Phenylalanine Losses in Neutralization Dialysis: Modeling and Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical
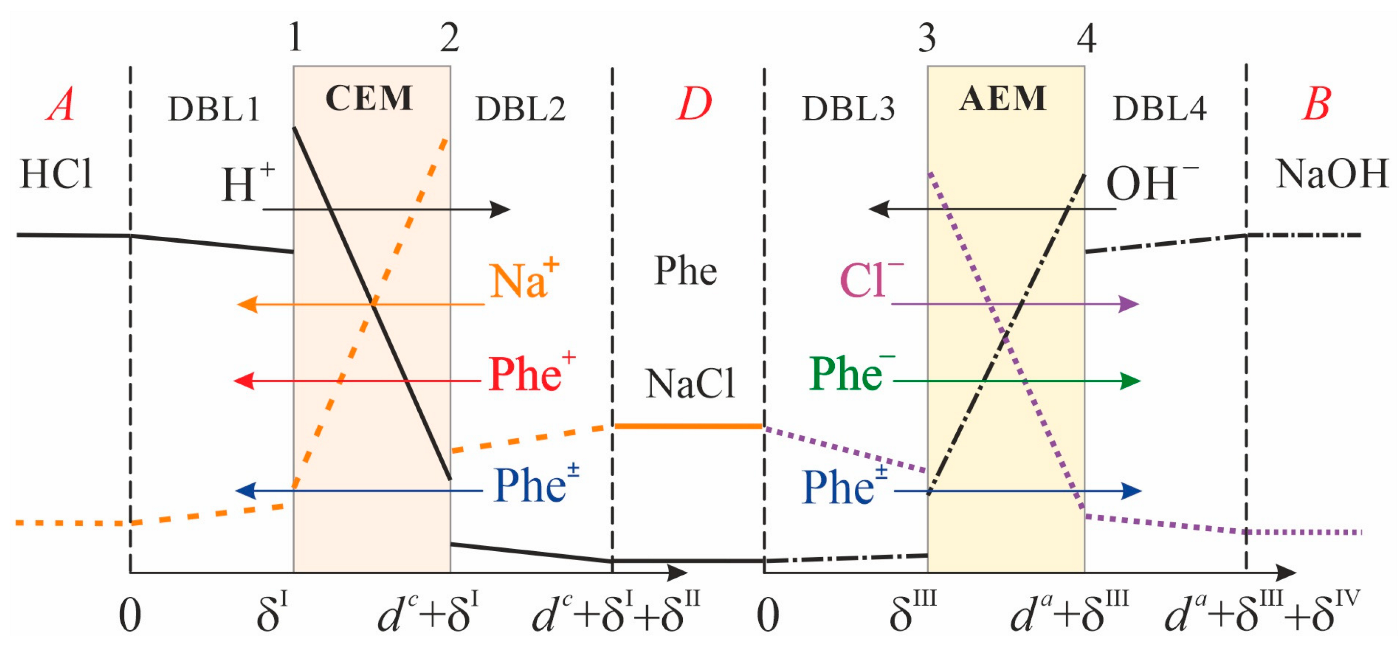
2.1. System under Study
2.2. Problem Formulation
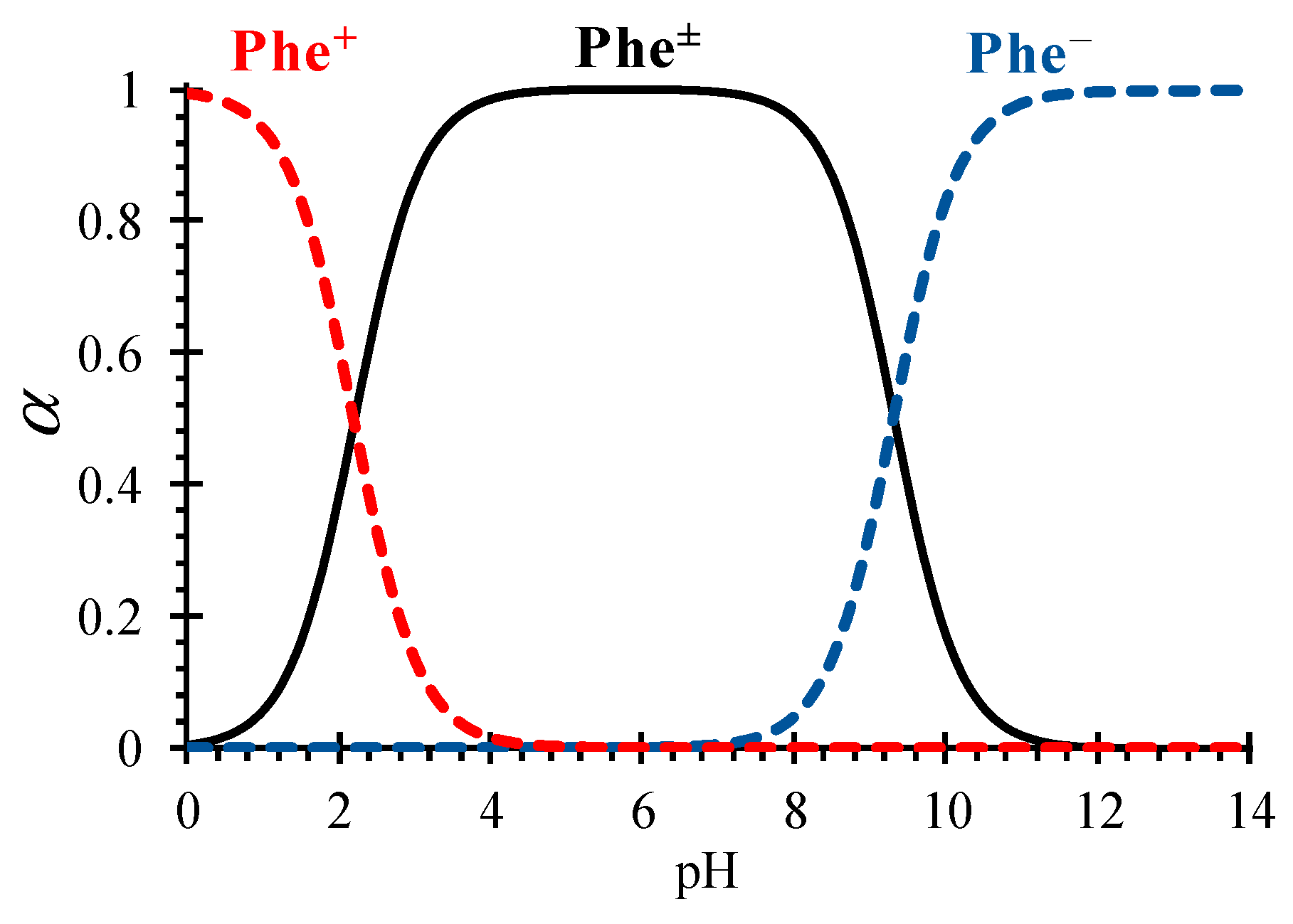
2.3. Parameters of the Model
3. Experimental
3.1. Neutralization Dialysis Process
3.2. Membranes
4. Results and Discussions
- (1)
- by the selection of membranes with desired properties (structure, thickness, ion-exchange capacity, nature of fixed ion-exchange groups, etc.);
- (2)
- by changing the hydrodynamic conditions in the compartments of the ND system, which affects the DBL thickness near the membrane surfaces;
- (3)
- by changing the concentration of acid and/or alkali in the corresponding compartments, which affects the concentration gradient between these compartments and the D compartment and, as a consequence, the ion fluxes.
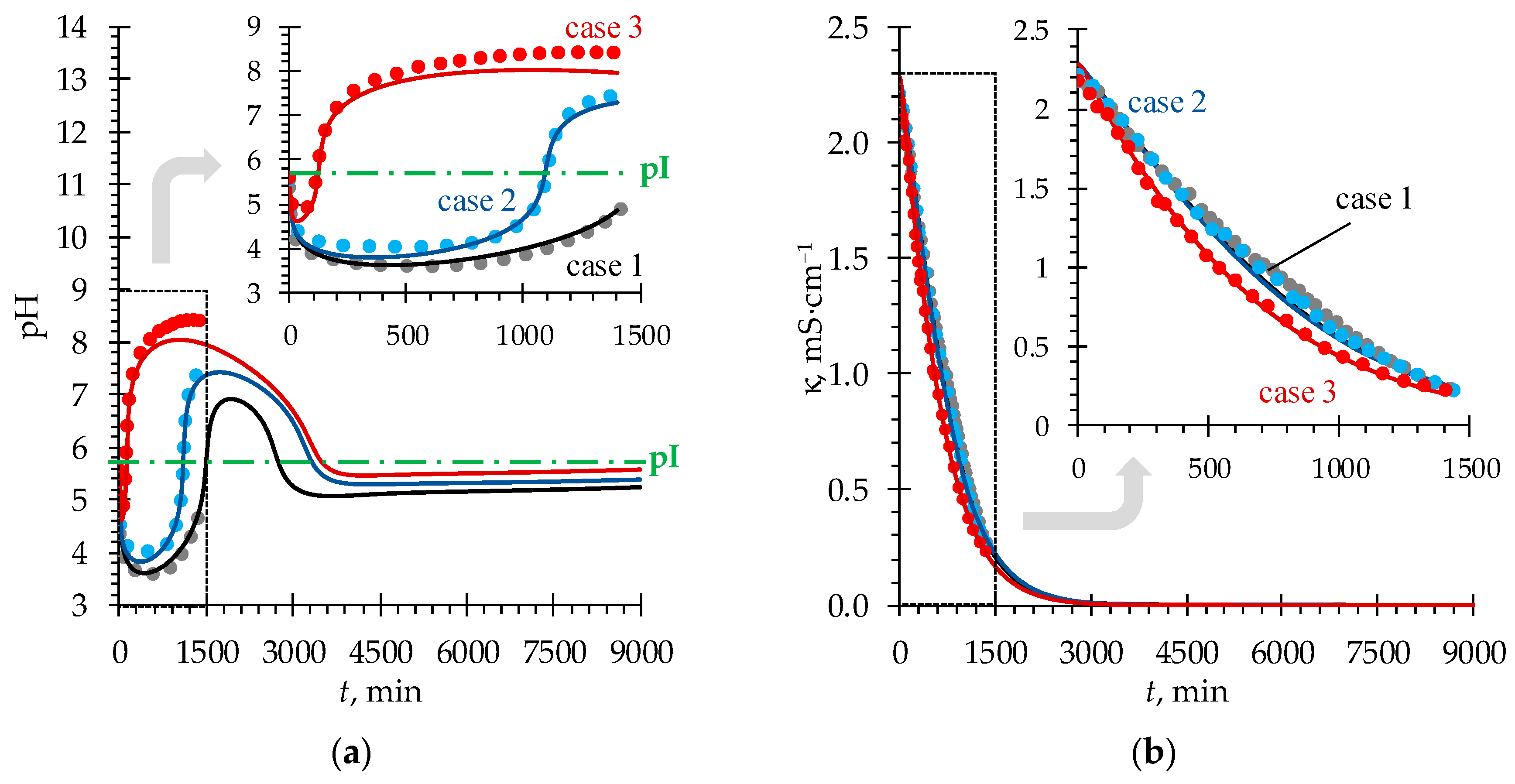
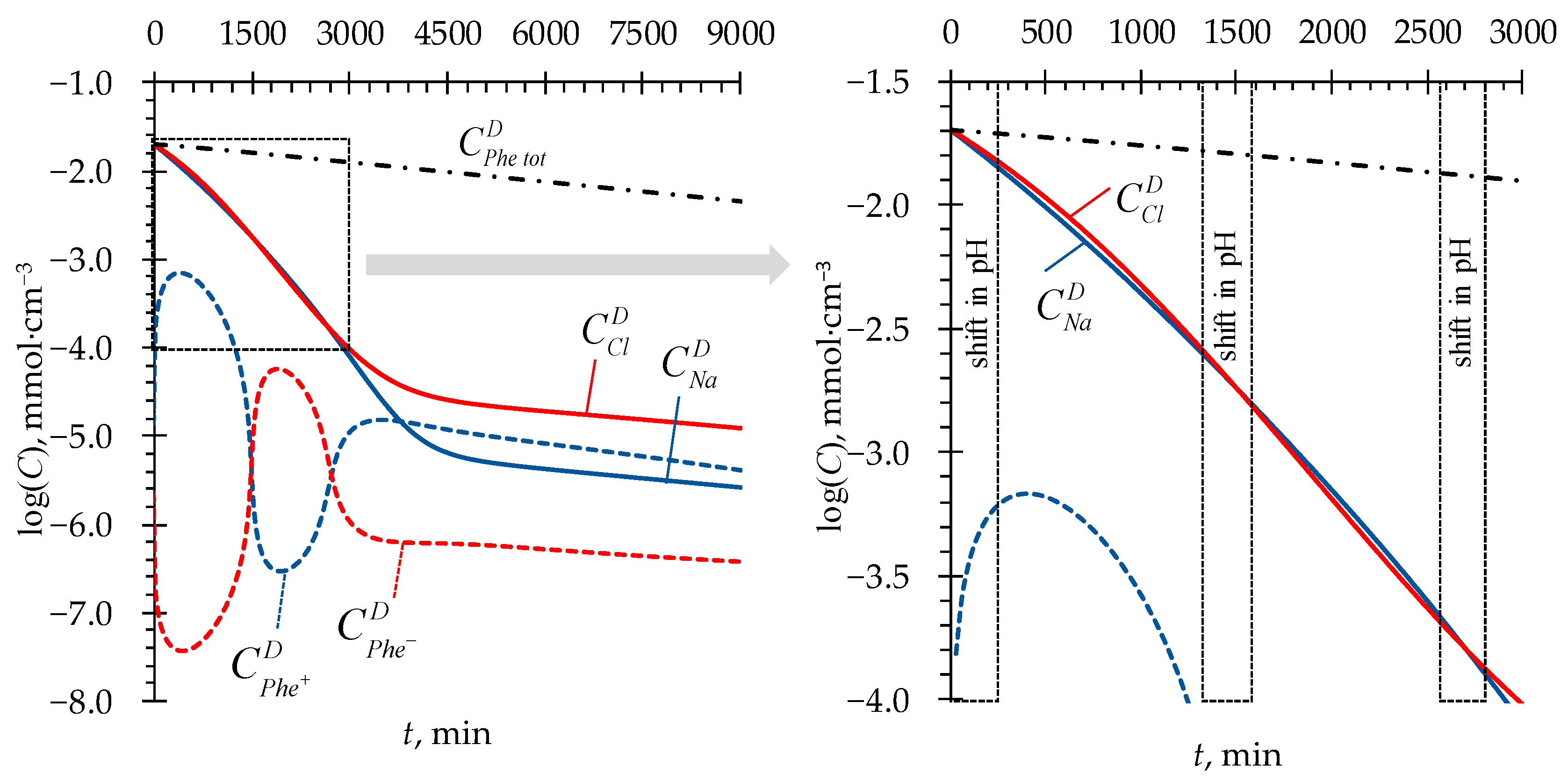
4.1. pH Fluctuations in Desalination Compartment
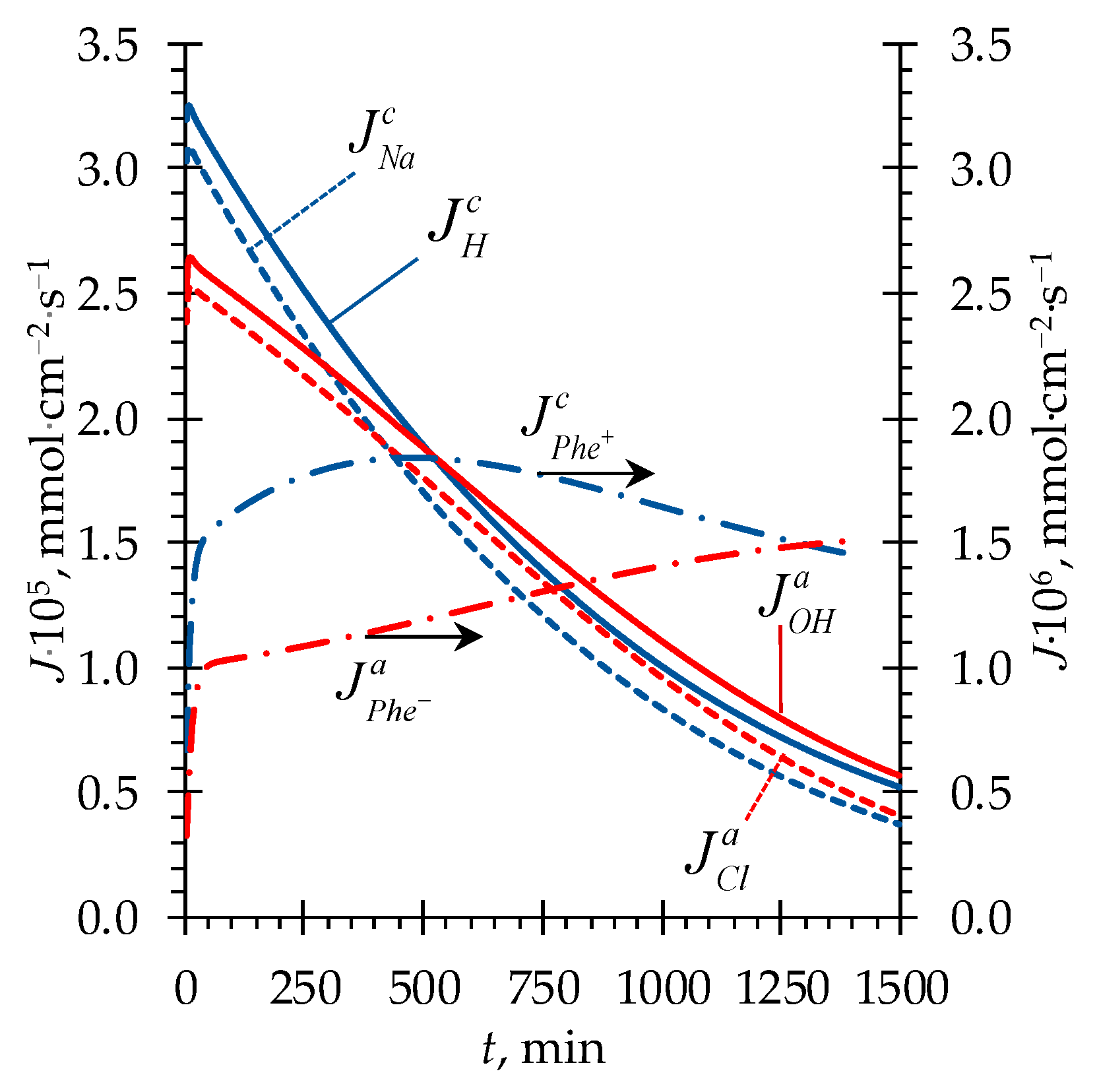
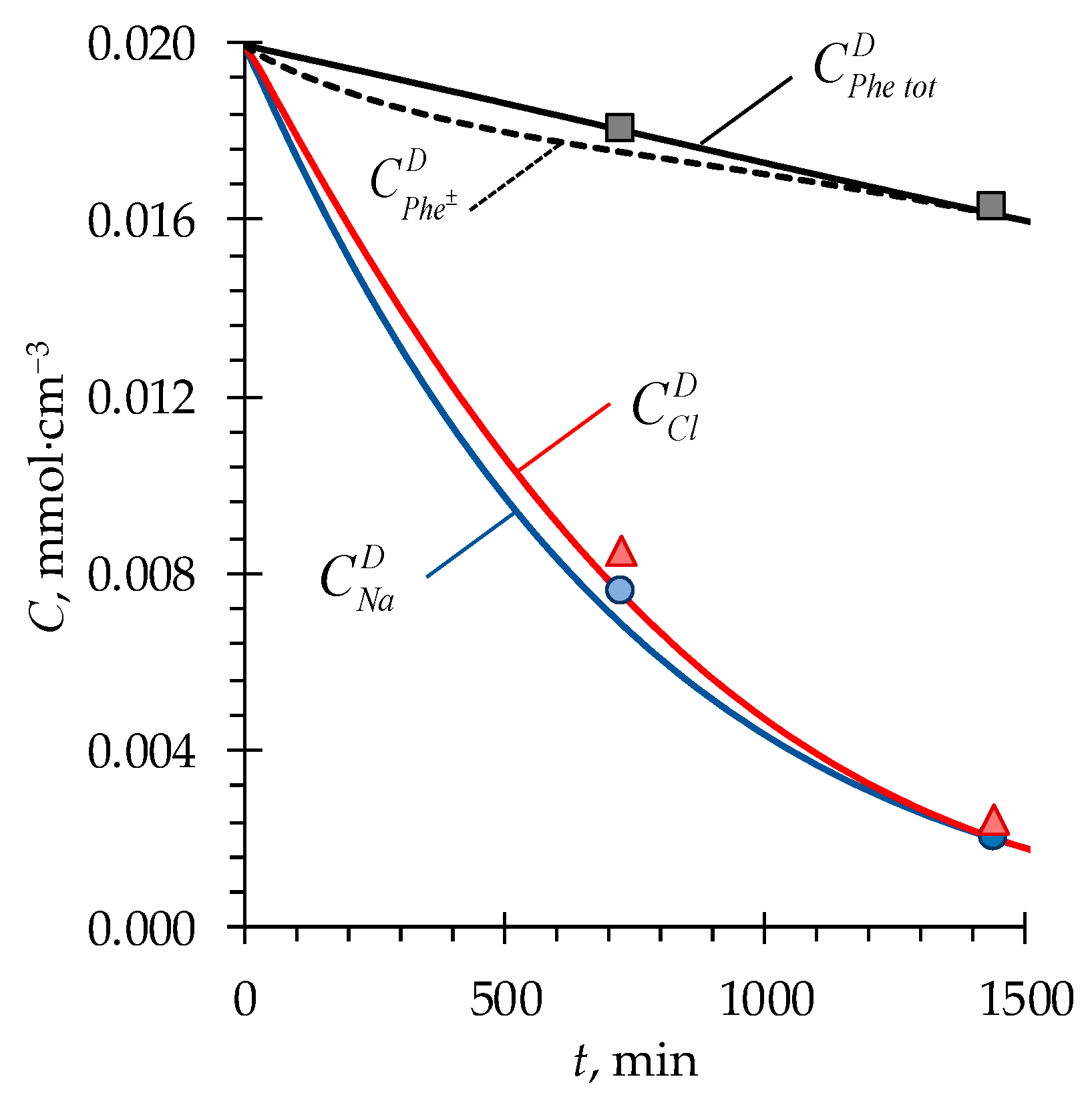
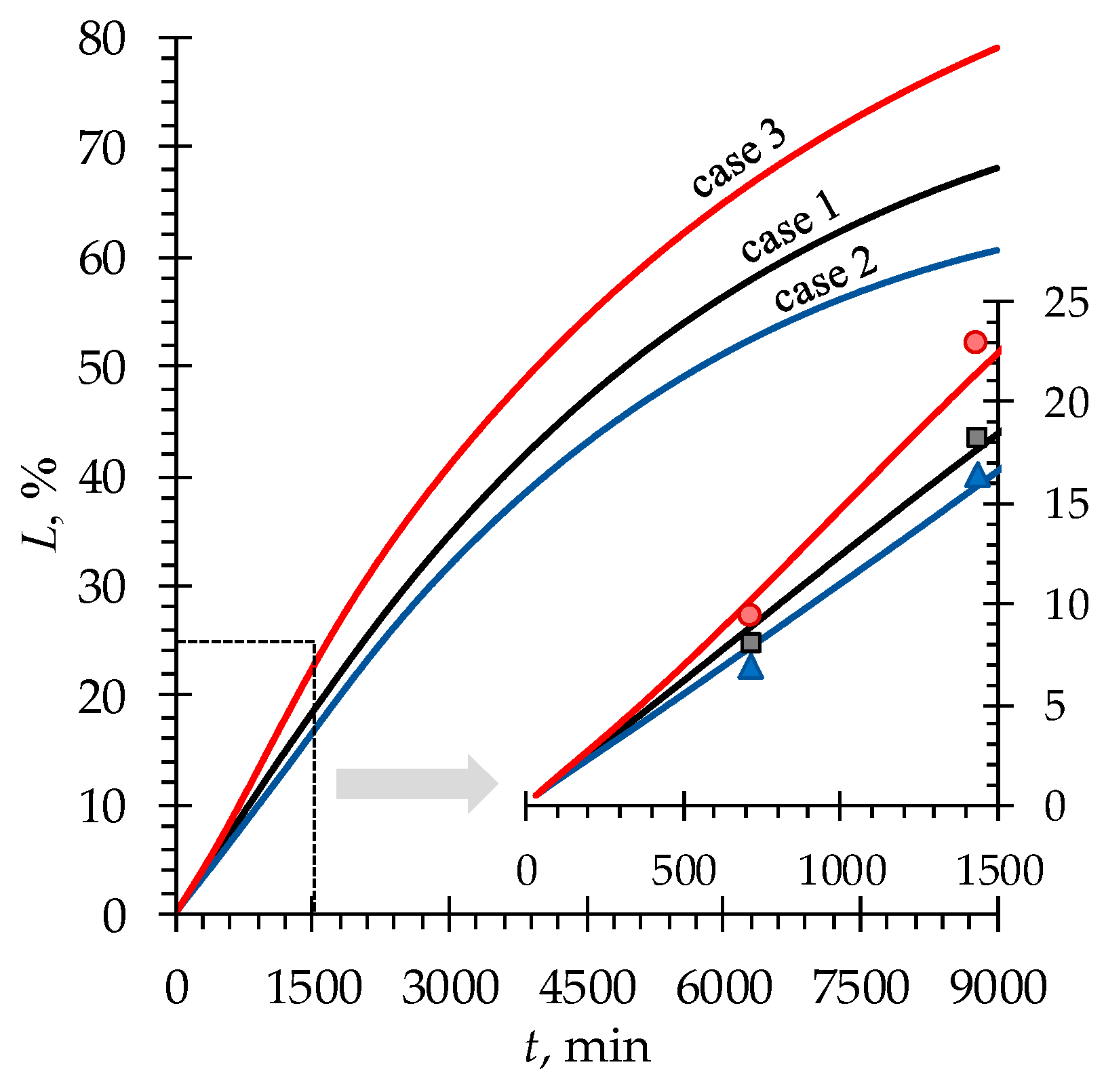
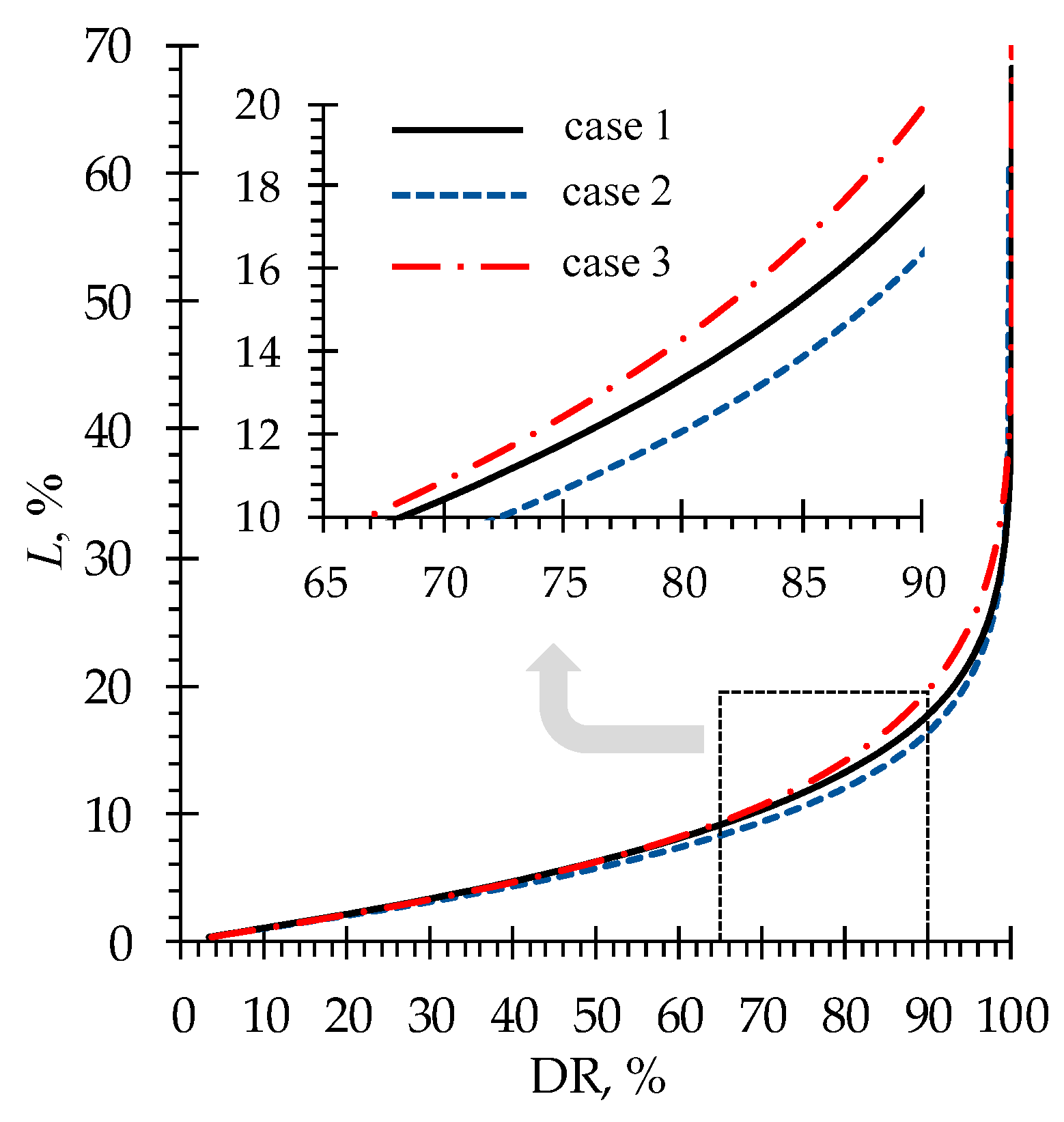
4.2. Phenylalanine Losses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Value | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| and | 140 and 150 | microns | CEM and AEM thickness, respectively * |
| 85 | The thickness of diffusion boundary layers **, k = I, II, III, IV (Figure 1) | ||
| 0.02 | mol·L−1 | Initial molar concentration of salt in the desalination compartment D (Table 2) | |
