Tuning PVDF Membrane Porosity and Wettability Resistance via Varying Substrate Morphology for the Desalination of Highly Saline Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.4. Membrane Performance
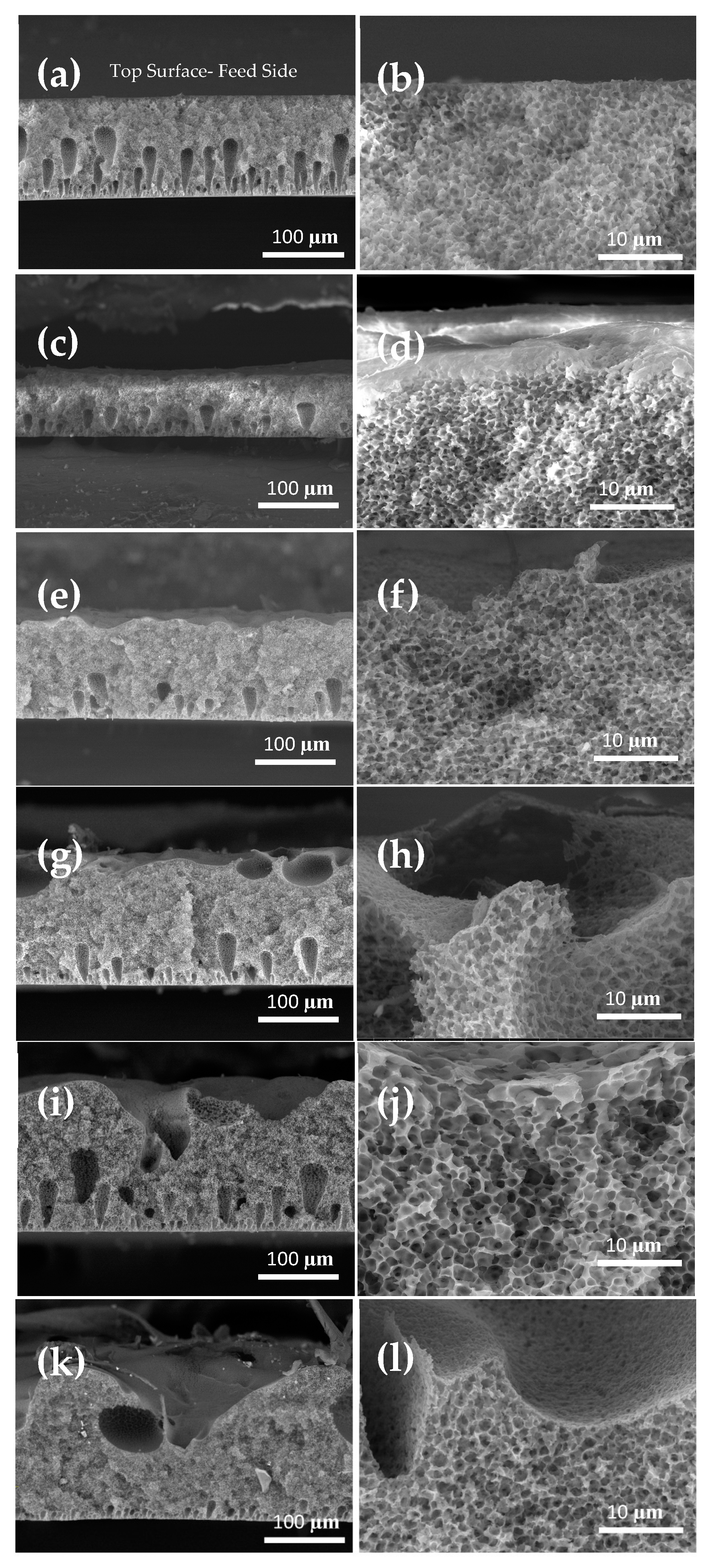
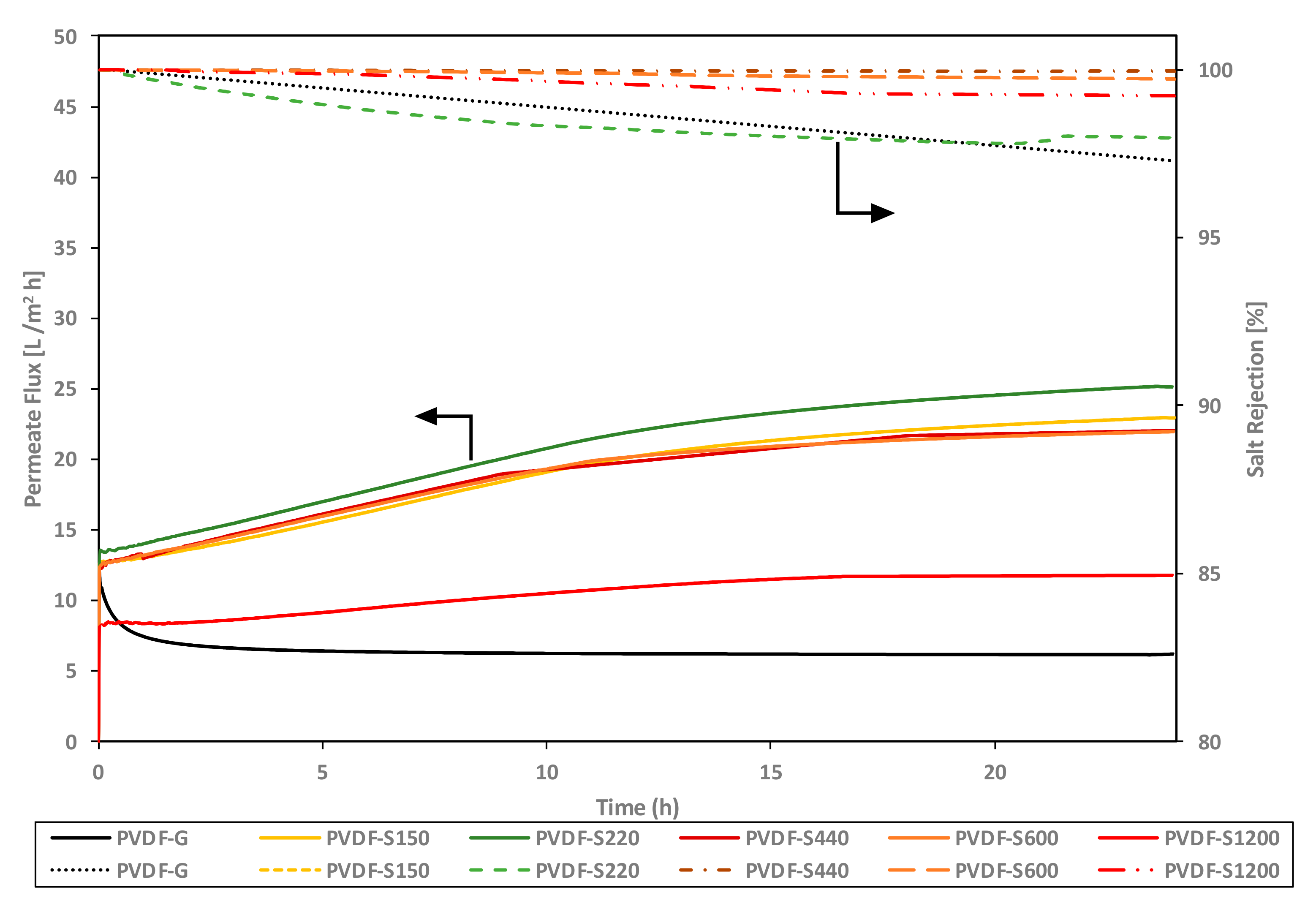
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veil, J.A. Produced Water Management Options and Technologies. In Produced Water; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szép, A.; Kohlheb, R. Water treatment technology for produced water. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 2372–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igunnu, E.T.; Chen, G.Z. Produced water treatment technologies. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2014, 9, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilstad, T.; Espedal, E. Membrane separation of produced water. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Micó, M.; Arnaldos, M.; Medina, F.; Contreras, S. State of the art of produced water treatment. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 186–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Produced water treatment by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 322, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhru’L-Razi, A.; Pendashteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.R.A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedonio, F.; Ali, A.; Poerio, T.; El-Sayed, E.; Drioli, E.; Abdel-Jawad, M. Direct contact membrane distillation for treatment of oilfield produced water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Produced water treatment: Application of Air Gap Membrane Distillation. Desalination 2013, 309, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, D.; Azeem, M.A.; Khalifa, A.; Falath, W.; Baroud, T.; Antar, M. Performance improvement of an air gap membrane distillation process with rotating fan. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 204, 117964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawad, S.M.; Lawal, D.U.; Khalifa, A.E.; Aljundi, I.H.; Antar, M.A.; Baroud, T.N. Analysis of water gap membrane distillation process with an internal gap circulation propeller. Desalination 2023, 551, 116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Chivas, A.R.; Nelemans, B.; Duke, M.; Gray, S.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Treatment of RO brine from CSG produced water by spiral-wound air gap membrane distillation—A pilot study. Desalination 2015, 366, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmali, M.; Fyfe, P.; Lincicome, D.; Sardari, K.