Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Nanoparticles Embedded Microfiltration Membrane for Selective Separation of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
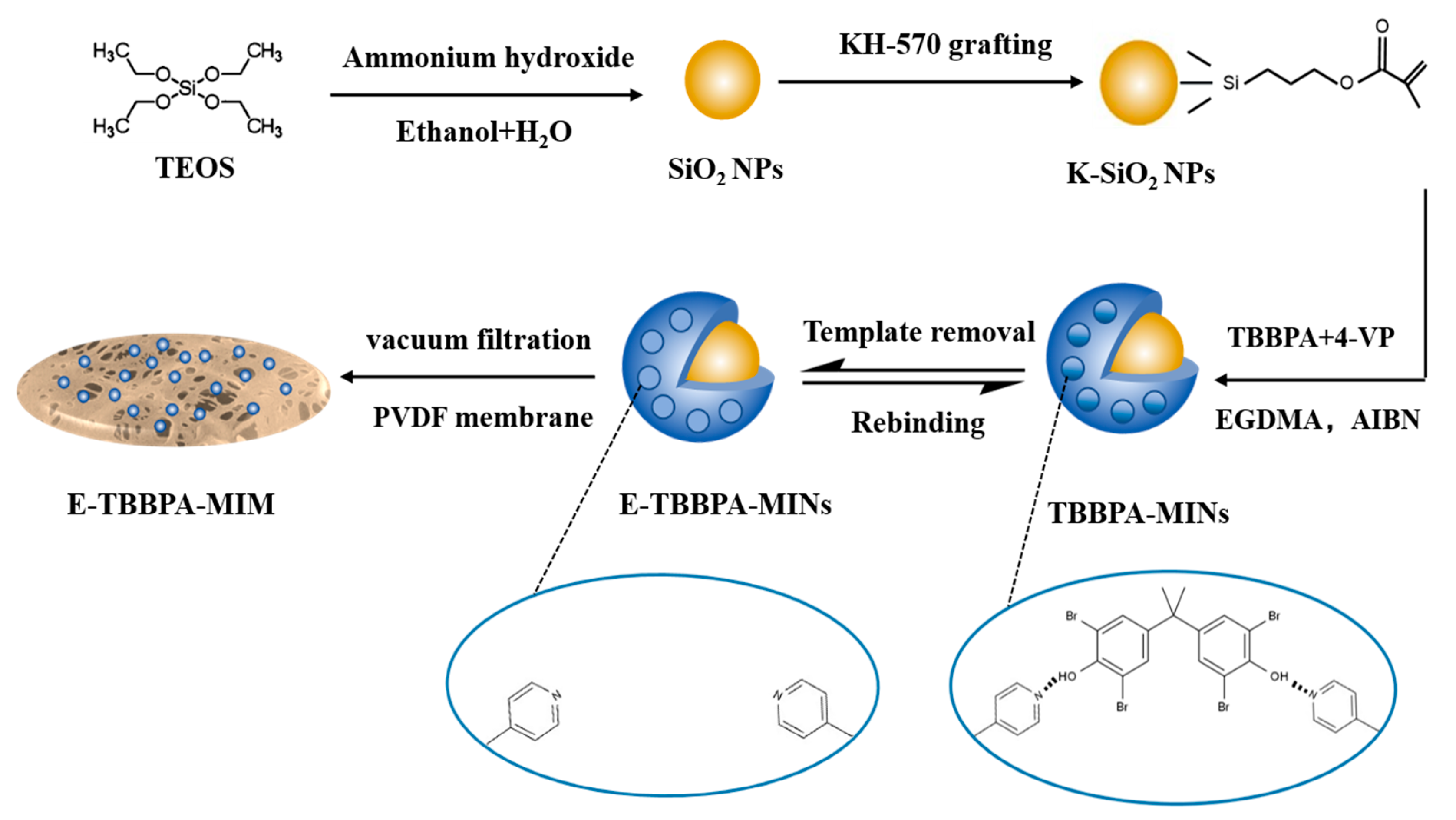
2.2. Synthesis of E-TBBPA-MINs and E-TBBPA-MIM
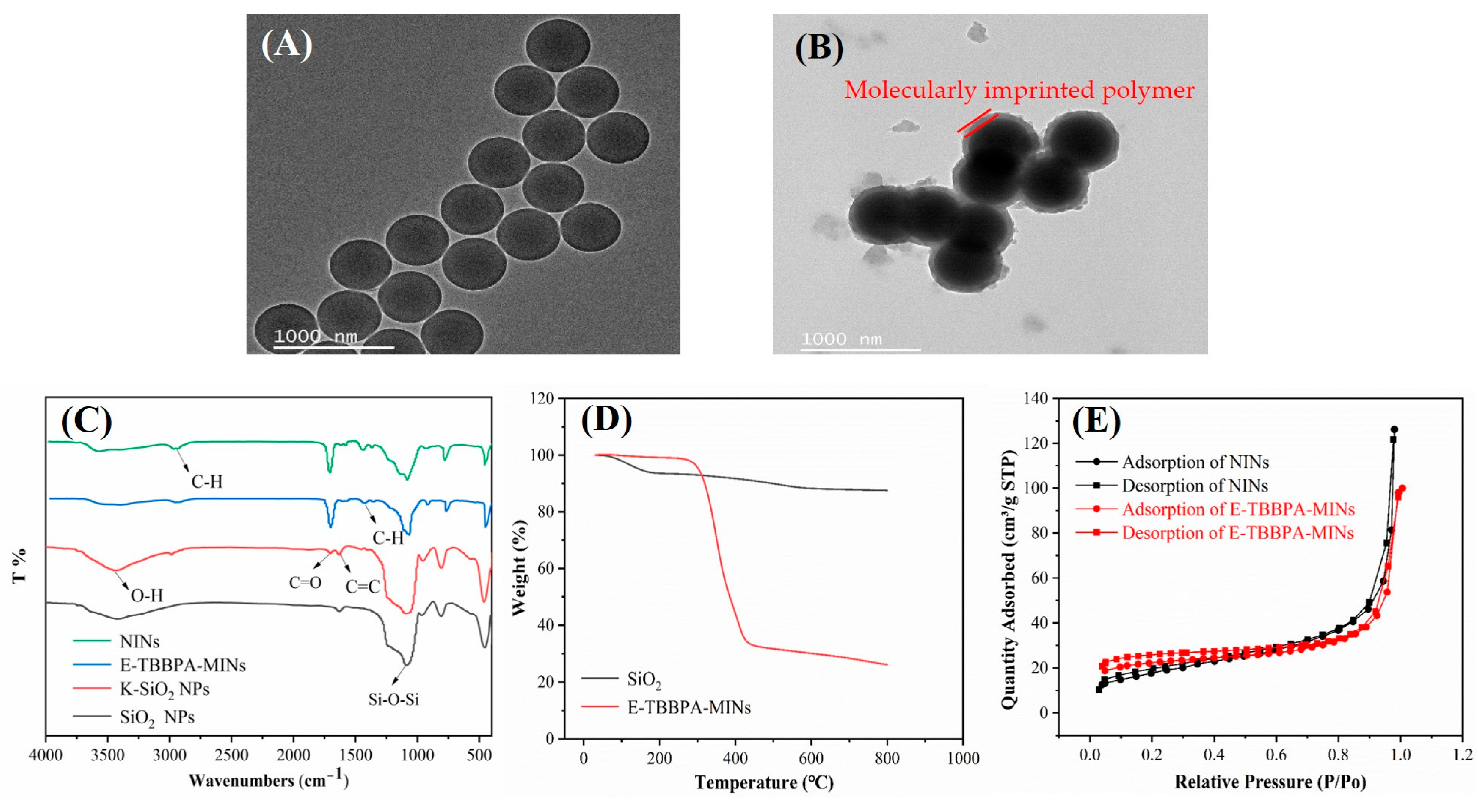
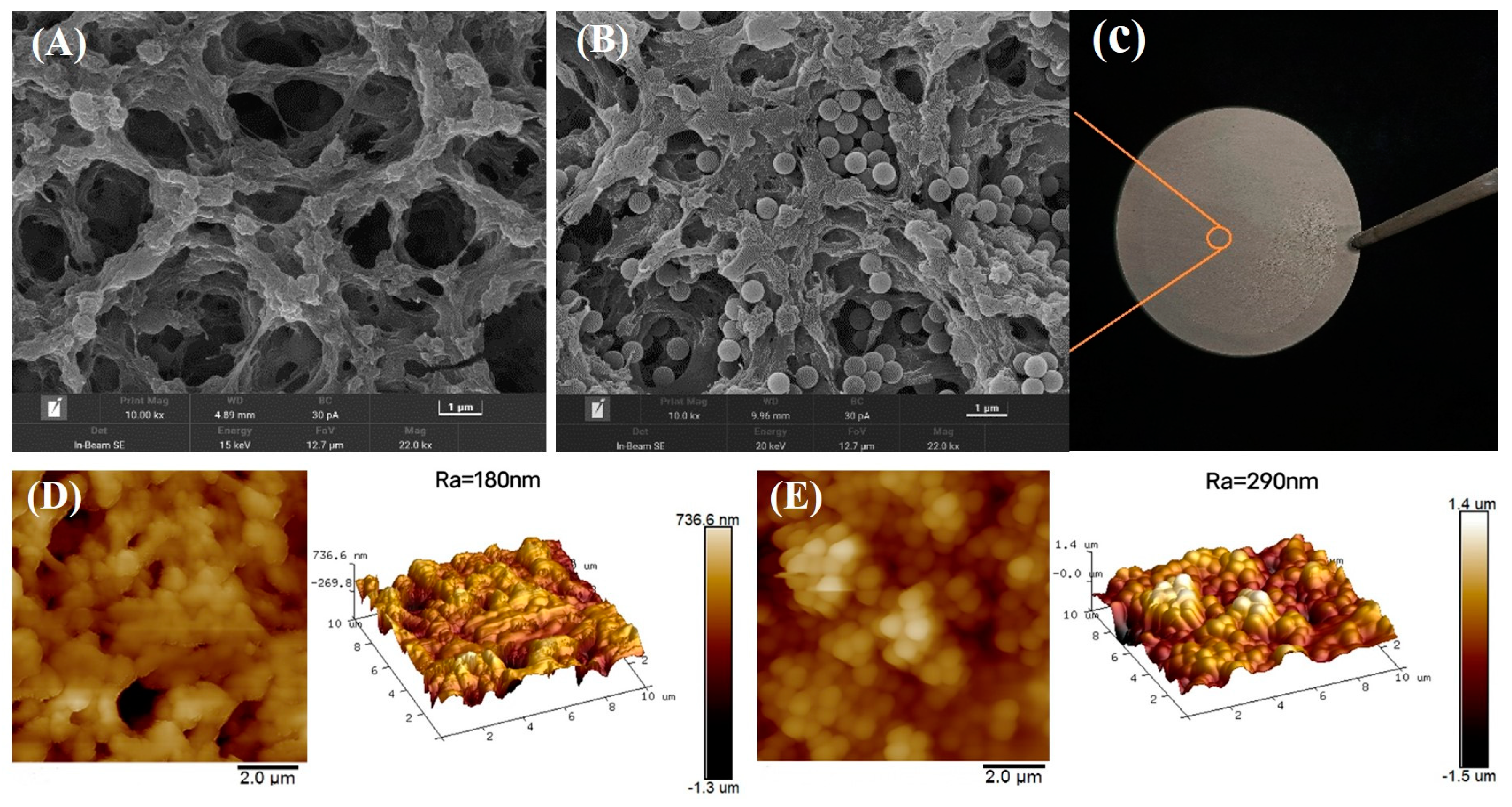
2.3. Characterization of E-TBBPA-MINs and E-TBBPA-MIM
2.4. Batch Rebinding Experiments
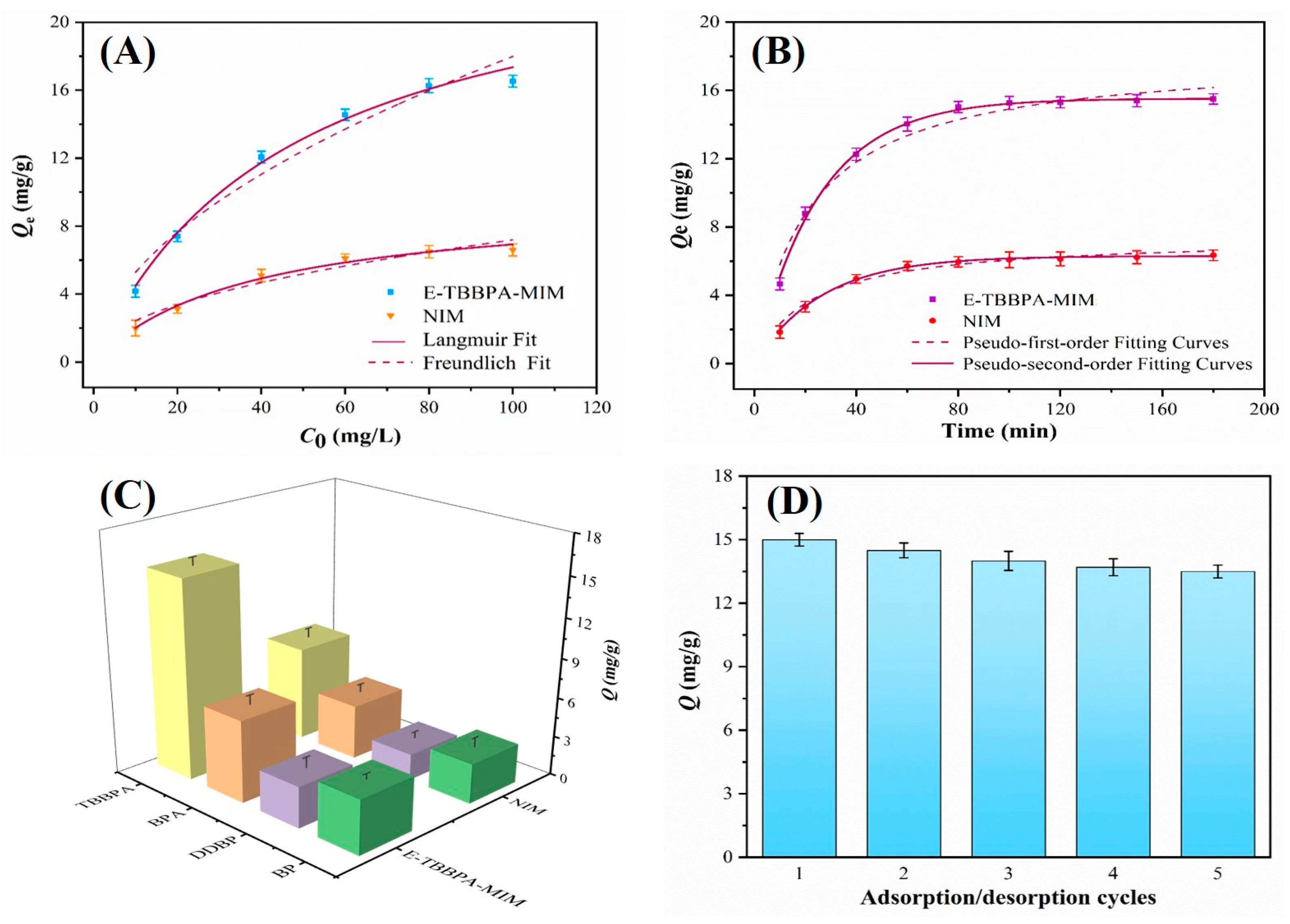
2.4.1. Adsorption Isotherms of E-TBBPA-MIM
2.4.2. Kinetic Absorption of E-TBBPA-MIM
2.4.3. Selective Rebinding Experiments
2.4.4. Stability Tests
2.5. Selective Permeation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of E-TBBPA-MINs Composition
3.2. Characterization of E-TBBPA-MINs and E-TBBPA-MIMs
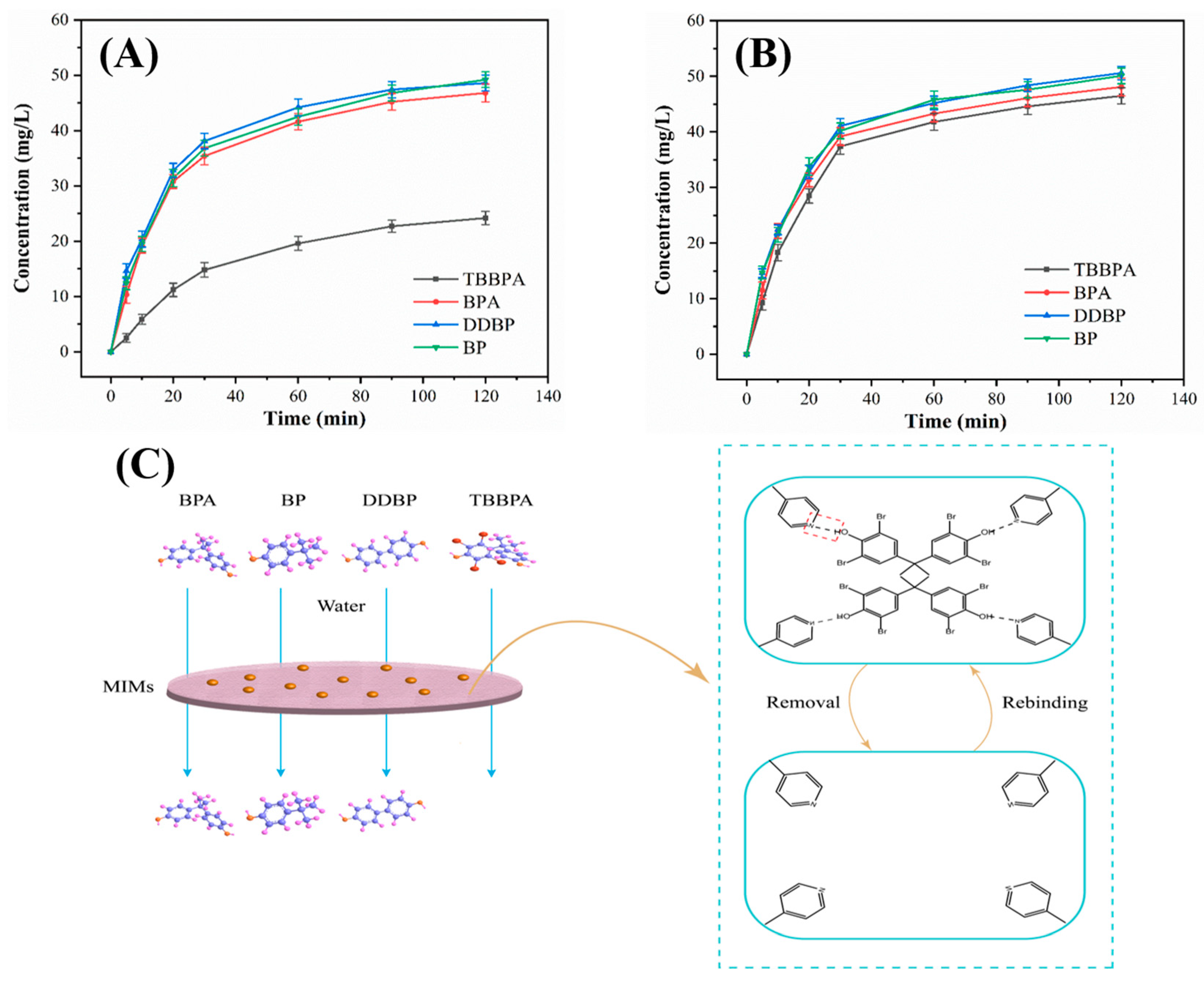
3.3. Adsorption Performance of E-TBBPA-MIM
3.4. Permselectivity Performance and Mechanism of E-TBBPA-MIM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TBBPA | Tetrabromobisphenol A |
| SiO2 NPs | Silica nanoparticles |
| KH-570 | 3-(methacryloyloxy) propyltrimethoxysilane |
| E-TBBPA-MINs | Eluted TBBPA molecularly imprinted nanoparticles |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| E-TBBPA-MIM | Eluted TBBPA molecularly imprinted membrane |
| BP | P-tert-butylphenol |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| DDBP | 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl |
| EDCs | Endocrine disrupting compounds |
| TTR | Transthyretin |
| MIMs | Molecularly imprinted membranes |
| MINs | Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles |
| MIPs | Molecularly imprinted polymers |
| 4-VP | 4-vinylpridine |
| EGDMA | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl orthosilicate |
| AIBN | 2,2′-azobis (2-methylpropionitrile) |
| K-SiO2 NPs | KH-570 modified silica nanoparticles |
| SEM-EDS | Energy-dispersive spectrometer |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectrometer |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| TGA | Thermo-gravimetric analysis |
| BET | Brunauer-Emmett-Teller |
| SDC | Contact angle meter |
| NINS | Non-imprinted nanoparticles |