| 0.1 or 0.05 | Initial molar concentration of acid in the acid compartment A (Table 2) | ||
| 0.1 or 0.2 | Initial molar concentration of alkali in the alkali compartment B (Table 2) | ||
| 0.02 | Initial molar concentration of phenylalanine in the desalination compartment D (Table 2) | ||
| VA and VB | 2 | L | Volume of solutions in the acid and alkali compartments, respectively |
| VD | 0.5 | Volume of the solution in the desalination compartment | |
| and | 1.85 and 1.99 | mmol·cm−3 | Ion-exchange capacity of CEM and AEM, respectively (in the swollen state) * |
| 1.34·10−5 | cm2·s−1 | Diffusion coefficients of Na+, Cl−, H+, OH−, Phe+, Phe−, and Phe± ions in solution at infinite dilution [22,34] | |
| 2.03·10−5 | |||
| 9.31·10−5 | |||
| 5.26·10−5 | |||
| 6.7·10−7 | |||
| 6.7·10−7 | |||
| 6.7·10−7 | |||
| 3.25·10−7 | Diffusion coefficients of Na+, H+, Phe+ ions in CEM and Cl−, OH−, Phe− ions in AEM ** | ||
| 9.0·10−6 | |||
| 1.1·10−7 | |||
| 2.25·10−7 | |||
| 7.8·10−7 | |||
| 0.75·10−7 | |||
| and | 3.3·10−8 and 2.3·10−8 | Diffusion coefficients of Phe± ions in CEM and AEM, respectively ** | |
| 10−14 | mol2·L−2 | Water ionization constant | |
| 6.31·10−3 | mol·L−1 | Equilibrium constant for chemical reaction (6) [22] | |
| 4.90·10−10 | Equilibrium constant for chemical reaction (7) [22] | ||
| and | 1 | – | Nikolskii equilibrium constant for exchange between H+ and Na+, H+, and Phe+ in CEM |
| and | 1 | – | Nikolskii equilibrium constant for exchange between OH− and Cl−, OH− and Phe− in AEM |
| T | 298 | K | Absolute temperature |
| R | 8.314 | J·(mol·K)−1 | Gas constant |
| F | 96,485 | C·mol−1 | Faraday constant |
