Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane for Separation of Soluble Toluene by Pervaporation Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
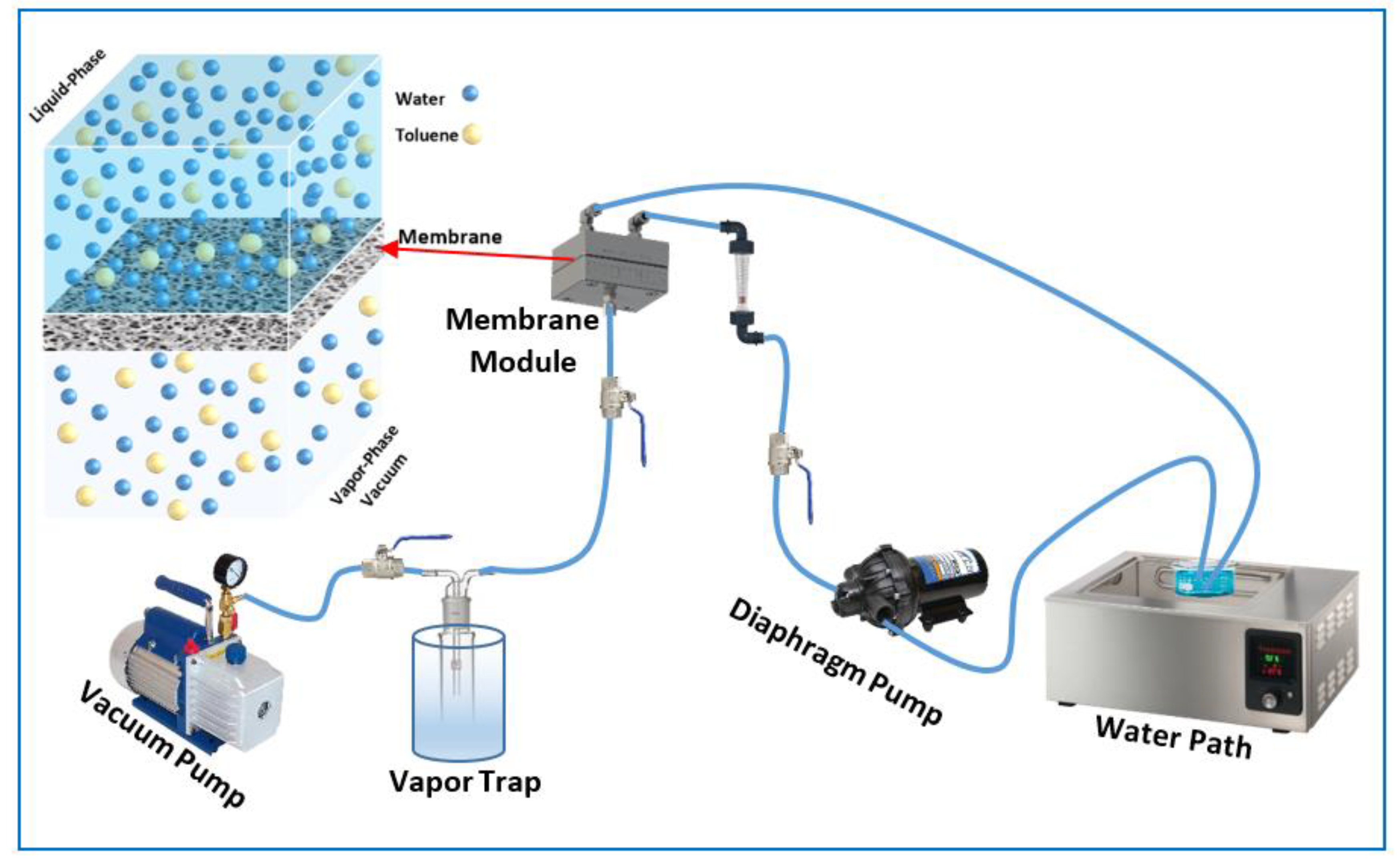
2.2. Pervaporation Process
2.3. Experimental Design
3. Results and Discussion
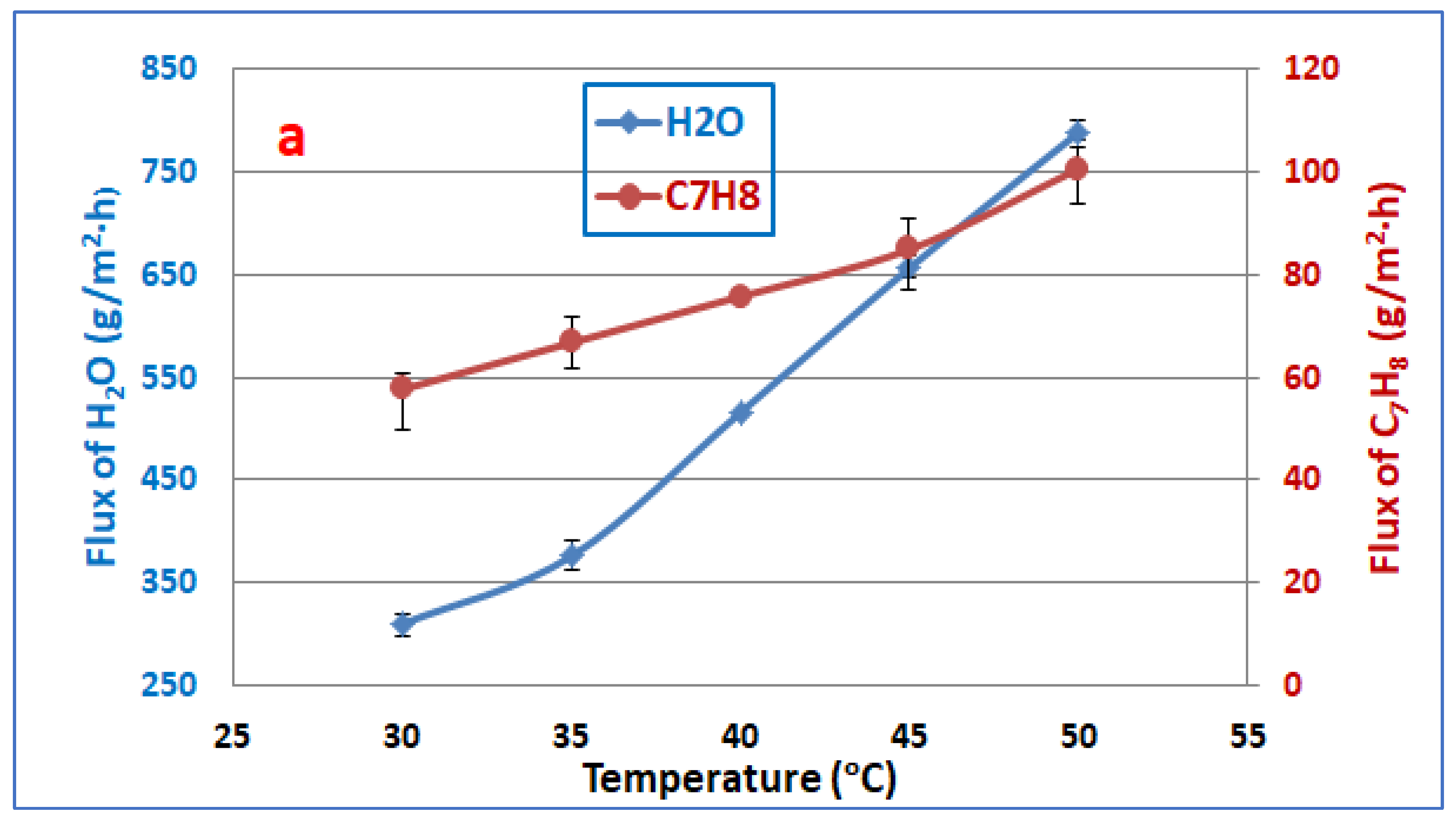
3.1. Feed Temperature
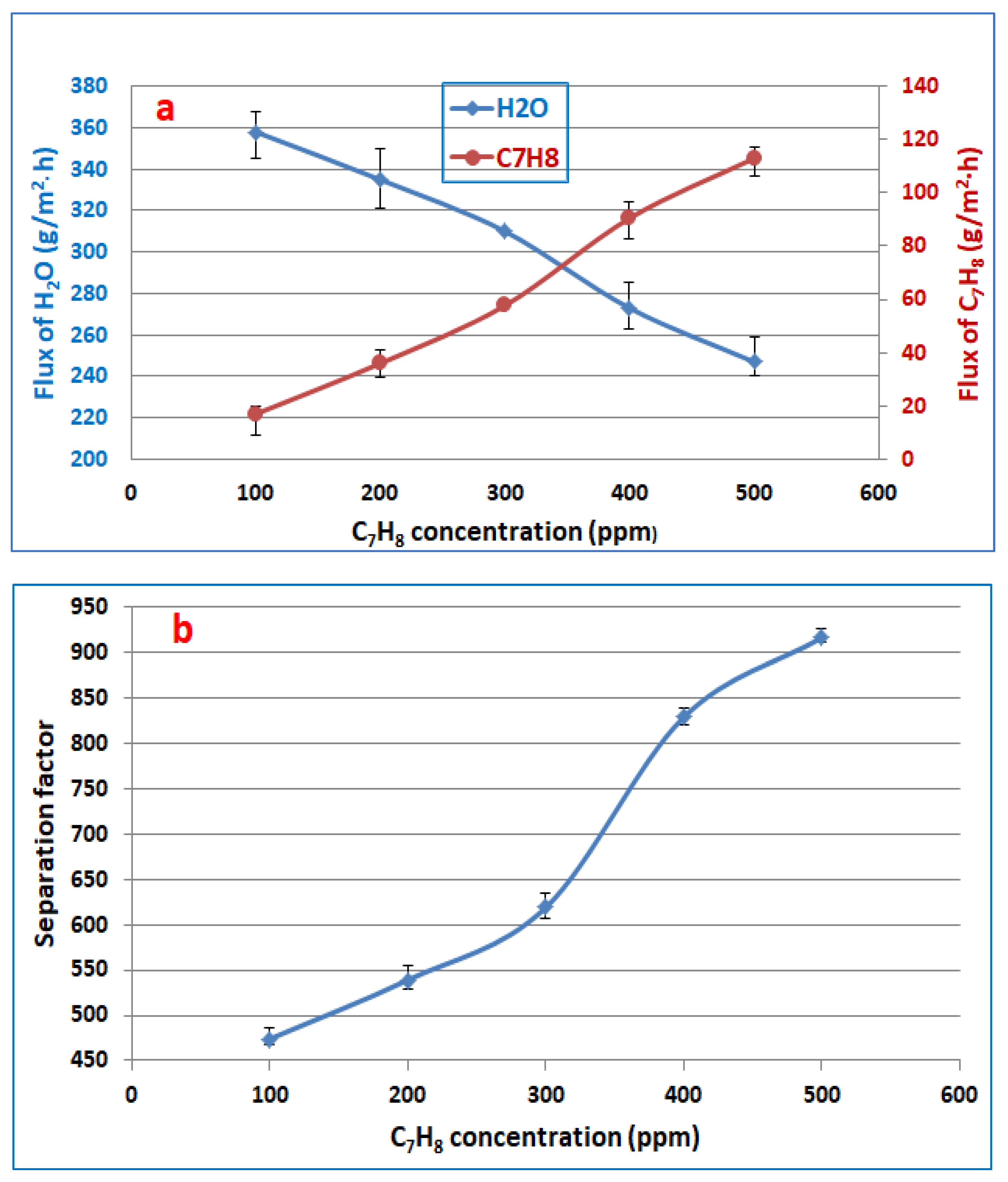
3.2. Feed Concentration
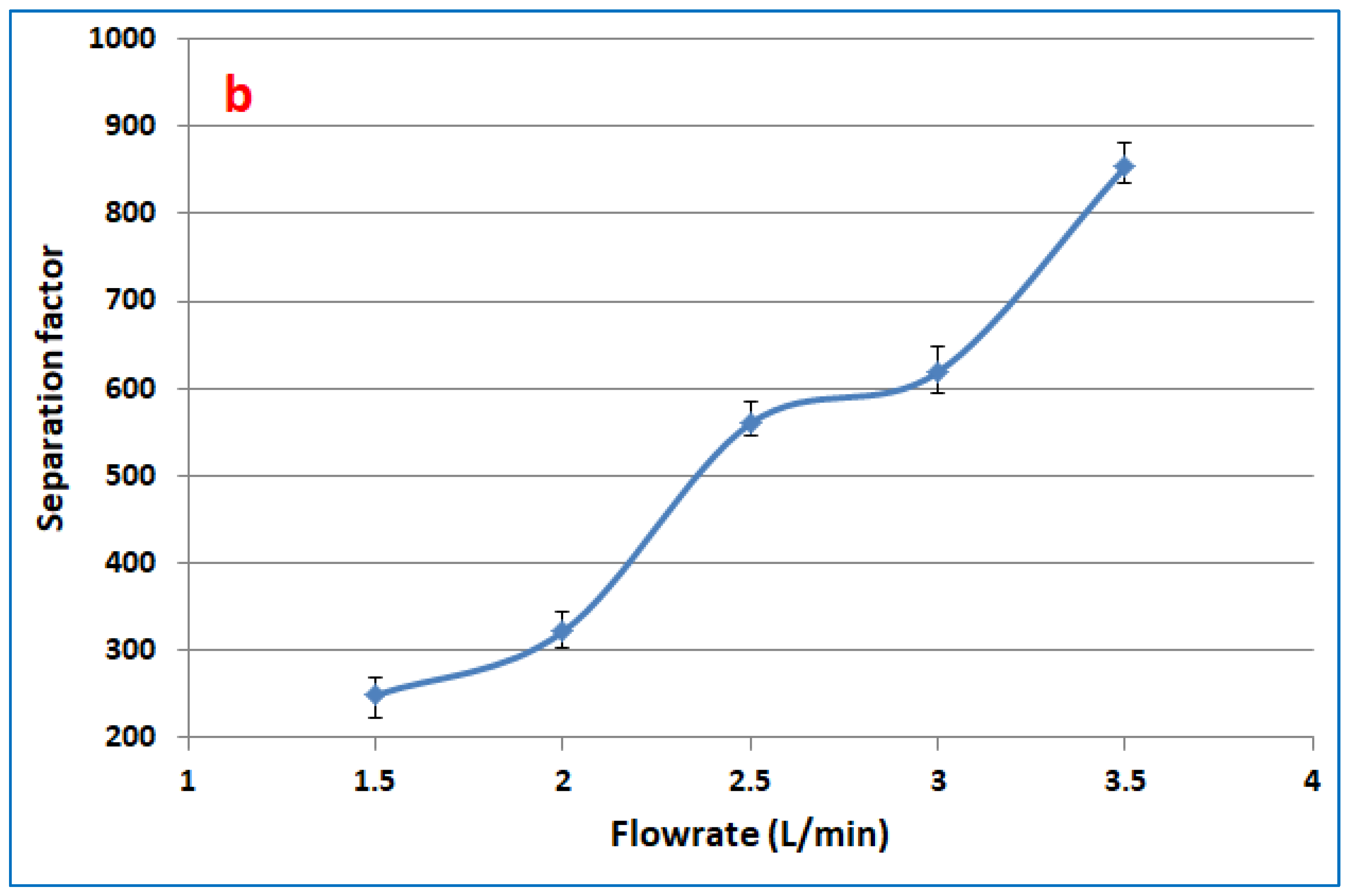
3.3. Effect of Feed Flowrate on the Toluene Partial Flux
3.4. RSM
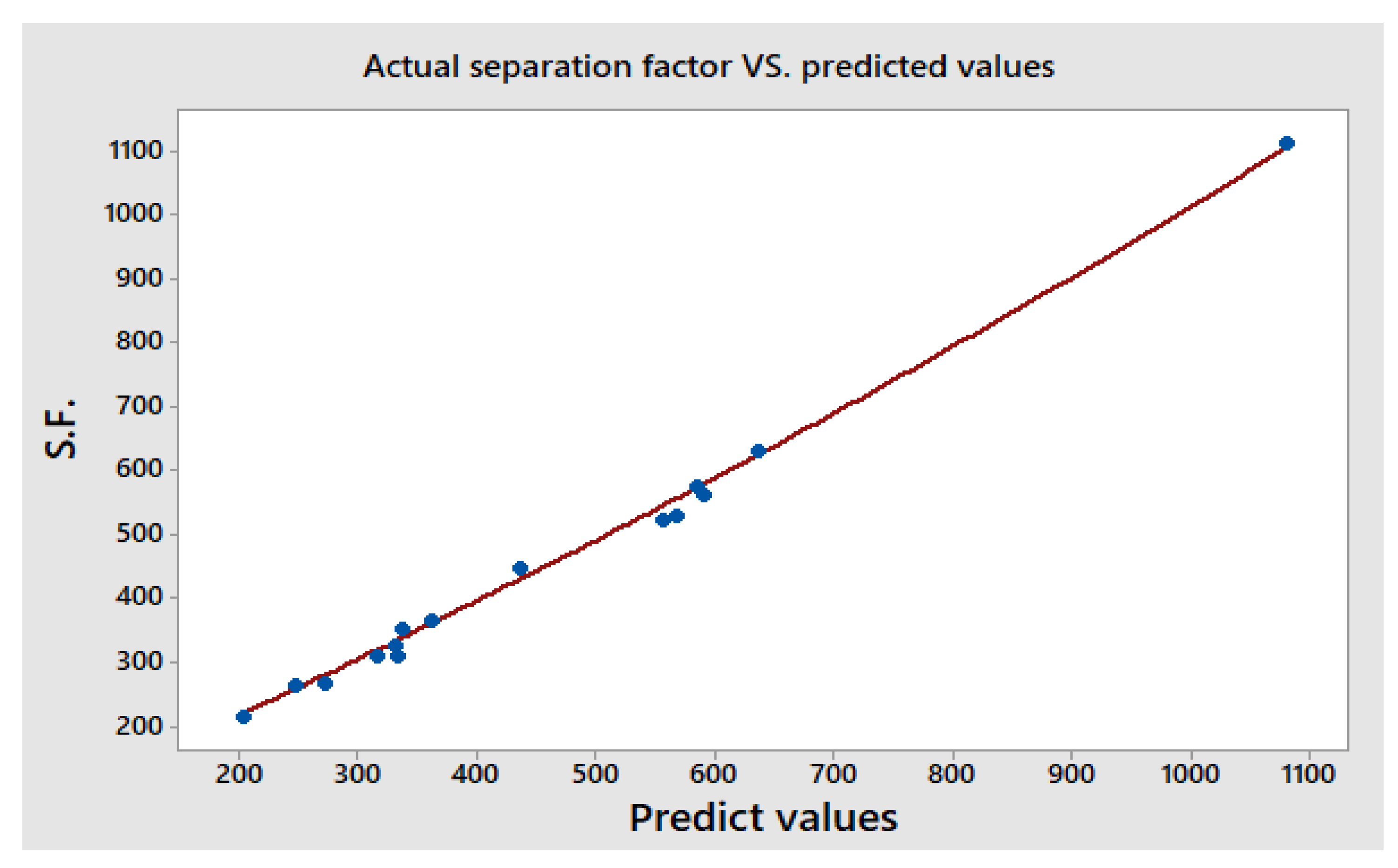
3.4.1. Predicted Model and ANOVA Calculations
3.4.2. Optimization of PV Process
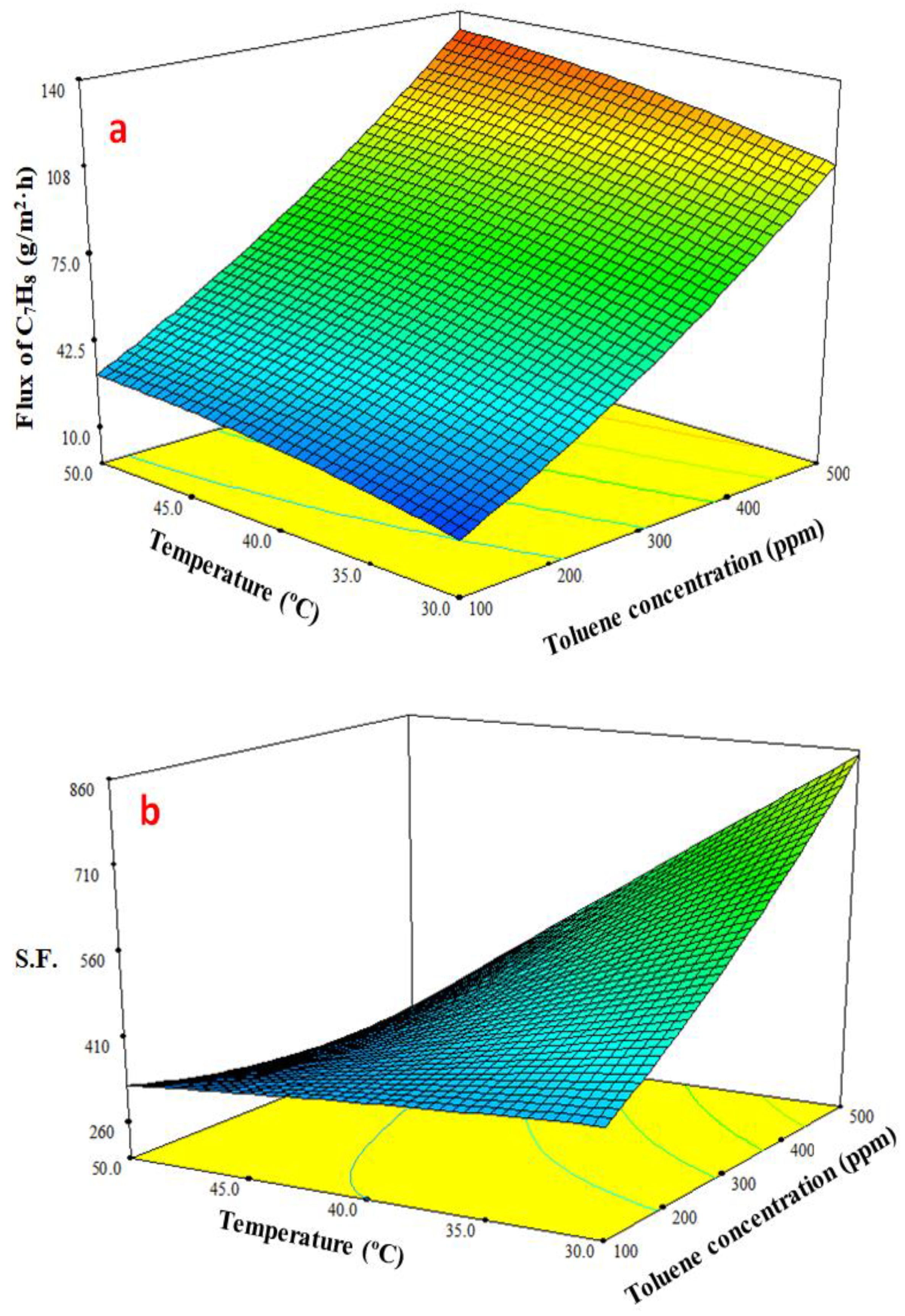
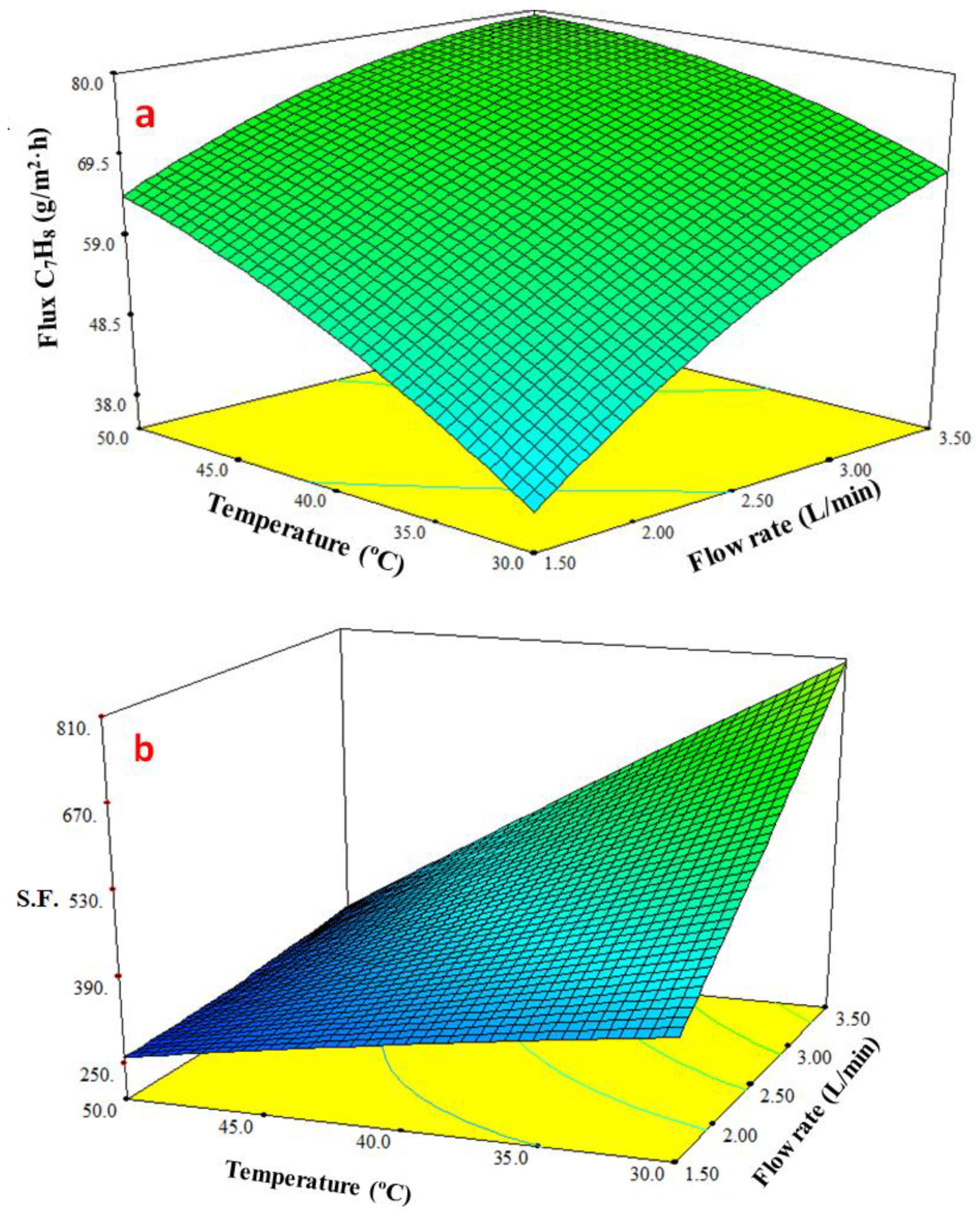
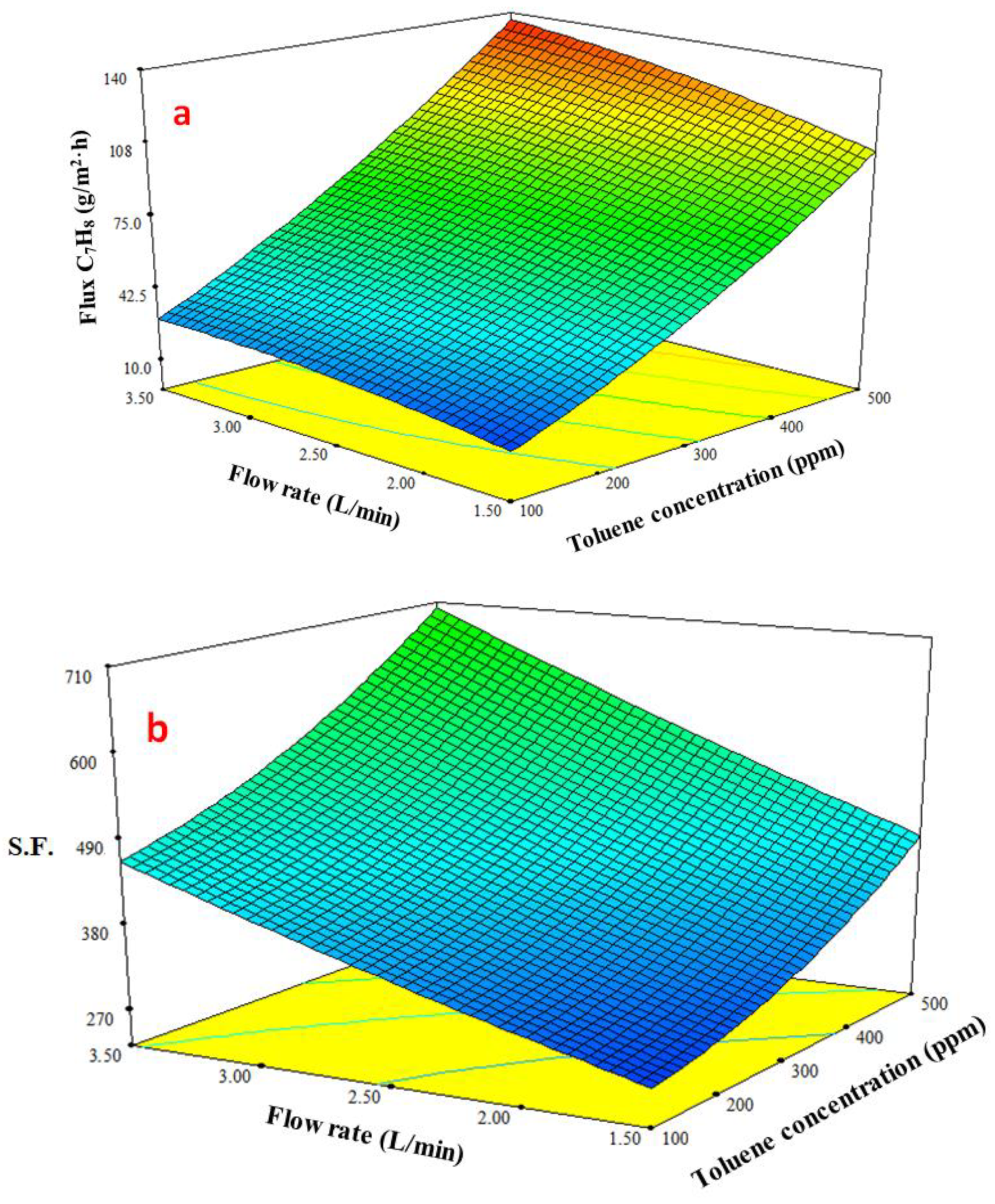
3.4.3. Response Surface Plots of Multiple Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uragami, T.; Ohshima, T.; Miyata, T. Removal of benzene from an aqueous solution of dilute benzene by various cross-linked poly(dimethylsiloxane) membranes during pervaporation. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9430–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouni, S.; Arous, O.; Abdessemed, D.; Nezzal, G.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Alcohol and alkane organic extraction using pervaporation process. Macromol. Symp. 2019, 386, 1800247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Usman, M.; Gull, N.; Jamil, T. An Overview on Pervaporation (an Advanced Separation Technique). J. Qual. Technol. Manag. 2013, IX, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Smitha, B.; Suhanya, D.; Sridhar, S.; Ramakrishna, M. Separation of organic–organic mixtures by pervaporation—A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 241, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Qiao, X.Y.; Lai, J.Y. Polyimides membranes for pervaporation and biofuels separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1135–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ray, S.K.; Kuila, S.B.; Samanta, H.S.; Singha, N.R. Systematic choice of crosslinker and filler