Effects of Critical Operation and Cleaning Parameters on Performances and Economic Benefits of Biogas Slurry Concentration by Forward Osmosis Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Materials
2.2. FO System
2.3. Influence Test of Different Process Parameters
2.4. Membrane Cleaning Test
2.5. Analytic Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FO Operation Parameters Optimization
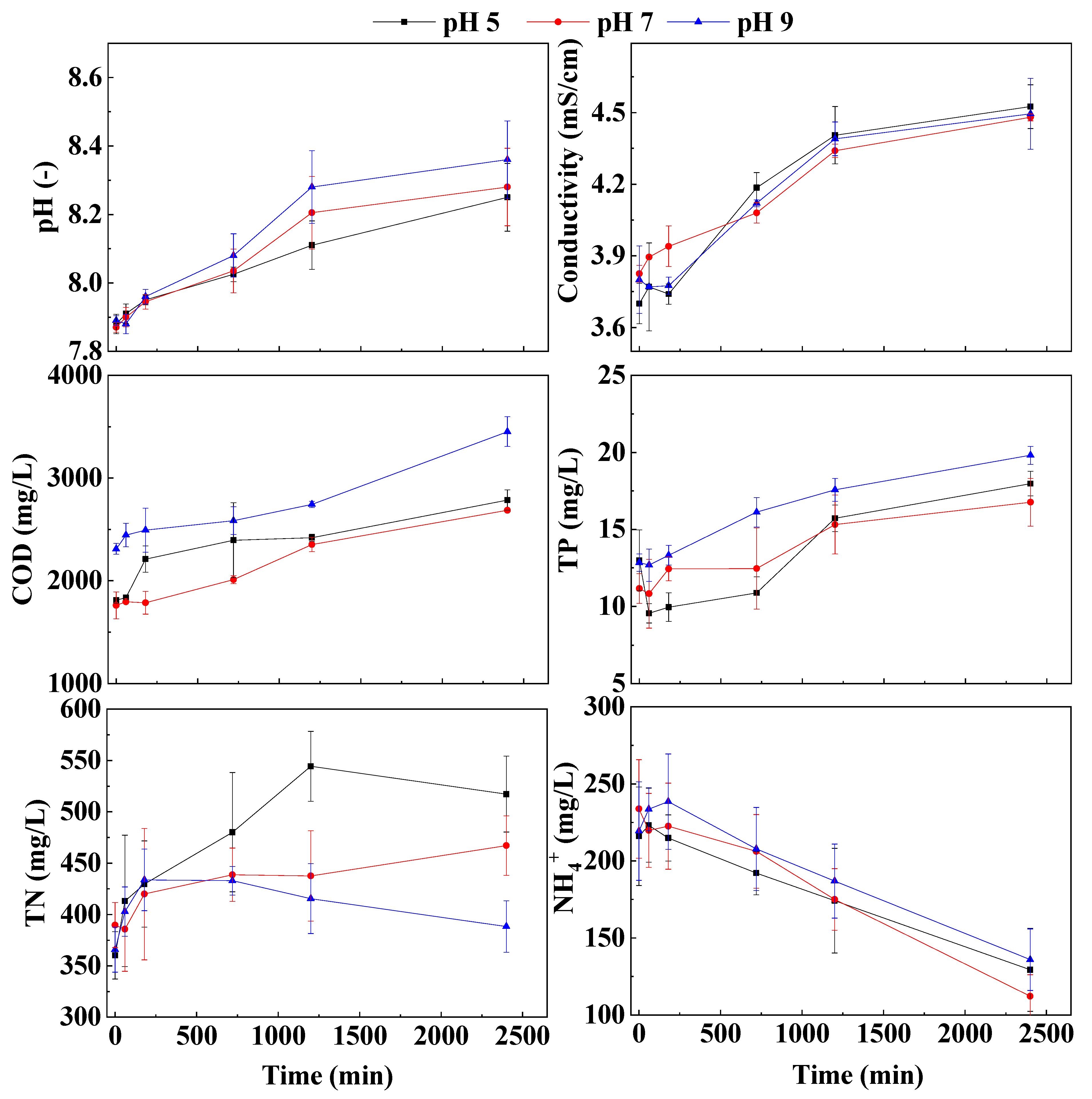
3.1.1. Influence of pH Value of Draw Solution
3.1.2. Effects of Draw Solution Concentration, Cross-Flow Velocity and Temperature
3.1.3. Correlation Analysis
3.2. Membrane Cleaning
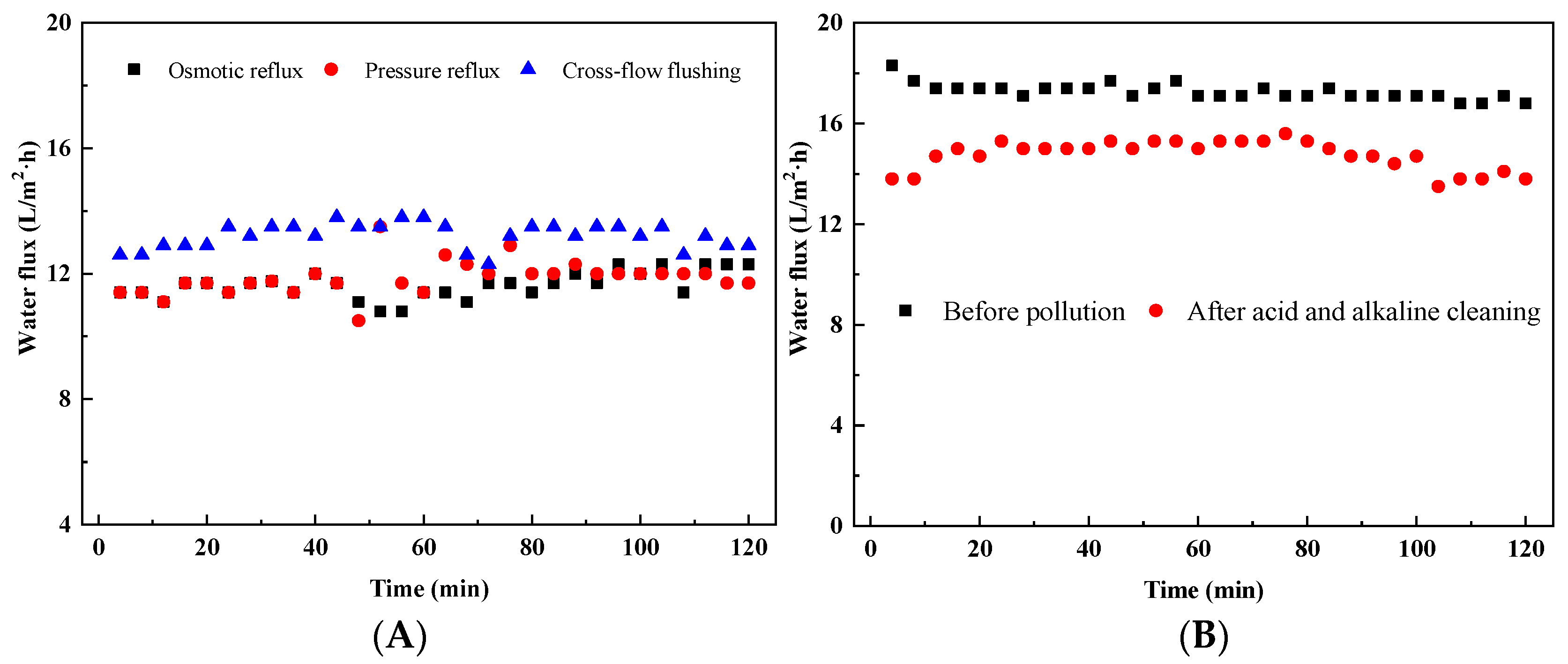
3.2.1. Effects of Membrane Fouling on Water Flux
3.2.2. Cleaning Effect of Physical Cleaning Method
3.2.3. The Effect of Acid and Alkaline Cleaning
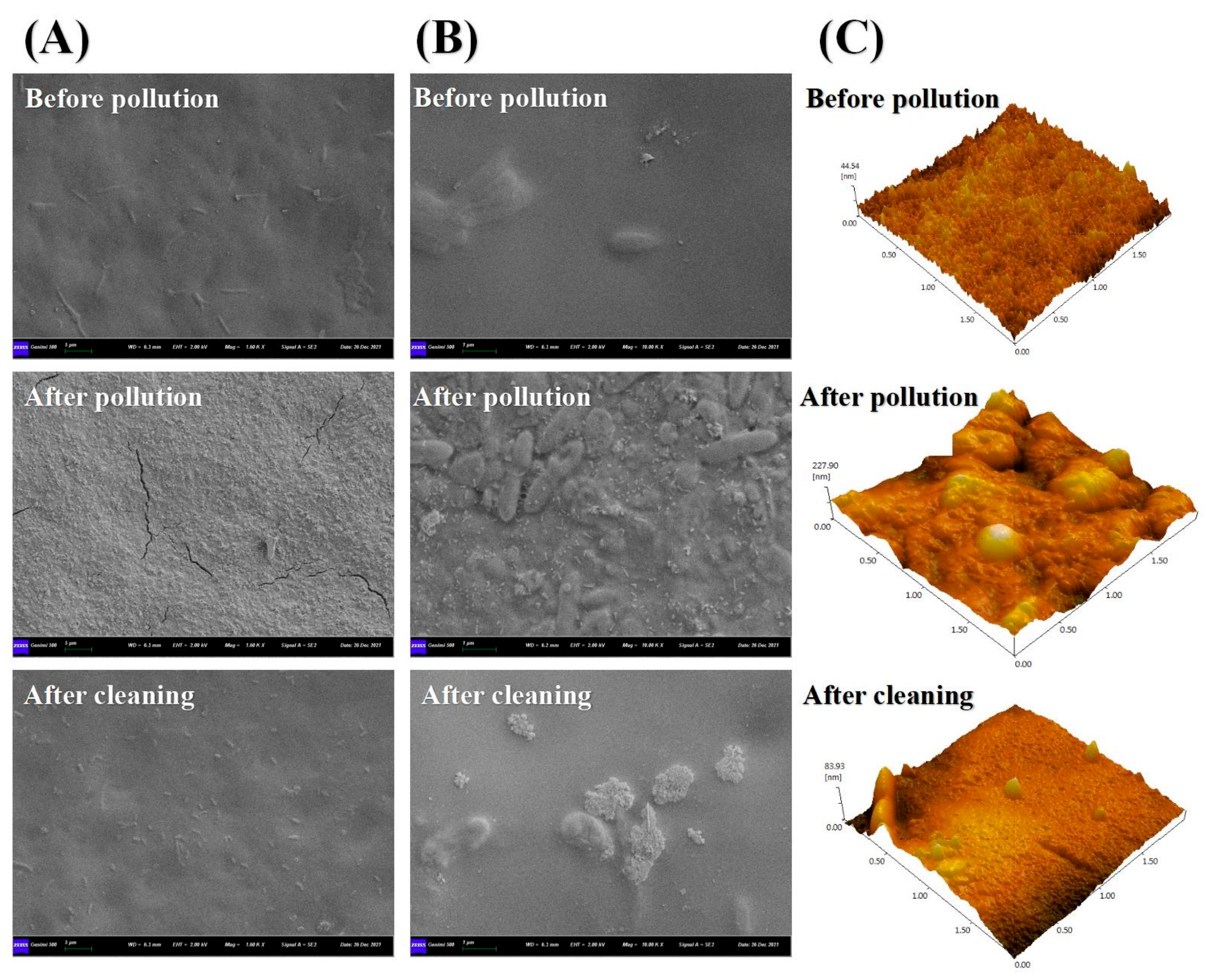
3.2.4. SEM-EDS Images of the Membrane before and after Cleaning
3.2.5. AFM Images before and after Membrane Cleaning
3.2.6. Changes in Basic Properties before and after Membrane Cleaning
3.2.7. Economic Cost Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilassi, S.; Taghavi, S.M.; Rodrigue, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Optimizing membrane module for biogas separation. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2019, 83, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Ghosh, P.; Kumar, M.; Vijay, V.K. Evaluation of biogas upgrading technologies and future perspectives: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11631–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, L. Spatial distribution of biogas potential, utilization ratio and development potential of biogas from agricultural waste in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Yi, D.; Wang, J. Poultry biogas slurry can partially substitute for mineral fertilizers in hydroponic lettuce production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-J.; Shao, D.-D.; Zhou, Z.; Xia, Q.-C.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.-L.; Zheng, T.; Sun, S.-P. Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) nanofiltration membranes towards efficient biogas slurry valorization. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyungeko, C.; Liang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.-w.; Sheteiwy, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Tian, G. Effect of biogas slurry application rate on colloidal phosphorus leaching in paddy soil: A column study. Geoderma 2018, 325, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, T.; Yuan, H.; Peng, N.; He, M. The valorization of biogas slurry with a pilot dual stage reverse osmosis membrane process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 142, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uald-Lamkaddam, I.; Dadrasnia, A.; Llenas, L.; Ponsá, S.; Colón, J.; Vega, E.; Mora, M. Application of Freeze Concentration Technologies to Valorize Nutrient-Rich Effluents Generated from the Anaerobic Digestion of Agro-Industrial Wastes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Qiu, Z.; Dai, Q.; Chen, J. Study of biogas slurry concentrated by reverse osmosis system: Characteristics, optimization, and mechanism. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Qiu, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, Z.; He, L. Ultrafiltration concentrated biogas slurry can reduce the organic pollution of groundwater in fertigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Resource recovery from digested manure centrate: Comparison between conventional and aquaporin thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.T.; Nguyen, L.N.; Johir, M.A.H.; Zhang, X.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Biogas sparging to control fouling and enhance resource recovery from anaerobically digested sludge centrate by forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Yin, R.; Dong, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, B. Effects of Different Draw Solutions on Biogas Slurry Concentration in Forward Osmosis Membrane: Performance and Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2022, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, R.A.; Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W.; Johnson, D.J.; Hilal, N. Evaluating Fertilizer-Drawn Forward Osmosis Performance in Treating Anaerobic Palm Oil Mill Effluent. Membranes 2021, 11, 566. