Performance Enhancement of Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-Supported SOFC by Electrophoretic Formation of Modifying BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3 and Ce0.8Sm0.1Pr0.1O1.9 Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Electrolytes
2.2. Synthesis of the Electrode Powders
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of PSDC and BCS-CuO Suspensions for EPD
2.4. Electrophoretic Deposition and Characterization of the PSDC and BCSCuO Films
2.5. Single-Cell Fabrication and Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
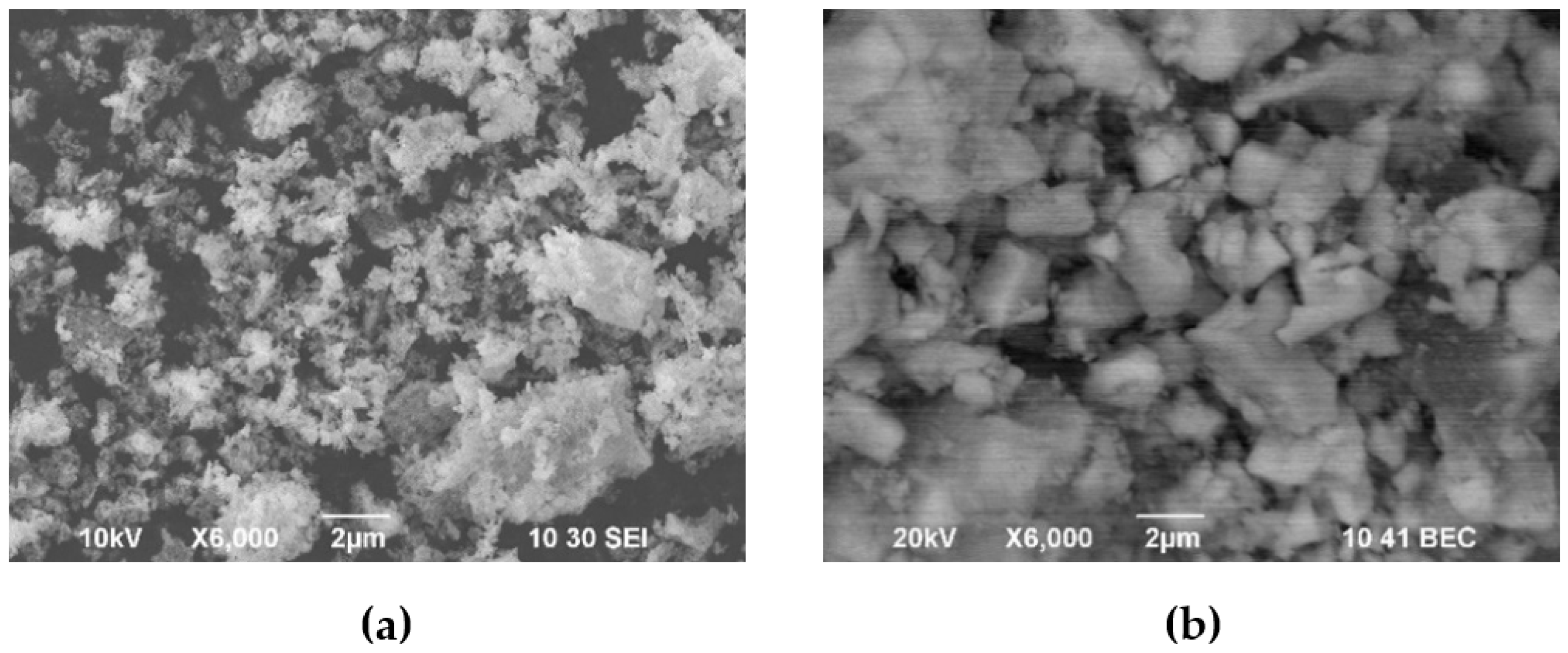
3.1. Characterization of the Initial Electrolyte and Electrolyte Powder Materials and Suspension Preparation for the EPD Process
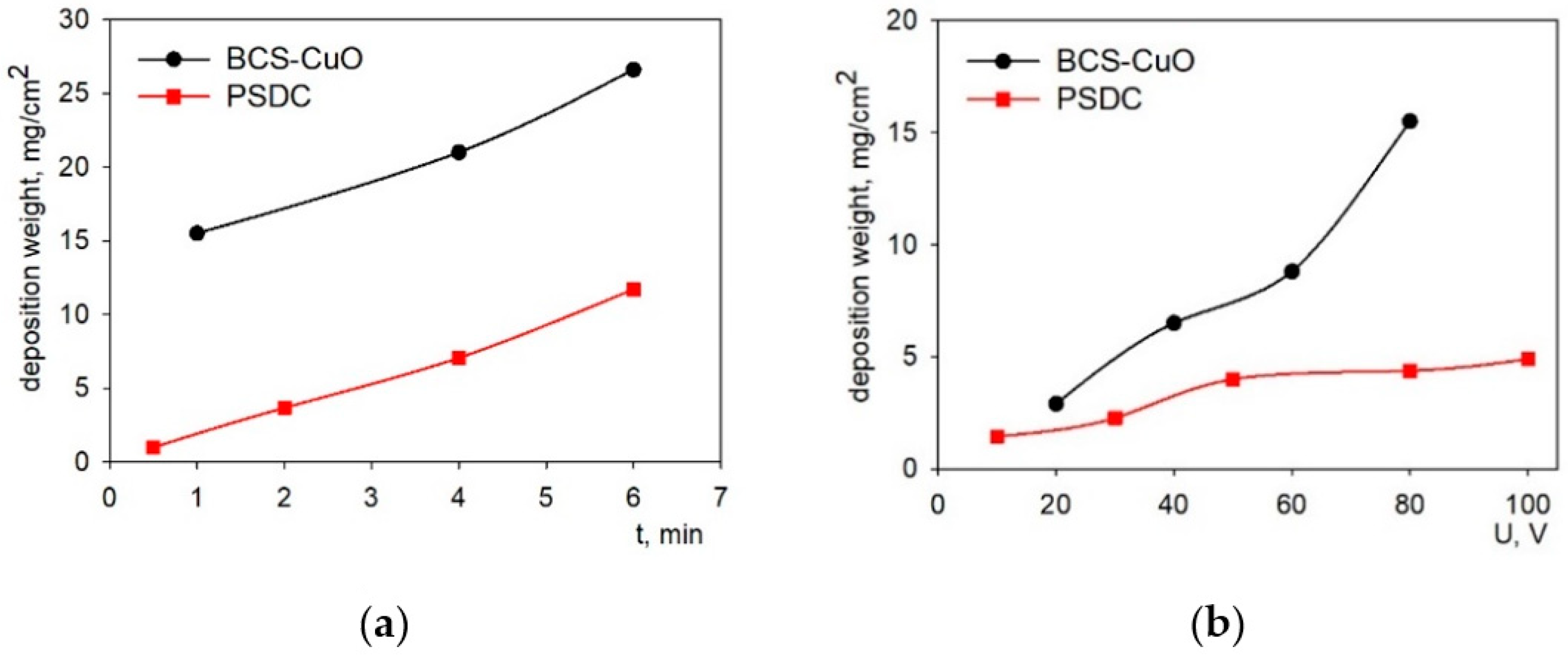
3.2. EPD from the PSDC and BCS-CuO Suspensions on a Ni-Foil Model Electrode: Selection of Deposition Modes
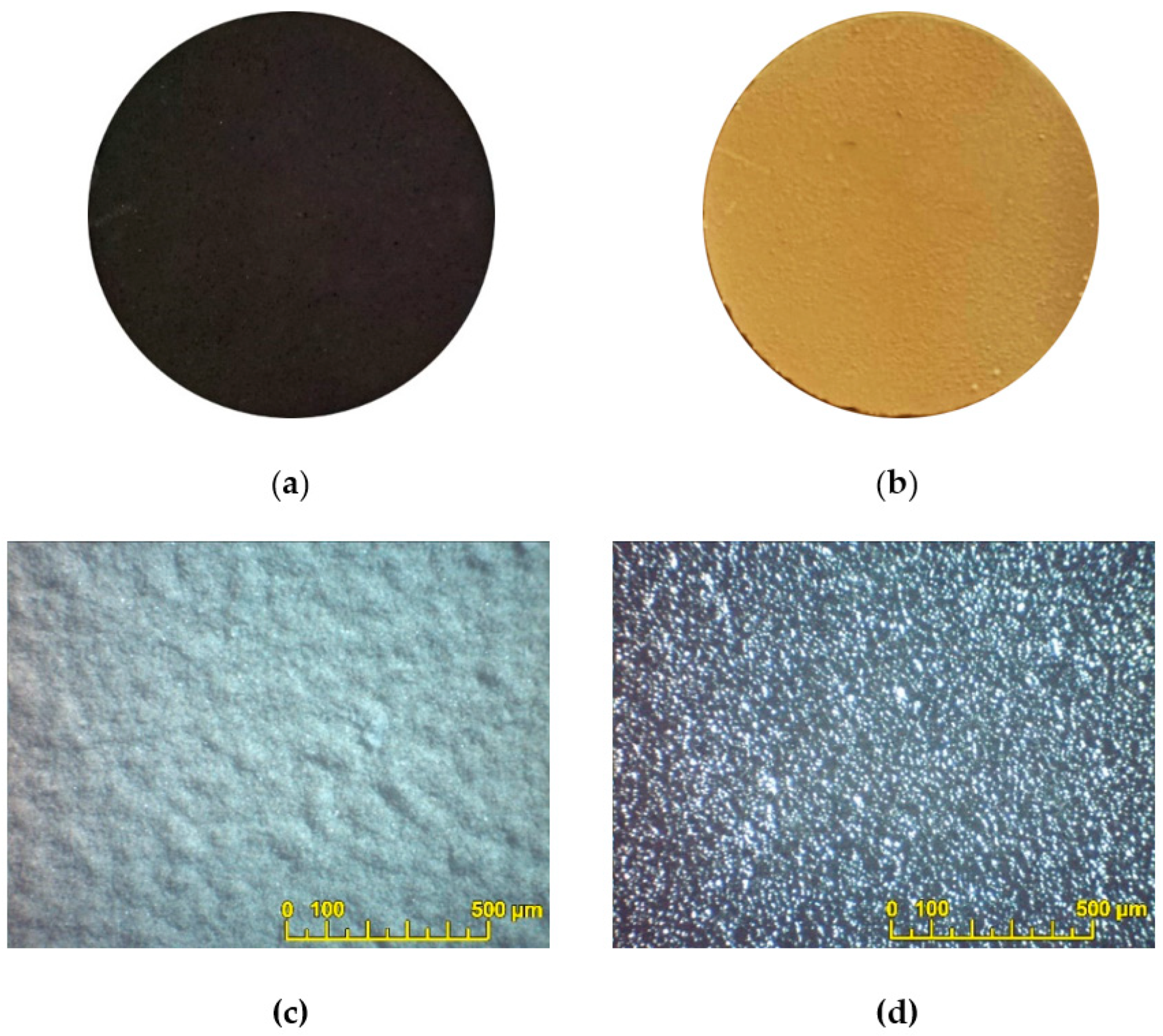
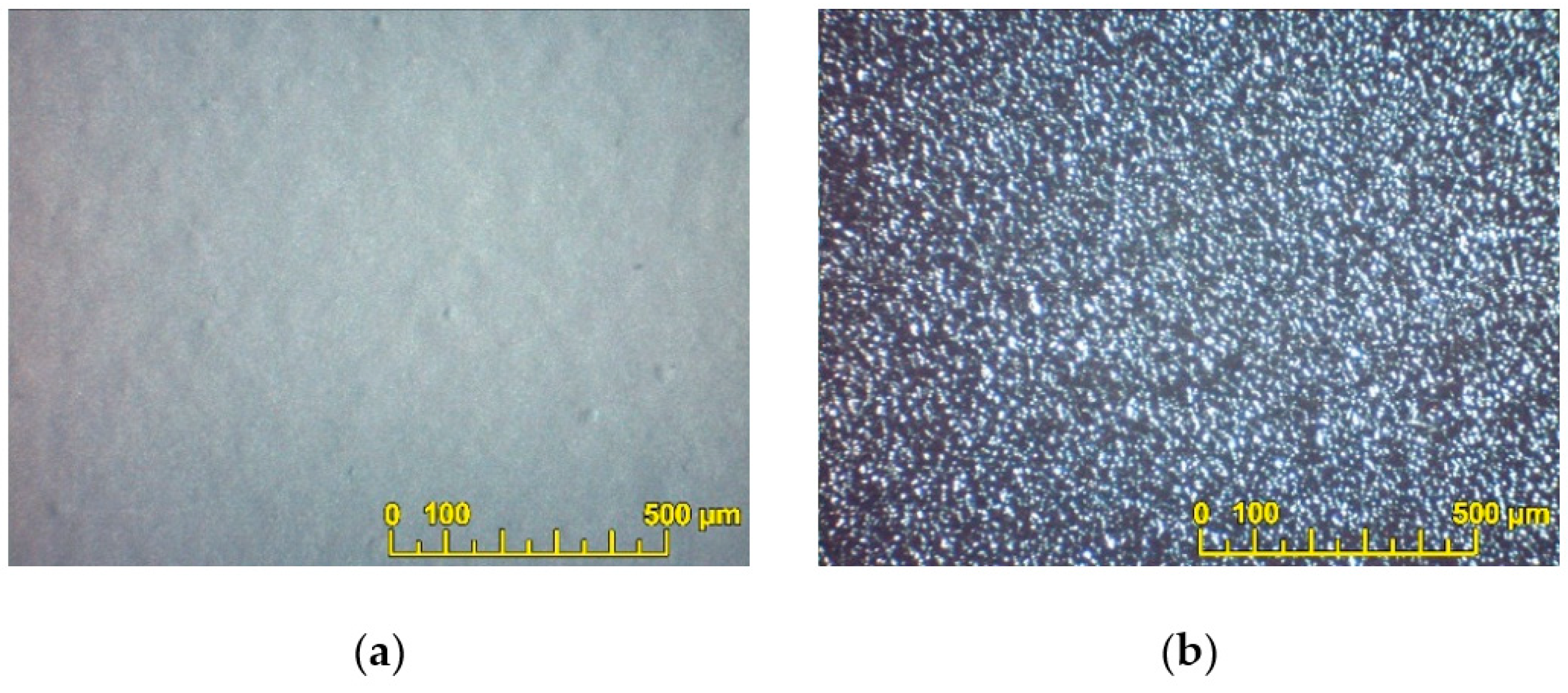
3.3. EPD of BCS-CuO Anode Barrier and PSDC Cathode Layers on Dense SDC Membranes with Predeposited PPy Sublayers
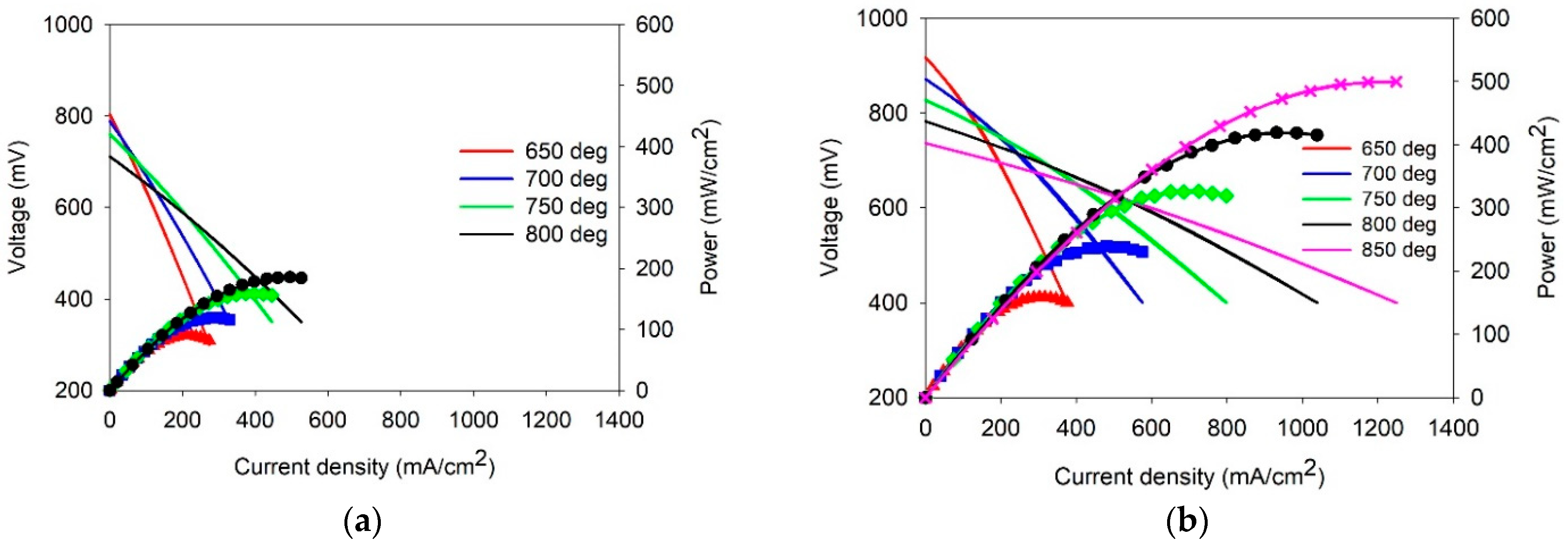
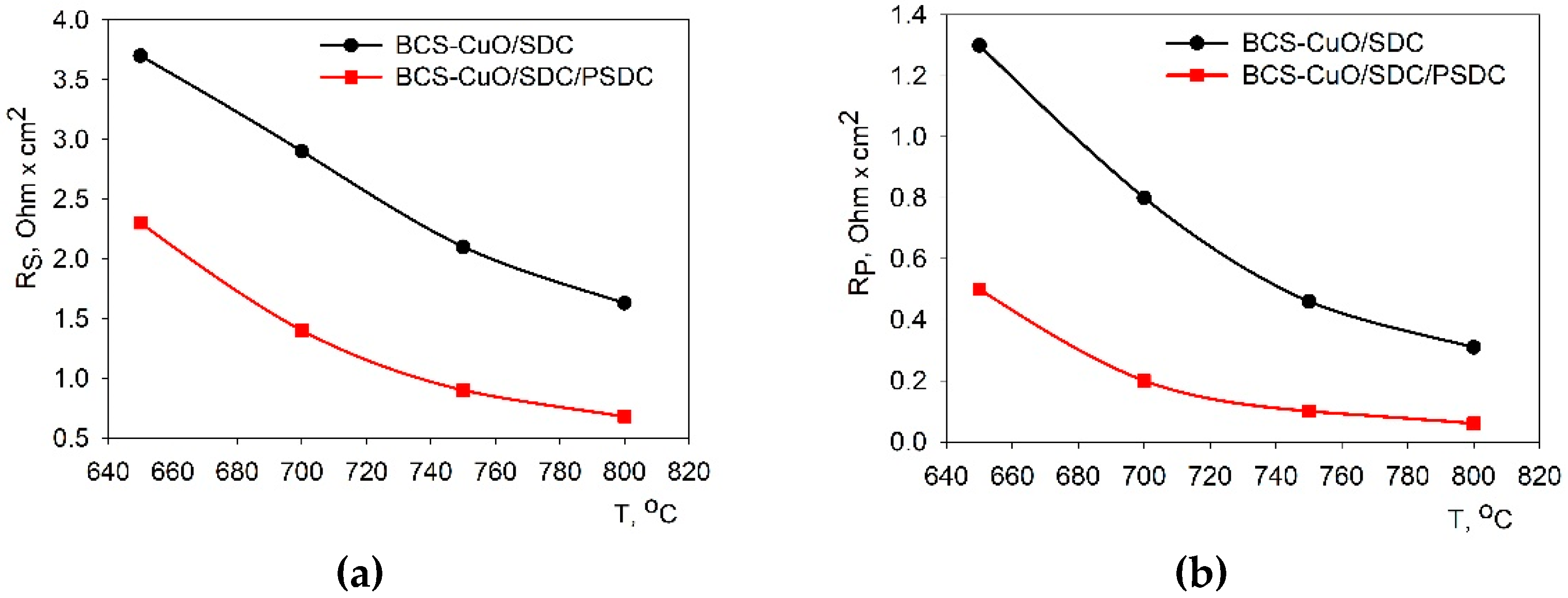
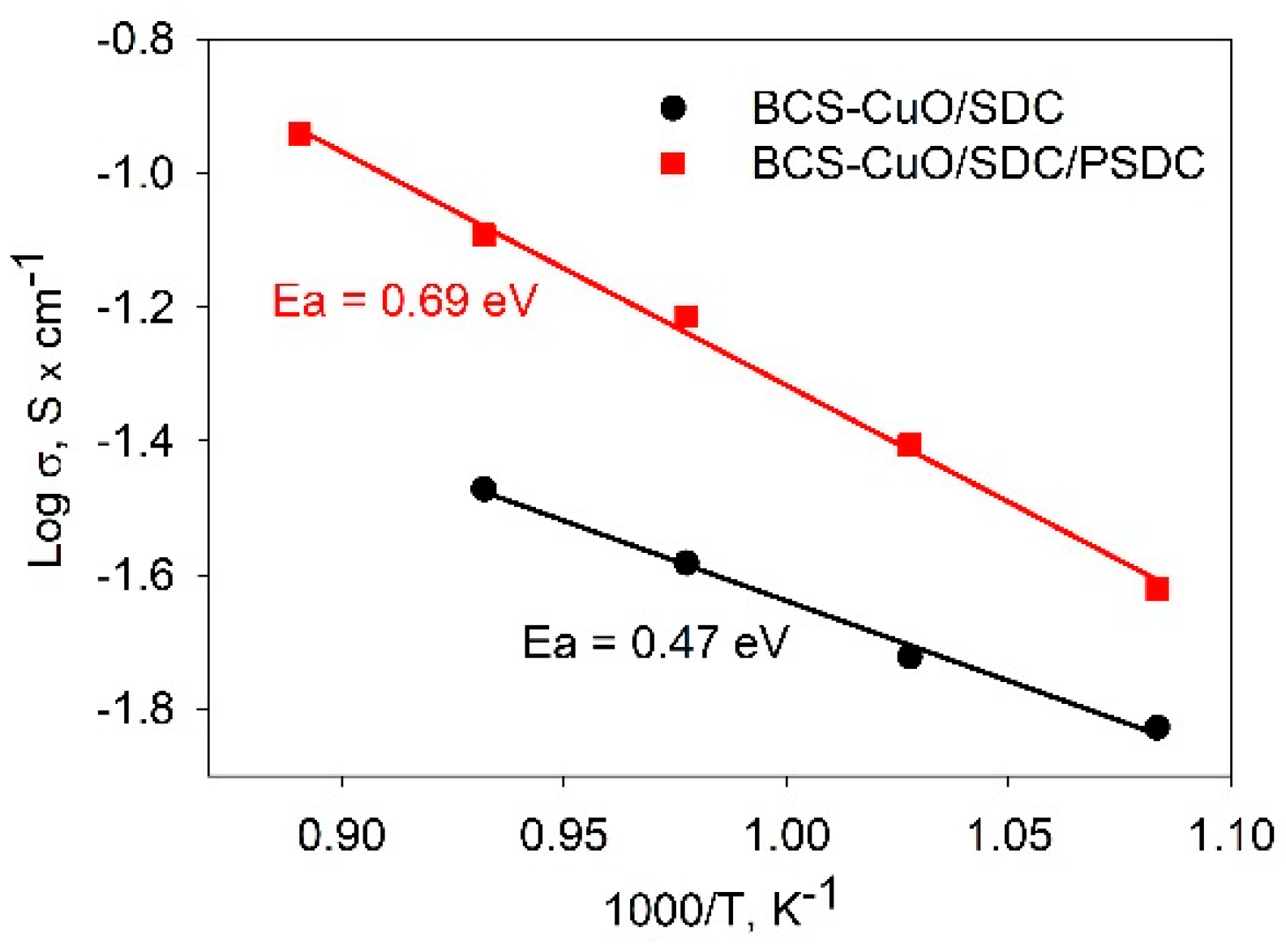
3.4. Comparative Electrochemical Testing the Single SOFCs with the Supporting SDC Electrolyte Membrane and Electrolyte Coatings Applied by EPD on the Anode and on the Anode/Cathode Side
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kusnezoff, M.; Trofimenko, N.; Müller, M.; Michaelis, A. Influence of Electrode Design and Contacting Layers on Performance of Electrolyte Supported SOFC/SOEC Single Cells. Materials 2016, 9, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarkova, E.A.; Agarkov, D.A.; Burmistrov, I.N.; Zadorozhnaya, O.Y.; Yalovenko, D.V.; Nepochatov, Y.K.; Bredikhin, S.I. Three-Layered Membranes for Planar Solid Oxide Fuel Cells of the Electrolyte-Supported Design: Characteristics and Applications. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2020, 56, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Riegraf, M.; Sata, N.; Bombarda, I.; Liensdorf, T.; Sitzmann, C.; Langhof, N.; Schafföner, S.; Walter, C.; Geipel, C.; et al. Properties and Performance of Electrolyte Supported SOFCs with EB-PVD Gd-Doped Ceria Thin-Films. ECS Trans. 2021, 103, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinkin, D.A.; Antonova, E.P.; Lesnichyova, A.S.; Tropin, E.S.; Chernov, M.E.; Chernov, E.I.; Farlenkov, A.S.; Khodimchuk, A.V.; Eremin, V.A.; Kovrova, A.I.; et al. Application of Promising Electrode Materials in Contact with a Thin-Layer ZrO2-Based Supporting Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Energies 2020, 13, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunyushkina, L.A. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with a Thin Film Electrolyte: A Review on Manufacturing Technologies and Electrochemical Characteristicses. Electrochem. Mater. Technol. 