for pervaporation membrane: A case study with dehydration of isopropyl alcohol-water mixtures by polyvinyl alcohol membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujiburohman, M.; Feng, X. Permselectivity, solubility and diffusivity of propyl propionate/water mixtures in poly(ether block amide) membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 300, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Kuila, S.B.; Das, P.; Ray, S.K. Separation of toluene-methanol mixtures by pervaporation using crosslink IPN membranes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R. Removal of Pyridine from Water by Pervaporation Using Crosslinked and Filled Natural Rubber Membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, N.M.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Leva, L.; Yave, W.; Alsalhy, Q.F. The combination of a new PERVAPTM membrane and molecular sieves enhances the ethanol drying process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2022, 174, 108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, H.; Chogle, A. Biofouling in reverse osmosis: Phenomena, monitoring, controlling and remediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, J.; Cerneaux, S.; Kujawski, W. Removal of hazardous volatile organic compounds from water by vacuum pervaporation with hydrophobic ceramic membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 474, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hömmerich, U.; Rautenbach, R. Design and optimization of combined pervaporation/distillation processes for the production of MTBE. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 146, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampranpiboon, P.; Jiraratananon, R.; Uttapap, D.; Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Pervaporation separation of ethyl butyrate and isopropanol with polyether block amide (PEBA) membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 173, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, W.; Cohen, Y. Removal of methyl tert-butyl ether from water by