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Selecting membranes for treating hydraulic fracturing produced waters by membrane distillation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sirkar, K.K. Desalination of brine and produced water by direct contact membrane distillation at high temperatures and pressures. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.; Zhang, Z.; Vidic, R.D. Laboratory and pilot-scale studies of membrane distillation for desalination of produced water from Permian Basin. Desalination 2022, 537, 115853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.M.; Kwon, Y.-N. Surface modification of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for enhanced wetting resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 491, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaz, M.; Sengupta, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Wickramasinghe, R. Surface Modification of PVDF Membranes for Treating Produced Waters by Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Prakash, P.; Sirkar, K.K. Deoiled Produced Water Treatment Using Direct-Contact Membrane Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13439–13448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, Z.; Carlson, K.H.; Lee, J.; Tong, T. Membrane fouling and reusability in membrane distillation of shale oil and gas produced water: Effects of membrane surface wettability. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 567, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ScienceDirect. Surface Modification of PVDF Membranes for Treating Produced Waters by Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586619304861?casa_token=C5bRuqAtzekAAAAA:8Q22oVpqzoVEXriJaoELZEv91maQW2xCvT8w8kVfp_ygAvYo-lOsxNVxOBEOXvbPEnlrezGOpnc (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.M.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Ng, B.C. Physicochemical study of polyvinylidene fluoride–Cloisite15A® composite membranes for membrane distillation application. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 63367–63379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchitphimon, S.; Wang, R.; Jiraratananon, R. Surface modification of polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF–HFP) hollow fiber membrane for membrane gas absorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes for Membrane Distillation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5710–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ma, Z.; Xiao, K.; Xiang, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Liang, S. Hierarchically