2022, 1, 20221006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.Y.; Kalinina, E.G. Place of Electrophoretic Deposition among Thin-Film Methods Adapted to the Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Technology: A Short Review. Int. J. Energy Prod. Manag. 2019, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ricote, S.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Chen, Y. Advanced Materials for Thin-Film Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Recent Progress and Challenges in Boosting the Device Performance at Low Temperatures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ghosh, S.; Aich, S.; Roy, B. Low Temperature Solid Oxide Electrolytes (LT-SOE): A Review. J. Power Sources 2017, 339, 103–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.S.; de Souza, T.M. Novel Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Technologies: A Literature Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26020–26036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.Y.; Kalinina, E.G. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Based on Ceramic Membranes with Mixed Conductivity: Improving Efficiency. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 703–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, D.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Yang, M. High Performance Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Based on Nanostructured Ceria-Based Electrolyte. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, N.; Tanwar, K.; Suman, R.; Kumar, D.; Upadhyay, S.; Parkash, O. A Brief Review on Ceria Based Solid Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 984–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, C.; Ferreira, A.; Santos, D.M.F. Towards the Commercialization of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Recent Advances in Materials and Integration Strategies. Fuels 2021, 2, 393–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.; Ou, X.; Fan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Ling, Y. Numerical Study on the Electron-Blocking Effect and Optimized Operation Parameters of Ceria-SOFCs with the Pure Sm Doping CeO2 Electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13318–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-H.; Huang, J.-L.; Fung, K.-Z.; Liu, H.-C.; Lii, D.-F. Nanostructure and Conductivity Study of Yttria Doped Zirconia Films Deposited on Samaria Doped Ceria. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7871–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-G.; Yoon, S.P.; Nam, S.W.; Hyun, S.-H.; Hong, S.-A. Fabrication and Characterization of a YSZ/YDC Composite Electrolyte by a Sol–Gel Coating Method. J. Power Sources 2002, 110, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, D.; Tomita, A.; Hibino, T.; Nagao, M.; Sano, M. Design of a Reduction-Resistant Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 Electrolyte through Growth of a Thin BaCe1−xSmxO3−α Layer over Electrolyte Surface. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, A318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, D.; Tomita, A.; Teranishi, S.; Hibino, T.; Sano, M. Improvement of a Reduction-Resistant CeSmO Electrolyte by Optimizing a Thin BaCeSmO Layer for Intermediate-Temperature SOFCs. Solid State Ion. 2005, 176, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.; Shubin, K.; Pikalova, E. Electrophoretic Deposition and Characterization of the Doped BaCeO3 Barrier Layers on a Supporting Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 Solid-State Electrolyte. Membranes 2022, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, H.; Sakai, N.; Horita, T.; Yamaji, K.; Brito, M.E. Solid Oxide Electrolytes for High Temperature Fuel Cells. Electrochemistry 2005, 73, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shri Prakash, B.; Pavitra, R.; Senthil Kumar, S.; Aruna, S.T. Electrolyte Bi-Layering Strategy to Improve the Performance of an Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell: A Review. J. Power Sources 2018, 381, 136–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Hosomi, T.; Murata, K.; Fukui, T.; Miyake, M. Fabrication of Bilayered YSZ/SDC Electrolyte Film by Electrophoretic Deposition for Reduced-Temperature Operating Anode-Supported SOFC. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.G.; Pikalova, E.Y. Electrophoretic Deposition of Dense Anode Barrier Layers of Doped ZrO2 and BaCeO3 on a Supporting Ce0.8Sm0.2O2−δ Solid Electrolyte: Problems and Search for Solutions in SOFC Technology. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løken, A.; Ricote, S.; Wachowski, S. Thermal and Chemical Expansion in Proton Ceramic Electrolytes and Compatible Electrodes. Crystals 2018, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, D.; Murashkina, A.; Pikalova, E.; Demin, A.; Podias, A.; Tsiakaras, P. BaCeO3: Materials Development, Properties and Application. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 60, 72–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koettgen, J.; Martin, M. The Ionic Conductivity of Sm-doped Ceria. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 3776–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, R.; Xia, C.; Meng, G. Effect of A-Site Deficiency in BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3−δ on the Electrode Performance for Proton Conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Solid State Ion. 2011, 192, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Osinkin, D.; Kalinina, E. Direct Electrophoretic Deposition and Characterization of Thin-Film Membranes Based on Doped BaCeO3 and CeO2 for Anode-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Membranes 2022, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Medvedev, D. Effect of Anode Gas Mixture Humidification on the Electrochemical Performance of the BaCeO3-Based Protonic Ceramic Fuel Cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 4016–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, E.P.; Kolchugin, A.A.; Pikalova, E.Y.; Medvedev, D.A.; Bogdanovich, N.M. Development