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, S.; Ji, X.; Shu, Q.; Tian, B.; He, T.; Zhang, L. Biogas slurry as draw solution of forward osmosis process to extract clean water from micro-polluted water for hydroponic cultivation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tal, G.; Hankins, N.P.; Gitis, V. Fouling and cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 1, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Li, S.; Ghaffour, N. Evaluation of different cleaning strategies for different types of forward osmosis membrane fouling and scaling. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.D.; Rantissi, T.; Gitis, V.; Hankins, N.P. Retention of natural organic matter by ultrafiltration and the mitigation of membrane fouling through pre-treatment, membrane enhancement, and cleaning—A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y. Insight into the magnetic lime coagulation-membrane distillation process for desulfurization wastewater treatment: From pollutant removal feature to membrane fouling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Schagerlöf, H.; Morkeberg Krogh, K.B.; Jönsson, A.-S.; Lipnizki, F. Investigations of alkaline and enzymatic membrane cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes fouled by thermomechanical pulping process water. Membranes 2018, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, S.; Djurić, M.; Milanović, S.; Tekić, M.N.; Lukić, N. Application of an ultrasound field in chemical cleaning of ceramic tubular membrane fouled with whey proteins. J. Food Eng. 2010, 101, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.; Andrade, L.; Grossi, L.; Pires, W.; Amaral, M. Acid mine drainage treatment by nanofiltration: A study of membrane fouling, chemical cleaning, and membrane ageing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Qi, G.; Xiao, K.; Sun, J.; Giannelis, E.P.