| NIMS | Non-imprinted membranes |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| Qe | Equilibrium adsorption capacity |
| Qt | Absorption capacity at different contact time |
| Q | Adsorption capacity |
| K | Static allocation coefficient |
| α | Imprinting factor |
| J | Permeation flux |
| P | Permeation coefficient |
| β | Permselectivity factors |
| Ra | Roughness |
References
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in US drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citulski, J.A.; Farahbakhsh, K. Fate of endocrine-active compounds during municipal biosolids treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8367–8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnotta, V.; Amodei, R.; Frasca, F.; Aversa, A.; Giordano, C. Impact of chemical endocrine disruptors and hormone modulators on the endocrine system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.W.; Wei, L.F.; Tang, Y.Y.; Kong, W.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Schnoor, J.L.; Jiang, G.B. Two typical glycosylated metabolites of tetrabromobisphenol A formed in plants: Excretion and deglycosylation in plant root zones. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.T.; Zhu, N.W.; Wei, X.R.; Li, F.; Wu, P.X.; Dang, Z.; Cui, B.F. Efficient peroxydisulfate activation with nZVI/CuO@BC nanocomposite derived from wastes for degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A in alkaline environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Y.Q.; Liu, G.Q.; Hu, B.; Lu, J. Degradation of tetrabromobisphenol S by thermo-activated persulphate oxidation: Reaction kinetics, transformation mechanisms, and brominated by-products. Environ. Technol. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.C.; Wu, P.P.; Zhao, Y.L.; Lai, Y.X.; Wang, F.; Li, S. Efficient electrochemical degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A using MnO2/MWCNT composites modified Ni foam as cathode: Kinetic analysis, mechanism and degradation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, G.; An, C.J.; Xin, X.Y.; Huang, C.; Rosendahl, S. Removal of Tetrabromobisphenol A by adsorption on pinecone-derived activated charcoals: Synchrotron FTIR, kinetics and surface functionality analyses. