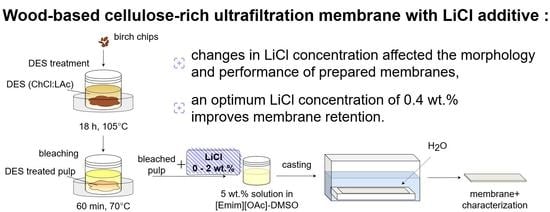
Effect of Low Concentrations of Lithium Chloride Additive on Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membrane Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. DES Treatment
2.2.2. Bleaching
2.2.3. Membrane Preparation
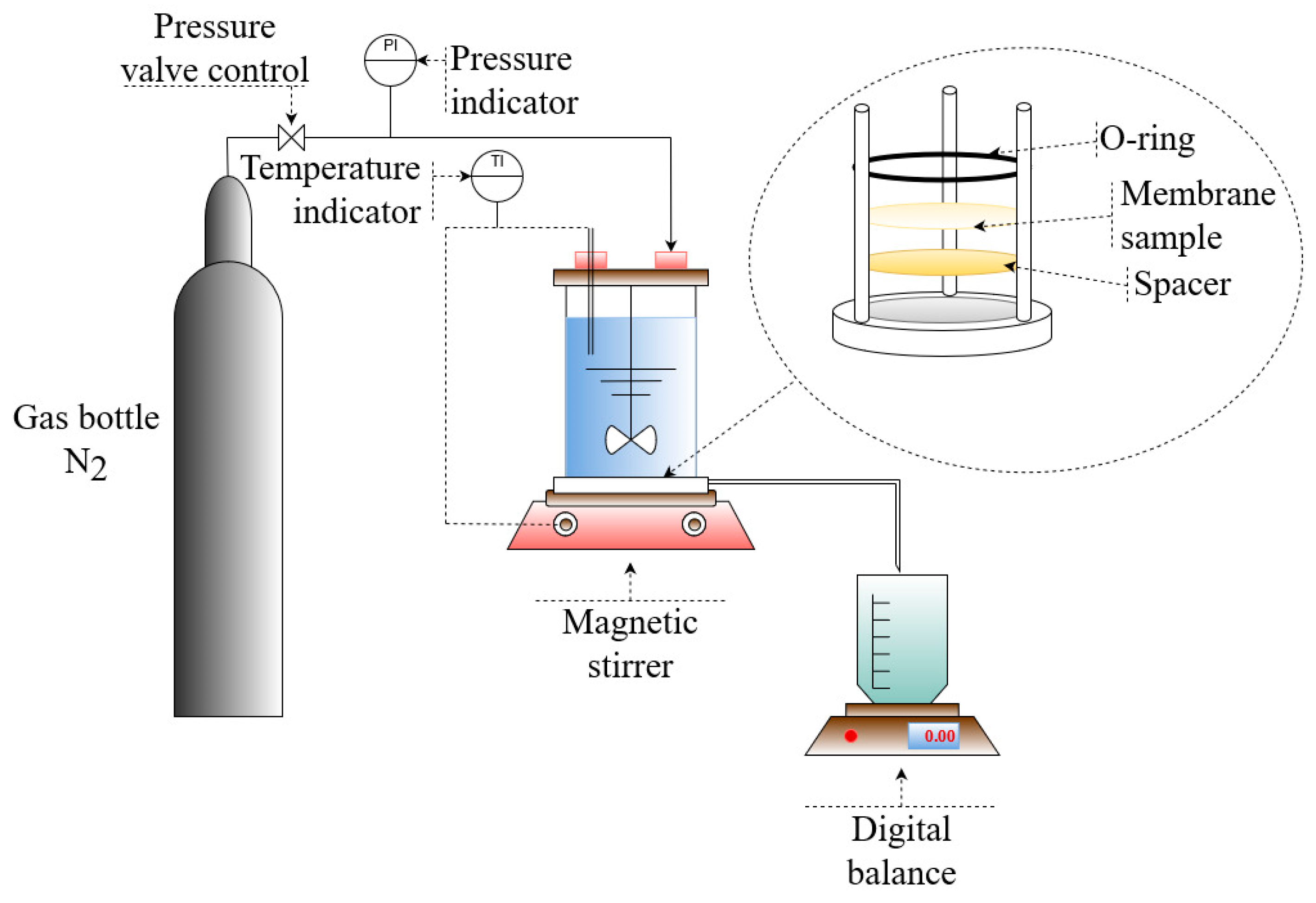
2.2.4. Casting Solutions Viscosity Measurements
2.2.5. Membrane Permeability and Retention Measurements
2.2.6. SEM Analysis
2.2.7. Examination of the Chemical Structure of the Membranes
2.2.8. Contact Angle Measurements
2.2.9. Contact Angle Measurements
2.2.10. Membrane Zeta Potential Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
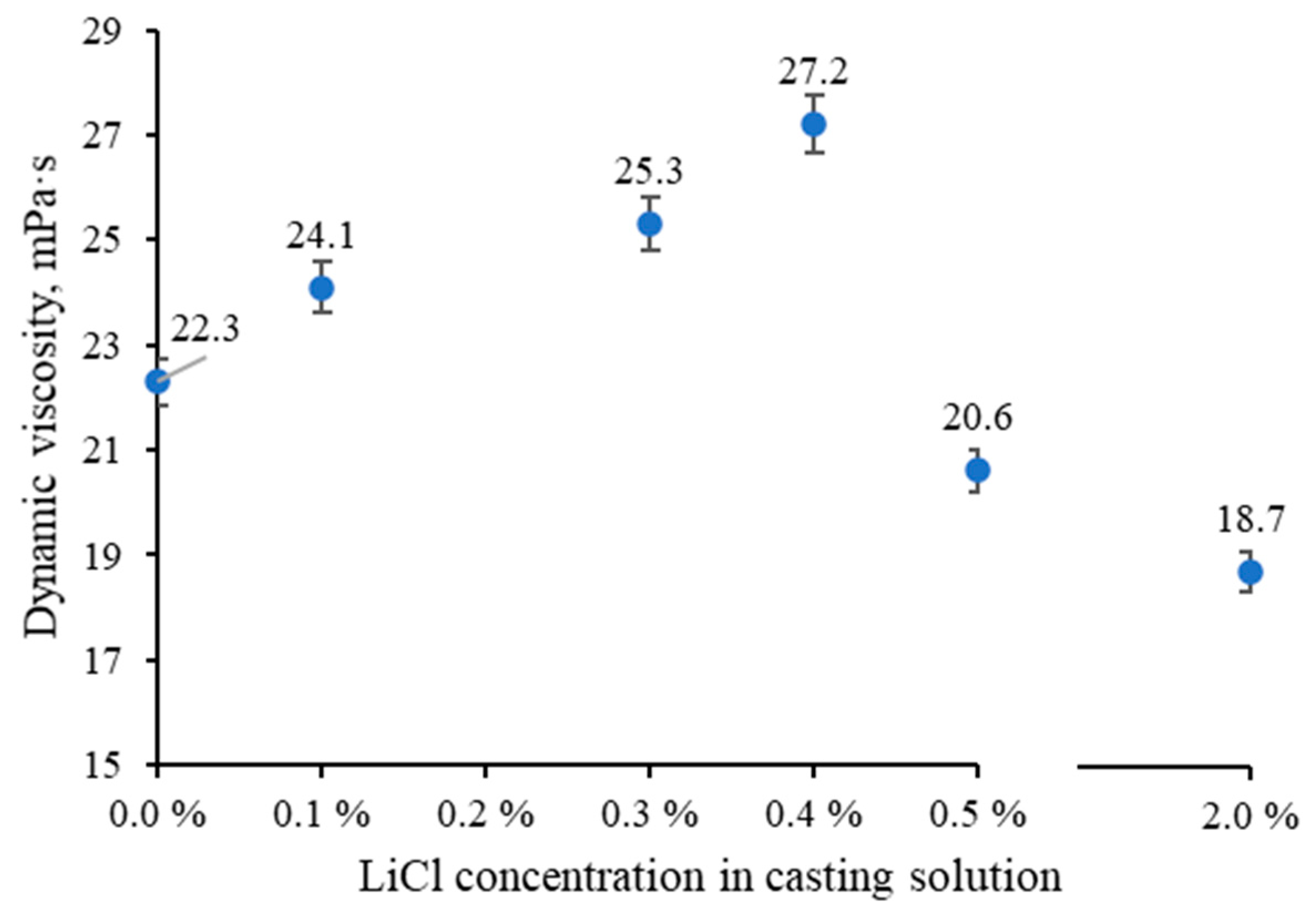
3.1. The Effect of LiCl Content on the Viscosity of Polymer Solution
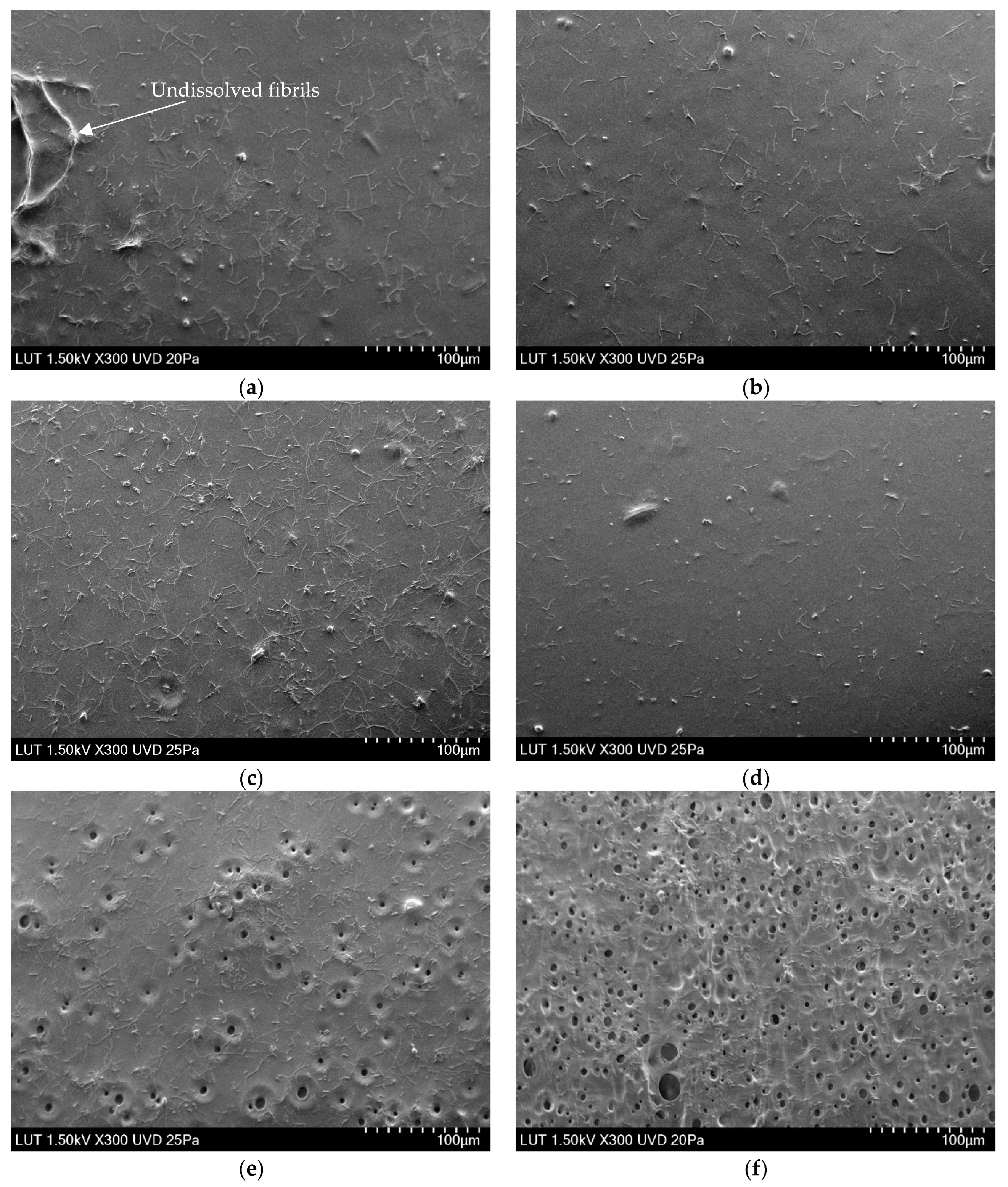
3.2. The Effect of LiCl Content on the Morphology of the Membranes
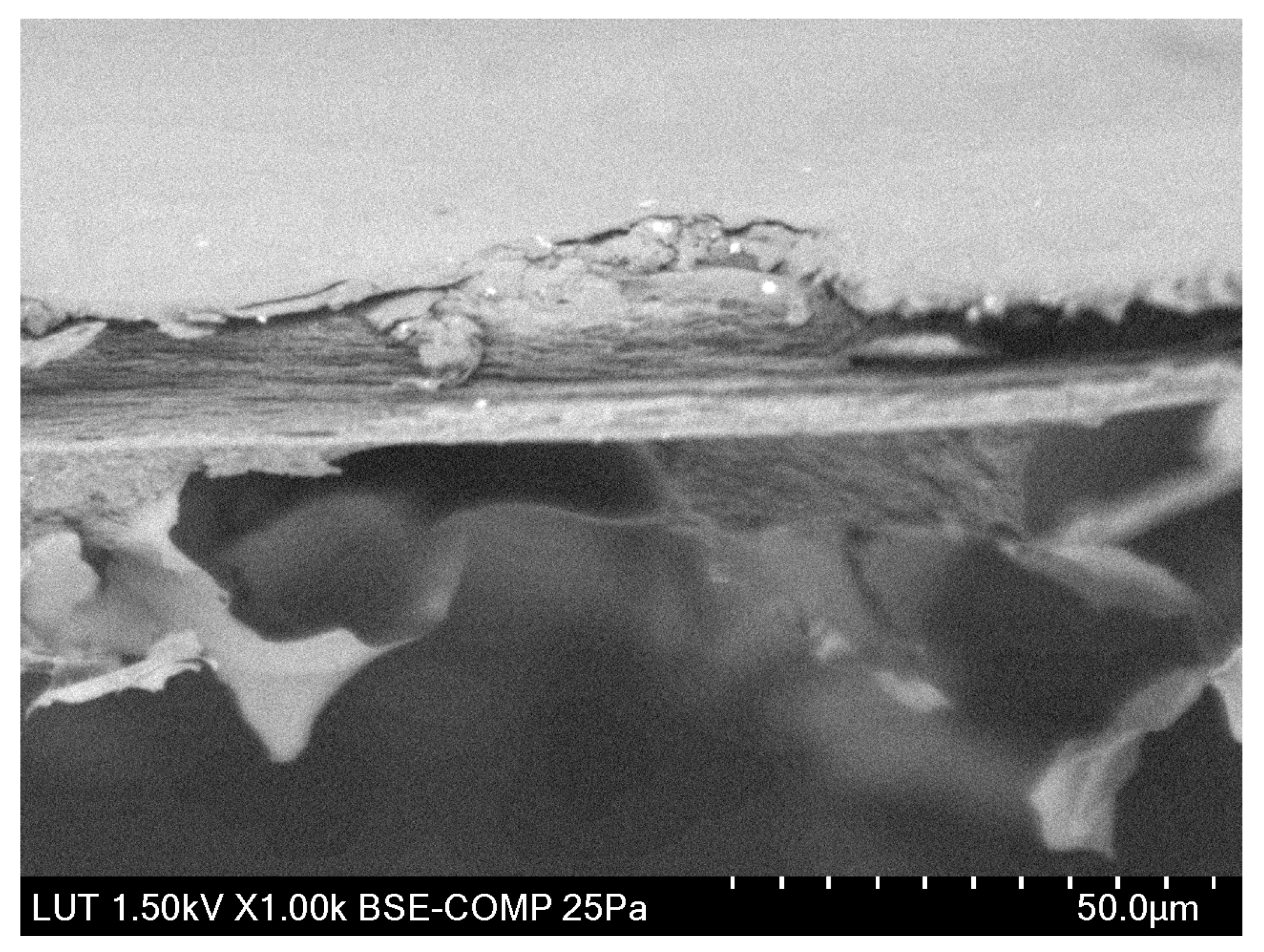
3.2.1. Physical Structure of the Membranes
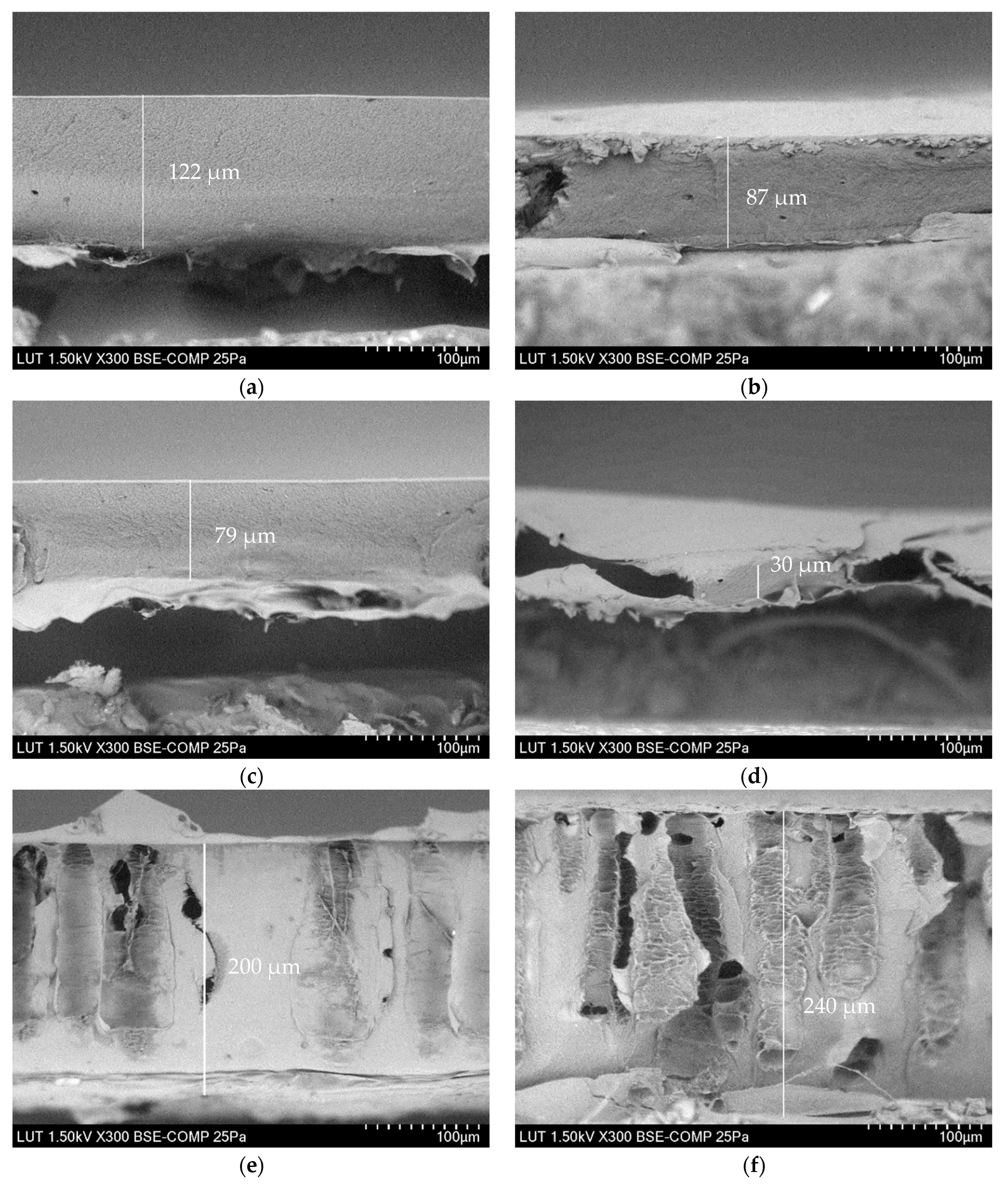
3.2.2. Thickness of the Membranes
3.3. The Effect of LiCl Content on the Chemical Structure of the Membranes
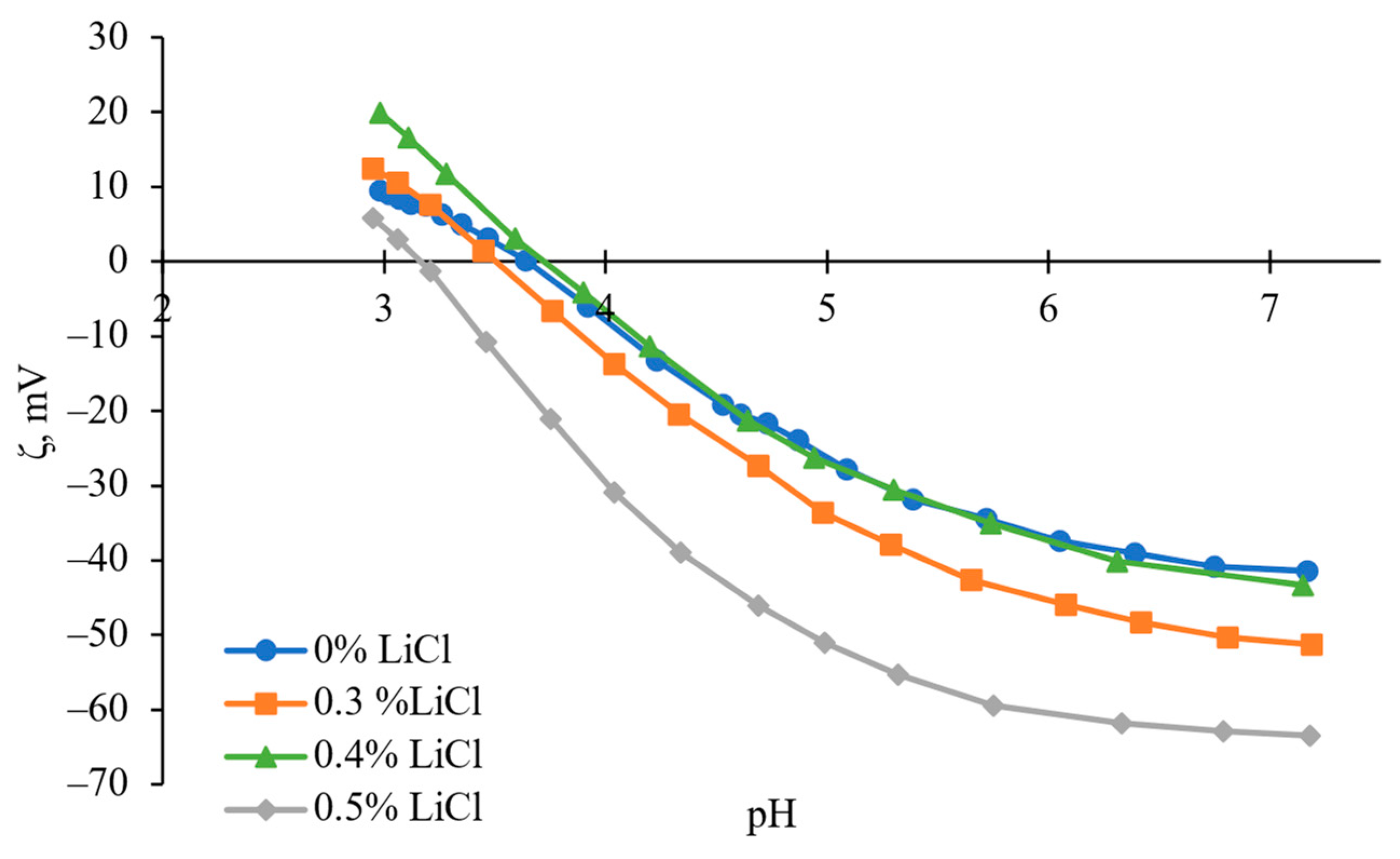
3.4. The Effect of LiCl Content on Hydrophilicity and Zeta Potential of the Membranes
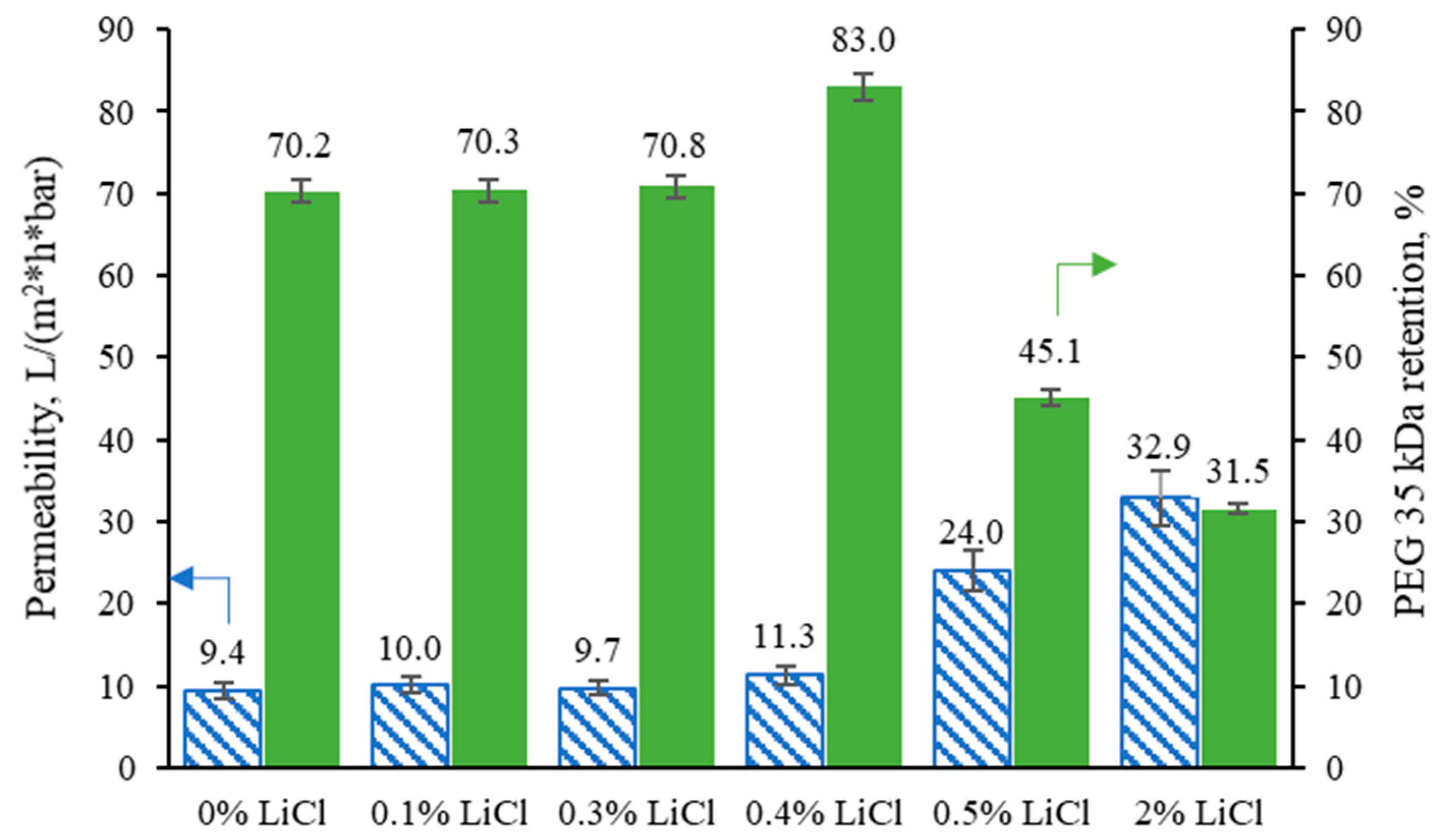
3.5. The Effect of LiCl Content on the Filtration Performance of the Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goh, P.S.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T. Waste Reutilization in Polymeric Membrane Fabrication: A New Direction in Membranes for Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.; Nunes, S.P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Figoli, A.; Lee, Y.M. Recent Advances in Polymer Membranes Employing Non-Toxic Solvents and Materials. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9815–9843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Gestel, T.; Doyenb, W.; Leysenb, R. Review of Pressure-Driven Membrane Processes. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Seoud, O.A.; Kostag, M.; Jedvert, K.; Malek, N.I. Cellulose Regeneration and Chemical Recycling: Closing the “Cellulose Gap” Using Environmentally Benign Solvents. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1900832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livazovic, S.; Li, Z.; Behzad, A.R.; Peinemann, K.V.; Nunes, S.P. Cellulose Multilayer Membranes Manufacture with Ionic Liquid. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 490, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Chakraborty, S.; Tow, E.W.; Plumlee, M.H.; Bellona, C.; Loutatidou, S.; Karimi, L.; Mikelonis, A.M.; Achilli, A.; Ghassemi, A.; et al. A Review of Polymeric Membranes and Processes for Potable Water Reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, L.; Medronho, B.; Antunes, F.E.; Topgaard, D.; Lindman, B. Dissolution State of Cellulose in Aqueous Systems. 1. Alkaline Solvents. Cellulose 2016, 23, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medronho, B.; Lindman, B. Competing Forces during Cellulose Dissolution: From Solvents to Mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medronho, B.; Lindman, B. Brief Overview on Cellulose Dissolution/Regeneration Interactions and Mechanisms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Michud, A.; Tanttu, M.; Asaadi, S.; Ma, Y.; Hauru, L.K.J.; Parviainen, A.; King, A.W.T.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Sixta, H. Ionic Liquids for the Production of Man-Made Cellulosic Fibers: Opportunities and Challenges. In Cellulose Chemistry and Properties: Fibers, Nanocelluloses and Advanced Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 133–168. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J. Processing and Valorization of Cellulose, Lignin and Lignocellulose Using Ionic Liquids. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, E.; Valls, C.; Roncero, M.B. Ionic Liquid-Assisted Bioconversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass for the Development of Value-Added Products. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushammala, H.; Mao, J. A Review on the Partial and Complete Dissolution and Fractionation of Wood and Lignocelluloses Using Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Polymers 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Effects of Anionic Structure and Lithium Salts Addition on the Dissolution of Cellulose in 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Solvent Systems. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, M.; Sardon, H.; Mecerreyes, D. Ionic Liquids and Cellulose: Dissolution, Chemical Modification and Preparation of New Cellulosic Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11922–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gericke, M.; Fardim, P.; Heinze, T. Ionic Liquids—Promising but Challenging Solvents for Homogeneous Derivatization of Cellulose. Molecules 2012, 17, 7458–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Zeynep Çulfaz-Emecen, P. Cellulose-Based Membranes via Phase Inversion Using [EMIM]OAc-DMSO Mixtures as Solvent. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Qiao, X.; Hou, X.; He, C. Fabrication of Cellulose Membrane with “Imprinted Morphology” and Low Crystallinity from Spherulitic [Bmim]Cl. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Green Solvents for Membrane Manufacture: Recent Trends and Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, A.; Vogler, R.J.; Patel, A.; Bezold, M.; Craven, J.; Liu, C.; Bhattacharyya, D. Composite Membranes Derived from Cellulose and Lignin Sulfonate for Selective Separations and Antifouling Aspects. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.L.; Fadel, S.M.; Abouzeid, R.E.; Abou Elseoud, W.S.; Hassan, E.A.; Berglund, L.; Oksman, K. Water Purification Ultrafiltration Membranes Using Nanofibers from Unbleached and Bleached Rice Straw. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanareeswaran, G.; Sriyamuna Devi, T.K.; Mohan, D. Development, Characterization and Separation Performance of Organic-Inorganic Membranes. Part II. Effect of Additives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 67, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanareeswaran, G.; Kumar, S.A. Effect of Additives Concentration on Performance of Cellulose Acetate and Polyethersulfone Blend Membranes. J. Porous Mater. 2010, 17, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Novel Method of Synthesizing Poly(Ether Sulfone) Membranes Containing Two Solvents and a Lithium Chloride Additive and Their Performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, B.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Bin Effect of PVP, Lithium Chloride, and Glycerol Additives on PVDF Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes Fabricated Using Simultaneous Spinning of TIPS and NIPS. Macromol. Res. 2015, 23, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Munari, S.; Turturro, A. High Performance Ultrafiltration Membranes Cast from LiCl Doped Solutions. Desalination 1988, 68, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Won, J.; Lee, H.; Kang, Y.S. Solution Properties of Poly(Amic Acid)-NMP Containing LiCl and Their Effects on Membrane Morphologies. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 196, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J. Preparation of PVDF-CTFE Hydrophobic Membranes for MD Application: Effect of LiCl-Based Mixed Additives. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 506, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Gonzalez, Y.; Aimar, P.; Lahitte, J.F.; Remigy, J.C. Towards Green Membranes: Preparation of Cellulose Acetate Ultrafiltration Membranes Using Methyl Lactate as a Biosolvent. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2011, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansod, P.G.; Sapkal, V.S.; Sapkal, R.S. The Optimization and Production Polyethersulfone Ultra Filtration Flat Sheet Membranes Using Lithium Chloride as Additives. Int. J. Eng. Res. Dev. 2012, 1, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sayyed, A.J.; Deshmukh, N.A.; Pinjari, D.V. A Critical Review of Manufacturing Processes Used in Regenerated Cellulosic Fibres: Viscose, Cellulose Acetate, Cuprammonium, LiCl/DMAc, Ionic Liquids, and NMMO Based Lyocell. Cellulose 2019, 26, 2913–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Liyanage, S.; Abidi, N.; Parajuli, P.; Rumi, S.S.; Shamshina, J.L. Utilization of Cellulose to Its Full Potential: A Review on Cellulose Dissolution, Regeneration, and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Shin, J.M.; Kang, T.H.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M.; Kim, U.J. Cellulose Dissolution in Aqueous Lithium Bromide Solutions. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Dong, C.; Pan, X. Enhanced Deconstruction and Dissolution of Lignocellulosic Biomass in Ionic Liquid at High Water Content by Lithium Chloride. Cellulose 2016, 23, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Gan, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xia, J.; Cao, Y. Enhancement of the Antioxidant Abilities of Lignin and Lignin-Carbohydrate Complex from Wheat Straw by Moderate Depolymerization via LiCl/DMSO Solvent Catalysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Mohan, D.R.; Rangarajan, R. Studies on Cellulose Acetate-Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes: II. Effect of Additive Concentration. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 268, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatina, A.; Anugwom, I.; Esmaeili, M.; Puro, L.; Virtanen, T.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. Preparation of Cellulose-Rich Membranes from Wood: Effect of Wood Pretreatment Process on Membrane Performance. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9505–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatina, A.; Liukkonen, A.; Bec, S.; Anugwom, I.; Nieminen, J.