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling behavior of superhydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membranes functionalized with surface-tailored nanoparticles: Implications for organic fouling in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Biofouling in sugarcane juice refining by nanofiltration membrane: Fouling mechanism and cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Dong, Y. Recent development of pressure retarded osmosis membranes for water and energy sustainability: A critical review. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, P. Fundamental Modeling of Membrane Systems: Membrane and Process Performance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vrasna, D.K.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuyama, H.; Gonzales, R.R. Microalgae dewatering using forward osmosis membrane: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 3073–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; Vu, M.T.; Nghiem, L.D. A preliminary assessment of forward osmosis to extract water from rumen fluid for artificial saliva. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.J.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Nghiem, L.D. Assessing the integration of forward osmosis and anaerobic digestion for simultaneous wastewater treatment and resource recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, C. Concentration of biogas slurry with forward osmosis technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Mondor, M.; Masse, L.; Ippersiel, D.; Lamarche, F.; Masse, D. Use of electrodialysis and reverse osmosis for the recovery and concentration of ammonia from swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7363–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ye, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiao, F. Optimization of forward osmosis process for concentration of biogas slurry. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Dhiman, S.; Basu, S.; Balakrishnan, M.; Petrinic, I.; Helix-Nielsen, C. Dewatering of sewage for nutrients and water recovery by Forward Osmosis (FO) using divalent draw solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulerson, C.R.; Popat, S.C.; Husson, S.M. Water recovery from bioreactor mixed liquors using forward osmosis with polyelectrolyte draw solutions. Membranes 2021, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzaimi, N.D.