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Y.; Ren, H.B.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. Room-temperature synthesis of microporous organic network for efficient adsorption and removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cordova, G.A.; Villa, J.E.L.; Khan, S.; Picasso, G.; Sotomayor, M.D.T. Surface molecularly imprinted core-shell nanoparticles and reflectance spectroscopy for direct determination of tartrazine in soft drinks. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1159, 338443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Huang, G.D.; Li, Y.P.; An, C.J.; Feng, R.F.; Wu, Y.H.; Shen, J. Functional PVDF ultrafiltration membrane for Tetrabromobisphenol-A (TBBPA) removal with high water recovery. Water. Res. 2020, 181, 115952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Cretin, M.; Esposito, G.; Oturan, M.A. Coupling of membrane filtration and advanced oxidation processes for removal of pharmaceutical residues: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.L.; Yue, X.Y.; Lin, F.Q.; Huang, F.; Zhang, B.T.; Lin, Z. Template-synthesized ultra-thin molecularly imprinted polymers membrane for the selective preconcentration of dyes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10959–10968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; He, W.B.; Yan, Y.; Song, J.P.; Xing, W.D.; Meng, M.J.; Gao, J.; Yan, Y.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ma, Z.F. A deep insight for TBBPA imprinting on PVP-assisted separation membrane: Elucidation of detailed chemical transition in membrane preparation and imprinting process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, X.W.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Surface-modified polystyrene beads as photografting imprinted polymer matrix for chromatographic separation of proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.M.; Zhou, L.C.; Wu, Q.; Bao, C.; Liu, M.Z. Preparation of novel magnetic molecular imprinted polymers nanospheres via reversible addition—Fragmentation chain transfer polymerization for selective