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen-mänttäri, M. Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance. Membranes 2022, 12, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L.; O’Connor, R.T. Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Lattice Type. Part II. A New Infrared Ratio for Estimation of Crystallinity in Celluloses I and II. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L.; O’Connor, R.T. Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Latticed Type. Part I. Spectra of Lattice Types I, II, III and of Amorphous Cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hallström, B. Membrane Characterization Using the Contact Angle Technique I. Methodology of the Captive Bubble Technique. Desalination 1990, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, T.; Long, N.; Yang, X. The Role of Polyvinyl Butyral Additive in Forming Desirable Pore Structure for Thin Film Composite Forward Osmosis Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.A.; Rudaz, C.; Budtova, T. Phase Diagram, Solubility Limit and Hydrodynamic Properties of Cellulose in Binary Solvents with Ionic Liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmar, A.S.M.; Koch, D.; Prymak, O.; Ulbricht, M. Factors Affecting the Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation of Cellulose from Ionic Liquid-Based Solutions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27314–27322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Loh, C.H.; Wang, R.; Widjajanti, W.; Torres, J. Fabrication of a Robust High-Performance FO Membrane by Optimizing Substrate Structure and Incorporating Aquaporin into Selective Layer. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 525, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Cao, Y.; Liang, D.T.; Tay, J.H. Effect of Additives on the Fabrication of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride-Co-Hexafluropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) Asymmetric Microporous Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 315, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, N.B.; Alkhudhiri, A.; AlRomaih, H.; Alalawi, A.; Leaper, M.C.; Hilal, N. Effect of Lithium Chloride Additive on Forward Osmosis Membranes Performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourizadeh, A.; Ismail, A.F. Effect of LiCl Concentration in the Polymer Dope on the Structure and Performance of Hydrophobic PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2 Absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Cristiano, A.