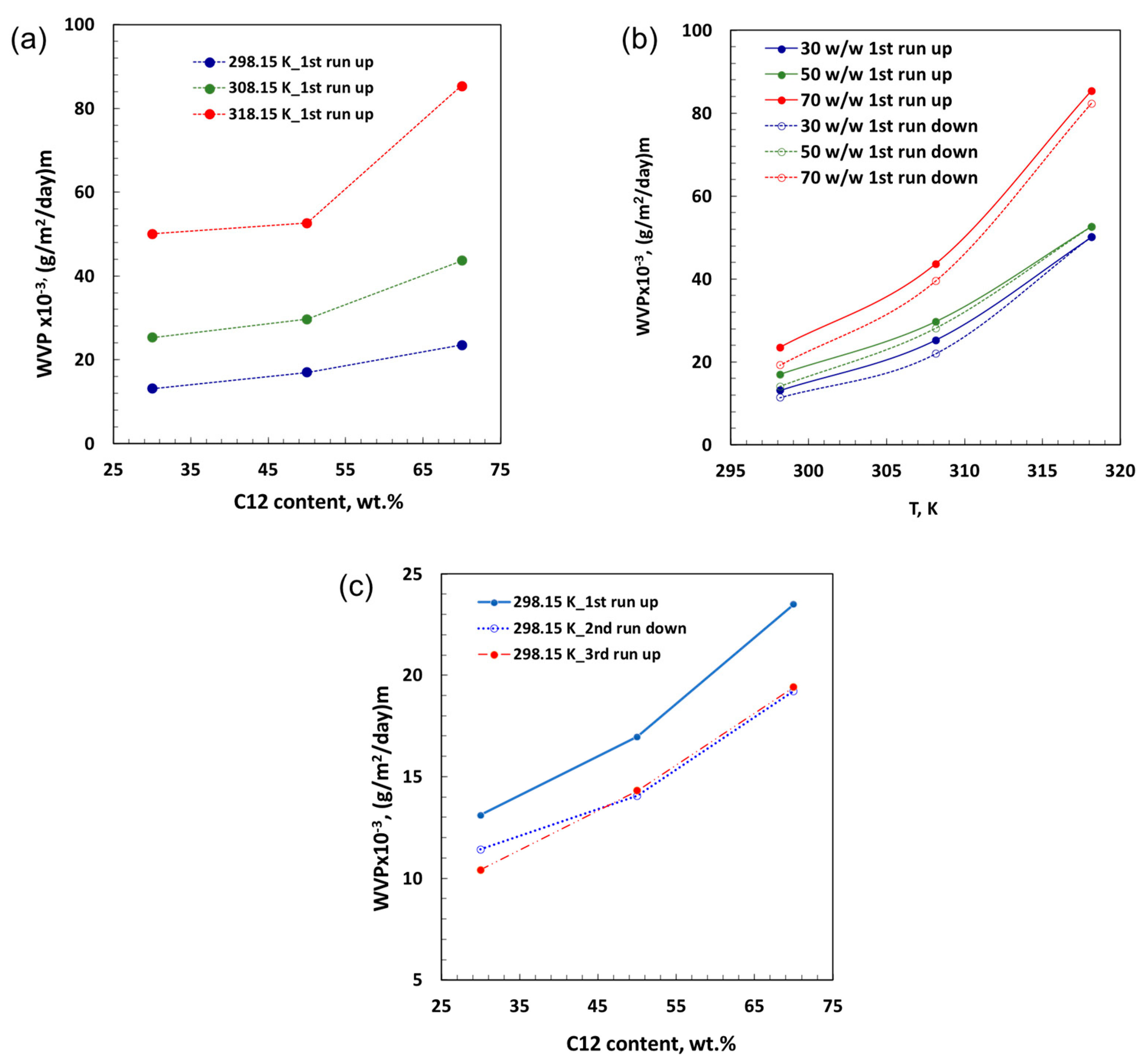
3. Experimental Results
4. Simulation Results
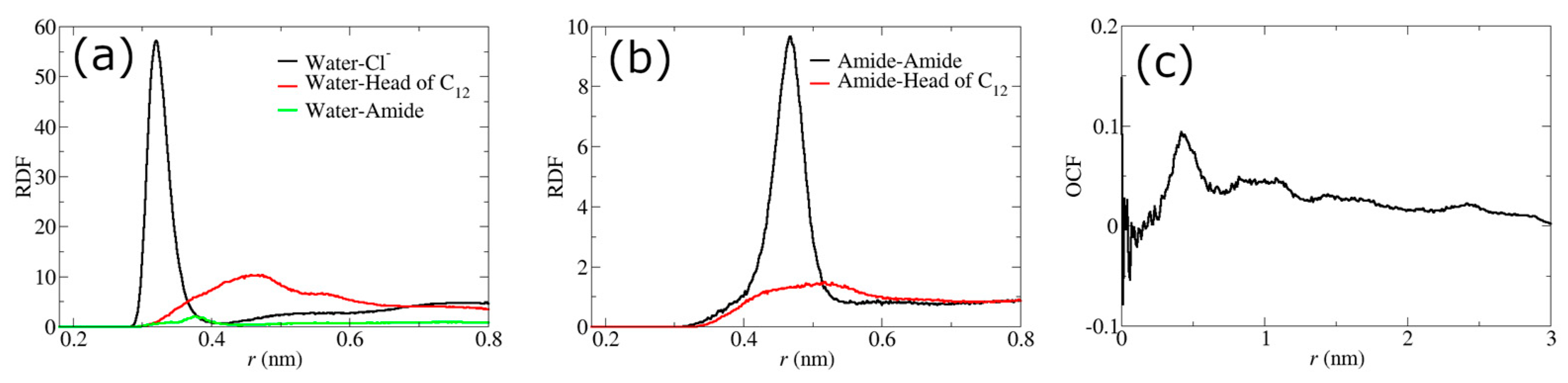
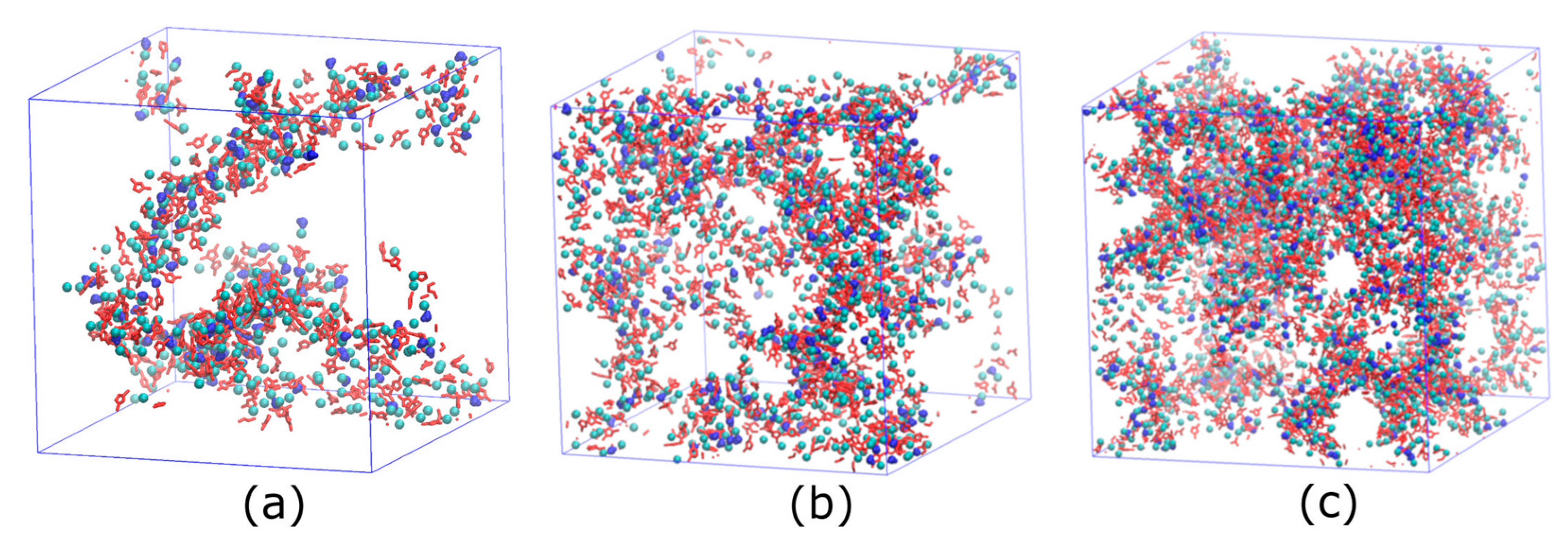
4.1. Water Pathway Formed by IL in Nanocomposite Membrane
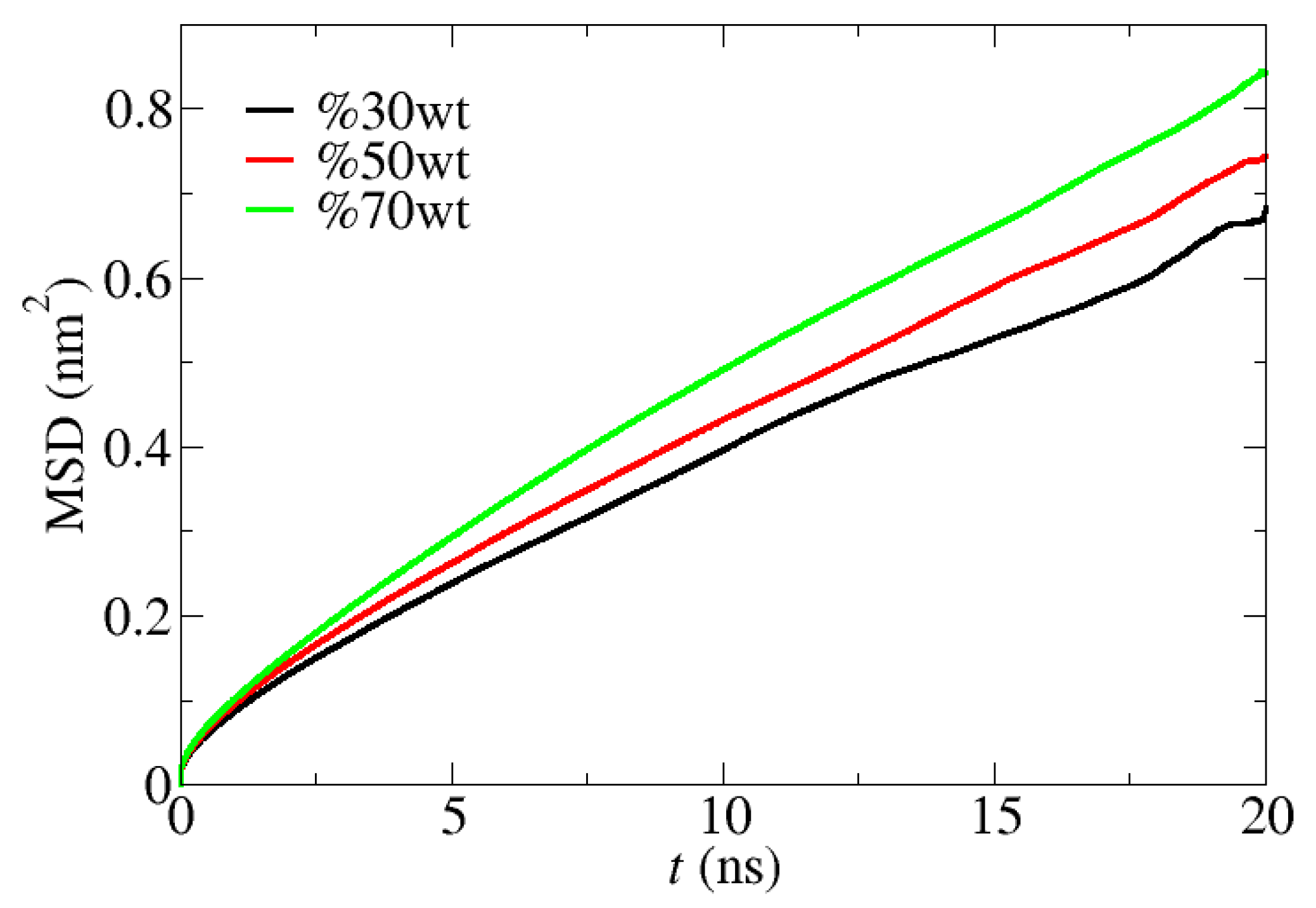
4.2. Influence of [C12C1im]Cl Concentration and Temperature
4.3. Influence of Water Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKeen, L.W. Thermoplastic Elastomers. In Fatigue and Tribological Properties of Plastics and Elastomers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 279–289. [Google Scholar]
- Schar, M.; Zweifel, L.; Arslan, D.; Grieder, S.; Maurer, C.; Brauner, C. Fused Filament Fabrication of Bio-Based Polyether-Block-Amide Polymers (PEBAX) and Their Related Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flesher, J.R. Pebax® polyether block amide—A new family of engineering thermoplastic elastomers. In Proceedings of the High Performance Polymers: Their Origin and Development: Proceedings of the Symposium on the History of High Performance Polymers at the American Chemical Society Meeting, New York, NY, USA, 15–18 April 1986; pp. 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Jonquieres, A.; Clément, R.; Lochon, P. Permeability of block copolymers to vapors and liquids. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1803–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Zhao, H.; Steunou, N.; Serre, C.; Malankowska, M.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Optimization of MIL-178(Fe) and Pebax® 3533 loading in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 121, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potreck, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Kosinski, T.; Wessling, M. Mixed water vapor/gas transport through the rubbery polymer PEBAX® 1074. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 338, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chakma, A.; Feng, X. Propylene separation from nitrogen by poly(ether block amide) composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. A review on membrane engineering for innovation in wearable fabrics and protective textiles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaounakis, M. Sports/Toys/Board Games. In Biopolymers: Applications and Trends; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 427–443. [Google Scholar]
- Barbucci, A.; Delucchi, M.; Cerisola, G. Organic coatings for concrete protection: Liquid water and water vapour permeabilities. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 30, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Zhang, N.; Zeng, X.; Zhong, B.; Yu, Y. Quasi-isotropically thermoconductive, antiwear and insulating hierarchically assembled hexagonal boron nitride nanosheet/epoxy composites for efficient microelectronic cooling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional nanofibers for environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. New performance of a modified poly(amide-12-b-ethyleneoxide). Polymer 2003, 44, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. Role of additives in the water vapor transport through block co-poly(amide/ether) membranes: Effects on surface and bulk polymer properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2381–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuffo, D. Microclimate for Cultural Heritage: Measurement, Risk Assessment, Conservation, Restoration, and Maintenance of Indoor and Outdoor Monuments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Xing, M.M.; Pan, N.; Maibach, H.I. Textiles and human skin, microclimate, cutaneous reactions: An overview. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.-S.; Kim, S. All-fabric intelligent temperature regulation system for smart clothing applications. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 27, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Rincón, M.; Jiménez-Junca, C.; Roa Duarte, C. A novel absorption process for small-scale natural gas dew point control and dehydration. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 29, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhatab, S.; Poe, W.A.; Speight, J.G. Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2006; pp. 323–364. [Google Scholar]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Pingitore, V.; Miriello, D.; Drioli, E. Functional carbon nanotubes for high-quality charge transfer and moisture regulation through membranes: Structural and functional insights. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 12919–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prefol, T.; Gain, O.; Sudre, G.; Gouanve, F.; Espuche, E. Development of Breathable Pebax((R))/PEG Films for Optimization of the Shelf-Life of Fresh Agri-Food Products. Membranes 2021, 11, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Fabiano, R.; Garavaglia, M.G.; Spisso, A.; Drioli, E. Study of the surface character as responsible for controlling interfacial forces at membrane-feed interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.H.; Kumar, M.; Peinemann, K.-V. Pebax®1657/Graphene oxide composite membranes for improved water vapor separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chang, Z.; Lin, L.; Xu, X. Effect of montmorillonite on PEBAX® 1074-based mixed matrix membranes to be used in humidifiers in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wang, Y. Phase behaviors of ionic liquids attributed to the dual ionic and organic nature. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2022, 74, 097601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and water stable 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 13, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids—Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, T.; Mu, X.; Mai, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G. Smart Supramolecular Self-Assembled Nanosystem: Stimulus-Responsive Hydrogen-Bonded Liquid Crystals. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fang, C.; Yang, L.; Li, K.; Zhu, K.; Liu, G.; Chen, J. The Novel Ionic Liquid and Its Related Self-Assembly in the Areas of Energy Storage and Conversion. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2200048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, Y.; Saielli, G. Effect of the chain length on the structure of ionic liquids: From spatial heterogeneity to ionic liquid crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Bisquert, J.; Palomares, E.; Otero, L.; Kuang, D.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Correlation between photovoltaic performance and impedance spectroscopy of dye-sensitized solar cells based on ionic liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6550–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlov, M.; Kloo, L. Ionic liquid electrolytes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dalton Trans. 2008, 20, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.R.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Ahn, K.D.; Kim, E. Electro-fluorescence switching of bis-imidazolium ionic liquids. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 4630–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, A.; Świderska-Mocek, A. Ionic liquids as electrolytes for Li-ion batteries—An overview of electrochemical studies. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Ivaska, A. Applications of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 607, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikolimi, K.; Sudhakar, A.A.; Ishida, Y. Functional Ionic Liquid Crystals. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11702–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Saielli, G. Metastable State during Melting and Solid-Solid Phase Transition of [C(n)Mim][NO(3)] (n = 4–12) Ionic Liquids by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Wang, Y. Phase Behaviors of Ionic Liquids Heating from Different Crystal Polymorphs toward the Same Smectic-A Ionic Liquid Crystal by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Crystals 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saielli, G. MD simulation of the mesomorphic behaviour of 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium nitrate: Assessment of the performance of a coarse-grained force field. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10279–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, M.J.; Whitmer, J.K. Charge Transport and Phase Behavior of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Crystals from Fully Atomistic Simulations. Materials 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Kubo, M.; Shiba, H. Molecular dynamics study of mesophase transitions upon annealing of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with long-alkyl chains. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 9796–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saielli, G.; Bagno, A.; Wang, Y. Insights on the isotropic-to-smectic A transition in ionic liquid crystals from coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations: The role of microphase segregation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3829–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of ionic liquids with membrane technology: A new approach for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. PVDF and HYFLON AD membranes: Ideal interfaces for contactor applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. Competitive hydrogen-bonding interactions in modified polymer membranes: A density functional theory investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Bai, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Exploring NH3 Transport Properties by Tailoring Ionic Liquids in Pebax-Based Hybrid Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9570–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi Estahbanati, E.; Omidkhah, M.; Ebadi Amooghin, A. Preparation and characterization of novel Ionic liquid/Pebax membranes for efficient CO 2 /light gases separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, W.; Mansouri, J.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Improving CO 2 separation performance of thin film composite hollow fiber with Pebax®1657/ionic liquid gel membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Izquierdo, L.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Highly stable Pebax® Renew® thin-film nanocomposite membranes with metal organic framework ZIF-94 and ionic liquid [Bmim][BF4] for CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 18822–18833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrezaei, K.; Abedini, R.; Lashkarbolooki, M.; Rahimpour, A. A preferential CO2 separation using binary phases membrane consisting of Pebax®1657 and [Omim][PF6] ionic liquid. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, F.; Zarca, G.; Urtiaga, A. Effect of feed pressure and long-term separation performance of Pebax-ionic liquid membranes for the recovery of difluoromethane (R32) from refrigerant mixture R410A. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorhisham, N.A.; Amri, D.; Mohamed, A.H.; Yahaya, N.; Ahmad, N.M.; Mohamad, S.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Osman, H. Characterisation techniques for analysis of imidazolium-based ionic liquids and application in polymer preparation: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.H.; Vovushua, H.; Villalobos, L.F.; Shevate, R.; Kumar, M.; Nunes, S.P.; Schwingenschlögl, U.; Peinemann, K.