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Mamah, S.C.; Malek, N.A.N.N.; Lim, J.W.; Wong, K.C.; Hilal, N. Strategies in forward osmosis membrane substrate fabrication and modification: A review. Membranes 2020, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Rajmohan, R.S.; Zarebska, A.; Tsapekos, P.; Hélix-Nielsen, C. Treating anaerobic effluents using forward osmosis for combined water purification and biogas production. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lee, S.; Maeng, S.K. Forward osmosis membrane fouling and cleaning for wastewater reuse. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2017, 7, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Chemical cleaning of potable water membranes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Hruza, J.; Yalcinkaya, F. Fouling and chemical cleaning of microfiltration membranes: A mini-review. Polymers 2021, 13, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


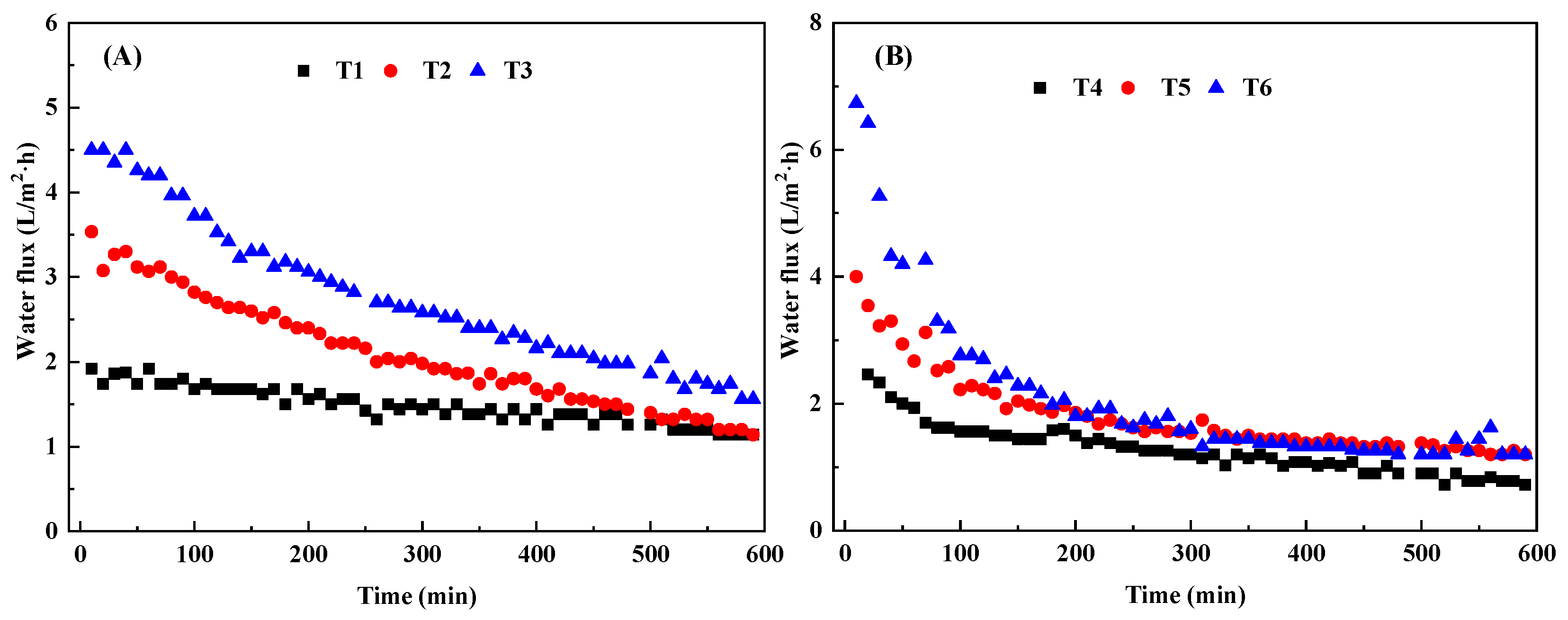
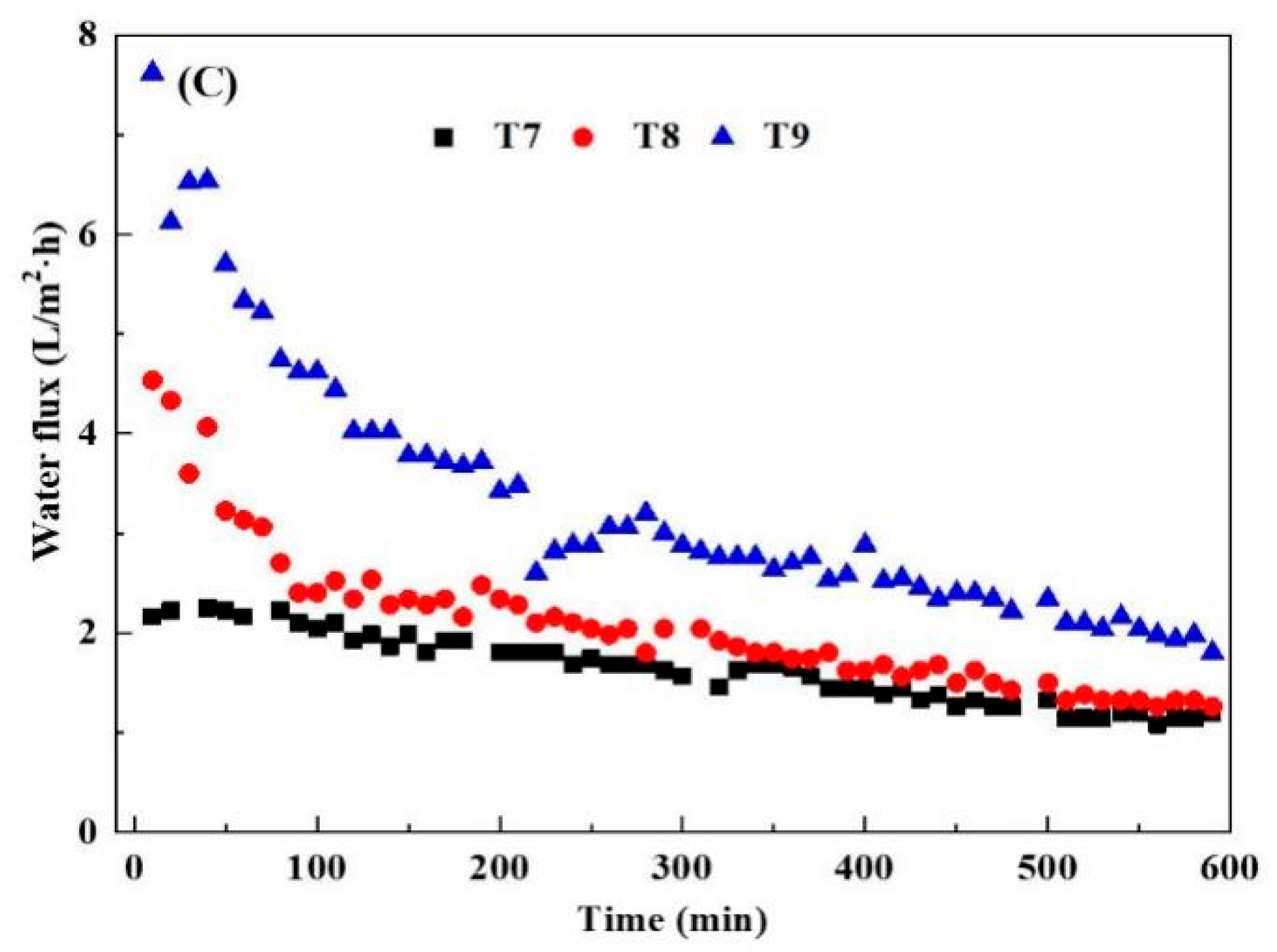

| Treatment | Temperature | Concentration | Cross-Flow Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|
| (°C) | (mol L−1) | (L min−1) | |
| T1 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| T2 | 15 | 1 | 1 |
| T3 | 15 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| T4 | 25 | 0.5 | 1 |
| T5 | 25 | 1 | 1.5 |
| T6 | 25 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| T7 | 45 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| T8 | 45 | 1 | 0.5 |
| T9 | 45 | 1.5 | 1 |
| Test Number | Factors | Water Flux (L/m2·h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Draw Solution Concentration (mol/L) | Cross-Flow Speed (L/min) | ||
| T1 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.84 |
| T2 | 15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.23 |
| T3 | 15 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4.39 |
