Engineered Approaches to Facile Identification of Tiny Microplastics in Polymeric and Ceramic Membrane Filtrations for Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silica Particle and Microplastic
2.2. Membrane Filtration Experiments
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Fouling Mechanisms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Different Types of Particles on the Filtration and Treatment Performance
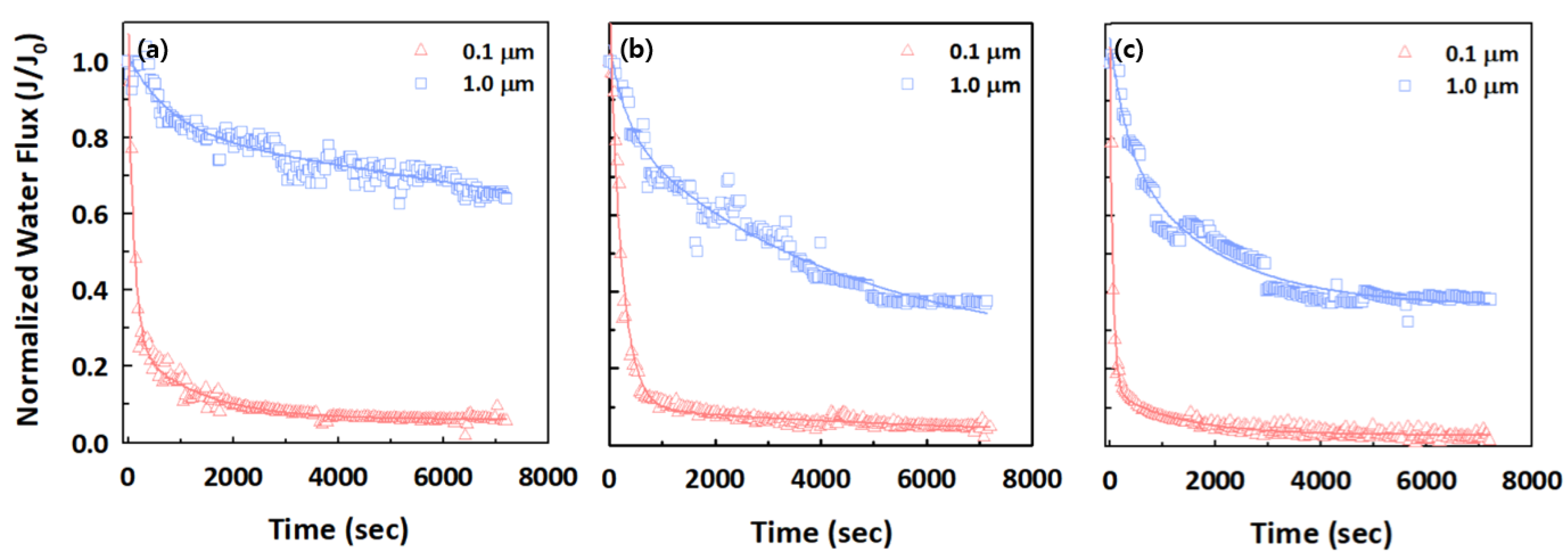
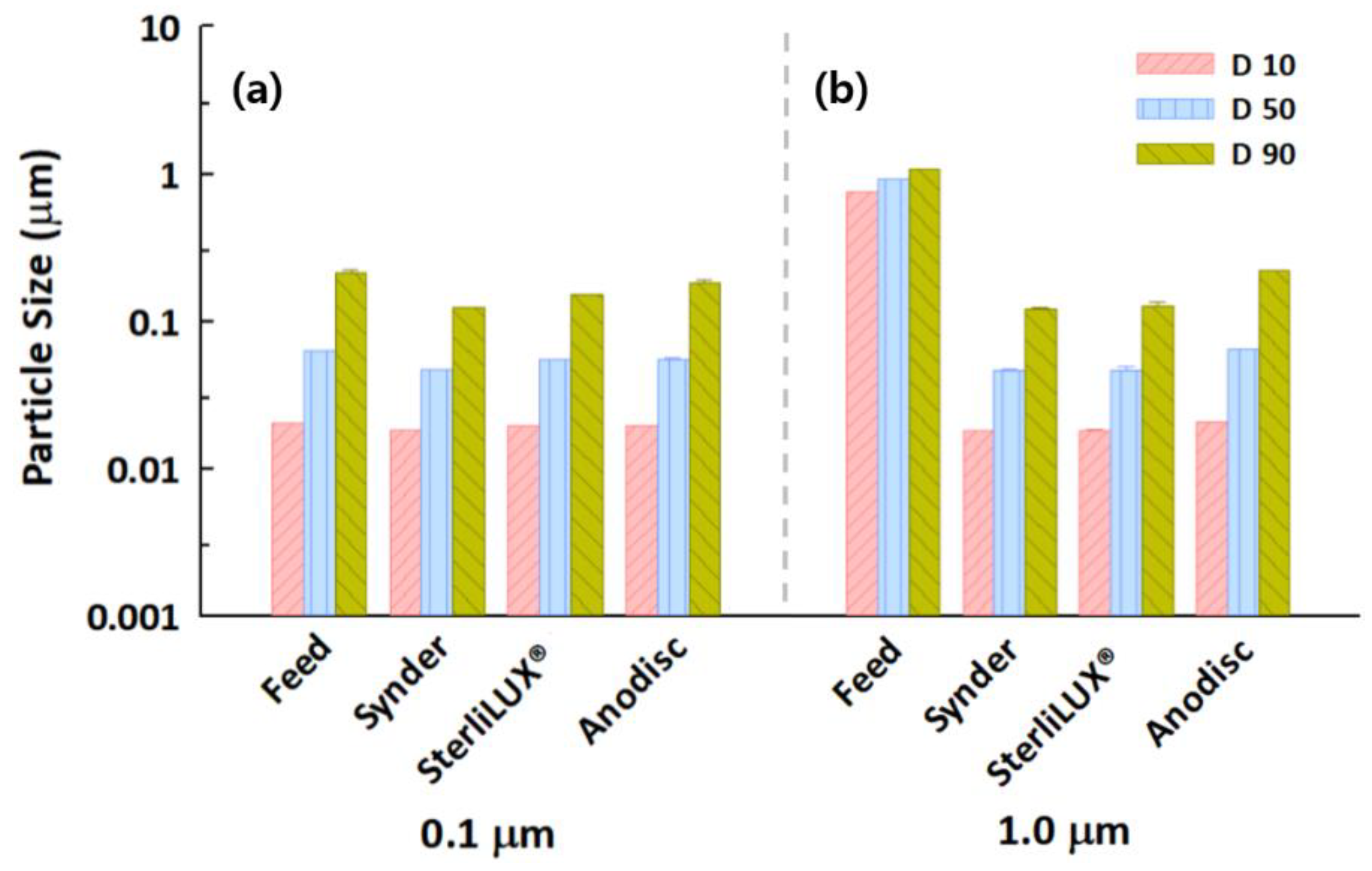
3.2. Effect of Different Sizes of PS Microplastics on Filtration and Treatment Performance
3.3. Effect of Different Types of Microplastics on Filtration and Treatment Performance
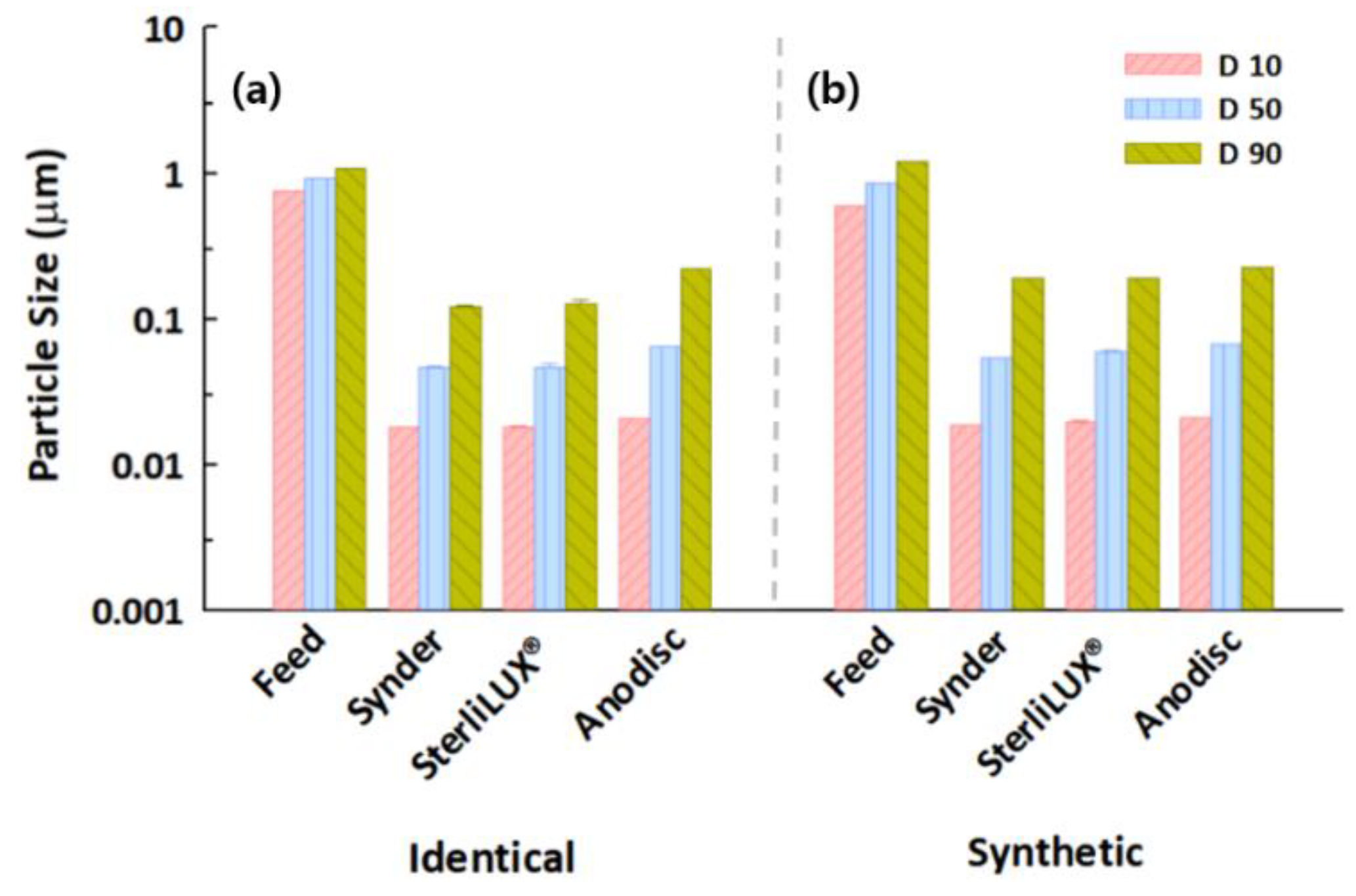
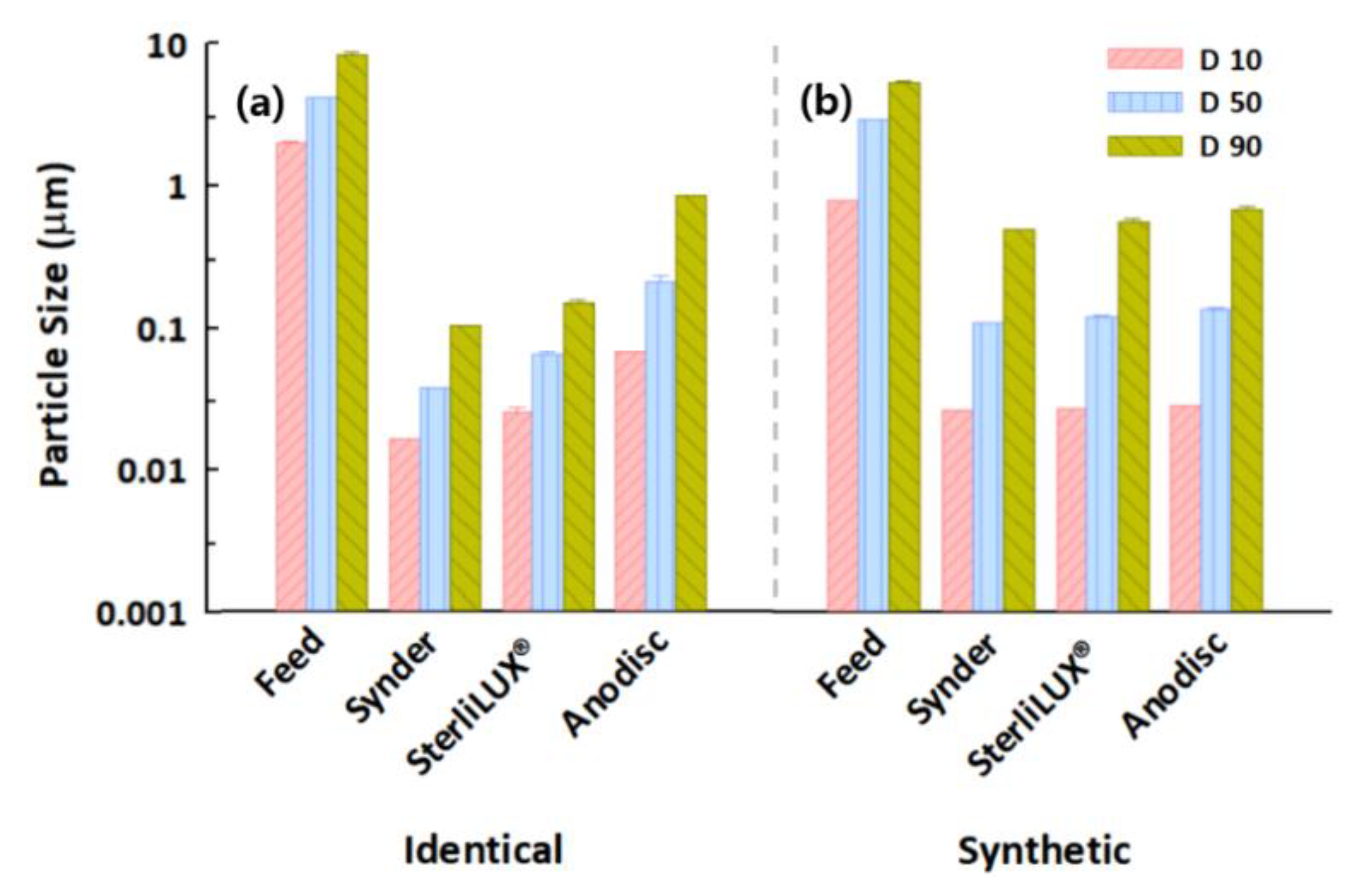
3.4. Filtration Behaviors of Microplastics in Identical and Synthetic Wastewater Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prata, J.C. Microplastics in wastewater: State of the knowledge on sources, fate and solutions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.P. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.K.; Fok, L. Characterisation of plastic microbeads in facial scrubs and their estimated emissions in Mainland China. Water Res. 2017, 122, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ni, B.-J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater Treatment Works (WwTW) as a Source of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, I.; Ding, T.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Micro- and nanoplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Occurrence, removal, fate, impacts and remediation technologies—A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution—Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Heinonen, M.; Pääkkönen, J.-P.; Vahtera, E.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Vahala, R. Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Heinonen, M.; Koistinen, A. How well is microlitter purified from wastewater?