textured superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane fabricated via nanocasting for enhanced membrane distillation performance. Desalination 2018, 443, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, C.; Lee, J.; Elimelech, M. Omniphobic Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Membrane for Desalination of Shale Gas Produced Water by Membrane Distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12275–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Yao, Y.; Xiang, R.; Wu, Y. Formation and characterization of polytetrafluoroethylene nanofiber membranes for vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abbassi, A.; Kiai, H.; Hafidi, A.; García-Payo, M.; Khayet, M. Treatment of olive mill wastewater by membrane distillation using polytetrafluoroethylene membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 98, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.V.; Dow, N.; Milne, N.; Zhang, J.; Naidoo, L.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Membrane Distillation Trial on Textile Wastewater Containing Surfactants Using Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic-Coated Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Influence of polypropylene membrane surface porosity on the performance of membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, P.; Xiao, C. Fabrication of super-hydrophobic polypropylene hollow fiber membrane and its application in membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 414, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Xu, Z.-K.; Liu, Z.-M.; Yuan, W.-F.; Xiang, H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Xu, Y.-Y. Microporous polypropylene and polyethylene hollow fiber membranes. Part 3. Experimental studies on membrane distillation for desalination. Desalination 2003, 155, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Xiao, W.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Ruan, X.; Yan, X.; He, G.; et al. Superhydrophobic polypropylene membrane with fabricated antifouling interface for vacuum membrane distillation treating high concentration sodium/magnesium saline water. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürmer, M.B.; Poletto, P.; Marcolin, M.; Duarte, J.; Zeni, M. Effect of non-solvents used in the coagulation bath on morphology of PVDF membranes. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A. Pore structure control of PVDF membranes using a 2-stage coagulation bath phase inversion process for application in membrane distillation (MD). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.-H.; Chen, L.-W. Pore formation mechanism of membranes from phase inversion process. Desalination 1995, 103, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Aernouts, B.; Saeys, W.; Vankelecom, I.F. Study of polymer concentration and evaporation time as phase inversion parameters for polysulfone-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikel, M.; Pünt, I.G.M.; Lammertink, R.; Wessling, M. Shrinkage effects during polymer phase separation on microfabricated molds. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 347, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lu, X. Preparation of super-hydrophobic PVDF membrane for MD purpose via hydroxyl induced crystallization-phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovkov, V.M.; Sokhoreva, V.V.; Sigfusson, T.I. Formation of chemically resistant track membranes based on polyvinylidene fluoride. Pet. Chem. 2012, 52, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, E.; Martínez-Gómez, A.; Tiemblo, P.; García, N. Exploring chemical and structural features to tailor wetting properties of PVDF and PVDF/PMMA surfaces. Polymer 2022, 262, 125441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Ray, S.S.; Huyen, D.T.T.; Kang, W.; Kwon, Y.-N. Chemical and surface engineered superhydrophobic patterned membrane with enhanced wetting and fouling resistance for improved membrane distillation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiei, S.; Mousavi, S.M.; Paterson, A.H. Development of hierarchical surface roughness on porous poly (vinylidene fluoride) membrane for membrane distillation process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Ye, H.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Hsiao, B.S. Self-roughened omniphobic coatings on nanofibrous membrane for membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, Y.; Ge, L.; Lin, R.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S. Amphiphobic PVDF composite membranes for anti-fouling direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; He, T. Scaling mitigation in membrane distillation: From superhydrophobic to slippery. Desalination 2019, 466, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Guo, H.