and efficient determination of tetrabromobisphenol A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Dong, C.K.; Qi, J.Y.; Yuan, Y.X. Synthesis of core-shell magnetic molecular imprinted polymer by the surface RAFT polymerization for the fast and selective removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Song, J.P.; Yan, Y.; Gao, J.; Xing, W.D.; Meng, M.J.; Yan, Y.S.; Ma, Z.F.; Wu, Y.L. A “graphdiyne-like” anti-fouling TBBPA molecularly imprinted membrane synthesized based on the delayed phase inversion method: A concomitant permeability and selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Gotipamul, P.P.; Rajan, K.D.; Kumar, G.M.; Chidambaram, S.; Rathinam, M. Rapid selective adsorption of hazardous dyes using charge controlled NiO layers encapsulated SiO2 core-shell nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 28969–28979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, Z.R.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.D.; Gao, L.; Wei, M.B.; Yan, Y.S.; Li, C.X. A polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted polymer on nanoparticles of type SiO2@rGO@Ag for the detection of lambda-cyhalothrin via SERS. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StöBer, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, S.; Gul, S.; Pividori, M.I.; Sotomayor, M.D.T. A novel core@shell magnetic molecular imprinted nanoparticles for selective determination of folic acid in different food samples. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 106, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoued-Grayaa, N.; Nasraoui, C.; Chevalier, Y.; Hbaieb, S. Design of molecularly imprinted polymer materials relying on hydrophobic interactions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Sheng, N.; Zhu, R.; Wei, F.D.; Cal, Z.; Zhai, M.J.; Du, S.H.; Hu, Q. Preparation of dummy template imprinted polymers at surface of silica microparticles for the selective extraction of trace bisphenol A from water samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, W.H.; Luan, Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhu, M.Y.; Yang, W.M. Synthesis of surface molecular imprinted polymers based on carboxyl-modified silica nanoparticles with the selective detection of dibutyl phthalate from tap water samples. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Fang, H.; Xu, H.; Yu, H.; Zhou, T.; Liu, C.; Che, G.; Wang, D. Hydrophilic modification of PVDF-based SERS imprinted membrane for the selective detection of L-tyrosine. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qin, Y.Y.; Li, C.X.; Wu, Y.L.; Meng, M.J.; Dong, Z.Q.; Sun, C.; Chen, M.N.; Yan, Y.S. Irregular dot array nanocomposite molecularly imprinted membranes with enhanced antibacterial property: Synergistic promotion of selectivity, rebinding capacity and flux. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Ping, M.; Wu, Z.C.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.W. Microfiltration membranes modified by silver-decorated biomimetic silica nanopollens for mitigating biofouling: Synergetic effects of nanopollens and silver nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Long, Y.M.; Nie, L.H.; Yao, S.Z. Molecularly imprinted thin film self-assembled on piezoelectric quartz crystal surface by the sol-gel process for protein recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Gao, B.; Feng, X. Adsorption and recognizing ability of molecular imprinted polymer MIP-PEI/SiO2 towards phenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, W.; Fan, T.; Yang, W. Preparation of surface molecularly imprinted polymers for selective removal and determination of sulphamethoxazole from aqueous media. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.M.; Ma, W.Q.; Ma, J.; Wen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.B. Synthesis and properties of bisphenol A molecular imprinted particle for selective recognition of BPA from water. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2012, 367, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.M.; Bai, H.; Wang, H.H.; Fei, G.Q.; Li, L.L.; Zhu, Y. Magnetically sensitive and high template affinity surface imprinted polymer prepared using porous TiO2-coated magnetite-silica nanoparticles for efficient removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from polluted water. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, N.; Khosravi, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Khorasani, M. Synthesis, characterization, and application of nano-molecularly imprinted polymer for fast solid-phase extraction of tartrazine from water environment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qin, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Meng, M.J.; Dong, Z.Q.; Yu, C.; Yan, Y.S.; Li, C.X.; Nyarko, F.K. Bidirectional molecularly imprinted membranes for selective recognition and separation of pyrimethamine: A double-faced loading strategy. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anene, A.; Kalfat, R.; Chevalier, Y.; Hbaieb, S. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based materials as thin films on silica supports for efficient adsorption of Patulin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 497, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Rong, J.; Mao, K.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, T.; Pan, J.M.; Qiu, F.X. A recognition strategy combining effective boron affinity technology and surface imprinting to prepare highly selective and easily recyclable polymer membrane for separation of drug molecule. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 624, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Qiu, F.X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.C.; Yang, D.Y.; Dai, Y.T. A facile strategy toward 3D hydrophobic composite resin network decorated with biological ellipsoidal structure rapeseed flower carbon for enhanced oils and organic solvents selective absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Li, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Choo, J.; Chen, L.X. Molecular imprinting: Green perspectives and strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lu, J.; Lin, X.Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, J.Y.; Lv, P.; Liu, X.L.; Meng, M.J.; Yan, Y.S. Bioinspired synthesis of janus nanocomposite-incorporated molecularly imprinted membranes for selective adsorption and separation applications. Acs Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9104–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, G.