—A detailed study on the stepwise removal of microlitter in a tertiary level wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2017, 109, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpaa, M.; Sillanpaa, M. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliwan, T.; Pungrasmi, W.; Lohwacharin, J. Effects of microplastic accumulation on floc characteristics and fouling behavior in a membrane bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The fate of microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.; Park, C. Preparation, characterization and application of low-cost pyrophyllite-alumina composite ceramic membranes for treating low-strength domestic wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 536, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Kim, S.; Park, C. Recent advances and future potential of anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: A review. Membr. Water Treat. 2020, 11, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, M.; Boo, C.; Song, I.-H.; Park, C. Investigating the potential of ammonium retention by graphene oxide ceramic nanofiltration membranes for the treatment of semiconductor wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hong, S.; Park, C. Comparison of filtration and treatment performance between polymeric and ceramic membranes in anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Klasmeier, J.; Fries, E. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics in sediments from Norderney. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dümichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Bannick, C.G.; Barthel, A.-K.; Senz, R.; Braun, U. Fast identification of microplastics in complex environmental samples by a thermal degradation method. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.-T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of polymer types and additives in marine microplastic particles using pyrolysis-GC/MS and scanning electron microscopy. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuelle, M.-T.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Kim, D.; Lim, H.J.; Park, C.; Chua, B.; Lee, J.W.; Yoon, Y.; Son, A. Chia seed-assisted separation and detection of polyvinyl chloride microplastics in water via gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löder, M.G.J.; Kuczera, M.; Mintenig, S.; Lorenz, C.; Gerdts, G. Focal plane array detector-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging for the analysis of microplastics in environmental samples. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.F.; Nolasco, M.M.; Ribeiro, A.M.P.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: Latest developments and future prospects. Water Res. 2018, 142, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erni-Cassola, G.; Gibson, M.I.; Thompson, R.C.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Lost, but Found with Nile Red: A Novel Method for Detecting and Quantifying Small Microplastics (1 mm to 20 mu m) in Environmental Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13641–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of microplastics in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.J.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.E. Identification methods in microplastic analysis: A review. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J. Tracing microplastics from raw water to drinking water treatment plants in Busan, South Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymanski, D.; Goldbeck, C.; Humpf, H.-U.; Fürst, P. Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 129, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, V.; Frezzotti, M.L.; Leoni, B. Raman Spectroscopy for the Analysis of Microplastics in Aquatic Systems. Appl. Spectrosc. 