of Electrochemically Active Electrodes for BaCe0.89Gd0.1Cu0.01O3−δ Proton Conducting Electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 2017, 306, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, E.P.; Osinkin, D.A.; Bogdanovich, N.M. On a Variation of the Kinetics of Hydrogen Oxidation on Ni–BaCe(Y,Gd)O3 Anode for Proton Ceramic Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 22638–22645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Bogdanovich, N.; Kolchugin, A.; Ermakova, L.; Khrustov, A.; Farlenkov, A.; Bronin, D. Methods to Increase Electrochemical Activity of Lanthanum Nickelate-Ferrite Electrodes for Intermediate and Low Temperature SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 35923–35937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-García, J.; Albarrán-Aroca, N.; Porras-Vázquez, J.M.; Losilla, E.R.; Marrero-López, D. Influence of Bi1.5Y0.5O3 Active Layer on the Performance of Nanostructured La0.8Sr0.2MnO3 Cathode. Appl. Nano 2020, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuh, D.; Muhammed Ali, S.A.; Yulianto, D.; Shukur, M.F.; Muchtar, A. Effect of Yttrium-Stabilized Bismuth Bilayer Electrolyte Thickness on the Electrochemical Performance of Anode-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 6310–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; He, T.; Wang, J.; Su, W. The Effect of Pr Co-Dopant on the Performance of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Sm-Doped Ceria Electrolyte. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 389, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, D.; Nasani, N.; Pukazhselvan, D.; Fagg, D.P. Increased Performance by Use of a Mixed Conducting Buffer Layer, Terbia-Doped Ceria, for Nd2NiO4+δ SOFC/SOEC Oxygen Electrodes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 31466–31474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovrova, A.I.; Gorelov, V.P.; Kuzmin, A.V.; Tropin, E.S.; Osinkin, D.A. Influence of Ce0.8R0.2O2–a (R = Y, Sm, Tb) Submicron Barrier Layers at the La2NiO4+δ/YSZ Boundary on the Electrochemical Performance of a Cathode. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2021, 25, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochentyn, B.; Błaszczak, P.; Gazda, M.; Fuerte, A.; Wang, S.-F.; Jasiński, P. Investigation of Praseodymium and Samarium Co-Doped Ceria as an Anode Catalyst for DIR-SOFC Fueled by Biogas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 29131–29142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, W.J.; Zhu, J.; Sharma, R.; Crozier, P.A. Electrical Conductivity and Grain Boundary Composition of Gd-Doped and Gd/Pr Co-Doped Ceria. Solid State Ion. 2015, 272, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübke, S. Electronic Conductivity of Gd-Doped Ceria with Additional Pr-Doping. Solid State Ion. 1999, 117, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharton, V.V.; Viskup, A.P.; Figueiredo, F.M.; Naumovich, E.N.; Shaulo, A.L.; Marques, F.M.B. Electrochemical Properties of Pr-Doped Ce(Gd)O2−δ. Mater. Lett. 2002, 53, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.Y.; Kalinina, E.G. Electrophoretic Deposition in the Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Technology: Fundamentals and Recent Advances. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.G.; Pikalova, E.Y. New Trends in the Development of Electrophoretic Deposition Method in the Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Technology: Theoretical Approaches, Experimental Solutions and Development Prospects. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2019, 88, 1179–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Kalinina, E.; Pikalova, N. Recent Advances in Electrophoretic Deposition of Thin-Film Electrolytes for Intermediate-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Mater. Technol. 2023, 2, 20232011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, G.; Nguyen, N.T.K.; Rendtorff, N.M.; Sakka, Y.; Uchikoshi, T. Electrophoretic Deposition for Obtaining Dense Lanthanum Silicate Oxyapatite (LSO). Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19283–19288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.; Pikalova, E.; Ermakova, L.; Bogdanovich, N. Challenges of Formation of Thin-Film Solid Electrolyte Layers on Non-Conductive Substrates by Electrophoretic Deposition. Coatings 2021, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.T.; Uchikoshi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Suzuki, T.S.; Sugiyama, T.; Furuya, K.; Matsuda, M.; Sakka, Y.; Munakata, F. Fabrication of GDC/LSGM/GDC Tri-Layers on Polypyrrole-Coated NiO-YSZ by Electrophoretic Deposition for Anode-Supported SOFC. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 117, 1246–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, W.; Yao, M.; Li, T.; Liu, X. Electrophoretic Deposition of Gadolinium-Doped Ceria as a Barrier Layer on Yttrium-Stabilized Zirconia Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2017, 17, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, W. A Novel Electronic Current-Blocked Stable Mixed Ionic Conductor for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, D.; Maragou, V.; Pikalova, E.; Demin, A.; Tsiakaras, P. Novel Composite Solid State Electrolytes on the Base of BaCeO3 and CeO2 for Intermediate Temperature Electrochemical Devices. J. Power Sources 2013, 221, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FullProf Suite. Crystallographic Tools for Rietveld, Profile Matching and Integrated-Intensity Refinements of X-ray and/or Neutron Data. Available online: https://www.ill.eu/sites/fullprof/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Mostafavi, E.; Babaei, A.; Ataie, A. La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3 Perovskite Cathode for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: A Comparative Study. Iran. J. Hydrog. Fuel Cell 2014, 1, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Lu, K. Perovskite-Type La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3, Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.2Fe0.8O3, and Sm0.5Sr0.5Co0.2Fe0.8O3 Cathode Materials and Their Chromium Poisoning for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 211, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, K.; Nishino, H.; Kakinuma, K.; Brito, M.E.; Uchida, H. Effect of Samaria-Doped Ceria (SDC) Interlayer on the Performance of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3−δ/SDC Composite Oxygen Electrode for Reversible Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 225, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SA, M.A.; Raharjo, J.; Anwar, M.; Khaerudini, D.S.; Muchtar, A.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Somalu, M.R. Carbonate-Based Lanthanum Strontium Cobalt Ferrite (LSCF)–Samarium-Doped Ceria (SDC) Composite Cathode for Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Bogdanovich, N.; Kolchugin, A.; Shubin, K.; Ermakova, L.; Eremeev, N.; Farlenkov, A.; Khrustov, A.; Filonova, E.; Sadykov, V. Development of Composite LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3−δ-Based Air Electrodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with a Thin-Film Bilayer Electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 16947–16964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, Y.A. Electric Explosion of Wires as a Method for Preparation of Nanopowders. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2003, 5, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besra, L.; Liu, M. A Review on Fundamentals and Applications of Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD). Prog. Mater. Sci. 2007, 52, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and Zeta Potential–What They Are and What They Are Not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusoulier, L.; Cloots, R.; Vertruyen, B.; Moreno, R.; Burgos-Montes, O.; Ferrari, B. YBa2Cu3O7−x Dispersion in Iodine Acetone for Electrophoretic Deposition: Surface Charging Mechanism in a Halogenated Organic Media. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.G.; Pikalova, E.Y. Modifying Suspensions for the Electrophoretic Deposition of BaCe0.5Zr0.3Y0.1Yb0.1O3–δ Solid Electrolyte. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 95, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja-Pertegal, J.L.; Díaz-Parralejo, A.; Macías-García, A.; Sánchez-González, J.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M. Design, Preparation, and Characterization of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) Coatings Obtained by Electrophoretic Deposition (EPD). Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 13312–13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelmehsara, M.E.; Mahmoudimehr, J. Techno-Economic Comparison of Anode-Supported, Cathode-Supported, and Electrolyte-Supported SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 15521–15530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Worrell, W.L.; Gorte, R.J.; Vohs, J.M. SOFCs for Direct Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Fuels with Samaria-Doped Ceria Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Hua, G.; Wang, L.; Ding, L.; Yuan, G. La0.6Ca0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ–Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 Composites as Symmetrical Bi-Electrodes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells through Infiltration and in-Situ Exsolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 24968–24977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ding, D.; Bai, Y.; He, T.; Liu, M. An Efficient SOFC Based on Samaria-Doped Ceria (SDC) Electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, B661–B665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, E.G.; Rusakova, D.S.; Shubin, K.S.; Ermakova, L.V.; Pikalova, E.Y. CeO2-Based Thin-Film Electrolyte Membranes for Intermediate Temperature SOFCs: Direct Electrophoretic Deposition on the Supporting Anode from Additive-Modified Suspensions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Miyayama, M. Fabrication and Fuel-Cell Properties of Sm-Doped CeO2 Electrolyte Film by Electrophoretic Deposition. Key Eng. Mater. 2007, 350, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabacı, A. Oxide Ionic Conductivity and Microstructures of Pr and Sm Co-Doped CeO2-Based Systems. Open Chem. 2018, 16, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eressa, L.A.; Rao, P.V.B. Electrical Properties of Praseodymium and Samarium Co-Doped Ceria Electrolyte for Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Application. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Shin, D. Enhanced Sintering Behavior Mechanism of Nanocrystalline BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3−δ by Cu Doping. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 7423–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material (Application) | Synthesis Method | Crystal Lattice Type, Space Group | Lattice Parameters, Å | Specific Surface Area, m2 g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC (supporting membrane) | SSR | cubic type structure, Fm-3m | a = 5.4324 (3) | 2.5 (1) |
| PSDC | CNC | cubic type structure, Fm-3m | a = 5.4314 (3) | 15.0 (3) |
| BCS-CuO | CNC | orthorombic structure, Pnma | a = 6.2311 (1), b = 8.8013 (2), c = 6.2272 (1) | 3.0 (1) |
| BCGCu | SSR | orthorombic structure, Pmcn | a = 6.2523 (1), b = 8.7912 (2), c = 6.2180 (1) | 2.4 (1) |
| EDB | CNC | cubic type structure, Fm-3m | a = 5.45082 (3) | 1.6 (1) |
| LSFC | CNC | rhombohedral structure, R3C | a = 5.4717 (2), b = 5.4717 (2), c = 13.4505 (4) | 2.2 (1) |
| LNF | MP | rhombohedral structure, R3C | a = 5.5220 (2), b = 5.5220 (2), c = 13.3028 (4) | 5.5 (1) |
| Suspension | UT, min | Zeta Potential, mV (pH) |
|---|---|---|
| PSDC | 5 125 | +16 (5.5) +23 (6.4) |
| BCS-CuO BCS-CuO + iodine | 5 125 125 | +11 (5.1) +11 (4.2) +11 (3.7) |