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Effect of Additives in the Casting Solution on the Formation of PVDF Membranes. Desalination 2006, 192, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Ahmed, I. A Production of Polyethersulfone Asymmetric Membranes Using Mixture of Two Solvents and Lithium Chloride as Additive. J. Teknol. 2007, 47, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Hossain, A.; Choi, Y.S.; Cheong, M.; Jang, H.G.; Lee, J.S. Imidazolium Chloride-Licl Melts as Efficient Solvents for Cellulose. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 3771–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.; Medronho, B.; Alves, L.; Costa, C.; Edlund, H.; Norgren, M. The Relevance of Structural Features of Cellulose and Its Interactions to Dissolution, Regeneration, Gelation and Plasticization Phenomena. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23704–23718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, C.G. Solubility of Highly Isotactic Polyacrylonitrile in Dimethyl Sulphoxide. J. Polym. Res. 2005, 12, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevstrueva, D.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Nikkola, J.; Mänttäri, M. Effect of Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of Cellulose Ultrafiltration Membranes Prepared via Immersion Precipitation with Ionic Liquid as Solvent. Membranes 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Lahti, J.; Virtanen, T.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. The Interplay Role of Vanillin, Water, and Coagulation Bath Temperature on Formation of Antifouling Polyethersulfone (PES) Membranes: Application in Wood Extract Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi Namaghi, H.; Haghighi Asl, A.; Pourafshari Chenar, M. Identification and Optimization of Key Parameters in Preparation of Thin Film Composite Membrane for Water Desalination Using Multi-Step Statistical Method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, B.; Noor, E. High Performance Membranes Using Lithium Additives: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, W.L.; Wang, D.M.; Lai, J.Y.; Chou, S.C. On the Initiation of Macrovoids in Polymeric Membranes—Effect of Polymer Chain Entanglement. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 505, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipner, H.; Fischer, S.; Brendler, E.; Voigt, W. Structural Changes of Cellulose Dissolved in Molten Salt Hydrates. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2000, 201, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzos, S.K.; Edye, L.A.; Wellard, R.M. The Undesirable Acetylation of Cellulose by the Acetate Ion of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Acetate. Cellulose 2012, 19, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Široký, J.; Blackburn, R.S.; Bechtold, T.; Taylor, J.; White, P. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis of Crystallinity Changes in Lyocell Following Continuous Treatment with Sodium Hydroxide. Cellulose 2010, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Abd Mutalib, M.; Jamil, S.M. Feasibility of Recycled Newspaper as Cellulose Source for Regenerated Cellulose Membrane Fabrication. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. High-Flux and Anti-Fouling Cellulose Nanofiltration Membranes Prepared via Phase Inversion with Ionic Liquid as Solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kai, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Z. Facile Fabrication of Cellulose Membrane Containing Polyiodides and Its Antibacterial Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 500, 144046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, R.; Agrawal, R.; Kumar, R.; Ramu, E.; Bansal, V.R.; Gupta, R.P.; Kumar, R.; Tuli, D.K.; Das, B. Evaluation of Recalcitrant Features Impacting Enzymatic Saccharification of Diverse Agricultural Residues Treated by Steam Explosion and Dilute Acid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60754–60762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Manasrah, M.; Kallioinen, M.; Ilvesniemi, H.; Mänttäri, M. Recovery of Galactoglucomannan from Wood Hydrolysate Using Regenerated Cellulose Ultrafiltration Membranes. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.; Ni, Y.; Huang, L.; Mondal, A.K.; Lin, S.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H. A Cellulose-Based Nanofiltration Membrane with a Stable Three-Layer Structure for the Treatment of Drinking Water. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8237–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reischl, M.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Ribitsch, V. Electrokinetic Investigations of Oriented Cellulose Polymers. Macromol. Symp. 2006, 244, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Su, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Z. A Facile Method for Synthesis of Pegylated Polyethersulfone and Its Application in Fabrication of Antifouling Ultrafiltration Membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 303, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Anugwom, I.