| Abbreviations | Description |
|---|---|
| AEM | anion-exchange membrane |
| CEM | cation-exchange membrane |
| DBL | diffusion boundary layer |
| DR | desalination rate |
| ER | exchange rate |
| ND | neutralization dialysis |
| Phe | phenylalanine |
| Superscripts/subscripts | |
| Superscripts “c” and “a” | relates to CEM and AEM, respectively |
| Superscripts “A”, “B”, and “D” | relates to acid, alkali (base), and desalination compartments, respectively |
| Subscript “j” | relates to a certain species. The type of species described by the index j is indicated in the place of its appearance |
References
- Igawa, M.; Echizenya, K.; Hayashita, T.; Seno, M. Donnan dialysis desalination. Chem. Lett. 1986, 15, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, M.; Echizenya, K.; Hayashita, T.; Seno, M. Neutralization Dialysis for Deionization. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 60, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, M.; SenGupta, A.K.; Greenleaf, J. Hydrogen ion (H+) in waste acid as a driver for environmentally sustainable processes: Opportunities and challenges. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, M.; Mikami, K.; Okochi, H. Transport characteristics of neutralization dialysis and desalination of tap water. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 76, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chérif, M.; Mkacher, I.; Dammak, L.; Ben Salah, A.; Walha, K.; Grande, D.; Nikonenko, V. Water desalination by neutralization dialysis with ion-exchange membranes: Flow rate and acid/alkali concentration effects. Desalination 