| T4 | 25 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.17 |
| T5 | 25 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 3.28 |
| T6 | 25 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 5.39 |
| T7 | 45 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.20 |
| T8 | 45 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 3.82 |
| T9 | 45 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 6.31 |
| Kij | 9.45 | 6.21 | 11.0 | |
| 10.8 | 10.3 | 11.7 | ||
| 12.3 | 16.1 | 9.87 | ||
| kij | 3.15 | 2.07 | 3.68 | |
| 3.61 | 3.44 | 3.90 | ||
| 4.11 | 5.36 | 3.29 | ||
| R | 0.497 | 1.37 | 0.393 | |
| Excellent level | A3 | B3 | C2 | |
| Primary and secondary factors | B > C > A | |||
| Optimal combination | A3B3C2 | |||
| Serial Number | Factors | Water Flux (L/m2·h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.84 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3.23 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4.39 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2.17 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.28 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5.39 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2.20 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3.82 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6.31 |
| T1 | 9.45 | 6.21 | 11.0 | |
| T2 | 10.8 | 10.3 | 11. 7 | |
| T3 | 12.3 | 16.1 | 9.87 | |
| t1 | 3.15 | 2.07 | 3.68 | |
| t2 | 3.61 | 3.44 | 3.90 | |
| t3 | 4.11 | 5.36 | 3.29 | |
| T | 32.6 | |||
| Total sum of squares | 18.5 | |||
| Factor sum of squares | 1.37 | 16.4 | 0.58 | |
| Error sum of squares | 0.19 | |||
| Total degrees of freedom | 8 | |||
| A degrees of freedom | 2 | |||
| B degrees of freedom | 2 | |||
| C degrees of freedom | 2 | |||
| Error degrees of freedom | 2 | |||
| Factors | SS | df | MS | F |
| A | 1.37 | 2 | 0.69 | 7.25 |
| B | 16.4 | 2 | 8.19 | 86.5 |
| C | 0.58 | 2 | 0.29 | 3.04 |
| Error | 0.19 | 2 | 0.09 | |
| Sum | 18.5 | 8 | ||
| Parameters | FO Membrane | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Water permeability coefficient, A (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) | After pollution | 0.658 ± 0.10 |