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Volkov, A.V.; He, T. Unprecedented scaling/fouling resistance of omniphobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane with silica nanoparticle coated micropillars in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, M.; Zou, L. Study of fouling and scaling in capacitive deionisation by using dissolved organic and inorganic salts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Jeong, N.; Tong, T. The effects of membrane surface wettability on pore wetting and scaling reversibility associated with mineral scaling in membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hou, D.; Fu, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Fabrication of PVDF nanofibrous hydrophobic composite membranes reinforced with fabric substrates via electrospinning for membrane distillation desalination. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, B. Excellent wetting resistance and anti-fouling performance of PVDF membrane modified with superhydrophobic papillae-like surfaces. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Li, X.-M.; He, T. Preparation of omniphobic PVDF membrane with hierarchical structure for treating saline oily wastewater using direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.J.; Guo, J.; Khanzada, N.K.; An, A.K. Omniphobic re-entrant PVDF membrane with ZnO nanoparticles composite for desalination of low surface tension oily seawater. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, N.; Leo, C. Fouling prevention in the membrane distillation of phenolic-rich solution using superhydrophobic PVDF membrane incorporated with TiO2 nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 167, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Wang, S. Fabrication of hierarchical poly (vinylidene fluoride) micro/nano-composite membrane with anti-fouling property for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Shim, W.-G.; He, T.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane containing carbon nanotubes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Gutierrez, L.; Derese, S.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Verliefde, A.R.; Mamba, B.; Mhlanga, S.D. A review of nanoparticle-enhanced membrane distillation membranes: Membrane synthesis and applications in water treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2757–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, Z.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Preparation of omniphobic PVDF membranes with silica nanoparticles for treating coking wastewater using direct contact membrane distillation: Electrostatic adsorption vs. chemical bonding. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharraz, J.A.; An, A.K. Patterned superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes for membrane distillation: Enhanced flux with improved fouling and wetting resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.A.; Lawal, D.U.; Al Abdulgader, H.; Baroud, T.N. Enhanced performance of superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane with sandpaper texture for highly saline water desalination in air-gap membrane distillation. Desalination 2022, 528, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; You, H.; Zang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, C. A facile patterning preparation of barnacle-like polypyrrole on sandpaper for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 18162–18173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, M.D.; Das, S.; Banpurkar, A.G.; Kulkarni, A. Regression analysis of wetting characteristics for different random surface roughness of polydimethylsiloxane using sandpapers. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gong, L.; Gong, Z.; Wang, D.; Yin, X.; Fan, M. Facile fabrication of a large-area and cost-effective PDMS-SERS substrate by sandpaper template-assisted lithography. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 4917–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.-R.; Jiang, C.-G.; Wu, C.-W. Effect of pillar height on the wettability of micro-textured surface: Volume-of-fluid simulations. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 74, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Special Wettability. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marmur, A.; Della Volpe, C.; Siboni, S.; Amirfazli, A.; Drelich, J.W. Contact angles and wettability: Towards common and accurate terminology. Surf. Innov. 2017, 5, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Duan, Y. Improve the mechanical durability of superhydrophobic/superamphiphobic coating through multiple cross-linked mesh structure. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Volkov, A.; He, T. Understanding the fouling/scaling resistance of superhydrophobic/omniphobic membranes in membrane distillation. Desalination 2021, 499, 114864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan-Birgi, P.; Ali, M.I.H.; Arafat, H.A. Estimation of liquid entry pressure in hydrophobic membranes using CFD tools. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Payo, M.C.; Izquierdo-Gil, M.A.; Fernández-Pineda, C. Wetting Study of Hydrophobic Membranes via Liquid Entry Pressure Measurements with Aqueous Alcohol Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 230, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almarzooqi, F.A.; Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A. Improving Liquid Entry Pressure of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Membranes by Exploiting the Role of Fabrication Parameters in Vapor-Induced Phase Separation VIPS and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation (NIPS) Processes. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Al Marzooqi, F.A.; Arafat, H.A. Shrinkage, defect and membrane distillation performance of composite PVDF membranes. Desalination 2015, 376, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Moghareh Abed, M.R.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kosar, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X. A study of thermodynamics and kinetics pertinent to formation of PVDF membranes by phase inversion. Desalination 2013, 309, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Formation of Flat Sheet Phase Inversion MD Membranes. In Membrane Distillation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes with Engineered Porosity: Role of Temperature and Substrate Morphology in Phase Inversion Processes. Available online: https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/articles/thesis/Polyvinylidene_fluoride_membranes_with_engineered_porosity_role_of_temperature_and_substrate_morphology_in_phase_inversion_processes/10288532 (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Agbaje, T.A.; Al-Gharabli, S.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Kujawa, J.; Arafat, H.A. PVDF/magnetite blend membranes for enhanced flux and salt rejection in membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 436, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Hilal, N. Air gap membrane distillation: A detailed study of high saline solution. Desalination 2017, 403, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Khayet, M. Production of drinking water from saline water by air-gap membrane distillation using polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, G.H.; Chin, J.Y.; Ooi, B.S.; Jawad, Z.A.; Leow, H.T.L.; Low, S.C. Superhydrophobic membrane with hierarchically 3D-microtexture to treat saline water by deploying membrane distillation. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 37, 101528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
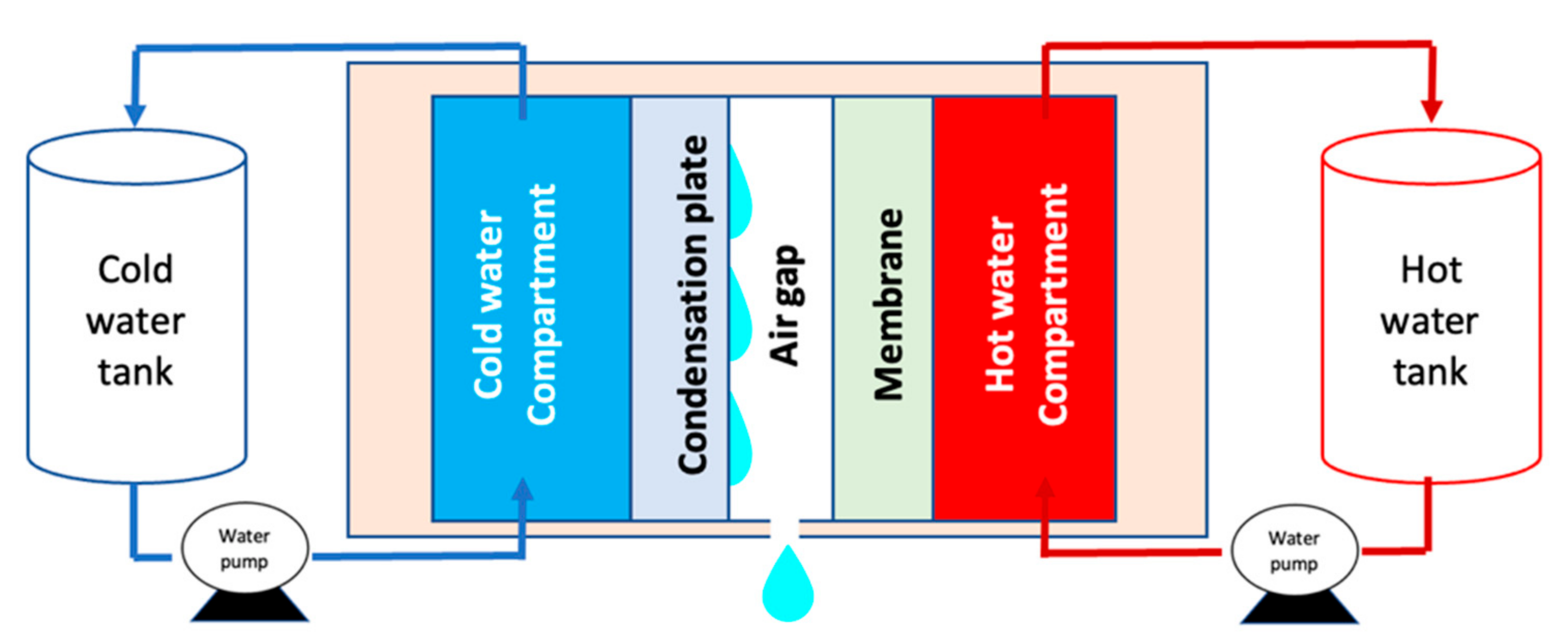
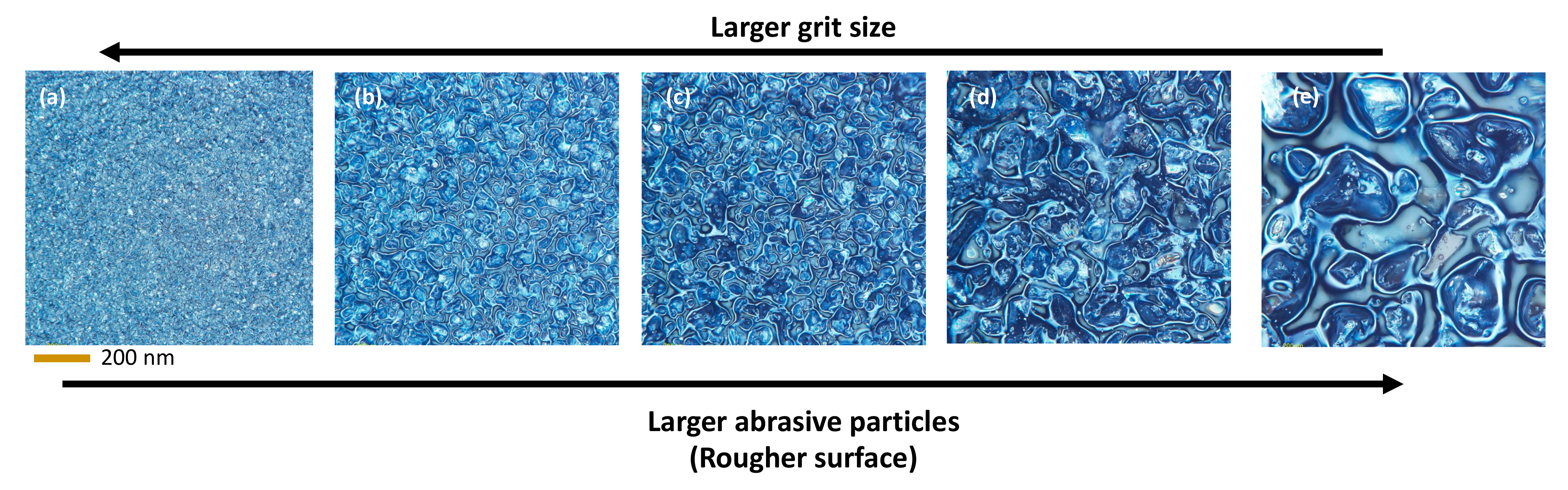

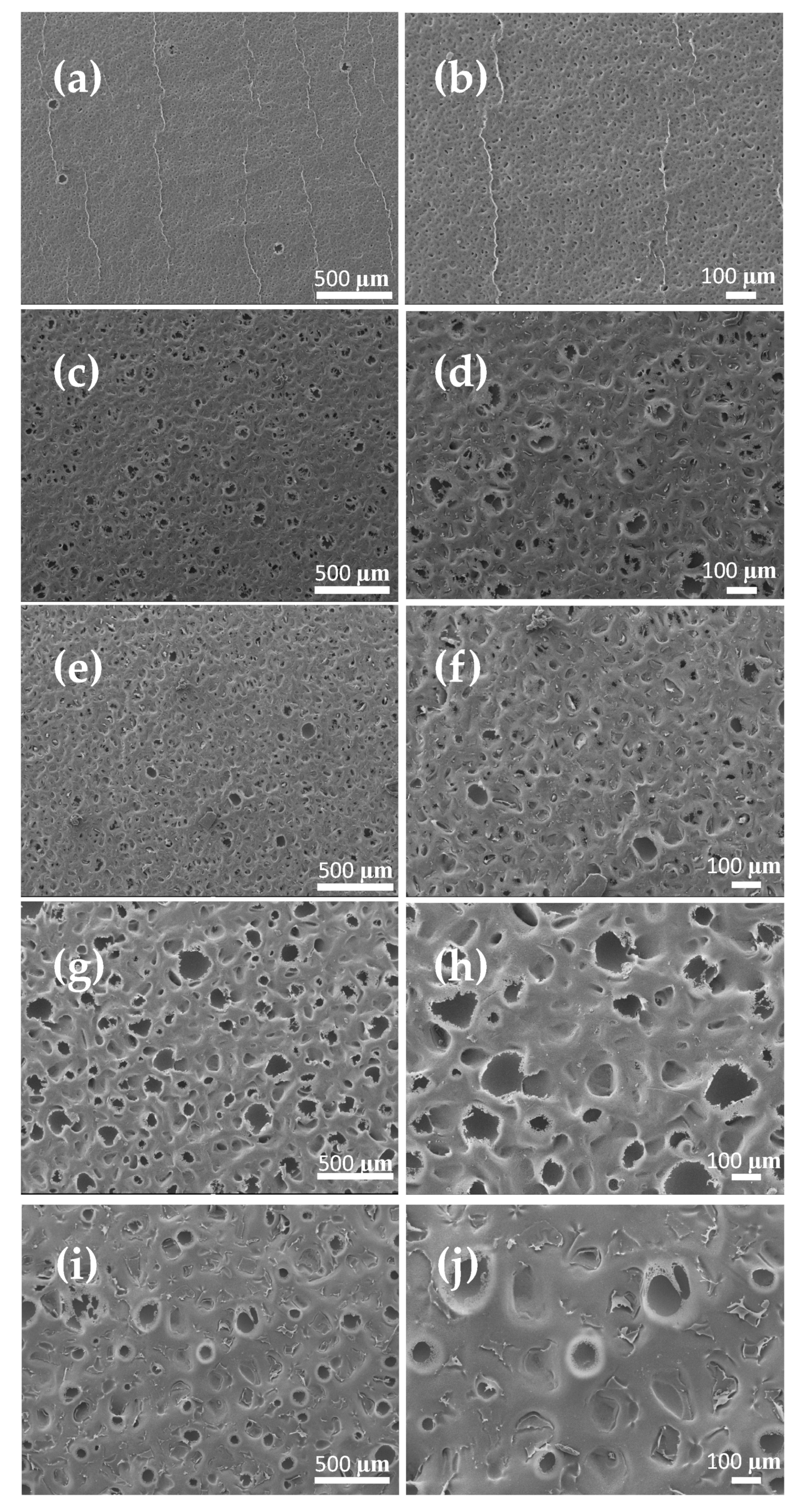
| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Effective membrane area | 7.3 × 10−4 m2 | |
| Coolant | Temperature | 20 ± 0.3 °C |
| Flow rate | 2 L/min | |
| Feed | Salinity | 70 g/L |
| Temperature | 70 ± 0.8 °C | |
| Flow rate | 0.8 L/min | |
| Width of the air gap | ≈0.002 m | |
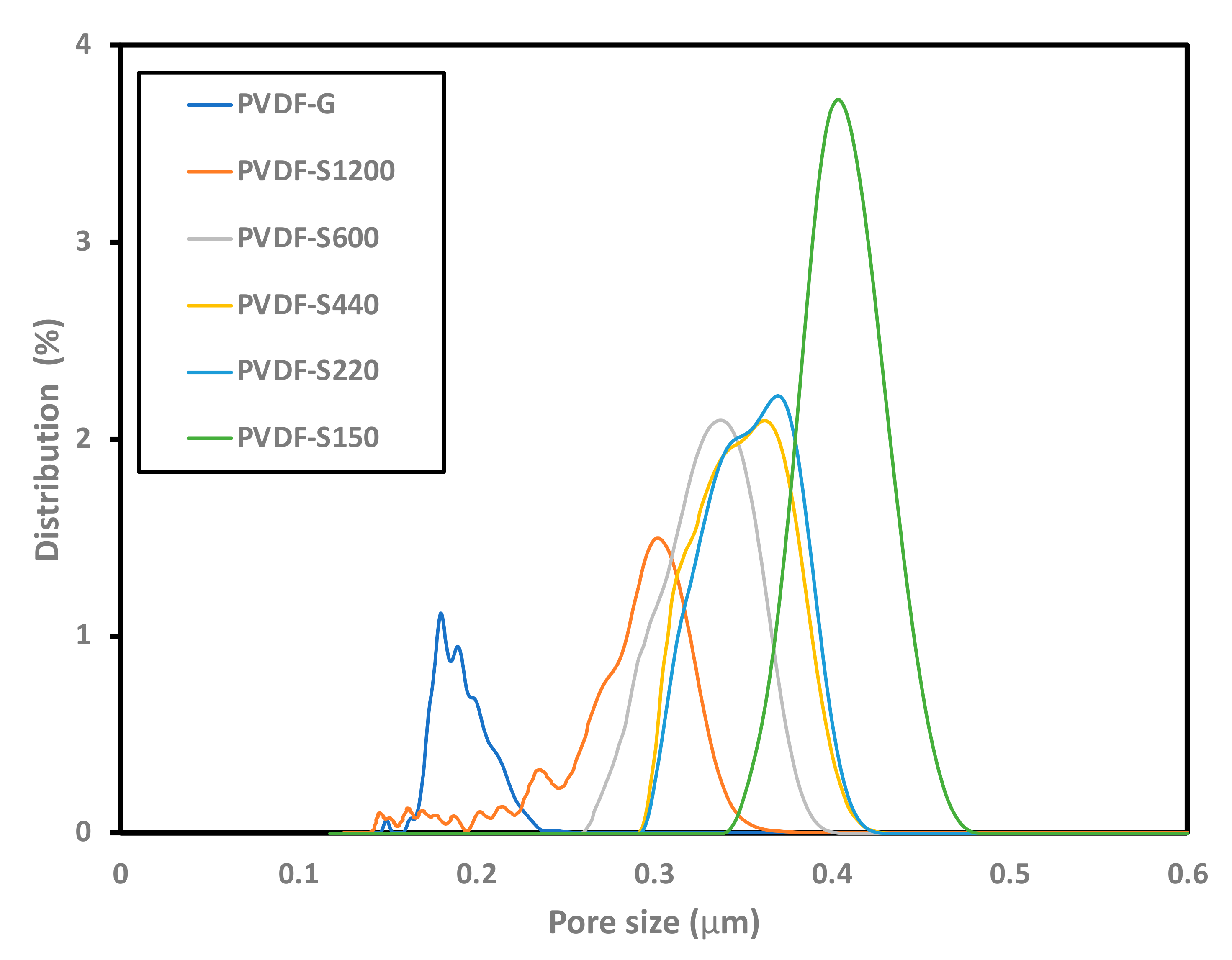