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q. Preparation and recognition properties of molecularly imprinted nanofiber membrane of chrysin. Polymers 2022, 14, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wu, F.; Wei, Z.X.; Yang, K.W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Pan, J.M. Capturing lithium using functional macroporous microspheres with multiple chambers from one-step double emulsion via a tailoring supramolecular route and postsynthetic interface modification. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.W.; Shi, S.N.; Qiu, F.X.; Xu, X.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, T. Enhanced As(III) removal from aqueous solutions by recyclable Cu@MNM composite membranes via synergistic oxidation and absorption. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.T.; Shi, Y.P. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective extraction of quercetagetin from calendula officinalis extract. Talanta 2015, 134, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.C.; Pan, J.M.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, F.X.; Niu, X.H.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.L. Three-in-one strategy for selective adsorption and effective separation of cis-diol containing luteolin from peanut shell coarse extract using PU/GO/BA-MOF composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, M.; Lv, P.; Yan, M.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, C. Bio-inspired adhesion: Fabrication of molecularly imprinted nanocomposite membranes by developing a hybrid organic-inorganic nanoparticles composite structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Xing, W.D.; Yan, J.Z.; Cui, J.Y.; Ma, F.G.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Yu, C.; Yan, M. Multilevel mineral-coated imprinted nanocomposite membranes for template-dependent recognition and separation: A well-designed strategy with PDA/CaCO3-based loading structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 575, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of NPs | Elemental Composition (at.%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | Si | Br | |