| After cleaning | 1.37 ± 0.22 | |
| Salt permeability coefficient, B (L·m−2·h−1·bar−1) | After pollution | 0.55 ± 0.09 |
| After cleaning | 2.52 ± 0.71 | |
| Membrane structure parameters, S (µm) | After pollution | 536 ± 41 |
| After cleaning | 475 ± 19 |
| Cleaning Method | Average Flux | Membrane Flux Recovery Rate | Unit Membrane Cleaning Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| (L/m3·h) | (%) | (Yuan) | |
| Initial | 18.3 | - | - |
| Osmotic reflux | 11.4 | 62.3 | 12 |
| Pressure reflux | 12 | 65.6 | 24 |
| Cross-flow cleaning | 13.5 | 73.8 | 14 |
| Acid–base cleaning | 15.3 | 83.6 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Fu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, L.; Wei, Q.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y. Effects of Critical Operation and Cleaning Parameters on Performances and Economic Benefits of Biogas Slurry Concentration by Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes 2023, 13, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030288
Zhang B, Fu T, Zhang Q, Wang X, Tang L, Wei Q, Li Y, Peng Y. Effects of Critical Operation and Cleaning Parameters on Performances and Economic Benefits of Biogas Slurry Concentration by Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes. 2023; 13(3):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bangxi, Tianhong Fu, Qinyu Zhang, Xiaomin Wang, Ling Tang, Quanquan Wei, Yun Li, and Yutao Peng. 2023. "Effects of Critical Operation and Cleaning Parameters on Performances and Economic Benefits of Biogas Slurry Concentration by Forward Osmosis Membrane" Membranes 13, no. 3: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030288
APA StyleZhang, B., Fu, T., Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Tang, L., Wei, Q., Li, Y., & Peng, Y. (2023). Effects of Critical Operation and Cleaning Parameters on Performances and Economic Benefits of Biogas Slurry Concentration by Forward Osmosis Membrane. Membranes, 13(3), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030288