2015, 361, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ou-Yang, W.; Bastos Sales, B.; Sun, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhao, R. Capacitive neutralization dialysis for direct energy generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9363–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, M.; Tanabe, H.; Ida, T.; Yamamoto, F.; Okochi, H. Separation of weak acids and bases by neutralization dialysis. Chem. Lett. 1993, 22, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleha, M.; Tishchenko, G.A. Neutralization dialysis for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, M.; Fukushi, Y.; Hayashita, T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Selective transport of aldehydes across an anion-exchange membrane via the formation of bisulfite adducts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1990, 29, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, V.I.; Saud, A.M.; Akberova, E.M. Effect of the mass fraction of ion-exchange resin in a Ralex CM cation-exchange membrane on demineralization of phenylalanine aqueous salt solutions by neutralization dialysis. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2021, 3, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porozhnyy, M.V.; Kozmai, A.E.; Mareev, A.A.; Gil, V.V. Theoretical and experimental study of neutralization dialysis of phenylalanine–mineral salt equimolar mixture of different concentrations. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronchuk, V.; Zmievskii, Y.; Dzyazko, Y.; Rozhdestvenska, L.; Zakharov, V. Whey desalination using polymer and inorganic membranes: Operation conditions. Acta Period. Technol. 2018, 49, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, G.Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, T.; Kentish, S.E. Transforming salty whey into cleaning chemicals using electrodialysis with bipolar membranes. Desalination 2020, 492, 114598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, G.A.; Tishchenko, G.; Bleha, M.; Shataeva, L. Theoretical analysis of neutralization dialysis in the three-compartment membrane cell. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 98, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, A.M.; Vasil’eva, V.I.; Goleva, E.A.; Akberova, E.M.; Kozlov, A.T. Selection of anion-exchange membrane for separation of phenylalanine and sodium chloride by neutralization dialysis. Sorbtsionnye i Khromatograficheskie Protsessy 2020, 20, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Yonemoto, T.; Tadaki, T. Modeling of ionic transport in neutralization dialytic deionization. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1993, 26, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmai, A.; Chérif, M.; Dammak, L.; Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Nikonenko, V. Modelling non-stationary ion transfer in neutralization dialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmai, A.; Goleva, E.; Vasil’eva, V.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N. Neutralization dialysis for phenylalanine and mineral salt separation. Simple theory and experiment. Membranes 2019, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck-Lacaze, L.