pervaporation using ceramic-supported polymer membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 229, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadaka-Amir, D.; Nasser, A.; Nir, S.; Mishael, Y.G. Removal of methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) from water by polymer-zeolite composites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 151, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, Q.G.; Han, G.L.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Pervaporation of water– ethanol and methanol–MTBE mixtures using poly(vinylalcohol)/cellulose acetate blended membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 448, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchuk, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Overview of technologies for removal of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkiewicz, I.; Kujawski, W.; Namiesnik, J. Pervaporation of volatile organohalogen compounds through polydimethylsiloxane membrane. Desalination 2010, 264, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, C.; Bagatin, R.; Tagliabue, M.; Vignola, R. Zeolites and related mesoporous materials for multi-talented environmental solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Vane, L.M.; Liu, S.X. Recent advances in VOCs removal from water by pervaporation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayet, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G. Response surface modelling and optimization in pervaporation. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 321, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Wan, Y.; Jin, W. Fabrication of high silicalite-1 content filled PDMS thin composite pervaporation membrane for the separation of ethanol from aqueous solutions. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 524, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Hu, S.; Miao, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Qin, P.; Tan, T. Two-stage pervaporation process for effective in situ removal acetone-butanol-ethanol from fermentation broth. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarova, M.; Bösch, P.; Friedl, A. POMS membrane for selective separation of ethanol from dilute alcohol-aqueous solutions by pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, K.; Pintauro, P.N.; Ponangi, R. Separation of dilute organic/water mixtures with asymmetric poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 117, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, K.; Pintauro, P.N. Asymmetric PVDF hollow-fiber membranes for organic/water pervaporation separations. J. Memb. Sci. 1997, 135, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.L. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 76th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; Volume 53, p. 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Toluene in Drinking-Water Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Matavos-Aramyan, S.; Bagheri, G.; Jazebizadeh, M.H. Pervaporation separation of toluene from aqueous solutions using nano-based peba/nax mixed matrix membrane. Silicon 2019, 11, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi Shahrabi, S.; Mortaheb, H.R.; Barzin, J.; Ehsani, M.R. Pervaporative performance of a PDMS/blended PES composite membrane for removal of toluene from water. Desalination 2012, 287, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, D.; Konieczny, K. Pervaporative separation of toluene from wastewaters by use of filled and unfilled poly(dimethylosiloxane) (PDMS) membranes. Desalination 2007, 241, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, D.; Konieczny, K. Applying filled and unfilled polyether-block-amide membranes to separation of toluene from wastewaters by pervaporation. Desalination 2008, 222, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhuis, H.H.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Smolders, C.A. Removal of trace organics from aqueous solutions. Effect of membrane thickness. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 61, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, A.