| Electrochemical Cell, Layer Thickness, μm | OCV, mV/T, °C | SPD, mW cm−2/T, °C | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiO-BCGCu (40)/ BCS-CuO (18)/SDC (550)/ LSFC-SDC (30)/ LNF-EDB-CuO (40) (EPD) | 805 (650) 789 (700) 760 (750) 712 (800) | 90 (650) 119 (700) 159 (750) 186 (800) | This study |
| NiO-BCGCu (40)/ BCS-CuO (18)/SDC (550)/ PSDC (6)/LSFC-SDC (30)/ LNF-EDB-CuO (40) (EPD) | 918 (650) 872 (700) 827 (750) 782 (800) | 159 (650) 240 (700) 326 (750) 419 (800) | This study |
| NiO-SDC/BCS (13)/ | 1002 (600) | 76 (600) 170 (700) | [18] |
| SDC (500)/Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3 | 857 (900) | 278 (800) 399(900) | |
| NiO-SDC/ SDC (500)/Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3 | 964 (600) 888 (700) 823 (800) 715 (900) | 62 (600) 126 (700) 170 (800) 85 (900) | [17] |
| NiO-SDC/Ce0.9Sm0.1O1.95 (500)/ La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3 | 838 (600) 768 (700) 714 (750) | 38 (600) 78 (700) 104 (750) | [35] |
| NiO-SDC/Ce0.9Sm0.08Pr0.02O1.95 (500)/La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3 | 783 (600) 751 (700) 717 (750) | 49 (600) 103 (700) 126 (750) | [35] |
| NiO-BCS-CuO (800)/BCS-CuO (13)/ SDC (18)/Pt (30) (EPD) | 1050 (650) 1000 (700) 900 (750) | 50 (650) 80 (700) 160 (750) | [28] |
| NiO-SDC/SDC (30)/La0.6Sr0.4CoO3−δ (EPD) | ~700 (600) | 161 (500) 281 (600) 272 (700) | [68] |
| NiO-BCS-SDC/BCS-SDC (30)/ Sm0.5Sr0.5 CoO3−δ–Ce0.8 Sm0.2O1.9 | 1017 (600) 1001 (650) 976 (700) | 216 (600) 343 (650) 505 (700) | [49] |
| NiO-BCS/SDC modified TiO2 (30)/Pt (EPD) | 920 (750) | 125 (750) | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pikalova, E.; Kalinina, E. Performance Enhancement of Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-Supported SOFC by Electrophoretic Formation of Modifying BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3 and Ce0.8Sm0.1Pr0.1O1.9 Layers. Membranes 2023, 13, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050484
Pikalova E, Kalinina E. Performance Enhancement of Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-Supported SOFC by Electrophoretic Formation of Modifying BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3 and Ce0.8Sm0.1Pr0.1O1.9 Layers. Membranes. 2023; 13(5):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050484
Chicago/Turabian StylePikalova, Elena, and Elena Kalinina. 2023. "Performance Enhancement of Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-Supported SOFC by Electrophoretic Formation of Modifying BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3 and Ce0.8Sm0.1Pr0.1O1.9 Layers" Membranes 13, no. 5: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050484
APA StylePikalova, E., & Kalinina, E. (2023). Performance Enhancement of Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-Supported SOFC by Electrophoretic Formation of Modifying BaCe0.8Sm0.2O3 and Ce0.8Sm0.1Pr0.1O1.9 Layers. Membranes, 13(5), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050484