-V. Highways for water molecules: Interplay between nanostructure and water vapor transport in block copolymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Deschamps, J.; Pádua, A.l.A.H. Modeling Ionic Liquids Using a Systematic All-Atom Force Field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.N.C.; Pádua, A.l.A.H. Molecular Force Field for Ionic Liquids Composed of Triflate or Bistriflylimide Anions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16893–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.; Chappelle, R. Restrained electrostatic potential atomic partial charges for condensed-phase simulations of carbohydrates. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2000, 527, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.V.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Kalugin, O.N. A new force field model for the simulation of transport properties of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 7910–7920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, H.W.; Swope, W.C.; Pitera, J.W.; Madura, J.D.; Dick, T.J.; Hura, G.L.; Head-Gordon, T. Development of an improved four-site water model for biomolecular simulations: TIP4P-Ew. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 9665–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: AnN⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocci, E.; Gugliuzza, A.; De Lorenzo, L.; Macchione, M.; De Luca, G.; Drioli, E. Transport properties of a co-poly(amide-12-b-ethylene oxide) membrane: A comparative study between experimental and molecular modelling results. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; De Luca, G.; Tocci, E.; De Lorenzo, L.; Drioli, E. Intermolecular interactions as controlling factor for water sorption into polymer membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 8868–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. Evaluation of CO2 permeation through functional assembled mono-layers: Relationships between structure and transport. Polymer 2005, 46, 9994–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J.P.; Xu, J.; Wilkes, G.L. Solid state structure–property behavior of semicrystalline poly (ether-block-amide) PEBAX® thermoplastic elastomers. Polymer 2003, 44, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Isfahani, A.P.; Muchtar, A.; Sakurai, K.; Shrestha, B.B.; Qin, D.; Yamaguchi, D.; Sivaniah, E.; Ghalei, B. Pebax/ionic liquid modified graphene oxide mixed matrix membranes for enhanced CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.; Hardacre, C.; Holbrey, J.; Johnston, S.; McMath, S.; Nieuwenhuyzen, M. Small-angle X-ray scattering studies of liquid crystalline 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium salts. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.T.; Voth, G.A. Molecular dynamics simulation of nanostructural organization in ionic liquid/water mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4812–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Atom Name | Partial Charge/e | Atom Name | Partial Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.885 | O1 | −0.585 |
