Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Resins and Membranes in Equilibrium Solutions of Inorganic Electrolytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Membranes and Comparison of Methods for Its Determination
2. Materials and Methods
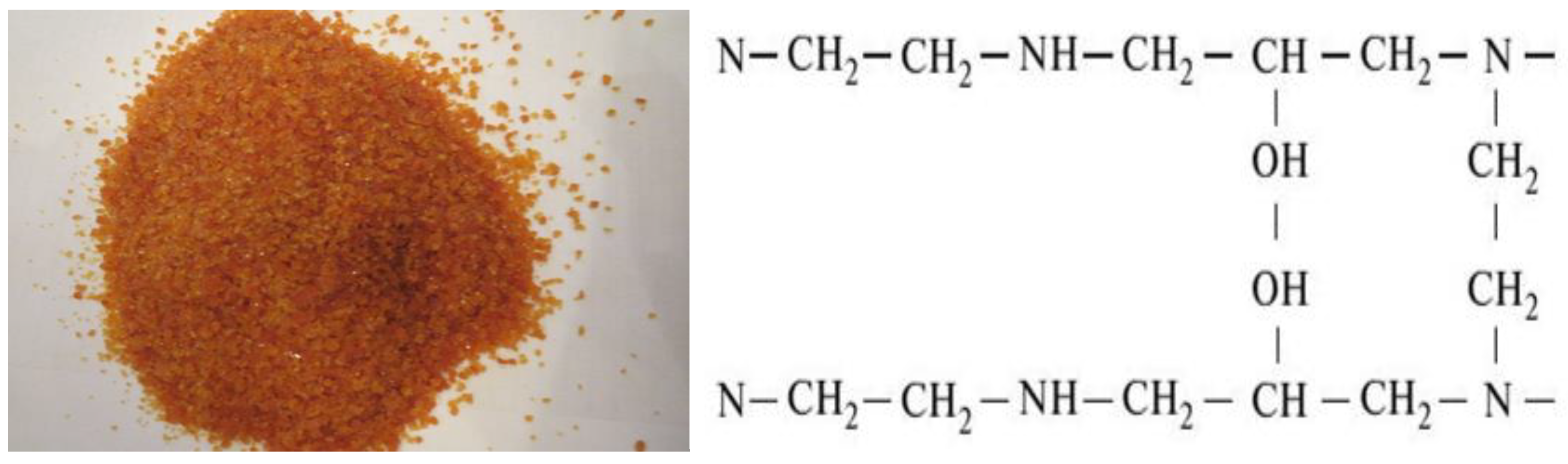
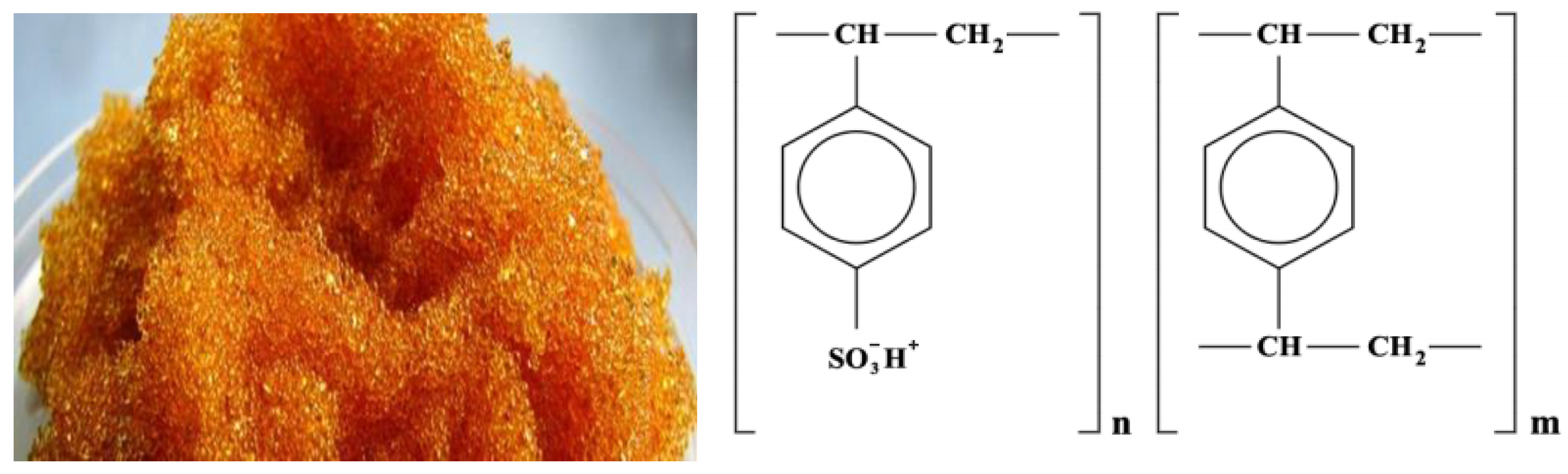
2.1. Research Objects
- The functional group is a sulfo group;
- The matrix is styrene-divinylbenzene;
- The structure is gel;
- Particle size 0.4–0.55 mm;
- Moisture content 48–58%;
- Full exchange capacity 4.9–5.1 mmol/g dry exchanger or 2.0 mg·mol/cm3;
- Specific volume, no more in H+ form 2.7 cm3/g.
- The functional group is a NR3+, =NH, =N
- The structure is a gel
- Particle size 0.4–2.0 mm
- Full statistical exchange capacity, not less than 2.3 mmol/cm3;
- Dynamic exchange capacity, m∙mol/m3, not less than 1000;
- The volume fraction of the working fraction, is not less than 92%;
- The mass fraction of moisture is no more than 5%;
- The specific volume, in OH− form is 3.4 ± 0.2 cm3/g.
- Heterogeneous membranes have little water permeability.
- For membranes MK-40 and MA-40 at 18 °C and a pressure of 37.2 nPa in distilled water, it is (1¸2) × 10−12 g/(cm2 × s).
- The diffusion permeability of these membranes is also low: 6.2 × 10−8 g/(cm2 × s) in 1 n. NaCl at 20 °C.
- Osmotic permeability of MK-40 and MA-40 membranes in 1 N. NaCl at 20 °C is 0.2 and 0.1 L/(m2 × h), respectively.
- Functional groups: -SO3H (MK-40), -NH2 +, = NH, = N (MA-40);
- Moisture content, %, no more than 40 (MK-40, MA-40);
- The content of the ion exchanger, % KU-2-8-65, EDE-10p-55;
- Transfer number in 0.01–0.2 N NaCl fraction, not less than 0.98 (MK-40), 0.94 (MA-40).