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J.; Li, G.; Kujawski, W. Fabrication of PDMS based membranes with improved separation efficiency in hydrophobic pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G. Studies on pervaporation separation of acetone, acetonitrile and ethanol from aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knozowska, K.; Kujawska, A.; Li, G.; Kujawa, J.; Bryjak, M.; Kujawski, W.; Lipnizki, F.; Ahrn, L.; Petrini, I.; Kujawski, J.K. Membrane assisted processing of acetone, butanol, and ethanol (ABE) aqueous streams. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2021, 166, 108462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Separation of isopropanol from water by pervaporation using silicone-based membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1992, 74, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Khaleel, S.R. Performance of vacuum poly (propylene) membrane distillation (VMD) for saline water desalination. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 120, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.G.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Majdi, H.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F. Ethanol Separation from an Ethanol—Water Solution Using Vacuum Membrane Distillation. Membrane 2022, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, S.H.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Salih, I.K. Separation of soluble benzene from an aqueous solution by pervaporation using a commercial polydimethylsiloxane membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, M.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A. Removal of styrene from petrochemical wastewater using pervaporation process. Desalination 2012, 284, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, J. Removing benzene from aqueous solution using CMS-filled PDMS pervaporation membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, G.O. Separation of volatile organic compounds (BTEX) from aqueous solutions by a composite organophilic hollow fiber membrane-based pervaporation process. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 319, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Athayde, A.L.; Daniels, R.; Ly, J.H.; Kamaruddin, H.D.; Pinnau, I. The role of boundary layers in the removal of volatile organic compounds from water by pervaporation. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 109, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, W.N.; Saeed, W.S.; Alwarthan, A.A.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Aouak, T. Extraction of organic volatile pollutants in over-saturated water by pervaporation technique using a poly (dimethylsiloxane)-based sealer as a membrane. Water 2021, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Figoli, A.; Khayet, M. Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; ISBN 9781782422563. [Google Scholar]
- Mook, W.T.; Aroua, M.K.; Chakrabarti, M.H.; Low, C.T.J.; Aravind, P.V.; Brandon, N.P. The application of nano-crystalline PbO2 as an anode for the simultaneous bio-electrochemical denitrification and organic matter removal in an up-flow undivided reactor. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 94, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhnazarova, S.; Kafarov, V. Experiment Optimization in Chemistry and Chemical Engineering; Mir Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Majooni, Y.; Mortaheb, H.R.; Khodadadi Dizaji, A. Enhancement in pervaporative performance of PDMS membrane for separation of styrene from wastewater by hybridizing with reduced graphene oxide. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| StdOrder | Temp. (°C) | Conc. (ppm) | Flowrate (L/min) | Flux (g/m2·h) | S.F. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 30 | 100 | 3.5 | 20.3 | 575.0 |
| 9 | 30 | 300 | 2.5 | 53.0 | 560.0 |
| 14 | 40 | 300 | 3.5 | 80.0 | 523.0 |
| 12 | 40 | 500 | 2.5 | 122.0 | 528.0 |
| 15 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 19 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 6 | 50 | 100 | 3.5 | 30.5 | 351.0 |
| 18 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 3 | 30 | 500 | 1.5 | 87.0 | 629.0 |