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. Utilization of DES-Lignin as a Bio-Based Hydrophilicity Promoter in the Fabrication of Antioxidant Polyethersulfone Membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanto, H.; Ulbricht, M. Influence of Ultrafiltration Membrane Characteristics on Adsorptive Fouling with Dextrans. J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 266, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, V.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Kreze, T.; Strnad, S. The Significance of Surface Charge and Structure on the Accessibility of Cellulose Fibres. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughi, E.; Amirilargani, M.; Mohammadi, T. Effect of PEG Additive and Coagulation Bath Temperature on the Morphology, Permeability and Thermal/Chemical Stability of Asymmetric CA Membranes. Desalination 2010, 262, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopatina, A.; Esmaeili, M.; Anugwom, I.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen-Mänttäri, M. Effect of Low Concentrations of Lithium Chloride Additive on Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membrane Performance. Membranes 2023, 13, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020198
Lopatina A, Esmaeili M, Anugwom I, Mänttäri M, Kallioinen-Mänttäri M. Effect of Low Concentrations of Lithium Chloride Additive on Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membrane Performance. Membranes. 2023; 13(2):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020198
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopatina, Anastasiia, Mohammadamin Esmaeili, Ikenna Anugwom, Mika Mänttäri, and Mari Kallioinen-Mänttäri. 2023. "Effect of Low Concentrations of Lithium Chloride Additive on Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membrane Performance" Membranes 13, no. 2: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020198
APA StyleLopatina, A., Esmaeili, M., Anugwom, I., Mänttäri, M., & Kallioinen-Mänttäri, M. (2023). Effect of Low Concentrations of Lithium Chloride Additive on Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membrane Performance. Membranes, 13(2), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020198