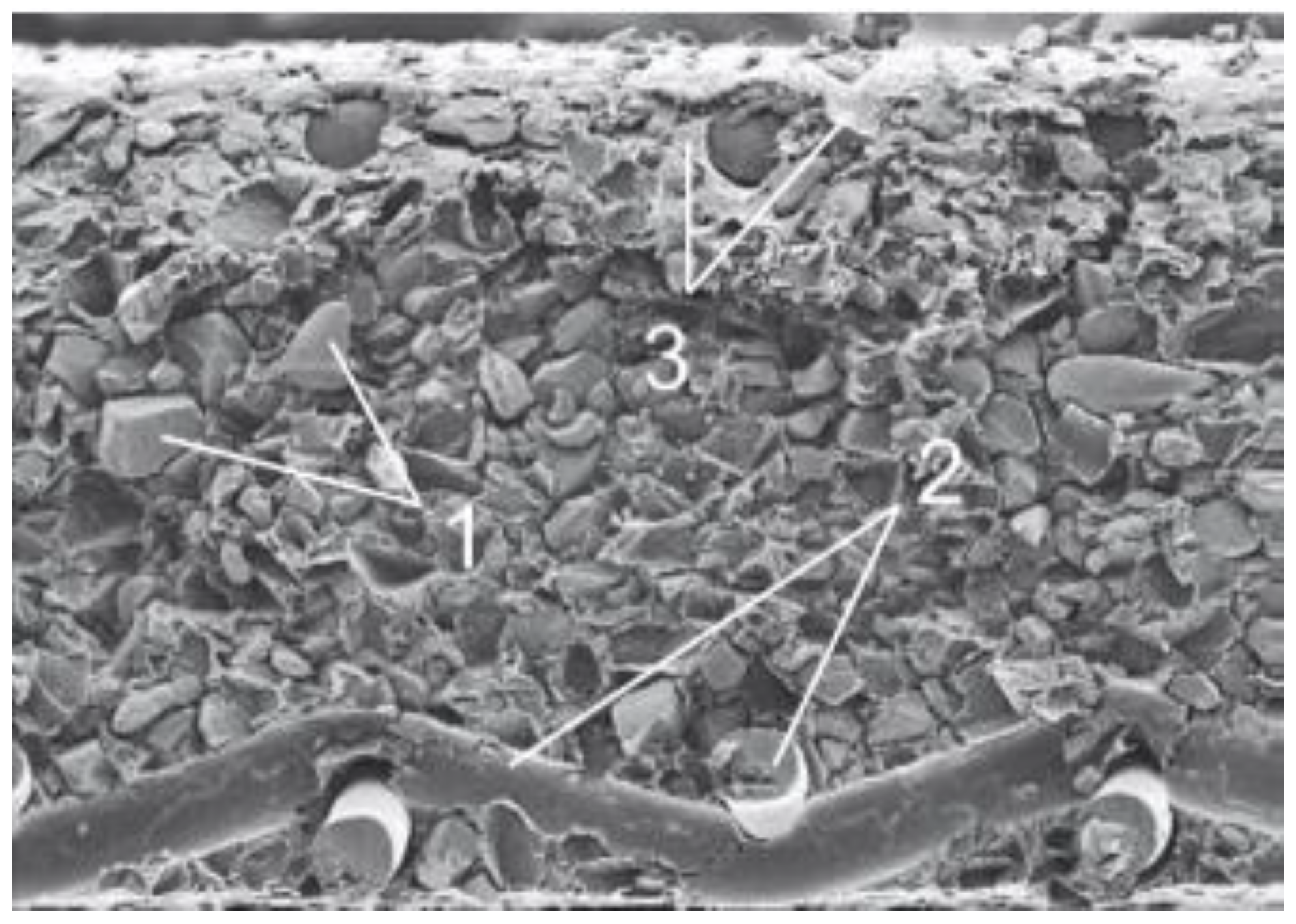
Preparation of Research Objects
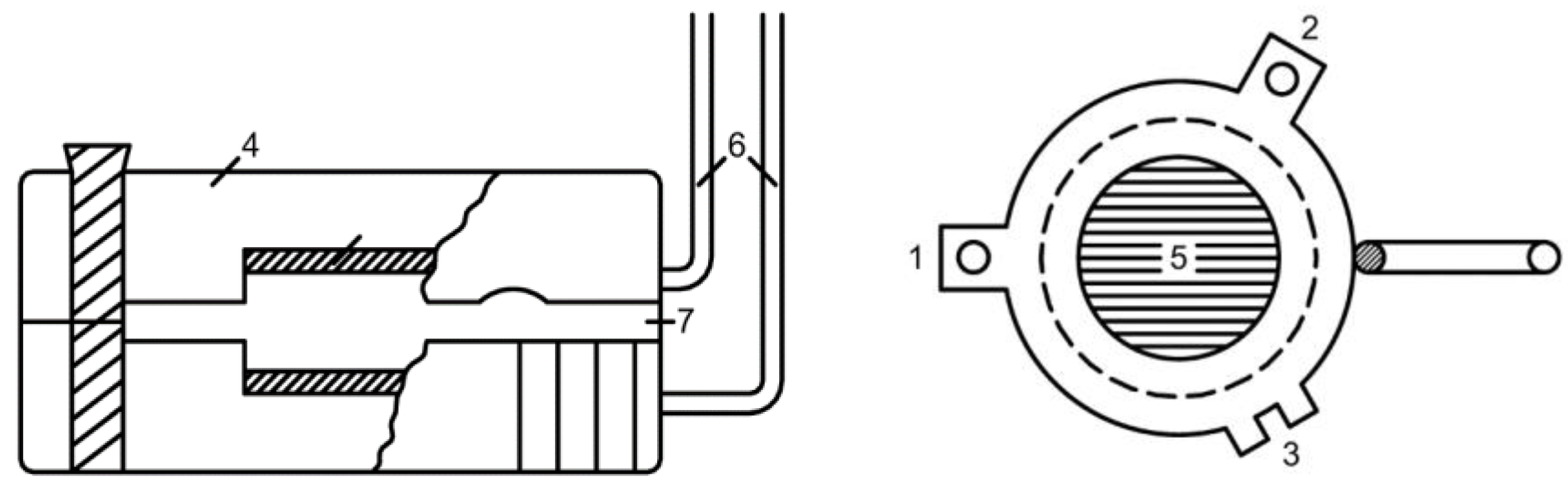
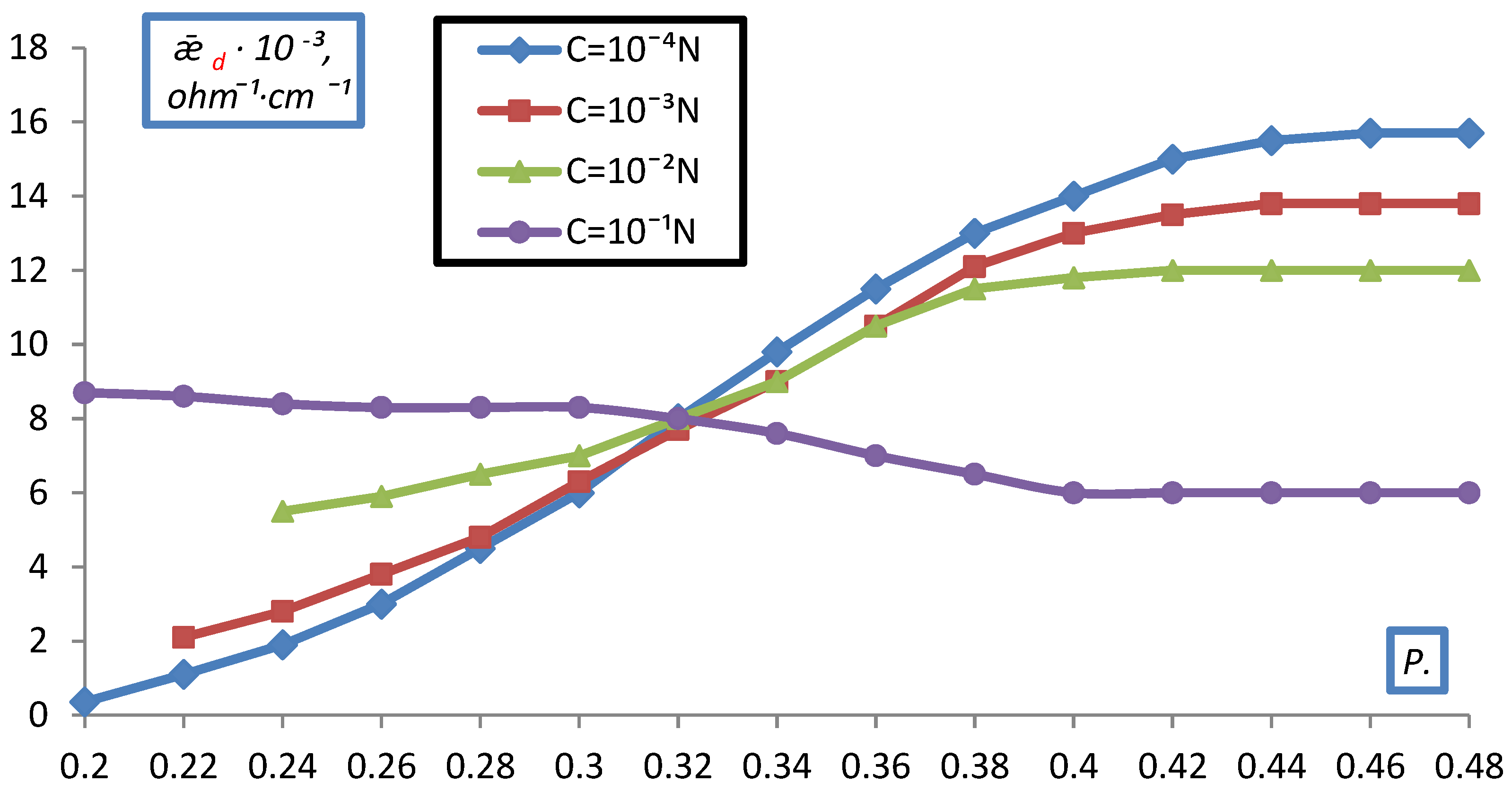
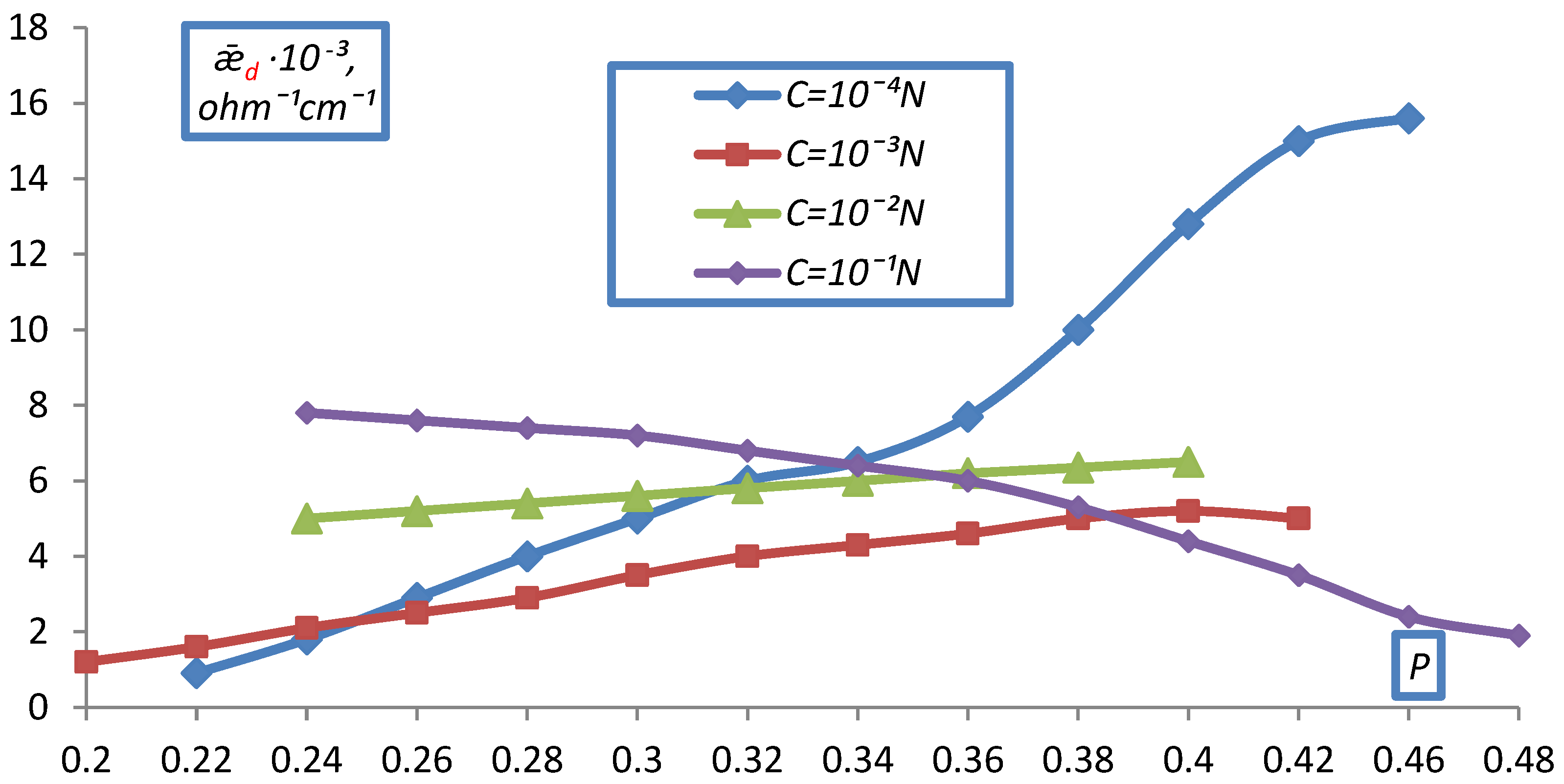
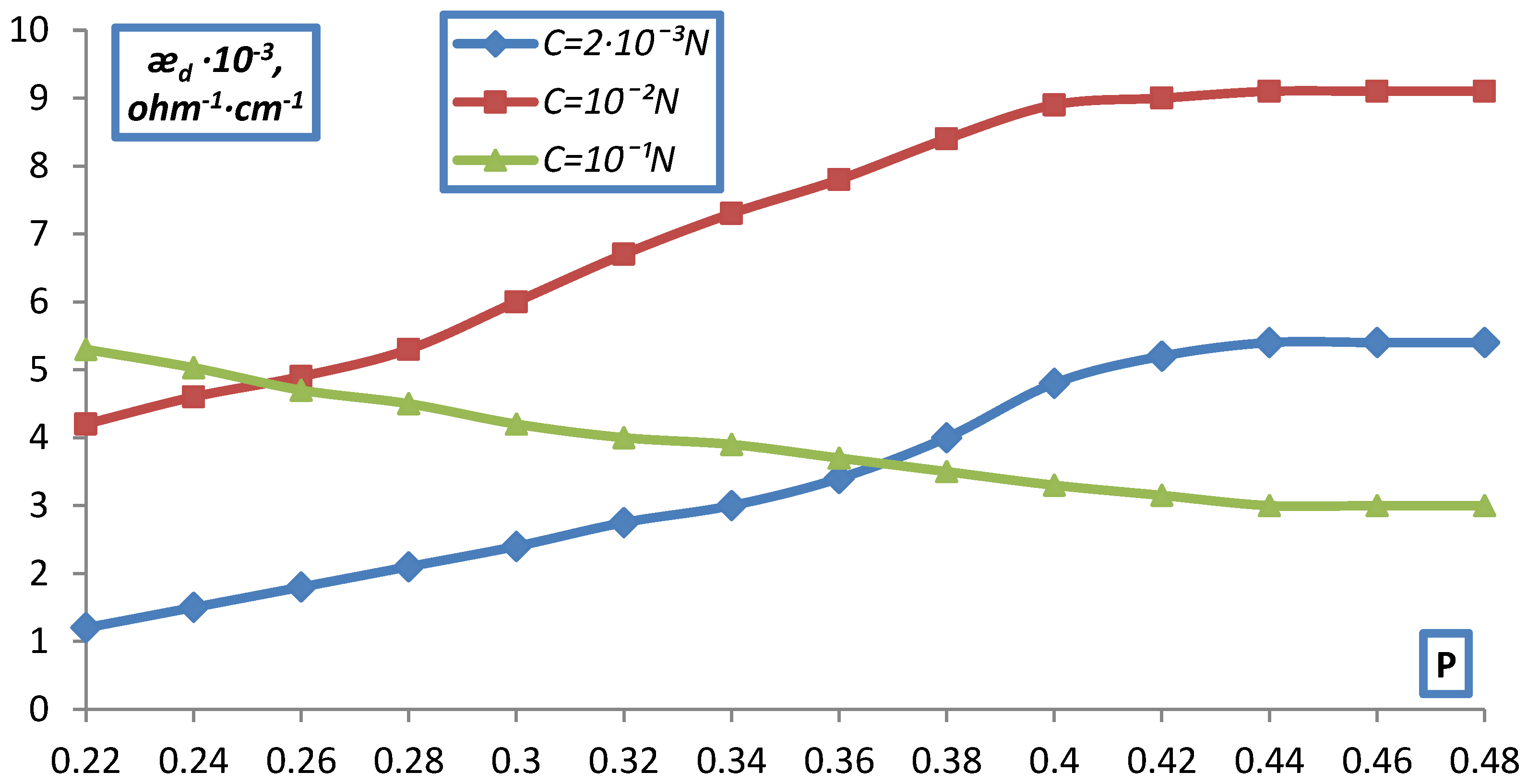
2.2. Measurement of Electrical Conductivity of a Bulk Layer of Ion Exchangers
- hd0, P0 respectively the height and volume fraction of the ion exchanger at the initial moment before compression;
- hd is the height of the bulk layer of the ion exchanger corresponding to the degrees of filling for which was determined P.
- The electrical conductivity of the bulk layer of ion exchangers was measured
- depending on the concentration of the equilibrium solution.