| 7 | 30 | 500 | 3.5 | 127.0 | 1110.8 |
| 1 | 30 | 100 | 1.5 | 7.9 | 215.0 |
| 8 | 50 | 500 | 3.5 | 139.0 | 310.0 |
| 17 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 10 | 50 | 300 | 2.5 | 74.0 | 265.0 |
| 4 | 50 | 500 | 1.5 | 121.0 | 264.0 |
| 16 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 13 | 40 | 300 | 1.5 | 46.0 | 325.0 |
| 20 | 40 | 300 | 2.5 | 70.0 | 447.0 |
| 11 | 40 | 100 | 2.5 | 23.7 | 364.0 |
| A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −122.3 | 3.68 | 0.0356 | 34.1 | −0.0273 | 16.5 × 10−5 | −3.23 | 11.69 × 10−4 | −0.361 | 0.02506 | |
| −993 | 30.8 | 2.474 | 432.0 | −0.046 | 72.1 × 10−5 | 6.9 | −0.06480 | −9.435 | 0.0792 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 26,443.9 | 2938.2 | 174.14 | 0.000 |
| Linear | 3 | 25,970.0 | 8656.7 | 513.05 | 0.000 |
| Tem. | 1 | 889.2 | 889.2 | 52.70 | 0.000 |
| Con. | 1 | 23,873.0 | 23,873.0 | 1414.85 | 0.000 |
| flow | 1 | 1207.8 | 1207.8 | 71.58 | 0.000 |
| Square | 3 | 124.7 | 41.6 | 2.46 | 0.122 |
| Tem. × Tem. | 1 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 1.22 | 0.296 |
| Con. × Con. | 1 | 120.5 | 120.5 | 7.14 | 0.023 |
| Flow × flow | 1 | 28.7 | 28.7 | 1.70 | 0.221 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 3 | 349.1 | 116.4 | 6.90 | 0.008 |
| Tem. × Con. | 1 | 43.7 | 43.7 | 2.59 | 0.139 |
| Tem. × flow | 1 | 104.4 | 104.4 | 6.19 | 0.032 |
| Con. × flow | 1 | 201.0 | 201.0 | 11.91 | 0.006 |
| Error | 10 | 168.7 | 16.9 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 5 | 168.7 | 33.7 | ||
| Pure Error | 5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Total | 19 | 26,612.6 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 697,438 | 77,493 | 118.98 | 0.000 |
| Linear | 3 | 485,146 | 161,715 | 248.29 | 0.000 |
| Tem. | 1 | 252,746 | 252,746 | 388.06 | 0.000 |
| Con. | 1 | 105,432 | 105,432 | 161.88 | 0.000 |
| flow | 1 | 126,968 | 126,968 | 194.94 | 0.000 |
| Square | 3 | 4697 | 1566 | 2.40 | 0.128 |
| Tem. × Tem. | 1 | 59 | 59 | 0.09 | 0.769 |
| Con. × Con. | 1 | 2290 | 2290 | 3.52 | 0.090 |