| SiO2 NPs | 0.6 | - | 65.7 | 33.6 | - |
| K-SiO2 NPs | 29.4 | - | 51.5 | 19.0 | - |
| TBBPA-MINs | 53.8 | 0.6 | 32.5 | 12.9 | 0.2 |
| E-TBBPA-MINs | 50.4 | 0.5 | 36.2 | 12.9 | - |
| NINs | 52.7 | 0.6 | 33.7 | 13.0 | - |
| Water Permeability a (L/m2·h) | Contact Angle (o) | Porosity (%) | Qe (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-TBBPA-MIM | 722.0 ± 14.0 | 14.3 ± 1.6 | 49.3 ± 1.0 | 19.2 ± 0.3 |
| PVDF membrane | 1256.0 ± 15.0 | 97.5 ± 1.7 | 72.4 ± 1.1 | 0.5 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Luo, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wei, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J. Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Nanoparticles Embedded Microfiltration Membrane for Selective Separation of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Water. Membranes 2023, 13, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060571
Zhang X, Luo X, Wei J, Zhang Y, Jiang M, Wei Q, Chen M, Wang X, Zhang X, Zheng J. Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Nanoparticles Embedded Microfiltration Membrane for Selective Separation of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Water. Membranes. 2023; 13(6):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060571
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xingran, Xiang Luo, Jiaqi Wei, Yuanyuan Zhang, Minmin Jiang, Qiaoyan Wei, Mei Chen, Xueye Wang, Xuehong Zhang, and Junjian Zheng. 2023. "Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Nanoparticles Embedded Microfiltration Membrane for Selective Separation of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Water" Membranes 13, no. 6: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060571
APA StyleZhang, X., Luo, X., Wei, J., Zhang, Y., Jiang, M., Wei, Q., Chen, M., Wang, X., Zhang, X., & Zheng, J. (2023). Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Silica Nanoparticles Embedded Microfiltration Membrane for Selective Separation of Tetrabromobisphenol A from Water. Membranes, 13(6), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13060571