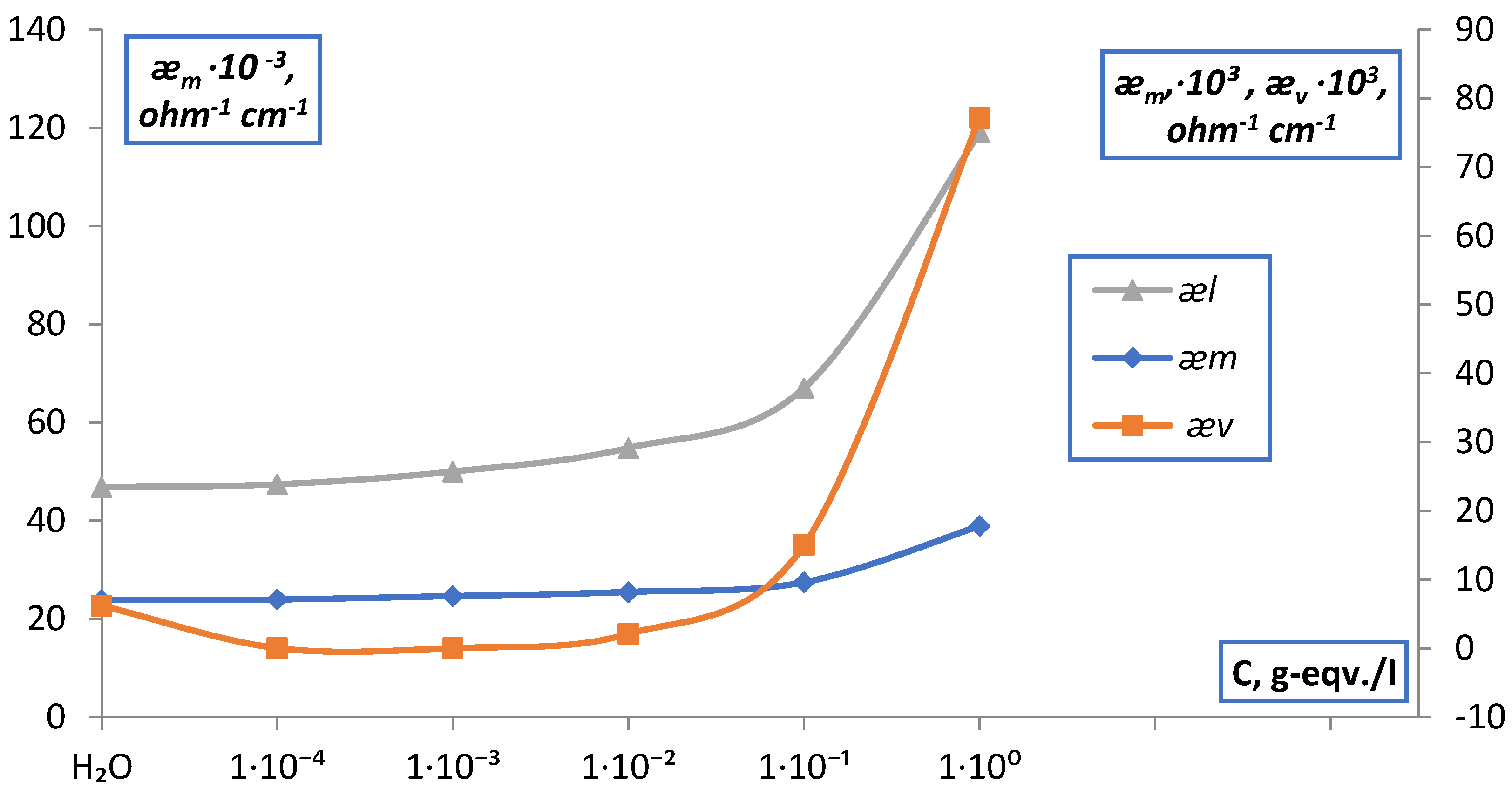
2.3. Measurement of Electrical Conductivity of Membranes
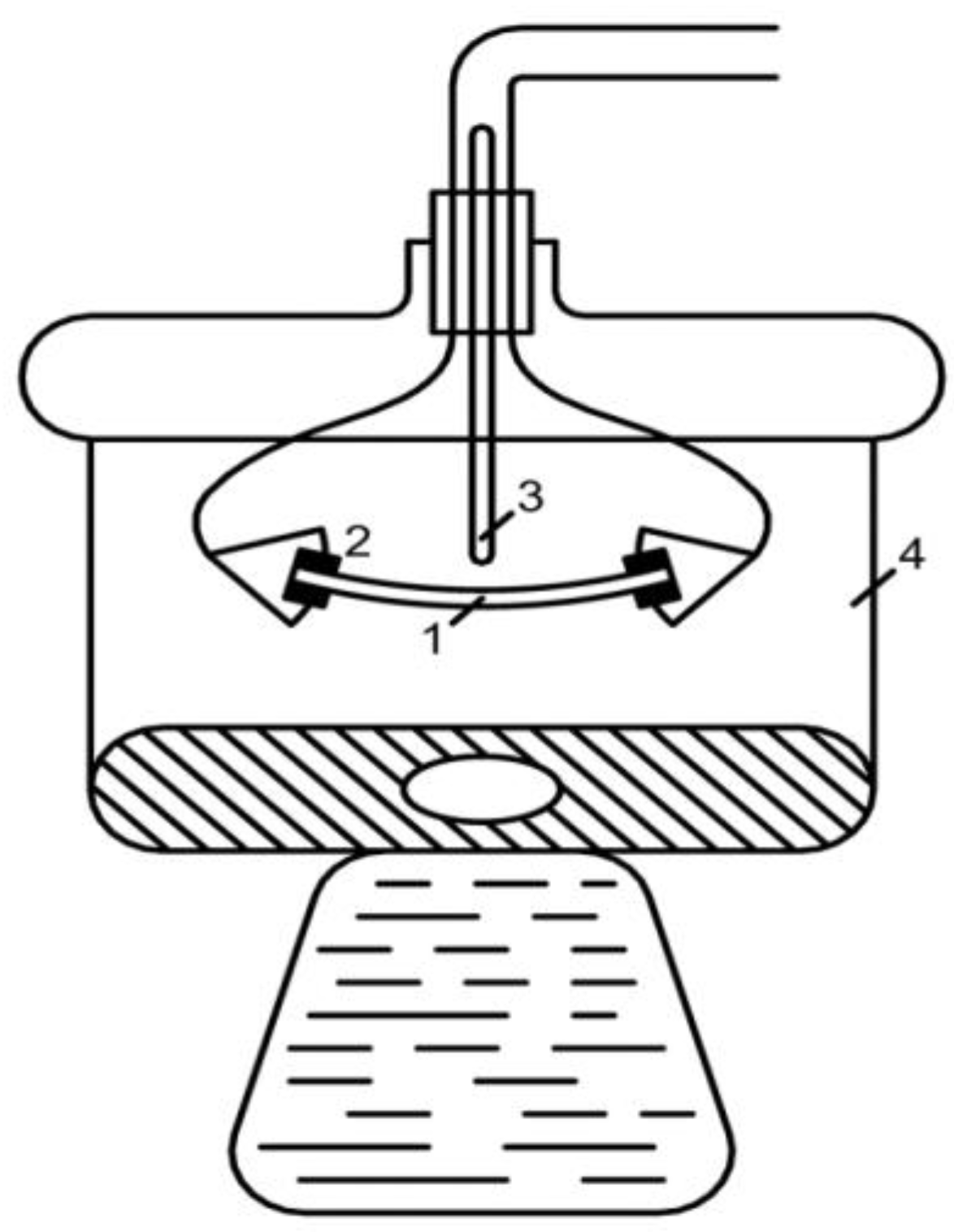
2.3.1. Measurement of the Conductivity of Membranes by the Difference Method
2.3.2. Measurement of Conductivity of Membranes by Contact Method
3. Result and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MK-40 | industrial cation exchange membrane |
| MA-40 | industrial anion exchange membrane |
| KU-2-8 | industrial cation exchanger |
| EDE-10p | industrial anion exchanger |
| l | electrical conductivity solution in the membrane, ohm−1∙cm−1 |
| m | electrical conductivity of ion exchange membranes, ohm−1∙cm−1 |
| d | electrical conductivity ion exchange resin, ohm−1∙cm−1 |
| ӕv | electrical conductivity solution, ohm−1∙cm−1 |
| β | coefficient of structural resistance |
| R | resistance, ohm |
| l | distance between the electrodes, cm. |
| α | efficiency coefficient |
| C | concentration, g-eqv./l |
| P | volume fraction of dry ion exchanger |
| N | normal concentration, g-eqv./l |
References
- Petrov, O.; Iwaszczuk, N.; Bejanidze, I.; Kharebava, T.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Nakashidze, N.; Petrov, A. Neutralization of Industrial Water by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, R.; Renata, A.; Ortigara, C.; Koncagül, E.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Lamizana-Diallo, B.M.; Zadeh, S.M.; Qadir, M.; Kjell’en, M.; Sjodin, J.; et al. The united nations world water development report 2017 wastewater: The untapped resource. United Nations World Water Dev. Rep. 2017, 5, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Zabolotsky, V.; Novak, L.; Kovalenko, A.; Nikonenko, V.; Urtenov, M.; Lebedev, K.; But, A.Y. Electroconvection in Systems with Heterogeneous Ion-Exchange Membranes. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejanidze, I.; Petrov, O.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Kharebava, T.; Nakashidze, N.; Didmanidze, N.; Davitadze, N.; Petrov, A. Sorption of organic electrolytes and surfactants from natural waters by heterogeneous membranes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Cassano, A.; Rastogi, N. Advances in Membrane Technologies for Water Treatment. Materials, Processes and Applications; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 666. ISBN 9781782421214. [Google Scholar]
- Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Belova, E.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Larchet, I. Intensive current transfer in membrane systems: Modelling, mechanisms and application in electrodialysis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 160, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejanidze, I.; Petrov, O.; Kharebava, T.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Davitadze, N.; Didmanidze, N. Study of the healing properties of natural sources of Georgia and modeling of their purification processes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P. Membrane-Based Technologies for Environmental Pollution Control; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; 784p, ISBN 9780128194553. [Google Scholar]
- Kharebava, T.; Bejanidze, I.; Tavdgiridze, G. Microbiological estimation of electrodialistic process of obtain potable water. Sci. J. Eur. Sci. Rev. 2017, 7–8, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Bejanidze, I.; Kharebava, T.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Didmanidze, N.; Davitadze, N. Monograph: The study of Composition and Physical and Chemical Properties of Some Natural Waters of Georgia. In Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal. Designing, Construction, Operation and Monitoring; Politechnika Lubelska: Lublin, Poland, 2020; pp. 8–23. ISBN 9788379474097. [Google Scholar]