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P. Determination of the pKa of poly (4-vinylpyridine)-based weak anion exchange membranes for the investigation of the side proton leakage. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metayer, M.; Legras, M.; Grigorchouk, O.; Nikonenko, V.; Langevin, D.; Labbe, M.; Lebrun, L.; Shaposhnik, V. Facilitated transport of a-alanine and phenylalanine through sulfonic cation-exchange membranes. Desalination 2002, 147, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaposhnik, V.A.; Eliseeva, T.V. Barrier effect during the electrodialysis of ampholytes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 161, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0849304873. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Q.; Wei, K.; Hassanvand, A.; Freeman, B.D.; Kentish, S.E. Single and binary ion sorption equilibria of monovalent and divalent ions in commercial ion exchange membranes. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasil’eva, V.I.; Shaposhnik, V.A.; Zemlyanukhina, I.A.; Grigorchuk, O.V. Facilitated diffusion of amino acids in ion-exchange membranes. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 77, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Donnan, F.G. Theory of membrane equilibria and membrane potentials in the presence of non-dialysing electrolytes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Belova, E.I.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Larchet, C. Intensive current transfer in membrane systems: Modelling, mechanisms and application in electrodialysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 160, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseeva, T.; Kharina, A. Desalination of neutral amino acid solutions in an electromembrane system. Membranes 2022, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Pan, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Shen, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Extraction of amphoteric amino acid by bipolar membrane electrodialysis: Methionine acid as a case study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.; Urtenov, M.; Mareev, S.; Pourcelly, G. Mathematical modeling of the effect of water splitting on ion transfer in the depleted diffusion layer near an ion-exchange membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan Readi, O.M.; Gironès, M.; Wiratha, W.; Nijmeijer, K. On the isolation of single basic amino acids with electrodialysis for the production of biobased chemicals. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, Y. Diffusion dialysis-concept, principle and applications. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 366, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Yao, Z. A comprehensive review on the synthesis and applications of ion exchange membranes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisseeva, T.V.; Shaposhnik, V.A.; Luschik, I.G. Demineralization and separation of amino acids by electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes. Desalination 2002, 149, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Stokes, R.H. Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd ed.; Dover Publications Inc.: Mignola, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0486422259. [Google Scholar]