2021, 75, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elert, A.M.; Becker, R.; Duemichen, E.; Eisentraut, P.; Falkenhagen, J.; Sturm, H.; Braun, U. Comparison of different methods for MP detection: What can we learn from them, and why asking the right question before measurements matters? Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, M.; Brehm, J.; Vollmer, M.; Jasinski, J.; Xu, C.; Zainuddin, S.; Fröhlich, T.; Schott, M.; Greiner, A.; Scheibel, T.; et al. Shape, size, and polymer dependent effects of microplastics on Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 426, 128136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.; Vogel, R.; Savage, J.; Vella, G.; Law, A.; Della Camera, G.; Hannon, G.; Peacock, B.; Mehn, D.; Ponti, J.; et al. Measuring particle size distribution and mass concentration of nanoplastics and microplastics: Addressing some analytical challenges in the sub-micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 588, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uurasjärvi, E.; Hartikainen, S.; Setälä, O.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Koistinen, A. Microplastic concentrations, size distribution, and polymer types in the surface waters of a northern European lake. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.; Cho, K.; Kwon, E.E.; Tsang, Y.F.; Rinklebe, J.; Park, C. Evaluating the feasibility of pyrophyllite-based ceramic membranes for treating domestic wastewater in anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C. Potential of ceramic ultrafiltration membranes for the treatment of anionic surfactants in laundry wastewater for greywater reuse. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, C. Fouling behavior and cleaning strategies of ceramic ultrafiltration membranes for the treatment and reuse of laundry wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Narbaitz, R.M. Novel hydrophilic surface modifying macromolecules for polymeric membranes: Polyurethane ends capped by hydroxy group. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tarabara, V.V. Pore blocking mechanisms during early stages of membrane fouling by colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.C.; Zydney, A.L. A Combined Pore Blockage and Cake Filtration Model for Protein Fouling during Microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerlage, S.F.E.; Kennedy, M.D.; Dickson, M.R.; El-Hodali, D.E.Y.; Schippers, J.C. The modified fouling index using ultrafiltration membranes (MFI-UF): Characterisation, filtration mechanisms and proposed reference membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Gao, W.; Liu, D. Ultrafiltration of dissolved organic matter in surface water by a polyvinylchloride hollow fiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-F.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Chandana, P.S.; Tsai, C.-Y. Effects of mass retention of dissolved organic matter and membrane pore size on membrane fouling and flux decline. Water Res. 2009, 43, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type | Material | Supplier | Pore Size (μm) 1 | Pore Size (nm) 2 | Roughness (nm) | Pure Water Permeability (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric | PVDF | Synder | 0.1 | 27.3 | 118.5 | 992.5 | 75.6 |
| PVDF | SteriLUX® | 0.1 | 45.6 | 37.8 | 1620.9 | 31.6 | |
| Ceramic | Al2O3 | Anodisc | 0.1 | 73.7 | 28.9 | 2439.8 | 95.1 |
| Particle | Membrane | Complete Pore Blocking | Standard Pore Blocking | Intermediate Pore Blocking | Cake Filtration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica | Synder | 0.9722 | 0.9972 | 0.9884 | 0.9954 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.9256 | 0.9979 | 0.9549 | 0.9733 | |
| Anodisc | 0.8303 | 0.9527 | 0.9560 | 0.9887 | |
| PS microplastic | Synder | 0.6525 | 0.9825 | 0.7778 | 0.8836 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.7583 | 0.9997 | 0.8946 | 0.8908 | |
| Anodisc | 0.7813 | 0.9525 | 0.7735 | 0.6617 |