- Sillanpaa, M. Advanced Water Treatment Electrochemical Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; 382p, ISBN 9780128192276. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, D. Study on the leachable behavior of cation exchange resins. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejanidze, I.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Kharebava, T.; Koncelidze, L.; Jun, C. Correction of the chemical composition of the washing waters received as a result of pH cation exchange of ion exchange resin. In Proceedings of the 19th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–6 July 2019; Volume 19, pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Campione, A.; Gurreri, L.; Ciofalo, M.; Micale, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A. Electrodialysis for water desalination: A critical assessment of recent developments on process fundamentals, models and applications. Desalination 2018, 434, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.-A.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Azoddein, A.A.M.; Hassell, D.G.; Dakhil, I.H.; Hasan, H.A. Electrodialysis Desalination for Water and Wastewater: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122231. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Hankins, N. Emerging Membrane Technology for Sustainable Water Treatment; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; 480p, ISBN 9780444633125. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura Bernardes, A.; Zoppas Ferreira, J.; Rodrigues, M.S. Electrodialysis and WaterReuse: Novel Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; ISBN 9783642402494. [Google Scholar]
- Gurreri, L.; Cipollina, A.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G. Electrodialysis for Wastewater Treatment—Part I: Fundamentals and Municipal Effluents. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-) Membranes-Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment-Advances and Emerging Processes; Basile, A., Comite, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 141–192. ISBN 9780128168233. [Google Scholar]
- Gurreri, L.; Cipollina, A.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G. Electrodialysis for Wastewater Treatment—Part II: Industrial Effluents. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-) Membranes-Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment-Advances and Emerging Processes; Basile, A., Comite, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 195–241. ISBN 9780128168233. [Google Scholar]
- Bejanidze, I.; Kharebava, T.; Davitadze, N.; Kontselidze, Z.; Kontselidze, L. Purification of Natural and Wastewater by Electromembrane Technology: Monograph; Series Membrane Technology; Publishing House Shota Rustaveli State University: Batumi, Georgia, 2019; p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Text of Lectures “World and Russian Membrane Market”. Contents Section Introduction. Membrane Market in the Russian Federation. 3 Brief Description of the Market. Refdb.ruMembrane Technology for Liquid and Gas Separations; MST041G; BCC Research: Wellesley, MA, USA, 2014; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Membranes Market—Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends and Forecast 2014–2020, Transparency Market Research. 2014. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/search.asp?Search=membranes&x=0&y=0&gclid=Cj0KCQiAr5iQBhCsARIsAPcwROPxBMSCuyFL79g1qgO7jqRQ2Avq_Uh5pNpjwlbddUUwZLhq5Nk8_fkaAv-KEALw_wcB (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Svittsov, A.A. Prospects for application of inorganic membrane in Russia. Mag. Water Mag. 2015, 5, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Membranes Market by Material (Polymeric, Ceramic), Technology (RO, UF, MF, NF), Application (Water & Wastewater Treatment, Industrial Processing), Region (North America, APAC, Europe, MEA, South America)—Global Forecast to 2024. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/membranes-market-1176.html (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Volkov, V.V. Membranes and nanotechnologies. Russ. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 656–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolyarov, V.A. Professional. Part 2: Raw materials and products of the industry of organic and inorganic substances. In New Handbook of Chemist and Technologist; Peace and Family: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2006; p. 5139. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, G.; Gurreri, L.; Airò Farulla, G.; Cipollina, A.; Pirrotta, A.; Micale, G.; Ciofalo, M. Membrane Deformation and Its Effects on Flow and Mass Transfer in the Electromembrane Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, S.; Crespo, J.; Velizarov, S. Profiled Ion Exchange Membranes: A Comprehensible Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apel, P.Y.; Bobreshova, O.V.; Volkov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Stenina, I.A.; Filippov, A.N.; Yampolskii, Y.P.; Yaroslavtsevc, A.B. Prospects of Membrane Science Development. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarapulova, V.; Shkorkina, I.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Kononenko, N.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Transport characteristics of fujifilm ion-exchange membranes as compared to homogeneousmembranes AMX and CMX and to heterogeneous membranes MK-40 and MA-41. Membranes 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarapulova, V.V.; Titorova, V.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Transport characteristics of homogeneous and heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes in sodium chloride, calcium chloride, and sodium sulfate solutions. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, R.S.; Bruning, K.; Zhu, S.; Flotron, S.; Miller, C.T.; Coronell, O. Influence of water uptake, charge, manning parameter, and contact angle on water and salt transport in commercial ion exchange membranes. Ind. Eng. Res. 2019, 58, 18663–18674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmai, A.E.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Zyryanova, S.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Dammak, L. A simple model for the response of an anion-exchange membrane to variation in concentration and pH of bathing solution. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 567, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.N.; Kononenko, N.A.; Demina, O.A. Diffusion of Electrolytes of different natures through the Cation-Exchange Membrane. Colloid J. 2017, 79, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długołecki, P.; Anet, B.; Metz, S.J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. Transport limitations in ion exchange membranes at low salt concentrations. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaning Membrane Market Research Liquid and Gas Media. Marketing Research RESEARCH. Techart. Available online: http://www.rusnanonet.ru/download/nano/file/russian-membrane-market.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- World and Russian Membrane Market. Available online: https://studylib.ru/doc/4939781/mirovoj-i-rossijskij-membrannyj-rynok--1-mb- (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Membranes—An Innovative Material for the Purification of Liquid and Gaseous Media. Marketing Research. RESEARCHTechart. Available online: http://www.cleandex.ru/articles/2015/09/13/membrans is an innovative material for clean liquids and gas (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Bejanidze, I.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Petrov, O.; Kharebava, T.; Davitadze, N.; Didmanidze, N. Electrical conductivity of ion-exchange membranes in solutions of simple electrolytes. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress Sustainable Development: Enviromental Protection, Energy Saving, Sustainable Enviromental Management, Lviv Oblast, Ukrane, 23–25 September 2020; p. 166, ISBN 978-617-655-199-7. [Google Scholar]
- Veerman, J. The effect of the NaCl bulk concentration on the resistance of ion exchange membranes—Measuring and modeling. Energies 2020, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitryasova, O.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Kochanek, A.; Sopilnyak, I. Correlation interaction between electrical conductivity and nitrate content in natural waters of small rivers. In Proceedings of the 16th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 30 June–6 July 2016; pp. 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Larchet, C.; Nouri, S.; Auclair, B.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Application of chronopotentiometry to determine the thickness of diffusion layer adjacent to an ion-exchange membrane under natural convection. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 139, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Vermaas, D.A.; Veerman, J.; Saakes, M.; Rijnaart, H.H.M.; Post, J.W.; Nijmeijer, K. Membrane resistance: The effect of salinity gradients over a cation exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badessa, T.S.; Shaposhnik, V.A. The dependence of electrical conductivity of ion exchange membranes on the charge of counter ions. Condens. Matter Interphases 2014, 16, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Hong, J.G.; Xie, S.; Xia, S.; Chen, Y. An integrative modeling and experimental study on the ionic resistance of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz, C.; Kamcev, L. Ionic conductivity of ion-exchange membranes: Measurement methods and dependence on salt concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, L.; Demina, O.A.; Dvorkina, G.A.; Parshikov, S.B.; Larchet, C.; Auclair, B. Comparative study of methods for determining the electrical conductivity of ion-exchange membranes. J. Electrochem. 2001, 37, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akberova, E. Structurally Caused Effects of Thermochemical Modification of Heterogeneous Ion-Exchange Membranes. Ph.D. Thesis, Voronezh State University, Voronezh, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Falina, I.V.; Demina, O.A.; Kononenko, N.A.; Annikova, L.A. Influence of inert components on the formation of conducting channels in ion-exchange membranes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Hoog, N.A.; Yntema, D.R. Method for determining ion exchange membrane resistance for electrodialysis systems. Desalination 2016, 380, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Sujanani, R.; Jang, E.-S.; Yan, N.; Moe, N.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Salt concentration dependence of ionic conductivity in ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Kingsbury, R.S.; Douglas, F.C.; Coronell, O. Impact of solution composition on the resistance of ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, O.; Kononenko, N.; Falina, I. A new approach to the characterization of ion-exchange membranes using a set of model parameters. Pet. Chem. 2014, 54, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niftaliev, S.I.; Kozaderova, O.A.; Kim, K.B. Electrically conductive properties of MK-40 and MA-41 membranes, investigated by impedance high-frequency spectroscopy. Bull. Voronezh State Univ. Eng. Technologies 2016, 1, 167–172. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamcev, J.; Paul, D.R.; Manning, G.S.; Freeman, B.D. Ion diffusion coeffcients in ion exchange membranes–Significance of counterion condensation. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5519–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedkaoui, Y.; Szymczyk, A.; Lounici, H.; Arous, O. A new lateral method for characterizing the electrical conductivity of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevakshenova, E.E.; Korzhova, E.S.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Electrical conductivity of anion-exchange membranes in solutions of salts of carbonic, phosphoric and tartaric acids. Sorpt. Chromatogr. Process. 2012, 12, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikov, S.; Kolot, D. Electrical conductivity of ion exchange membranes in solutions containing carboxylic acids. Sci. J. KubSAU 2016, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, O.A.; Kononenko, N.A.; Falina, I.A.; Demin, A.V. Theoretical Estimation of Differential Coefficients of Ion-Exchange Membrane Diffusion Permeability. Colloid J. 2017, 79, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichka, V.S.; Mareev, S.A.; Porozhnyy, M.V.; Shkirskaya, S.A.; Safronova, E.Y.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Modified Microheterogeneous Model for Describing Electrical Conductivity of Membranes in Dilute Electrolyte Solutions. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Długołecki, P.; Ogonowski, P.; Metz, S.J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. On the resistances of membrane, diffusion boundary layer and double layer in ion exchange membrane transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Unusual concentration dependence of ion-exchange membrane conductivity in ampholyte-containing solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Gil, M.A.; Barragán, V.M.; Villaluenga, J.P.G.; Godino, M.P. Water uptake and salt transport through Nafion cation-exchange membranes with different thicknesses. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Coma, L.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Carmona, J.; Palacio, L.; Prádanos, P.