Biomimetic Stratum Corneum Liposome Models: Lamellar Organization and Permeability Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Model Stratum Corneum Lipid Liposome (SCLL)
2.3. Particle Size and a Polydispersity Index of SCLL
2.4. Calcein Leakage Assay
2.5. Sample Preparation for Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Experiment
2.6. Sample Preparation for Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.7. Sample Preparation for FT-IR Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Multilamellar and Unilamellar SCLLs Model Membranes
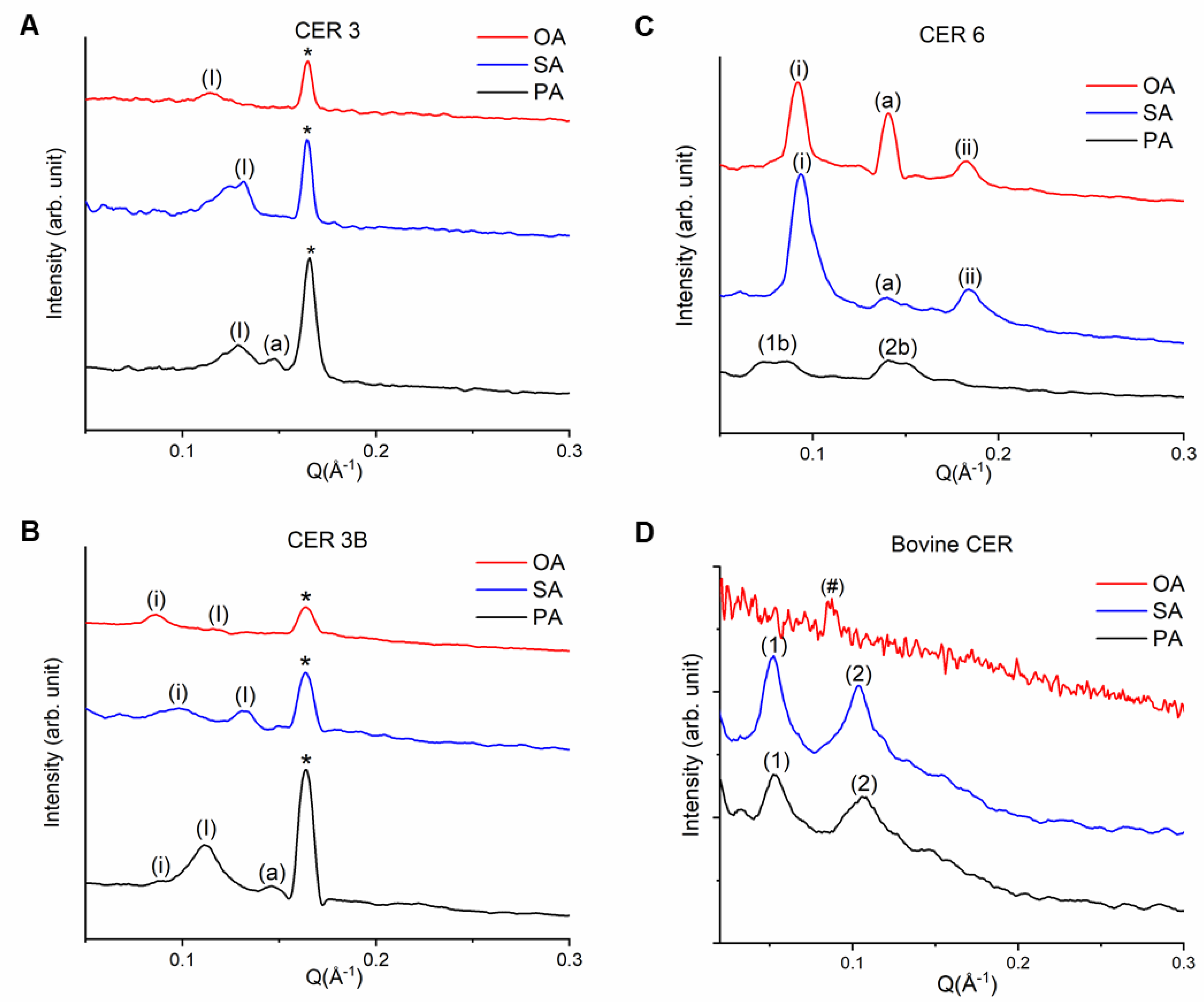
3.2. Lamellar Organization of SCLL Model Membranes
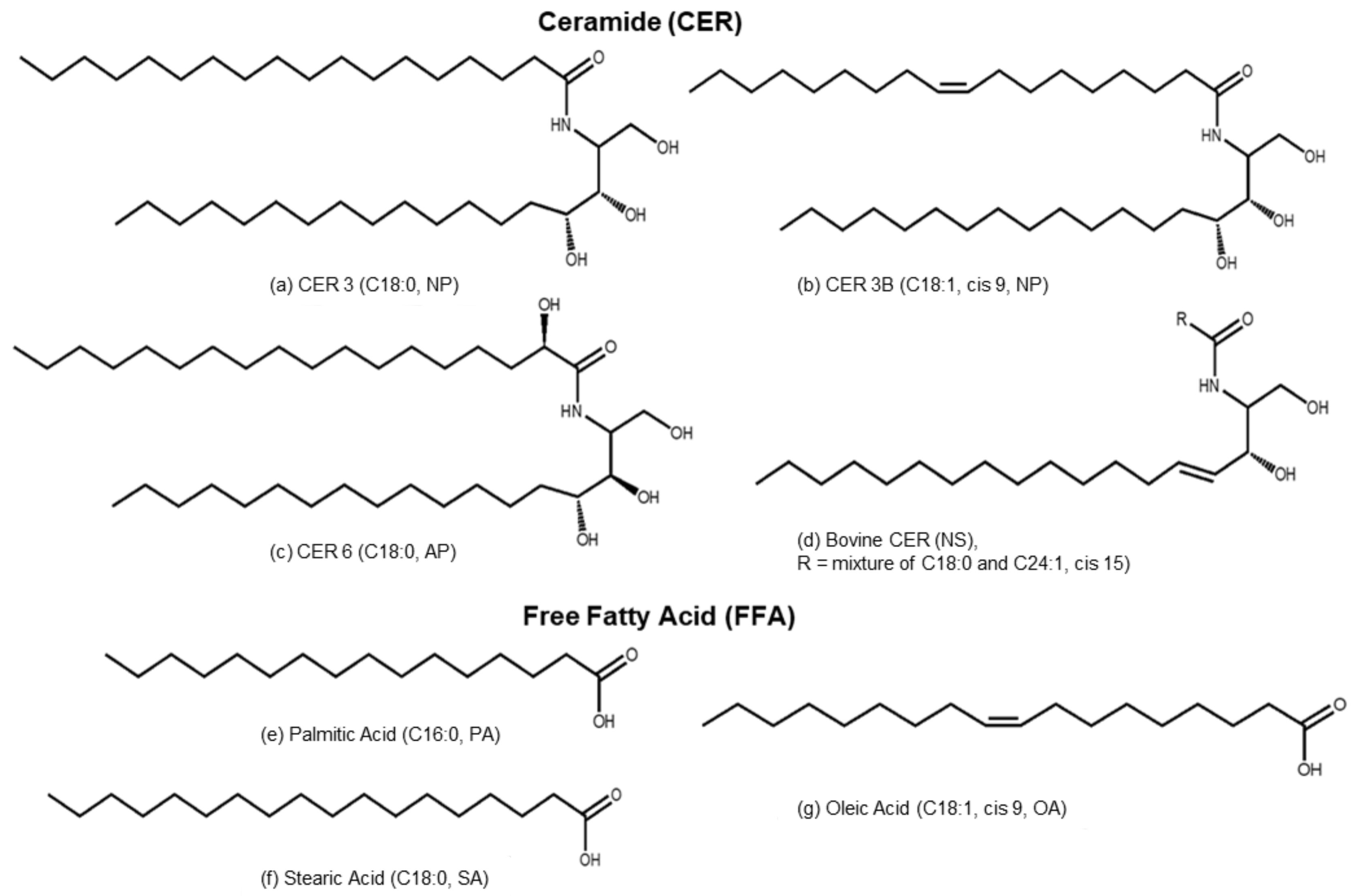
3.2.1. Phytosphingosines CERs and FFAs
3.2.2. Sphingosine CER and FFAs
3.3. Thermal Profiles of SCLL Model Membranes
3.3.1. CER 3
3.3.2. CER 3B
3.3.3. CER 6
3.3.4. Bovine CER
3.4. Mechanical Extrusion and Characterization of SCLLs
3.5. Fluorescence Dye Leakage Assay
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wertz, P.W.; van den Bergh, B. The physical, chemical and functional properties of lipids in the skin and other biological barriers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1998, 91, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.E.; Downing, D.T. A new 6-hydroxy-4-sphingenine-containing ceramide in human skin. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepulak, M.; Leleń, K.; Malejczyk, M.; Majewski, S.; Arct, J. Review paper Biological activity of ceramides and other sphingolipids. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. Postępy Dermatol. I Alergol. 2012, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Downing, D.T. Lipid organization in pig stratum corneum. J. Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; van der Spek, J.A.; Bras, W. Structural Investigations of Human Stratum Corneum by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.Y.; Mitra, A.K.; White, S.H.; Menon, G.K.; Ghadially, R.; Elias, P.M. Membrane structures in normal and essential fatty acid-deficient stratum corneum: Characterization by ruthenium tetroxide staining and x-ray diffraction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, K.C.; Swartzendruber, D.C.; Wertz, P.W.; Downing, D.T. Presence of intact intercellular lipid lamellae in the upper layers of the stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1987, 88, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.H.; Mirejovsky, D.; King, G.I. Structure of lamellar lipid domains and corneocyte envelopes of murine stratum corneum. An X-ray diffraction study. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Gooris, G.S.; Groen, D.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J.; Demé, B.; Bouwstra, J.A. Stratum corneum lipid matrix: Location of acyl ceramide and cholesterol in the unit cell of the long periodicity phase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Honeywell-Nguyen, P.L.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. Structure of the skin barrier and its modulation by vesicular formulations. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, J.C.; Doucet, J.; Lévêque, J.L.; Tsoucaris, G. Oriented structure in human stratum corneum revealed by X-ray diffraction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, I.; Han, H.; Hollander, L.; Svensson, S.; Ofverstedt, L.; Anwar, J.; Brewer, J.; Bloksgaard, M.; Laloeuf, A.; Nosek, D.; et al. The human skin barrier is organized as stacked bilayers of fully extended ceramides with cholesterol molecules associated with the ceramide sphingoid moiety. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, S.; Vielhaber, G.; Vietzke, J.P.; Wittern, K.P.; Hintze, U.; Wepf, R. High-pressure freezing provides new information on human epidermis: Simultaneous protein antigen and lamellar lipid structure preservation. Study on human epidermis by cryoimmobilization. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Dubochet, J.; Norlén, L. Nanostructure of the epidermal extracellular space as observed by cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections of human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masukawa, Y.; Narita, H.; Shimizu, E.; Kondo, N.; Sugai, Y.; Oba, T.; Homma, R.; Ishikawa, J.; Takagi, Y.; Kitahara, T.; et al. Characterization of overall ceramide species in human stratum corneum. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, D.; Gooris, G.S.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J.; van Mechelen, J.B.; Demé, B.; Bouwstra, J.A. Disposition of ceramide in model lipid membranes determined by neutron diffraction. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Groen, D.; Gooris, G.S.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J.; Deme, B.; Bouwstra, J.A. Localization of cholesterol and fatty acid in a model lipid membrane: A neutron diffraction approach. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Ponec, M. The skin barrier in healthy and diseased state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Kariman, Z.; van Kerckhove, L.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. The role of ceramide chain length distribution on the barrier properties of the skin lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Dubbelaar, F.E.R.; Weerheim, A.M.; IJzerman, A.P.; Ponec, M. Role of ceramide 1 in the molecular organization of the stratum corneum lipids. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Infrared spectroscopic study of stratum corneum model membranes prepared from human ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugel, C.; Yagoubi, N.; Baillet, A. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy: A chemometric approach for studying the lipid organisation of the stratum corneum. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2005, 135, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, M.W.; Gooris, G.S.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Bras, W.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Novel lipid mixtures based on synthetic ceramides reproduce the unique stratum corneum lipid organization. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Klauda, J.B. Models for the Stratum Corneum Lipid Matrix: Effects of Ceramide Concentration, Ceramide Hydroxylation, and Free Fatty Acid Protonation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 11996–12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Klauda, J.B. Molecular Structure of the Long Periodicity Phase in the Stratum Corneum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16930–16943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rerek, M.E.; Chen; Markovic, B.; Van Wyck, D.; Garidel, P.; Mendelsohn, R.; Moore, D.J. Phytosphingosine and Sphingosine Ceramide Headgroup Hydrogen Bonding: Structural Insights through Thermotropic Hydrogen/Deuterium Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9355–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, M.; Gooris, G.