| C2 | 0.104 | O2 | −0.612 |
| C3 | −0.106 | O3 | −0.396 |
| C4 | 0.642 | O4 | −0.531 |
| C5 | 0.702 | O5 | −0.266 |
| C6 | 0.119 | O6 | −0.414 |
| C7 | 0.027 | N1 | −0.699 |
| C8 | −0.159 | NA | 0.176 |
| CA | −0.28 | NB | 0.176 |
| CB | −0.136 | H1 | 0.053 |
| CC | −0.096 | H2 | 0.423 |
| CD | −0.192 | H3 | 0.378 |
| CR | −0.072 | H4 | 0.064 |
| CW | −0.192 | HA | 0.144 |
| Cl | −0.8 | HB | 0.144 |
| HW | 0.216 | HC | 0.048 |
| HR | 0.168 | HD | 0.064 |
| Atom Name | Partial Charge/e | |
|---|---|---|
| Oew | 0 | |
| V | −1.04844 | |
| Hew1 | 0.52422 | |
| Hew2 | 0.52422 | |
| Valence bond | Bond length/nm | kbond/kJ mol−1 nm−2 |
| Oew-Hew1 | 0.09572 | 502,416.0 |
| Oew-Hew2 | 0.09572 | 502,416.0 |
| Valence angle | Angle/° | kangle/kJ mol−1 rad−2 |
| Hew1-Oew-Hew2 | 104.52 | 628.02 |
| [C12C1im]Cl Concentrations in Weight | PEBAX Chains | [C12C1im]Cl Ion Pairs | Water Molecules | Water/C12 Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 125 | 1/3 |
| 50% | 6 | 870 | 290 | 1/3 |
| 70% | 6 | 2040 | 680 | 1/3 |
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 125 | 1/3 |
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 250 | 2/3 |
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 375 | 1 |
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 750 | 2 |
| 30% | 6 | 375 | 3750 | 10 |
| Diffusion Coefficient 10−5 cm2/s | 30 w/w% | 50 w/w% | 70 w/w% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water molecules | 298 K | 0.00520 | 0.00563 | 0.00658 |
| 318 K | 0.01026 | 0.01449 | 0.01718 | |
| Cl− | 298 K | 0.00032 | 0.00048 | 0.00062 |
| 318 K | 0.00083 | 0.00139 | 0.00182 | |
| N1 | 298 K | 0.00038 | 0.00051 | 0.00060 |
| 318 K | 0.00072 | 0.00118 | 0.00163 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Li, S.; Tocci, E.; Saielli, G.; Gugliuzza, A.; Wang, Y. Pathway for Water Transport through Breathable Nanocomposite Membranes of PEBAX with Ionic Liquid [C12C1im]Cl. Membranes 2023, 13, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090749
Cheng Z, Li S, Tocci E, Saielli G, Gugliuzza A, Wang Y. Pathway for Water Transport through Breathable Nanocomposite Membranes of PEBAX with Ionic Liquid [C12C1im]Cl. Membranes. 2023; 13(9):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090749
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Ziqi, Shen Li, Elena Tocci, Giacomo Saielli, Annarosa Gugliuzza, and Yanting Wang. 2023. "Pathway for Water Transport through Breathable Nanocomposite Membranes of PEBAX with Ionic Liquid [C12C1im]Cl" Membranes 13, no. 9: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090749
APA StyleCheng, Z., Li, S., Tocci, E., Saielli, G., Gugliuzza, A., & Wang, Y. (2023). Pathway for Water Transport through Breathable Nanocomposite Membranes of PEBAX with Ionic Liquid [C12C1im]Cl. Membranes, 13(9), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13090749