| Samples | Maximum Pore Size (µm) | Mean Pore Size (µm) | Minimum Pore Size (µm) | Porosity (%) | Thickness (µm) | LEP (bar) | Shrinkage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-G | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 73.2 | 100.4 | 0.8 | 8 |
| PVDF-S150 | 0.44 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 81 | 145.5 | 0.5 | 0 |
| PVDF-S220 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 78.1 | 138.2 | 0.6 | 0 |
| PVDF-S400 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 74.8 | 117.5 | 1.0 | 0 |
| PVDF-S600 | 0.37 | 0.32 | 0.26 | 75.2 | 124.2 | 0.7 | 0 |
| PVDF-S1200 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 74 | 110.0 | 0.5 | 5.8 |
| Membrane | PTFE Commercial | PVDF Commercial | PVDF Hierarchically Textured Superhydrophobic Membrane Fabricated via Nanocasting | PVDF Superhydrophobic Membrane with Hierarchical 3D Microtexture | PVDF-S400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [79] | [80] | [26] | [81] | (This work) | |
| Air Gap (mm) | Air gap (NA) | Air gap (2 mm) | Direct contact | Direct contact | Air gap (2 mm) |
| Feed TDS (wt% NaCl) | 5.8 | 6 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 7 |
| Feed Temp. (°C) | 50 | 80 | 60 | 60 | 70 |
| Feed Flow rate (L/min) | 1.5 | 0.35 | 1.08 | 0.6 | 08 |
| Coolant Temp. (°C) | 10 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Coolant Flow rate (L/min) | 8.5 | 1.2 m/s | 1.08 | 0.5 | 2 |
| Flux (L/m2·h) | 10.8 (Duration: NA) | 9 (Duration: NA) | 14 (Duration: 24 h) | 24 (Duration: only 3 h) | 20 (Duration: after 24 h) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baroud, T.N. Tuning PVDF Membrane Porosity and Wettability Resistance via Varying Substrate Morphology for the Desalination of Highly Saline Water. Membranes 2023, 13, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040395
Baroud TN. Tuning PVDF Membrane Porosity and Wettability Resistance via Varying Substrate Morphology for the Desalination of Highly Saline Water. Membranes. 2023; 13(4):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040395
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaroud, Turki N. 2023. "Tuning PVDF Membrane Porosity and Wettability Resistance via Varying Substrate Morphology for the Desalination of Highly Saline Water" Membranes 13, no. 4: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040395
APA StyleBaroud, T. N. (2023). Tuning PVDF Membrane Porosity and Wettability Resistance via Varying Substrate Morphology for the Desalination of Highly Saline Water. Membranes, 13(4), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040395