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J. Acylceramide Head Group Architecture Affects Lipid Organization in Synthetic Ceramide Mixtures. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.L.; Valério, J.; Funari, S.S.; Melo, E. The thermotropism and prototropism of ternary mixtures of ceramide C16, cholesterol and palmitic acid. An exploratory study. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.N.; Silva, L.C.; Futerman, A.H.; Prieto, M. Effect of ceramide structure on membrane biophysical properties: The role of acyl chain length and unsaturation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 2753–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.C.; Hartkamp, R.; Iacovella, C.R.; Bunge, A.L.; McCabe, C. Effect of Ceramide Tail Length on the Structure of Model Stratum Corneum Lipid Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Školová, B.; Kováčik, A.; Tesař, O.; Opálka, L.; Vávrová, K. Phytosphingosine, sphingosine and dihydrosphingosine ceramides in model skin lipid membranes: Permeability and biophysics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhonen, M.; Li, S.K.; Higuchi, W.I.; Herron, J.N. A Liposome Permeability Model for Stratum Corneum Lipid Bilayers Based on Commercial Lipids. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4278–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuříková, B.A.; Procházková, K.; Filková, B.; Diblíková, P.; Svoboda, J.; Kováčik, A.; Vávrová, K.; Zbytovská, J. Simplified stratum corneum model membranes for studying the effects of permeation enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čuříková-Kindlová, B.A.; Diat, O.; Štěpánek, F.; Vávrová, K.; Zbytovská, J. Probing the interactions among sphingosine and phytosphingosine ceramides with non- and alpha-hydroxylated acyl chains in skin lipid model membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garidel, P.; Fölting, B.; Schaller, I.; Kerth, A. The microstructure of the stratum corneum lipid barrier: Mid-infrared spectroscopic studies of hydrated ceramide:palmitic acid:cholesterol model systems. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 150, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, M.A.; Ryabova, N.Y.; Balagurov, A.M.; Dante, S.; Hauss, T.; Zbytovska, J.; Wartewig, S.; Neubert, R.H.H. New insights into the structure and hydration of a stratum corneum lipid model membrane by neutron diffraction. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbytovská, J.; Vávrová, K.; Kiselev, M.A.; Lessieur, P.; Wartewig, S.; Neubert, R.H.H. The effects of transdermal permeation enhancers on thermotropic phase behaviour of a stratum corneum lipid model. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 351, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Neubert, R.H.H. State of the art in Stratum Corneum research: The biophysical properties of ceramides. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 216, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.; Lange, S.; Dobner, B.; Sonnenberger, S.; Hauß, T.; Neubert, R.H.H. Investigation of a CER[NP]- and [AP]-Based Stratum Corneum Modeling Membrane System: Using Specifically Deuterated CER Together with a Neutron Diffraction Approach. Langmuir 2018, 34, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, R.; Rettig, W.; Wartewig, S.; Wegener, M.; Wienhold, A. Structure of stratum corneum lipids characterized by FT-Raman spectroscopy and DSC. II. Mixtures of ceramides and saturated fatty acids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1997, 89, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, T.N.; Schroeter, A.; Hauß, T.; Neubert, R.H.H. Lipophilic penetration enhancers and their impact to the bilayer structure of stratum corneum lipid model membranes: Neutron diffraction studies based on the example Oleic Acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Chandar, P. Stratum corneum fatty acids: Their critical role in preserving barrier integrity during cleansing. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarguren, M.; López, D.J.; Escribá, P.V. The effect of natural and synthetic fatty acids on membrane structure, microdomain organization, cellular functions and human health. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khnykin, D.; Miner, J.H.; Jahnsen, F. Role of fatty acid transporters in epidermis: Implications for health and disease. Dermato-endocrinology 2011, 3, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowat, A.C.; Kitson, N.; Thewalt, J.L. Interactions of oleic acid and model stratum corneum membranes as seen by 2H NMR. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Maza, A.; Manich, A.M.; Coderch, L.; Bosch, P.; Parra, J.L. The formation of liposomes in vitro by mixtures of lipids modeling the composition of the stratum corneum. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 101, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W.; Abraham, W.; Landmann, L.; Downing, D.T. Preparation of Liposomes from Stratum Corneum Lipids. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1986, 87, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, M.; Gácsi, A.; Berkó, S.; Kovács, A.; Csányi, E. Stratum corneum lipid liposomes for investigating skin penetration enhancer effects. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27464–27469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, R.M.; Fung, L.W.M. A New Model System for Lipid Interactions in Stratum Corneum Vesicles: Effects of Lipid Composition, Calcium, and pH. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.S.; GuhaSarkar, S.; Banerjee, R. Stratum corneum modulation by chemical enhancers and lipid nanostructures: Implications for transdermal drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garidel, P. Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigations of phytosphingosine ceramide membrane organisation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Thewalt, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Kitson, N. A Model Membrane Approach to the Epidermal Permeability Barrier: An X-ray Diffraction Study. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 7717–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, M.W.; Gooris, G.S.; Dolbnya, I.P.; Bras, W.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. The phase behaviour of skin lipid mixtures based on synthetic ceramides. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 124, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glombitza, B.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Influence of different ceramides on the structure of in vitro model lipid systems of the stratum corneum lipid matrix. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 117, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Infrared spectroscopy studies of mixtures prepared with synthetic ceramides varying in head group architecture: Coexistence of liquid and crystalline phases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochalek, M.; Heissler, S.; Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H.H. Characterization of lipid model membranes designed for studying impact of ceramide species on drug diffusion and penetration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochorová, M.; Audrlická, P.; Červená, M.; Kováčik, A.; Kopečná, M.; Opálka, L.; Pullmannová, P.; Vávrová, K. Permeability and microstructure of cholesterol-depleted skin lipid membranes and human stratum corneum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 535, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uche, L.E.; Gooris, G.S.; Beddoes, C.M.; Bouwstra, J.A. New insight into phase behavior and permeability of skin lipid models based on sphingosine and phytosphingosine ceramides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kováčik, A.; Šilarová, M.; Pullmannová, P.; Maixner, J.; Vávrová, K. Effects of 6-Hydroxyceramides on the Thermotropic Phase Behavior and Permeability of Model Skin Lipid Membranes. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2890–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoopes, M.I.; Noro, M.G.; Longo, M.L.; Faller, R. Bilayer Structure and Lipid Dynamics in a Model Stratum Corneum with Oleic Acid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3164–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Moore, T.C.; Iacovella, C.R.; Strickland, L.A.; McCabe, C. Simulation Study of the Structure and Phase Behavior of Ceramide Bilayers and the Role of Lipid Headgroup Chemistry. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 5116–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntsche, J.; Herre, A.; Fahr, A.; Funari, S.S.; Garidel, P. Comparative SAXS and DSC study on stratum corneum structural organization in an epidermal cell culture model (ROC): Impact of cultivation time. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The cornified envelope: A model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clas, S.-D.; Dalton, C.R.; Hancock, B.C. Differential scanning calorimetry: Applications in drug development. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Vries, M.A.S.-d.; van der Spek, J.A.; Bras, W. Structure of human stratum corneum as a function of temperature and hydration: A wide-angle X-ray diffraction study. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 84, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.L.; Nunes, S.C.C.; Eusébio, M.E.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Sousa, J.J.S. Thermal Behaviour of Human Stratum Corneum. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.L.; Nunes, S.C.C.; Eusébio, M.E.S.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C. Study of human stratum corneum and extracted lipids by thermomicroscopy and DSC. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2006, 140, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duzee, B.F. Thermal Analysis of Human Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 65, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.L.; Guy, R.H.; Golden, G.M.; Mak, V.H.W.; Francoeur, M.L. Characterization of Low-Temperature (i.e., <65 °C) Lipid Transitions in Human Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Školová, B.; Janůšová, B.; Zbytovská, J.; Gooris, G.; Bouwstra, J.; Slepička, P.; Berka, P.; Roh, J.; Palát, K.; Hrabálek, A.; et al. Ceramides in the Skin Lipid Membranes: Length Matters. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15624–15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, G.M.; Guzek, D.B.; Harris, R.R.; McKie, J.E.; Potts, R.O. Lipid Thermotropic Transitions in Human Stratum Corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1986, 86, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaddi, H.K.; Ho, P.C.; Chan, S.Y. Terpenes in propylene glycol as skin-penetration enhancers: Permeation and partition of haloperidol, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; VanWyck, D.; Xiao, X.; Mack Correa, M.C.; Gunn, E.; Flach, C.R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Walters, R.M. Oleic Acid Disorders Stratum Corneum Lipids in Langmuir Monolayers. Langmuir 2013, 29, 4857–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinilla, C.M.B.; Thys, R.C.S.; Brandelli, A. Antifungal properties of phosphatidylcholine-oleic acid liposomes encapsulating garlic against environmental fungal in wheat bread. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 293, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadian, Z.; Sahari, M.A.; Moghimi, H.R.; Barzegar, M. Formulation, characterization and optimization of liposomes containing eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids; a methodology approach. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, T.J. Organization of skin stratum corneum extracellular lamellae: Diffraction evidence for asymmetric distribution of cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forslind, B. A domain mosaic model of the skin barrier. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1994, 74, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlén, L. Skin barrier structure and function: The single gel phase model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 117, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damien, F.; Boncheva, M. The Extent of Orthorhombic Lipid Phases in the Stratum Corneum Determines the Barrier Efficiency of Human Skin In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, D.; Poole, D.S.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Is an orthorhombic lateral packing and a proper lamellar organization important for the skin barrier function? Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ceramide | PA | SA | OA |
|---|---|---|---|
| CER 3 (C18:0, NP) 1 | 132.3 (0.07) | 128.6 (0.04) | 122.8 (0.09) |
| CER 3B (C18:1; cis 9, NP) 1 | 144.7 (0.14) | 147.0 (0.14) | 166.2 (0.07) |
| CER 6 (C18:0, AP) 1 | 169.8 (0.11) | 134.7 (0.01) | 152.6 (0.08) |
| Bovine CER (NS) 1 | 164.7 (0.01) | 162.0 (0.08) | 165.0 (0.06) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, S.; Ho, J.C.S.; Teo, D.L.C.; Gupta, S.; Nallani, M. Biomimetic Stratum Corneum Liposome Models: Lamellar Organization and Permeability Studies. Membranes 2023, 13, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020135
Roy S, Ho JCS, Teo DLC, Gupta S, Nallani M. Biomimetic Stratum Corneum Liposome Models: Lamellar Organization and Permeability Studies. Membranes. 2023; 13(2):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020135
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Susmita, James C. S. Ho, Douglas L. C. Teo, Shikhar Gupta, and Madhavan Nallani. 2023. "Biomimetic Stratum Corneum Liposome Models: Lamellar Organization and Permeability Studies" Membranes 13, no. 2: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020135
APA StyleRoy, S., Ho, J. C. S., Teo, D. L. C., Gupta, S., & Nallani, M. (2023). Biomimetic Stratum Corneum Liposome Models: Lamellar Organization and Permeability Studies. Membranes, 13(2), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020135