| Flow × flow | 1 | 129 | 129 | 0.20 | 0.666 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 3 | 207,594 | 69,198 | 106.25 | 0.000 |
| Tem. × Con. | 1 | 134,369 | 134,369 | 206.31 | 0.000 |
| Tem. × flow | 1 | 71,215 | 71,215 | 109.34 | 0.000 |
| Con. × flow | 1 | 2010 | 2010 | 3.09 | 0.109 |
| Error | 10 | 6513 | 651 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 5 | 6513 | 1303 | ||
| Pure Error | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 19 | 703,951 |
| Parameters | Stand. Dev. | R2 | R2(adj) | R2(pred) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permeate flux | 4.10769 | 99.37% | 98.80% | 94.04% |
| Separation factor | 25.5207 | 99.07% | 98.24% | 90.53% |
| Temp. (°C) | Conc. (ppm) | Flow (L/min) | S.F. Fit | Flux Fit (g/m2·h) | Composite Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 500 | 3.5 | 1080.26 | 125.855 | 0.932233 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasheed, S.H.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Majdi, H.S. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane for Separation of Soluble Toluene by Pervaporation Process. Membranes 2023, 13, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030289
Rasheed SH, Ibrahim SS, Alsalhy QF, Majdi HS. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane for Separation of Soluble Toluene by Pervaporation Process. Membranes. 2023; 13(3):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030289
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasheed, Salam H., Salah S. Ibrahim, Qusay F. Alsalhy, and Hasan Sh. Majdi. 2023. "Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane for Separation of Soluble Toluene by Pervaporation Process" Membranes 13, no. 3: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030289
APA StyleRasheed, S. H., Ibrahim, S. S., Alsalhy, Q. F., & Majdi, H. S. (2023). Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Membrane for Separation of Soluble Toluene by Pervaporation Process. Membranes, 13(3), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030289