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ibañez, R.; Ortiz, I. Modeling the influence of divalent ions on membrane resistance and electric power in reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 592, 117385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.N. A Cell Model of the Ion-Exchange Membrane. Electrical Conductivity and Electroosmotic Permeability. Colloid J. 2018, 80, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B. Electrodialysis of Ammonium and Nitrate-Containing Aqueous Solutions. Ph.D. Thesis, Voronezh State University, Voronezh, Russia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karpenko-Foal, L.; Berezina, N. Determination of structural, selective, electrokinetic and percolation characteristics of ion-exchange membranes from conducting data. Desalination 2009, 245, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Akberova, E.; Nebavskaya, K. Effect of thermochemical treatment on surface morphology and hydrophobicity of heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes. Rus. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 88, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, N.; Gnusin, N.; Demina, O.; Timofeev, S. Electric transport of water in membrane systems. Description of the experiment and model. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 86, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnusin, N.; Berezina, N.; Kononenko, N.; Demina, O. Transport structural parameters for the characterization of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butilski, I.D. Research of the Surface Morphology of Ion-Exchange Membranes and Its Influence on Electrochemical Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, Kuban State University, Krasnodar, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]

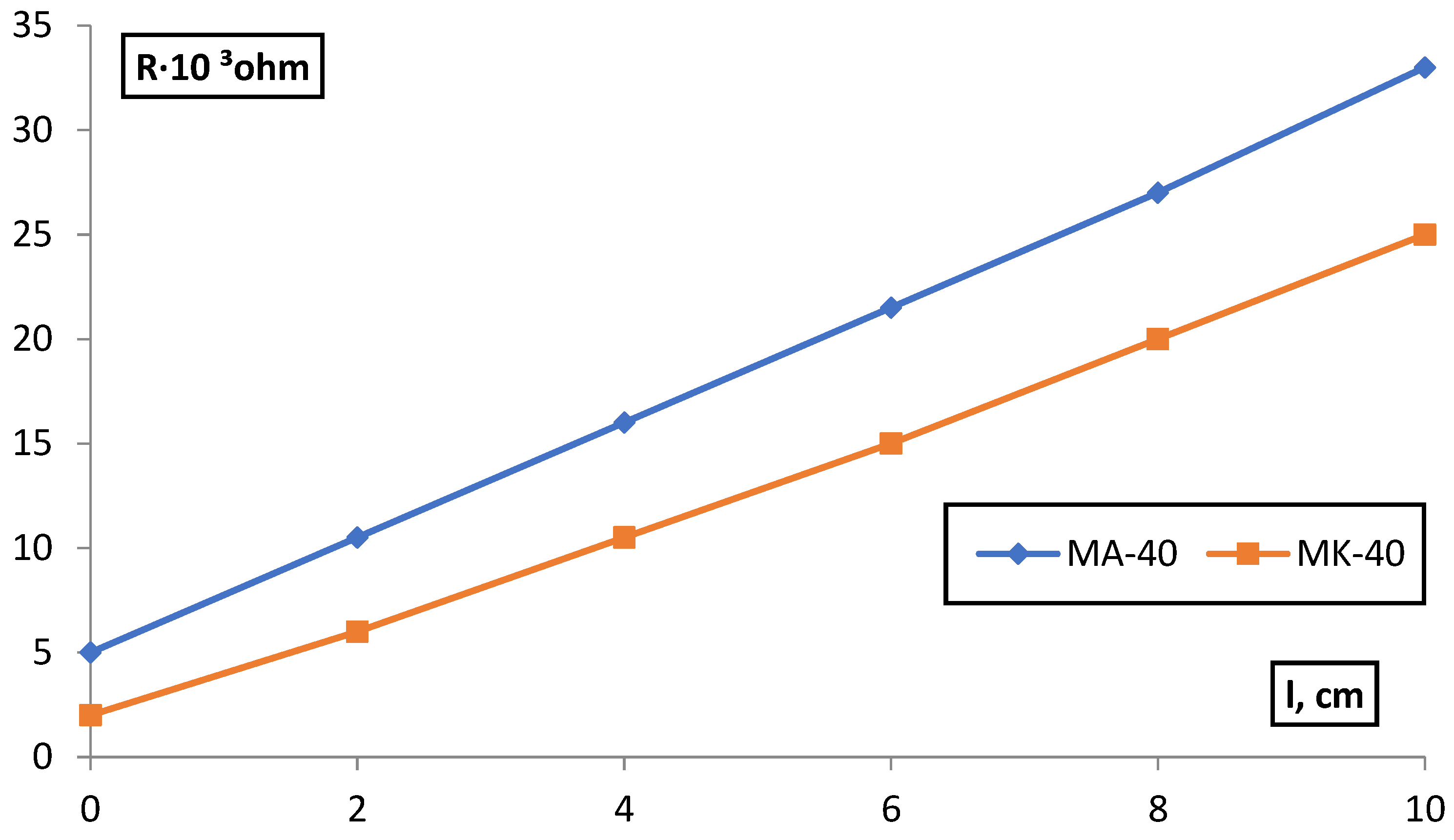

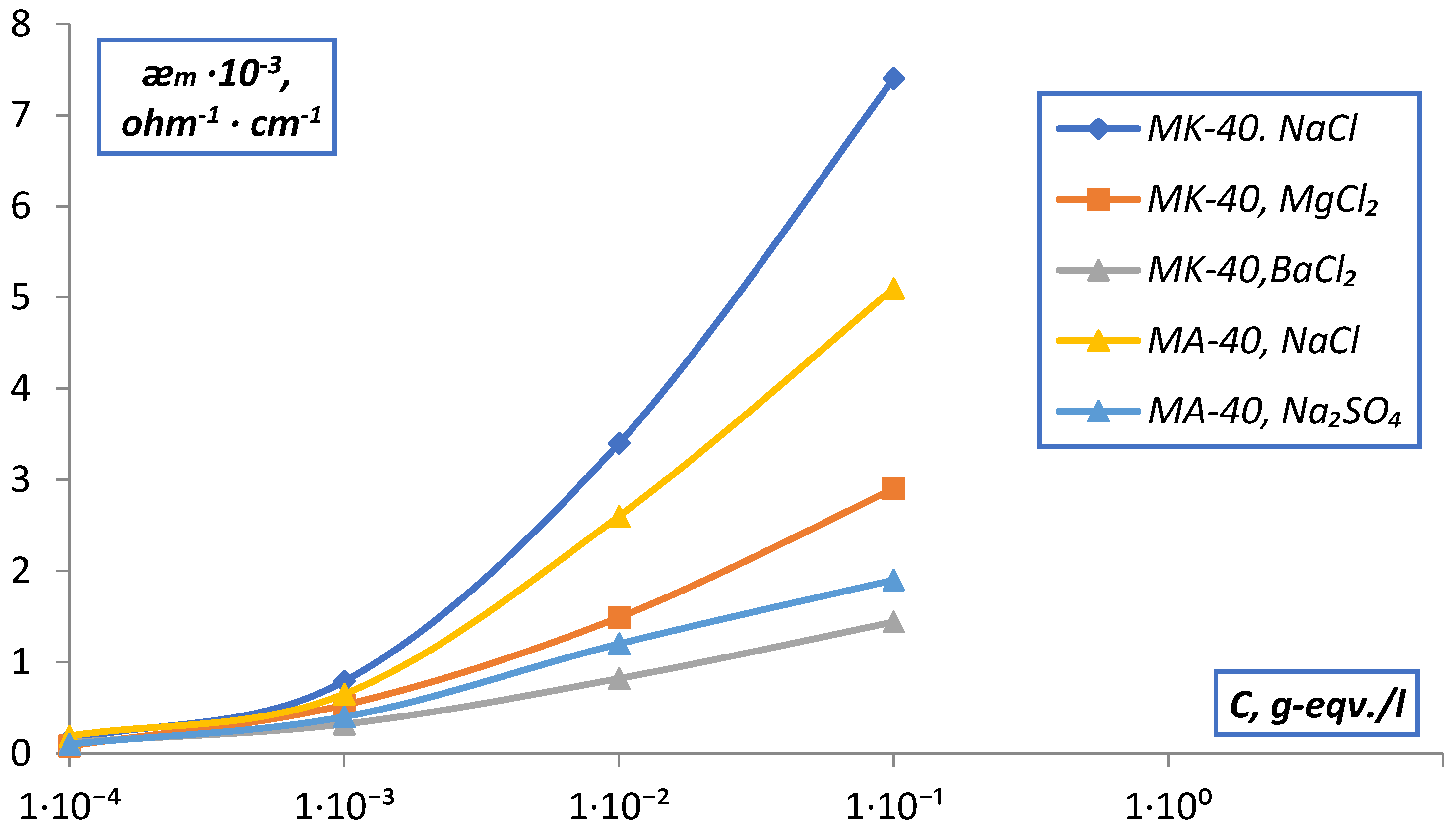
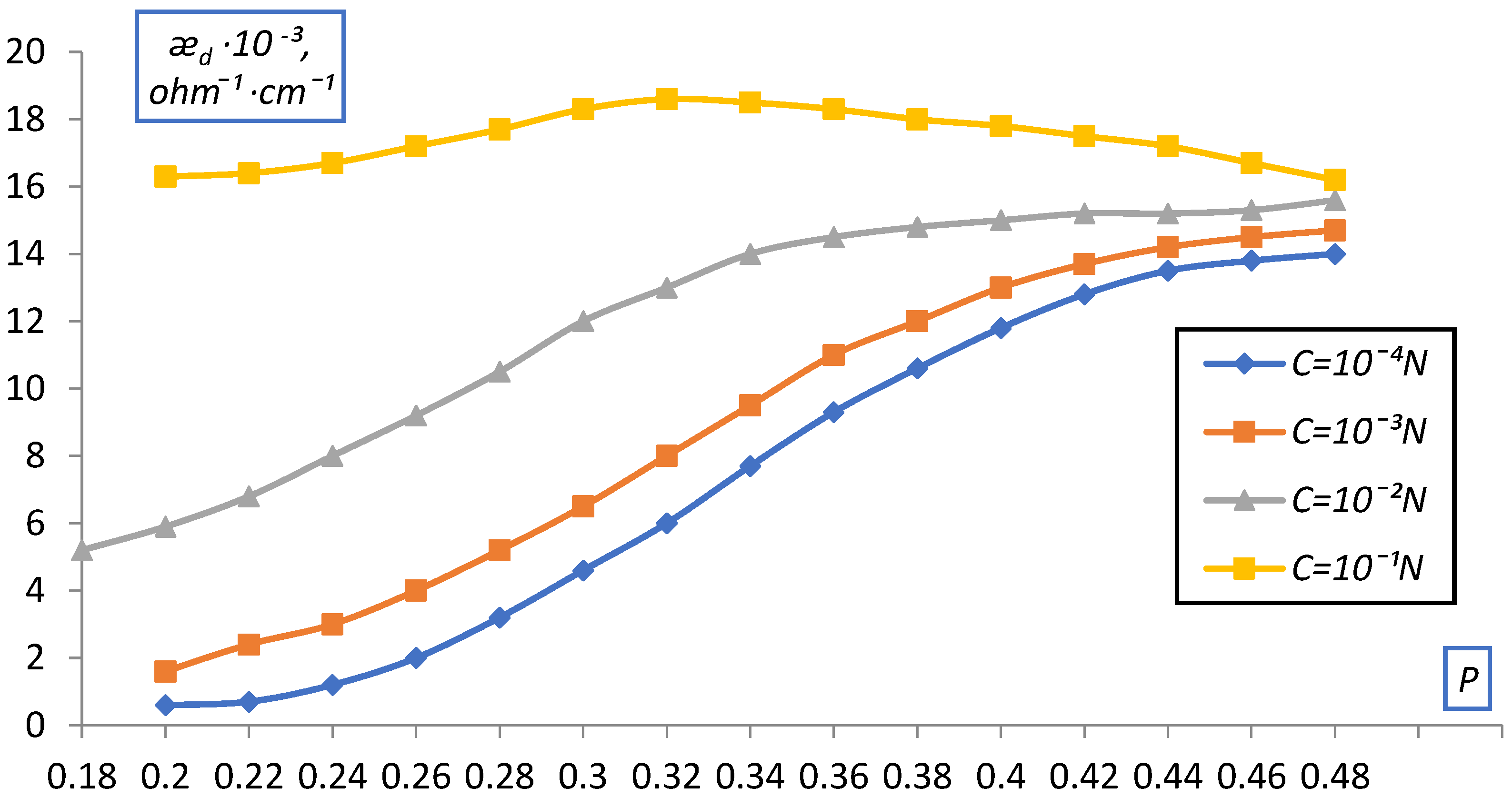
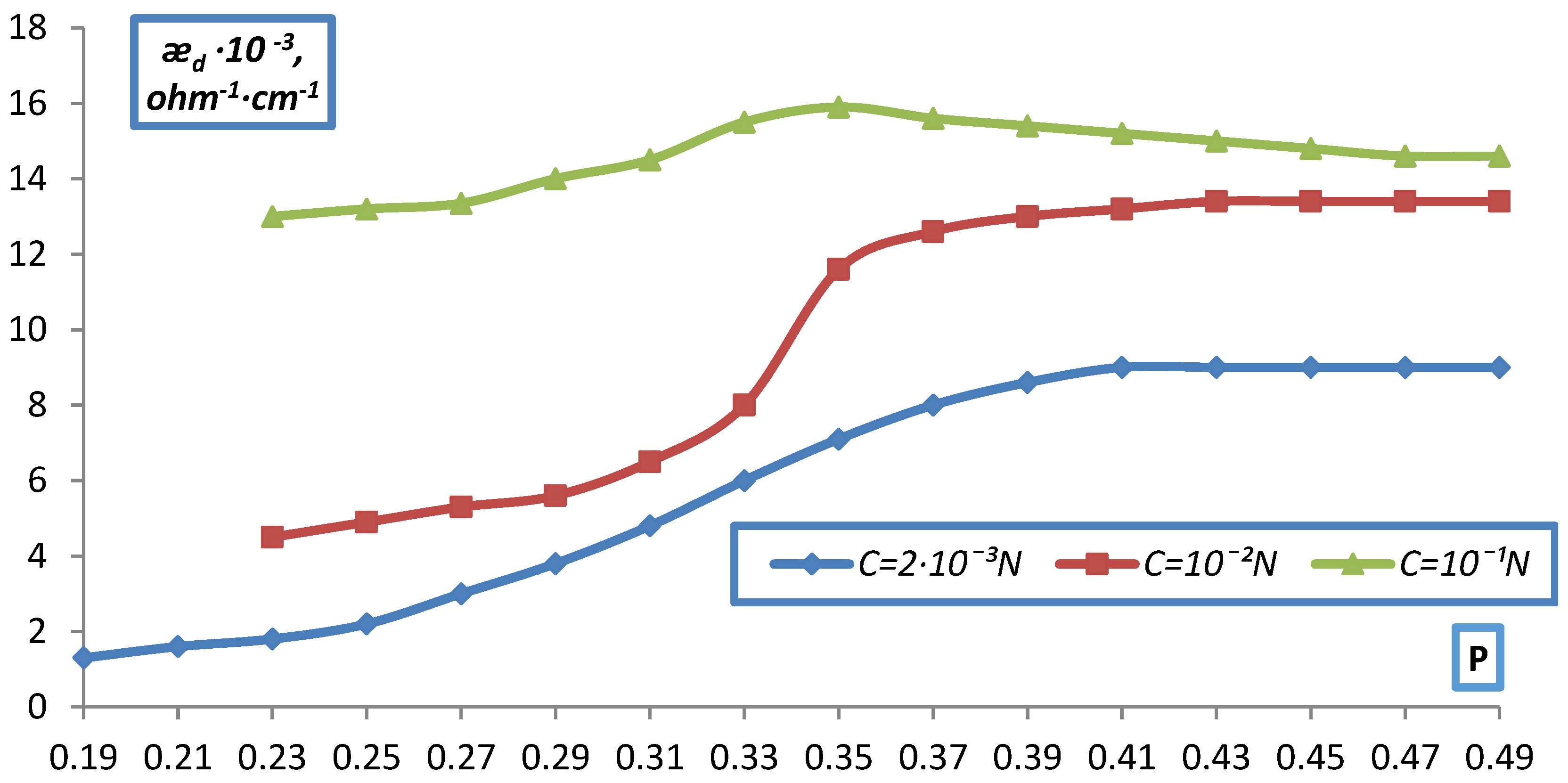

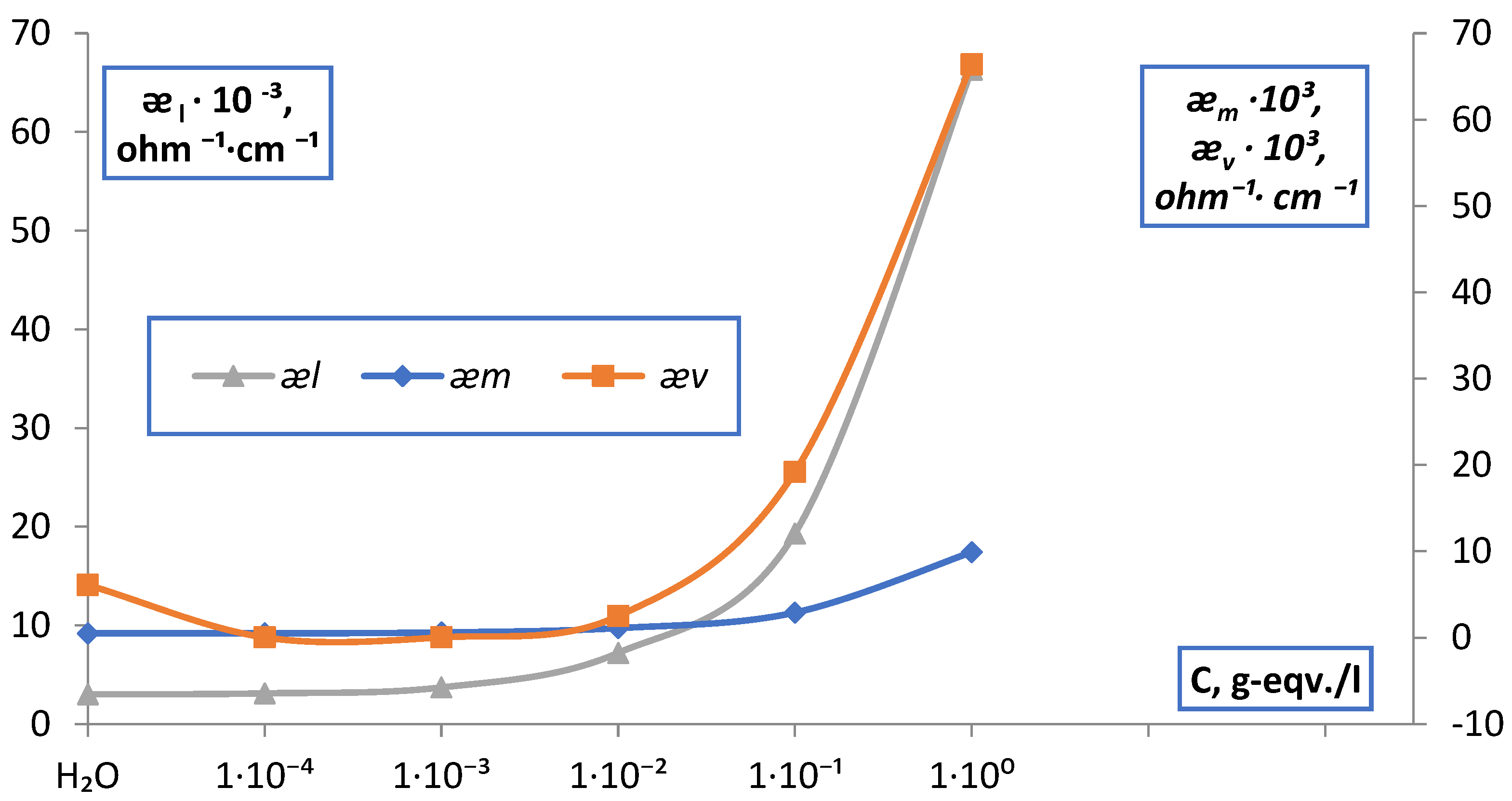
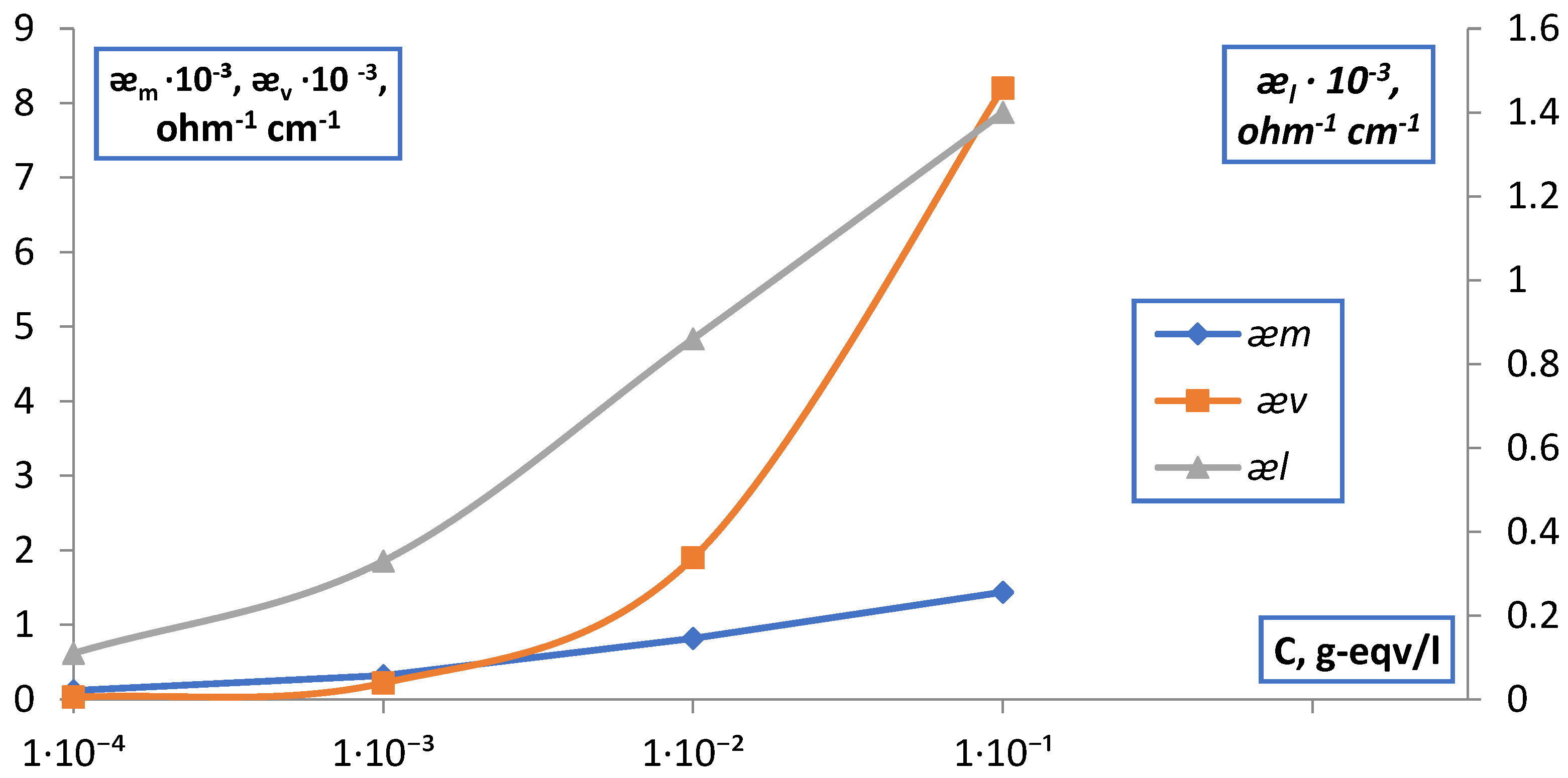
| C, g-eqv./l | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte | Ion Exchanger/Solution | Ion Exchanger-Membrane/Contact Method | Membrane–Solution/Contact Method | Ion Exchanger Membrane/Difference Method | Membrane–Solution/Difference Method |
| NaCl | 0.21 | 1.5 | 0.079 | 0.06 | |
| MgCl2 | 0.067 | 0.15 | 0.024 | 0.04 | |
| BaCl2 | 0.047 | 0.15 | 0.006 | 0.045 | 0.001 |
| NaCl | 0.16 | 2.2 | 0.056 | 0.03 | |
| Na2SO4 | 0.047 | 0.15 | 0.017 | 0.148 | 0.011 |
| Ion Exchanger | Form | Density, g/cm3 | Moisture Content, ω0,% | Volume Fraction of Dry Ion Exchanger P0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KU-2-8 | Na+ | 1.40 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Mg+2 | 1.45 | 055 | 0.45 | |
| Ba+2 | 1.73 | 0.52 | 0.48 | |
| EDE-10p | Cl− | 1.29 | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| SO4−2 | 1.34 | 0.54 | 0.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrov, O.; Iwaszczuk, N.; Bejanidze, I.; Kharebava, T.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Didmanidze, N.; Nakashidze, N. Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Resins and Membranes in Equilibrium Solutions of Inorganic Electrolytes. Membranes 2022, 12, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020243
Petrov O, Iwaszczuk N, Bejanidze I, Kharebava T, Pohrebennyk V, Didmanidze N, Nakashidze N. Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Resins and Membranes in Equilibrium Solutions of Inorganic Electrolytes. Membranes. 2022; 12(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020243
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrov, Oleksandr, Natalia Iwaszczuk, Irina Bejanidze, Tina Kharebava, Volodymyr Pohrebennyk, Nato Didmanidze, and Nunu Nakashidze. 2022. "Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Resins and Membranes in Equilibrium Solutions of Inorganic Electrolytes" Membranes 12, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020243
APA StylePetrov, O., Iwaszczuk, N., Bejanidze, I., Kharebava, T., Pohrebennyk, V., Didmanidze, N., & Nakashidze, N. (2022). Study of the Electrical Conductivity of Ion-Exchange Resins and Membranes in Equilibrium Solutions of Inorganic Electrolytes. Membranes, 12(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020243