| Membrane | CSE | ASE |
|---|---|---|
| Ion-exchange capacity, mmol·cm−3 | 1.85 | 1.99 |
| Water content, % | 42.0 | 24.4 |
| Conductivity (in 0.1 M NaCl), mS·cm−1 | 7.37 | 3.77 |
| Conductivity (in 0.1 M Phe, CSE at pH = 0.5, ASE at pH = 13.1), mS·cm−1 | 5.67 | 2.32 |
| Conductivity (CSE in 0.1 M HCl, ASE in 0.1 M NaOH), mS·cm−1 | 71.12 | 6.76 |
| Thickness in swollen state, microns | 140 | 150 |
| Case | , mol·L−1 | , mol·L−1 | , mol·L−1 | , mol·L−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| case 1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| case 2 | 0.05 | 0.1 | ||
| case 3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozmai, A.; Porozhnyy, M.; Gil, V.; Dammak, L. Phenylalanine Losses in Neutralization Dialysis: Modeling and Experiment. Membranes 2023, 13, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050506
Kozmai A, Porozhnyy M, Gil V, Dammak L. Phenylalanine Losses in Neutralization Dialysis: Modeling and Experiment. Membranes. 2023; 13(5):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050506
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozmai, Anton, Mikhail Porozhnyy, Violetta Gil, and Lasaad Dammak. 2023. "Phenylalanine Losses in Neutralization Dialysis: Modeling and Experiment" Membranes 13, no. 5: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050506
APA StyleKozmai, A., Porozhnyy, M., Gil, V., & Dammak, L. (2023). Phenylalanine Losses in Neutralization Dialysis: Modeling and Experiment. Membranes, 13(5), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050506