| PS Microplastic | Membrane | Complete Pore Blocking | Standard Pore Blocking | Intermediate Pore Blocking | Cake Filtration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 μm | Synder | 0.6525 | 0.9825 | 0.7778 | 0.8836 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.7583 | 0.9997 | 0.8946 | 0.8908 | |
| Anodisc | 0.7813 | 0.9525 | 0.7735 | 0.6617 | |
| 1.0 μm | Synder | 0.9794 | 1.0000 | 0.9793 | 0.9732 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.9724 | 0.9999 | 0.9657 | 0.9565 | |
| Anodisc | 0.9603 | 0.9997 | 0.9751 | 0.9839 |
| Microplastic | Membrane | Complete Pore Blocking | Standard Pore Blocking | Intermediate Pore Blocking | Cake Filtration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polystylene (PS) | Synder | 0.9794 | 1.0000 | 0.9793 | 0.9732 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.9724 | 0.9999 | 0.9657 | 0.9565 | |
| Anodisc | 0.9603 | 0.9997 | 0.9751 | 0.9839 | |
| Polyethylene (PE) | Synder | 0.9703 | 0.9997 | 0.9842 | 0.9924 |
| SteriLUX® | 0.9827 | 1.0000 | 0.9813 | 0.9791 | |
| Anodisc | 0.9675 | 0.9998 | 0.9870 | 0.9874 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kook, H.; Park, C. Engineered Approaches to Facile Identification of Tiny Microplastics in Polymeric and Ceramic Membrane Filtrations for Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060565
Kook H, Park C. Engineered Approaches to Facile Identification of Tiny Microplastics in Polymeric and Ceramic Membrane Filtrations for Wastewater Treatment. Membranes. 2022; 12(6):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060565
Chicago/Turabian StyleKook, Heejin, and Chanhyuk Park. 2022. "Engineered Approaches to Facile Identification of Tiny Microplastics in Polymeric and Ceramic Membrane Filtrations for Wastewater Treatment" Membranes 12, no. 6: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060565
APA StyleKook, H., & Park, C. (2022). Engineered Approaches to Facile Identification of Tiny Microplastics in Polymeric and Ceramic Membrane Filtrations for Wastewater Treatment. Membranes, 12(6), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060565







